camera sensor on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
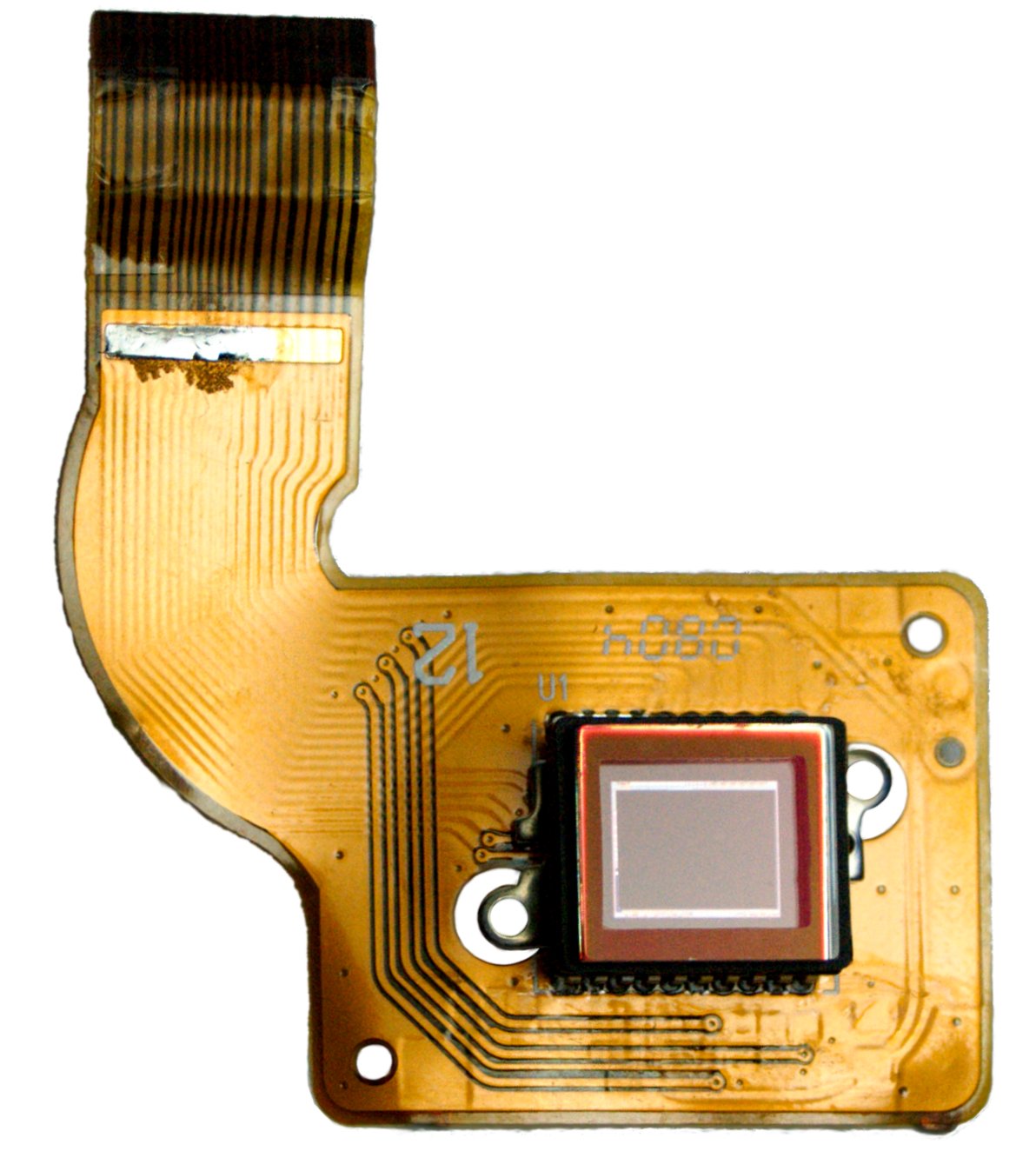
 An image sensor or imager is a sensor that detects and conveys information used to make an
An image sensor or imager is a sensor that detects and conveys information used to make an

 The two main types of digital image sensors are the
The two main types of digital image sensors are the
, home page Another approach is to utilize the very fine dimensions available in modern CMOS technology to implement a CCD like structure entirely in CMOS technology: such structures can be achieved by separating individual poly-silicon gates by a very small gap; though still a product of research hybrid sensors can potentially harness the benefits of both CCD and CMOS imagers.ieee.org - CCD in CMOS
Padmakumar R. Rao et al., "CCD structures implemented in standard 0.18 µm CMOS technology"
 There are several main types of color image sensors, differing by the type of color-separation mechanism:
* Bayer-filter sensor, low-cost and most common, using a
There are several main types of color image sensors, differing by the type of color-separation mechanism:
* Bayer-filter sensor, low-cost and most common, using a
 Special sensors are used in various applications such as
Special sensors are used in various applications such as
Digital Camera Sensor Performance Summary
by Roger Clark * (with graphical buckets and rainwater analogies) {{Authority control Digital photography MOSFETs

 An image sensor or imager is a sensor that detects and conveys information used to make an
An image sensor or imager is a sensor that detects and conveys information used to make an image
An image is a visual representation of something. It can be two-dimensional, three-dimensional, or somehow otherwise feed into the visual system to convey information. An image can be an artifact, such as a photograph or other two-dimensiona ...
. It does so by converting the variable attenuation
In physics, attenuation (in some contexts, extinction) is the gradual loss of flux intensity through a medium. For instance, dark glasses attenuate sunlight, lead attenuates X-rays, and water and air attenuate both light and sound at variable at ...
of light waves (as they pass through or reflect off objects) into signals
In signal processing, a signal is a function that conveys information about a phenomenon. Any quantity that can vary over space or time can be used as a signal to share messages between observers. The ''IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing'' ...
, small bursts of current
Currents, Current or The Current may refer to:
Science and technology
* Current (fluid), the flow of a liquid or a gas
** Air current, a flow of air
** Ocean current, a current in the ocean
*** Rip current, a kind of water current
** Current (stre ...
that convey the information. The waves can be light or other electromagnetic radiation. Image sensors are used in electronic
Electronic may refer to:
*Electronics, the science of how to control electric energy in semiconductor
* ''Electronics'' (magazine), a defunct American trade journal
*Electronic storage, the storage of data using an electronic device
*Electronic co ...
imaging devices of both analog and digital
Digital usually refers to something using discrete digits, often binary digits.
Technology and computing Hardware
*Digital electronics, electronic circuits which operate using digital signals
**Digital camera, which captures and stores digital i ...
types, which include digital camera
A digital camera is a camera that captures photographs in digital memory. Most cameras produced today are digital, largely replacing those that capture images on photographic film. Digital cameras are now widely incorporated into mobile devices ...
s, camera module
{{unreferenced, date=August 2017
A camera module is an image sensor integrated with a lens, control electronics, and an interface like CSI, Ethernet or plain raw low-voltage differential signaling.
See also
* IP camera
* Mobile Industry Process ...
s, camera phones
A camera phone is a mobile phone which is able to capture photographs and often record video using one or more built-in digital cameras. It can also send the resulting image wirelessly and conveniently. The first commercial phone with color cam ...
, optical mouse devices, medical imaging
Medical imaging is the technique and process of imaging the interior of a body for clinical analysis and medical intervention, as well as visual representation of the function of some organs or tissues (physiology). Medical imaging seeks to rev ...
equipment, night vision
Night vision is the ability to see in low-light conditions, either naturally with scotopic vision or through a night-vision device. Night vision requires both sufficient spectral range and sufficient intensity range. Humans have poor night vi ...
equipment such as thermal imaging
Infrared thermography (IRT), thermal video and/or thermal imaging, is a process where a thermal camera captures and creates an image of an object by using infrared radiation emitted from the object in a process, which are examples of infrared ...
devices, radar, sonar, and others. As technology changes, electronic and digital imaging tends to replace chemical and analog imaging.
The two main types of electronic image sensors are the charge-coupled device
A charge-coupled device (CCD) is an integrated circuit containing an array of linked, or coupled, capacitors. Under the control of an external circuit, each capacitor can transfer its electric charge to a neighboring capacitor. CCD sensors are a ...
(CCD) and the active-pixel sensor
An active-pixel sensor (APS) is an image sensor where each pixel sensor unit cell has a photodetector (typically a pinned photodiode) and one or more active transistors. In a metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) active-pixel sensor, MOSFET, MOS fie ...
(CMOS
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS, pronounced "sea-moss", ) is a type of metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) fabrication process that uses complementary and symmetrical pairs of p-type and n-type MOSF ...
sensor). Both CCD and CMOS sensors are based on metal–oxide–semiconductor
The metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET, MOS-FET, or MOS FET) is a type of field-effect transistor (FET), most commonly fabricated by the controlled oxidation of silicon. It has an insulated gate, the voltage of which d ...
(MOS) technology, with CCDs based on MOS capacitor
The metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET, MOS-FET, or MOS FET) is a type of field-effect transistor (FET), most commonly fabricated by the controlled oxidation of silicon. It has an insulated gate, the voltage of which d ...
s and CMOS sensors based on MOSFET
The metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET, MOS-FET, or MOS FET) is a type of field-effect transistor (FET), most commonly fabricated by the controlled oxidation of silicon. It has an insulated gate, the voltage of which d ...
(MOS field-effect transistor) amplifiers
An amplifier, electronic amplifier or (informally) amp is an electronic device that can increase the magnitude of a signal (a time-varying voltage or current). It may increase the power significantly, or its main effect may be to boost the v ...
. Analog sensors for invisible radiation tend to involve vacuum tubes of various kinds, while digital sensors include flat-panel detector
Flat-panel detectors are a class of solid-state x-ray digital radiography devices similar in principle to the image sensors used in digital photography and video. They are used in both projectional radiography and as an alternative to x-ray ima ...
s.
CCD vs. CMOS sensors

charge-coupled device
A charge-coupled device (CCD) is an integrated circuit containing an array of linked, or coupled, capacitors. Under the control of an external circuit, each capacitor can transfer its electric charge to a neighboring capacitor. CCD sensors are a ...
(CCD) and the active-pixel sensor
An active-pixel sensor (APS) is an image sensor where each pixel sensor unit cell has a photodetector (typically a pinned photodiode) and one or more active transistors. In a metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) active-pixel sensor, MOSFET, MOS fie ...
(CMOS sensor), fabricated in complementary MOS
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS, pronounced "sea-moss", ) is a type of metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) fabrication process that uses complementary and symmetrical pairs of p-type and n-type MOSF ...
(CMOS) or N-type MOS ( NMOS or Live MOS) technologies. Both CCD and CMOS sensors are based on MOS technology, with MOS capacitor
The metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET, MOS-FET, or MOS FET) is a type of field-effect transistor (FET), most commonly fabricated by the controlled oxidation of silicon. It has an insulated gate, the voltage of which d ...
s being the building blocks of a CCD, and MOSFET
The metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET, MOS-FET, or MOS FET) is a type of field-effect transistor (FET), most commonly fabricated by the controlled oxidation of silicon. It has an insulated gate, the voltage of which d ...
amplifiers being the building blocks of a CMOS sensor.
Cameras integrated in small consumer products generally use CMOS sensors, which are usually cheaper and have lower power consumption in battery powered devices than CCDs. CCD sensors are used for high end broadcast quality video cameras, and CMOS sensors dominate in still photography and consumer goods where overall cost is a major concern. Both types of sensor accomplish the same task of capturing light and converting it into electrical signals.
Each cell of a CCD image sensor is an analog device. When light strikes the chip it is held as a small electrical charge in each photo sensor. The charges in the line of pixels nearest to the (one or more) output amplifiers are amplified and output, then each line of pixels shifts its charges one line closer to the amplifiers, filling the empty line closest to the amplifiers. This process is then repeated until all the lines of pixels have had their charge amplified and output.
A CMOS image sensor has an amplifier for each pixel compared to the few amplifiers of a CCD. This results in less area for the capture of photons than a CCD, but this problem has been overcome by using microlenses in front of each photodiode, which focus light into the photodiode that would have otherwise hit the amplifier and not been detected. Some CMOS imaging sensors also use Back-side illumination to increase the number of photons that hit the photodiode. CMOS sensors can potentially be implemented with fewer components, use less power, and/or provide faster readout than CCD sensors. They are also less vulnerable to static electricity discharges.
Another design, a hybrid CCD/CMOS architecture (sold under the name "sCMOS
sCMOS (''scientific Complementary Metal–Oxide–Semiconductor'') are a type of CMOS image sensor (CIS). These sensors are commonly used as components in specific observational scientific instruments, such as microscopes and telescopes. sCMOS i ...
") consists of CMOS readout integrated circuits (ROICs) that are bump bonded to a CCD imaging substrate – a technology that was developed for infrared staring arrays and has been adapted to silicon-based detector technology.scmos.com, home page Another approach is to utilize the very fine dimensions available in modern CMOS technology to implement a CCD like structure entirely in CMOS technology: such structures can be achieved by separating individual poly-silicon gates by a very small gap; though still a product of research hybrid sensors can potentially harness the benefits of both CCD and CMOS imagers.ieee.org - CCD in CMOS
Padmakumar R. Rao et al., "CCD structures implemented in standard 0.18 µm CMOS technology"
Performance
There are many parameters that can be used to evaluate the performance of an image sensor, includingdynamic range
Dynamic range (abbreviated DR, DNR, or DYR) is the ratio between the largest and smallest values that a certain quantity can assume. It is often used in the context of signals, like sound and light. It is measured either as a ratio or as a base- ...
, signal-to-noise ratio
Signal-to-noise ratio (SNR or S/N) is a measure used in science and engineering that compares the level of a desired signal to the level of background noise. SNR is defined as the ratio of signal power to the noise power, often expressed in de ...
, and low-light sensitivity. For sensors of comparable types, the signal-to-noise ratio and dynamic range improve as the size increases.
Exposure-time control
Exposure time
In photography, shutter speed or exposure time is the length of time that the film or digital sensor inside the camera is exposed to light (that is, when the camera's shutter is open) when taking a photograph.
The amount of light that rea ...
of image sensors is generally controlled by either a conventional mechanical shutter, as in film cameras, or by an electronic shutter
In photography, a shutter is a device that allows light to pass for a determined period, exposing photographic film or a photosensitive digital sensor to light in order to capture a permanent image of a scene. A shutter can also be used to allow p ...
. Electronic shuttering can be "global", in which case the entire image sensor area's accumulation of photoelectrons starts and stops simultaneously, or "rolling" in which case the exposure interval of each row immediate precedes that row's readout, in a process that "rolls" across the image frame (typically from top to bottom in landscape format). Global electronic shuttering is less common, as it requires "storage" circuits to hold charge from the end of the exposure interval until the readout process gets there, typically a few milliseconds later.
Color separation
color filter array
In digital imaging, a color filter array (CFA), or color filter mosaic (CFM), is a mosaic of tiny color filters placed over the pixel sensors of an image sensor to capture color information.
The term is also used in reference to e paper devices ...
that passes red, green, and blue light to selected pixel sensors. Each individual sensor element is made sensitive to red, green, or blue by means of a color gel
Color (American English) or colour (British English) is the visual perceptual property deriving from the spectrum of light interacting with the photoreceptor cells of the eyes. Color categories and physical specifications of color are associa ...
made of chemical dyes patterned over the elements. The most common filter matrix, the Bayer pattern
A Bayer filter mosaic is a color filter array (CFA) for arranging RGB color filters on a square grid of photosensors. Its particular arrangement of color filters is used in most single-chip digital image sensors used in digital cameras, camco ...
, uses two green pixels for each red and blue. This results in less resolution for red and blue colors. The missing color samples may interpolated using a demosaicing algorithm, or ignored altogether by lossy compression
In information technology, lossy compression or irreversible compression is the class of data compression methods that uses inexact approximations and partial data discarding to represent the content. These techniques are used to reduce data size ...
. In order to improve color information, techniques like color co-site sampling
Colour co-site sampling is a system of photographic colour sensing, wherein 4, 16 or 36 images are collected from the sensor and merged to form a single image. Each subsequent image physically moves the sensor by exactly one pixel, in order to col ...
use a piezo mechanism to shift the color sensor in pixel steps.
* Foveon X3 sensor, using an array of layered pixel sensors, separating light via the inherent wavelength-dependent absorption property of silicon, such that every location senses all three color channels. This method is similar to how color film for photography works.
* 3CCD
A three-CCD (3CCD) camera is a camera whose imaging system uses three separate charge-coupled devices (CCDs), each one receiving filtered red, green, or blue color ranges. Light coming in from the lens is split by a beam-splitter prism into th ...
, using three discrete image sensors, with the color separation done by a dichroic prism
A dichroic prism is a prism that splits light into two beams of differing wavelength (colour). A trichroic prism assembly combines two dichroic prisms to split an image into 3 colours, typically as red, green and blue of the RGB colour model. ...
. The dichroic elements provide a sharper color separation, thus improving color quality. Because each sensor is equally sensitive within its passband, and at full resolution, 3-CCD sensors produce better color quality and better low light performance. 3-CCD sensors produce a full 4:4:4 signal, which is preferred in television broadcasting, video editing and chroma key
Chroma key compositing, or chroma keying, is a visual-effects and post-production technique for compositing (layering) two images or video streams together based on colour hues ( chroma range). The technique has been used in many fields to ...
visual effects.
Specialty sensors
 Special sensors are used in various applications such as
Special sensors are used in various applications such as thermography
Infrared thermography (IRT), thermal video and/or thermal imaging, is a process where a thermal camera captures and creates an image of an object by using infrared radiation emitted from the object in a process, which are examples of infrared i ...
, creation of multi-spectral image
Multispectral imaging captures image data within specific wavelength ranges across the electromagnetic spectrum. The wavelengths may be separated by filters or detected with the use of instruments that are sensitive to particular wavelengths, ...
s, video laryngoscopes, gamma camera
A gamma camera (γ-camera), also called a scintillation camera or Anger camera, is a device used to image gamma radiation emitting radioisotopes, a technique known as scintigraphy. The applications of scintigraphy include early drug development ...
s, sensor arrays for x-ray
An X-ray, or, much less commonly, X-radiation, is a penetrating form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation. Most X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 picometers to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30 ...
s, and other highly sensitive arrays for astronomy
Astronomy () is a natural science that studies celestial objects and phenomena. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and evolution. Objects of interest include planets, moons, stars, nebulae, galax ...
.
While in general digital cameras use a flat sensor, Sony prototyped a curved sensor in 2014 to reduce/eliminate Petzval field curvature
Petzval field curvature, named for Joseph Petzval, describes the optical aberration in which a flat object normal to the optical axis (or a non-flat object past the hyperfocal distance) cannot be brought properly into focus on a flat image plan ...
that occurs with a flat sensor. Use of a curved sensor allows a shorter and smaller diameter of the lens with reduced elements and components with greater aperture and reduced light fall-off at the edge of the photo.
History
Early analog sensors for visible light werevideo camera tube
Video camera tubes were devices based on the cathode ray tube that were used in television cameras to capture television images, prior to the introduction of charge-coupled device (CCD) image sensors in the 1980s. Several different types of tub ...
s. They date back to the 1930s, and several types were developed up until the 1980s. By the early 1990s, they had been replaced by modern solid-state
Solid state, or solid matter, is one of the four fundamental states of matter.
Solid state may also refer to:
Electronics
* Solid-state electronics, circuits built of solid materials
* Solid state ionics, study of ionic conductors and their ...
CCD image sensors.
The basis for modern solid-state image sensors is MOS technology, which originates from the invention of the MOSFET by Mohamed M. Atalla
Mohamed M. Atalla ( ar, محمد عطاالله; August 4, 1924 – December 30, 2009) was an Egyptian-American engineer, physicist, cryptographer, inventor and entrepreneur. He was a semiconductor pioneer who made important contributions to ...
and Dawon Kahng
Dawon Kahng ( ko, 강대원; May 4, 1931 – May 13, 1992) was a Korean-American electrical engineer and inventor, known for his work in solid-state electronics. He is best known for inventing the MOSFET (metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effe ...
at Bell Labs
Nokia Bell Labs, originally named Bell Telephone Laboratories (1925–1984),
then AT&T Bell Laboratories (1984–1996)
and Bell Labs Innovations (1996–2007),
is an American industrial research and scientific development company owned by mult ...
in 1959. Later research on MOS technology led to the development of solid-state semiconductor image sensors, including the charge-coupled device
A charge-coupled device (CCD) is an integrated circuit containing an array of linked, or coupled, capacitors. Under the control of an external circuit, each capacitor can transfer its electric charge to a neighboring capacitor. CCD sensors are a ...
(CCD) and later the active-pixel sensor
An active-pixel sensor (APS) is an image sensor where each pixel sensor unit cell has a photodetector (typically a pinned photodiode) and one or more active transistors. In a metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) active-pixel sensor, MOSFET, MOS fie ...
(CMOS
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS, pronounced "sea-moss", ) is a type of metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) fabrication process that uses complementary and symmetrical pairs of p-type and n-type MOSF ...
sensor).
The passive-pixel sensor (PPS) was the precursor to the active-pixel sensor (APS). A PPS consists of passive pixels which are read out without amplification, with each pixel consisting of a photodiode and a MOSFET
The metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET, MOS-FET, or MOS FET) is a type of field-effect transistor (FET), most commonly fabricated by the controlled oxidation of silicon. It has an insulated gate, the voltage of which d ...
switch. It is a type of photodiode array
A photodiode is a light-sensitive semiconductor diode. It produces current when it absorbs photons.
The package of a photodiode allows light (or infrared or ultraviolet radiation, or X-rays) to reach the sensitive part of the device. The packag ...
, with pixels containing a p-n junction, integrated capacitor
A capacitor is a device that stores electrical energy in an electric field by virtue of accumulating electric charges on two close surfaces insulated from each other. It is a passivity (engineering), passive electronic component with two termi ...
, and MOSFETs as selection transistors. A photodiode array was proposed by G. Weckler in 1968. This was the basis for the PPS. These early photodiode arrays were complex and impractical, requiring selection transistors to be fabricated within each pixel, along with on-chip multiplexer circuits. The noise
Noise is unwanted sound considered unpleasant, loud or disruptive to hearing. From a physics standpoint, there is no distinction between noise and desired sound, as both are vibrations through a medium, such as air or water. The difference aris ...
of photodiode arrays was also a limitation to performance, as the photodiode readout bus
A bus (contracted from omnibus, with variants multibus, motorbus, autobus, etc.) is a road vehicle that carries significantly more passengers than an average car or van. It is most commonly used in public transport, but is also in use for cha ...
capacitance resulted in increased noise level. Correlated double sampling Correlated double sampling (CDS) is a method to measure electrical values such as voltages or currents that allows removing an undesired offset. It is used often when measuring sensor outputs. The output of the sensor is measured twice: once in a kn ...
(CDS) could also not be used with a photodiode array without external memory. However, in 1914 Deputy Consul General Carl R. Loop, reported to the state department in a Consular Report on Archibald M. Low's Televista system that "It is stated that the selenium in the transmitting screen may be replaced by any diamagnetic material".
In June 2022, Samsung Electronics announced that it had created a 200 million pixel image sensor. The 200MP ISOCELL HP3 has 0.56 micrometer pixels with Samsung reporting that previous sensors had 064 micrometer pixels, a 12% decrease since 2019. The new sensor contains 200 million pixels in a 2 x 1.4 inch lens.
Charge-coupled device
Thecharge-coupled device
A charge-coupled device (CCD) is an integrated circuit containing an array of linked, or coupled, capacitors. Under the control of an external circuit, each capacitor can transfer its electric charge to a neighboring capacitor. CCD sensors are a ...
(CCD) was invented by Willard S. Boyle
Willard Sterling Boyle, (August 19, 1924May 7, 2011) was a Canadian physicist. He was a pioneer in the field of laser technology and co-inventor of the charge-coupled device.
As director of Space Science and Exploratory Studies at Bellcomm he h ...
and George E. Smith
George Elwood Smith (born May 10, 1930) is an American scientist, applied physicist, and co-inventor of the charge-coupled device (CCD). He was awarded a one-quarter share in the 2009 Nobel Prize in Physics for "the invention of an imaging semico ...
at Bell Labs in 1969. While researching MOS technology, they realized that an electric charge was the analogy of the magnetic bubble and that it could be stored on a tiny MOS capacitor
The metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET, MOS-FET, or MOS FET) is a type of field-effect transistor (FET), most commonly fabricated by the controlled oxidation of silicon. It has an insulated gate, the voltage of which d ...
. As it was fairly straightforward to fabricate a series of MOS capacitors in a row, they connected a suitable voltage to them so that the charge could be stepped along from one to the next. The CCD is a semiconductor circuit that was later used in the first digital video cameras for television broadcasting.
Early CCD sensors suffered from shutter lag. This was largely resolved with the invention of the pinned photodiode
A photodiode is a light-sensitive semiconductor diode. It produces current when it absorbs photons.
The package of a photodiode allows light (or infrared or ultraviolet radiation, or X-rays) to reach the sensitive part of the device. The packag ...
(PPD). It was invented by Nobukazu Teranishi, Hiromitsu Shiraki and Yasuo Ishihara at NEC in 1980. It was a photodetector structure with low lag, low noise
Noise is unwanted sound considered unpleasant, loud or disruptive to hearing. From a physics standpoint, there is no distinction between noise and desired sound, as both are vibrations through a medium, such as air or water. The difference aris ...
, high quantum efficiency
The term quantum efficiency (QE) may apply to incident photon to converted electron (IPCE) ratio of a photosensitive device, or it may refer to the TMR effect of a Magnetic Tunnel Junction.
This article deals with the term as a measurement of ...
and low dark current. In 1987, the PPD began to be incorporated into most CCD devices, becoming a fixture in consumer electronic
Consumer electronics or home electronics are electronic ( analog or digital) equipment intended for everyday use, typically in private homes. Consumer electronics include devices used for entertainment, communications and recreation. Usually ...
video cameras and then digital still camera
A digital camera is a camera that captures photographs in digital memory. Most cameras produced today are digital, largely replacing those that capture images on photographic film. Digital cameras are now widely incorporated into mobile devic ...
s. Since then, the PPD has been used in nearly all CCD sensors and then CMOS sensors.
Active-pixel sensor
The NMOSactive-pixel sensor
An active-pixel sensor (APS) is an image sensor where each pixel sensor unit cell has a photodetector (typically a pinned photodiode) and one or more active transistors. In a metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) active-pixel sensor, MOSFET, MOS fie ...
(APS) was invented by Olympus in Japan during the mid-1980s. This was enabled by advances in MOS semiconductor device fabrication, with MOSFET scaling
The metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET, MOS-FET, or MOS FET) is a type of field-effect transistor (FET), most commonly fabricated by the controlled oxidation of silicon. It has an insulated gate, the voltage of which d ...
reaching smaller micron and then sub-micron levels. The first NMOS APS was fabricated by Tsutomu Nakamura's team at Olympus in 1985. The CMOS
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS, pronounced "sea-moss", ) is a type of metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) fabrication process that uses complementary and symmetrical pairs of p-type and n-type MOSF ...
active-pixel sensor (CMOS sensor) was later improved by a group of scientists at the NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory in 1993. By 2007, sales of CMOS sensors had surpassed CCD sensors. By the 2010s, CMOS sensors largely displaced CCD sensors in all new applications.
Other image sensors
The first commercialdigital camera
A digital camera is a camera that captures photographs in digital memory. Most cameras produced today are digital, largely replacing those that capture images on photographic film. Digital cameras are now widely incorporated into mobile devices ...
, the Cromemco Cyclops
The Cromemco Cyclops, introduced in 1975 by Cromemco, was the first commercial all-digital camera using a digital metal-oxide-semiconductor (MOS) image sensor. It was also the first digital camera to be interfaced to a microcomputer. The dig ...
in 1975, used a 32×32 MOS image sensor. It was a modified MOS dynamic RAM (DRAM
Dynamic random-access memory (dynamic RAM or DRAM) is a type of random-access semiconductor memory that stores each bit of data in a memory cell, usually consisting of a tiny capacitor and a transistor, both typically based on metal-oxi ...
) memory chip.
MOS image sensors are widely used in optical mouse technology. The first optical mouse, invented by Richard F. Lyon
Richard "Dick" Francis Lyon (born 1952) is an American inventor, scientist, and engineer. He is one of the two people who independently invented the first optical mouse devices in 1980. He has worked in many aspects of signal processing and wa ...
at Xerox in 1980, used a 5µm NMOS integrated circuit sensor chip. Since the first commercial optical mouse, the IntelliMouse
IntelliMouse is a series of computer mice from Microsoft. The IntelliMouse series is credited with a number of innovations; Microsoft was among the first mouse vendors to introduce a scroll wheel, an optical mouse, and dedicated auxiliary buttons ...
introduced in 1999, most optical mouse devices use CMOS sensors.
In February 2018, researchers at Dartmouth College announced a new image sensing technology that the researchers call QIS, for Quanta Image Sensor. Instead of pixels, QIS chips have what the researchers call "jots." Each jot can detect a single particle of light, called a photon.
See also
*List of sensors used in digital cameras
The following is a list of image resolutions implemented in the image sensors used in various digital cameras.
:{, class="wikitable sortable"
, -
! Width (px)
! Height (px)
! Aspect ratio
! Actual pixel count
! Megapixels
! Camera examples
, -
, ...
* Contact image sensor
Contact image sensors (CIS) are image sensors used in flatbed scanners almost in direct contact with the object to be scanned. Charge-coupled devices (CCDs), the other kind of sensor often used in scanners, use mirrors to bounce light to a stati ...
(CIS)
* Electro-optical sensor
Electro-optical sensors are electronic detectors that convert light, or a change in light, into an electronic signal. These sensors are able to detect electromagnetic radiation from the infrared up to the ultraviolet wavelengths. They are used in ...
* Video camera tube
Video camera tubes were devices based on the cathode ray tube that were used in television cameras to capture television images, prior to the introduction of charge-coupled device (CCD) image sensors in the 1980s. Several different types of tub ...
* Semiconductor detector
* Fill factor
* Full-frame digital SLR
A full-frame DSLR is a digital single-lens reflex camera (DSLR) with a 35 mm image sensor format (). Historically, 35 mm was one of the standard film formats, alongside larger ones, such as medium format and large format. The full-f ...
* Image resolution
Image resolution is the detail an image holds. The term applies to digital images, film images, and other types of images. "Higher resolution" means more image detail.
Image resolution can be measured in various ways. Resolution quantifies how cl ...
* Image sensor format
In digital photography, the image sensor format is the shape and size of the image sensor.
The image sensor format of a digital camera determines the angle of view of a particular lens when used with a particular sensor. Because the image se ...
, the sizes and shapes of common image sensors
* Color filter array
In digital imaging, a color filter array (CFA), or color filter mosaic (CFM), is a mosaic of tiny color filters placed over the pixel sensors of an image sensor to capture color information.
The term is also used in reference to e paper devices ...
, mosaic of tiny color filters over color image sensors
* Sensitometry, the scientific study of light-sensitive materials
* History of television, the development of electronic imaging technology since the 1880s
* List of large sensor interchangeable-lens video cameras
List of digital video cameras with an image sensor larger than 2/3 inch and producing video in a horizontal resolution equal or higher than 1920 pixels.
Digital video cameras
Still cameras with video mode
See also
* List of 4K video re ...
* Oversampled binary image sensor
* Computer vision
Computer vision is an interdisciplinary scientific field that deals with how computers can gain high-level understanding from digital images or videos. From the perspective of engineering, it seeks to understand and automate tasks that the human ...
* Push broom scanner
* Whisk broom scanner A whisk broom or spotlight sensor, also known as an across-track scanner, is a technology for obtaining satellite images with optical cameras. It is used for passive remote sensing from space. In a whisk broom sensor, a mirror scans across the sat ...
References
External links
Digital Camera Sensor Performance Summary
by Roger Clark * (with graphical buckets and rainwater analogies) {{Authority control Digital photography MOSFETs