Cognitive Planning on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Cognitive planning is one of the executive functions. It encompasses the neurological processes involved in the formulation, evaluation and selection of a sequence of thoughts and actions to achieve a desired goal. Various studies utilizing a combination of neuropsychological, neuropharmacological and functional
Cognitive planning is one of the executive functions. It encompasses the neurological processes involved in the formulation, evaluation and selection of a sequence of thoughts and actions to achieve a desired goal. Various studies utilizing a combination of neuropsychological, neuropharmacological and functional
 There are a variety of neuropsychological tests which can be used to measure variance of planning ability between the subject and controls.
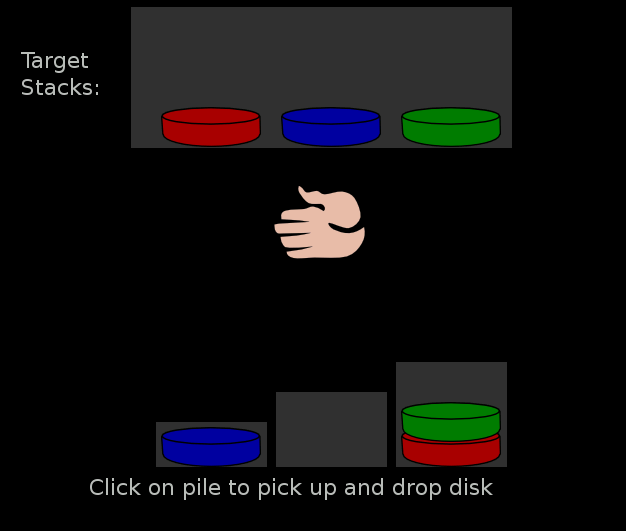
* Tower of Hanoi (TOH-R), a puzzle invented in 1883 by the French mathematician Édouard Lucas. There are variations of the puzzle - the classic version consists of three rods and usually seven to nine discs of subsequently smaller size. Planning is a key component of the problem solving skills necessary to achieve the objective, which is to move the entire stack to another rod, obeying the following rules:
**Only one disk may be moved at a time.
**Each move consists of taking the upper disk from one of the rods and sliding it onto another rod, on top of the other disks that may already be present on that rod.
**No disk may be placed on top of a smaller disk.
There are a variety of neuropsychological tests which can be used to measure variance of planning ability between the subject and controls.
* Tower of Hanoi (TOH-R), a puzzle invented in 1883 by the French mathematician Édouard Lucas. There are variations of the puzzle - the classic version consists of three rods and usually seven to nine discs of subsequently smaller size. Planning is a key component of the problem solving skills necessary to achieve the objective, which is to move the entire stack to another rod, obeying the following rules:
**Only one disk may be moved at a time.
**Each move consists of taking the upper disk from one of the rods and sliding it onto another rod, on top of the other disks that may already be present on that rod.
**No disk may be placed on top of a smaller disk.
 *
*
 Cognitive planning is one of the executive functions. It encompasses the neurological processes involved in the formulation, evaluation and selection of a sequence of thoughts and actions to achieve a desired goal. Various studies utilizing a combination of neuropsychological, neuropharmacological and functional
Cognitive planning is one of the executive functions. It encompasses the neurological processes involved in the formulation, evaluation and selection of a sequence of thoughts and actions to achieve a desired goal. Various studies utilizing a combination of neuropsychological, neuropharmacological and functional neuroimaging
Neuroimaging is the use of quantitative (computational) techniques to study the structure and function of the central nervous system, developed as an objective way of scientifically studying the healthy human brain in a non-invasive manner. Incr ...
approaches have suggested there is a positive relationship between impaired planning ability and damage to the frontal lobe
The frontal lobe is the largest of the four major lobes of the brain in mammals, and is located at the front of each cerebral hemisphere (in front of the parietal lobe and the temporal lobe). It is parted from the parietal lobe by a groove be ...
.
A specific area within the mid-dorsolateral frontal cortex located in the frontal lobe has been implicated as playing an intrinsic role in both cognitive planning and associated executive traits such as working memory.
Disruption of the neural pathway
In neuroanatomy, a neural pathway is the connection formed by axons that project from neurons to make synapses onto neurons in another location, to enable neurotransmission (the sending of a signal from one region of the nervous system to an ...
s, via various mechanisms such as traumatic brain injury
A traumatic brain injury (TBI), also known as an intracranial injury, is an injury to the brain caused by an external force. TBI can be classified based on severity (ranging from mild traumatic brain injury TBI/concussionto severe traumatic br ...
, or the effects of neurodegenerative disease
A neurodegenerative disease is caused by the progressive loss of structure or function of neurons, in the process known as neurodegeneration. Such neuronal damage may ultimately involve cell death. Neurodegenerative diseases include amyotrophic ...
s between this area of the frontal cortex and the basal ganglia
The basal ganglia (BG), or basal nuclei, are a group of subcortical nuclei, of varied origin, in the brains of vertebrates. In humans, and some primates, there are some differences, mainly in the division of the globus pallidus into an exter ...
specifically the striatum (cortico-striatal pathway), may disrupt the processes required for normal planning function.
Individuals who were born with very low birth weight (VLBW - <1500 grams) and extremely low birth weight (ELBW) are at greater risk of various cognitive deficits including planning ability.
Neuropsychological test
 There are a variety of neuropsychological tests which can be used to measure variance of planning ability between the subject and controls.
* Tower of Hanoi (TOH-R), a puzzle invented in 1883 by the French mathematician Édouard Lucas. There are variations of the puzzle - the classic version consists of three rods and usually seven to nine discs of subsequently smaller size. Planning is a key component of the problem solving skills necessary to achieve the objective, which is to move the entire stack to another rod, obeying the following rules:
**Only one disk may be moved at a time.
**Each move consists of taking the upper disk from one of the rods and sliding it onto another rod, on top of the other disks that may already be present on that rod.
**No disk may be placed on top of a smaller disk.
There are a variety of neuropsychological tests which can be used to measure variance of planning ability between the subject and controls.
* Tower of Hanoi (TOH-R), a puzzle invented in 1883 by the French mathematician Édouard Lucas. There are variations of the puzzle - the classic version consists of three rods and usually seven to nine discs of subsequently smaller size. Planning is a key component of the problem solving skills necessary to achieve the objective, which is to move the entire stack to another rod, obeying the following rules:
**Only one disk may be moved at a time.
**Each move consists of taking the upper disk from one of the rods and sliding it onto another rod, on top of the other disks that may already be present on that rod.
**No disk may be placed on top of a smaller disk.
 *
*Tower of London
The Tower of London, officially His Majesty's Royal Palace and Fortress of the Tower of London, is a historic castle on the north bank of the River Thames in central London. It lies within the London Borough of Tower Hamlets, which is sep ...
(TOL) is another test that was developed in 1982 (Shallice 1982) specifically to detect deficits in planning as may occur with damage to the frontal lobe. test participants with damage to the left anterior frontal lobe demonstrated planning deficits (i.e., greater number of moves required for solution).
In test, participants with damage to the right anterior, and left or right posterior areas of the frontal lobes showed no impairment. The results implicating the left anterior frontal lobes involvement in solving the TOL were supported in concomitant neuroimaging studies which also showed a reduction in regional cerebral blood flow to the left pre-frontal lobe. For the number of moves, a significant negative correlation was observed for the left prefrontal area, i.e. subjects that took more time planning their moves showed greater activation in the left prefrontal area.
References
Bibliography
J P Das, Binod C Kar, Rauno K Parrila, ''Cognitive Planning: The Psychological Basis of Intelligent Behaviour''. Sage Publications Pvt. Ltd; illustrated edition. {{ISBN, 978-0-8039-9287-0 Neuropsychological assessment Cognitive psychology Cognitive science Motor control