blood-letting on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Bloodletting (or blood-letting) is the withdrawal of blood from a patient to prevent or cure illness and disease. Bloodletting, whether by a physician or by
 Passages from the Ebers Papyrus may indicate that bloodletting by scarification was an accepted practice in Ancient Egypt.
Egyptian burials have been reported to contain bloodletting instruments.
According to some accounts, the Egyptians based the idea on their observations of the
Passages from the Ebers Papyrus may indicate that bloodletting by scarification was an accepted practice in Ancient Egypt.
Egyptian burials have been reported to contain bloodletting instruments.
According to some accounts, the Egyptians based the idea on their observations of the

 Even after the humoral system fell into disuse, the practice was continued by
Even after the humoral system fell into disuse, the practice was continued by 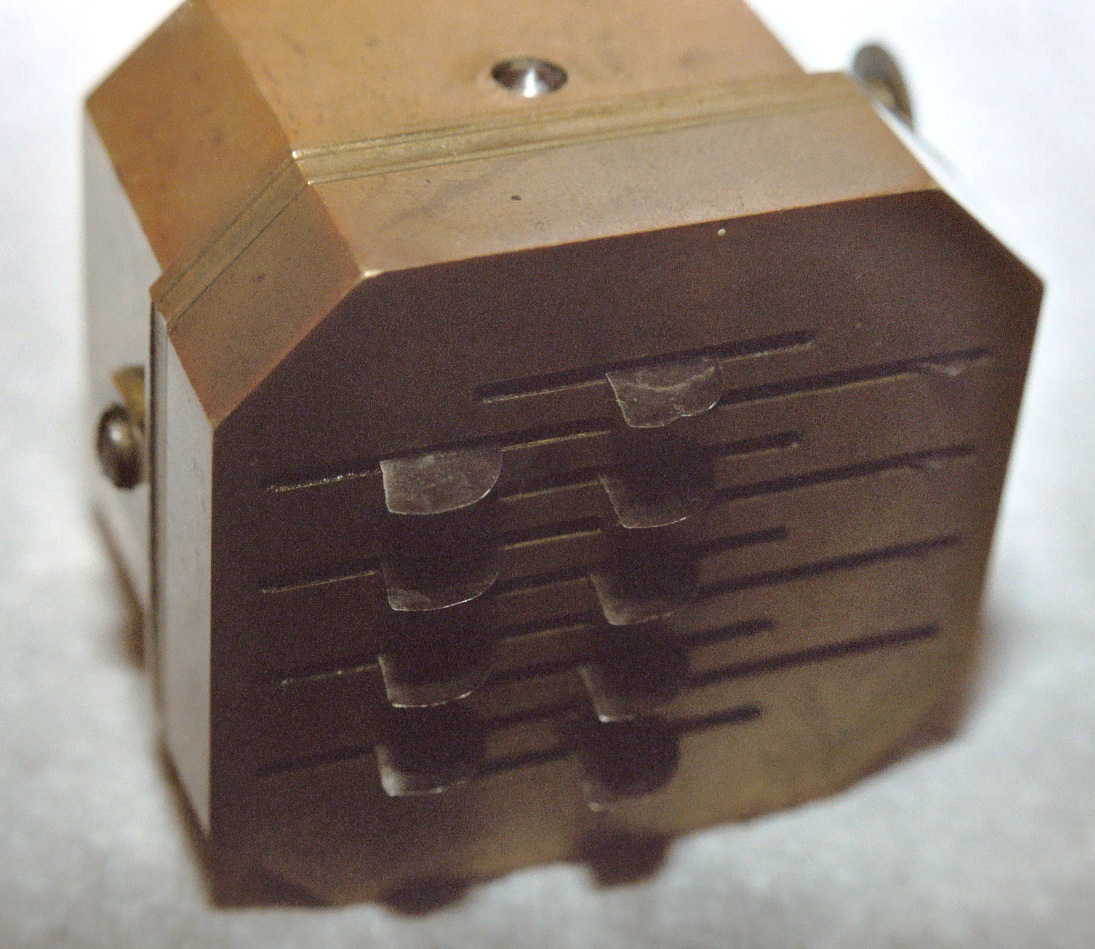

 A number of different methods were employed. The most common was ''phlebotomy'', or ''venesection'' (often called "breathing a vein"), in which blood was drawn from one or more of the larger external veins, such as those in the forearm or neck. In ''arteriotomy'', an artery was punctured, although generally only in the temples. In ''scarification'' (not to be confused with scarification, a method of body modification), the "superficial" vessels were attacked, often using a syringe, a spring-loaded lancet, or a glass cup that contained heated air, producing a vacuum within (see
A number of different methods were employed. The most common was ''phlebotomy'', or ''venesection'' (often called "breathing a vein"), in which blood was drawn from one or more of the larger external veins, such as those in the forearm or neck. In ''arteriotomy'', an artery was punctured, although generally only in the temples. In ''scarification'' (not to be confused with scarification, a method of body modification), the "superficial" vessels were attacked, often using a syringe, a spring-loaded lancet, or a glass cup that contained heated air, producing a vacuum within (see
p. 79, Spring, 2004, retrieved on 11 November 2012 One reason for the continued popularity of bloodletting (and purging) was that, while
One reason for the continued popularity of bloodletting (and purging) was that, while
Globinmed.com.
, holistic-online.com.Ayurveda
Cancer.org.
/ref>Treating Herpes Zoster (Shingles) with Bloodletting Therapy: Acupuncture and Chinese Medicine
Unani is based on a form of humorism, and so in that system, bloodletting is used to correct supposed humoral imbalance.
The History and Progression of Bloodletting
Huge collection of antique bloodletting instruments
"Breathing a Vein"
phisick.com 14 Nov 2011 {{Use dmy dates, date=January 2021 Blood Bleeding Medical tests Medical treatments Obsolete medical procedures Traditional medicine Pseudoscience
leech
Leeches are segmented parasitic or predatory worms that comprise the subclass Hirudinea within the phylum Annelida. They are closely related to the oligochaetes, which include the earthworm, and like them have soft, muscular segmented bodie ...
es, was based on an ancient system of medicine in which blood and other bodily fluids were regarded as "humours
Humorism, the humoral theory, or humoralism, was a system of medicine detailing a supposed makeup and workings of the human body, adopted by Ancient Greek and Roman physicians and philosophers.
Humorism began to fall out of favor in the 1850s ...
" that had to remain in proper balance to maintain health. It is claimed to have been the most common medical practice performed by surgeons from antiquity
Antiquity or Antiquities may refer to:
Historical objects or periods Artifacts
*Antiquities, objects or artifacts surviving from ancient cultures
Eras
Any period before the European Middle Ages (5th to 15th centuries) but still within the histo ...
until the late 19th century, a span of over 2,000 years. In Europe, the practice continued to be relatively common until the end of the 19th century.B.) Anderson, Julie, Emm Barnes, and Enna Shackleton. "The Art of Medicine: Over 2,000 Years of Images and Imagination ardcover" The Art of Medicine: Over 2, 000 Years of Images and Imagination: Julie Anderson, Emm Barnes, Emma Shackleton: : The Ilex Press Limited, 2013. The practice has now been abandoned by modern-style medicine for all except a few very specific medical conditions. In the overwhelming majority of cases, the historical use of bloodletting was harmful to patients.
Today, the term ''phlebotomy
Phlebotomy is the process of making a puncture in a vein, usually in the arm, with a cannula for the purpose of drawing blood. The procedure itself is known as a venipuncture, which is also used for intravenous therapy. A person who performs a ph ...
'' refers to the drawing of blood for laboratory analysis or blood transfusion
Blood transfusion is the process of transferring blood products into a person's circulation intravenously. Transfusions are used for various medical conditions to replace lost components of the blood. Early transfusions used whole blood, but mo ...
. ''Therapeutic phlebotomy'' refers to the drawing of a unit of blood in specific cases like hemochromatosis, polycythemia vera, porphyria cutanea tarda, etc., to reduce the number of red blood cells. The traditional medical practice of bloodletting is today considered to be a pseudoscience.
In the ancient world
 Passages from the Ebers Papyrus may indicate that bloodletting by scarification was an accepted practice in Ancient Egypt.
Egyptian burials have been reported to contain bloodletting instruments.
According to some accounts, the Egyptians based the idea on their observations of the
Passages from the Ebers Papyrus may indicate that bloodletting by scarification was an accepted practice in Ancient Egypt.
Egyptian burials have been reported to contain bloodletting instruments.
According to some accounts, the Egyptians based the idea on their observations of the hippopotamus
The hippopotamus ( ; : hippopotamuses or hippopotami; ''Hippopotamus amphibius''), also called the hippo, common hippopotamus, or river hippopotamus, is a large semiaquatic mammal native to sub-Saharan Africa. It is one of only two extant ...
, confusing its red secretions with blood and believing that it scratched itself to relieve distress.
In Greece, bloodletting was in use in the 5th century BC during the lifetime of Hippocrates, who mentions this practice but generally relied on dietary techniques. Erasistratus
Erasistratus (; grc-gre, Ἐρασίστρατος; c. 304 – c. 250 BC) was a Greek anatomist and royal physician under Seleucus I Nicator of Syria. Along with fellow physician Herophilus, he founded a school of anatomy in Alexandria, where th ...
, however, theorized that many diseases were caused by plethoras, or overabundances, in the blood and advised that these plethoras be treated, initially, by exercise, sweating
Perspiration, also known as sweating, is the production of fluids secreted by the sweat glands in the skin of mammals.
Two types of sweat glands can be found in humans: eccrine glands and apocrine glands. The eccrine sweat glands are distri ...
, reduced food intake, and vomiting. His student Herophilus
Herophilos (; grc-gre, Ἡρόφιλος; 335–280 BC), sometimes Latinised Herophilus, was a Greek physician regarded as one of the earliest anatomists. Born in Chalcedon, he spent the majority of his life in Alexandria. He was the first sci ...
also opposed bloodletting. But a contemporary Greek physician, Archagathus, one of the first to practice in Rome, did believe in the value of bloodletting.
"Bleeding" a patient to health was modeled on the process of menstruation. Hippocrates believed that menstruation functioned to "purge women of bad humours". During the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post-Roman Republic, Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings aro ...
, the Greek physician Galen, who subscribed to the teachings of Hippocrates, advocated physician-initiated bloodletting.
The popularity of bloodletting in the classical Mediterranean world was reinforced by the ideas of Galen, after he discovered that not only vein
Veins are blood vessels in humans and most other animals that carry blood towards the heart. Most veins carry deoxygenated blood from the tissues back to the heart; exceptions are the pulmonary and umbilical veins, both of which carry oxygenated ...
s but also arteries
An artery (plural arteries) () is a blood vessel in humans and most animals that takes blood away from the heart to one or more parts of the body (tissues, lungs, brain etc.). Most arteries carry oxygenated blood; the two exceptions are the p ...
were filled with blood, not air as was commonly believed at the time. There were two key concepts in his system of bloodletting. The first was that blood was created and then used up; it did not circulate, and so it could "stagnate" in the extremities. The second was that humoral
Humoral immunity is the aspect of immunity that is mediated by macromolecules - including secreted antibodies, complement proteins, and certain antimicrobial peptides - located in extracellular fluids. Humoral immunity is named so because it i ...
balance was the basis of illness or health, the four humours being blood, phlegm, black bile, and yellow bile, relating to the four Greek classical element
Classical elements typically refer to earth, water, air, fire, and (later) aether which were proposed to explain the nature and complexity of all matter in terms of simpler substances. Ancient cultures in Greece, Tibet, and India had simila ...
s of air, water, earth, and fire respectively. Galen believed that blood was the dominant humour and the one in most need of control. In order to balance the humours, a physician would either remove "excess" blood (plethora) from the patient or give them an emetic
Vomiting (also known as emesis and throwing up) is the involuntary, forceful expulsion of the contents of one's stomach through the mouth and sometimes the nose.
Vomiting can be the result of ailments like food poisoning, gastroenteriti ...
to induce vomiting, or a diuretic
A diuretic () is any substance that promotes diuresis, the increased production of urine. This includes forced diuresis. A diuretic tablet is sometimes colloquially called a water tablet. There are several categories of diuretics. All diuretics in ...
to induce urination.
Galen created a complex system of how much blood should be removed based on the patient's age, constitution, the season, the weather and the place. "Do-it-yourself" bleeding instructions following these systems were developed. Symptoms of plethora were believed to include fever, apoplexy
Apoplexy () is rupture of an internal organ and the accompanying symptoms. The term formerly referred to what is now called a stroke. Nowadays, health care professionals do not use the term, but instead specify the anatomic location of the bleedi ...
, and headache. The blood to be let was of a specific nature determined by the disease: either arterial or venous
Veins are blood vessels in humans and most other animals that carry blood towards the heart. Most veins carry deoxygenated blood from the tissues back to the heart; exceptions are the pulmonary and umbilical veins, both of which carry oxygenated ...
, and distant or close to the area of the body affected. He linked different blood vessels with different organs
In biology, an organ is a collection of tissues joined in a structural unit to serve a common function. In the hierarchy of life, an organ lies between tissue and an organ system. Tissues are formed from same type cells to act together in a ...
, according to their supposed drainage. For example, the vein in the right hand would be let for liver problems and the vein in the left hand for problems with the spleen. The more severe the disease, the more blood would be let. Fevers required copious amounts of bloodletting.
Middle Ages
The Talmud recommended a specific day of the week and days of the month for bloodletting in the Shabbat tractate, and similar rules, though less codified, can be found among Christian writings advising whichsaints' days
The calendar of saints is the traditional Christian method of organizing a liturgical year by associating each day with one or more saints and referring to the day as the feast day or feast of said saint. The word "feast" in this context doe ...
were favourable for bloodletting. During medieval times bleeding charts were common, showing specific bleeding sites on the body in alignment with the planets and zodiacs. Islamic medical authors also advised bloodletting, particularly for fevers. It was practised according to seasons and certain phases of the Moon in the lunar calendar
A lunar calendar is a calendar based on the monthly cycles of the Moon's phases ( synodic months, lunations), in contrast to solar calendars, whose annual cycles are based only directly on the solar year. The most commonly used calendar, the Gre ...
. The practice was probably passed by the Greeks with the translation of ancient texts to Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walte ...
and is different than bloodletting by cupping mentioned in the traditions of Muhammad. When Muslim theories became known in the Latin-speaking countries of Europe, bloodletting became more widespread. Together with cautery
Cauterization (or cauterisation, or cautery) is a medical practice or technique of burning a part of a body to remove or close off a part of it. It destroys some tissue in an attempt to mitigate bleeding and damage, remove an undesired growth, or ...
, it was central to Arab
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, No ...
ic surgery; the key texts '' Kitab al-Qanun'' and especially '' Al-Tasrif li-man 'ajaza 'an al-ta'lif'' both recommended it. It was also known in Ayurvedic
Ayurveda () is an alternative medicine system with historical roots in the Indian subcontinent. The theory and practice of Ayurveda is pseudoscientific. Ayurveda is heavily practiced in India and Nepal, where around 80% of the population repor ...
medicine, described in the ''Susruta Samhita''.
Use through the 19th century

surgeons
In modern medicine, a surgeon is a medical professional who performs surgery. Although there are different traditions in different times and places, a modern surgeon usually is also a licensed physician or received the same medical training as ...
and barber-surgeons
The barber surgeon, one of the most common European medical practitioners of the Middle Ages, was generally charged with caring for soldiers during and after battle. In this era, surgery was seldom conducted by physicians, but instead by barber ...
. Though the bloodletting was often ''recommended'' by physicians, it was carried out by barbers. This led to the distinction between physicians and surgeons. The red-and-white-striped pole of the barbershop, still in use today, is derived from this practice: the red symbolizes blood while the white symbolizes the bandages. Bloodletting was used to "treat" a wide range of diseases, becoming a standard treatment for almost every ailment, and was practiced prophylactically as well as therapeutically.



 A number of different methods were employed. The most common was ''phlebotomy'', or ''venesection'' (often called "breathing a vein"), in which blood was drawn from one or more of the larger external veins, such as those in the forearm or neck. In ''arteriotomy'', an artery was punctured, although generally only in the temples. In ''scarification'' (not to be confused with scarification, a method of body modification), the "superficial" vessels were attacked, often using a syringe, a spring-loaded lancet, or a glass cup that contained heated air, producing a vacuum within (see
A number of different methods were employed. The most common was ''phlebotomy'', or ''venesection'' (often called "breathing a vein"), in which blood was drawn from one or more of the larger external veins, such as those in the forearm or neck. In ''arteriotomy'', an artery was punctured, although generally only in the temples. In ''scarification'' (not to be confused with scarification, a method of body modification), the "superficial" vessels were attacked, often using a syringe, a spring-loaded lancet, or a glass cup that contained heated air, producing a vacuum within (see fire cupping
Cupping therapy is a form of alternative medicine in which a local suction is created on the skin with the application of heated cups. Its practice mainly occurs in Asia but also in Eastern Europe, the Middle East, and Latin America. Cupping has ...
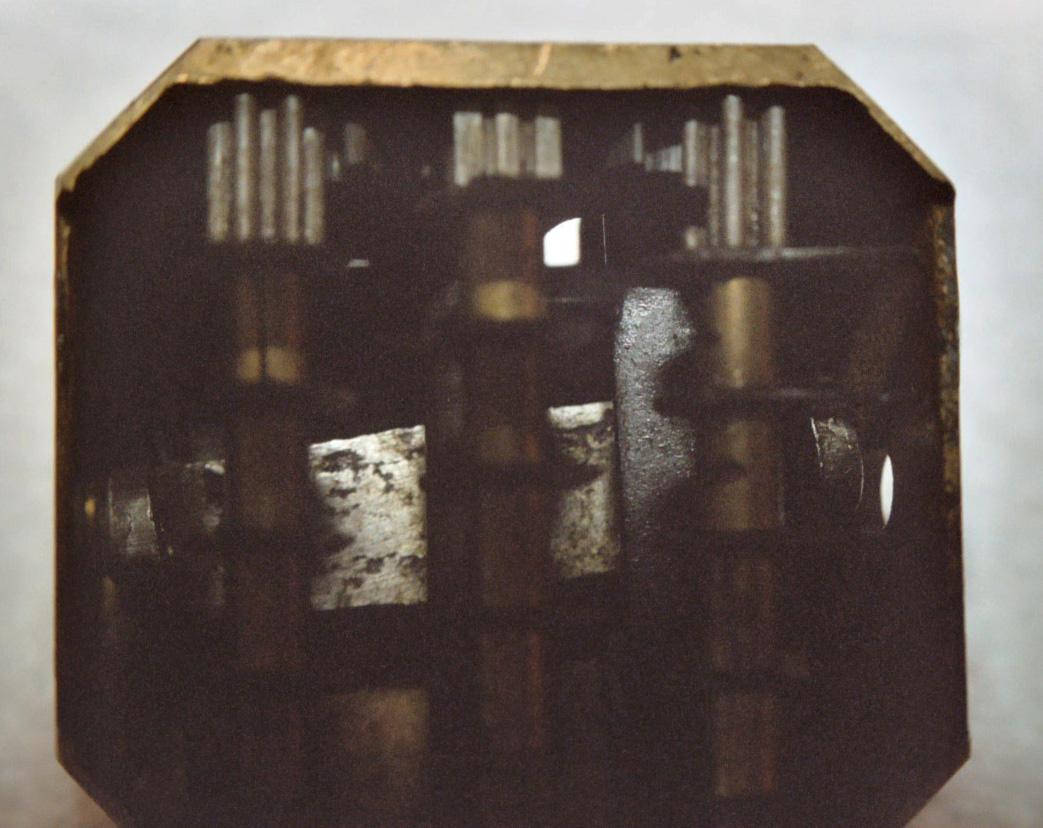
). There was also a specific bloodletting tool called a ''scarificator'', used primarily in 19th century medicine. It has a spring-loaded mechanism with gears that snaps the blades out through slits in the front cover and back in, in a circular motion. The case is cast brass, and the mechanism and blades steel. One knife bar gear has slipped teeth, turning the blades in a different direction than those on the other bars. The last photo and the diagram show the depth adjustment bar at the back and sides.
Leech
Leeches are segmented parasitic or predatory worms that comprise the subclass Hirudinea within the phylum Annelida. They are closely related to the oligochaetes, which include the earthworm, and like them have soft, muscular segmented bodie ...
es could also be used. The withdrawal of so much blood as to induce syncope (fainting) was considered beneficial, and many sessions would only end when the patient began to swoon.
William Harvey disproved the basis of the practice in 1628, and the introduction of scientific medicine
Medicine is the science and practice of caring for a patient, managing the diagnosis, prognosis, prevention, treatment, palliation of their injury or disease, and promoting their health. Medicine encompasses a variety of health care practice ...
, ''la méthode numérique'', allowed Pierre Charles Alexandre Louis
Pierre-Charles-Alexandre Louis (14 April 178722 August 1872) was a French physician, clinician and pathologist known for his studies on tuberculosis, typhoid fever, and pneumonia, but Louis's greatest contribution to medicine was the development o ...
to demonstrate that phlebotomy was entirely ineffective in the treatment of pneumonia and various fevers in the 1830s. Nevertheless, in 1838, a lecturer at the Royal College of Physicians would still state that "blood-letting is a remedy which, when judiciously employed, it is hardly possible to estimate too highly", and Louis was dogged by the sanguinary Broussais, who could recommend leeches fifty at a time. Some physicians resisted Louis' work because they "were not prepared to discard therapies 'validated by both tradition and their own experience on account of somebody else's numbers'."
During this era, bloodletting was used to treat almost every disease. One British medical text recommended bloodletting for acne, asthma, cancer, cholera, coma, convulsions, diabetes, epilepsy, gangrene, gout, herpes, indigestion, insanity, jaundice, leprosy, ophthalmia, plague, pneumonia, scurvy, smallpox, stroke, tetanus, tuberculosis, and for some one hundred other diseases. Bloodletting was even used to treat most forms of hemorrhaging such as nosebleed, excessive menstruation, or hemorrhoidal bleeding. Before surgery or at the onset of childbirth, blood was removed to prevent inflammation. Before amputation, it was customary to remove a quantity of blood equal to the amount believed to circulate in the limb that was to be removed.Carter (2005) p. 6
There were also theories that bloodletting would cure "heartsickness" and "heartbreak". A French physician, Jacques Ferrand wrote a book in 1623 on the uses of bloodletting to cure a broken heart. He recommended bloodletting to the point of heart failure (literal).Lydia Kang MD & Nate Pederson, ''Quackery: A Brief History of the Worst Ways to Cure Everything'' "Bleed Yourself to Bliss" (Workman Publishing Company; 2017)
Leeches became especially popular in the early 19th century. In the 1830s, the French imported about 40 million leeches a year for medical purposes, and in the next decade, England imported 6 million leeches a year from France alone. Through the early decades of the century, hundreds of millions of leeches were used by physicians throughout Europe.Carter (2005) p. 7
Bloodletting was also popular in the young United States of America, where Benjamin Rush
Benjamin Rush (April 19, 1813) was a Founding Father of the United States who signed the United States Declaration of Independence, and a civic leader in Philadelphia, where he was a physician, politician, social reformer, humanitarian, educato ...
(a signatory of the Declaration of Independence) saw the state of the arteries as the key to disease, recommending levels of bloodletting that were high even for the time. George Washington
George Washington (February 22, 1732, 1799) was an American military officer, statesman, and Founding Father who served as the first president of the United States from 1789 to 1797. Appointed by the Continental Congress as commander of th ...
asked to be bled heavily after he developed a throat infection from weather exposure. Within a ten-hour period, a total of 124–126 ounces (3.75 liters) of blood was withdrawn prior to his death from a throat infection in 1799.The Permanente Journal Volume 8 No. 2: The asphyxiating and exsanguinating death of president george washingtonp. 79, Spring, 2004, retrieved on 11 November 2012
 One reason for the continued popularity of bloodletting (and purging) was that, while
One reason for the continued popularity of bloodletting (and purging) was that, while anatomical
Anatomy () is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. Anatomy is a branch of natural science that deals with the structural organization of living things. It is an old science, having it ...
knowledge, surgical and diagnostic skills increased tremendously in Europe from the 17th century, the key to curing disease remained elusive, and the underlying belief was that it was better to give any treatment than nothing at all. The psychological benefit of bloodletting to the patient (a placebo effect) may sometimes have outweighed the physiological problems it caused. Bloodletting slowly lost favour during the 19th century, after French physician Dr. Pierre Louis conducted an experiment in which he studied the effect of bloodletting on pneumonia patients. A number of other ineffective or harmful treatments were available as placebos—mesmerism
Animal magnetism, also known as mesmerism, was a protoscientific theory developed by German doctor Franz Mesmer in the 18th century in relation to what he claimed to be an invisible natural force (''Lebensmagnetismus'') possessed by all livi ...
, various processes involving the new technology of electricity, many potions, tonics, and elixirs. Yet, bloodletting persisted during the 19th century partly because it was readily available to people of any socioeconomic status.
Controversy and use into the 20th century
Bloodletting gradually declined in popularity over the course of the 19th century, becoming rather uncommon in most places, before its validity was thoroughly debated. In the medical community of Edinburgh, bloodletting was abandoned in practice before it was challenged in theory, a contradiction highlighted by physician-physiologistJohn Hughes Bennett
John Hughes Bennett PRCPE FRSE (31 August 1812 – 25 September 1875) was an English physician, physiologist and pathologist. His main contribution to medicine has been the first description of leukemia as a blood disorder (1845). The first pers ...
. Authorities such as Austin Flint I
Austin Flint I (October 20, 1812 – March 13, 1886) was an American physician. He was a founder of Buffalo Medical College, precursor to The State University of New York at Buffalo. He served as president of the American Medical Association.
...
, Hiram Corson, and William Osler
Sir William Osler, 1st Baronet, (; July 12, 1849 – December 29, 1919) was a Canadian physician and one of the "Big Four" founding professors of Johns Hopkins Hospital. Osler created the first residency program for specialty training of phy ...
became prominent supporters of bloodletting in the 1880s and onwards, disputing Bennett's premise that bloodletting had fallen into disuse because it did not work. These advocates framed bloodletting as an orthodox medical practice, to be used in spite of its general unpopularity. Some physicians considered bloodletting useful for a more limited range of purposes, such as to "clear out" infected or weakened blood or its ability to "cause hæmorrhages to cease"—as evidenced in a call for a "fair trial for blood-letting as a remedy" in 1871.
Some researchers used statistical methods for evaluating treatment effectiveness to discourage bloodletting. But at the same time, publications by Philip Pye-Smith and others defended bloodletting on scientific grounds.
Bloodletting persisted into the 20th century and was recommended in the 1923 edition of the textbook '' The Principles and Practice of Medicine''. The textbook was originally written by Sir William Osler and continued to be published in new editions under new authors following Osler's death in 1919.
Phlebotomy
Bloodletting is used today in the treatment of a few diseases, including hemochromatosis andpolycythemia
Polycythemia (also known as polycythaemia) is a laboratory finding in which the hematocrit (the volume percentage of red blood cells in the blood) and/or hemoglobin concentration are increased in the blood. Polycythemia is sometimes called e ...
; however, these rare diseases were unknown and undiagnosable before the advent of scientific medicine. It is practiced by specifically trained practitioners in hospitals, using modern techniques, and is also known as a therapeutic phlebotomy.
In most cases, phlebotomy
Phlebotomy is the process of making a puncture in a vein, usually in the arm, with a cannula for the purpose of drawing blood. The procedure itself is known as a venipuncture, which is also used for intravenous therapy. A person who performs a ph ...
now refers to the removal of ''small'' quantities of blood for diagnostic purposes. However, in the case of hemochromatosis, bloodletting (by venipuncture
In medicine, venipuncture or venepuncture is the process of obtaining intravenous access for the purpose of venous blood sampling (also called '' phlebotomy'') or intravenous therapy. In healthcare, this procedure is performed by medical labo ...
) has become the mainstay treatment option. In the U.S., according to an academic article posted in the ''Journal of Infusion Nursing'' with data published in 2010, the primary use of phlebotomy was to take blood that would one day be reinfused back into a person.
In alternative medicine
Though bloodletting as a general health measure has been shown to be pseudoscience, it is still commonly indicated for a wide variety of conditions in theAyurvedic
Ayurveda () is an alternative medicine system with historical roots in the Indian subcontinent. The theory and practice of Ayurveda is pseudoscientific. Ayurveda is heavily practiced in India and Nepal, where around 80% of the population repor ...
, Unani
Unani or Yunani medicine ( Urdu: ''tibb yūnānī'') is Perso-Arabic traditional medicine as practiced in Muslim culture in South Asia and modern day Central Asia. Unani medicine is pseudoscientific. The Indian Medical Association describes ...
, and traditional Chinese
A tradition is a belief or behavior (folk custom) passed down within a group or society with symbolic meaning or special significance with origins in the past. A component of cultural expressions and folklore, common examples include holidays or ...
systems of alternative medicine
Alternative medicine is any practice that aims to achieve the healing effects of medicine despite lacking biological plausibility, testability, repeatability, or evidence from clinical trials. Complementary medicine (CM), complementary and alt ...
.Unani System of Medicine PracticeGlobinmed.com.
, holistic-online.com.Ayurveda
Cancer.org.
/ref>Treating Herpes Zoster (Shingles) with Bloodletting Therapy: Acupuncture and Chinese Medicine
Unani is based on a form of humorism, and so in that system, bloodletting is used to correct supposed humoral imbalance.
See also
* Bloodstopping *Blood donation
A blood donation occurs when a person voluntarily has blood drawn and used for transfusions and/or made into biopharmaceutical medications by a process called fractionation (separation of whole blood components). Donation may be of whole bloo ...
* Cupping therapy
Cupping therapy is a form of alternative medicine in which a local suction is created on the skin with the application of heated cups. Its practice mainly occurs in Asia but also in Eastern Europe, the Middle East, and Latin America. Cupping has ...
* Hematology
Hematology ( always spelled haematology in British English) is the branch of medicine concerned with the study of the cause, prognosis, treatment, and prevention of diseases related to blood. It involves treating diseases that affect the produc ...
* History of medicine
The history of medicine is both a study of medicine throughout history as well as a multidisciplinary field of study that seeks to explore and understand medical practices, both past and present, throughout human societies.
More than just histo ...
* Trepanation
Trepanning, also known as trepanation, trephination, trephining or making a burr hole (the verb ''trepan'' derives from Old French from Medieval Latin from Greek , literally "borer, auger"), is a surgical intervention in which a hole is dri ...
* Humorism
Humorism, the humoral theory, or humoralism, was a system of medicine detailing a supposed makeup and workings of the human body, adopted by Ancient Greek and Roman physicians and philosophers.
Humorism began to fall out of favor in the 1850s ...
* Fleams
* Panacea
In Greek mythology, Panacea (Greek ''Πανάκεια'', Panakeia), a goddess of universal remedy, was the daughter of Asclepius and Epione. Panacea and her four sisters each performed a facet of Apollo's art:
* Panacea (the goddess of univers ...
References
Books cited
* * Carter, K. Codell (2012). ''The Decline of Therapeutic Bloodletting and the Collapse of Traditional Medicine''. New Brunswick & London: Transaction Publishers. . *Further reading
* McGrew, Roderick. ''Encyclopedia of Medical History'' (1985), brief history pp. 32–34External links
The History and Progression of Bloodletting
Huge collection of antique bloodletting instruments
"Breathing a Vein"
phisick.com 14 Nov 2011 {{Use dmy dates, date=January 2021 Blood Bleeding Medical tests Medical treatments Obsolete medical procedures Traditional medicine Pseudoscience