Cardiomegaly on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Cardiomegaly (sometimes megacardia or megalocardia) is a medical condition in which the
 * Chest X-Ray:
* Chest X-Ray: 
 * Cardiac catheterization and biopsy: In this procedure, a thin tube (catheter) is inserted into the groin and threaded through the blood vessels to the heart, where a small sample (biopsy) of the heart, if indicated, can be extracted for laboratory analysis.
* For deceased people, cardiomegaly at autopsy has been suggested when the heart weighs more than >399 grams in women and >449 grams in men.
* Cardiac catheterization and biopsy: In this procedure, a thin tube (catheter) is inserted into the groin and threaded through the blood vessels to the heart, where a small sample (biopsy) of the heart, if indicated, can be extracted for laboratory analysis.
* For deceased people, cardiomegaly at autopsy has been suggested when the heart weighs more than >399 grams in women and >449 grams in men.
American Heart Association
{{portal bar, Medicine
heart
The heart is a muscular organ in most animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the body, while carrying metabolic waste such as carbon dioxide to t ...
is enlarged. As such, it is more commonly referred to simply as "having an enlarged heart". It is usually the result of underlying conditions that make the heart work harder, such as obesity
Obesity is a medical condition, sometimes considered a disease, in which excess body fat has accumulated to such an extent that it may negatively affect health. People are classified as obese when their body mass index (BMI)—a person's ...
, heart valve disease, high blood pressure ( hypertension), and coronary artery disease. Cardiomyopathy is also associated with cardiomegaly.
Cardiomegaly can be serious depending on what part of the heart is enlarged, and can result in congestive heart failure
Heart failure (HF), also known as congestive heart failure (CHF), is a syndrome, a group of signs and symptoms caused by an impairment of the heart's blood pumping function. Symptoms typically include shortness of breath, excessive fatigue, ...
. Recent studies suggest that cardiomegaly is associated with a higher risk of sudden cardiac death
Cardiac arrest is when the heart suddenly and unexpectedly stops beating. It is a medical emergency that, without immediate medical intervention, will result in sudden cardiac death within minutes. Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) and possib ...
.
Cardiomegaly may improve over time, but many people with an enlarged heart (dilated cardiomyopathy) need lifelong treatment with medication. Having an immediate family member who has or had cardiomegaly may indicate that a person is more susceptible to getting this condition.
Signs and symptoms
For many people, cardiomegaly is asymptomatic. For others, if the enlarged heart begins to affect the body's ability to pump blood effectively, then symptoms associated with congestive heart failure may arise, including: * Heart palpitations – the irregular beating of the heart, usually associated with a valve issue inside the heart. * Severe shortness of breath (especially when physically active) – irregularly unable to catch one's breath. * Chest pain * Coughing, when lying down * Fatigue * Swelling in legs * Increased abdominal girth * Weight gain * Edema – swelling * Fainting There is not much variation in these symptoms because they are mostly specific to the chest area. However, some are more common than others depending on each patient.Causes
The causes of cardiomegaly are not well understood and many cases of cardiomegaly have no known cause. Prevention of cardiomegaly starts with detection. If a person has a family history of cardiomegaly, one should let one's doctor know so that treatments can be implemented to help prevent the worsening of the condition. In addition, prevention includes avoiding certain lifestyle risk factors such as tobacco use and controlling one's highcholesterol
Cholesterol is any of a class of certain organic molecules called lipids. It is a sterol (or modified steroid), a type of lipid. Cholesterol is biosynthesized by all animal cells and is an essential structural component of animal cell mem ...
, high blood pressure, and diabetes
Diabetes, also known as diabetes mellitus, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level ( hyperglycemia) over a prolonged period of time. Symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst and increased ...
. Non-lifestyle risk factors include a family history of cardiomegaly, coronary artery disease (CAD), congenital heart failure, atherosclerotic
Atherosclerosis is a pattern of the disease arteriosclerosis in which the wall of the artery develops abnormalities, called lesions. These lesions may lead to narrowing due to the buildup of atheromatous plaque. At onset there are usually no ...
disease, valvular heart disease
Valvular heart disease is any cardiovascular disease process involving one or more of the four valves of the heart (the aortic and mitral valves on the left side of heart and the pulmonic and tricuspid valves on the right side of heart). These ...
, exposure to cardiac toxins, sleep-disordered breathing (such as sleep apnea), sustained cardiac arrhythmias
Arrhythmias, also known as cardiac arrhythmias, heart arrhythmias, or dysrhythmias, are irregularities in the heartbeat, including when it is too fast or too slow. A resting heart rate that is too fast – above 100 beats per minute in adults ...
, abnormal electrocardiograms
Electrocardiography is the process of producing an electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG), a recording of the heart's electrical activity. It is an electrogram of the heart which is a graph of voltage versus time of the electrical activity of the hear ...
, and cardiomegaly on chest X-ray. Lifestyle factors that can help prevent cardiomegaly include eating a healthy diet, controlling blood pressure, exercise, medications, and not abusing alcohol and cocaine. Current research and the evidence of previous cases link the following (below) as possible causes of cardiomegaly.
The most common known causes of cardiomegaly are congenital (patients are born with the condition based on a genetic inheritance), high blood pressure (which can enlarge the left ventricle causing the heart muscle to weaken over time), and coronary artery disease. In the latter case, the disease creates blockages in the heart's blood supply, leading to tissue death which causes other areas of the heart to work harder, causing the heart to expand in size.
Other possible causes include:
* Heart valve disease
* Cardiomyopathy (disease of the heart muscle)
* Pulmonary
The lungs are the primary organs of the respiratory system in humans and most other animals, including some snails and a small number of fish. In mammals and most other vertebrates, two lungs are located near the backbone on either side of ...
hypertension
* Pericardial effusion (fluid around the heart)
* Thyroid
The thyroid, or thyroid gland, is an endocrine gland in vertebrates. In humans it is in the neck and consists of two connected lobes. The lower two thirds of the lobes are connected by a thin band of tissue called the thyroid isthmus. The thy ...
Disorders
* Hemochromatosis
Iron overload or hemochromatosis (also spelled ''haemochromatosis'' in British English) indicates increased total accumulation of iron in the body from any cause and resulting organ damage. The most important causes are hereditary haemochromatos ...
(excessive iron in the blood)
* Amyloidosis
* Chagas disease, an important cause of cardiomegaly in Latin America
Latin America or
* french: Amérique Latine, link=no
* ht, Amerik Latin, link=no
* pt, América Latina, link=no, name=a, sometimes referred to as LatAm is a large cultural region in the Americas where Romance languages — languages derived f ...
* Viral infection of the heart
* Pregnancy, with enlarged heart developing around the time of delivery (peripartum cardiomyopathy)
* Kidney disease requiring dialysis
* Alcohol or cocaine abuse
* HIV infection
* Diabetes
Mechanism
Cardiomegaly is a condition affecting the cardiovascular system, specifically the heart. This condition is strongly associated with congestive heart failure. Within the heart, the working fibers of themyocardial
Cardiac muscle (also called heart muscle, myocardium, cardiomyocytes and cardiac myocytes) is one of three types of vertebrate muscle tissues, with the other two being skeletal muscle and smooth muscle. It is an involuntary, striated muscle that ...
tissue increase in size. As the heart works harder the actin
Actin is a family of globular multi-functional proteins that form microfilaments in the cytoskeleton, and the thin filaments in muscle fibrils. It is found in essentially all eukaryotic cells, where it may be present at a concentration of ov ...
and myosin filaments experience less overlap which increases the size of the myocardial fibers. If there is less overlap of the protein filaments within the sarcomeres
A sarcomere (Greek σάρξ ''sarx'' "flesh", μέρος ''meros'' "part") is the smallest functional unit of striated muscle tissue. It is the repeating unit between two Z-lines. Skeletal muscles are composed of tubular muscle cells (called musc ...
of the muscle fibers, they will not be able to effectively pull on one another. If the heart tissue gets too big and stretches too far, then those filaments cannot effectively pull on one another to shorten the muscle fibers, impacting the heart's sliding filament mechanism. If fibers cannot shorten properly and the heart cannot contract properly, then blood cannot be effectively pumped to the lungs to be re-oxygenated or to the body to deliver oxygen to the working tissues of the body.
A person with an enlarged heart is more susceptible to forming blood clots in the lining of their heart. These clots can also be formed in other parts of the body. Once they enter the bloodstream, it makes it difficult for the organs in the body to receive blood, due to the blockage caused by the clots. This can impact other body systems as well and lead to other problems.
Diagnosis
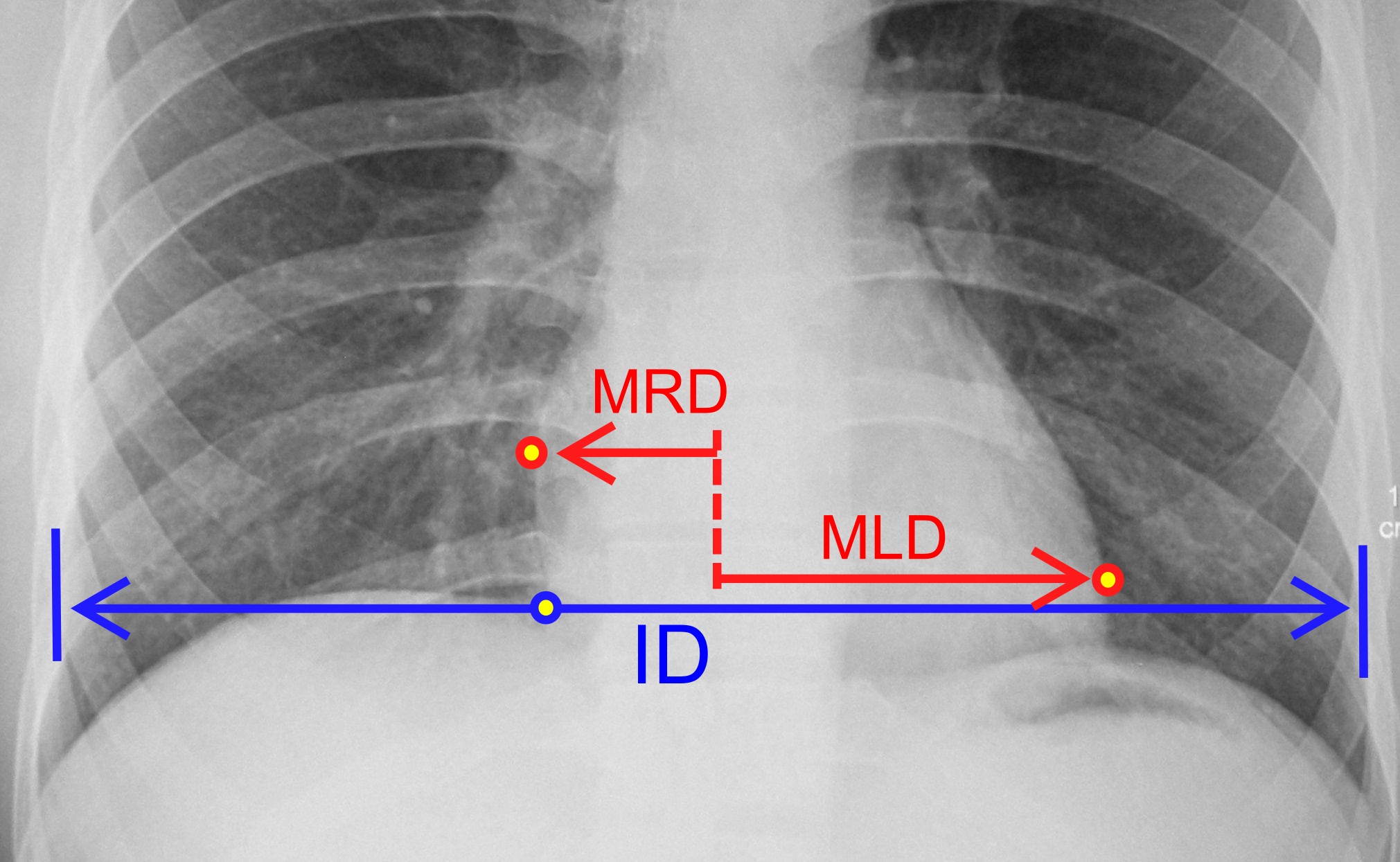
There are many techniques and tests used to diagnose an enlarged heart. The results of these tests can often be used to see how efficiently the heart is pumping, determine which chambers of the heart are enlarged, look for evidence of previous heart attacks and determine if a person has congenital heart disease. * Chest X-Ray:
* Chest X-Ray: X-ray
An X-ray, or, much less commonly, X-radiation, is a penetrating form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation. Most X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 picometers to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30&nb ...
images help to visualize the condition of the lungs and heart. If the heart is enlarged on an X-ray, other tests will usually be needed to find the cause. A useful measurement on X-ray is the ''cardio-thoracic ratio'', which is the transverse diameter of the heart, compared with that of the thoracic cage
The rib cage, as an enclosure that comprises the ribs, vertebral column and sternum in the thorax of most vertebrates, protects vital organs such as the heart, lungs and great vessels.
The sternum, together known as the thoracic cage, is a sem ...
." These diameters are taken from PA chest x-rays using the widest point of the chest and measuring as far as the lung pleura, not the lateral skin margins. If the cardiac thoracic ratio is greater than 50%, pathology is suspected, assuming the x-ray has been taken correctly. The measurement was first proposed in 1919 to screen military recruits. A newer approach to using these x-rays for evaluating heart health takes the ratio of heart area to chest area and has been called the two-dimensional cardiothoracic ratio.
* Electrocardiogram: This test records the electrical activity of the heart through electrodes attached to the person's skin. Impulses are recorded as waves and displayed on a monitor or printed on paper. This test helps diagnose heart rhythm problems and assess the damage to a person's heart from a heart attack.
* Echocardiogram
An echocardiography, echocardiogram, cardiac echo or simply an echo, is an ultrasound of the heart.
It is a type of medical imaging of the heart, using standard ultrasound or Doppler ultrasound.
Echocardiography has become routinely used in th ...
: This test for diagnosing and monitoring an enlarged heart uses sound waves to produce a video image of the heart. With this test, the four chambers of the heart can be evaluated.
* Stress test: A stress test, also called an exercise stress test, provides information about how well the heart works during physical activity. It usually involves walking on a treadmill or riding a stationary bike while the heart rhythm, blood pressure, and breathing are monitored.
* Cardiac computerized tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). In a cardiac CT scan, one lies on a table inside a machine called a gantry. An X-ray tube inside the machine rotates around the body and collects images of the heart and chest. In a cardiac MRI, one lies on a table inside a long tube-like machine that uses a magnetic field and radio waves to produce signals that create images of the heart.
* Blood tests: Blood tests may be ordered to check the levels of substances in the blood that may show a heart problem. Blood tests can also help rule out other conditions that may cause one's symptoms.

 * Cardiac catheterization and biopsy: In this procedure, a thin tube (catheter) is inserted into the groin and threaded through the blood vessels to the heart, where a small sample (biopsy) of the heart, if indicated, can be extracted for laboratory analysis.
* For deceased people, cardiomegaly at autopsy has been suggested when the heart weighs more than >399 grams in women and >449 grams in men.
* Cardiac catheterization and biopsy: In this procedure, a thin tube (catheter) is inserted into the groin and threaded through the blood vessels to the heart, where a small sample (biopsy) of the heart, if indicated, can be extracted for laboratory analysis.
* For deceased people, cardiomegaly at autopsy has been suggested when the heart weighs more than >399 grams in women and >449 grams in men.
Classification
Cardiomegaly can be classified by the main enlarged location of the heart, and/or by the structure of the enlargement. There are also specific additional subtypes. For example, the athletic heart syndrome is a non-pathological
Pathology is the study of the causes and effects of disease or injury. The word ''pathology'' also refers to the study of disease in general, incorporating a wide range of biology research fields and medical practices. However, when used in th ...
condition commonly seen in sports medicine
Sports medicine is a branch of medicine that deals with physical fitness and the treatment and prevention of injuries related to sports and exercise. Although most sports teams have employed team physicians for many years, it is only since the ...
in which the human heart is enlarged, and the resting heart rate
Heart rate (or pulse rate) is the frequency of the heartbeat measured by the number of contractions (beats) of the heart per minute (bpm). The heart rate can vary according to the body's physical needs, including the need to absorb oxygen and excr ...
is lower
Lower may refer to:
*Lower (surname)
*Lower Township, New Jersey
*Lower Receiver (firearms)
*Lower Wick Gloucestershire, England
See also
*Nizhny
Nizhny (russian: Ни́жний; masculine), Nizhnyaya (; feminine), or Nizhneye (russian: Ни́� ...
than normal.
By enlarged location
*Ventricular hypertrophy
Ventricular hypertrophy (VH) is thickening of the walls of a ventricle (lower chamber) of the heart. Although left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) is more common, right ventricular hypertrophy (RVH), as well as concurrent hypertrophy of both ventr ...
** Left
** Right
Rights are legal, social, or ethical principles of freedom or entitlement; that is, rights are the fundamental normative rules about what is allowed of people or owed to people according to some legal system, social convention, or ethical ...
/ Cor pulmonale
Pulmonary heart disease, also known as cor pulmonale, is the enlargement and failure of the right ventricle of the heart as a response to increased vascular resistance (such as from pulmonic stenosis) or high blood pressure in the lungs.
Chroni ...
* Atrial enlargement
Atrial enlargement refers to a condition where the left atrium or right atrium of the heart is larger than would be expected. It can also affect both atria.
Types include:
* Left atrial enlargement
* Right atrial enlargement
References
Ca ...
** Left
** Right
Rights are legal, social, or ethical principles of freedom or entitlement; that is, rights are the fundamental normative rules about what is allowed of people or owed to people according to some legal system, social convention, or ethical ...
Structure of enlargement
Dilated cardiomyopathy
Dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) is a condition in which the heart becomes enlarged and cannot pump blood effectively. Symptoms vary from none to feeling tired, leg swelling, and shortness of breath. It may also result in chest pain or fainting. Co ...
is the most common type of cardiomegaly. In this condition, the walls of the left and/or right ventricles of the heart become thin and stretched. The result is an enlarged heart.
In the other types of cardiomegaly, the heart's large muscular left ventricle becomes abnormally thick. Hypertrophy is usually what causes left ventricular enlargement. Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is typically an inherited condition.
Treatment
Treatments for cardiomegaly include a combination of medication treatment and medical/surgical procedures. Below are some of the treatment options for individuals with cardiomegaly: Medications *Diuretics
A diuretic () is any substance that promotes diuresis, the increased production of urine. This includes forced diuresis. A diuretic tablet is sometimes colloquially called a water tablet. There are several categories of diuretics. All diuretics i ...
: to lower the amount of sodium and water in the body, which can help lower the pressure in the arteries and heart.
* Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors: to lower the blood pressure and improve the heart's pumping ability.
* Angiotensin receptor blockers
Angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs), formally angiotensin II receptor type 1 (AT1) antagonists, also known as angiotensin receptor blockers, angiotensin II receptor antagonists, or AT1 receptor antagonists, are a group of pharmaceuticals tha ...
(ARBs): to provide the benefits of ACE inhibitors for those who can't take ACE inhibitors.
* Beta blockers
Beta blockers, also spelled β-blockers, are a class of medications that are predominantly used to manage abnormal heart rhythms, and to protect the heart from a second heart attack after a first heart attack ( secondary prevention). They are ...
: to lower blood pressure and improve heart function.
* Digoxin: to help improve the pumping function of the heart and lessen the need for hospitalization for heart failure.
* Anticoagulants
Anticoagulants, commonly known as blood thinners, are chemical substances that prevent or reduce coagulation of blood, prolonging the clotting time. Some of them occur naturally in blood-eating animals such as leeches and mosquitoes, where they ...
: to reduce the risk of blood clots that could cause a heart attack or stroke.
* Anti-arrhythmics: to keep the heart beating with a normal rhythm.
Medical devices to regulate the heartbeat
* Pacemaker: Coordinates the contractions between the left and right ventricle. In people who may be at risk of serious arrhythmias
Arrhythmias, also known as cardiac arrhythmias, heart arrhythmias, or dysrhythmias, are irregularities in the heartbeat, including when it is too fast or too slow. A resting heart rate that is too fast – above 100 beats per minute in adults ...
, drug therapy or an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator
An implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD) or automated implantable cardioverter defibrillator (AICD) is a device implantable inside the body, able to perform defibrillation, and depending on the type, cardioversion and pacing of the h ...
(ICD) may be used.
* ICDs: Small devices implanted in the chest to constantly monitor the heart rhythm and deliver electrical shocks when needed to control abnormal, rapid heartbeats. The devices can also work as pacemakers.
Surgical procedures
* Heart valve surgery: If an enlarged heart is caused by a problem with one of the heart valves, one may have surgery to remove the valve and replace it with either an artificial valve or a tissue valve from a pig, cow or deceased human donor. If blood leaks backward through a valve (valve regurgitation), the leaky valve may be surgically repaired or replaced.
* Coronary bypass surgery: If an enlarged heart is related to coronary artery disease, one may opt to have coronary artery bypass surgery.
* Left ventricular assist device: (LVAD): This implantable mechanical pump helps a weak heart pump. LVADs are often implanted while a patient waits for a heart transplant or, if the patient is not a heart transplant candidate, as a long-term treatment for heart failure.
* Heart transplant
A heart transplant, or a cardiac transplant, is a surgical transplant procedure performed on patients with end-stage heart failure or severe coronary artery disease when other medical or surgical treatments have failed. , the most common procedu ...
: If medications can't control the symptoms, a heart transplant is often a final option.
Cardiomegaly can progress and certain complications are common:
* Heart failure: One of the most serious types of enlarged heart, an enlarged left ventricle, increases the risk of heart failure. In heart failure, the heart muscle weakens, and the ventricles stretch (dilate) to the point that the heart can't pump blood efficiently throughout the body.
* Blood clots: Having an enlarged heart may make one more susceptible to forming blood clots in the lining of the heart. If clots enter the bloodstream, they can block blood flow to vital organs, even causing a heart attack or stroke. Clots that develop on the right side of the heart may travel to the lungs, a dangerous condition called a pulmonary embolism
Pulmonary embolism (PE) is a blockage of an artery in the lungs by a substance that has moved from elsewhere in the body through the bloodstream ( embolism). Symptoms of a PE may include shortness of breath, chest pain particularly upon breathin ...
.
* Heart murmur
Heart murmurs are unique heart sounds produced when blood flows across a heart valve or blood vessel. This occurs when turbulent blood flow creates a sound loud enough to hear with a stethoscope. Turbulent blood flow is not smooth. The sound di ...
: For people who have an enlarged heart, two of the heart's four valves — the mitral
The mitral valve (), also known as the bicuspid valve or left atrioventricular valve, is one of the four heart valves. It has two cusps or flaps and lies between the left atrium and the left ventricle of the heart. The heart valves are all one-w ...
and tricuspid valves — may not close properly because they become dilated, leading to a backflow of blood. This flow creates sounds called heart murmurs.
* The exact mortality rate for people with cardiomegaly is unknown. However, many people live for a very long time with an enlarged heart and, if detected early, treatment can help improve the condition and prolong their lives.
* For some people cardiomegaly is a temporary condition, which can resolve on its own, making one's lifestyle normal like before. Others may have a permanent enlargement, which would then need to be taken care of by the above treatment options.
Lifestyle changes
* Smoking cessation
* Limiting alcohol and caffeine intake
* Maintaining a healthy weight
* Increasing fruits and vegetables in a daily diet
* Limiting consumption of high-fat and/or high-sugar foods
* Getting adequate restful sleep
References
Further reading
* * * *External links
American Heart Association
{{portal bar, Medicine