Chemical Analysis on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Analytical chemistry studies and uses instruments and methods to separate, identify, and quantify matter. In practice, separation, identification or quantification may constitute the entire analysis or be combined with another method. Separation isolates
Analytical chemistry studies and uses instruments and methods to separate, identify, and quantify matter. In practice, separation, identification or quantification may constitute the entire analysis or be combined with another method. Separation isolates
 Analytical chemistry has been important since the early days of chemistry, providing methods for determining which elements and chemicals are present in the object in question. During this period, significant contributions to analytical chemistry included the development of systematic elemental analysis by
Analytical chemistry has been important since the early days of chemistry, providing methods for determining which elements and chemicals are present in the object in question. During this period, significant contributions to analytical chemistry included the development of systematic elemental analysis by
 Although modern analytical chemistry is dominated by sophisticated instrumentation, the roots of analytical chemistry and some of the principles used in modern instruments are from traditional techniques, many of which are still used today. These techniques also tend to form the backbone of most undergraduate analytical chemistry educational labs.
Although modern analytical chemistry is dominated by sophisticated instrumentation, the roots of analytical chemistry and some of the principles used in modern instruments are from traditional techniques, many of which are still used today. These techniques also tend to form the backbone of most undergraduate analytical chemistry educational labs.

 Mass spectrometry measures
Mass spectrometry measures
 Separation processes are used to decrease the complexity of material mixtures. Chromatography, electrophoresis and
Separation processes are used to decrease the complexity of material mixtures. Chromatography, electrophoresis and
 The visualization of single molecules, single cells, biological tissues, and nanomaterials is an important and attractive approach in analytical science. Also, hybridization with other traditional analytical tools is revolutionizing analytical science.
The visualization of single molecules, single cells, biological tissues, and nanomaterials is an important and attractive approach in analytical science. Also, hybridization with other traditional analytical tools is revolutionizing analytical science.
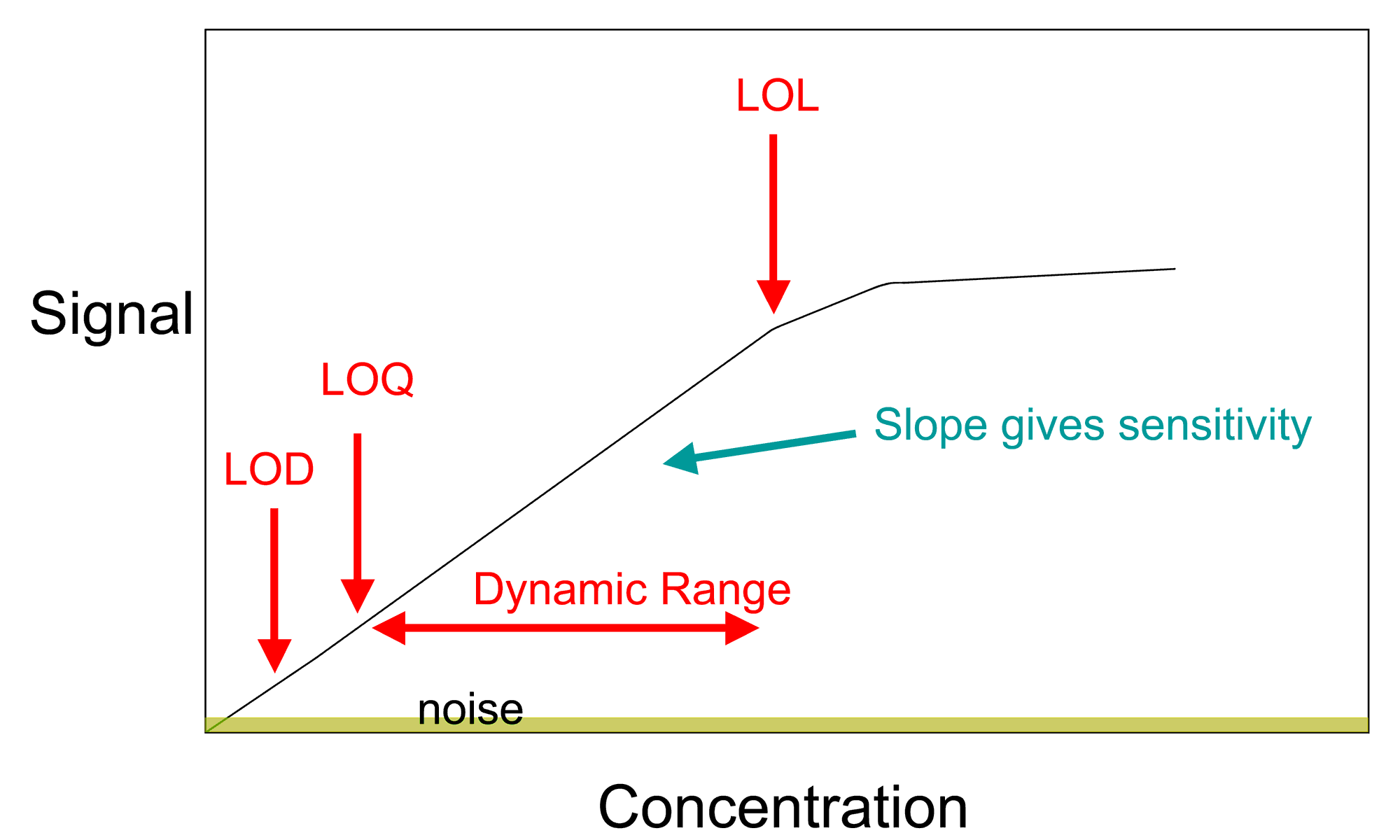 A general method for analysis of concentration involves the creation of a
A general method for analysis of concentration involves the creation of a

 Analytical chemistry has applications including in
Analytical chemistry has applications including in
Infografik
an
animation
showing the progress of analytical chemistry
aas
Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometer {{Authority control Materials science
 Analytical chemistry studies and uses instruments and methods to separate, identify, and quantify matter. In practice, separation, identification or quantification may constitute the entire analysis or be combined with another method. Separation isolates
Analytical chemistry studies and uses instruments and methods to separate, identify, and quantify matter. In practice, separation, identification or quantification may constitute the entire analysis or be combined with another method. Separation isolates analyte
An analyte, component (in clinical chemistry), or chemical species is a substance or chemical constituent that is of interest in an analytical procedure. The purest substances are referred to as analytes, such as 24 karat gold, NaCl, water, e ...
s. Qualitative analysis identifies analytes, while quantitative analysis determines the numerical amount or concentration.
Analytical chemistry consists of classical, wet chemical methods and modern, instrumental methods. Classical qualitative methods use separations such as precipitation, extraction Extraction may refer to:
Science and technology
Biology and medicine
* Comedo extraction, a method of acne treatment
* Dental extraction, the surgical removal of a tooth from the mouth
Computing and information science
* Data extraction, the pr ...
, and distillation. Identification may be based on differences in color, odor, melting point, boiling point, solubility, radioactivity or reactivity. Classical quantitative analysis uses mass or volume changes to quantify amount. Instrumental methods may be used to separate samples using chromatography, electrophoresis or field flow fractionation
Field-flow fractionation, abbreviated FFF, is a separation technique which does not have a stationary phase. It is similar to liquid chromatography as it works on dilute solutions or suspensions of the solute. Separation is achieved by applying ...
. Then qualitative and quantitative analysis can be performed, often with the same instrument and may use light interaction, heat interaction, electric fields
Electric Fields are an Aboriginal Australian electronic music duo made up of vocalist Zaachariaha Fielding and keyboard player and producer Michael Ross. Electric Fields combine modern electric-soul music with Aboriginal culture and sing in Pi ...
or magnetic fields
A magnetic field is a vector field that describes the magnetic influence on moving electric charges, electric currents, and magnetic materials. A moving charge in a magnetic field experiences a force perpendicular to its own velocity and to ...
. Often the same instrument can separate, identify and quantify an analyte.
Analytical chemistry is also focused on improvements in experimental design
The design of experiments (DOE, DOX, or experimental design) is the design of any task that aims to describe and explain the variation of information under conditions that are hypothesized to reflect the variation. The term is generally associ ...
, chemometrics, and the creation of new measurement tools. Analytical chemistry has broad applications to medicine, science, and engineering.
History
 Analytical chemistry has been important since the early days of chemistry, providing methods for determining which elements and chemicals are present in the object in question. During this period, significant contributions to analytical chemistry included the development of systematic elemental analysis by
Analytical chemistry has been important since the early days of chemistry, providing methods for determining which elements and chemicals are present in the object in question. During this period, significant contributions to analytical chemistry included the development of systematic elemental analysis by Justus von Liebig
Justus Freiherr von Liebig (12 May 1803 – 20 April 1873) was a German scientist who made major contributions to agricultural and biological chemistry, and is considered one of the principal founders of organic chemistry. As a professor at the ...
and systematized organic analysis based on the specific reactions of functional groups.
The first instrumental analysis was flame emissive spectrometry developed by Robert Bunsen and Gustav Kirchhoff who discovered rubidium
Rubidium is the chemical element with the symbol Rb and atomic number 37. It is a very soft, whitish-grey solid in the alkali metal group, similar to potassium and caesium. Rubidium is the first alkali metal in the group to have a density higher ...
(Rb) and caesium
Caesium ( IUPAC spelling) (or cesium in American English) is a chemical element with the symbol Cs and atomic number 55. It is a soft, silvery-golden alkali metal with a melting point of , which makes it one of only five elemental metals that a ...
(Cs) in 1860.
Most of the major developments in analytical chemistry took place after 1900. During this period, instrumental analysis became progressively dominant in the field. In particular, many of the basic spectroscopic and spectrometric techniques were discovered in the early 20th century and refined in the late 20th century.
The separation sciences follow a similar time line of development and also became increasingly transformed into high performance instruments. In the 1970s many of these techniques began to be used together as hybrid techniques to achieve a complete characterization of samples.
Starting in the 1970s, analytical chemistry became progressively more inclusive of biological questions ( bioanalytical chemistry), whereas it had previously been largely focused on inorganic or small organic molecules. Lasers have been increasingly used as probes and even to initiate and influence a wide variety of reactions. The late 20th century also saw an expansion of the application of analytical chemistry from somewhat academic chemical questions to forensic, environmental, industrial and medical
Medicine is the science and practice of caring for a patient, managing the diagnosis, prognosis, prevention, treatment, palliation of their injury or disease, and promoting their health. Medicine encompasses a variety of health care practic ...
questions, such as in histology
Histology,
also known as microscopic anatomy or microanatomy, is the branch of biology which studies the microscopic anatomy of biological tissues. Histology is the microscopic counterpart to gross anatomy, which looks at larger structures vis ...
.
Modern analytical chemistry is dominated by instrumental analysis. Many analytical chemists focus on a single type of instrument. Academics tend to either focus on new applications and discoveries or on new methods of analysis. The discovery of a chemical present in blood that increases the risk of cancer would be a discovery that an analytical chemist might be involved in. An effort to develop a new method might involve the use of a tunable laser to increase the specificity and sensitivity of a spectrometric method. Many methods, once developed, are kept purposely static so that data can be compared over long periods of time. This is particularly true in industrial quality assurance (QA), forensic and environmental applications. Analytical chemistry plays an increasingly important role in the pharmaceutical industry where, aside from QA, it is used in the discovery of new drug candidates and in clinical applications where understanding the interactions between the drug and the patient are critical.
Classical methods
 Although modern analytical chemistry is dominated by sophisticated instrumentation, the roots of analytical chemistry and some of the principles used in modern instruments are from traditional techniques, many of which are still used today. These techniques also tend to form the backbone of most undergraduate analytical chemistry educational labs.
Although modern analytical chemistry is dominated by sophisticated instrumentation, the roots of analytical chemistry and some of the principles used in modern instruments are from traditional techniques, many of which are still used today. These techniques also tend to form the backbone of most undergraduate analytical chemistry educational labs.
Qualitative analysis
Qualitative analysis determines the presence or absence of a particular compound, but not the mass or concentration. By definition, qualitative analyses do not measure quantity.Chemical tests
There are numerous qualitative chemical tests, for example, the acid test for gold and the Kastle-Meyer test for the presence of blood.Flame test
Inorganic qualitative analysis generally refers to a systematic scheme to confirm the presence of certain aqueous ions or elements by performing a series of reactions that eliminate a range of possibilities and then confirm suspected ions with a confirming test. Sometimes small carbon-containing ions are included in such schemes. With modern instrumentation, these tests are rarely used but can be useful for educational purposes and in fieldwork or other situations where access to state-of-the-art instruments is not available or expedient.Quantitative analysis
Quantitative analysis is the measurement of the quantities of particular chemical constituents present in a substance. Quantities can be measured by mass (gravimetric analysis) or volume (volumetric analysis).Gravimetric analysis
The gravimetric analysis involves determining the amount of material present by weighing the sample before and/or after some transformation. A common example used in undergraduate education is the determination of the amount of water in a hydrate by heating the sample to remove the water such that the difference in weight is due to the loss of water.Volumetric analysis
Titration involves the addition of a reactant to a solution being analyzed until some equivalence point is reached. Often the amount of material in the solution being analyzed may be determined. Most familiar to those who have taken chemistry during secondary education is the acid-base titration involving a color-changing indicator. There are many other types of titrations, for example, potentiometric titrations. These titrations may use different types of indicators to reach some equivalence point.Instrumental methods

Spectroscopy
Spectroscopy measures the interaction of the molecules with electromagnetic radiation. Spectroscopy consists of many different applications such asatomic absorption spectroscopy
Atomic absorption spectroscopy (AAS) and atomic emission spectroscopy (AES) is a spectroanalytical procedure for the quantitative determination of chemical elemlight) by free atoms in the gaseous state. Atomic absorption spectroscopy is based o ...
, atomic emission spectroscopy
Atomic may refer to:
* Of or relating to the atom, the smallest particle of a chemical element that retains its chemical properties
* Atomic physics, the study of the atom
* Atomic Age, also known as the "Atomic Era"
* Atomic scale, distances comp ...
, ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy, X-ray spectroscopy, fluorescence spectroscopy, infrared spectroscopy
Infrared spectroscopy (IR spectroscopy or vibrational spectroscopy) is the measurement of the interaction of infrared radiation with matter by absorption, emission, or reflection. It is used to study and identify chemical substances or function ...
, Raman spectroscopy, dual polarization interferometry, nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, most commonly known as NMR spectroscopy or magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS), is a spectroscopic technique to observe local magnetic fields around atomic nuclei. The sample is placed in a magnetic fie ...
, photoemission spectroscopy, Mössbauer spectroscopy and so on.
Mass spectrometry
 Mass spectrometry measures
Mass spectrometry measures mass-to-charge ratio
The mass-to-charge ratio (''m''/''Q'') is a physical quantity relating the ''mass'' (quantity of matter) and the ''electric charge'' of a given particle, expressed in units of kilograms per coulomb (kg/C). It is most widely used in the electrody ...
of molecules using electric
Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and motion of matter that has a property of electric charge. Electricity is related to magnetism, both being part of the phenomenon of electromagnetism, as described ...
and magnetic fields. There are several ionization methods: electron ionization
Electron ionization (EI, formerly known as electron impact ionization and electron bombardment ionization) is an ionization method in which energetic electrons interact with solid or gas phase atoms or molecules to produce ions. EI was one of t ...
, chemical ionization
Chemical ionization (CI) is a soft ionization technique used in mass spectrometry. This was first introduced by Burnaby Munson and Frank H. Field in 1966. This technique is a branch of gaseous ion-molecule chemistry. Reagent gas molecules (ofte ...
, electrospray ionization
Electrospray ionization (ESI) is a technique used in mass spectrometry to produce ions using an electrospray in which a high voltage is applied to a liquid to create an aerosol. It is especially useful in producing ions from macromolecules becaus ...
, fast atom bombardment, matrix assisted laser desorption/ionization, and others. Also, mass spectrometry is categorized by approaches of mass analyzers: magnetic-sector
A sector instrument is a general term for a class of mass spectrometer that uses a static electric (E) or magnetic (B) sector or some combination of the two (separately in space) as a mass analyzer. Popular combinations of these sectors have been ...
, quadrupole mass analyzer, quadrupole ion trap, time-of-flight, Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance
Fourier-transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry is a type of mass analyzer (or mass spectrometer) for determining the mass-to-charge ratio (''m''/''z'') of ions based on the cyclotron frequency of the ions in a fixed magnetic field. Th ...
, and so on.
Electrochemical analysis
Electroanalytical methods measure the potential ( volts) and/orcurrent
Currents, Current or The Current may refer to:
Science and technology
* Current (fluid), the flow of a liquid or a gas
** Air current, a flow of air
** Ocean current, a current in the ocean
*** Rip current, a kind of water current
** Current (stre ...
( amps) in an electrochemical cell containing the analyte. These methods can be categorized according to which aspects of the cell are controlled and which are measured. The four main categories are potentiometry
A potentiometer is an instrument for measuring voltage or 'potential difference' by comparison of an unknown voltage with a known reference voltage. If a sensitive indicating instrument is used, very little current is drawn from the source of the ...
(the difference in electrode potentials is measured), coulometry Coulometry determines the amount of matter transformed during an electrolysis reaction by measuring the amount of electricity (in coulombs) consumed or produced. It can be used for precision measurements of charge, and the amperes even used to have ...
(the transferred charge is measured over time), amperometry (the cell's current is measured over time), and voltammetry
Voltammetry is a category of electroanalytical methods used in analytical chemistry and various industrial processes. In voltammetry, information about an analyte is obtained by measuring the current as the potential is varied. The analytical dat ...
(the cell's current is measured while actively altering the cell's potential).
Thermal analysis
Calorimetry and thermogravimetric analysis measure the interaction of a material and heat.Separation
 Separation processes are used to decrease the complexity of material mixtures. Chromatography, electrophoresis and
Separation processes are used to decrease the complexity of material mixtures. Chromatography, electrophoresis and field flow fractionation
Field-flow fractionation, abbreviated FFF, is a separation technique which does not have a stationary phase. It is similar to liquid chromatography as it works on dilute solutions or suspensions of the solute. Separation is achieved by applying ...
are representative of this field.
Hybrid techniques
Combinations of the above techniques produce a "hybrid" or "hyphenated" technique. Several examples are in popular use today and new hybrid techniques are under development. For example, gas chromatography-mass spectrometry, gas chromatography-infrared spectroscopy
Infrared spectroscopy (IR spectroscopy or vibrational spectroscopy) is the measurement of the interaction of infrared radiation with matter by absorption, emission, or reflection. It is used to study and identify chemical substances or function ...
, liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry, liquid chromatography- NMR spectroscopy, liquid chromatography-infrared spectroscopy, and capillary electrophoresis-mass spectrometry.
Hyphenated separation techniques refer to a combination of two (or more) techniques to detect and separate chemicals from solutions. Most often the other technique is some form of chromatography. Hyphenated techniques are widely used in chemistry and biochemistry
Biochemistry or biological chemistry is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. A sub-discipline of both chemistry and biology, biochemistry may be divided into three fields: structural biology, enzymology and ...
. A slash is sometimes used instead of hyphen
The hyphen is a punctuation mark used to join words and to separate syllables of a single word. The use of hyphens is called hyphenation. ''Son-in-law'' is an example of a hyphenated word. The hyphen is sometimes confused with dashes ( figure ...
, especially if the name of one of the methods contains a hyphen itself.
Microscopy
 The visualization of single molecules, single cells, biological tissues, and nanomaterials is an important and attractive approach in analytical science. Also, hybridization with other traditional analytical tools is revolutionizing analytical science.
The visualization of single molecules, single cells, biological tissues, and nanomaterials is an important and attractive approach in analytical science. Also, hybridization with other traditional analytical tools is revolutionizing analytical science. Microscopy
Microscopy is the technical field of using microscopes to view objects and areas of objects that cannot be seen with the naked eye (objects that are not within the resolution range of the normal eye). There are three well-known branches of mic ...
can be categorized into three different fields: optical microscopy, electron microscopy
An electron microscope is a microscope that uses a beam of accelerated electrons as a source of illumination. As the wavelength of an electron can be up to 100,000 times shorter than that of visible light photons, electron microscopes have a hi ...
, and scanning probe microscopy. Recently, this field is rapidly progressing because of the rapid development of the computer and camera industries.
Lab-on-a-chip
Devices that integrate (multiple) laboratory functions on a single chip of only millimeters to a few square centimeters in size and that are capable of handling extremely small fluid volumes down to less than picoliters.Errors
Error can be defined as numerical difference between observed value and true value. The experimental error can be divided into two types, systematic error and random error. Systematic error results from a flaw in equipment or the design of an experiment while random error results from uncontrolled or uncontrollable variables in the experiment. In error the true value and observed value in chemical analysis can be related with each other by the equation : where * is the absolute error. * is the true value. * is the observed value. An error of a measurement is an inverse measure of accurate measurement, i.e. smaller the error greater the accuracy of the measurement. Errors can be expressed relatively. Given the relative error(): : The percent error can also be calculated: : If we want to use these values in a function, we may also want to calculate the error of the function. Let be a function with variables. Therefore, thepropagation of uncertainty
In statistics, propagation of uncertainty (or propagation of error) is the effect of variables' uncertainties (or errors, more specifically random errors) on the uncertainty of a function based on them. When the variables are the values of ex ...
must be calculated in order to know the error in :
:
Standards
Standard curve
 A general method for analysis of concentration involves the creation of a
A general method for analysis of concentration involves the creation of a calibration curve
In analytical chemistry, a calibration curve, also known as a standard curve, is a general method for determining the concentration of a substance in an unknown sample by comparing the unknown to a set of standard samples of known concentration ...
. This allows for the determination of the amount of a chemical in a material by comparing the results of an unknown sample to those of a series of known standards. If the concentration of element or compound in a sample is too high for the detection range of the technique, it can simply be diluted in a pure solvent. If the amount in the sample is below an instrument's range of measurement, the method of addition can be used. In this method, a known quantity of the element or compound under study is added, and the difference between the concentration added and the concentration observed is the amount actually in the sample.
Internal standards
Sometimes aninternal standard An internal standard in analytical chemistry is a chemical substance that is added in a constant amount to samples, the blank and calibration standards in a chemical analysis. This substance can then be used for calibration by plotting the ratio of ...
is added at a known concentration directly to an analytical sample to aid in quantitation. The amount of analyte present is then determined relative to the internal standard as a calibrant. An ideal internal standard is an isotopically enriched analyte which gives rise to the method of isotope dilution
Isotope dilution analysis is a method of determining the quantity of chemical substances. In its most simple conception, the method of isotope dilution comprises the addition of known amounts of isotopically enriched substance to the analyzed samp ...
.
Standard addition
The method ofstandard addition
The method of standard addition is a type of quantitative analysis approach often used in analytical chemistry whereby the standard is added directly to the aliquots of analyzed sample. This method is used in situations where sample matrix also ...
is used in instrumental analysis to determine the concentration of a substance (analyte
An analyte, component (in clinical chemistry), or chemical species is a substance or chemical constituent that is of interest in an analytical procedure. The purest substances are referred to as analytes, such as 24 karat gold, NaCl, water, e ...
) in an unknown sample by comparison to a set of samples of known concentration, similar to using a calibration curve
In analytical chemistry, a calibration curve, also known as a standard curve, is a general method for determining the concentration of a substance in an unknown sample by comparing the unknown to a set of standard samples of known concentration ...
. Standard addition can be applied to most analytical techniques and is used instead of a calibration curve
In analytical chemistry, a calibration curve, also known as a standard curve, is a general method for determining the concentration of a substance in an unknown sample by comparing the unknown to a set of standard samples of known concentration ...
to solve the matrix effect
In chemical analysis, matrix refers to the components of a sample other than the analyte of interest. The matrix can have a considerable effect on the way the analysis is conducted and the quality of the results are obtained; such effects are call ...
problem.
Signals and noise
One of the most important components of analytical chemistry is maximizing the desired signal while minimizing the associatednoise
Noise is unwanted sound considered unpleasant, loud or disruptive to hearing. From a physics standpoint, there is no distinction between noise and desired sound, as both are vibrations through a medium, such as air or water. The difference aris ...
. The analytical figure of merit is known as the signal-to-noise ratio
Signal-to-noise ratio (SNR or S/N) is a measure used in science and engineering that compares the level of a desired signal to the level of background noise. SNR is defined as the ratio of signal power to the noise power, often expressed in de ...
(S/N or SNR).
Noise can arise from environmental factors as well as from fundamental physical processes.
Thermal noise
Thermal noise results from the motion of charge carriers (usually electrons) in an electrical circuit generated by their thermal motion. Thermal noise is white noise meaning that the power spectral density is constant throughout the frequency spectrum. Theroot mean square
In mathematics and its applications, the root mean square of a set of numbers x_i (abbreviated as RMS, or rms and denoted in formulas as either x_\mathrm or \mathrm_x) is defined as the square root of the mean square (the arithmetic mean of the ...
value of the thermal noise in a resistor is given by
:
where ''k''B is Boltzmann's constant
The Boltzmann constant ( or ) is the proportionality factor that relates the average relative kinetic energy of particles in a gas with the thermodynamic temperature of the gas. It occurs in the definitions of the kelvin and the gas constant, ...
, ''T'' is the temperature, ''R'' is the resistance, and is the bandwidth
Bandwidth commonly refers to:
* Bandwidth (signal processing) or ''analog bandwidth'', ''frequency bandwidth'', or ''radio bandwidth'', a measure of the width of a frequency range
* Bandwidth (computing), the rate of data transfer, bit rate or thr ...
of the frequency .
Shot noise
Shot noise is a type of electronic noise that occurs when the finite number of particles (such as electrons in an electronic circuit or photons in an optical device) is small enough to give rise to statistical fluctuations in a signal. Shot noise is a Poisson process, and the charge carriers that make up the current follow a Poisson distribution. The root mean square current fluctuation is given by : where ''e'' is theelementary charge
The elementary charge, usually denoted by is the electric charge carried by a single proton or, equivalently, the magnitude of the negative electric charge carried by a single electron, which has charge −1 . This elementary charge is a fundame ...
and ''I'' is the average current. Shot noise is white noise.
Flicker noise
Flicker noise is electronic noise with a 1/''ƒ'' frequency spectrum; as ''f'' increases, the noise decreases. Flicker noise arises from a variety of sources, such as impurities in a conductive channel, generation, and recombination noise in a transistor due to base current, and so on. This noise can be avoided by modulation of the signal at a higher frequency, for example, through the use of alock-in amplifier
A lock-in amplifier is a type of amplifier that can extract a signal with a known carrier wave from an extremely noisy environment. Depending on the dynamic reserve of the instrument, signals up to a million times smaller than noise components, p ...
.
Environmental noise

Environmental noise
Environmental noise is an accumulation of noise pollution that occurs outside. This noise can be caused by transport, industrial, and recreational activities.
Noise is frequently described as 'unwanted sound'. Within this context, environmenta ...
arises from the surroundings of the analytical instrument. Sources of electromagnetic noise are power lines
Electric power transmission is the bulk movement of electrical energy from a generating site, such as a power plant, to an electrical substation. The interconnected lines that facilitate this movement form a ''transmission network''. This is d ...
, radio and television stations, wireless device
Wireless communication (or just wireless, when the context allows) is the transfer of information between two or more points without the use of an electrical conductor, optical fiber or other continuous guided medium for the transfer. The most ...
s, compact fluorescent lamps and electric motors. Many of these noise sources are narrow bandwidth and, therefore, can be avoided. Temperature and vibration isolation Vibration isolation is the process of isolating an object, such as a piece of equipment, from the source of vibrations.
Vibration is undesirable in many domains, primarily engineered systems and habitable spaces, and methods have been developed to p ...
may be required for some instruments.
Noise reduction
Noise reduction can be accomplished either incomputer hardware
Computer hardware includes the physical parts of a computer, such as the case, central processing unit (CPU), random access memory (RAM), monitor, mouse, keyboard, computer data storage, graphics card, sound card, speakers and motherboard.
...
or software. Examples of hardware noise reduction are the use of shielded cable, analog filter
Analogue Filter (signal processing), filters are a basic building block of signal processing much used in electronics. Amongst their many applications are the separation of an audio signal before application to bass (music), bass, mid-range spe ...
ing, and signal modulation. Examples of software noise reduction are digital filter
In signal processing, a digital filter is a system that performs mathematical operations on a sampled, discrete-time signal to reduce or enhance certain aspects of that signal. This is in contrast to the other major type of electronic filter, t ...
ing, ensemble average
In physics, specifically statistical mechanics, an ensemble (also statistical ensemble) is an idealization consisting of a large number of virtual copies (sometimes infinitely many) of a system, considered all at once, each of which represents a ...
, boxcar average, and correlation methods.
Applications
 Analytical chemistry has applications including in
Analytical chemistry has applications including in forensic science
Forensic science, also known as criminalistics, is the application of science to criminal and civil laws, mainly—on the criminal side—during criminal investigation, as governed by the legal standards of admissible evidence and criminal ...
, bioanalysis
Bioanalysis is a sub-discipline of analytical chemistry covering the quantitative measurement of xenobiotics (drugs and their metabolites, and biological molecules in unnatural locations or concentrations) and biotics (macromolecules, proteins, ...
, clinical analysis, environmental analysis
Environmental analysis is the use of analytical chemistry and other techniques to study the environment. The purpose of this is commonly to monitor and study levels of pollutants in the atmosphere, rivers and other specific settings. Other enviro ...
, and materials analysis
Material is a substance or mixture of substances that constitutes an object. Materials can be pure or impure, living or non-living matter. Materials can be classified on the basis of their physical and chemical properties, or on their geologica ...
. Analytical chemistry research is largely driven by performance (sensitivity, detection limit, selectivity, robustness, dynamic range
Dynamic range (abbreviated DR, DNR, or DYR) is the ratio between the largest and smallest values that a certain quantity can assume. It is often used in the context of signals, like sound and light. It is measured either as a ratio or as a base- ...
, linear range
The linear range is that range of input or output values for which an electronic amplifier produces an output signal that is a direct, linear function of the input signal. That is, the output can be represented by the equation:
:''Output'' = ''In ...
, accuracy, precision, and speed), and cost (purchase, operation, training, time, and space). Among the main branches of contemporary analytical atomic spectrometry, the most widespread and universal are optical and mass spectrometry. In the direct elemental analysis of solid samples, the new leaders are laser-induced breakdown and laser ablation
Laser ablation or photoablation (also called laser blasting) is the process of removing material from a solid (or occasionally liquid) surface by irradiating it with a laser beam. At low laser flux, the material is heated by the absorbed laser ...
mass spectrometry, and the related techniques with transfer of the laser ablation products into inductively coupled plasma. Advances in design of diode lasers and optical parametric oscillators promote developments in fluorescence and ionization spectrometry and also in absorption techniques where uses of optical cavities for increased effective absorption pathlength are expected to expand. The use of plasma- and laser-based methods is increasing. An interest towards absolute (standardless) analysis has revived, particularly in emission spectrometry.
Great effort is being put into shrinking the analysis techniques to chip Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) is a type of immunoprecipitation experimental technique used to investigate the interaction between proteins and DNA in the cell. It aims to determine whether specific proteins are associated with specific geno ...
size. Although there are few examples of such systems competitive with traditional analysis techniques, potential advantages include size/portability, speed, and cost. (micro total analysis system
Total Analysis System (TAS) describes a device that automates and includes all necessary steps for chemical analysis of a sample e.g. sampling, sample transport, filtration, dilution, chemical reactions, separation and detection.
µTAS
A new ...
(µTAS) or lab-on-a-chip
A lab-on-a-chip (LOC) is a device that integrates one or several laboratory functions on a single integrated circuit (commonly called a "chip") of only millimeters to a few square centimeters to achieve automation and high-throughput screening. ...
). Microscale chemistry
Microscale chemistry (often referred to as small-scale chemistry, in German: Chemie im Mikromaßstab) is an analytical method and also a teaching method widely used at school and at university levels, working with small quantities of chemical sub ...
reduces the amounts of chemicals used.
Many developments improve the analysis of biological systems. Examples of rapidly expanding fields in this area are genomics
Genomics is an interdisciplinary field of biology focusing on the structure, function, evolution, mapping, and editing of genomes. A genome is an organism's complete set of DNA, including all of its genes as well as its hierarchical, three-dim ...
, DNA sequencing and related research in genetic fingerprinting
DNA profiling (also called DNA fingerprinting) is the process of determining an individual's DNA characteristics. DNA analysis intended to identify a species, rather than an individual, is called DNA barcoding.
DNA profiling is a forensic tec ...
and DNA microarray; proteomics
Proteomics is the large-scale study of proteins. Proteins are vital parts of living organisms, with many functions such as the formation of structural fibers of muscle tissue, enzymatic digestion of food, or synthesis and replication of DNA. I ...
, the analysis of protein concentrations and modifications, especially in response to various stressors, at various developmental stages, or in various parts of the body, metabolomics, which deals with metabolites; transcriptomics, including mRNA and associated fields; lipidomics
Lipidomics is the large-scale study of pathways and networks of cellular lipids in biological systems The word "lipidome" is used to describe the complete lipid profile within a cell, tissue, organism, or ecosystem and is a subset of the "metabolo ...
- lipids and its associated fields; peptidomics - peptides and its associated fields; and metallomics, dealing with metal concentrations and especially with their binding to proteins and other molecules.
Analytical chemistry has played a critical role in the understanding of basic science to a variety of practical applications, such as biomedical applications, environmental monitoring, quality control of industrial manufacturing, forensic science, and so on.
The recent developments in computer automation and information technologies have extended analytical chemistry into a number of new biological fields. For example, automated DNA sequencing machines were the basis for completing human genome projects leading to the birth of genomics
Genomics is an interdisciplinary field of biology focusing on the structure, function, evolution, mapping, and editing of genomes. A genome is an organism's complete set of DNA, including all of its genes as well as its hierarchical, three-dim ...
. Protein identification and peptide sequencing by mass spectrometry opened a new field of proteomics
Proteomics is the large-scale study of proteins. Proteins are vital parts of living organisms, with many functions such as the formation of structural fibers of muscle tissue, enzymatic digestion of food, or synthesis and replication of DNA. I ...
. In addition to automating specific processes, there is effort to automate larger sections of lab testing, such as in companies like Emerald Cloud Lab
Emerald Cloud Lab (ECL) is a privately-owned biotech startup. The company focuses on advancing laboratory virtualization, for chemistry and biotechnology, by building the first fully functional cloud lab, allowing scientists to conduct all of their ...
and Transcriptic.
Analytical chemistry has been an indispensable area in the development of nanotechnology. Surface characterization instruments, electron microscopes and scanning probe microscopes enable scientists to visualize atomic structures with chemical characterizations.
See also
* Important publications in analytical chemistry * List of chemical analysis methods * List of materials analysis methods * Measurement uncertainty * Metrology * Sensory analysis - in the field of Food science * Virtual instrumentation * Microanalysis *Quality of analytical results
Quality of measurements made in chemistry and other areas is an important issue in today’s world as measurements influence quality of life, cross-border trade and commerce. In this respect, EN ISO 17025 is the main standard used by testing and ...
* Working range
References
Further reading
* Gurdeep, Chatwal Anand (2008). ''Instrumental Methods of Chemical Analysis'' Himalaya Publishing House (India) * Ralph L. Shriner, Reynold C. Fuson, David Y. Curtin, Terence C. Morill: ''The systematic identification of organic compounds - a laboratory manual'', Verlag Wiley, New York 1980, 6. edition, . *Bettencourt da Silva, R; Bulska, E; Godlewska-Zylkiewicz, B; Hedrich, M; Majcen, N; Magnusson, B; Marincic, S; Papadakis, I; Patriarca, M; Vassileva, E; Taylor, P; Analytical measurement: measurement uncertainty and statistics, 2012, .External links
*Infografik
an
animation
showing the progress of analytical chemistry
aas
Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometer {{Authority control Materials science