Cirrocumulus Cloud on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Cirrocumulus is one of the three main genus-types of high-altitude tropospheric
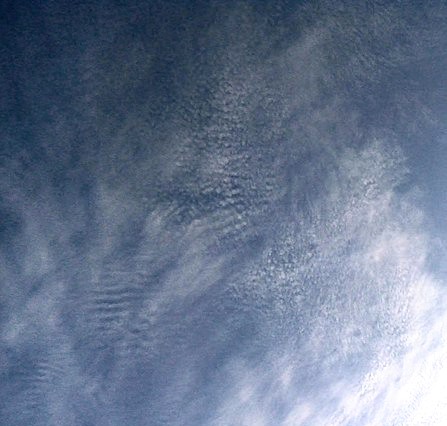
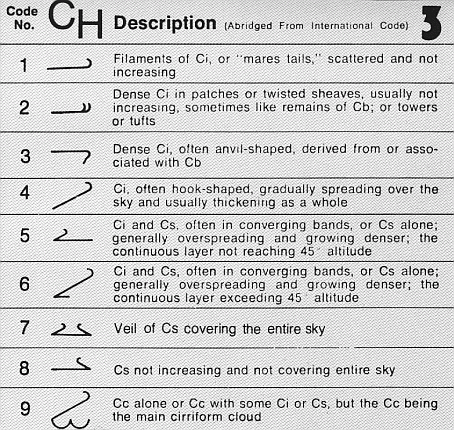 Cirrocumulus is a cloud of the ''stratocumuliform'' physical category that shows both stratiform and cumuliform characteristics and typically appears as white, patchy sheets with ripples or tufts without gray shading. Each cloudlet appears no larger than a finger held at arm's length. These often are organized in rows like other cumuliform and stratocumuliform clouds, but since they are so small, cirrocumulus patches take on a finer appearance, sometimes also referred to colloquially as "herringbone" or as a " mackerel sky". Cirrocumulus is coded CH9 for the main genus-type and all subforms.
Cirrocumulus is distinguished from
Cirrocumulus is a cloud of the ''stratocumuliform'' physical category that shows both stratiform and cumuliform characteristics and typically appears as white, patchy sheets with ripples or tufts without gray shading. Each cloudlet appears no larger than a finger held at arm's length. These often are organized in rows like other cumuliform and stratocumuliform clouds, but since they are so small, cirrocumulus patches take on a finer appearance, sometimes also referred to colloquially as "herringbone" or as a " mackerel sky". Cirrocumulus is coded CH9 for the main genus-type and all subforms.
Cirrocumulus is distinguished from

International Cloud Atlas – Cirrocumulus
{{DEFAULTSORT:Cirrocumulus Cloud Cirrus Cumulus
cloud
In meteorology, a cloud is an aerosol consisting of a visible mass of miniature liquid droplets, frozen crystals, or other particles suspended in the atmosphere of a planetary body or similar space. Water or various other chemicals may ...
s, the other two being cirrus
Cirrus may refer to:
Science
*Cirrus (biology), any of various thin, thread-like structures on the body of an animal
*Cirrus (botany), a tendril
* Infrared cirrus, in astronomy, filamentary structures seen in infrared light
*Cirrus cloud, a typ ...
and cirrostratus
Cirrostratus is a high-level, very thin, generally uniform ''stratiform'' genus-type of cloud. It is made out of ice-crystals, which are pieces of frozen water. It is difficult to detect and it can make halos. These are made when the cloud takes ...
. They usually occur at an altitude of . Like lower-altitude cumuliform and stratocumuliform clouds, cirrocumulus signifies convection
Convection is single or multiphase fluid flow that occurs spontaneously due to the combined effects of material property heterogeneity and body forces on a fluid, most commonly density and gravity (see buoyancy). When the cause of the c ...
. Unlike other high-altitude tropospheric clouds like cirrus and cirrostratus, cirrocumulus includes a small amount of liquid water droplets, although these are in a supercooled
Supercooling, also known as undercooling, is the process of lowering the temperature of a liquid or a gas below its melting point without it becoming a solid. It achieves this in the absence of a seed crystal or nucleus around which a crysta ...
state. Ice crystals are the predominant component, and typically, the ice crystals cause the supercooled water drops in the cloud to rapidly freeze, transforming the cirrocumulus into cirrostratus. This process can also produce precipitation in the form of a virga
In meteorology, a virga, also called a dry storm, is an observable streak or shaft of precipitation falling from a cloud that evaporates or sublimates before reaching the ground. A shaft of precipitation that does not evaporate before rea ...
consisting of ice or snow. Thus, cirrocumulus clouds are usually short-lived., p.21 They usually only form as part of a short-lived transitional phase within an area of cirrus clouds and can also form briefly as a result of the breaking up of part of a cumulonimbus anvil.
Properly, the term cirrocumulus refers to each cloud, but is typically also used to refer to an entire patch of cirrocumulus. When used in this way, each cirrocumulus element is referred to as a "cloudlet".
Appearance
 Cirrocumulus is a cloud of the ''stratocumuliform'' physical category that shows both stratiform and cumuliform characteristics and typically appears as white, patchy sheets with ripples or tufts without gray shading. Each cloudlet appears no larger than a finger held at arm's length. These often are organized in rows like other cumuliform and stratocumuliform clouds, but since they are so small, cirrocumulus patches take on a finer appearance, sometimes also referred to colloquially as "herringbone" or as a " mackerel sky". Cirrocumulus is coded CH9 for the main genus-type and all subforms.
Cirrocumulus is distinguished from
Cirrocumulus is a cloud of the ''stratocumuliform'' physical category that shows both stratiform and cumuliform characteristics and typically appears as white, patchy sheets with ripples or tufts without gray shading. Each cloudlet appears no larger than a finger held at arm's length. These often are organized in rows like other cumuliform and stratocumuliform clouds, but since they are so small, cirrocumulus patches take on a finer appearance, sometimes also referred to colloquially as "herringbone" or as a " mackerel sky". Cirrocumulus is coded CH9 for the main genus-type and all subforms.
Cirrocumulus is distinguished from altocumulus
Altocumulus (From Latin ''Altus'', "high", ''cumulus'', "heaped") is a middle-altitude cloud genus that belongs mainly to the ''stratocumuliform'' physical category characterized by globular masses or rolls in layers or patches, the individual ele ...
in several ways, although the two stratocumuliform genus types can occasionally occur together with no clear demarcation between them. Cirrocumulus generally occur at higher altitudes than altocumulus, thus the "cloudlets" appear smaller, as they are more distant from observation at ground level. They are also colder. Cirrocumulus clouds never cast self-shadows and are translucent to a certain degree. They are also typically found amongst other cirrus clouds in the sky and are usually themselves seen to be transforming into these other types of cirrus. This often occurs at the leading edge of a warm front, where many types of cirriform clouds can be present.
Cirrocumulus clouds tend to reflect the red and yellow colours during a sunset and sunrise, so they have been referred to as "one of the most beautiful clouds". This occurs because they reflect the unscattered rays of light from the early morning or evening sun, and those rays are yellow, orange, red, and sometimes purple.
Forecasting
Cirrocumulus usually only forms in patches. If it forms in patches with cirrus or cirrostratus and the clouds spread across the sky, it usually means rain in 8–10 hours (can be more if the front is slow-moving). Only small patches of cirrocumulus and perhaps some wisps of cirrus usually mean a continuation of good weather (although this may also be seen in conjunction with showers and thunderstorms). If it is seen after rain, it usually means improving the weather.Subtypes
* Species: '' Cirrocumulus stratiformis'' (Cc str) is one of four species and appears in the form of relatively flat stratocumuliform sheets or patches. The species ''Cirrocumulus lenticularis
Cirrocumulus lenticularis is a type of cirrocumulus cloud. The name ''cirrocumulus lenticularis'' is derived from Latin, meaning "like a lentil". Cirrocumulus lenticularis are smooth clouds that have the appearance of a lens or an almond. They usu ...
'' (Cc len) takes its name from the lens-shaped structure of this cloud which is tapered at each end. '' Cirrocumulus castellanus'' (Cc cas) has cumuliform buildups that give the cloud a partly or mainly turreted appearance. When the cumuliform parts have more of a tufted appearance, it is given the species name '' Cirrocumulus floccus'' (Cc flo). Cirrocumulus with castellanus buildups can show some vertical extent, but are not usually classified as vertical or multi-étage clouds.
** Varieties: This genus type is always translucent and so has no opacity-based varieties. However, like cirrus, certain cirrocumulus species can sometimes be divided into pattern-based varieties. The ''undulatus'' variety has a wavy undulating base and is seen mostly with the stratiformis and lenticularis species types. The ''lacunosus'' variety contains circular holes caused by downdrafts in the cloud and is associated mainly with the species stratiformis, castellanus, and floccus.
*** Precipitation-based supplementary feature: Cirrocumulus occasionally produces ''virga'', precipitation that evaporates before reaching the ground..
*** Cloud-based supplementary feature: ''Mamma'' in the form of downward forming bubbles is infrequently seen as a cloud-based supplementary feature.
*** Mother clouds: This genus type has no recognized genitus mother clouds. However cirrocumulus stratiformis ''cirromutatus'' or ''cirrostratomutatus'' can result from sheets or filaments of high cloud taking on a stratocumuliform structure as a result of high altitude convection. A high layer of white or light grey altocumulus of a particular species can thin out into pure white cirrocumulus ''altocumulomutatus'' of the same species.

References
External links
International Cloud Atlas – Cirrocumulus
{{DEFAULTSORT:Cirrocumulus Cloud Cirrus Cumulus