Compass Rose on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A compass rose, sometimes called a wind rose, rose of the winds or compass star, is a figure on a
A compass rose, sometimes called a wind rose, rose of the winds or compass star, is a figure on a
 According to the chronicler Einhard (), the Frankish king
According to the chronicler Einhard (), the Frankish king
 * (N) Tramontana
* (NE) Greco (or Bora)
* (E) Levante
* (SE) Scirocco (or Exaloc)
* (S) Ostro (or Mezzogiorno)
* (SW) Libeccio (or Garbino)
* (W) Ponente
* (NW) Maestro (or Mistral)
The exact origin of the mariner's eight-wind rose is obscure. Only two of its point names (''Ostro'', ''Libeccio'') have Classical etymologies, the rest of the names seem to be autonomously derived. Two
* (N) Tramontana
* (NE) Greco (or Bora)
* (E) Levante
* (SE) Scirocco (or Exaloc)
* (S) Ostro (or Mezzogiorno)
* (SW) Libeccio (or Garbino)
* (W) Ponente
* (NW) Maestro (or Mistral)
The exact origin of the mariner's eight-wind rose is obscure. Only two of its point names (''Ostro'', ''Libeccio'') have Classical etymologies, the rest of the names seem to be autonomously derived. Two
Wind Rose.
File:Portolan windrose (plain).jpg, Early 32-wind compass rose, shown as a mere collection of color-coded rhumblines, from a Genoese nautical chart (c. 1325)
File:Compass rose from Catalan Atlas (1375).jpg, First ornate compass rose depicted on a chart, from the Catalan Atlas (1375), with the
 The contemporary compass rose appears as two rings, one smaller and set inside the other. The outside ring denotes true cardinal directions while the smaller inside ring denotes magnetic cardinal directions.
The contemporary compass rose appears as two rings, one smaller and set inside the other. The outside ring denotes true cardinal directions while the smaller inside ring denotes magnetic cardinal directions. 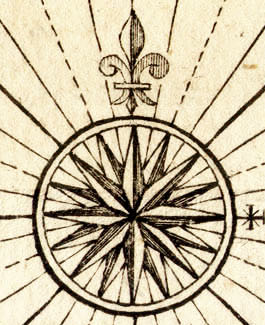 16-point compass roses are constructed by bisecting the angles of the principal winds to come up with intermediate compass points, known as
16-point compass roses are constructed by bisecting the angles of the principal winds to come up with intermediate compass points, known as
File:Compass rose en 04p.svg, A 4-point compass rose
File:Compass rose en 08p.svg, An 8-point compass rose
File:Brosen windrose.svg, A 16-point compass rose
File:Brosen windrose Full.svg, A 32-point compass rose
File:Kompassrose.svg, A 360 degree and 6400 NATO mil compass rose
Origins of the Compass Rose
The Rose of the Winds
an example of a rose with 26 directions.
Compass Rose of Piedro Reinel, 1504
an example of a 32-point rose with cross for east (the Christian Holy Land) and fleur-di-lis for north.
Brief compass rose history info
{{DEFAULTSORT:Compass Rose Navigation Cartography
compass
A compass is a device that shows the cardinal directions used for navigation and geographic orientation. It commonly consists of a magnetized needle or other element, such as a compass card or compass rose, which can pivot to align itself wit ...
, map
A map is a symbolic depiction emphasizing relationships between elements of some space, such as objects, regions, or themes.
Many maps are static, fixed to paper or some other durable medium, while others are dynamic or interactive. Although ...
, nautical chart
A nautical chart is a graphic representation of a sea area and adjacent coastal regions. Depending on the scale of the chart, it may show depths of water and heights of land ( topographic map), natural features of the seabed, details of the co ...
, or monument used to display the orientation of the cardinal directions (north
North is one of the four compass points or cardinal directions. It is the opposite of south and is perpendicular to east and west. ''North'' is a noun, adjective, or adverb indicating direction or geography.
Etymology
The word ''north ...
, east
East or Orient is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from west and is the direction from which the Sun rises on the Earth.
Etymology
As in other languages, the word is formed from the fac ...
, south, and west
West or Occident is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from east and is the direction in which the Sun sets on the Earth.
Etymology
The word "west" is a Germanic word passed into some ...
) and their intermediate points. It is also the term for the graduated markings found on the traditional magnetic compass
A compass is a device that shows the cardinal directions used for navigation and geographic orientation. It commonly consists of a magnetized needle or other element, such as a compass card or compass rose, which can pivot to align itself with ...
. Today, a form of compass rose is found on, or featured in, almost all navigation
Navigation is a field of study that focuses on the process of monitoring and controlling the movement of a craft or vehicle from one place to another.Bowditch, 2003:799. The field of navigation includes four general categories: land navigation, ...
systems, including nautical chart
A nautical chart is a graphic representation of a sea area and adjacent coastal regions. Depending on the scale of the chart, it may show depths of water and heights of land ( topographic map), natural features of the seabed, details of the co ...
s, non-directional beacon
A non-directional beacon (NDB) or non-directional radio beacon is a radio beacon which does not include directional information. Radio beacons are radio transmitters at a known location, used as an aviation or marine navigational aid. NDB are i ...
s (NDB), VHF omnidirectional range
Very high frequency omnirange station (VOR) is a type of short-range radio navigation system for aircraft, enabling aircraft with a receiving unit to determine its position and stay on course by receiving radio signals transmitted by a network ...
(VOR) systems, global-positioning systems (GPS
The Global Positioning System (GPS), originally Navstar GPS, is a satellite-based radionavigation system owned by the United States government and operated by the United States Space Force. It is one of the global navigation satellite sy ...
), and similar equipment.
Types
Linguistic anthropological studies have shown that most human communities have four points of cardinal direction. The names given to these directions are usually derived from either locally-specific geographic features (e.g. "towards the hills", "towards the sea") or from celestial bodies (especially the sun) or from atmospheric features (winds, temperature). Most mobile populations tend to adopt sunrise and sunset for East and West and the direction from where different winds blow to denote North and South.Classical
Theancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic p ...
s originally maintained distinct and separate systems of points and winds. The four Greek cardinal points
The four cardinal directions, or cardinal points, are the four main compass directions: north, east, south, and west, commonly denoted by their initials N, E, S, and W respectively. Relative to north, the directions east, south, and west are at ...
(, , and ) were based on celestial bodies and used for orientation. The four Greek winds
Wind is the natural movement of air or other gases relative to a planet's surface. Winds occur on a range of scales, from thunderstorm flows lasting tens of minutes, to local breezes generated by heating of land surfaces and lasting a few ...
(, , , ) were confined to meteorology
Meteorology is a branch of the atmospheric sciences (which include atmospheric chemistry and physics) with a major focus on weather forecasting. The study of meteorology dates back millennia, though significant progress in meteorology did no ...
. Nonetheless, both systems were gradually conflated, and wind names came eventually to denote cardinal directions as well.
In his meteorological studies, Aristotle
Aristotle (; grc-gre, Ἀριστοτέλης ''Aristotélēs'', ; 384–322 BC) was a Greek philosopher and polymath during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. Taught by Plato, he was the founder of the Peripatetic school of ph ...
identified ten distinct winds: two north-south winds (, ) and four sets of east-west winds blowing from different latitudes—the Arctic circle (, ), the summer solstice horizon (, ), the equinox
A solar equinox is a moment in time when the Sun crosses the Earth's equator, which is to say, appears directly above the equator, rather than north or south of the equator. On the day of the equinox, the Sun appears to rise "due east" and se ...
(, ) and the winter solstice
The winter solstice, also called the hibernal solstice, occurs when either of Earth's poles reaches its maximum tilt away from the Sun. This happens twice yearly, once in each hemisphere (Northern and Southern). For that hemisphere, the winter ...
(, ). Aristotle's system was asymmetric. To restore balance, Timosthenes Timosthenes of Rhodes (Greek: ) (fl. 270 BCE) was a Greek navigator, geographer and admiral in Ptolemaic navy. He is credited with inventing the system of twelve winds that became known as the Greek 12-wind rose.
Career
In the 280s–270s BCE, ...
of Rhodes added two more winds to produce the classical 12-wind rose, and began using the winds to denote geographical direction in navigation. Eratosthenes deducted two winds from Aristotle's system, to produce the classical 8-wind rose.
The Romans
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
(e.g. Seneca
Seneca may refer to:
People and language
* Seneca (name), a list of people with either the given name or surname
* Seneca people, one of the six Iroquois tribes of North America
** Seneca language, the language of the Seneca people
Places Extrat ...
, Pliny
Pliny may refer to:
People
* Pliny the Elder (23–79 CE), ancient Roman nobleman, scientist, historian, and author of ''Naturalis Historia'' (''Pliny's Natural History'')
* Pliny the Younger (died 113), ancient Roman statesman, orator, w ...
) adopted the Greek 12-wind system, and replaced its names with Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
equivalents, e.g. , , , , etc. The '' De architectura'' of the Roman architect Vitruvius
Vitruvius (; c. 80–70 BC – after c. 15 BC) was a Roman architect and engineer during the 1st century BC, known for his multi-volume work entitled '' De architectura''. He originated the idea that all buildings should have three attribut ...
describes 24 winds.
Charlemagne
Charlemagne ( , ) or Charles the Great ( la, Carolus Magnus; german: Karl der Große; 2 April 747 – 28 January 814), a member of the Carolingian dynasty, was King of the Franks from 768, King of the Lombards from 774, and the first ...
himself came up with his own names for the classical 12 winds. During the Migration Period, the Germanic names for the cardinal directions entered the Romance languages
The Romance languages, sometimes referred to as Latin languages or Neo-Latin languages, are the various modern languages that evolved from Vulgar Latin. They are the only extant subgroup of the Italic languages in the Indo-European language ...
, where they replaced the Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
names ''borealis'' with north, ''australis'' with south, ''occidentalis'' with west and ''orientalis'' with east.
The following table gives a rough equivalence of the classical 12-wind rose with the modern compass directions (Note: the directions are imprecise since it is not clear at what angles the classical winds are supposed to be with each other; some have argued that they should be equally spaced at 30 degrees each; for more details, see the article on Classical compass winds
In the ancient Mediterranean world, the classical compass winds were names for the points of geographic direction and orientation, in association with the winds as conceived of by the ancient Greeks and Romans. Ancient wind roses typically had tw ...
).
Sidereal
The sidereal compass rose demarcates the compass points by the position of stars in the night sky, rather than winds.Arab
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
navigators in the Red Sea
The Red Sea ( ar, البحر الأحمر - بحر القلزم, translit=Modern: al-Baḥr al-ʾAḥmar, Medieval: Baḥr al-Qulzum; or ; Coptic: ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϩⲁϩ ''Phiom Enhah'' or ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϣⲁⲣⲓ ''Phiom ǹšari''; ...
and the Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or ~19.8% of the water on Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia to the east. To the south it is bounded by t ...
, who depended on celestial navigation, were using a 32-point sidereal compass rose before the end of the 10th century. In the northern hemisphere, the steady Pole Star ( Polaris) was used for the N-S axis; the less-steady Southern Cross had to do for the southern hemisphere, as the southern pole star, Sigma Octantis, is too dim to be easily seen from Earth with the naked eye. The other thirty points on the sidereal rose were determined by the rising and setting positions of fifteen bright stars. Reading from North to South, in their rising and setting positions, these are:
The western half of the rose would be the same stars in their setting position. The true position of these stars is only approximate to their theoretical equidistant rhumbs on the sidereal compass. Stars with the same declination formed a "linear constellation" or ' to provide direction as the night progressed.
A similar sidereal compass was used by Polynesian and Micronesian navigators in the Pacific Ocean, although different stars were used in a number of cases, clustering around the East-West axis.
Mariner's
In Europe, the Classical 12-wind system continued to be taught in academic settings during the Medieval era, but seafarers in the Mediterranean came up with their own distinct 8-wind system. The mariners used names derived from the Mediterranean lingua franca, composed principally of Ligurian, mixed with Venetian, Sicilian, Provençal, Catalan,Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
and Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walter ...
terms from around the Mediterranean basin. Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walter ...
words stand out: ''Scirocco'' (SE) from ''al-Sharq'' (الشرق – east in Arabic) and the variant ''Garbino'' (SW), from ''al-Gharb'' (الغرب – west in Arabic). This suggests the mariner's rose was probably acquired by southern Italian seafarers not from their classical Roman ancestors, but rather from Norman Sicily in the 11th to 12th centuries. The coasts of the Maghreb
The Maghreb (; ar, الْمَغْرِب, al-Maghrib, lit=the west), also known as the Arab Maghreb ( ar, المغرب العربي) and Northwest Africa, is the western part of North Africa and the Arab world. The region includes Algeria, ...
and Mashriq
The Mashriq ( ar, ٱلْمَشْرِق), sometimes spelled Mashreq or Mashrek, is a term used by Arabs to refer to the eastern part of the Arab world, located in Western Asia and eastern North Africa. Poetically the "Place of Sunrise", th ...
are SW and SE of Sicily respectively; the ''Greco'' (a NE wind), reflects the position of Byzantine-held Calabria-Apulia to the northeast of Arab Sicily, while the ''Maestro'' (a NW wind) is a reference to the Mistral wind
The mistral ( ca, Mestral, el, Μαΐστρος, it, Maestrale, mt, Majjistral, Corsican language, Corsican: ''Maestrale'') is a strong, cold, northwesterly wind that blows from southern France into the Gulf of Lion in the northern Mediterra ...
that blows from the southern French coast towards northwest Sicily.
The 32-point compass used for navigation in the Mediterranean by the 14th century, had increments of 11° between points. Only the eight principal winds (N, NE, E, SE, S, SW, W, NW) were given special names. The eight half-wind
The points of the compass are a set of horizontal, Radius, radially arrayed compass directions (or Azimuth#In navigation, azimuths) used in navigation and cartography. A compass rose is primarily composed of four cardinal directions—north, east ...
s just combined the names of the two principal winds, e.g. Greco-Tramontana for NNE, Greco-Levante for ENE, and so on. Quarter-winds were more cumbersomely phrased, with the closest principal wind named first and the next-closest principal wind second, e.g. "Quarto di Tramontana verso Greco" (literally, "one quarter wind from North towards Northeast", i.e. North by East), and "Quarto di Greco verso Tramontana" ("one quarter wind from NE towards N", i.e. Northeast by North). Boxing the compass
The points of the compass are a set of horizontal, radially arrayed compass directions (or azimuths) used in navigation and cartography. A compass rose is primarily composed of four cardinal directions—north, east, south, and west—each ...
(naming all 32 winds) was expected of all Medieval mariners.
Depiction on nautical charts
In the earliest medievalportolan chart
Portolan charts are nautical charts, first made in the 13th century in the Mediterranean basin and later expanded to include other regions. The word ''portolan'' comes from the Italian ''portulano'', meaning "related to ports or harbors", and wh ...
s of the 14th century, compass roses were depicted as mere collections of color-coded compass rhumb lines: black for the eight main winds, green for the eight half-winds and red for the sixteen quarter-winds. The average portolan chart had sixteen such roses (or confluence of lines), spaced out equally around the circumference of a large implicit circle.
The cartographer Cresques Abraham
Abraham Cresques (, 1325–1387), whose real name was Cresques (son of) Abraham, was a 14th-century Jews, Jewish Cartography, cartographer from Palma, Majorca, Palma, Majorca (then part of the Crown of Aragon). In collaboration with his son, Jeh ...
of Majorca, in his Catalan Atlas of 1375, was the first to draw an ornate compass rose on a map. By the end of the 15th century, Portuguese cartographers began drawing multiple ornate compass roses throughout the chart, one upon each of the sixteen circumference roses (unless the illustration conflicted with coastal details).
The points on a compass rose were frequently labeled by the initial letters of the mariner's principal winds (T, G, L, S, O, L, P, M). From the outset, the custom also began to distinguish the north from the other points by a specific visual marker. Medieval Italian cartographers typically used a simple arrowhead or circumflex-hatted T (an allusion to the compass needle) to designate the north, while the Majorcan cartographic school typically used a stylized Pole Star
A pole star or polar star is a star, preferably bright, nearly aligned with the axis of a rotating astronomical body.
Currently, Earth's pole stars are Polaris (Alpha Ursae Minoris), a bright magnitude-2 star aligned approximately with its ...
for its north mark. The use of the fleur-de-lis
The fleur-de-lis, also spelled fleur-de-lys (plural ''fleurs-de-lis'' or ''fleurs-de-lys''), is a lily (in French, and mean 'flower' and 'lily' respectively) that is used as a decorative design or symbol.
The fleur-de-lis has been used in the ...
as north mark was introduced by Pedro Reinel, and quickly became customary in compass roses (and is still often used today). Old compass roses also often used a Christian cross at Levante (E), indicating the direction of Jerusalem
Jerusalem (; he, יְרוּשָׁלַיִם ; ar, القُدس ) (combining the Biblical and common usage Arabic names); grc, Ἱερουσαλήμ/Ἰεροσόλυμα, Hierousalḗm/Hierosóluma; hy, Երուսաղեմ, Erusałēm. i ...
from the point of view of the Mediterranean sea.Dan Reboussin (2005)Wind Rose.
University of Florida
The University of Florida (Florida or UF) is a public land-grant research university in Gainesville, Florida. It is a senior member of the State University System of Florida, traces its origins to 1853, and has operated continuously on its ...
. Retrieved on 2009-04-26.
The twelve Classical winds (or a subset of them) were also sometimes depicted on portolan charts, albeit not on a compass rose, but rather separately on small disks or coins on the edges of the map.
The compass rose was also depicted on traverse boards used on board ships to record headings sailed at set time intervals.
Pole Star
A pole star or polar star is a star, preferably bright, nearly aligned with the axis of a rotating astronomical body.
Currently, Earth's pole stars are Polaris (Alpha Ursae Minoris), a bright magnitude-2 star aligned approximately with its ...
as north mark.
File:WInd Rose Aguiar.svg, More ornate compass rose, with letters of traditional winds, a cross pattée
A cross pattée, cross patty or cross paty, also known as a cross formy or cross formée (french: croix pattée, german: Tatzenkreuz), is a type of Christian cross with arms that are narrow at the centre, and often flared in a curve or straight ...
(referring to Jerusalem) for east, and a compass needle as north mark, from a nautical chart by Jorge de Aguiar (1492)
File:Compass rose Cantino.svg, Highly ornate compass rose, with fleur-de-lis
The fleur-de-lis, also spelled fleur-de-lys (plural ''fleurs-de-lis'' or ''fleurs-de-lys''), is a lily (in French, and mean 'flower' and 'lily' respectively) that is used as a decorative design or symbol.
The fleur-de-lis has been used in the ...
as north mark and cross pattée as east mark, from the Cantino planisphere (1502)
Modern depictions
 The contemporary compass rose appears as two rings, one smaller and set inside the other. The outside ring denotes true cardinal directions while the smaller inside ring denotes magnetic cardinal directions.
The contemporary compass rose appears as two rings, one smaller and set inside the other. The outside ring denotes true cardinal directions while the smaller inside ring denotes magnetic cardinal directions. True north
True north (also called geodetic north or geographic north) is the direction along Earth's surface towards the geographic North Pole or True North Pole.
Geodetic north differs from ''magnetic'' north (the direction a compass points toward t ...
refers to the geographical location of the north pole
The North Pole, also known as the Geographic North Pole or Terrestrial North Pole, is the point in the Northern Hemisphere where the Earth's rotation, Earth's axis of rotation meets its surface. It is called the True North Pole to distingu ...
while magnetic north
The north magnetic pole, also known as the magnetic north pole, is a point on the surface of Earth's Northern Hemisphere at which the planet's magnetic field points vertically downward (in other words, if a magnetic compass needle is allowed t ...
refers to the direction towards which the north pole of a magnetic object (as found in a compass
A compass is a device that shows the cardinal directions used for navigation and geographic orientation. It commonly consists of a magnetized needle or other element, such as a compass card or compass rose, which can pivot to align itself wit ...
) will point. The angular difference between true and magnetic north is called variation, which varies depending on location. The angular difference between magnetic heading and compass heading is called deviation which varies by vessel and its heading. North arrows are often included in contemporary maps as part of the map layout
Map layout, also called map composition or (cartographic) page layout, is the part of cartographic design that involves assembling various map elements on a page. This may include the map image itself, along with titles, legends, scale indicator ...
.
The modern compass rose has eight principal winds. Listed clockwise, these are:
Although modern compasses use the names of the eight principal directions (N, NE, E, SE, etc.), older compasses use the traditional Italianate wind names of Medieval origin (Tramontana, Greco, Levante, etc.)
4-point compass roses use only the four "basic winds" or "cardinal directions
The four cardinal directions, or cardinal points, are the four main compass directions: north, east, south, and west, commonly denoted by their initials N, E, S, and W respectively. Relative to north, the directions east, south, and west are at ...
" (North, East, South, West), with angles of difference at 90°.
8-point compass roses use the eight principal winds—that is, the four cardinal directions (N, E, S, W) plus the four "intercardinal" or "ordinal directions
The four cardinal directions, or cardinal points, are the four main compass directions: north, east, south, and west, commonly denoted by their initials N, E, S, and W respectively. Relative to north, the directions east, south, and west are at ...
" (NE, SE, SW, NW), at angles of difference of 45°.
12-point compass roses, with markings 30° apart, are often painted on airport ramp
The airport apron, apron, flight line, ramp, or tarmac is the area of an airport where aircraft are parked, unloaded or loaded, refueled, boarded, or maintained. Although the use of the apron is covered by regulations, such as lighting on vehic ...
s to assist with the adjustment of aircraft magnetic compass compensators.
 16-point compass roses are constructed by bisecting the angles of the principal winds to come up with intermediate compass points, known as
16-point compass roses are constructed by bisecting the angles of the principal winds to come up with intermediate compass points, known as half-wind
The points of the compass are a set of horizontal, Radius, radially arrayed compass directions (or Azimuth#In navigation, azimuths) used in navigation and cartography. A compass rose is primarily composed of four cardinal directions—north, east ...
s, at angles of difference of 22°. The names of the half-winds are simply combinations of the principal winds to either side, principal then ordinal. E.g. North-northeast (NNE), East-northeast (ENE), etc. Using gradians, of which there are 400 in a circle, the sixteen-point rose has twenty-five gradians per point.
32-point compass roses are constructed by bisecting these angles, and coming up with quarter-winds at 11° angles of difference. Quarter-wind names are constructed with the names "X by Y", which can be read as "one quarter wind from X toward Y", where X is one of the eight principal winds and Y is one of the two adjacent cardinal directions. For example, North-by-east (NbE) is one quarter wind from North towards East, Northeast-by-north (NEbN) is one quarter wind from Northeast toward North. Naming all 32 points on the rose is called "boxing the compass
The points of the compass are a set of horizontal, radially arrayed compass directions (or azimuths) used in navigation and cartography. A compass rose is primarily composed of four cardinal directions—north, east, south, and west—each ...
".
The 32-point rose has 11° between points, but is easily found by halving divisions and may have been easier for those not using a 360° circle. Eight points make a right angle and a point is easy to estimate allowing bearings to be given such as "two points off the starboard bow".
Use as symbol
* TheNATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two No ...
symbol uses a four pointed rose.
* Outward Bound uses the compass rose as the logo for various schools around the world.
* An 8-point compass rose was the logo of Varig
VARIG (acronym for Viação Aérea RIo-Grandense, ''Rio Grandean Airways'') was the first airline founded in Brazil, in 1927. From 1965 until 1990, it was Brazil's leading airline, and virtually its only international one. In 2005, Varig went ...
, the largest airline in Brazil for many decades until its bankruptcy in 2006.
* An 8-point compass rose is a prominent feature in the logo of the Seattle Mariners
The Seattle Mariners are an American professional baseball team based in Seattle. They compete in Major League Baseball (MLB) as a member club of the American League (AL) West division. The team joined the American League as an expansion team ...
Major League Baseball
Major League Baseball (MLB) is a professional baseball organization and the oldest major professional sports league in the world. MLB is composed of 30 total teams, divided equally between the National League (NL) and the American League (AL), ...
club.
* Hong Kong Correctional Services
Hong Kong Correctional Services (also called Correctional Services Department (CSD)) is responsible for the management of prisoners and prisons in Hong Kong. The Commissioner of Correctional Services reports to the Secretary for Security.
...
's crest uses four point star.
* The compass rose is used as the symbol of the worldwide Anglican Communion
The Anglican Communion is the third largest Christian communion after the Roman Catholic and Eastern Orthodox churches. Founded in 1867 in London, the communion has more than 85 million members within the Church of England and other ...
of churches.
* A 16-point compass rose was IBM's logo for the System/360 product line.
* A 16-point compass rose is the official logo of the Spanish National University of Distance Education (Universidad Nacional de Educación a Distancia or UNED).
* A 16-point compass rose is present on the seal and the flag of the Central Intelligence Agency
The Central Intelligence Agency (CIA ), known informally as the Agency and historically as the Company, is a civilian foreign intelligence service of the federal government of the United States, officially tasked with gathering, processing, ...
of the Federal government of the United States (the CIA).
In popular culture
*''The Compass Rose
''The Compass Rose'' is a 1982 collection of short stories by American writer Ursula K. Le Guin, and illustrated by Anne Yvonne Gilbert in 1983. It is organized into sections on the theme of directions, though not strictly compass-related as the ...
'' is a 1982 collection of short stories by Ursula K. Le Guin.
See also
*Nautical star
The nautical star is a symbolic star representing the North Star, associated with the sea services of the United States armed forces and with tattoo culture. It is usually rendered as a five-pointed star in dark and light shades counterchanged in ...
* Pelorus (instrument)
In marine navigation, a pelorus is a reference tool for maintaining bearing of a vessel at sea. It is a "simplified compass" without a directive element, suitably mounted and provided with vanes to permit observation of relative bearings.
The i ...
* Points of the compass
* Rhumbline network
* Wind Rose
References
External links
Origins of the Compass Rose
The Rose of the Winds
an example of a rose with 26 directions.
Compass Rose of Piedro Reinel, 1504
an example of a 32-point rose with cross for east (the Christian Holy Land) and fleur-di-lis for north.
Brief compass rose history info
{{DEFAULTSORT:Compass Rose Navigation Cartography