cDNA library on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A cDNA library is a combination of cloned cDNA (
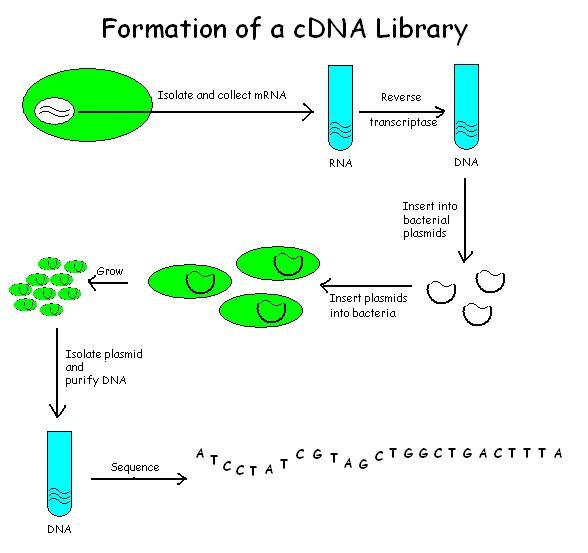 cDNA is created from a mature mRNA from a eukaryotic cell with the use of reverse transcriptase. In eukaryotes, a poly-(A) tail (consisting of a long sequence of adenine nucleotides) distinguishes mRNA from
cDNA is created from a mature mRNA from a eukaryotic cell with the use of reverse transcriptase. In eukaryotes, a poly-(A) tail (consisting of a long sequence of adenine nucleotides) distinguishes mRNA from
Functional Annotation of the Mouse database
(
examples of cDNA synthesis and cloning
Molecular biology DNA
complementary DNA
In genetics, complementary DNA (cDNA) is DNA synthesized from a single-stranded RNA (e.g., messenger RNA (mRNA) or microRNA (miRNA)) template in a reaction catalyzed by the enzyme reverse transcriptase. cDNA is often used to express a spec ...
) fragments inserted into a collection of host cells, which constitute some portion of the transcriptome of the organism and are stored as a " library". cDNA is produced from fully transcribed mRNA found in the nucleus
Nucleus ( : nuclei) is a Latin word for the seed inside a fruit. It most often refers to:
* Atomic nucleus, the very dense central region of an atom
*Cell nucleus, a central organelle of a eukaryotic cell, containing most of the cell's DNA
Nucl ...
and therefore contains only the expressed genes of an organism. Similarly, tissue-specific cDNA libraries can be produced. In eukaryotic cells the mature mRNA is already spliced
Spliced may refer to:
*Spliced, the result of rope splicing
Rope splicing in ropework is the forming of a semi-permanent joint between two ropes or two parts of the same rope by partly untwisting and then interweaving their strands. Splices c ...
, hence the cDNA produced lacks introns
An intron is any nucleotide sequence within a gene that is not expressed or operative in the final RNA product. The word ''intron'' is derived from the term ''intragenic region'', i.e. a region inside a gene."The notion of the cistron .e., gene. ...
and can be readily expressed in a bacterial cell. While information in cDNA libraries is a powerful and useful tool since gene products are easily identified, the libraries lack information about enhancers
In genetics, an enhancer is a short (50–1500 bp) region of DNA that can be bound by proteins ( activators) to increase the likelihood that transcription of a particular gene will occur. These proteins are usually referred to as transcriptio ...
, introns
An intron is any nucleotide sequence within a gene that is not expressed or operative in the final RNA product. The word ''intron'' is derived from the term ''intragenic region'', i.e. a region inside a gene."The notion of the cistron .e., gene. ...
, and other regulatory elements found in a genomic DNA library
In molecular biology, a library is a collection of DNA fragments that is stored and propagated in a population of micro-organisms through the process of molecular cloning. There are different types of DNA libraries, including cDNA libraries ( ...
.
cDNA Library Construction
 cDNA is created from a mature mRNA from a eukaryotic cell with the use of reverse transcriptase. In eukaryotes, a poly-(A) tail (consisting of a long sequence of adenine nucleotides) distinguishes mRNA from
cDNA is created from a mature mRNA from a eukaryotic cell with the use of reverse transcriptase. In eukaryotes, a poly-(A) tail (consisting of a long sequence of adenine nucleotides) distinguishes mRNA from tRNA
Transfer RNA (abbreviated tRNA and formerly referred to as sRNA, for soluble RNA) is an adaptor molecule composed of RNA, typically 76 to 90 nucleotides in length (in eukaryotes), that serves as the physical link between the mRNA and the amino a ...
and rRNA
Ribosomal ribonucleic acid (rRNA) is a type of non-coding RNA which is the primary component of ribosomes, essential to all cells. rRNA is a ribozyme which carries out protein synthesis in ribosomes. Ribosomal RNA is transcribed from ribosomal ...
and can therefore be used as a primer
Primer may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Films
* ''Primer'' (film), a 2004 feature film written and directed by Shane Carruth
* ''Primer'' (video), a documentary about the funk band Living Colour
Literature
* Primer (textbook), a te ...
site for reverse transcription. This has the problem that not all transcripts, such as those for the histone, encode a poly-A tail
Polyadenylation is the addition of a poly(A) tail to an RNA transcript, typically a messenger RNA (mRNA). The poly(A) tail consists of multiple adenosine monophosphates; in other words, it is a stretch of RNA that has only adenine bases. In euka ...
.
mRNA extraction
Firstly, mRNA template needs to be isolated for the creation of cDNA libraries. Since mRNA only contains exons, the integrity of the isolated mRNA should be considered so that the protein encoded can still be produced. Isolated mRNA should range from 500 bp to 8 kb. Several methods exist for purifying RNA such astrizol
TRIzol is a widely used chemical solution used in the extraction of DNA, RNA, and proteins from cells. The solution was initially used and published by Piotr Chomczyński and Nicoletta Sacchi in 1987.
TRIzol is the brand name of guanidinium th ...
extraction and column purification
Spin column-based nucleic acid purification is a solid phase extraction method to quickly purify nucleic acids. This method relies on the fact that nucleic acid will bind to the solid phase of silica under certain conditions.
Procedure
The stages ...
. Column purification can be done using oligomeric dT nucleotide coated resins, and features of mRNA such as having a poly-A tail can be exploited where only mRNA sequences containing said feature will bind. The desired mRNA bound to the column is then eluted
In analytical and organic chemistry, elution is the process of extracting one material from another by washing with a solvent; as in washing of loaded ion-exchange resins to remove captured ions.
In a liquid chromatography experiment, for exa ...
.
cDNA construction
Once mRNA is purified, an ''oligo-dT'' primer (a short sequence of deoxy-thymidine nucleotides) is bound to the poly-A tail of the RNA. The primer is required to initiate DNA synthesis by the enzyme reverse transcriptase. This results in the creation of RNA-DNA hybrids where a single strand of complementary DNA is bound to a strand of mRNA. To remove the mRNA, the RNAse H enzyme is used to cleave the backbone of the mRNA and generate free 3'-OH groups, which is important for the replacement of mRNA with DNA.DNA polymerase
A DNA polymerase is a member of a family of enzymes that catalyze the synthesis of DNA molecules from nucleoside triphosphates, the molecular precursors of DNA. These enzymes are essential for DNA replication and usually work in groups to create ...
I is then added, the cleaved RNA acts as a primer the DNA polymerase I can identify and initiate replacement of RNA nucleotides with those of DNA. This is provided by the sscDNA itself by coiling on itself at the 3' end, generating a '' hairpin loop''. The polymerase extends the 3'-OH end, and later the loop at 3' end is opened by the scissoring action of ''S1 nuclease''. Restriction endonucleases
A restriction enzyme, restriction endonuclease, REase, ENase or'' restrictase '' is an enzyme that cleaves DNA into fragments at or near specific recognition sites within molecules known as restriction sites. Restriction enzymes are one class ...
and DNA ligase are then used to clone the sequences into bacterial plasmids.
The cloned bacteria are then selected, commonly through the use of antibiotic selection. Once selected, stocks of the bacteria are created which can later be grown and sequenced to compile the cDNA library.
cDNA Library uses
cDNA libraries are commonly used when reproducing eukaryotic genomes, as the amount of information is reduced to remove the large numbers of non-coding regions from the library. cDNA libraries are used to express eukaryotic genes in prokaryotes. Prokaryotes do not have introns in their DNA and therefore do not possess any enzymes that can cut it out during transcription process. cDNA does not have introns and therefore can be expressed in prokaryotic cells. cDNA libraries are most useful inreverse genetics
Reverse genetics is a method in molecular genetics that is used to help understand the function(s) of a gene by analysing the phenotypic effects caused by genetically engineering specific nucleic acid sequences within the gene. The process proc ...
where the additional genomic information is of less use. Additionally, cDNA libraries are frequently used in functional cloning
Functional cloning is a molecular cloning technique that relies on prior knowledge of the encoded protein’s sequence or function for gene identification. In this assay, a genomic or cDNA library is screened to identify the genetic sequence of a ...
to identify genes based on the encoded protein's function. When studying eukaryotic DNA, expression libraries are constructed using complementary DNA (cDNA) to help ensure the insert is truly a gene.{{Cite book, title=Biotechnology : applying the genetic revolution, last=P., first=Clark, David, date=2009, publisher=Academic Press/Elsevier, others=Pazdernik, Nanette Jean., isbn=9780121755522, location=Amsterdam, oclc=226038060
cDNA Library vs. Genomic DNA Library
cDNA library lacks the non-coding and regulatory elements found in genomic DNA. Genomic DNA libraries provide more detailed information about the organism, but are more resource-intensive to generate and keep.Cloning of cDNA
cDNA molecules can be cloned by using restriction site linkers. Linkers are short, double stranded pieces of DNA (oligodeoxyribonucleotide) about 8 to 12 nucleotide pairs long that include a restriction endonuclease cleavage site e.g. BamHI. Both the cDNA and the linker have blunt ends which can be ligated together using a high concentration of T4 DNA ligase. Then sticky ends are produced in the cDNA molecule by cleaving the cDNA ends (which now have linkers with an incorporated site) with the appropriate endonuclease. Acloning vector
A cloning vector is a small piece of DNA that can be stably maintained in an organism, and into which a foreign DNA fragment can be inserted for cloning purposes. The cloning vector may be DNA taken from a virus, the cell of a higher organism, or ...
( plasmid) is then also cleaved with the appropriate endonuclease. Following "sticky end
DNA ends refer to the properties of the ends of linear DNA molecules, which in molecular biology are described as "sticky" or "blunt" based on the shape of the complementary strands at the terminus. In sticky ends, one strand is longer than the ...
" ligation of the insert into the vector the resulting recombinant DNA molecule is transferred into '' E. coli'' host cell for cloning.
See also
*Functional cloning
Functional cloning is a molecular cloning technique that relies on prior knowledge of the encoded protein’s sequence or function for gene identification. In this assay, a genomic or cDNA library is screened to identify the genetic sequence of a ...
References
External links
Functional Annotation of the Mouse database
(
FANTOM FANTOM (Functional Annotation of the Mouse/Mammalian Genome) is an international research consortium first established in 2000 as part of the RIKEN research institute in Japan. The original meeting gathered international scientists from diverse bac ...
)
examples of cDNA synthesis and cloning
Molecular biology DNA