Computer engineering (CoE or CpE) is a branch of
electrical engineering
Electrical engineering is an engineering discipline concerned with the study, design, and application of equipment, devices, and systems which use electricity, electronics, and electromagnetism. It emerged as an identifiable occupation in the l ...
and
computer science that integrates several fields of
computer science and
electronic engineering
Electronics engineering is a sub-discipline of electrical engineering which emerged in the early 20th century and is distinguished by the additional use of active components such as semiconductor devices to amplify and control electric current fl ...
required to develop
computer hardware
Computer hardware includes the physical parts of a computer, such as the case, central processing unit (CPU), random access memory (RAM), monitor, mouse, keyboard, computer data storage, graphics card, sound card, speakers and motherboard.
...
and
software
Software is a set of computer programs and associated documentation and data. This is in contrast to hardware, from which the system is built and which actually performs the work.
At the lowest programming level, executable code consists o ...
. Computer engineers not only require training in
electronic engineering
Electronics engineering is a sub-discipline of electrical engineering which emerged in the early 20th century and is distinguished by the additional use of active components such as semiconductor devices to amplify and control electric current fl ...
,
software design
Software design is the process by which an agent creates a specification of a software artifact intended to accomplish goals, using a set of primitive components and subject to constraints. Software design may refer to either "all the activity ...
, and hardware-software integration, but also in
software engineering
Software engineering is a systematic engineering approach to software development.
A software engineer is a person who applies the principles of software engineering to design, develop, maintain, test, and evaluate computer software. The term ''p ...
. It uses the techniques and principles of electrical engineering and computer science, but also covers areas such as artificial intelligence (AI), robotics, computer networks, computer architecture and operating systems. Computer engineers are involved in many hardware and software aspects of
computing, from the design of individual
microcontroller
A microcontroller (MCU for ''microcontroller unit'', often also MC, UC, or μC) is a small computer on a single VLSI integrated circuit (IC) chip. A microcontroller contains one or more CPUs (processor cores) along with memory and programmable ...
s,
microprocessor
A microprocessor is a computer processor where the data processing logic and control is included on a single integrated circuit, or a small number of integrated circuits. The microprocessor contains the arithmetic, logic, and control circu ...
s,
personal computers
A personal computer (PC) is a multi-purpose microcomputer whose size, capabilities, and price make it feasible for individual use. Personal computers are intended to be operated directly by an end user, rather than by a computer expert or techn ...
, and
supercomputer
A supercomputer is a computer with a high level of performance as compared to a general-purpose computer. The performance of a supercomputer is commonly measured in floating-point operations per second (FLOPS) instead of million instructions ...
s, to
circuit design
The process of circuit design can cover systems ranging from complex electronic systems down to the individual transistors within an integrated circuit. One person can often do the design process without needing a planned or structured design p ...
. This field of engineering not only focuses on how computer systems themselves work, yet it also demands them to integrate into the larger picture.
Robots" \n\n\n\n\nThe robots exclusion standard, also known as the robots exclusion protocol or simply robots.txt, is a standard used by websites to indicate to visiting web crawlers and other web robots which portions of the site they are allowed to visi ...
are one of the applications of computer engineering.
Computer Engineering usually deals with areas including
writing software and
firmware
In computing, firmware is a specific class of computer software that provides the low-level control for a device's specific hardware. Firmware, such as the BIOS of a personal computer, may contain basic functions of a device, and may provide h ...
for
embedded microcontroller
A microcontroller (MCU for ''microcontroller unit'', often also MC, UC, or μC) is a small computer on a single VLSI integrated circuit (IC) chip. A microcontroller contains one or more CPUs (processor cores) along with memory and programmable ...
s, designing
VLSI
Very large-scale integration (VLSI) is the process of creating an integrated circuit (IC) by combining millions or billions of MOS transistors onto a single chip. VLSI began in the 1970s when MOS integrated circuit (Metal Oxide Semiconductor) ...
chips
''CHiPs'' is an American crime drama television series created by Rick Rosner and originally aired on NBC from September 15, 1977, to May 1, 1983. It follows the lives of two motorcycle officers of the California Highway Patrol (CHP). The se ...
, designing
analog sensor
A sensor is a device that produces an output signal for the purpose of sensing a physical phenomenon.
In the broadest definition, a sensor is a device, module, machine, or subsystem that detects events or changes in its environment and sends ...
s, designing
mixed signal circuit board
A printed circuit board (PCB; also printed wiring board or PWB) is a medium used in electrical and electronic engineering to connect electronic components to one another in a controlled manner. It takes the form of a laminated sandwich struct ...
s, and designing
operating system
An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware, software resources, and provides common daemon (computing), services for computer programs.
Time-sharing operating systems scheduler (computing), schedule tasks for ef ...
s. Computer engineers are also suited for
robotics
Robotics is an interdisciplinarity, interdisciplinary branch of computer science and engineering. Robotics involves design, construction, operation, and use of robots. The goal of robotics is to design machines that can help and assist human ...
research, which relies heavily on using
digital systems
Digital electronics is a field of electronics involving the study of digital signals and the engineering of devices that use or produce them. This is in contrast to analog electronics and analog signals.
Digital electronic circuits are usuall ...
to control and monitor
electrical systems
Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and motion of matter that has a property of electric charge. Electricity is related to magnetism, both being part of the phenomenon of electromagnetism, as described by ...
like
motor
An engine or motor is a machine designed to convert one or more forms of energy into mechanical energy.
Available energy sources include potential energy (e.g. energy of the Earth's gravitational field as exploited in hydroelectric power gene ...
s,
communications
Communication (from la, communicare, meaning "to share" or "to be in relation with") is usually defined as the transmission of information. The term may also refer to the message communicated through such transmissions or the field of inquir ...
, and
sensor
A sensor is a device that produces an output signal for the purpose of sensing a physical phenomenon.
In the broadest definition, a sensor is a device, module, machine, or subsystem that detects events or changes in its environment and sends ...
s.
In many institutions of higher learning, computer engineering students are allowed to choose areas of in-depth study in their junior and senior year because the full breadth of knowledge used in the design and application of computers is beyond the scope of an
undergraduate degree
An undergraduate degree (also called first degree or simply degree) is a colloquial term for an academic degree earned by a person who has completed undergraduate courses. In the United States, it is usually offered at an institution of higher ...
. Other institutions may require
engineering students to complete one or two years of
general engineering before declaring computer engineering as their primary focus.

History
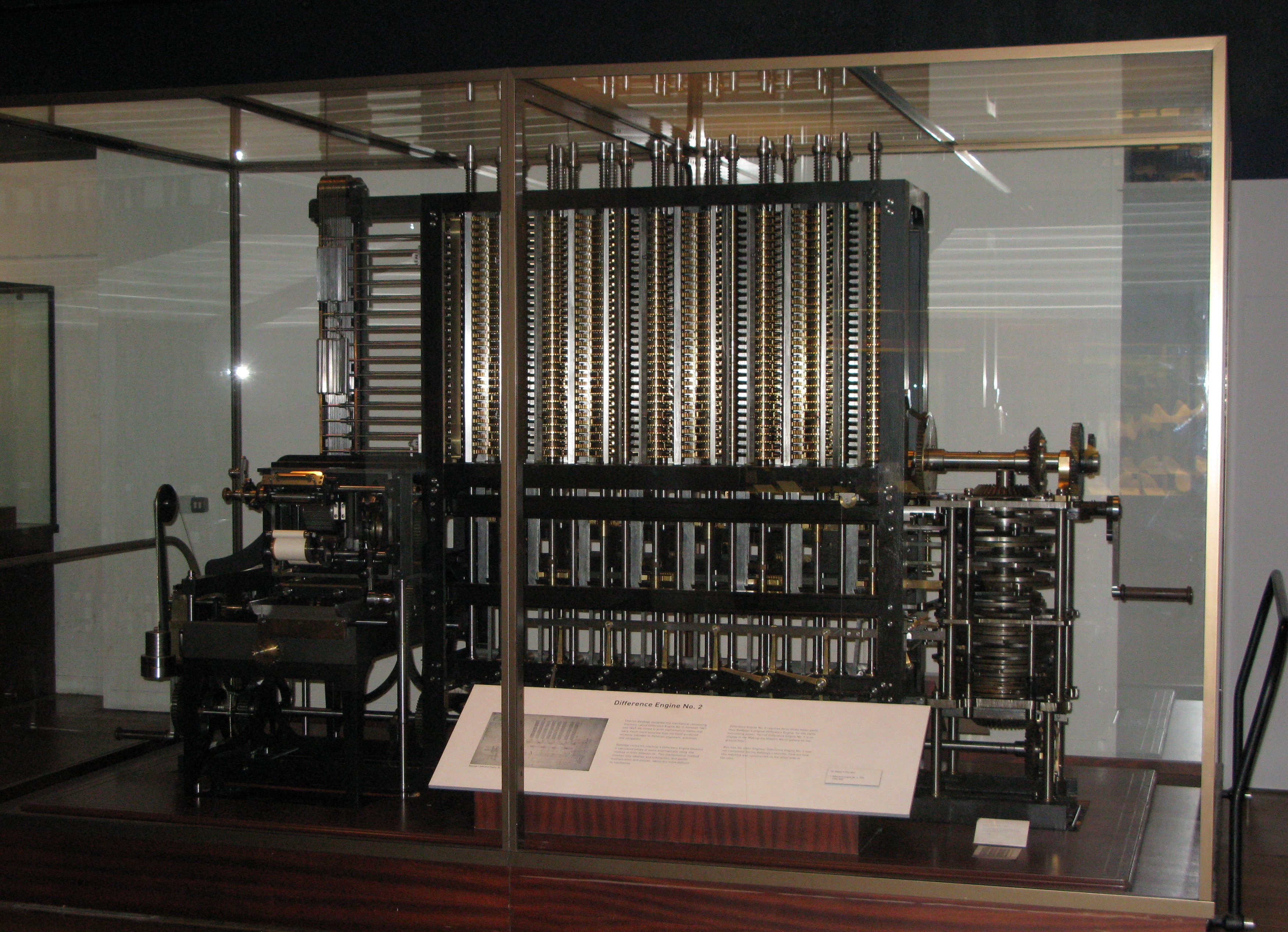

Computer engineering began in 1939 when
John Vincent Atanasoff
John Vincent Atanasoff, , (October 4, 1903 – June 15, 1995) was an American physicist and inventor from mixed Bulgarian-Irish origin, best known for being credited with inventing the first electronic digital computer.
Atanasoff invented the ...
and
Clifford Berry
Clifford Edward Berry (April 19, 1918 – October 30, 1963) helped John Vincent Atanasoff create the first digital electronic computer in 1939, the Atanasoff–Berry computer (ABC).
Biography
Clifford Berry was born April 19, 1918, in Gladbr ...
began developing the world's first electronic
digital computer
A computer is a machine that can be programmed to carry out sequences of arithmetic or logical operations (computation) automatically. Modern digital electronic computers can perform generic sets of operations known as programs. These prog ...
through
physics
Physics is the natural science that studies matter, its fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of knowledge which relat ...
,
mathematics, and
electrical engineering
Electrical engineering is an engineering discipline concerned with the study, design, and application of equipment, devices, and systems which use electricity, electronics, and electromagnetism. It emerged as an identifiable occupation in the l ...
. John Vincent Atanasoff was once a physics and mathematics teacher for
Iowa State University
Iowa State University of Science and Technology (Iowa State University, Iowa State, or ISU) is a public land-grant research university in Ames, Iowa. Founded in 1858 as the Iowa Agricultural College and Model Farm, Iowa State became one of the n ...
and Clifford Berry a former graduate under electrical engineering and physics. Together, they created the
Atanasoff-Berry computer, also known as the ABC which took five years to complete.
While the original ABC was dismantled and discarded in the 1940s a tribute was made to the late inventors, a replica of the ABC was made in 1997 where it took a team of researchers and engineers four years and $350,000 to build.
The modern
personal computer
A personal computer (PC) is a multi-purpose microcomputer whose size, capabilities, and price make it feasible for individual use. Personal computers are intended to be operated directly by an end user, rather than by a computer expert or techn ...
emerged in the 1970s, after several breakthroughs in
semiconductor
A semiconductor is a material which has an electrical conductivity value falling between that of a conductor, such as copper, and an insulator, such as glass. Its resistivity falls as its temperature rises; metals behave in the opposite way. ...
technology. These include the first working
transistor
upright=1.4, gate (G), body (B), source (S) and drain (D) terminals. The gate is separated from the body by an insulating layer (pink).
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to Electronic amplifier, amplify or electronic switch, switch e ...
by
William Shockley
William Bradford Shockley Jr. (February 13, 1910 – August 12, 1989) was an American physicist and inventor. He was the manager of a research group at Bell Labs that included John Bardeen and Walter Brattain. The three scientists were jointly ...
,
John Bardeen
John Bardeen (; May 23, 1908 – January 30, 1991) was an American physicist and engineer. He is the only person to be awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics twice: first in 1956 with William Shockley and Walter Brattain for the invention of the tran ...
and
Walter Brattain
Walter Houser Brattain (; February 10, 1902 – October 13, 1987) was an American physicist at Bell Labs who, along with fellow scientists John Bardeen and William Shockley, invented the point-contact transistor in December 1947. They shared t ...
at
Bell Labs
Nokia Bell Labs, originally named Bell Telephone Laboratories (1925–1984),
then AT&T Bell Laboratories (1984–1996)
and Bell Labs Innovations (1996–2007),
is an American industrial research and scientific development company owned by mult ...
in 1947,
planar process
The planar process is a manufacturing process used in the semiconductor industry to build individual components of a transistor, and in turn, connect those transistors together. It is the primary process by which silicon integrated circuit chips a ...
by
Jean Hoerni
Jean Amédée Hoerni (September 26, 1924 – January 12, 1997) was a Swiss-American engineer. He was a silicon transistor pioneer, and a member of the " traitorous eight". He developed the planar process, an important technology for reliably f ...
,
the
monolithic integrated circuit
An integrated circuit or monolithic integrated circuit (also referred to as an IC, a chip, or a microchip) is a set of electronic circuits on one small flat piece (or "chip") of semiconductor material, usually silicon. Large numbers of tiny ...
chip by
Robert Noyce
Robert Norton Noyce (December 12, 1927 – June 3, 1990), nicknamed "the Mayor of Silicon Valley", was an American physicist and entrepreneur who co-founded Fairchild Semiconductor in 1957 and Intel Corporation in 1968. He is also credited wit ...
at
Fairchild Semiconductor
Fairchild Semiconductor International, Inc. was an American semiconductor company based in San Jose, California. Founded in 1957 as a division of Fairchild Camera and Instrument, it became a pioneer in the manufacturing of transistors and of int ...
in 1959,
the
metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistor
The metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET, MOS-FET, or MOS FET) is a type of field-effect transistor (FET), most commonly fabricated by the controlled oxidation of silicon. It has an insulated gate, the voltage of which d ...
(MOSFET, or MOS transistor) by
Mohamed Atalla
Mohamed M. Atalla ( ar, محمد عطاالله; August 4, 1924 – December 30, 2009) was an Egyptian-American engineer, physicist, cryptographer, inventor and entrepreneur. He was a semiconductor pioneer who made important contributions t ...
and
Dawon Kahng
Dawon Kahng ( ko, 강대원; May 4, 1931 – May 13, 1992) was a Korean-American electrical engineer and inventor, known for his work in solid-state electronics. He is best known for inventing the MOSFET (metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effe ...
at Bell Labs in 1959,
and the single-chip
microprocessor
A microprocessor is a computer processor where the data processing logic and control is included on a single integrated circuit, or a small number of integrated circuits. The microprocessor contains the arithmetic, logic, and control circu ...
(
Intel 4004
The Intel 4004 is a 4-bit central processing unit (CPU) released by Intel Corporation in 1971. Sold for US$60, it was the first commercially produced microprocessor, and the first in a long line of Intel CPUs.
The 4004 was the first signific ...
) by
Federico Faggin
Federico Faggin (, ; born 1 December 1941) is an Italian physicist, engineer, inventor and entrepreneur. He is best known for designing the first commercial microprocessor, the Intel 4004. He led the 4004 (MCS-4) project and the design group du ...
,
Marcian Hoff
Marcian Edward "Ted" Hoff Jr. (born October 28, 1937 in Rochester, New York) is one of the inventors of the microprocessor.
Education and work history
Hoff received a bachelor's degree in electrical engineering from the Rensselaer Polytechnic Inst ...
,
Masatoshi Shima
is a Japanese electronics engineer. He was one of the architects of the world's first microprocessor, the Intel 4004. In 1968, Shima worked for Busicom in Japan, and did the logic design for a specialized CPU to be translated into three-chip cu ...
and
Stanley Mazor
Stanley Mazor is an American microelectronics engineer who was born on 22 October 1941 in Chicago, Illinois. He is one of the co-inventors of the world's first microprocessor architecture, the Intel 4004, together with Ted Hoff, Masatoshi Shi ...
at
Intel
Intel Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Santa Clara, California. It is the world's largest semiconductor chip manufacturer by revenue, and is one of the developers of the x86 seri ...
in 1971.
History of computer engineering education
The first computer engineering degree program in the United States was established in 1971 at
Case Western Reserve University
Case Western Reserve University (CWRU) is a Private university, private research university in Cleveland, Cleveland, Ohio. Case Western Reserve was established in 1967, when Western Reserve University, founded in 1826 and named for its location i ...
in
Cleveland,
Ohio
Ohio () is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States. Of the fifty U.S. states, it is the 34th-largest by area, and with a population of nearly 11.8 million, is the seventh-most populous and tenth-most densely populated. The sta ...
. , there were 250
ABET
The ABET (incorporated as the Accreditation Board for Engineering and Technology, Inc.) is a non-governmental organization that accredits post-secondary education programs in applied and natural sciences, computing, engineering and engineerin ...
-accredited computer engineering programs in the U.S. In Europe, accreditation of computer engineering schools is done by a variety of agencies part of the
EQANIE
EQANIE (European Quality Assurance Network for Informatics Education e.V.) is a non-profit association seeking to enhance evaluation and quality assurance of informatics study programmes and education in Europe. It was founded on January 9, 2009 in ...
network. Due to increasing job requirements for engineers who can concurrently design hardware,
software
Software is a set of computer programs and associated documentation and data. This is in contrast to hardware, from which the system is built and which actually performs the work.
At the lowest programming level, executable code consists o ...
, firmware, and manage all forms of computer systems used in industry, some tertiary institutions around the world offer a
bachelor's degree
A bachelor's degree (from Middle Latin ''baccalaureus'') or baccalaureate (from Modern Latin ''baccalaureatus'') is an undergraduate academic degree awarded by colleges and universities upon completion of a course of study lasting three to six y ...
generally called computer engineering. Both computer engineering and
electronic engineering
Electronics engineering is a sub-discipline of electrical engineering which emerged in the early 20th century and is distinguished by the additional use of active components such as semiconductor devices to amplify and control electric current fl ...
programs include analog and digital circuit design in their curriculum. As with most engineering disciplines, having a sound knowledge of
mathematics and science is necessary for computer engineers.
Education
Computer engineering is referred to as
computer science and engineering
Computer Science and Engineering (CSE) is an academic program at many universities which comprises scientific and engineering aspects of computing. CSE is also a term often used in Europe to translate the name of engineering informatics academic ...
at some universities. Most entry-level computer engineering jobs require at least a bachelor's degree in computer engineering (or computer science and engineering). Typically one must learn an array of
mathematics such as
calculus
Calculus, originally called infinitesimal calculus or "the calculus of infinitesimals", is the mathematical study of continuous change, in the same way that geometry is the study of shape, and algebra is the study of generalizations of arithm ...
,
algebra
Algebra () is one of the broad areas of mathematics. Roughly speaking, algebra is the study of mathematical symbols and the rules for manipulating these symbols in formulas; it is a unifying thread of almost all of mathematics.
Elementary a ...
and
trigonometry
Trigonometry () is a branch of mathematics that studies relationships between side lengths and angles of triangles. The field emerged in the Hellenistic world during the 3rd century BC from applications of geometry to astronomical studies. ...
and some
computer science classes. Degrees in
electronic or
electric engineering also suffice due to the similarity of the two fields. Because hardware engineers commonly work with computer software systems, a strong background in computer programming is necessary. According to BLS, "a computer engineering major is similar to electrical engineering but with some computer science courses added to the curriculum".
Some large firms or specialized jobs require a master's degree.
It is also important for computer engineers to keep up with rapid advances in technology. Therefore, many continue learning throughout their careers. This can be helpful, especially when it comes to learning new skills or improving existing ones. For example, as the relative cost of fixing a bug increases the further along it is in the software development cycle, there can be greater cost savings attributed to developing and testing for quality code as soon as possible in the process, particularly before release.
Profession: Computer engineer
A person with a profession in computer engineering is called a computer engineer.
Applications and practice
There are two major focuses in computer engineering: hardware and software.
Computer hardware engineering
According to the
BLS, Job Outlook employment for computer hardware engineers, the expected ten-year growth from 2019 to 2029 for computer hardware engineering was an estimated 2% and a total of 71,100 jobs. ("Slower than average" in their own words when compared to other occupations)".
This is a decrease from the 2014 to 2024 BLS computer hardware engineering estimate of 3% and a total of 77,700 jobs. "
and is down from 7% for the 2012 to 2022 BLS estimate
and is further down from 9% in the BLS 2010 to 2020 estimate.
" Today, computer hardware is somehow equal to electronic and computer engineering (ECE) and has been divided into many subcategories; the most significant is embedded system design.
Computer software engineering
According to the U.S.
Bureau of Labor Statistics
The Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) is a unit of the United States Department of Labor. It is the principal fact-finding agency for the U.S. government in the broad field of labor economics and statistics and serves as a principal agency of th ...
(BLS), "computer applications software engineers and computer systems software engineers are projected to be among the faster than average growing occupations" The expected ten-year growth as of 2014 for computer software engineering was an estimated seventeen percent and there was a total of 1,114,000 jobs that same year.
This is down from the 2012 to 2022 BLS estimate of 22% for software developers.
And, further down from the 30% 2010 to 2020 BLS estimate.
In addition, growing concerns over cybersecurity add up to put computer software engineering high above the average rate of increase for all fields. However, some of the work will be outsourced in foreign countries. Due to this, job growth will not be as fast as during the last decade, as jobs that would have gone to computer software engineers in the United States would instead go to computer software engineers in countries such as India.
In addition, the BLS Job Outlook for Computer Programmers, 2014–24 has an −8% (a decline, in their words),
a Job Outlook, 2019-29 a -9% (Decline),
and a 10% decline for 2021-2031
for those who program computers (i.e. embedded systems) who are not computer application developers. Furthermore, women in software fields has been declining over the years even faster than other engineering fields.
Computer engineering licensing and practice
Computer engineering is generally practiced within larger product development firms, and such practice may not be subject to licensing. However, independent consultants who advertise computer engineering, just like any form of engineering, may be subject to state laws which restrict
professional engineer
Regulation and licensure in engineering is established by various jurisdictions of the world to encourage life, public welfare, safety, well-being, then environment and other interests of the general public and to define the licensure process thro ...
practice to only those who have received the appropriate License.
National Council of Examiners for Engineering and Surveying
The National Council of Examiners for Engineering and Surveying (NCEES) is an American non-profit organization dedicated to advancing professional licensure for engineers and surveyors. The Council’s members are the engineering and surveying lice ...
(NCEES) first offered a
Principles and Practice of Engineering Examination for computer engineering
PE Electrical and Computer exam, [NCEES]
/ref> in 2003.
Specialty areas
There are many specialty areas in the field of computer engineering.
Processor design
Processor design process involves choosing an instruction set and a certain execution paradigm (e.g. VLIW or RISC) and results in a microarchitecture, which might be described in e.g. VHDL or Verilog. CPU design is divided into design of the following components: datapaths (such as ALUs and pipelines), control unit: logic which controls the datapaths, memory components such as register files, caches, clock circuitry such as clock drivers, PLLs, clock distribution networks, pad transceiver circuitry, logic gate cell library which is used to implement the logic.
Coding, cryptography, and information protection
 Computer engineers work in coding, cryptography, and information protection to develop new methods for protecting various information, such as digital images and music, fragmentation, copyright infringement and other forms of tampering. Examples include work on wireless communications, multi-antenna systems, optical transmission, and
Computer engineers work in coding, cryptography, and information protection to develop new methods for protecting various information, such as digital images and music, fragmentation, copyright infringement and other forms of tampering. Examples include work on wireless communications, multi-antenna systems, optical transmission, and digital watermarking
A digital watermark is a kind of marker covertly embedded in a noise-tolerant signal such as audio, video or image data. It is typically used to identify ownership of the copyright of such signal. "Watermarking" is the process of hiding digital inf ...
.
Communications and wireless networks
Those focusing on communications and wireless networks, work advancements in telecommunications systems and networks (especially wireless networks), modulation and error-control coding, and information theory. High-speed network design Network planning and design is an iterative process, encompassing
topological design, network-synthesis, and network-realization, and is aimed at ensuring that a new telecommunications network or service meets the needs of the subscriber and op ...
, interference suppression and modulation, design, and analysis of fault-tolerant system
Fault tolerance is the property that enables a system to continue operating properly in the event of the failure of one or more faults within some of its components. If its operating quality decreases at all, the decrease is proportional to the ...
, and storage and transmission schemes are all a part of this specialty.
Compilers and operating systems
 This specialty focuses on
This specialty focuses on compilers
In computing, a compiler is a computer program that translates computer code written in one programming language (the ''source'' language) into another language (the ''target'' language). The name "compiler" is primarily used for programs that ...
and operating systems
An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware, software resources, and provides common daemon (computing), services for computer programs.
Time-sharing operating systems scheduler (computing), schedule tasks for ef ...
design and development. Engineers in this field develop new operating system architecture, program analysis techniques, and new techniques to assure quality. Examples of work in this field include post-link-time code transformation algorithm development and new operating system development.
Computational science and engineering
Computational science and engineering is a relatively new discipline. According to the Sloan Career Cornerstone Center, individuals working in this area, "computational methods are applied to formulate and solve complex mathematical problems in engineering and the physical and the social sciences. Examples include aircraft design, the plasma processing of nanometer features on semiconductor wafers, VLSI
Very large-scale integration (VLSI) is the process of creating an integrated circuit (IC) by combining millions or billions of MOS transistors onto a single chip. VLSI began in the 1970s when MOS integrated circuit (Metal Oxide Semiconductor) ...
circuit design, radar detection systems, ion transport through biological channels, and much more".
Computer networks, mobile computing, and distributed systems
In this specialty, engineers build integrated environments for computing, communications, and information access
Information access is the freedom or ability to identify, obtain and make use of database or information effectively.
There are various research efforts in information access for which the objective is to simplify and make it more effective for ...
. Examples include shared-channel wireless networks, adaptive resource management in various systems, and improving the quality of service in mobile and ATM environments. Some other examples include work on wireless network systems and fast Ethernet cluster wired systems.
Computer systems: architecture, parallel processing, and dependability
 Engineers working in computer systems work on research projects that allow for reliable, secure, and high-performance computer systems. Projects such as designing processors for multi-threading and parallel processing are included in this field. Other examples of work in this field include the development of new theories, algorithms, and other tools that add performance to computer systems.
Engineers working in computer systems work on research projects that allow for reliable, secure, and high-performance computer systems. Projects such as designing processors for multi-threading and parallel processing are included in this field. Other examples of work in this field include the development of new theories, algorithms, and other tools that add performance to computer systems.CPU design
Processor design is a subfield of computer engineering and electronics engineering (fabrication) that deals with creating a processor, a key component of computer hardware.
The design process involves choosing an instruction set and a certain exec ...
, cache hierarchy
Cache hierarchy, or multi-level caches, refers to a memory architecture that uses a hierarchy of memory stores based on varying access speeds to cache data. Highly requested data is cached in high-speed access memory stores, allowing swifter access ...
layout, memory organization
There are several ways to organise memories with respect to the way they are connected to the cache:
# one-word-wide memory organisation
# wide memory organisation
# interleaved memory organisation
# independent memory organisation
One-Word-Wide ...
and load balancing.
Computer vision and robotics
 In this specialty, computer engineers focus on developing visual sensing technology to sense an environment, representation of an environment, and manipulation of the environment. The gathered three-dimensional information is then implemented to perform a variety of tasks. These include improved human modeling, image communication, and human-computer interfaces, as well as devices such as special-purpose cameras with versatile vision sensors.
In this specialty, computer engineers focus on developing visual sensing technology to sense an environment, representation of an environment, and manipulation of the environment. The gathered three-dimensional information is then implemented to perform a variety of tasks. These include improved human modeling, image communication, and human-computer interfaces, as well as devices such as special-purpose cameras with versatile vision sensors.
Embedded systems
 Individuals working in this area design technology for enhancing the speed, reliability, and performance of systems. Embedded systems are found in many devices from a small FM radio to the space shuttle. According to the Sloan Cornerstone Career Center, ongoing developments in embedded systems include "automated vehicles and equipment to conduct search and rescue, automated transportation systems, and human-robot coordination to repair equipment in space."
Individuals working in this area design technology for enhancing the speed, reliability, and performance of systems. Embedded systems are found in many devices from a small FM radio to the space shuttle. According to the Sloan Cornerstone Career Center, ongoing developments in embedded systems include "automated vehicles and equipment to conduct search and rescue, automated transportation systems, and human-robot coordination to repair equipment in space."system-on-chip
A system on a chip or system-on-chip (SoC ; pl. ''SoCs'' ) is an integrated circuit that integrates most or all components of a computer or other electronic system. These components almost always include a central processing unit (CPU), memory ...
design, architecture of edge computing and the Internet of things
The Internet of things (IoT) describes physical objects (or groups of such objects) with sensors, processing ability, software and other technologies that connect and exchange data with other devices and systems over the Internet or other comm ...
.
Integrated circuits, VLSI design, testing and CAD
This specialty of computer engineering requires adequate knowledge of electronics and electrical systems. Engineers working in this area work on enhancing the speed, reliability, and energy efficiency of next-generation very-large-scale integrated (VLSI
Very large-scale integration (VLSI) is the process of creating an integrated circuit (IC) by combining millions or billions of MOS transistors onto a single chip. VLSI began in the 1970s when MOS integrated circuit (Metal Oxide Semiconductor) ...
) circuits and microsystems. An example of this specialty is work done on reducing the power consumption of VLSI algorithms and architecture.
Signal, image and speech processing
Computer engineers in this area develop improvements in human-computer interaction, including speech recognition
Speech recognition is an interdisciplinary subfield of computer science and computational linguistics that develops methodologies and technologies that enable the recognition and translation of spoken language into text by computers with the mai ...
and synthesis, medical and scientific imaging, or communications systems. Other work in this area includes computer vision development such as recognition of human facial features.
Quantum computing
See also
Related fields
Associations
* Association of Computer Engineers and Technicians
* IEEE Computer Society
The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) is a 501(c)(3) professional association for electronic engineering and electrical engineering (and associated disciplines) with its corporate office in New York City and its operatio ...
* Association for Computing Machinery
The Association for Computing Machinery (ACM) is a US-based international learned society for computing. It was founded in 1947 and is the world's largest scientific and educational computing society. The ACM is a non-profit professional membe ...
References
External links
*
{{DEFAULTSORT:Computer Engineering
Electrical and computer engineering
Engineering disciplines


 Computer engineering began in 1939 when
Computer engineering began in 1939 when  Computer engineers work in coding, cryptography, and information protection to develop new methods for protecting various information, such as digital images and music, fragmentation, copyright infringement and other forms of tampering. Examples include work on wireless communications, multi-antenna systems, optical transmission, and
Computer engineers work in coding, cryptography, and information protection to develop new methods for protecting various information, such as digital images and music, fragmentation, copyright infringement and other forms of tampering. Examples include work on wireless communications, multi-antenna systems, optical transmission, and  This specialty focuses on
This specialty focuses on  Engineers working in computer systems work on research projects that allow for reliable, secure, and high-performance computer systems. Projects such as designing processors for multi-threading and parallel processing are included in this field. Other examples of work in this field include the development of new theories, algorithms, and other tools that add performance to computer systems.
Computer architecture includes
Engineers working in computer systems work on research projects that allow for reliable, secure, and high-performance computer systems. Projects such as designing processors for multi-threading and parallel processing are included in this field. Other examples of work in this field include the development of new theories, algorithms, and other tools that add performance to computer systems.
Computer architecture includes