anurans on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A frog is any member of a diverse and largely carnivorous group of short-bodied, tailless
A frog is any member of a diverse and largely carnivorous group of short-bodied, tailless
 The Anura include all modern frogs and any
The Anura include all modern frogs and any  Frogs and toads are broadly classified into three suborders: Archaeobatrachia, which includes four families of primitive frogs; Mesobatrachia, which includes five families of more evolutionary intermediate frogs; and Neobatrachia, by far the largest group, which contains the remaining families of modern frogs, including most common species throughout the world. The suborder Neobatrachia is further divided into the two superfamilies Hyloidea and Ranoidea. This classification is based on such morphological features as the number of vertebrae, the structure of the pectoral girdle, and the morphology of tadpoles. While this classification is largely accepted, relationships among families of frogs are still debated.
Some species of anurans hybridize readily. For instance, the
Frogs and toads are broadly classified into three suborders: Archaeobatrachia, which includes four families of primitive frogs; Mesobatrachia, which includes five families of more evolutionary intermediate frogs; and Neobatrachia, by far the largest group, which contains the remaining families of modern frogs, including most common species throughout the world. The suborder Neobatrachia is further divided into the two superfamilies Hyloidea and Ranoidea. This classification is based on such morphological features as the number of vertebrae, the structure of the pectoral girdle, and the morphology of tadpoles. While this classification is largely accepted, relationships among families of frogs are still debated.
Some species of anurans hybridize readily. For instance, the
 In 2008, '' Gerobatrachus hottoni'', a
In 2008, '' Gerobatrachus hottoni'', a
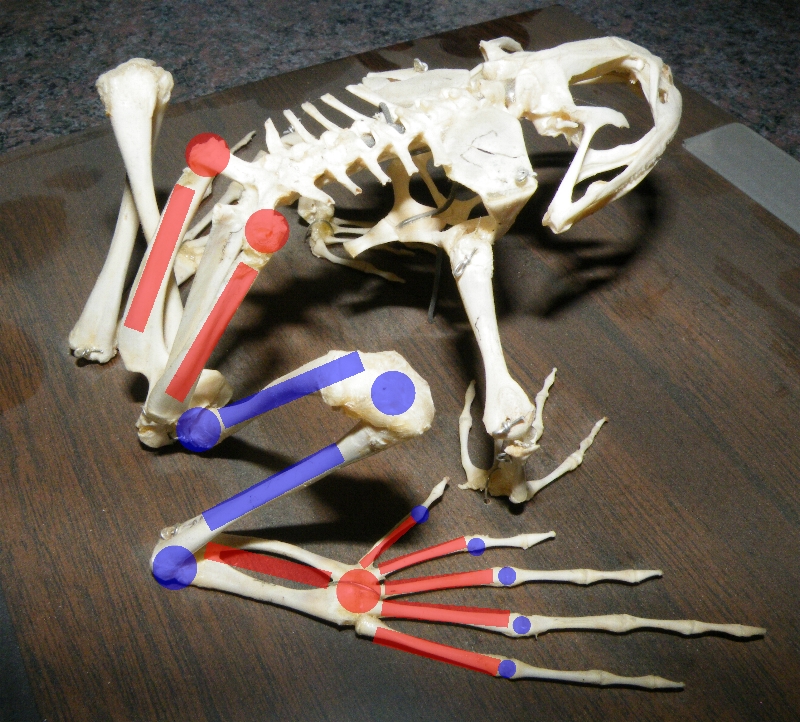 Frogs have no tail, except as larvae, and most have long hind legs, elongated ankle bones, webbed toes, no claws, large eyes, and a smooth or warty skin. They have short vertebral columns, with no more than 10 free vertebrae and fused tailbones (urostyle or coccyx). Frogs range in size from ''
Frogs have no tail, except as larvae, and most have long hind legs, elongated ankle bones, webbed toes, no claws, large eyes, and a smooth or warty skin. They have short vertebral columns, with no more than 10 free vertebrae and fused tailbones (urostyle or coccyx). Frogs range in size from ''
 The muscular system has been similarly modified. The hind limbs of ancestral frogs presumably contained pairs of muscles which would act in opposition (one muscle to flex the knee, a different muscle to extend it), as is seen in most other limbed animals. However, in modern frogs, almost all muscles have been modified to contribute to the action of jumping, with only a few small muscles remaining to bring the limb back to the starting position and maintain posture. The muscles have also been greatly enlarged, with the main leg muscles accounting for over 17% of the total mass of frogs.
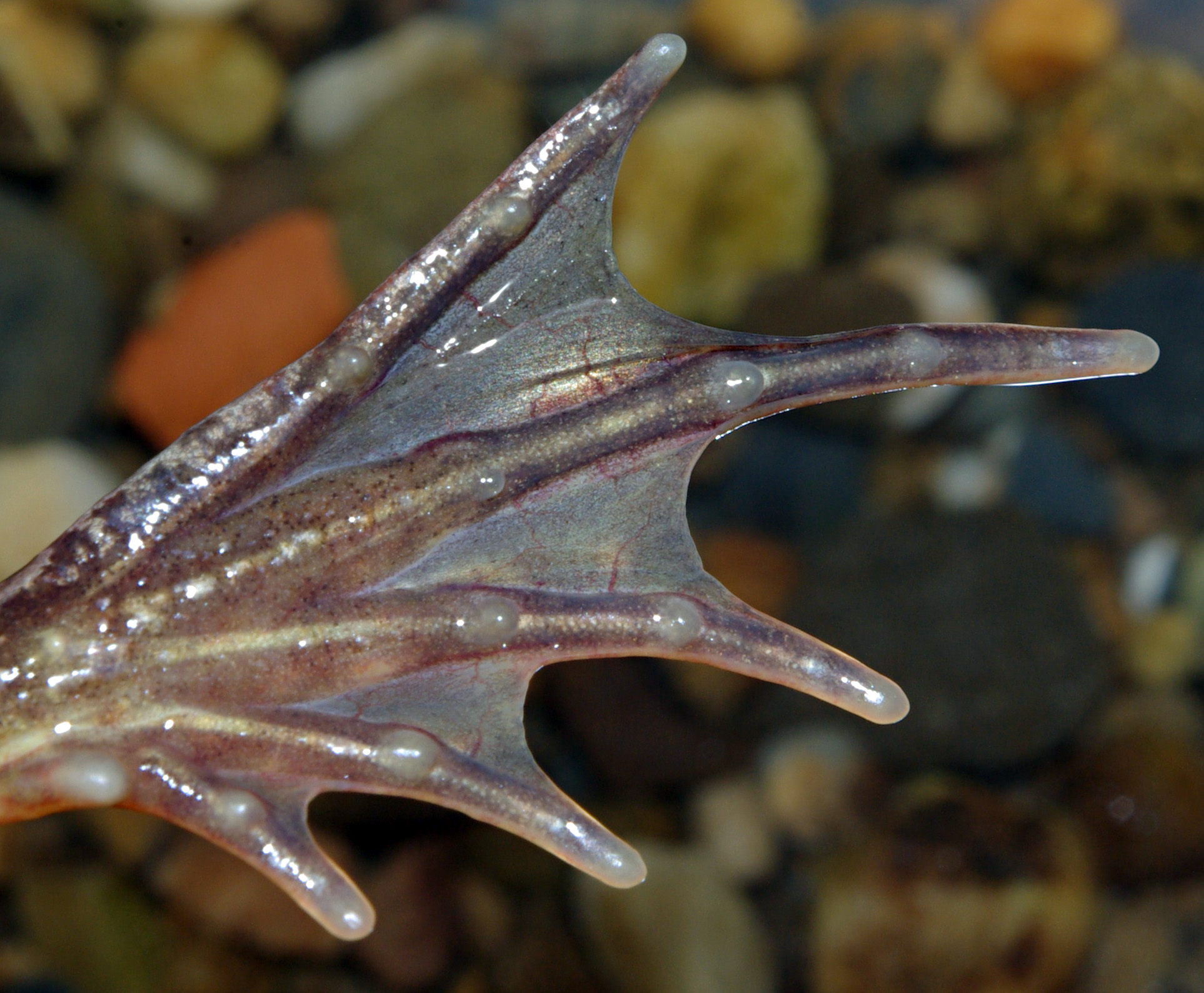
Many frogs have webbed feet and the degree of webbing is directly proportional to the amount of time the species spends in the water. The completely aquatic
The muscular system has been similarly modified. The hind limbs of ancestral frogs presumably contained pairs of muscles which would act in opposition (one muscle to flex the knee, a different muscle to extend it), as is seen in most other limbed animals. However, in modern frogs, almost all muscles have been modified to contribute to the action of jumping, with only a few small muscles remaining to bring the limb back to the starting position and maintain posture. The muscles have also been greatly enlarged, with the main leg muscles accounting for over 17% of the total mass of frogs.
Many frogs have webbed feet and the degree of webbing is directly proportional to the amount of time the species spends in the water. The completely aquatic 
File:WoodFrog DarienLakesStatePark 2020-06-16 (02).jpg, Wood Frog:(''Lithobates sylvaticus or Rana sylvatica'') uses

 The call or croak of a frog is unique to its species. Frogs create this sound by passing air through the
The call or croak of a frog is unique to its species. Frogs create this sound by passing air through the
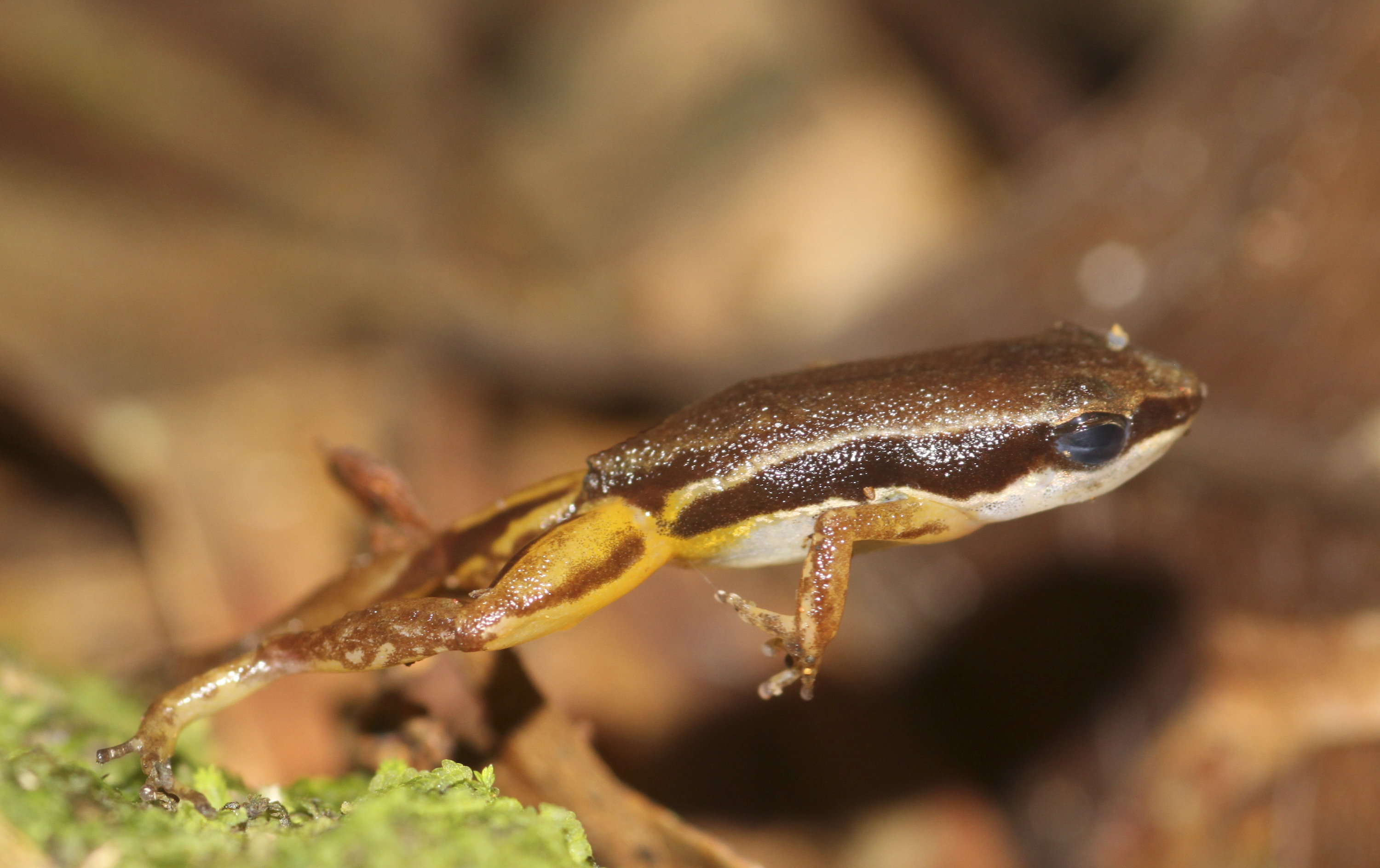 ;Jumping
Frogs are generally recognized as exceptional jumpers and, relative to their size, the best jumpers of all vertebrates. The striped rocket frog, ''Litoria nasuta'', can leap over , a distance that is more than fifty times its body length of . There are tremendous differences between species in jumping capability. Within a species, jump distance increases with increasing size, but relative jumping distance (body-lengths jumped) decreases. The Euphlyctis cyanophlyctis, Indian skipper frog (''Euphlyctis cyanophlyctis'') has the ability to leap out of the water from a position floating on the surface. The tiny northern cricket frog (''Acris crepitans'') can "skitter" across the surface of a pond with a series of short rapid jumps.
Slow-motion photography shows that the muscles have passive flexibility. They are first stretched while the frog is still in the crouched position, then they are contracted before being stretched again to launch the frog into the air. The fore legs are folded against the chest and the hind legs remain in the extended, streamlined position for the duration of the jump. In some extremely capable jumpers, such as the Cuban tree frog (''Osteopilus septentrionalis'') and the northern leopard frog (''Rana pipiens''), the peak power exerted during a jump can exceed that which the muscle is theoretically capable of producing. When the muscles contract, the energy is first transferred into the stretched tendon which is wrapped around the ankle bone. Then the muscles stretch again at the same time as the tendon releases its energy like a catapult to produce a powerful acceleration beyond the limits of muscle-powered acceleration. A similar mechanism has been documented in locusts and grasshoppers.
Early hatching of froglets can have negative effects on frog jumping performance and overall locomotion. The hindlimbs are unable to completely form, which results in them being shorter and much weaker relative to a normal hatching froglet. Early hatching froglets may tend to depend on other forms of locomotion more often, such as swimming and walking.
;Walking and running
;Jumping
Frogs are generally recognized as exceptional jumpers and, relative to their size, the best jumpers of all vertebrates. The striped rocket frog, ''Litoria nasuta'', can leap over , a distance that is more than fifty times its body length of . There are tremendous differences between species in jumping capability. Within a species, jump distance increases with increasing size, but relative jumping distance (body-lengths jumped) decreases. The Euphlyctis cyanophlyctis, Indian skipper frog (''Euphlyctis cyanophlyctis'') has the ability to leap out of the water from a position floating on the surface. The tiny northern cricket frog (''Acris crepitans'') can "skitter" across the surface of a pond with a series of short rapid jumps.
Slow-motion photography shows that the muscles have passive flexibility. They are first stretched while the frog is still in the crouched position, then they are contracted before being stretched again to launch the frog into the air. The fore legs are folded against the chest and the hind legs remain in the extended, streamlined position for the duration of the jump. In some extremely capable jumpers, such as the Cuban tree frog (''Osteopilus septentrionalis'') and the northern leopard frog (''Rana pipiens''), the peak power exerted during a jump can exceed that which the muscle is theoretically capable of producing. When the muscles contract, the energy is first transferred into the stretched tendon which is wrapped around the ankle bone. Then the muscles stretch again at the same time as the tendon releases its energy like a catapult to produce a powerful acceleration beyond the limits of muscle-powered acceleration. A similar mechanism has been documented in locusts and grasshoppers.
Early hatching of froglets can have negative effects on frog jumping performance and overall locomotion. The hindlimbs are unable to completely form, which results in them being shorter and much weaker relative to a normal hatching froglet. Early hatching froglets may tend to depend on other forms of locomotion more often, such as swimming and walking.
;Walking and running
 Frogs in the families Bufonidae, Rhinophrynidae, and
Frogs in the families Bufonidae, Rhinophrynidae, and  Frogs that live in or visit water have adaptations that improve their swimming abilities. The hind limbs are heavily muscled and strong. The webbing between the toes of the hind feet increases the area of the foot and helps propel the frog powerfully through the water. Members of the family Pipidae are wholly aquatic and show the most marked specialization. They have inflexible vertebral columns, flattened, streamlined bodies, lateral line systems, and powerful hind limbs with large webbed feet. Tadpoles mostly have large tail fins which provide thrust when the tail is moved from side to side.
;Burrowing
Some frogs have become adapted for burrowing and a life underground. They tend to have rounded bodies, short limbs, small heads with bulging eyes, and hind feet adapted for excavation. An extreme example of this is the purple frog (''Nasikabatrachus sahyadrensis'') from southern India which feeds on termites and spends almost its whole life underground. It emerges briefly during the monsoon to mate and breed in temporary pools. It has a tiny head with a pointed snout and a plump, rounded body. Because of this fossorial existence, it was Species description, first described in 2003, being new to the scientific community at that time, although previously known to local people.
Frogs that live in or visit water have adaptations that improve their swimming abilities. The hind limbs are heavily muscled and strong. The webbing between the toes of the hind feet increases the area of the foot and helps propel the frog powerfully through the water. Members of the family Pipidae are wholly aquatic and show the most marked specialization. They have inflexible vertebral columns, flattened, streamlined bodies, lateral line systems, and powerful hind limbs with large webbed feet. Tadpoles mostly have large tail fins which provide thrust when the tail is moved from side to side.
;Burrowing
Some frogs have become adapted for burrowing and a life underground. They tend to have rounded bodies, short limbs, small heads with bulging eyes, and hind feet adapted for excavation. An extreme example of this is the purple frog (''Nasikabatrachus sahyadrensis'') from southern India which feeds on termites and spends almost its whole life underground. It emerges briefly during the monsoon to mate and breed in temporary pools. It has a tiny head with a pointed snout and a plump, rounded body. Because of this fossorial existence, it was Species description, first described in 2003, being new to the scientific community at that time, although previously known to local people.
 The spadefoot toads of North America are also adapted to underground life. The Plains spadefoot toad (''Spea bombifrons'') is typical and has a flap of keratinised bone attached to one of the Metatarsus, metatarsals of the hind feet which it uses to dig itself backwards into the ground. As it digs, the toad wriggles its hips from side to side to sink into the loose soil. It has a shallow burrow in the summer from which it emerges at night to forage. In winter, it digs much deeper and has been recorded at a depth of . The tunnel is filled with soil and the toad hibernates in a small chamber at the end. During this time, urea accumulates in its tissues and water is drawn in from the surrounding damp soil by osmosis to supply the toad's needs. Spadefoot toads are "explosive breeders", all emerging from their burrows at the same time and converging on temporary pools, attracted to one of these by the calling of the first male to find a suitable breeding location.
The burrowing frogs of Australia have a rather different lifestyle. The western spotted frog (''Heleioporus albopunctatus'') digs a burrow beside a river or in the bed of an ephemeral stream and regularly emerges to forage. Mating takes place and eggs are laid in a foam nest inside the burrow. The eggs partially develop there, but do not hatch until they are submerged following heavy rainfall. The tadpoles then swim out into the open water and rapidly complete their development. Madagascan burrowing frogs are less fossorial and mostly bury themselves in leaf litter. One of these, the Scaphiophryne marmorata, green burrowing frog (''Scaphiophryne marmorata''), has a flattened head with a short snout and well-developed metatarsal tubercles on its hind feet to help with excavation. It also has greatly enlarged terminal discs on its fore feet that help it to clamber around in bushes. It breeds in temporary pools that form after rains.
;Climbing
The spadefoot toads of North America are also adapted to underground life. The Plains spadefoot toad (''Spea bombifrons'') is typical and has a flap of keratinised bone attached to one of the Metatarsus, metatarsals of the hind feet which it uses to dig itself backwards into the ground. As it digs, the toad wriggles its hips from side to side to sink into the loose soil. It has a shallow burrow in the summer from which it emerges at night to forage. In winter, it digs much deeper and has been recorded at a depth of . The tunnel is filled with soil and the toad hibernates in a small chamber at the end. During this time, urea accumulates in its tissues and water is drawn in from the surrounding damp soil by osmosis to supply the toad's needs. Spadefoot toads are "explosive breeders", all emerging from their burrows at the same time and converging on temporary pools, attracted to one of these by the calling of the first male to find a suitable breeding location.
The burrowing frogs of Australia have a rather different lifestyle. The western spotted frog (''Heleioporus albopunctatus'') digs a burrow beside a river or in the bed of an ephemeral stream and regularly emerges to forage. Mating takes place and eggs are laid in a foam nest inside the burrow. The eggs partially develop there, but do not hatch until they are submerged following heavy rainfall. The tadpoles then swim out into the open water and rapidly complete their development. Madagascan burrowing frogs are less fossorial and mostly bury themselves in leaf litter. One of these, the Scaphiophryne marmorata, green burrowing frog (''Scaphiophryne marmorata''), has a flattened head with a short snout and well-developed metatarsal tubercles on its hind feet to help with excavation. It also has greatly enlarged terminal discs on its fore feet that help it to clamber around in bushes. It breeds in temporary pools that form after rains.
;Climbing
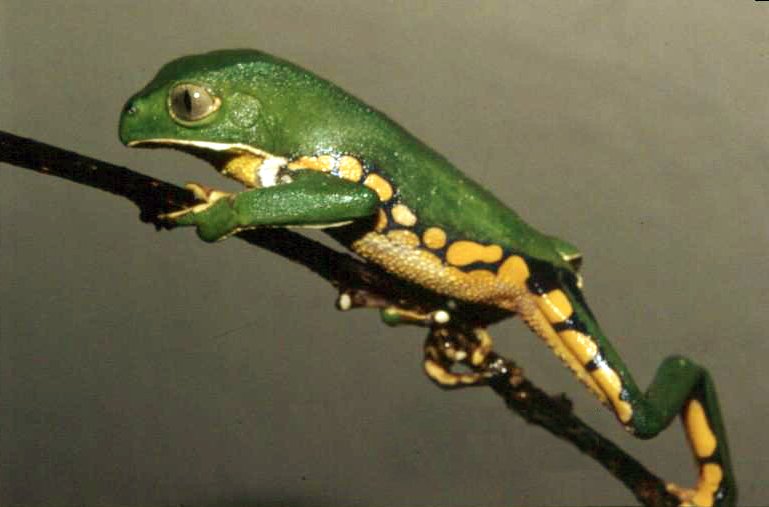

 Tree frogs live high in the canopy (biology), canopy, where they scramble around on the branches, twigs, and leaves, sometimes never coming down to earth. The "true" tree frogs belong to the family Hylidae, but members of other frog families have independently adopted an arboreal habit, a case of convergent evolution. These include the glass frogs (Centrolenidae), the Hyperoliidae, bush frogs (Hyperoliidae), some of the narrow-mouthed frogs (Microhylidae), and the Rhacophoridae, shrub frogs (Rhacophoridae). Most tree frogs are under in length, with long legs and long toes with adhesive pads on the tips. The surface of the toe pads is formed from a closely packed layer of flat-topped, hexagonal epidermis (skin), epidermal cells separated by grooves into which glands secrete mucus. These toe pads, moistened by the mucus, provide the grip on any wet or dry surface, including glass. The forces involved include boundary friction of the toe pad epidermis on the surface and also surface tension and viscosity. Tree frogs are very acrobatic and can catch insects while hanging by one toe from a twig or clutching onto the blade of a windswept reed. Some members of the subfamily Phyllomedusinae have Opposable thumb#Opposition and apposition, opposable toes on their feet. The Phyllomedusa ayeaye, reticulated leaf frog (''Phyllomedusa ayeaye'') has a single opposed Digit (anatomy), digit on each fore foot and two opposed digits on its hind feet. This allows it to grasp the stems of bushes as it clambers around in its riverside habitat.
;Gliding
During the evolutionary history of frogs, several different groups have independently taken to the air. Some frogs in the tropical rainforest are specially adapted for gliding from tree to tree or parachuting to the forest floor. Typical of them is Rhacophorus nigropalmatus, Wallace's flying frog (''Rhacophorus nigropalmatus'') from Malaysia and Borneo. It has large feet with the fingertips expanded into flat adhesive discs and the digits fully webbed. Flaps of skin occur on the lateral margins of the limbs and across the tail region. With the digits splayed, the limbs outstretched, and these flaps spread, it can glide considerable distances, but is unable to undertake powered flight. It can alter its direction of travel and navigate distances of up to between trees.
Tree frogs live high in the canopy (biology), canopy, where they scramble around on the branches, twigs, and leaves, sometimes never coming down to earth. The "true" tree frogs belong to the family Hylidae, but members of other frog families have independently adopted an arboreal habit, a case of convergent evolution. These include the glass frogs (Centrolenidae), the Hyperoliidae, bush frogs (Hyperoliidae), some of the narrow-mouthed frogs (Microhylidae), and the Rhacophoridae, shrub frogs (Rhacophoridae). Most tree frogs are under in length, with long legs and long toes with adhesive pads on the tips. The surface of the toe pads is formed from a closely packed layer of flat-topped, hexagonal epidermis (skin), epidermal cells separated by grooves into which glands secrete mucus. These toe pads, moistened by the mucus, provide the grip on any wet or dry surface, including glass. The forces involved include boundary friction of the toe pad epidermis on the surface and also surface tension and viscosity. Tree frogs are very acrobatic and can catch insects while hanging by one toe from a twig or clutching onto the blade of a windswept reed. Some members of the subfamily Phyllomedusinae have Opposable thumb#Opposition and apposition, opposable toes on their feet. The Phyllomedusa ayeaye, reticulated leaf frog (''Phyllomedusa ayeaye'') has a single opposed Digit (anatomy), digit on each fore foot and two opposed digits on its hind feet. This allows it to grasp the stems of bushes as it clambers around in its riverside habitat.
;Gliding
During the evolutionary history of frogs, several different groups have independently taken to the air. Some frogs in the tropical rainforest are specially adapted for gliding from tree to tree or parachuting to the forest floor. Typical of them is Rhacophorus nigropalmatus, Wallace's flying frog (''Rhacophorus nigropalmatus'') from Malaysia and Borneo. It has large feet with the fingertips expanded into flat adhesive discs and the digits fully webbed. Flaps of skin occur on the lateral margins of the limbs and across the tail region. With the digits splayed, the limbs outstretched, and these flaps spread, it can glide considerable distances, but is unable to undertake powered flight. It can alter its direction of travel and navigate distances of up to between trees.

 In explosive breeders, the first male that finds a suitable breeding location, such as a temporary pool, calls loudly and other frogs of both sexes converge on the pool. Explosive breeders tend to call in unison creating a chorus that can be heard from far away. The spadefoot toads (''Scaphiopus spp.'') of North America fall into this category. Mate selection and courtship is not as important as speed in reproduction. In some years, suitable conditions may not occur and the frogs may go for two or more years without breeding. Some female New Mexico Spadefoot Toad, New Mexico spadefoot toads (''Spea multiplicata'') only spawn half of the available eggs at a time, perhaps retaining some in case a better reproductive opportunity arises later.
At the breeding site, the male mounts the female and grips her tightly round the body. Typically,
In explosive breeders, the first male that finds a suitable breeding location, such as a temporary pool, calls loudly and other frogs of both sexes converge on the pool. Explosive breeders tend to call in unison creating a chorus that can be heard from far away. The spadefoot toads (''Scaphiopus spp.'') of North America fall into this category. Mate selection and courtship is not as important as speed in reproduction. In some years, suitable conditions may not occur and the frogs may go for two or more years without breeding. Some female New Mexico Spadefoot Toad, New Mexico spadefoot toads (''Spea multiplicata'') only spawn half of the available eggs at a time, perhaps retaining some in case a better reproductive opportunity arises later.
At the breeding site, the male mounts the female and grips her tightly round the body. Typically,
 Frogs may lay their in eggs as clumps, surface films, strings, or individually. Around half of species deposit eggs in water, others lay eggs in vegetation, on the ground or in excavations. The tiny Yellow-Striped Pygmy Eleuth, yellow-striped pygmy eleuth (''Eleutherodactylus limbatus'') lays eggs singly, burying them in moist soil. The Smoky Jungle Frog, smoky jungle frog (''Leptodactylus pentadactylus'') makes a nest of foam in a hollow. The eggs hatch when the nest is flooded, or the tadpoles may complete their development in the foam if flooding does not occur. The red-eyed treefrog (''Agalychnis callidryas'') deposits its eggs on a leaf above a pool and when they hatch, the larvae fall into the water below.
In certain species, such as the wood frog (''Rana sylvatica''), Symbiosis, symbiotic unicellular green algae are present in the gelatinous material. It is thought that these may benefit the developing larvae by providing them with extra oxygen through photosynthesis. The interior of globular egg clusters of the Wood Frog, wood frog has been also been found to be up to 6 °C (11 °F) warmer than the surrounding water and this speeds up the development of the larvae. The larvae developing in the eggs can detect vibrations caused by nearby predatory wasps or snakes, and will hatch early to avoid being eaten. In general, the length of the egg stage depends on the species and the environmental conditions. Aquatic eggs normally hatch within one week when the capsule splits as a result of enzymes released by the developing larvae.
Direct development, where eggs hatch into juveniles like small adults, is also known in many frogs, for example, ''Ischnocnema henselii,'' ''Common coquí, Eleutherodactylus coqui'', and ''Raorchestes ochlandrae'' and ''Raorchestes chalazodes.''
Frogs may lay their in eggs as clumps, surface films, strings, or individually. Around half of species deposit eggs in water, others lay eggs in vegetation, on the ground or in excavations. The tiny Yellow-Striped Pygmy Eleuth, yellow-striped pygmy eleuth (''Eleutherodactylus limbatus'') lays eggs singly, burying them in moist soil. The Smoky Jungle Frog, smoky jungle frog (''Leptodactylus pentadactylus'') makes a nest of foam in a hollow. The eggs hatch when the nest is flooded, or the tadpoles may complete their development in the foam if flooding does not occur. The red-eyed treefrog (''Agalychnis callidryas'') deposits its eggs on a leaf above a pool and when they hatch, the larvae fall into the water below.
In certain species, such as the wood frog (''Rana sylvatica''), Symbiosis, symbiotic unicellular green algae are present in the gelatinous material. It is thought that these may benefit the developing larvae by providing them with extra oxygen through photosynthesis. The interior of globular egg clusters of the Wood Frog, wood frog has been also been found to be up to 6 °C (11 °F) warmer than the surrounding water and this speeds up the development of the larvae. The larvae developing in the eggs can detect vibrations caused by nearby predatory wasps or snakes, and will hatch early to avoid being eaten. In general, the length of the egg stage depends on the species and the environmental conditions. Aquatic eggs normally hatch within one week when the capsule splits as a result of enzymes released by the developing larvae.
Direct development, where eggs hatch into juveniles like small adults, is also known in many frogs, for example, ''Ischnocnema henselii,'' ''Common coquí, Eleutherodactylus coqui'', and ''Raorchestes ochlandrae'' and ''Raorchestes chalazodes.''
 The larvae that emerge from the eggs, known as tadpoles (or occasionally polliwogs). Tadpoles lack eyelids and limbs, and have cartilaginous skeletons, gills for respiration (external gills at first, internal gills later), and tails they use for swimming. As a general rule, free-living larvae are fully aquatic, but at least one species (''Nannophrys ceylonensis'') has semiterrestrial tadpoles which live among wet rocks.
From early in its development, a gill pouch covers the tadpole's gills and front legs. The lungs soon start to develop and are used as an accessory breathing organ. Some species go through metamorphosis while still inside the egg and hatch directly into small frogs. Tadpoles lack true teeth, but the jaws in most species have two elongated, parallel rows of small,
The larvae that emerge from the eggs, known as tadpoles (or occasionally polliwogs). Tadpoles lack eyelids and limbs, and have cartilaginous skeletons, gills for respiration (external gills at first, internal gills later), and tails they use for swimming. As a general rule, free-living larvae are fully aquatic, but at least one species (''Nannophrys ceylonensis'') has semiterrestrial tadpoles which live among wet rocks.
From early in its development, a gill pouch covers the tadpole's gills and front legs. The lungs soon start to develop and are used as an accessory breathing organ. Some species go through metamorphosis while still inside the egg and hatch directly into small frogs. Tadpoles lack true teeth, but the jaws in most species have two elongated, parallel rows of small,
 Frogs are primary predators and an important part of the
Frogs are primary predators and an important part of the
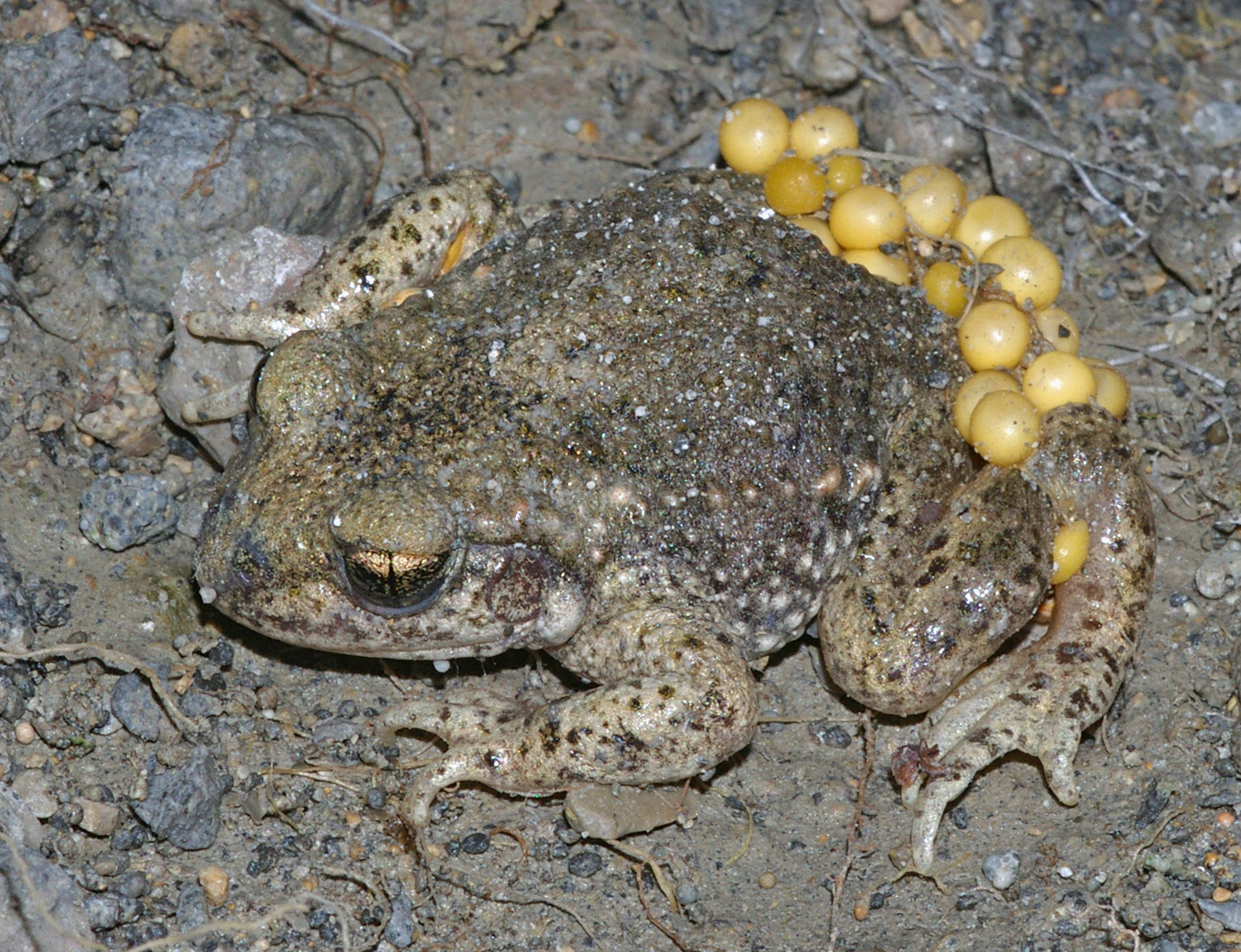

 Although care of offspring is poorly understood in frogs, up to an estimated 20% of amphibian species may care for their young in some way. The evolution of biparental care in tropical frogs, evolution of parental care in frogs is driven primarily by the size of the water body in which they breed. Those that breed in smaller water bodies tend to have greater and more complex parental care behaviour. Because predation of eggs and larvae is high in large water bodies, some frog species started to lay their eggs on land. Once this happened, the desiccating terrestrial environment demands that one or both parents keep them moist to ensure their survival. The subsequent need to transport hatched tadpoles to a water body required an even more intense form of parental care.
In small pools, predators are mostly absent and competition between tadpoles becomes the variable that constrains their survival. Certain frog species avoid this competition by making use of smaller phytotelmata (water-filled leaf wikt:axil, axils or small woody cavities) as sites for depositing a few tadpoles. While these smaller rearing sites are free from competition, they also lack sufficient nutrients to support a tadpole without parental assistance. Frog species that changed from the use of larger to smaller phytotelmata have evolved a strategy of providing their offspring with nutritive but unfertilized eggs. The female strawberry poison-dart frog (''Oophaga pumilio'') lays her eggs on the forest floor. The male frog guards them from predation and carries water in his cloaca to keep them moist. When they hatch, the female moves the tadpoles on her back to a water-holding bromeliad or other similar water body, depositing just one in each location. She visits them regularly and feeds them by laying one or two unfertilized eggs in the phytotelma, continuing to do this until the young are large enough to undergo metamorphosis. The granular poison frog (''Oophaga granulifera'') looks after its tadpoles in a similar way.
Many other diverse forms of parental care are seen in frogs. The tiny male ''Colostethus subpunctatus'' stands guard over his egg cluster, laid under a stone or log. When the eggs hatch, he transports the tadpoles on his back to a temporary pool, where he partially immerses himself in the water and one or more tadpoles drop off. He then moves on to another pool. The male common midwife toad (''Alytes obstetricans'') carries the eggs around with him attached to his hind legs. He keeps them damp in dry weather by immersing himself in a pond, and prevents them from getting too wet in soggy vegetation by raising his hindquarters. After three to six weeks, he travels to a pond and the eggs hatch into tadpoles. The tungara frog (''Physalaemus pustulosus'') builds a floating nest from foam to protect its eggs from predation. The foam is made from proteins and lectins, and seems to have antimicrobial properties. Several pairs of frogs may form a colonial nest on a previously built raft. The eggs are laid in the centre, followed by alternate layers of foam and eggs, finishing with a foam capping.
Some frogs protect their offspring inside their own bodies. Both male and female pouched frogs (''Assa darlingtoni'') guard their eggs, which are laid on the ground. When the eggs hatch, the male lubricates his body with the jelly surrounding them and immerses himself in the egg mass. The tadpoles wriggle into skin pouches on his side, where they develop until they metamorphose into juvenile frogs. The female gastric-brooding frog (''Rheobatrachus'' sp.) from Australia, now probably extinct, swallows her fertilized eggs, which then develop inside her stomach. She ceases to feed and stops secreting stomach acid. The tadpoles rely on the yolks of the eggs for nourishment. After six or seven weeks, they are ready for metamorphosis. The mother regurgitates the tiny frogs, which hop away from her mouth. The female Darwin's frog (''Rhinoderma darwinii'') from Chile lays up to 40 eggs on the ground, where they are guarded by the male. When the tadpoles are about to hatch, they are engulfed by the male, which carries them around inside his much-enlarged vocal sac. Here they are immersed in a frothy, viscous liquid that contains some nourishment to supplement what they obtain from the yolks of the eggs. They remain in the sac for seven to ten weeks before undergoing metamorphosis, after which they move into the male's mouth and emerge.
Although care of offspring is poorly understood in frogs, up to an estimated 20% of amphibian species may care for their young in some way. The evolution of biparental care in tropical frogs, evolution of parental care in frogs is driven primarily by the size of the water body in which they breed. Those that breed in smaller water bodies tend to have greater and more complex parental care behaviour. Because predation of eggs and larvae is high in large water bodies, some frog species started to lay their eggs on land. Once this happened, the desiccating terrestrial environment demands that one or both parents keep them moist to ensure their survival. The subsequent need to transport hatched tadpoles to a water body required an even more intense form of parental care.
In small pools, predators are mostly absent and competition between tadpoles becomes the variable that constrains their survival. Certain frog species avoid this competition by making use of smaller phytotelmata (water-filled leaf wikt:axil, axils or small woody cavities) as sites for depositing a few tadpoles. While these smaller rearing sites are free from competition, they also lack sufficient nutrients to support a tadpole without parental assistance. Frog species that changed from the use of larger to smaller phytotelmata have evolved a strategy of providing their offspring with nutritive but unfertilized eggs. The female strawberry poison-dart frog (''Oophaga pumilio'') lays her eggs on the forest floor. The male frog guards them from predation and carries water in his cloaca to keep them moist. When they hatch, the female moves the tadpoles on her back to a water-holding bromeliad or other similar water body, depositing just one in each location. She visits them regularly and feeds them by laying one or two unfertilized eggs in the phytotelma, continuing to do this until the young are large enough to undergo metamorphosis. The granular poison frog (''Oophaga granulifera'') looks after its tadpoles in a similar way.
Many other diverse forms of parental care are seen in frogs. The tiny male ''Colostethus subpunctatus'' stands guard over his egg cluster, laid under a stone or log. When the eggs hatch, he transports the tadpoles on his back to a temporary pool, where he partially immerses himself in the water and one or more tadpoles drop off. He then moves on to another pool. The male common midwife toad (''Alytes obstetricans'') carries the eggs around with him attached to his hind legs. He keeps them damp in dry weather by immersing himself in a pond, and prevents them from getting too wet in soggy vegetation by raising his hindquarters. After three to six weeks, he travels to a pond and the eggs hatch into tadpoles. The tungara frog (''Physalaemus pustulosus'') builds a floating nest from foam to protect its eggs from predation. The foam is made from proteins and lectins, and seems to have antimicrobial properties. Several pairs of frogs may form a colonial nest on a previously built raft. The eggs are laid in the centre, followed by alternate layers of foam and eggs, finishing with a foam capping.
Some frogs protect their offspring inside their own bodies. Both male and female pouched frogs (''Assa darlingtoni'') guard their eggs, which are laid on the ground. When the eggs hatch, the male lubricates his body with the jelly surrounding them and immerses himself in the egg mass. The tadpoles wriggle into skin pouches on his side, where they develop until they metamorphose into juvenile frogs. The female gastric-brooding frog (''Rheobatrachus'' sp.) from Australia, now probably extinct, swallows her fertilized eggs, which then develop inside her stomach. She ceases to feed and stops secreting stomach acid. The tadpoles rely on the yolks of the eggs for nourishment. After six or seven weeks, they are ready for metamorphosis. The mother regurgitates the tiny frogs, which hop away from her mouth. The female Darwin's frog (''Rhinoderma darwinii'') from Chile lays up to 40 eggs on the ground, where they are guarded by the male. When the tadpoles are about to hatch, they are engulfed by the male, which carries them around inside his much-enlarged vocal sac. Here they are immersed in a frothy, viscous liquid that contains some nourishment to supplement what they obtain from the yolks of the eggs. They remain in the sac for seven to ten weeks before undergoing metamorphosis, after which they move into the male's mouth and emerge.

 At first sight, frogs seem rather defenceless because of their small size, slow movement, thin skin, and lack of defensive structures, such as spines, claws or teeth. Many use camouflage to avoid detection, the skin often being spotted or streaked in neutral colours that allow a stationary frog to merge into its surroundings. Some can make prodigious leaps, often into water, that help them to evade potential attackers, while many have other defensive adaptations and strategies.
The skin of many frogs contains mild toxic substances called bufotoxins to make them unpalatable to potential predators. Most toads and some frogs have large poison glands, the parotoid glands, located on the sides of their heads behind the eyes and other glands elsewhere on their bodies. These glands secrete mucus and a range of toxins that make frogs slippery to hold and distasteful or poisonous. If the noxious effect is immediate, the predator may cease its action and the frog may escape. If the effect develops more slowly, the predator may learn to avoid that species in future. Poisonous frogs tend to advertise their toxicity with bright colours, an adaptive strategy known as aposematism. The Poison dart frog, poison dart frogs in the family Dendrobatidae do this. They are typically red, orange, or yellow, often with contrasting black markings on their bodies. ''Allobates zaparo'' is not poisonous, but mimics the appearance of two different toxic species with which it shares a common range in an effort to deceive predators. Other species, such as the European Fire-bellied Toad, European fire-bellied toad (''Bombina bombina''), have their warning colour underneath. They "flash" this when attacked, adopting a pose that exposes the vivid colouring on their bellies.
At first sight, frogs seem rather defenceless because of their small size, slow movement, thin skin, and lack of defensive structures, such as spines, claws or teeth. Many use camouflage to avoid detection, the skin often being spotted or streaked in neutral colours that allow a stationary frog to merge into its surroundings. Some can make prodigious leaps, often into water, that help them to evade potential attackers, while many have other defensive adaptations and strategies.
The skin of many frogs contains mild toxic substances called bufotoxins to make them unpalatable to potential predators. Most toads and some frogs have large poison glands, the parotoid glands, located on the sides of their heads behind the eyes and other glands elsewhere on their bodies. These glands secrete mucus and a range of toxins that make frogs slippery to hold and distasteful or poisonous. If the noxious effect is immediate, the predator may cease its action and the frog may escape. If the effect develops more slowly, the predator may learn to avoid that species in future. Poisonous frogs tend to advertise their toxicity with bright colours, an adaptive strategy known as aposematism. The Poison dart frog, poison dart frogs in the family Dendrobatidae do this. They are typically red, orange, or yellow, often with contrasting black markings on their bodies. ''Allobates zaparo'' is not poisonous, but mimics the appearance of two different toxic species with which it shares a common range in an effort to deceive predators. Other species, such as the European Fire-bellied Toad, European fire-bellied toad (''Bombina bombina''), have their warning colour underneath. They "flash" this when attacked, adopting a pose that exposes the vivid colouring on their bellies.
 Some frogs, such as the
Some frogs, such as the
 Frogs live on all the continents except Antarctica, but they are not present on certain islands, especially those far away from continental land masses. Many species are isolated in restricted ranges by changes of climate or inhospitable territory, such as stretches of sea, mountain ridges, deserts, forest clearance, road construction, or other man-made barriers. Usually, a greater diversity of frogs occurs in tropical areas than in temperate regions, such as Europe. Some frogs inhabit arid areas, such as deserts, and rely on specific adaptations to survive. Members of the Australian genus ''Cyclorana'' bury themselves underground where they create a water-impervious cocoon in which to aestivation, aestivate during dry periods. Once it rains, they emerge, find a temporary pool, and breed. Egg and tadpole development is very fast in comparison to those of most other frogs, so breeding can be completed before the pond dries up. Some frog species are adapted to a cold environment. The wood frog (''Rana sylvatica''), whose habitat extends into the Arctic Circle, buries itself in the ground during winter. Although much of its body freezes during this time, it maintains a high concentration of glucose in its vital organs, which protects them from damage.
Frogs live on all the continents except Antarctica, but they are not present on certain islands, especially those far away from continental land masses. Many species are isolated in restricted ranges by changes of climate or inhospitable territory, such as stretches of sea, mountain ridges, deserts, forest clearance, road construction, or other man-made barriers. Usually, a greater diversity of frogs occurs in tropical areas than in temperate regions, such as Europe. Some frogs inhabit arid areas, such as deserts, and rely on specific adaptations to survive. Members of the Australian genus ''Cyclorana'' bury themselves underground where they create a water-impervious cocoon in which to aestivation, aestivate during dry periods. Once it rains, they emerge, find a temporary pool, and breed. Egg and tadpole development is very fast in comparison to those of most other frogs, so breeding can be completed before the pond dries up. Some frog species are adapted to a cold environment. The wood frog (''Rana sylvatica''), whose habitat extends into the Arctic Circle, buries itself in the ground during winter. Although much of its body freezes during this time, it maintains a high concentration of glucose in its vital organs, which protects them from damage.
 In 2006, of 4,035 species of amphibians that depend on water during some lifecycle stage, 1,356 (33.6%) were considered to be threatened. This is likely to be an underestimate because it excludes 1,427 species for which evidence was insufficient to assess their status. Frog populations have declined dramatically since the 1950s. More than one-third of frog species are considered to be threatened with extinction, and more than 120 species are believed to have become extinct since the 1980s. Among these species are the gastric-brooding frogs of Australia and the golden toad of Costa Rica. The latter is of particular concern to scientists because it inhabited the pristine Monteverde Cloud Forest Reserve and its population crashed in 1987, along with about 20 other frog species in the area. This could not be linked directly to human activities, such as deforestation, and was outside the range of normal fluctuations in population size. Elsewhere, habitat loss is a significant cause of frog population decline, as are pollutants, climate change, increased ultraviolet, UVB radiation, and the introduction of Indigenous (ecology), non-native predators and competitors. A Canadian study conducted in 2006 suggested heavy traffic in their environment was a larger threat to frog populations than was habitat loss. Emerging infectious diseases, including
In 2006, of 4,035 species of amphibians that depend on water during some lifecycle stage, 1,356 (33.6%) were considered to be threatened. This is likely to be an underestimate because it excludes 1,427 species for which evidence was insufficient to assess their status. Frog populations have declined dramatically since the 1950s. More than one-third of frog species are considered to be threatened with extinction, and more than 120 species are believed to have become extinct since the 1980s. Among these species are the gastric-brooding frogs of Australia and the golden toad of Costa Rica. The latter is of particular concern to scientists because it inhabited the pristine Monteverde Cloud Forest Reserve and its population crashed in 1987, along with about 20 other frog species in the area. This could not be linked directly to human activities, such as deforestation, and was outside the range of normal fluctuations in population size. Elsewhere, habitat loss is a significant cause of frog population decline, as are pollutants, climate change, increased ultraviolet, UVB radiation, and the introduction of Indigenous (ecology), non-native predators and competitors. A Canadian study conducted in 2006 suggested heavy traffic in their environment was a larger threat to frog populations than was habitat loss. Emerging infectious diseases, including
 Frog legs are eaten by humans in many parts of the world. Indonesia is the world's largest exporter of frog meat, exporting more than 5,000 tonnes of frog meat each year, mostly to France, Belgium and Luxembourg.̺ Originally, they were supplied from local wild populations, but overexploitation led to a diminution in the supply. This resulted in the development of Aquaculture, frog farming and a global trade in frogs. The main importing countries are France, Belgium, Luxembourg, and the United States, while the chief exporting nations are Indonesia and China. The annual global trade in the
Frog legs are eaten by humans in many parts of the world. Indonesia is the world's largest exporter of frog meat, exporting more than 5,000 tonnes of frog meat each year, mostly to France, Belgium and Luxembourg.̺ Originally, they were supplied from local wild populations, but overexploitation led to a diminution in the supply. This resulted in the development of Aquaculture, frog farming and a global trade in frogs. The main importing countries are France, Belgium, Luxembourg, and the United States, while the chief exporting nations are Indonesia and China. The annual global trade in the
 Because frog toxins are extraordinarily diverse, they have raised the interest of biochemists as a "natural pharmacy". The alkaloid epibatidine, a painkiller 200 times more potent than morphine, is made by some species of Poison dart frog, poison dart frogs. Other chemicals isolated from the skins of frogs may offer resistance to HIV infection. Dart poisons are under active investigation for their potential as therapeutic drugs.
It has long been suspected that pre-Columbian Mesoamericans used a toxic secretion produced by the cane toad as a hallucinogen, but more likely they used substances secreted by the Colorado River toad (''Bufo alvarius''). These contain bufotenin (5-MeO-DMT), a psychoactive drug, psychoactive compound that has been used in modern times as a recreational drug. Typically, the skin secretions are dried and then smoked. Illicit drug use by licking the skin of a toad has been reported in the media, but this may be an urban myth.
Exudations from the skin of the golden poison frog (''Phyllobates terribilis'') are traditionally used by native Colombians to poison the darts they use for hunting. The tip of the projectile is rubbed over the back of the frog and the dart is launched from a blowgun. The combination of the two alkaloid toxins batrachotoxin and homobatrachotoxin is so powerful, one frog contains enough poison to kill an estimated 22,000 mice. Two other species, the Kokoe poison dart frog (''Phyllobates aurotaenia'') and the black-legged dart frog (''Phyllobates bicolor'') are also used for this purpose. These are less toxic and less abundant than the golden poison frog. They are impaled on pointed sticks and may be heated over a fire to maximise the quantity of poison that can be transferred to the dart.
Because frog toxins are extraordinarily diverse, they have raised the interest of biochemists as a "natural pharmacy". The alkaloid epibatidine, a painkiller 200 times more potent than morphine, is made by some species of Poison dart frog, poison dart frogs. Other chemicals isolated from the skins of frogs may offer resistance to HIV infection. Dart poisons are under active investigation for their potential as therapeutic drugs.
It has long been suspected that pre-Columbian Mesoamericans used a toxic secretion produced by the cane toad as a hallucinogen, but more likely they used substances secreted by the Colorado River toad (''Bufo alvarius''). These contain bufotenin (5-MeO-DMT), a psychoactive drug, psychoactive compound that has been used in modern times as a recreational drug. Typically, the skin secretions are dried and then smoked. Illicit drug use by licking the skin of a toad has been reported in the media, but this may be an urban myth.
Exudations from the skin of the golden poison frog (''Phyllobates terribilis'') are traditionally used by native Colombians to poison the darts they use for hunting. The tip of the projectile is rubbed over the back of the frog and the dart is launched from a blowgun. The combination of the two alkaloid toxins batrachotoxin and homobatrachotoxin is so powerful, one frog contains enough poison to kill an estimated 22,000 mice. Two other species, the Kokoe poison dart frog (''Phyllobates aurotaenia'') and the black-legged dart frog (''Phyllobates bicolor'') are also used for this purpose. These are less toxic and less abundant than the golden poison frog. They are impaled on pointed sticks and may be heated over a fire to maximise the quantity of poison that can be transferred to the dart.

AmphibiaWeb
Gallery of Frogs
nbsp;– Photography and images of various frog species
The Whole Frog Project
nbsp;– Virtual frog dissection and anatomy
''San Francisco Chronicle'', 20 April 1992
nbsp;– Features many unusual frogs
''Scientific American'': Researchers Pinpoint Source of Poison Frogs' Deadly Defenses
Time-lapse video showing the egg's development until hatching
Frog vocalisations from around the world
nbsp;– From the British Library Sound Archive
Frog calls
nbsp;– From Manitoba, Canada {{Featured article Frogs, 01 Articles containing video clips Extant Hettangian first appearances
 A frog is any member of a diverse and largely carnivorous group of short-bodied, tailless
A frog is any member of a diverse and largely carnivorous group of short-bodied, tailless amphibian
Amphibians are four-limbed and ectothermic vertebrates of the class Amphibia. All living amphibians belong to the group Lissamphibia. They inhabit a wide variety of habitats, with most species living within terrestrial, fossorial, arbor ...
s composing the order Anura (ανοὐρά, literally ''without tail'' in Ancient Greek). The oldest fossil "proto-frog" ''Triadobatrachus
''Triadobatrachus'' is an extinct genus of salientian frog-like amphibians, including only one known species, ''Triadobatrachus massinoti''. It is the oldest member of the frog lineage known, and an excellent example of a transitional fossil. It ...
'' is known from the Early Triassic
The Early Triassic is the first of three epochs of the Triassic Period of the geologic timescale. It spans the time between Ma and Ma (million years ago). Rocks from this epoch are collectively known as the Lower Triassic Series, which is a ...
of Madagascar
Madagascar (; mg, Madagasikara, ), officially the Republic of Madagascar ( mg, Repoblikan'i Madagasikara, links=no, ; french: République de Madagascar), is an island country in the Indian Ocean, approximately off the coast of East Afric ...
, but molecular clock dating suggests their split from other amphibians may extend further back to the Permian
The Permian ( ) is a geologic period and stratigraphic system which spans 47 million years from the end of the Carboniferous Period million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Triassic Period 251.9 Mya. It is the last period of the Paleoz ...
, 265 million years ago
The abbreviation Myr, "million years", is a unit of a quantity of (i.e. ) years, or 31.556926 teraseconds.
Usage
Myr (million years) is in common use in fields such as Earth science and cosmology. Myr is also used with Mya (million years ago). ...
. Frogs are widely distributed, ranging from the tropics
The tropics are the regions of Earth surrounding the Equator. They are defined in latitude by the Tropic of Cancer in the Northern Hemisphere at N and the Tropic of Capricorn in
the Southern Hemisphere at S. The tropics are also referre ...
to subarctic
The subarctic zone is a region in the Northern Hemisphere immediately south of the true Arctic, north of humid continental regions and covering much of Alaska, Canada, Iceland, the north of Scandinavia, Siberia, and the Cairngorms. Generally ...
regions, but the greatest concentration of species diversity
Species diversity is the number of different species that are represented in a given community (a dataset). The effective number of species refers to the number of equally abundant species needed to obtain the same mean proportional species abundan ...
is in tropical rainforest. Frogs account for around 88% of extant amphibian species. They are also one of the five most diverse vertebrate
Vertebrates () comprise all animal taxa within the subphylum Vertebrata () ( chordates with backbones), including all mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish. Vertebrates represent the overwhelming majority of the phylum Chordata, wi ...
orders. Warty frog species tend to be called toad
Toad is a common name for certain frogs, especially of the family Bufonidae, that are characterized by dry, leathery skin, short legs, and large bumps covering the parotoid glands.
A distinction between frogs and toads is not made in scient ...
s, but the distinction between frogs and toads is informal, not from taxonomy
Taxonomy is the practice and science of categorization or classification.
A taxonomy (or taxonomical classification) is a scheme of classification, especially a hierarchical classification, in which things are organized into groups or types. ...
or evolutionary history.
An adult frog has a stout body, protruding eye
Eyes are organs of the visual system. They provide living organisms with vision, the ability to receive and process visual detail, as well as enabling several photo response functions that are independent of vision. Eyes detect light and con ...
s, anteriorly-attached tongue
The tongue is a muscular organ in the mouth of a typical tetrapod. It manipulates food for mastication and swallowing as part of the digestive process, and is the primary organ of taste. The tongue's upper surface (dorsum) is covered by taste b ...
, limbs folded underneath, and no tail
The tail is the section at the rear end of certain kinds of animals’ bodies; in general, the term refers to a distinct, flexible appendage to the torso. It is the part of the body that corresponds roughly to the sacrum and coccyx in mammals, ...
(the tail of tailed frogs is an extension of the male cloaca). Frogs have gland
In animals, a gland is a group of cells in an animal's body that synthesizes substances (such as hormones) for release into the bloodstream ( endocrine gland) or into cavities inside the body or its outer surface ( exocrine gland).
Structure
...
ular skin, with secretions ranging from distasteful to toxic. Their skin varies in colour from well-camouflage
Camouflage is the use of any combination of materials, coloration, or illumination for concealment, either by making animals or objects hard to see, or by disguising them as something else. Examples include the leopard's spotted coat, the b ...
d dappled brown, grey and green to vivid patterns of bright red or yellow and black to show toxicity and ward off predators. Adult frogs live in fresh water and on dry land; some species are adapted for living underground or in trees.
Frogs typically lay their eggs
Humans and human ancestors have scavenged and eaten animal eggs for millions of years. Humans in Southeast Asia had domesticated chickens and harvested their eggs for food by 1,500 BCE. The most widely consumed eggs are those of fowl, especial ...
in water. The eggs hatch into aquatic larva
A larva (; plural larvae ) is a distinct juvenile form many animals undergo before metamorphosis into adults. Animals with indirect development such as insects, amphibians, or cnidarians typically have a larval phase of their life cycle. ...
e called tadpole
A tadpole is the larval stage in the biological life cycle of an amphibian. Most tadpoles are fully aquatic, though some species of amphibians have tadpoles that are terrestrial. Tadpoles have some fish-like features that may not be found i ...
s that have tails and internal gill
A gill () is a respiratory organ that many aquatic organisms use to extract dissolved oxygen from water and to excrete carbon dioxide. The gills of some species, such as hermit crabs, have adapted to allow respiration on land provided they ar ...
s. They have highly specialized rasping mouth parts suitable for herbivorous
A herbivore is an animal anatomically and physiologically adapted to eating plant material, for example foliage or marine algae, for the main component of its diet. As a result of their plant diet, herbivorous animals typically have mouthpar ...
, omnivorous or planktivorous
A planktivore is an aquatic organism that feeds on planktonic food, including zooplankton and phytoplankton. Planktivorous organisms encompass a range of some of the planet's smallest to largest multicellular animals in both the present day and i ...
diets. The life cycle is completed when they metamorphose into adults. A few species deposit eggs on land or bypass the tadpole stage. Adult frogs generally have a carnivorous diet consisting of small invertebrates, but omnivorous species exist and a few feed on plant matter. Frog skin has a rich microbiome
A microbiome () is the community of microorganisms that can usually be found living together in any given habitat. It was defined more precisely in 1988 by Whipps ''et al.'' as "a characteristic microbial community occupying a reasonably wel ...
which is important to their health. Frogs are extremely efficient at converting what they eat into body mass. They are an important food source for predators
Predation is a biological interaction where one organism, the predator, kills and eats another organism, its prey. It is one of a family of common feeding behaviours that includes parasitism and micropredation (which usually do not kill th ...
and part of the food web
A food web is the natural interconnection of food chains and a graphical representation of what-eats-what in an ecological community. Another name for food web is consumer-resource system. Ecologists can broadly lump all life forms into one ...
dynamics of many of the world's ecosystem
An ecosystem (or ecological system) consists of all the organisms and the physical environment with which they interact. These biotic and abiotic components are linked together through nutrient cycles and energy flows. Energy enters the syste ...
s. The skin is semi-permeable
Semipermeable membrane is a type of biological or synthetic, polymeric membrane that will allow certain molecules or ions to pass through it by osmosis. The rate of passage depends on the pressure, concentration, and temperature of the m ...
, making them susceptible to dehydration, so they either live in moist places or have special adaptations to deal with dry habitats. Frogs produce a wide range of vocalizations, particularly in their breeding season, and exhibit many different kinds of complex behaviors to attract mates, to fend off predators and to generally survive.
Frogs are valued as food by humans and also have many cultural roles in literature, symbolism and religion. They are also seen as environmental bellwether
A bellwether is a leader or an indicator of trends.bellwether
" ''Cambridge Dictionary''. Re ...
s, with declines in frog populations often viewed as early warning signs of environmental damage. Frog populations have declined significantly since the 1950s. More than one third of species are considered to be " ''Cambridge Dictionary''. Re ...
threatened
Threatened species are any species (including animals, plants and fungi) which are vulnerable to endangerment in the near future. Species that are threatened are sometimes characterised by the population dynamics measure of ''critical depensa ...
with extinct
Extinction is the termination of a kind of organism or of a group of kinds (taxon), usually a species. The moment of extinction is generally considered to be the death of the last individual of the species, although the capacity to breed and ...
ion and over 120 are believed to have become extinct since the 1980s. The number of malformations among frogs is on the rise and an emerging fungal
A fungus (plural, : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of Eukaryote, eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and Mold (fungus), molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified ...
disease, chytridiomycosis
Chytridiomycosis ( ) is an infectious disease in amphibians, caused by the chytrid fungi '' Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis'' and ''Batrachochytrium salamandrivorans''. Chytridiomycosis has been linked to dramatic population declines or exti ...
, has spread around the world. Conservation biologists are working to understand the causes of these problems and to resolve them.
Etymology and taxonomy
The use of the common names ''frog'' and ''toad
Toad is a common name for certain frogs, especially of the family Bufonidae, that are characterized by dry, leathery skin, short legs, and large bumps covering the parotoid glands.
A distinction between frogs and toads is not made in scient ...
'' has no taxonomic justification. From a classification perspective, all members of the order Anura are frogs, but only members of the family Bufonidae are considered "true toads". The use of the term ''frog'' in common names usually refers to species that are aquatic or semi-aquatic and have smooth, moist skins; the term ''toad'' generally refers to species that are terrestrial with dry, warty skins. There are numerous exceptions to this rule. The European fire-bellied toad
The European fire-bellied toad (''Bombina bombina'') is a species of fire-bellied toad native to eastern parts of mainland Europe, where it can be found near waterbodies such as ponds and marshes. It is known for its red colored belly used to wa ...
(''Bombina bombina'') has a slightly warty skin and prefers a watery habitat whereas the Panamanian golden frog (''Atelopus zeteki'') is in the toad family Bufonidae and has a smooth skin.
Etymology
The origin of the order name ''Anura''—and its original spelling ''Anoures''—is the Ancient Greek " alpha privative" prefix ( from before a vowel) 'without', and () 'animal tail'. meaning "tailless". It refers to the tailless character of these amphibians. The origins of the word ''frog'' are uncertain and debated. The word is first attested inOld English
Old English (, ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the early Middle Ages. It was brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlers in the mid-5th c ...
as , but the usual Old English word for the frog was (with variants such as and ), and it is agreed that the word ''frog'' is somehow related to this. Old English remained in dialectal use in English as ''frosh'' and ''frosk'' into the nineteenth century, and is paralleled widely in other Germanic languages
The Germanic languages are a branch of the Indo-European language family spoken natively by a population of about 515 million people mainly in Europe, North America, Oceania and Southern Africa. The most widely spoken Germanic language, ...
, with examples in the modern languages including German , Norwegian , Icelandic , and Dutch
Dutch commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
* Dutch people ()
* Dutch language ()
Dutch may also refer to:
Places
* Dutch, West Virginia, a community in the United States
* Pennsylvania Dutch Country
People ...
'. These words allow reconstruction of a Common Germanic
Proto-Germanic (abbreviated PGmc; also called Common Germanic) is the reconstructed proto-language of the Germanic branch of the Indo-European languages.
Proto-Germanic eventually developed from pre-Proto-Germanic into three Germanic br ...
ancestor . The third edition of the '' Oxford English Dictionary'' finds that the etymology of is uncertain, but agrees with arguments that it could plausibly derive from a Proto-Indo-European
Proto-Indo-European (PIE) is the reconstructed common ancestor of the Indo-European language family. Its proposed features have been derived by linguistic reconstruction from documented Indo-European languages. No direct record of Proto-Indo-E ...
base along the lines of , meaning 'jump'.
How Old English gave rise to is, however, uncertain, as the development does not involve a regular sound-change. Instead, it seems that there was a trend in Old English to coin nicknames for animals ending in -''g'', with examples—themselves all of uncertain etymology—including ''dog'', ''hog'', ''pig, stag'', and '. ''Frog'' appears to have been adapted from as part of this trend.
Meanwhile, the word ''toad'', first attested as Old English , is unique to English and is likewise of uncertain etymology. It is the basis for the word ''tadpole'', first attested as Middle English
Middle English (abbreviated to ME) is a form of the English language that was spoken after the Norman conquest of 1066, until the late 15th century. The English language underwent distinct variations and developments following the Old English ...
, apparently meaning 'toad-head'.
Taxonomy
About 88% ofamphibian
Amphibians are four-limbed and ectothermic vertebrates of the class Amphibia. All living amphibians belong to the group Lissamphibia. They inhabit a wide variety of habitats, with most species living within terrestrial, fossorial, arbor ...
species are classified in the order Anura. These include over 7,500 species in 55 families
Family (from la, familia) is a group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or affinity (by marriage or other relationship). The purpose of the family is to maintain the well-being of its members and of society. Ideal ...
, of which the Craugastoridae (850 spp.), Hylidae
Hylidae is a wide-ranging family of frogs commonly referred to as "tree frogs and their allies". However, the hylids include a diversity of frog species, many of which do not live in trees, but are terrestrial or semiaquatic.
Taxonomy and s ...
(724 spp.), Microhylidae
The Microhylidae, commonly known as narrow-mouthed frogs, are a geographically widespread family of frogs. The 683 species are in 63 genera and 11 subfamilies, which is the largest number of genera of any frog family.
Evolution
A molecular phylo ...
(688 spp.), and Bufonidae (621 spp.) are the richest in species.
 The Anura include all modern frogs and any
The Anura include all modern frogs and any fossil
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved ...
species that fit within the anuran definition. The characteristics of anuran adults include: 9 or fewer presacral vertebrae, the presence of a urostyle formed of fused vertebrae, no tail, a long and forward-sloping ilium, shorter fore limbs than hind limbs, radius
In classical geometry, a radius ( : radii) of a circle or sphere is any of the line segments from its center to its perimeter, and in more modern usage, it is also their length. The name comes from the latin ''radius'', meaning ray but also the ...
and ulna
The ulna (''pl''. ulnae or ulnas) is a long bone found in the forearm that stretches from the elbow to the smallest finger, and when in anatomical position, is found on the medial side of the forearm. That is, the ulna is on the same side of t ...
fused, tibia
The tibia (; ), also known as the shinbone or shankbone, is the larger, stronger, and anterior (frontal) of the two bones in the leg below the knee in vertebrates (the other being the fibula, behind and to the outside of the tibia); it connects ...
and fibula
The fibula or calf bone is a leg bone on the lateral side of the tibia, to which it is connected above and below. It is the smaller of the two bones and, in proportion to its length, the most slender of all the long bones. Its upper extremity ...
fused, elongated ankle bones, absence of a prefrontal bone, presence of a hyoid plate, a lower jaw
In anatomy, the mandible, lower jaw or jawbone is the largest, strongest and lowest bone in the human facial skeleton. It forms the lower jaw and holds the lower teeth in place. The mandible sits beneath the maxilla. It is the only movable bone ...
without teeth (with the exception of '' Gastrotheca guentheri'') consisting of three pairs of bones (angulosplenial, dentary, and mentomeckelian, with the last pair being absent in Pipoidea), an unsupported tongue, lymph
Lymph (from Latin, , meaning "water") is the fluid that flows through the lymphatic system, a system composed of lymph vessels (channels) and intervening lymph nodes whose function, like the venous system, is to return fluid from the tissues to ...
spaces underneath the skin, and a muscle, the protractor lentis, attached to the lens of the eye. The anuran larva or tadpole has a single central respiratory spiracle and mouthparts consisting of keratin
Keratin () is one of a family of structural fibrous proteins also known as ''scleroproteins''. Alpha-keratin (α-keratin) is a type of keratin found in vertebrates. It is the key structural material making up scales, hair, nails, feathers, hor ...
ous beaks and denticles.
 Frogs and toads are broadly classified into three suborders: Archaeobatrachia, which includes four families of primitive frogs; Mesobatrachia, which includes five families of more evolutionary intermediate frogs; and Neobatrachia, by far the largest group, which contains the remaining families of modern frogs, including most common species throughout the world. The suborder Neobatrachia is further divided into the two superfamilies Hyloidea and Ranoidea. This classification is based on such morphological features as the number of vertebrae, the structure of the pectoral girdle, and the morphology of tadpoles. While this classification is largely accepted, relationships among families of frogs are still debated.
Some species of anurans hybridize readily. For instance, the
Frogs and toads are broadly classified into three suborders: Archaeobatrachia, which includes four families of primitive frogs; Mesobatrachia, which includes five families of more evolutionary intermediate frogs; and Neobatrachia, by far the largest group, which contains the remaining families of modern frogs, including most common species throughout the world. The suborder Neobatrachia is further divided into the two superfamilies Hyloidea and Ranoidea. This classification is based on such morphological features as the number of vertebrae, the structure of the pectoral girdle, and the morphology of tadpoles. While this classification is largely accepted, relationships among families of frogs are still debated.
Some species of anurans hybridize readily. For instance, the edible frog
The edible frog (''Pelophylax'' kl. ''esculentus'') is a species of common European frog, also known as the common water frog or green frog (however, this latter term is also used for the North American species '' Rana clamitans'').
It is used ...
(''Pelophylax esculentus'') is a hybrid between the pool frog
The pool frog (''Pelophylax lessonae'') is a European frog in the family Ranidae. Its specific name was chosen by the Italian herpetologist Lorenzo Camerano in 1882, in order to honour his master Michele Lessona.
Description
The pool frog is ...
(''P. lessonae'') and the marsh frog
The marsh frog (''Pelophylax ridibundus'') is a species of water frog native to Europe and parts of western Asia.
Description
The marsh frog is the largest type of frog in most of its range, with males growing to a size around 100 mm (3.9 ...
(''P. ridibundus''). The fire-bellied toads ''Bombina bombina'' and '' B. variegata'' are similar in forming hybrids. These are less fertile than their parents, giving rise to a hybrid zone where the hybrids are prevalent.
Evolution
The origins and evolutionary relationships between the three main groups of amphibians are hotly debated. A molecular phylogeny based on rDNA analysis dating from 2005 suggests that salamanders andcaecilian
Caecilians (; ) are a group of limbless, vermiform or serpentine amphibians. They mostly live hidden in the ground and in stream substrates, making them the least familiar order of amphibians. Caecilians are mostly distributed in the tropics of ...
s are more closely related to each other than they are to frogs and the divergence
In vector calculus, divergence is a vector operator that operates on a vector field, producing a scalar field giving the quantity of the vector field's source at each point. More technically, the divergence represents the volume density of t ...
of the three groups took place in the Paleozoic
The Paleozoic (or Palaeozoic) Era is the earliest of three geologic eras of the Phanerozoic Eon.
The name ''Paleozoic'' ( ;) was coined by the British geologist Adam Sedgwick in 1838
by combining the Greek words ''palaiós'' (, "old") and ...
or early Mesozoic
The Mesozoic Era ( ), also called the Age of Reptiles, the Age of Conifers, and colloquially as the Age of the Dinosaurs is the second-to-last era of Earth's geological history, lasting from about , comprising the Triassic, Jurassic and Cretaceo ...
before the breakup of the supercontinent Pangaea and soon after their divergence from the lobe-finned fishes. This would help account for the relative scarcity of amphibian fossils from the period before the groups split. Another molecular phylogenetic analysis conducted about the same time concluded that lissamphibians first appeared about 330 million years ago and that the temnospondyl-origin hypothesis is more credible than other theories. The neobatrachians seemed to have originated in Africa/India, the salamanders in East Asia and the caecilians in tropical Pangaea. Other researchers, while agreeing with the main thrust of this study, questioned the choice of calibration points used to synchronise the data. They proposed that the date of lissamphibian diversification should be placed in the Permian
The Permian ( ) is a geologic period and stratigraphic system which spans 47 million years from the end of the Carboniferous Period million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Triassic Period 251.9 Mya. It is the last period of the Paleoz ...
, rather less than 300 million years ago, a date in better agreement with the palaeontological data. A further study in 2011 using both extinct and living taxa sampled for morphological, as well as molecular data, came to the conclusion that Lissamphibia is monophyletic
In cladistics for a group of organisms, monophyly is the condition of being a clade—that is, a group of taxa composed only of a common ancestor (or more precisely an ancestral population) and all of its lineal descendants. Monophyletic grou ...
and that it should be nested within Lepospondyli rather than within Temnospondyli. The study postulated that Lissamphibia originated no earlier than the late Carboniferous
The Carboniferous ( ) is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic that spans 60 million years from the end of the Devonian Period million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Permian Period, million years ago. The name ''Carbonif ...
, some 290 to 305 million years ago. The split between Anura and Caudata was estimated as taking place 292 million years ago, rather later than most molecular studies suggest, with the caecilians splitting off 239 million years ago.
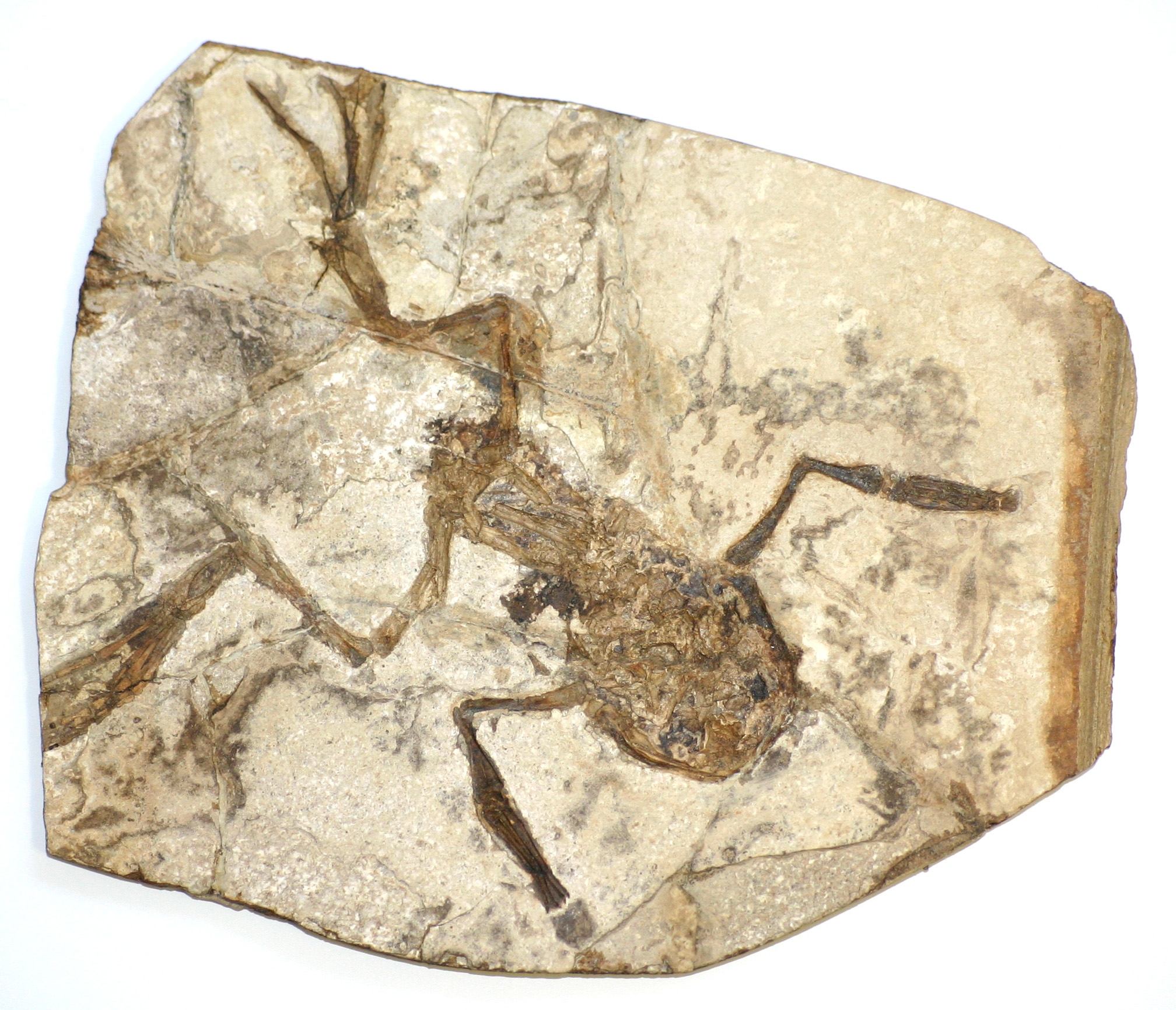
 In 2008, '' Gerobatrachus hottoni'', a
In 2008, '' Gerobatrachus hottoni'', a temnospondyl
Temnospondyli (from Greek τέμνειν, ''temnein'' 'to cut' and σπόνδυλος, ''spondylos'' 'vertebra') is a diverse order of small to giant tetrapods—often considered primitive amphibians—that flourished worldwide during the Carb ...
with many frog- and salamander-like characteristics, was discovered in Texas
Texas (, ; Spanish language, Spanish: ''Texas'', ''Tejas'') is a state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States. At 268,596 square miles (695,662 km2), and with more than 29.1 million residents in 2 ...
. It dated back 290 million years and was hailed as a missing link, a stem
Stem or STEM may refer to:
Plant structures
* Plant stem, a plant's aboveground axis, made of vascular tissue, off which leaves and flowers hang
* Stipe (botany), a stalk to support some other structure
* Stipe (mycology), the stem of a mushro ...
batrachian close to the common ancestor of frogs and salamanders, consistent with the widely accepted hypothesis that frogs and salamanders are more closely related to each other (forming a clade
A clade (), also known as a monophyletic group or natural group, is a group of organisms that are monophyletic – that is, composed of a common ancestor and all its lineal descendants – on a phylogenetic tree. Rather than the English term, ...
called Batrachia) than they are to caecilians. However, others have suggested that ''Gerobatrachus hottoni'' was only a dissorophoid temnospondyl unrelated to extant amphibians.
Salientia (Latin ''salire'' (''salio''), "to jump") is the name of the total group that includes modern frogs in the order Anura as well as their close fossil relatives, the "proto-frogs" or "stem-frogs". The common features possessed by these proto-frogs include 14 presacral vertebrae (modern frogs have eight or 9), a long and forward-sloping ilium in the pelvis
The pelvis (plural pelves or pelvises) is the lower part of the trunk, between the abdomen and the thighs (sometimes also called pelvic region), together with its embedded skeleton (sometimes also called bony pelvis, or pelvic skeleton).
The ...
, the presence of a frontoparietal bone, and a lower jaw
In anatomy, the mandible, lower jaw or jawbone is the largest, strongest and lowest bone in the human facial skeleton. It forms the lower jaw and holds the lower teeth in place. The mandible sits beneath the maxilla. It is the only movable bone ...
without teeth. The earliest known amphibians that were more closely related to frogs than to salamanders are '' Triadobatrachus massinoti'', from the early Triassic
The Triassic ( ) is a geologic period and system which spans 50.6 million years from the end of the Permian Period 251.902 million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Jurassic Period 201.36 Mya. The Triassic is the first and shortest period ...
period of Madagascar
Madagascar (; mg, Madagasikara, ), officially the Republic of Madagascar ( mg, Repoblikan'i Madagasikara, links=no, ; french: République de Madagascar), is an island country in the Indian Ocean, approximately off the coast of East Afric ...
(about 250 million years ago), and '' Czatkobatrachus polonicus'', from the Early Triassic of Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populou ...
(about the same age as ''Triadobatrachus''). The skull of ''Triadobatrachus'' is frog-like, being broad with large eye sockets, but the fossil has features diverging from modern frogs. These include a longer body with more vertebrae. The tail has separate vertebrae unlike the fused urostyle or coccyx in modern frogs. The tibia and fibula bones are also separate, making it probable that ''Triadobatrachus'' was not an efficient leaper.
The earliest known "true frogs" that fall into the anuran lineage proper all lived in the early Jurassic period. One such early frog species, '' Prosalirus bitis'', was discovered in 1995
File:1995 Events Collage V2.png, From left, clockwise: O.J. Simpson is acquitted of the murders of Nicole Brown Simpson and Ronald Goldman from the year prior in "The Trial of the Century" in the United States; The Great Hanshin earthquake stri ...
in the Kayenta Formation of Arizona
Arizona ( ; nv, Hoozdo Hahoodzo ; ood, Alĭ ṣonak ) is a state in the Southwestern United States. It is the 6th largest and the 14th most populous of the 50 states. Its capital and largest city is Phoenix. Arizona is part of the Fo ...
and dates back to the Early Jurassic epoch (199.6 to 175 million years ago), making ''Prosalirus'' somewhat more recent than ''Triadobatrachus''. Like the latter, ''Prosalirus'' did not have greatly enlarged legs, but had the typical three-pronged pelvic
The pelvis (plural pelves or pelvises) is the lower part of the trunk, between the abdomen and the thighs (sometimes also called pelvic region), together with its embedded skeleton (sometimes also called bony pelvis, or pelvic skeleton).
The ...
structure of modern frogs. Unlike ''Triadobatrachus'', ''Prosalirus'' had already lost nearly all of its tail and was well adapted for jumping. Another Early Jurassic frog is '' Vieraella herbsti'', which is known only from dorsal and ventral impressions of a single animal and was estimated to be from snout to vent. '' Notobatrachus degiustoi'' from the middle Jurassic is slightly younger, about 155–170 million years old. The main evolutionary changes in this species involved the shortening of the body and the loss of the tail. The evolution of modern Anura likely was complete by the Jurassic period. Since then, evolutionary changes in chromosome numbers have taken place about 20 times faster in mammals than in frogs, which means speciation is occurring more rapidly in mammals.
According to genetic studies, the families Hyloidea, Microhylidae
The Microhylidae, commonly known as narrow-mouthed frogs, are a geographically widespread family of frogs. The 683 species are in 63 genera and 11 subfamilies, which is the largest number of genera of any frog family.
Evolution
A molecular phylo ...
, and the clade Natatanura (comprising about 88% of living frogs) diversified simultaneously some 66 million years ago, soon after the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event
The Cretaceous–Paleogene (K–Pg) extinction event (also known as the Cretaceous–Tertiary extinction) was a sudden mass extinction of three-quarters of the plant and animal species on Earth, approximately 66 million years ago. With th ...
associated with the Chicxulub impactor
The Chicxulub crater () is an impact crater buried underneath the Yucatán Peninsula in Mexico. Its center is offshore near the community of Chicxulub, after which it is named. It was formed slightly over 66 million years ago when a large as ...
. All origins of arboreality (e.g. in Hyloidea and Natatanura) follow from that time and the resurgence of forest that occurred afterwards.
Frog fossils have been found on all of the earth's continents. In 2020, it was announced that 40 million year old helmeted frog fossils had been discovered by a team of vertebrate paleontologists in Seymour Island
Seymour Island or Marambio Island, is an island in the chain of 16 major islands around the tip of the Graham Land on the Antarctic Peninsula. Graham Land is the closest part of Antarctica to South America. It lies within the section of the isl ...
on the Antarctic Peninsula, indicating that this region was once home to frogs related to those now living in South American ''Nothofagus'' forest.
Phylogeny
A cladogram showing the relationships of the differentfamilies
Family (from la, familia) is a group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or affinity (by marriage or other relationship). The purpose of the family is to maintain the well-being of its members and of society. Ideal ...
of frogs in the clade Anura can be seen in the table below. This diagram, in the form of a tree
In botany, a tree is a perennial plant with an elongated stem, or trunk, usually supporting branches and leaves. In some usages, the definition of a tree may be narrower, including only woody plants with secondary growth, plants that ar ...
, shows how each frog family is related to other families, with each node representing a point of common ancestry. It is based on Frost ''et al.'' (2006), Heinicke ''et al.'' (2009) and Pyron and Wiens (2011).
Morphology and physiology
 Frogs have no tail, except as larvae, and most have long hind legs, elongated ankle bones, webbed toes, no claws, large eyes, and a smooth or warty skin. They have short vertebral columns, with no more than 10 free vertebrae and fused tailbones (urostyle or coccyx). Frogs range in size from ''
Frogs have no tail, except as larvae, and most have long hind legs, elongated ankle bones, webbed toes, no claws, large eyes, and a smooth or warty skin. They have short vertebral columns, with no more than 10 free vertebrae and fused tailbones (urostyle or coccyx). Frogs range in size from ''Paedophryne amauensis
''Paedophryne amauensis'' is a species of microhylid frog endemic to eastern Papua New Guinea. At in snout-to-vent length, it is considered the world's smallest known vertebrate. (See also Ecological guild.)
The species was listed in the '' ...
'' of Papua New Guinea
Papua New Guinea (abbreviated PNG; , ; tpi, Papua Niugini; ho, Papua Niu Gini), officially the Independent State of Papua New Guinea ( tpi, Independen Stet bilong Papua Niugini; ho, Independen Stet bilong Papua Niu Gini), is a country i ...
that is in snout–to– vent length to the up to and goliath frog (''Conraua goliath'') of central Africa. There are prehistoric, extinct species that reached even larger sizes.
Feet and legs
The structure of the feet and legs varies greatly among frog species, depending in part on whether they live primarily on the ground, in water, in trees, or in burrows. Frogs must be able to move quickly through their environment to catch prey and escape predators, and numerous adaptations help them to do so. Most frogs are either proficient at jumping or are descended from ancestors that were, with much of themusculoskeletal
The human musculoskeletal system (also known as the human locomotor system, and previously the activity system) is an organ system that gives humans the ability to move using their muscular and skeletal systems. The musculoskeletal system provi ...
morphology modified for this purpose. The tibia, fibula, and tarsals have been fused into a single, strong bone
A bone is a rigid organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells, store minerals, provide structure and support for the body, an ...
, as have the radius and ulna in the fore limbs (which must absorb the impact on landing). The metatarsals
The metatarsal bones, or metatarsus, are a group of five long bones in the foot, located between the tarsal bones of the hind- and mid-foot and the phalanges of the toes. Lacking individual names, the metatarsal bones are numbered from the me ...
have become elongated to add to the leg length and allow frogs to push against the ground for a longer period on take-off. The ilium has elongated and formed a mobile joint with the sacrum
The sacrum (plural: ''sacra'' or ''sacrums''), in human anatomy, is a large, triangular bone at the base of the spine that forms by the fusing of the sacral vertebrae (S1S5) between ages 18 and 30.
The sacrum situates at the upper, back part ...
which, in specialist jumpers such as ranids and hylids, functions as an additional limb joint to further power the leaps. The tail vertebrae have fused into a urostyle which is retracted inside the pelvis. This enables the force to be transferred from the legs to the body during a leap.

 The muscular system has been similarly modified. The hind limbs of ancestral frogs presumably contained pairs of muscles which would act in opposition (one muscle to flex the knee, a different muscle to extend it), as is seen in most other limbed animals. However, in modern frogs, almost all muscles have been modified to contribute to the action of jumping, with only a few small muscles remaining to bring the limb back to the starting position and maintain posture. The muscles have also been greatly enlarged, with the main leg muscles accounting for over 17% of the total mass of frogs.
Many frogs have webbed feet and the degree of webbing is directly proportional to the amount of time the species spends in the water. The completely aquatic
The muscular system has been similarly modified. The hind limbs of ancestral frogs presumably contained pairs of muscles which would act in opposition (one muscle to flex the knee, a different muscle to extend it), as is seen in most other limbed animals. However, in modern frogs, almost all muscles have been modified to contribute to the action of jumping, with only a few small muscles remaining to bring the limb back to the starting position and maintain posture. The muscles have also been greatly enlarged, with the main leg muscles accounting for over 17% of the total mass of frogs.
Many frogs have webbed feet and the degree of webbing is directly proportional to the amount of time the species spends in the water. The completely aquatic African dwarf frog
The African dwarf frog is a genus of aquatic frog native to parts of Equatorial Africa. It is common in the pet trade and is often mistaken for the African clawed frog, a similar-looking frog in the same family. African dwarf frogs (''Hymenochir ...
(''Hymenochirus'' sp.) has fully webbed toes, whereas those of White's tree frog (''Litoria caerulea''), an arboreal species, are only a quarter or half webbed. Exceptions include flying frog
A flying frog (also called a gliding frog) is a frog that has the ability to achieve gliding flight. This means it can descend at an angle less than 45° relative to the horizontal. Other nonflying arboreal frogs can also descend, but only at angle ...
s in the Hylidae
Hylidae is a wide-ranging family of frogs commonly referred to as "tree frogs and their allies". However, the hylids include a diversity of frog species, many of which do not live in trees, but are terrestrial or semiaquatic.
Taxonomy and s ...
and Rhacophoridae
The Rhacophoridae are a family of frogs that occur in tropical sub-Saharan Africa, South India and Sri Lanka, Japan, northeastern India to eastern China and Taiwan, south through the Philippines and Greater Sundas, and Sulawesi. They are commonly ...
, which also have fully webbed toes used in gliding.
Arboreal frogs have pads located on the ends of their toes to help grip vertical surfaces. These are not suction pads, the surface consisting instead of columnar cells with flat tops with small gaps between them lubricated by mucous glands. When the frog applies pressure, the cells adhere to irregularities on the surface and the grip is maintained through surface tension
Surface tension is the tendency of liquid surfaces at rest to shrink into the minimum surface area possible. Surface tension is what allows objects with a higher density than water such as razor blades and insects (e.g. water striders) to ...
. This allows the frog to climb on smooth surfaces, but the system does not function efficiently when the pads are excessively wet.
In many arboreal frogs, a small "intercalary structure" on each toe increases the surface area touching the substrate. Furthermore, many arboreal frogs have hip joints that allow both hopping and walking. Some frogs that live high in trees even possess an elaborate degree of webbing between their toes. This allows the frogs to "parachute" or make a controlled glide from one position in the canopy to another.
Ground-dwelling frogs generally lack the adaptations of aquatic and arboreal frogs. Most have smaller toe pads, if any, and little webbing. Some burrowing frogs such as Couch's spadefoot (''Scaphiopus couchii'') have a flap-like toe extension on the hind feet, a keratin
Keratin () is one of a family of structural fibrous proteins also known as ''scleroproteins''. Alpha-keratin (α-keratin) is a type of keratin found in vertebrates. It is the key structural material making up scales, hair, nails, feathers, hor ...
ised tubercle
In anatomy, a tubercle (literally 'small tuber', Latin for 'lump') is any round nodule, small eminence, or warty outgrowth found on external or internal organs of a plant or an animal.
In plants
A tubercle is generally a wart-like projectio ...
often referred to as a spade, that helps them to burrow.
Sometimes during the tadpole stage, one of the developing rear legs is eaten by a predator such as a dragonfly nymph. In some cases, the full leg still grows, but in others it does not, although the frog may still live out its normal lifespan with only three limbs. Occasionally, a parasitic flatworm (''Ribeiroia ondatrae
''Ribeiroia ondatrae'', or the frog-mutating flatworm is a parasite in the genus ''Ribeiroia'' which is believed to be responsible for many of the recent increases in amphibian limb malformations, particularly missing, malformed, and additiona ...
'') digs into the rear of a tadpole, causing a rearrangement of the limb bud cells and the frog develops one or more extra legs.

Skin
A frog's skin is protective, has a respiratory function, can absorb water, and helps control body temperature. It has many glands, particularly on the head and back, which often exude distasteful and toxic substances ( granular glands). The secretion is often sticky and helps keep the skin moist, protects against the entry of moulds and bacteria, and make the animal slippery and more able to escape from predators. The skin is shed every few weeks. It usually splits down the middle of the back and across the belly, and the frog pulls its arms and legs free. The sloughed skin is then worked towards the head where it is quickly eaten. Being cold-blooded, frogs have to adopt suitable behaviour patterns to regulate their temperature. To warm up, they can move into the sun or onto a warm surface; if they overheat, they can move into the shade or adopt a stance that exposes the minimum area of skin to the air. This posture is also used to prevent water loss and involves the frog squatting close to the substrate with its hands and feet tucked under its chin and body. The colour of a frog's skin is used for thermoregulation. In cool damp conditions, the colour will be darker than on a hot dry day. The grey foam-nest tree frog (''Chiromantis xerampelina'') is even able to turn white to minimize the chance of overheating. Many frogs are able to absorb water and oxygen directly through the skin, especially around the pelvic area, but the permeability of a frog's skin can also result in water loss. Glands located all over the body exude mucus which helps keep the skin moist and reduces evaporation. Some glands on the hands and chest of males are specialized to produce sticky secretions to aid inamplexus
Amplexus (Latin "embrace") is a type of mating behavior exhibited by some externally fertilizing species (chiefly amphibians and horseshoe crabs) in which a male grasps a female with his front legs as part of the mating process, and at the same ...
. Similar glands in tree frogs produce a glue-like substance on the adhesive discs of the feet. Some arboreal frogs reduce water loss by having a waterproof layer of skin, and several South American species coat their skin with a waxy secretion. Other frogs have adopted behaviours to conserve water, including becoming nocturnal and resting in a water-conserving position. Some frogs may also rest in large groups with each frog pressed against its neighbours. This reduces the amount of skin exposed to the air or a dry surface, and thus reduces water loss. Woodhouse's toad (''Bufo woodhousii''), if given access to water after confinement in a dry location, sits in the shallows to rehydrate. The male hairy frog (''Trichobatrachus robustus'') has dermal papillae
The dermis or corium is a layer of skin between the epidermis (with which it makes up the cutis) and subcutaneous tissues, that primarily consists of dense irregular connective tissue and cushions the body from stress and strain. It is divided in ...
projecting from its lower back and thighs, giving it a bristly appearance. They contain blood vessels and are thought to increase the area of the skin available for respiration.
Some species have bony plates embedded in their skin, a trait that appears to have evolved independently several times. In certain other species, the skin at the top of the head is compacted and the connective tissue of the dermis is co-ossified with the bones of the skull ( exostosis).
Camouflage
Camouflage is the use of any combination of materials, coloration, or illumination for concealment, either by making animals or objects hard to see, or by disguising them as something else. Examples include the leopard's spotted coat, the b ...
is a common defensive mechanism in frogs. Features such as warts and skin fold
Skin folds or skinfolds are areas of skin that are naturally folded. Many skin folds are distinct, heritable anatomical features, and may be used for identification of animal species, while others are non-specific and may be produced either by ind ...
s are usually on ground-dwelling frogs, for whom smooth skin would not provide such effective camouflage. Certain frogs change colour between night and day, as light and moisture stimulate the pigment cells and cause them to expand or contract. Some are even able to control their skin texture. The Pacific tree frog
The Pacific tree frog (''Pseudacris regilla''), also known as the Pacific chorus frog, has a range spanning the Pacific Northwest, from Northern California, Oregon, and Washington to British Columbia in Canada and extreme southern Alaska. They l ...
(''Pseudacris regilla'') has green and brown morphs, plain or spotted, and changes colour depending on the time of year and general background colour.
disruptive coloration
Disruptive coloration (also known as disruptive camouflage or disruptive patterning) is a form of camouflage that works by breaking up the outlines of an animal, soldier or military vehicle with a strongly contrasting pattern. It is often comb ...
including black eye markings similar to voids between leaves, bands of the dorsal skin (dorsolateral dermal plica) similar to a leaf midrib
This glossary of botanical terms is a list of definitions of terms and concepts relevant to botany and plants in general. Terms of plant morphology are included here as well as at the more specific Glossary of plant morphology and Glossary ...
as well as stains, spots & leg stripes similar to fallen leaf features.
File:Hip-pocket Frog - Assa darlingtoni.jpg, alt=Frog barely recognisable against brown decaying leaf litter., Pouched frog (''Assa darlingtoni'') camouflaged against leaf litter.
Respiration and circulation
Like other amphibians,oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as ...
can pass through their highly permeable skins. This unique feature allows them to remain in places without access to the air, respiring through their skins. Ribs are generally absent, so the lungs are filled by buccal pumping
Buccal pumping is "breathing with one's cheeks": a method of ventilation used in respiration in which the animal moves the floor of its mouth in a rhythmic manner that is externally apparent.Brainerd, E. L. (1999). New perspectives on the evolution ...
and a frog deprived of its lungs can maintain its body functions without them. The fully aquatic Bornean flat-headed frog (''Barbourula kalimantanensis'') is the first frog known to lack lungs entirely.
Frogs have three-chambered heart
The heart is a muscular organ in most animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the body, while carrying metabolic waste such as carbon dioxide to ...
s, a feature they share with lizard
Lizards are a widespread group of Squamata, squamate reptiles, with over 7,000 species, ranging across all continents except Antarctica, as well as most oceanic island chains. The group is paraphyletic since it excludes the snakes and Amphisbae ...
s. Oxygenated blood from the lungs and de-oxygenated blood from the respiring tissues enter the heart through separate atria. When these chambers contract, the two blood streams pass into a common ventricle before being pumped via a spiral valve to the appropriate vessel, the aorta
The aorta ( ) is the main and largest artery in the human body, originating from the left ventricle of the heart and extending down to the abdomen, where it splits into two smaller arteries (the common iliac arteries). The aorta distributes ...
for oxygenated blood and pulmonary artery for deoxygenated blood.
Some species of frog have adaptations that allow them to survive in oxygen deficient water. The Titicaca water frog (''Telmatobius culeus'') is one such species and has wrinkly skin that increases its surface area to enhance gas exchange. It normally makes no use of its rudimentary lungs but will sometimes raise and lower its body rhythmically while on the lake bed to increase the flow of water around it.
Digestion and excretion
Frogs have maxillary teeth along their upper jaw which are used to hold food before it is swallowed. These teeth are very weak, and cannot be used to chew or catch and harm agile prey. Instead, the frog uses its sticky, cleft tongue to catch flies and other small moving prey. The tongue normally lies coiled in the mouth, free at the back and attached to the mandible at the front. It can be shot out and retracted at great speed. Some frogs have no tongue and just stuff food into their mouths with their hands. The African bullfrog ('' Pyxicephalus''), which preys on relatively large animals such as mice and other frogs, has cone shaped bony projections called odontoid processes at the front of the lower jaw which function like teeth. The eyes assist in the swallowing of food as they can be retracted through holes in the skull and help push food down the throat. The food then moves through the oesophagus into the stomach where digestive enzymes are added and it is churned up. It then proceeds to the small intestine (duodenum and ileum) where most digestion occurs. Pancreatic juice from the pancreas, and bile, produced by the liver and stored in the gallbladder, are secreted into the small intestine, where the fluids digest the food and the nutrients are absorbed. The food residue passes into the large intestine where excess water is removed and the wastes are passed out through thecloaca
In animal anatomy, a cloaca ( ), plural cloacae ( or ), is the posterior orifice that serves as the only opening for the digestive, reproductive, and urinary tracts (if present) of many vertebrate animals. All amphibians, reptiles and birds, a ...
.
Although adapted to terrestrial life, frogs resemble freshwater fish in their inability to conserve body water effectively. When they are on land, much water is lost by evaporation from the skin. The excretory system is similar to that of mammals and there are two kidney
The kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped organs found in vertebrates. They are located on the left and right in the retroperitoneal space, and in adult humans are about in length. They receive blood from the paired renal arteries; blo ...
s that remove nitrogenous products from the blood. Frogs produce large quantities of dilute urine in order to flush out toxic products from the kidney tubules. The nitrogen is excreted as ammonia
Ammonia is an inorganic compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula . A stable binary hydride, and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a distinct pungent smell. Biologically, it is a common nitrogenous w ...
by tadpoles and aquatic frogs but mainly as urea
Urea, also known as carbamide, is an organic compound with chemical formula . This amide has two amino groups (–) joined by a carbonyl functional group (–C(=O)–). It is thus the simplest amide of carbamic acid.
Urea serves an important ...
, a less toxic product, by most terrestrial adults. A few species of tree frog with little access to water excrete the even less toxic uric acid
Uric acid is a heterocyclic compound of carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, and hydrogen with the formula C5H4N4O3. It forms ions and salts known as urates and acid urates, such as ammonium acid urate. Uric acid is a product of the metabolic breakdown o ...
. The urine passes along paired ureters to the urinary bladder
The urinary bladder, or simply bladder, is a hollow organ in humans and other vertebrates that stores urine from the kidneys before disposal by urination. In humans the bladder is a distensible organ that sits on the pelvic floor. Urine enters ...
from which it is vented periodically into the cloaca. All bodily wastes exit the body through the cloaca which terminates in a cloacal vent.
Reproductive system
In the male frog, the two testes are attached to the kidneys andsemen
Semen, also known as seminal fluid, is an organic bodily fluid created to contain spermatozoa. It is secreted by the gonads (sexual glands) and other sexual organs of male or hermaphroditic animals and can fertilize the female ovum. Semen i ...
passes into the kidneys through fine tubes called efferent ducts
The efferent ducts (or efferent ductules or ductuli efferentes or ductus efferentes or vasa efferentia) connect the rete testis with the initial section of the epididymis.Hess 2018
There are two basic designs for efferent ductule structure:
* a ...
. It then travels on through the ureters, which are consequently known as urinogenital ducts. There is no penis, and sperm is ejected from the cloaca directly onto the eggs as the female lays them. The ovaries of the female frog are beside the kidneys and the eggs pass down a pair of oviducts and through the cloaca to the exterior.
When frogs mate, the male climbs on the back of the female and wraps his fore limbs round her body, either behind the front legs or just in front of the hind legs. This position is called amplexus
Amplexus (Latin "embrace") is a type of mating behavior exhibited by some externally fertilizing species (chiefly amphibians and horseshoe crabs) in which a male grasps a female with his front legs as part of the mating process, and at the same ...
and may be held for several days. The male frog has certain hormone-dependent secondary sexual characteristics. These include the development of special pads on his thumbs in the breeding season, to give him a firm hold. The grip of the male frog during amplexus stimulates the female to release eggs, usually wrapped in jelly, as spawn. In many species the male is smaller and slimmer than the female. Males have vocal cords and make a range of croaks, particularly in the breeding season, and in some species they also have vocal sac
The vocal sac is the flexible membrane of skin possessed by most male frogs and toads. The purpose of the vocal sac is usually as an amplification of their mating or advertisement call. The presence or development of the vocal sac is one way o ...
s to amplify the sound.
Nervous system
Frogs have a highly developed nervous system that consists of a brain, spinal cord and nerves. Many parts of frog brains correspond with those of humans. It consists of two olfactory lobes, two cerebral hemispheres, a pineal body, two optic lobes, a cerebellum and a medulla oblongata. Muscular coordination and posture are controlled by thecerebellum
The cerebellum (Latin for "little brain") is a major feature of the hindbrain of all vertebrates. Although usually smaller than the cerebrum, in some animals such as the mormyrid fishes it may be as large as or even larger. In humans, the cer ...
, and the medulla oblongata
The medulla oblongata or simply medulla is a long stem-like structure which makes up the lower part of the brainstem. It is anterior and partially inferior to the cerebellum. It is a cone-shaped neuronal mass responsible for autonomic (involun ...
regulates respiration, digestion and other automatic functions. The relative size of the cerebrum
The cerebrum, telencephalon or endbrain is the largest part of the brain containing the cerebral cortex (of the two cerebral hemispheres), as well as several subcortical structures, including the hippocampus, basal ganglia, and olfactory bulb. In ...
in frogs is much smaller than it is in humans. Frogs have ten pairs of cranial nerves
Cranial nerves are the nerves that emerge directly from the brain (including the brainstem), of which there are conventionally considered twelve pairs. Cranial nerves relay information between the brain and parts of the body, primarily to and f ...
which pass information from the outside directly to the brain, and ten pairs of spinal nerves
A spinal nerve is a mixed nerve, which carries motor, sensory, and autonomic signals between the spinal cord and the body. In the human body there are 31 pairs of spinal nerves, one on each side of the vertebral column. These are grouped into the ...
which pass information from the extremities to the brain through the spinal cord. By contrast, all amniotes
Amniotes are a clade of tetrapod vertebrates that comprises sauropsids (including all reptiles and birds, and extinct parareptiles and non-avian dinosaurs) and synapsids (including pelycosaurs and therapsids such as mammals). They are dist ...
(mammals, birds and reptiles) have twelve pairs of cranial nerves.

Sight
The eyes of most frogs are located on either side of the head near the top and project outwards as hemispherical bulges. They providebinocular vision
In biology, binocular vision is a type of vision in which an animal has two eyes capable of facing the same direction to perceive a single three-dimensional image of its surroundings. Binocular vision does not typically refer to vision where an ...
over a field of 100° to the front and a total visual field of almost 360°. They may be the only part of an otherwise submerged frog to protrude from the water. Each eye has closable upper and lower lids and a nictitating membrane which provides further protection, especially when the frog is swimming. Members of the aquatic family Pipidae have the eyes located at the top of the head, a position better suited for detecting prey in the water above. The iris
Iris most often refers to:
*Iris (anatomy), part of the eye
*Iris (mythology), a Greek goddess
* ''Iris'' (plant), a genus of flowering plants
* Iris (color), an ambiguous color term
Iris or IRIS may also refer to:
Arts and media
Fictional ent ...
es come in a range of colours and the pupils in a range of shapes. The common toad
The common toad, European toad, or in Anglophone parts of Europe, simply the toad (''Bufo bufo'', from Latin ''bufo'' "toad"), is a frog found throughout most of Europe (with the exception of Ireland, Iceland, and some Mediterranean islands), in ...
(''Bufo bufo'') has golden irises and horizontal slit-like pupils, the red-eyed tree frog (''Agalychnis callidryas'') has vertical slit pupils, the poison dart frog
Poison dart frog (also known as dart-poison frog, poison frog or formerly known as poison arrow frog) is the common name of a group of frogs in the family Dendrobatidae which are native to tropical Central and South America. These species are ...
has dark irises, the fire-bellied toad
fire-bellied toads are a group of six species of small frogs (most species typically no longer than ) belonging to the genus ''Bombina''.
The name "fire-bellied" is derived from the brightly colored red- or yellow-and-black patterns on the toa ...
(''Bombina spp.'') has triangular pupils and the tomato frog (''Dyscophus spp.'') has circular ones. The irises of the southern toad (''Anaxyrus terrestris'') are patterned so as to blend in with the surrounding camouflaged skin.
The distant vision of a frog is better than its near vision. Calling frogs will quickly become silent when they see an intruder or even a moving shadow but the closer an object is, the less well it is seen. When a frog shoots out its tongue to catch an insect it is reacting to a small moving object that it cannot see well and must line it up precisely beforehand because it shuts its eyes as the tongue is extended. Although it was formerly debated, more recent research has shown that frogs can see in colour, even in very low light.
Hearing
Frogs can hear both in the air and below water. They do not have external ears; the eardrums ( tympanic membranes) are directly exposed or may be covered by a layer of skin and are visible as a circular area just behind the eye. The size and distance apart of the eardrums is related to the frequency and wavelength at which the frog calls. In some species such as the bullfrog, the size of the tympanum indicates the sex of the frog; males have tympani that are larger than their eyes while in females, the eyes and tympani are much the same size. A noise causes the tympanum to vibrate and the sound is transmitted to the middle and inner ear. The middle ear contains semicircular canals which help control balance and orientation. In the inner ear, the auditory hair cells are arranged in two areas of the cochlea, the basilar papilla and the amphibian papilla. The former detects high frequencies and the latter low frequencies. Because the cochlea is short, frogs use electrical tuning to extend their range of audible frequencies and help discriminate different sounds. This arrangement enables detection of the territorial and breeding calls of their conspecifics. In some species that inhabit arid regions, the sound of thunder or heavy rain may arouse them from a dormant state. A frog may be startled by an unexpected noise but it will not usually take any action until it has located the source of the sound by sight.Call
 The call or croak of a frog is unique to its species. Frogs create this sound by passing air through the
The call or croak of a frog is unique to its species. Frogs create this sound by passing air through the larynx
The larynx (), commonly called the voice box, is an organ in the top of the neck involved in breathing, producing sound and protecting the trachea against food aspiration. The opening of larynx into pharynx known as the laryngeal inlet is abo ...
in the throat. In most calling frogs, the sound is amplified by one or more vocal sacs, membranes of skin under the throat or on the corner of the mouth, that distend during the amplification of the call. Some frog calls are so loud that they can be heard up to a mile (1.6km) away. Additionally, some species have been found to use man-made structures such as drain pipes for artificial amplification of their call. The coastal tailed frog (''Ascaphus truei'') lives in mountain streams in North America and does not vocalize.
The main function of calling is for male frogs to attract mates. Males may call individually or there may be a chorus of sound where numerous males have converged on breeding sites. In many frog species, such as the common tree frog (''Polypedates leucomystax''), females reply to males' calls, which acts to reinforce reproductive activity in a breeding colony. Female frogs prefer males that produce sounds of greater intensity and lower frequency, attributes that stand out in a crowd. The rationale for this is thought to be that by demonstrating his prowess, the male shows his fitness to produce superior offspring.
A different call is emitted by a male frog or unreceptive female when mounted by another male. This is a distinct chirruping sound and is accompanied by a vibration of the body. Tree frogs and some non-aquatic species have a rain call that they make on the basis of humidity cues prior to a shower. Many species also have a territorial call that is used to drive away other males. All of these calls are emitted with the mouth of the frog closed. A distress call, emitted by some frogs when they are in danger, is produced with the mouth open resulting in a higher-pitched call. It is typically used when the frog has been grabbed by a predator and may serve to distract or disorient the attacker so that it releases the frog.
left, Distinctive low "jug-o-rum" sound of banded bullfrog.
Many species of frog have deep calls. The croak of the American bullfrog
The American bullfrog (''Lithobates catesbeianus''), often simply known as the bullfrog in Canada and the United States, is a large true frog native to eastern North America. It typically inhabits large permanent water bodies such as swamps, p ...
(''Rana catesbiana'') is sometimes written as "jug o' rum". The Pacific tree frog
The Pacific tree frog (''Pseudacris regilla''), also known as the Pacific chorus frog, has a range spanning the Pacific Northwest, from Northern California, Oregon, and Washington to British Columbia in Canada and extreme southern Alaska. They l ...
(''Pseudacris regilla'') produces the onomatopoeic
Onomatopoeia is the process of creating a word that phonetically imitates, resembles, or suggests the sound that it describes. Such a word itself is also called an onomatopoeia. Common onomatopoeias include animal noises such as ''oink'', '' ...
"ribbit" often heard in films. Other renderings of frog calls into speech include "brekekekex koax koax", the call of the marsh frog ('' Pelophylax ridibundus'') in ''The Frogs'', an Ancient Greek comic drama by Aristophanes
Aristophanes (; grc, Ἀριστοφάνης, ; c. 446 – c. 386 BC), son of Philippus, of the deme Kydathenaion ( la, Cydathenaeum), was a comic playwright or comedy-writer of ancient Athens and a poet of Old Attic Comedy. Eleven of his ...
. The calls of the Concave-eared torrent frog
''Odorrana tormota'', also known as the concave-eared torrent frog, is a species of frog native to China. Its distribution is restricted to Huangshan Mountains in Anhui and Jiande and Anji counties in northern Zhejiang. It occurs in fast-flowi ...
(''Amolops tormotus'') are unusual in many aspects. The males are notable for their varieties of calls where upward and downward frequency modulations take place. When they communicate, they produce calls that fall in the ultrasound
Ultrasound is sound waves with frequencies higher than the upper audible limit of human hearing. Ultrasound is not different from "normal" (audible) sound in its physical properties, except that humans cannot hear it. This limit varies ...
frequency range. The last aspect that makes this species of frog's calls unusual is that nonlinear acoustic phenomena are important components in their acoustic signals.
Torpor
During extreme conditions, some frogs enter a state of torpor and remain inactive for months. In colder regions, many species of froghibernate
Hibernation is a state of minimal activity and metabolic depression undergone by some animal species. Hibernation is a seasonal heterothermy characterized by low body-temperature, slow breathing and heart-rate, and low metabolic rate. It mos ...
in winter. Those that live on land such as the American toad (''Bufo americanus'') dig a burrow and make a hibernaculum in which to lie dormant. Others, less proficient at digging, find a crevice or bury themselves in dead leaves. Aquatic species such as the American bullfrog
The American bullfrog (''Lithobates catesbeianus''), often simply known as the bullfrog in Canada and the United States, is a large true frog native to eastern North America. It typically inhabits large permanent water bodies such as swamps, p ...
(''Rana catesbeiana'') normally sink to the bottom of the pond where they lie, semi-immersed in mud but still able to access the oxygen dissolved in the water. Their metabolism slows down and they live on their energy reserves. Some frogs such as the wood frog, moor frog, or spring peeper can even survive being frozen. Ice crystals form under the skin and in the body cavity but the essential organs are protected from freezing by a high concentration of glucose. An apparently lifeless, frozen frog can resume respiration and its heartbeat can restart when conditions warm up.
At the other extreme, the striped burrowing frog (''Cyclorana alboguttata'') regularly aestivates during the hot, dry season in Australia, surviving in a dormant state without access to food and water for nine or ten months of the year. It burrows underground and curls up inside a protective cocoon formed by its shed skin. Researchers at the University of Queensland
, mottoeng = By means of knowledge and hard work
, established =
, endowment = A$224.3 million
, budget = A$2.1 billion
, type = Public research university
, chancellor = Peter Varghese
, vice_chancellor = Deborah Terry
, city = B ...
have found that during aestivation, the metabolism
Metabolism (, from el, μεταβολή ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run ...
of the frog is altered and the operational efficiency of the mitochondria
A mitochondrion (; ) is an organelle found in the cells of most Eukaryotes, such as animals, plants and fungi. Mitochondria have a double membrane structure and use aerobic respiration to generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is u ...
is increased. This means that the limited amount of energy available to the comatose frog is used in a more efficient manner. This survival mechanism is only useful to animals that remain completely unconscious for an extended period of time and whose energy requirements are low because they are cold-blooded and have no need to generate heat. Other research showed that, to provide these energy requirements, muscles atrophy, but hind limb muscles are preferentially unaffected. Frogs have been found to have upper critical temperatures of around 41 degrees Celsius.
Locomotion
Different species of frog use a number of methods of moving around including jumping, running, walking, aquatic locomotion, swimming, burrowing, climbing and Flying frog, gliding. ;Jumping
Frogs are generally recognized as exceptional jumpers and, relative to their size, the best jumpers of all vertebrates. The striped rocket frog, ''Litoria nasuta'', can leap over , a distance that is more than fifty times its body length of . There are tremendous differences between species in jumping capability. Within a species, jump distance increases with increasing size, but relative jumping distance (body-lengths jumped) decreases. The Euphlyctis cyanophlyctis, Indian skipper frog (''Euphlyctis cyanophlyctis'') has the ability to leap out of the water from a position floating on the surface. The tiny northern cricket frog (''Acris crepitans'') can "skitter" across the surface of a pond with a series of short rapid jumps.
Slow-motion photography shows that the muscles have passive flexibility. They are first stretched while the frog is still in the crouched position, then they are contracted before being stretched again to launch the frog into the air. The fore legs are folded against the chest and the hind legs remain in the extended, streamlined position for the duration of the jump. In some extremely capable jumpers, such as the Cuban tree frog (''Osteopilus septentrionalis'') and the northern leopard frog (''Rana pipiens''), the peak power exerted during a jump can exceed that which the muscle is theoretically capable of producing. When the muscles contract, the energy is first transferred into the stretched tendon which is wrapped around the ankle bone. Then the muscles stretch again at the same time as the tendon releases its energy like a catapult to produce a powerful acceleration beyond the limits of muscle-powered acceleration. A similar mechanism has been documented in locusts and grasshoppers.
Early hatching of froglets can have negative effects on frog jumping performance and overall locomotion. The hindlimbs are unable to completely form, which results in them being shorter and much weaker relative to a normal hatching froglet. Early hatching froglets may tend to depend on other forms of locomotion more often, such as swimming and walking.
;Walking and running
;Jumping
Frogs are generally recognized as exceptional jumpers and, relative to their size, the best jumpers of all vertebrates. The striped rocket frog, ''Litoria nasuta'', can leap over , a distance that is more than fifty times its body length of . There are tremendous differences between species in jumping capability. Within a species, jump distance increases with increasing size, but relative jumping distance (body-lengths jumped) decreases. The Euphlyctis cyanophlyctis, Indian skipper frog (''Euphlyctis cyanophlyctis'') has the ability to leap out of the water from a position floating on the surface. The tiny northern cricket frog (''Acris crepitans'') can "skitter" across the surface of a pond with a series of short rapid jumps.
Slow-motion photography shows that the muscles have passive flexibility. They are first stretched while the frog is still in the crouched position, then they are contracted before being stretched again to launch the frog into the air. The fore legs are folded against the chest and the hind legs remain in the extended, streamlined position for the duration of the jump. In some extremely capable jumpers, such as the Cuban tree frog (''Osteopilus septentrionalis'') and the northern leopard frog (''Rana pipiens''), the peak power exerted during a jump can exceed that which the muscle is theoretically capable of producing. When the muscles contract, the energy is first transferred into the stretched tendon which is wrapped around the ankle bone. Then the muscles stretch again at the same time as the tendon releases its energy like a catapult to produce a powerful acceleration beyond the limits of muscle-powered acceleration. A similar mechanism has been documented in locusts and grasshoppers.
Early hatching of froglets can have negative effects on frog jumping performance and overall locomotion. The hindlimbs are unable to completely form, which results in them being shorter and much weaker relative to a normal hatching froglet. Early hatching froglets may tend to depend on other forms of locomotion more often, such as swimming and walking.
;Walking and running
 Frogs in the families Bufonidae, Rhinophrynidae, and
Frogs in the families Bufonidae, Rhinophrynidae, and Microhylidae
The Microhylidae, commonly known as narrow-mouthed frogs, are a geographically widespread family of frogs. The 683 species are in 63 genera and 11 subfamilies, which is the largest number of genera of any frog family.
Evolution
A molecular phylo ...
have short back legs and tend to walk rather than jump. When they try to move rapidly, they speed up the rate of movement of their limbs or resort to an ungainly hopping gait. The Great Plains narrow-mouthed toad (''Gastrophryne olivacea'') has been described as having a gait that is "a combination of running and short hops that are usually only an inch or two in length". In an experiment, Bufo fowleri, Fowler's toad (''Bufo fowleri'') was placed on a treadmill which was turned at varying speeds. By measuring the toad's uptake of oxygen it was found that hopping was an inefficient use of resources during sustained locomotion but was a useful strategy during short bursts of high-intensity activity.
The Kassina maculata, red-legged running frog (''Kassina maculata'') has short, slim hind limbs unsuited to jumping. It can move fast by using a running gait in which the two hind legs are used alternately. Slow-motion photography shows, unlike a horse that can trot or gallop, the frog's gait remained similar at slow, medium, and fast speeds. This species can also climb trees and shrubs, and does so at night to catch insects. The Indian skipper frog (''Euphlyctis cyanophlyctis'') has broad feet and can run across the surface of the water for several metres (yards).
;Swimming
 Frogs that live in or visit water have adaptations that improve their swimming abilities. The hind limbs are heavily muscled and strong. The webbing between the toes of the hind feet increases the area of the foot and helps propel the frog powerfully through the water. Members of the family Pipidae are wholly aquatic and show the most marked specialization. They have inflexible vertebral columns, flattened, streamlined bodies, lateral line systems, and powerful hind limbs with large webbed feet. Tadpoles mostly have large tail fins which provide thrust when the tail is moved from side to side.
;Burrowing
Some frogs have become adapted for burrowing and a life underground. They tend to have rounded bodies, short limbs, small heads with bulging eyes, and hind feet adapted for excavation. An extreme example of this is the purple frog (''Nasikabatrachus sahyadrensis'') from southern India which feeds on termites and spends almost its whole life underground. It emerges briefly during the monsoon to mate and breed in temporary pools. It has a tiny head with a pointed snout and a plump, rounded body. Because of this fossorial existence, it was Species description, first described in 2003, being new to the scientific community at that time, although previously known to local people.
Frogs that live in or visit water have adaptations that improve their swimming abilities. The hind limbs are heavily muscled and strong. The webbing between the toes of the hind feet increases the area of the foot and helps propel the frog powerfully through the water. Members of the family Pipidae are wholly aquatic and show the most marked specialization. They have inflexible vertebral columns, flattened, streamlined bodies, lateral line systems, and powerful hind limbs with large webbed feet. Tadpoles mostly have large tail fins which provide thrust when the tail is moved from side to side.
;Burrowing
Some frogs have become adapted for burrowing and a life underground. They tend to have rounded bodies, short limbs, small heads with bulging eyes, and hind feet adapted for excavation. An extreme example of this is the purple frog (''Nasikabatrachus sahyadrensis'') from southern India which feeds on termites and spends almost its whole life underground. It emerges briefly during the monsoon to mate and breed in temporary pools. It has a tiny head with a pointed snout and a plump, rounded body. Because of this fossorial existence, it was Species description, first described in 2003, being new to the scientific community at that time, although previously known to local people.
 The spadefoot toads of North America are also adapted to underground life. The Plains spadefoot toad (''Spea bombifrons'') is typical and has a flap of keratinised bone attached to one of the Metatarsus, metatarsals of the hind feet which it uses to dig itself backwards into the ground. As it digs, the toad wriggles its hips from side to side to sink into the loose soil. It has a shallow burrow in the summer from which it emerges at night to forage. In winter, it digs much deeper and has been recorded at a depth of . The tunnel is filled with soil and the toad hibernates in a small chamber at the end. During this time, urea accumulates in its tissues and water is drawn in from the surrounding damp soil by osmosis to supply the toad's needs. Spadefoot toads are "explosive breeders", all emerging from their burrows at the same time and converging on temporary pools, attracted to one of these by the calling of the first male to find a suitable breeding location.
The burrowing frogs of Australia have a rather different lifestyle. The western spotted frog (''Heleioporus albopunctatus'') digs a burrow beside a river or in the bed of an ephemeral stream and regularly emerges to forage. Mating takes place and eggs are laid in a foam nest inside the burrow. The eggs partially develop there, but do not hatch until they are submerged following heavy rainfall. The tadpoles then swim out into the open water and rapidly complete their development. Madagascan burrowing frogs are less fossorial and mostly bury themselves in leaf litter. One of these, the Scaphiophryne marmorata, green burrowing frog (''Scaphiophryne marmorata''), has a flattened head with a short snout and well-developed metatarsal tubercles on its hind feet to help with excavation. It also has greatly enlarged terminal discs on its fore feet that help it to clamber around in bushes. It breeds in temporary pools that form after rains.
;Climbing
The spadefoot toads of North America are also adapted to underground life. The Plains spadefoot toad (''Spea bombifrons'') is typical and has a flap of keratinised bone attached to one of the Metatarsus, metatarsals of the hind feet which it uses to dig itself backwards into the ground. As it digs, the toad wriggles its hips from side to side to sink into the loose soil. It has a shallow burrow in the summer from which it emerges at night to forage. In winter, it digs much deeper and has been recorded at a depth of . The tunnel is filled with soil and the toad hibernates in a small chamber at the end. During this time, urea accumulates in its tissues and water is drawn in from the surrounding damp soil by osmosis to supply the toad's needs. Spadefoot toads are "explosive breeders", all emerging from their burrows at the same time and converging on temporary pools, attracted to one of these by the calling of the first male to find a suitable breeding location.
The burrowing frogs of Australia have a rather different lifestyle. The western spotted frog (''Heleioporus albopunctatus'') digs a burrow beside a river or in the bed of an ephemeral stream and regularly emerges to forage. Mating takes place and eggs are laid in a foam nest inside the burrow. The eggs partially develop there, but do not hatch until they are submerged following heavy rainfall. The tadpoles then swim out into the open water and rapidly complete their development. Madagascan burrowing frogs are less fossorial and mostly bury themselves in leaf litter. One of these, the Scaphiophryne marmorata, green burrowing frog (''Scaphiophryne marmorata''), has a flattened head with a short snout and well-developed metatarsal tubercles on its hind feet to help with excavation. It also has greatly enlarged terminal discs on its fore feet that help it to clamber around in bushes. It breeds in temporary pools that form after rains.
;Climbing

 Tree frogs live high in the canopy (biology), canopy, where they scramble around on the branches, twigs, and leaves, sometimes never coming down to earth. The "true" tree frogs belong to the family Hylidae, but members of other frog families have independently adopted an arboreal habit, a case of convergent evolution. These include the glass frogs (Centrolenidae), the Hyperoliidae, bush frogs (Hyperoliidae), some of the narrow-mouthed frogs (Microhylidae), and the Rhacophoridae, shrub frogs (Rhacophoridae). Most tree frogs are under in length, with long legs and long toes with adhesive pads on the tips. The surface of the toe pads is formed from a closely packed layer of flat-topped, hexagonal epidermis (skin), epidermal cells separated by grooves into which glands secrete mucus. These toe pads, moistened by the mucus, provide the grip on any wet or dry surface, including glass. The forces involved include boundary friction of the toe pad epidermis on the surface and also surface tension and viscosity. Tree frogs are very acrobatic and can catch insects while hanging by one toe from a twig or clutching onto the blade of a windswept reed. Some members of the subfamily Phyllomedusinae have Opposable thumb#Opposition and apposition, opposable toes on their feet. The Phyllomedusa ayeaye, reticulated leaf frog (''Phyllomedusa ayeaye'') has a single opposed Digit (anatomy), digit on each fore foot and two opposed digits on its hind feet. This allows it to grasp the stems of bushes as it clambers around in its riverside habitat.
;Gliding
During the evolutionary history of frogs, several different groups have independently taken to the air. Some frogs in the tropical rainforest are specially adapted for gliding from tree to tree or parachuting to the forest floor. Typical of them is Rhacophorus nigropalmatus, Wallace's flying frog (''Rhacophorus nigropalmatus'') from Malaysia and Borneo. It has large feet with the fingertips expanded into flat adhesive discs and the digits fully webbed. Flaps of skin occur on the lateral margins of the limbs and across the tail region. With the digits splayed, the limbs outstretched, and these flaps spread, it can glide considerable distances, but is unable to undertake powered flight. It can alter its direction of travel and navigate distances of up to between trees.
Tree frogs live high in the canopy (biology), canopy, where they scramble around on the branches, twigs, and leaves, sometimes never coming down to earth. The "true" tree frogs belong to the family Hylidae, but members of other frog families have independently adopted an arboreal habit, a case of convergent evolution. These include the glass frogs (Centrolenidae), the Hyperoliidae, bush frogs (Hyperoliidae), some of the narrow-mouthed frogs (Microhylidae), and the Rhacophoridae, shrub frogs (Rhacophoridae). Most tree frogs are under in length, with long legs and long toes with adhesive pads on the tips. The surface of the toe pads is formed from a closely packed layer of flat-topped, hexagonal epidermis (skin), epidermal cells separated by grooves into which glands secrete mucus. These toe pads, moistened by the mucus, provide the grip on any wet or dry surface, including glass. The forces involved include boundary friction of the toe pad epidermis on the surface and also surface tension and viscosity. Tree frogs are very acrobatic and can catch insects while hanging by one toe from a twig or clutching onto the blade of a windswept reed. Some members of the subfamily Phyllomedusinae have Opposable thumb#Opposition and apposition, opposable toes on their feet. The Phyllomedusa ayeaye, reticulated leaf frog (''Phyllomedusa ayeaye'') has a single opposed Digit (anatomy), digit on each fore foot and two opposed digits on its hind feet. This allows it to grasp the stems of bushes as it clambers around in its riverside habitat.
;Gliding
During the evolutionary history of frogs, several different groups have independently taken to the air. Some frogs in the tropical rainforest are specially adapted for gliding from tree to tree or parachuting to the forest floor. Typical of them is Rhacophorus nigropalmatus, Wallace's flying frog (''Rhacophorus nigropalmatus'') from Malaysia and Borneo. It has large feet with the fingertips expanded into flat adhesive discs and the digits fully webbed. Flaps of skin occur on the lateral margins of the limbs and across the tail region. With the digits splayed, the limbs outstretched, and these flaps spread, it can glide considerable distances, but is unable to undertake powered flight. It can alter its direction of travel and navigate distances of up to between trees.
Life history
Reproduction
Two main types of reproduction occur in frogs, prolonged breeding and explosive breeding. In the former, adopted by the majority of species, adult frogs at certain times of year assemble at a pond, lake or stream to breed. Many frogs return to the bodies of water in which they developed as larvae. This often results in annual migrations involving thousands of individuals. In explosive breeders, mature adult frogs arrive at breeding sites in response to certain trigger factors such as rainfall occurring in an arid area. In these frogs, mating and spawning take place promptly and the speed of larval growth is rapid in order to make use of the ephemeral pools before they dry up. Among prolonged breeders, males usually arrive at the breeding site first and remain there for some time whereas females tend to arrive later and depart soon after they have spawned. This means that males outnumber females at the water's edge and defend territories from which they expel other males. They advertise their presence by calling, often alternating their croaks with neighbouring frogs. Larger, stronger males tend to have deeper calls and maintain higher quality territories. Females select their mates at least partly on the basis of the depth of their voice. In some species there are satellite males who have no territory and do not call. They may intercept females that are approaching a calling male or take over a vacated territory. Calling is an energy-sapping activity. Sometimes the two roles are reversed and a calling male gives up its territory and becomes a satellite. In explosive breeders, the first male that finds a suitable breeding location, such as a temporary pool, calls loudly and other frogs of both sexes converge on the pool. Explosive breeders tend to call in unison creating a chorus that can be heard from far away. The spadefoot toads (''Scaphiopus spp.'') of North America fall into this category. Mate selection and courtship is not as important as speed in reproduction. In some years, suitable conditions may not occur and the frogs may go for two or more years without breeding. Some female New Mexico Spadefoot Toad, New Mexico spadefoot toads (''Spea multiplicata'') only spawn half of the available eggs at a time, perhaps retaining some in case a better reproductive opportunity arises later.
At the breeding site, the male mounts the female and grips her tightly round the body. Typically,
In explosive breeders, the first male that finds a suitable breeding location, such as a temporary pool, calls loudly and other frogs of both sexes converge on the pool. Explosive breeders tend to call in unison creating a chorus that can be heard from far away. The spadefoot toads (''Scaphiopus spp.'') of North America fall into this category. Mate selection and courtship is not as important as speed in reproduction. In some years, suitable conditions may not occur and the frogs may go for two or more years without breeding. Some female New Mexico Spadefoot Toad, New Mexico spadefoot toads (''Spea multiplicata'') only spawn half of the available eggs at a time, perhaps retaining some in case a better reproductive opportunity arises later.
At the breeding site, the male mounts the female and grips her tightly round the body. Typically, amplexus
Amplexus (Latin "embrace") is a type of mating behavior exhibited by some externally fertilizing species (chiefly amphibians and horseshoe crabs) in which a male grasps a female with his front legs as part of the mating process, and at the same ...
takes place in the water, the female releases her eggs and the male covers them with sperm; fertilization is external fertilization, external. In many species such as the Great Plains toad (''Bufo cognatus''), the male restrains the eggs with his back feet, holding them in place for about three minutes. Members of the West African genus ''Nimbaphrynoides'' are unique among frogs in that they are Viviparity, viviparous; ''Limnonectes larvaepartus'', ''Eleutherodactylus jasperi'' and members of the Tanzanian genus ''Nectophrynoides'' are the only frogs known to be Ovoviviparity, ovoviviparous. In these species, fertilization is Internal fertilization, internal and females give birth to fully developed juvenile frogs, except ''L. larvaepartus'', which give birth to tadpoles.
Life cycle
Eggs / frogspawn
 Frogs may lay their in eggs as clumps, surface films, strings, or individually. Around half of species deposit eggs in water, others lay eggs in vegetation, on the ground or in excavations. The tiny Yellow-Striped Pygmy Eleuth, yellow-striped pygmy eleuth (''Eleutherodactylus limbatus'') lays eggs singly, burying them in moist soil. The Smoky Jungle Frog, smoky jungle frog (''Leptodactylus pentadactylus'') makes a nest of foam in a hollow. The eggs hatch when the nest is flooded, or the tadpoles may complete their development in the foam if flooding does not occur. The red-eyed treefrog (''Agalychnis callidryas'') deposits its eggs on a leaf above a pool and when they hatch, the larvae fall into the water below.
In certain species, such as the wood frog (''Rana sylvatica''), Symbiosis, symbiotic unicellular green algae are present in the gelatinous material. It is thought that these may benefit the developing larvae by providing them with extra oxygen through photosynthesis. The interior of globular egg clusters of the Wood Frog, wood frog has been also been found to be up to 6 °C (11 °F) warmer than the surrounding water and this speeds up the development of the larvae. The larvae developing in the eggs can detect vibrations caused by nearby predatory wasps or snakes, and will hatch early to avoid being eaten. In general, the length of the egg stage depends on the species and the environmental conditions. Aquatic eggs normally hatch within one week when the capsule splits as a result of enzymes released by the developing larvae.
Direct development, where eggs hatch into juveniles like small adults, is also known in many frogs, for example, ''Ischnocnema henselii,'' ''Common coquí, Eleutherodactylus coqui'', and ''Raorchestes ochlandrae'' and ''Raorchestes chalazodes.''
Frogs may lay their in eggs as clumps, surface films, strings, or individually. Around half of species deposit eggs in water, others lay eggs in vegetation, on the ground or in excavations. The tiny Yellow-Striped Pygmy Eleuth, yellow-striped pygmy eleuth (''Eleutherodactylus limbatus'') lays eggs singly, burying them in moist soil. The Smoky Jungle Frog, smoky jungle frog (''Leptodactylus pentadactylus'') makes a nest of foam in a hollow. The eggs hatch when the nest is flooded, or the tadpoles may complete their development in the foam if flooding does not occur. The red-eyed treefrog (''Agalychnis callidryas'') deposits its eggs on a leaf above a pool and when they hatch, the larvae fall into the water below.
In certain species, such as the wood frog (''Rana sylvatica''), Symbiosis, symbiotic unicellular green algae are present in the gelatinous material. It is thought that these may benefit the developing larvae by providing them with extra oxygen through photosynthesis. The interior of globular egg clusters of the Wood Frog, wood frog has been also been found to be up to 6 °C (11 °F) warmer than the surrounding water and this speeds up the development of the larvae. The larvae developing in the eggs can detect vibrations caused by nearby predatory wasps or snakes, and will hatch early to avoid being eaten. In general, the length of the egg stage depends on the species and the environmental conditions. Aquatic eggs normally hatch within one week when the capsule splits as a result of enzymes released by the developing larvae.
Direct development, where eggs hatch into juveniles like small adults, is also known in many frogs, for example, ''Ischnocnema henselii,'' ''Common coquí, Eleutherodactylus coqui'', and ''Raorchestes ochlandrae'' and ''Raorchestes chalazodes.''
Tadpoles
 The larvae that emerge from the eggs, known as tadpoles (or occasionally polliwogs). Tadpoles lack eyelids and limbs, and have cartilaginous skeletons, gills for respiration (external gills at first, internal gills later), and tails they use for swimming. As a general rule, free-living larvae are fully aquatic, but at least one species (''Nannophrys ceylonensis'') has semiterrestrial tadpoles which live among wet rocks.
From early in its development, a gill pouch covers the tadpole's gills and front legs. The lungs soon start to develop and are used as an accessory breathing organ. Some species go through metamorphosis while still inside the egg and hatch directly into small frogs. Tadpoles lack true teeth, but the jaws in most species have two elongated, parallel rows of small,
The larvae that emerge from the eggs, known as tadpoles (or occasionally polliwogs). Tadpoles lack eyelids and limbs, and have cartilaginous skeletons, gills for respiration (external gills at first, internal gills later), and tails they use for swimming. As a general rule, free-living larvae are fully aquatic, but at least one species (''Nannophrys ceylonensis'') has semiterrestrial tadpoles which live among wet rocks.
From early in its development, a gill pouch covers the tadpole's gills and front legs. The lungs soon start to develop and are used as an accessory breathing organ. Some species go through metamorphosis while still inside the egg and hatch directly into small frogs. Tadpoles lack true teeth, but the jaws in most species have two elongated, parallel rows of small, keratin
Keratin () is one of a family of structural fibrous proteins also known as ''scleroproteins''. Alpha-keratin (α-keratin) is a type of keratin found in vertebrates. It is the key structural material making up scales, hair, nails, feathers, hor ...
ized structures called keradonts in their upper jaws. Their lower jaws usually have three rows of keradonts surrounded by a horny beak, but the number of rows can vary and the exact arrangements of mouth parts provide a means for species identification. In the Pipidae, with the exception of ''Hymenochirus'', the tadpoles have paired anterior barbels, which make them resemble small catfish. Their tails are stiffened by a notochord, but does not contain any bony or cartilaginous elements except for a few vertebrae at the base which forms the urostyle during metamorphosis. This has been suggested as an adaptation to their lifestyles; because the transformation into frogs happens very fast, the tail is made of soft tissue only, as bone and cartilage take a much longer time to be broken down and absorbed. The tail fin and tip is fragile and will easily tear, which is seen as an adaptation to escape from predators which tries to grasp them by the tail.
Tadpoles are typically herbivorous
A herbivore is an animal anatomically and physiologically adapted to eating plant material, for example foliage or marine algae, for the main component of its diet. As a result of their plant diet, herbivorous animals typically have mouthpar ...
, feeding mostly on algae, including diatoms filtered from the water through the gill
A gill () is a respiratory organ that many aquatic organisms use to extract dissolved oxygen from water and to excrete carbon dioxide. The gills of some species, such as hermit crabs, have adapted to allow respiration on land provided they ar ...
s. Some species are carnivorous at the tadpole stage, eating insects, smaller tadpoles, and fish. The Cuban tree frog (''Osteopilus septentrionalis'') is one of a number of species in which the tadpoles can be Cannibalism, cannibalistic. Tadpoles that develop legs early may be eaten by the others, so late developers may have better long-term survival prospects.
Tadpoles are highly vulnerable to being eaten by fish, newts, predatory diving beetles, and birds, particularly water bird, such as storks and herons and domestic ducks. Some tadpoles, including those of the cane toad (''Bufo marinus''), are poisonous. The tadpole stage may be as short as a week in explosive breeders or it may last through one or more winters followed by metamorphosis in the spring.
Metamorphosis
At the end of the tadpole stage, a frog undergoes metamorphosis in which its body makes a sudden transition into the adult form. This metamorphosis typically lasts only 24 hours, and is initiated by production of the hormone thyroxine. This causes different tissues to develop in different ways. The principal changes that take place include the development of the lungs and the disappearance of the gills and gill pouch, making the front legs visible. The lower jaw transforms into the big mandible of the carnivorous adult, and the long, spiral gut of the herbivorous tadpole is replaced by the typical short gut of a predator. The nervous system becomes adapted for hearing and stereoscopic vision, and for new methods of locomotion and feeding. The eyes are repositioned higher up on the head and the eyelids and associated glands are formed. The eardrum, middle ear, and inner ear are developed. The skin becomes thicker and tougher, the lateral line system is lost, and skin glands are developed. The final stage is the disappearance of the tail, but this takes place rather later, the tissue being used to produce a spurt of growth in the limbs. Frogs are at their most vulnerable to predators when they are undergoing metamorphosis. At this time, the tail is being lost and locomotion by means of limbs is only just becoming established.Adults
Adult frogs may live in or near water, but few are fully aquatic. Almost all frog species are carnivore, carnivorous as adults, preying on invertebrates, including insects, crabs, spiders, mites, annelid, worms, snails, and slugs. A few of the larger ones may eat other frogs, small mammals and reptiles, and fish. A few species also eat plant matter; the tree frog ''Xenohyla truncata'' is partly herbivorous, its diet including a large proportion of fruit, ''Leptodactylus mystaceus'' has been found to eat plants, and folivory occurs in ''Euphlyctis hexadactylus'', with plants constituting 79.5% of its diet by volume. Many frogs use their sticky tongues to catch prey, while others simply grab them with their mouths. Adult frogs are themselves attacked by many predators. The northern leopard frog (''Rana pipiens'') is eaten by herons, hawks, fish, large salamanders, snakes, raccoons, skunks, mink, bullfrogs, and other animals. Frogs are primary predators and an important part of the
Frogs are primary predators and an important part of the food web
A food web is the natural interconnection of food chains and a graphical representation of what-eats-what in an ecological community. Another name for food web is consumer-resource system. Ecologists can broadly lump all life forms into one ...
. Being Ectotherm, cold-blooded, they make efficient use of the food they eat with little energy being used for metabolic processes, while the rest is transformed into biomass (ecology), biomass. They are themselves eaten by secondary predators and are the primary terrestrial consumers of invertebrates, most of which feed on plants. By reducing herbivory, they play a part in increasing the growth of plants and are thus part of a delicately balanced ecosystem.
Little is known about the longevity of frogs and toads in the wild, but some can live for many years. Skeletochronology is a method of examining bones to determine age. Using this method, the ages of mountain yellow-legged frogs (''Rana muscosa'') were studied, the phalanges of the toes showing seasonal lines where growth slows in winter. The oldest frogs had ten bands, so their age was believed to be 14 years, including the four-year tadpole stage. Captive frogs and toads have been recorded as living for up to 40 years, an age achieved by a European common toad (''Bufo bufo''). The cane toad (''Bufo marinus'') has been known to survive 24 years in captivity, and the American bullfrog (''Rana catesbeiana'') 14 years. Frogs from temperate climates hibernate during the winter, and four species are known to be able to withstand freezing during this time, including the wood frog (''Rana sylvatica'').
Parental care

 Although care of offspring is poorly understood in frogs, up to an estimated 20% of amphibian species may care for their young in some way. The evolution of biparental care in tropical frogs, evolution of parental care in frogs is driven primarily by the size of the water body in which they breed. Those that breed in smaller water bodies tend to have greater and more complex parental care behaviour. Because predation of eggs and larvae is high in large water bodies, some frog species started to lay their eggs on land. Once this happened, the desiccating terrestrial environment demands that one or both parents keep them moist to ensure their survival. The subsequent need to transport hatched tadpoles to a water body required an even more intense form of parental care.
In small pools, predators are mostly absent and competition between tadpoles becomes the variable that constrains their survival. Certain frog species avoid this competition by making use of smaller phytotelmata (water-filled leaf wikt:axil, axils or small woody cavities) as sites for depositing a few tadpoles. While these smaller rearing sites are free from competition, they also lack sufficient nutrients to support a tadpole without parental assistance. Frog species that changed from the use of larger to smaller phytotelmata have evolved a strategy of providing their offspring with nutritive but unfertilized eggs. The female strawberry poison-dart frog (''Oophaga pumilio'') lays her eggs on the forest floor. The male frog guards them from predation and carries water in his cloaca to keep them moist. When they hatch, the female moves the tadpoles on her back to a water-holding bromeliad or other similar water body, depositing just one in each location. She visits them regularly and feeds them by laying one or two unfertilized eggs in the phytotelma, continuing to do this until the young are large enough to undergo metamorphosis. The granular poison frog (''Oophaga granulifera'') looks after its tadpoles in a similar way.
Many other diverse forms of parental care are seen in frogs. The tiny male ''Colostethus subpunctatus'' stands guard over his egg cluster, laid under a stone or log. When the eggs hatch, he transports the tadpoles on his back to a temporary pool, where he partially immerses himself in the water and one or more tadpoles drop off. He then moves on to another pool. The male common midwife toad (''Alytes obstetricans'') carries the eggs around with him attached to his hind legs. He keeps them damp in dry weather by immersing himself in a pond, and prevents them from getting too wet in soggy vegetation by raising his hindquarters. After three to six weeks, he travels to a pond and the eggs hatch into tadpoles. The tungara frog (''Physalaemus pustulosus'') builds a floating nest from foam to protect its eggs from predation. The foam is made from proteins and lectins, and seems to have antimicrobial properties. Several pairs of frogs may form a colonial nest on a previously built raft. The eggs are laid in the centre, followed by alternate layers of foam and eggs, finishing with a foam capping.
Some frogs protect their offspring inside their own bodies. Both male and female pouched frogs (''Assa darlingtoni'') guard their eggs, which are laid on the ground. When the eggs hatch, the male lubricates his body with the jelly surrounding them and immerses himself in the egg mass. The tadpoles wriggle into skin pouches on his side, where they develop until they metamorphose into juvenile frogs. The female gastric-brooding frog (''Rheobatrachus'' sp.) from Australia, now probably extinct, swallows her fertilized eggs, which then develop inside her stomach. She ceases to feed and stops secreting stomach acid. The tadpoles rely on the yolks of the eggs for nourishment. After six or seven weeks, they are ready for metamorphosis. The mother regurgitates the tiny frogs, which hop away from her mouth. The female Darwin's frog (''Rhinoderma darwinii'') from Chile lays up to 40 eggs on the ground, where they are guarded by the male. When the tadpoles are about to hatch, they are engulfed by the male, which carries them around inside his much-enlarged vocal sac. Here they are immersed in a frothy, viscous liquid that contains some nourishment to supplement what they obtain from the yolks of the eggs. They remain in the sac for seven to ten weeks before undergoing metamorphosis, after which they move into the male's mouth and emerge.
Although care of offspring is poorly understood in frogs, up to an estimated 20% of amphibian species may care for their young in some way. The evolution of biparental care in tropical frogs, evolution of parental care in frogs is driven primarily by the size of the water body in which they breed. Those that breed in smaller water bodies tend to have greater and more complex parental care behaviour. Because predation of eggs and larvae is high in large water bodies, some frog species started to lay their eggs on land. Once this happened, the desiccating terrestrial environment demands that one or both parents keep them moist to ensure their survival. The subsequent need to transport hatched tadpoles to a water body required an even more intense form of parental care.
In small pools, predators are mostly absent and competition between tadpoles becomes the variable that constrains their survival. Certain frog species avoid this competition by making use of smaller phytotelmata (water-filled leaf wikt:axil, axils or small woody cavities) as sites for depositing a few tadpoles. While these smaller rearing sites are free from competition, they also lack sufficient nutrients to support a tadpole without parental assistance. Frog species that changed from the use of larger to smaller phytotelmata have evolved a strategy of providing their offspring with nutritive but unfertilized eggs. The female strawberry poison-dart frog (''Oophaga pumilio'') lays her eggs on the forest floor. The male frog guards them from predation and carries water in his cloaca to keep them moist. When they hatch, the female moves the tadpoles on her back to a water-holding bromeliad or other similar water body, depositing just one in each location. She visits them regularly and feeds them by laying one or two unfertilized eggs in the phytotelma, continuing to do this until the young are large enough to undergo metamorphosis. The granular poison frog (''Oophaga granulifera'') looks after its tadpoles in a similar way.
Many other diverse forms of parental care are seen in frogs. The tiny male ''Colostethus subpunctatus'' stands guard over his egg cluster, laid under a stone or log. When the eggs hatch, he transports the tadpoles on his back to a temporary pool, where he partially immerses himself in the water and one or more tadpoles drop off. He then moves on to another pool. The male common midwife toad (''Alytes obstetricans'') carries the eggs around with him attached to his hind legs. He keeps them damp in dry weather by immersing himself in a pond, and prevents them from getting too wet in soggy vegetation by raising his hindquarters. After three to six weeks, he travels to a pond and the eggs hatch into tadpoles. The tungara frog (''Physalaemus pustulosus'') builds a floating nest from foam to protect its eggs from predation. The foam is made from proteins and lectins, and seems to have antimicrobial properties. Several pairs of frogs may form a colonial nest on a previously built raft. The eggs are laid in the centre, followed by alternate layers of foam and eggs, finishing with a foam capping.
Some frogs protect their offspring inside their own bodies. Both male and female pouched frogs (''Assa darlingtoni'') guard their eggs, which are laid on the ground. When the eggs hatch, the male lubricates his body with the jelly surrounding them and immerses himself in the egg mass. The tadpoles wriggle into skin pouches on his side, where they develop until they metamorphose into juvenile frogs. The female gastric-brooding frog (''Rheobatrachus'' sp.) from Australia, now probably extinct, swallows her fertilized eggs, which then develop inside her stomach. She ceases to feed and stops secreting stomach acid. The tadpoles rely on the yolks of the eggs for nourishment. After six or seven weeks, they are ready for metamorphosis. The mother regurgitates the tiny frogs, which hop away from her mouth. The female Darwin's frog (''Rhinoderma darwinii'') from Chile lays up to 40 eggs on the ground, where they are guarded by the male. When the tadpoles are about to hatch, they are engulfed by the male, which carries them around inside his much-enlarged vocal sac. Here they are immersed in a frothy, viscous liquid that contains some nourishment to supplement what they obtain from the yolks of the eggs. They remain in the sac for seven to ten weeks before undergoing metamorphosis, after which they move into the male's mouth and emerge.
Defence

 At first sight, frogs seem rather defenceless because of their small size, slow movement, thin skin, and lack of defensive structures, such as spines, claws or teeth. Many use camouflage to avoid detection, the skin often being spotted or streaked in neutral colours that allow a stationary frog to merge into its surroundings. Some can make prodigious leaps, often into water, that help them to evade potential attackers, while many have other defensive adaptations and strategies.
The skin of many frogs contains mild toxic substances called bufotoxins to make them unpalatable to potential predators. Most toads and some frogs have large poison glands, the parotoid glands, located on the sides of their heads behind the eyes and other glands elsewhere on their bodies. These glands secrete mucus and a range of toxins that make frogs slippery to hold and distasteful or poisonous. If the noxious effect is immediate, the predator may cease its action and the frog may escape. If the effect develops more slowly, the predator may learn to avoid that species in future. Poisonous frogs tend to advertise their toxicity with bright colours, an adaptive strategy known as aposematism. The Poison dart frog, poison dart frogs in the family Dendrobatidae do this. They are typically red, orange, or yellow, often with contrasting black markings on their bodies. ''Allobates zaparo'' is not poisonous, but mimics the appearance of two different toxic species with which it shares a common range in an effort to deceive predators. Other species, such as the European Fire-bellied Toad, European fire-bellied toad (''Bombina bombina''), have their warning colour underneath. They "flash" this when attacked, adopting a pose that exposes the vivid colouring on their bellies.
At first sight, frogs seem rather defenceless because of their small size, slow movement, thin skin, and lack of defensive structures, such as spines, claws or teeth. Many use camouflage to avoid detection, the skin often being spotted or streaked in neutral colours that allow a stationary frog to merge into its surroundings. Some can make prodigious leaps, often into water, that help them to evade potential attackers, while many have other defensive adaptations and strategies.
The skin of many frogs contains mild toxic substances called bufotoxins to make them unpalatable to potential predators. Most toads and some frogs have large poison glands, the parotoid glands, located on the sides of their heads behind the eyes and other glands elsewhere on their bodies. These glands secrete mucus and a range of toxins that make frogs slippery to hold and distasteful or poisonous. If the noxious effect is immediate, the predator may cease its action and the frog may escape. If the effect develops more slowly, the predator may learn to avoid that species in future. Poisonous frogs tend to advertise their toxicity with bright colours, an adaptive strategy known as aposematism. The Poison dart frog, poison dart frogs in the family Dendrobatidae do this. They are typically red, orange, or yellow, often with contrasting black markings on their bodies. ''Allobates zaparo'' is not poisonous, but mimics the appearance of two different toxic species with which it shares a common range in an effort to deceive predators. Other species, such as the European Fire-bellied Toad, European fire-bellied toad (''Bombina bombina''), have their warning colour underneath. They "flash" this when attacked, adopting a pose that exposes the vivid colouring on their bellies.
poison dart frog
Poison dart frog (also known as dart-poison frog, poison frog or formerly known as poison arrow frog) is the common name of a group of frogs in the family Dendrobatidae which are native to tropical Central and South America. These species are ...
s, are especially toxic. The native peoples of South America extract poison from these frogs to apply to their Dart (missile), weapons for hunting, although few species are toxic enough to be used for this purpose. At least two non-poisonous frog species in tropical America (''Eleutherodactylus, Eleutherodactylus gaigei'' and ''Lithodytes lineatus'') Batesian mimicry, mimic the colouration of dart poison frogs for self-protection. Some frogs obtain poisons from the ants and other arthropods they eat. Others, such as the Australian corroboree frogs (''Pseudophryne corroboree'' and ''Pseudophryne pengilleyi''), can synthesize the alkaloids themselves. The chemicals involved may be irritants, hallucinogens, seizure, convulsants, neurotoxin, nerve poisons or vasoconstrictors. Many predators of frogs have become adapted to tolerate high levels of these poisons, but other creatures, including humans who handle the frogs, may be severely affected.
Some frogs use bluff or deception. The European common toad (''Bufo bufo'') adopts a characteristic stance when attacked, inflating its body and standing with its hindquarters raised and its head lowered. The bullfrog (''Rana catesbeiana'') crouches down with eyes closed and head tipped forward when threatened. This places the parotoid glands in the most effective position, the other glands on its back begin to ooze noxious secretions and the most vulnerable parts of its body are protected. Another tactic used by some frogs is to "scream", the sudden loud noise tending to startle the predator. The gray tree frog (''Hyla versicolor'') makes an explosive sound that sometimes repels the shrew ''Blarina brevicauda''. Although toads are avoided by many predators, the Common Garter Snake, common garter snake (''Thamnophis sirtalis'') regularly feeds on them. The strategy employed by juvenile American toads (''Bufo americanus'') on being approached by a snake is to crouch down and remain immobile. This is usually successful, with the snake passing by and the toad remaining undetected. If it is encountered by the snake's head, however, the toad hops away before crouching defensively.
Distribution
 Frogs live on all the continents except Antarctica, but they are not present on certain islands, especially those far away from continental land masses. Many species are isolated in restricted ranges by changes of climate or inhospitable territory, such as stretches of sea, mountain ridges, deserts, forest clearance, road construction, or other man-made barriers. Usually, a greater diversity of frogs occurs in tropical areas than in temperate regions, such as Europe. Some frogs inhabit arid areas, such as deserts, and rely on specific adaptations to survive. Members of the Australian genus ''Cyclorana'' bury themselves underground where they create a water-impervious cocoon in which to aestivation, aestivate during dry periods. Once it rains, they emerge, find a temporary pool, and breed. Egg and tadpole development is very fast in comparison to those of most other frogs, so breeding can be completed before the pond dries up. Some frog species are adapted to a cold environment. The wood frog (''Rana sylvatica''), whose habitat extends into the Arctic Circle, buries itself in the ground during winter. Although much of its body freezes during this time, it maintains a high concentration of glucose in its vital organs, which protects them from damage.
Frogs live on all the continents except Antarctica, but they are not present on certain islands, especially those far away from continental land masses. Many species are isolated in restricted ranges by changes of climate or inhospitable territory, such as stretches of sea, mountain ridges, deserts, forest clearance, road construction, or other man-made barriers. Usually, a greater diversity of frogs occurs in tropical areas than in temperate regions, such as Europe. Some frogs inhabit arid areas, such as deserts, and rely on specific adaptations to survive. Members of the Australian genus ''Cyclorana'' bury themselves underground where they create a water-impervious cocoon in which to aestivation, aestivate during dry periods. Once it rains, they emerge, find a temporary pool, and breed. Egg and tadpole development is very fast in comparison to those of most other frogs, so breeding can be completed before the pond dries up. Some frog species are adapted to a cold environment. The wood frog (''Rana sylvatica''), whose habitat extends into the Arctic Circle, buries itself in the ground during winter. Although much of its body freezes during this time, it maintains a high concentration of glucose in its vital organs, which protects them from damage.
Conservation
 In 2006, of 4,035 species of amphibians that depend on water during some lifecycle stage, 1,356 (33.6%) were considered to be threatened. This is likely to be an underestimate because it excludes 1,427 species for which evidence was insufficient to assess their status. Frog populations have declined dramatically since the 1950s. More than one-third of frog species are considered to be threatened with extinction, and more than 120 species are believed to have become extinct since the 1980s. Among these species are the gastric-brooding frogs of Australia and the golden toad of Costa Rica. The latter is of particular concern to scientists because it inhabited the pristine Monteverde Cloud Forest Reserve and its population crashed in 1987, along with about 20 other frog species in the area. This could not be linked directly to human activities, such as deforestation, and was outside the range of normal fluctuations in population size. Elsewhere, habitat loss is a significant cause of frog population decline, as are pollutants, climate change, increased ultraviolet, UVB radiation, and the introduction of Indigenous (ecology), non-native predators and competitors. A Canadian study conducted in 2006 suggested heavy traffic in their environment was a larger threat to frog populations than was habitat loss. Emerging infectious diseases, including
In 2006, of 4,035 species of amphibians that depend on water during some lifecycle stage, 1,356 (33.6%) were considered to be threatened. This is likely to be an underestimate because it excludes 1,427 species for which evidence was insufficient to assess their status. Frog populations have declined dramatically since the 1950s. More than one-third of frog species are considered to be threatened with extinction, and more than 120 species are believed to have become extinct since the 1980s. Among these species are the gastric-brooding frogs of Australia and the golden toad of Costa Rica. The latter is of particular concern to scientists because it inhabited the pristine Monteverde Cloud Forest Reserve and its population crashed in 1987, along with about 20 other frog species in the area. This could not be linked directly to human activities, such as deforestation, and was outside the range of normal fluctuations in population size. Elsewhere, habitat loss is a significant cause of frog population decline, as are pollutants, climate change, increased ultraviolet, UVB radiation, and the introduction of Indigenous (ecology), non-native predators and competitors. A Canadian study conducted in 2006 suggested heavy traffic in their environment was a larger threat to frog populations than was habitat loss. Emerging infectious diseases, including chytridiomycosis
Chytridiomycosis ( ) is an infectious disease in amphibians, caused by the chytrid fungi '' Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis'' and ''Batrachochytrium salamandrivorans''. Chytridiomycosis has been linked to dramatic population declines or exti ...
and ranavirus, are also devastating populations.
Many environmental scientists believe amphibians, including frogs, are good biological indicator species, indicators of broader ecosystem
An ecosystem (or ecological system) consists of all the organisms and the physical environment with which they interact. These biotic and abiotic components are linked together through nutrient cycles and energy flows. Energy enters the syste ...
health because of their intermediate positions in food chains, their permeable skins, and typically biphasic lives (aquatic larvae and terrestrial adults). It appears that species with both aquatic eggs and larvae are most affected by the decline, while those with direct development are the most resistant.
Frog mutations and genetic defects have increased since the 1990s. These often include missing legs or extra legs. Various causes have been identified or hypothesized, including an increase in Ultraviolet, ultraviolet radiation affecting the spawn on the surface of ponds, chemical contamination from pesticides and fertilizers, and parasites such as the trematode ''Ribeiroia ondatrae
''Ribeiroia ondatrae'', or the frog-mutating flatworm is a parasite in the genus ''Ribeiroia'' which is believed to be responsible for many of the recent increases in amphibian limb malformations, particularly missing, malformed, and additiona ...
''. Probably all these are involved in a complex way as stressors, environmental factors contributing to rates of disease, and vulnerability to attack by parasites. Malformations impair mobility and the individuals may not survive to adulthood. An increase in the number of frogs eaten by birds may actually increase the likelihood of parasitism of other frogs, because the trematode's complex lifecycle includes the Planorbidae, ramshorn snail and several intermediate hosts such as birds.
In a few cases, captive breeding programs have been established and have largely been successful. The World Association of Zoos and Aquariums named 2008 as the "Year of the Frog" in order to draw attention to the conservation issues faced by them.
The cane toad (''Bufo marinus'') is a very adaptable species native to South and Central America. In the 1930s, it was introduced into Puerto Rico, and later various other islands in the Pacific and Caribbean region, as a biological pest control agent. In 1935, 3000 toads were liberated in the sugar cane fields of Queensland, Australia, in an attempt to control cane beetles such as ''Dermolepida albohirtum'', the larvae of which damage and kill the canes. Initial results in many of these countries were positive, but it later became apparent that the toads upset the ecological balance in their new environments. They bred freely, competed with native frog species, ate bees and other harmless native invertebrates, had few predators in their adopted habitats, and poisoned pets, carnivorous birds, and mammals. In many of these countries, they are now regarded both as pests and invasive species, and scientists are looking for a biological method to control them.
Human uses
Culinary
American bullfrog
The American bullfrog (''Lithobates catesbeianus''), often simply known as the bullfrog in Canada and the United States, is a large true frog native to eastern North America. It typically inhabits large permanent water bodies such as swamps, p ...
(''Rana catesbeiana''), mostly farmed in China, varies between 1200 and 2400 tonnes.
The Leptodactylus fallax, mountain chicken frog, so-called as it tastes of chicken, is now endangered, in part due to human consumption, and was a major food choice of the Dominicans. Coon, possum, partridges, prairie hen, and frogs were among the fare Mark Twain recorded as part of American cuisine.
Scientific research
In November, 1970, NASA sent two bullfrogs into space for six days during the Orbiting Frog Otolith mission to test weightlessness. Frogs are used for dissections in high school and university anatomy classes, often first being injected with coloured substances to enhance contrasts among the biological systems. This practice is declining due to animal welfare concerns, and "digital frogs" are now available for virtual dissection. Frogs have served as Animal testing, experimental animals throughout the history of science. Eighteenth-century biologist Luigi Galvani discovered the link between electricity and the nervous system by studying frogs. He created Frog galvanometer, one of the first tools for measuring electric current out of a frog leg. In 1852, H. F. Stannius used a frog's heart in a procedure called a Stannius ligature to demonstrate the ventricle and atria beat independently of each other and at different rates. The African clawed frog or platanna (''Xenopus laevis'') was first widely used in laboratories in pregnancy tests in the first half of the 20th century. A sample of urine from a pregnant woman injected into a female frog induces it to layeggs
Humans and human ancestors have scavenged and eaten animal eggs for millions of years. Humans in Southeast Asia had domesticated chickens and harvested their eggs for food by 1,500 BCE. The most widely consumed eggs are those of fowl, especial ...
, a discovery made by English zoologist Lancelot Hogben. This is because a hormone, human chorionic gonadotropin, is present in substantial quantities in the urine of women during pregnancy. In 1952, Robert William Briggs, Robert Briggs and Thomas J. King cloned a frog by somatic cell nuclear transfer. This same technique was later used to create Dolly (sheep), Dolly the sheep, and their experiment was the first time a successful nuclear transplantation had been accomplished in higher animals.
Frogs are used in cloning research and other branches of embryology. Although alternative pregnancy tests have been developed, biologists continue to use ''Xenopus'' as a model organism in developmental biology because their embryos are large and easy to manipulate, they are readily obtainable, and can easily be kept in the laboratory. ''Xenopus laevis'' is increasingly being displaced by its smaller relative, ''Xenopus tropicalis'', which reaches its reproductive age in five months rather than the one to two years for ''X. laevis'', thus facilitating faster studies across generations.
Genomes of ''Xenopus laevis'', ''X. tropicalis'', ''Rana catesbeiana'', ''Rhinella marina'', and ''Nanorana parkeri'' have been sequenced and deposited in the National Center for Biotechnology Information, NCBI Genome database.
As pets
Due to being inexpensive and relatively easy to care for, many species of frogs and toads have become popular as exotic pets. They are undemanding and require low maintenance. Both frogs and toads can be housed in paludariums, terrariums and aquariums.Pharmaceutical
 Because frog toxins are extraordinarily diverse, they have raised the interest of biochemists as a "natural pharmacy". The alkaloid epibatidine, a painkiller 200 times more potent than morphine, is made by some species of Poison dart frog, poison dart frogs. Other chemicals isolated from the skins of frogs may offer resistance to HIV infection. Dart poisons are under active investigation for their potential as therapeutic drugs.
It has long been suspected that pre-Columbian Mesoamericans used a toxic secretion produced by the cane toad as a hallucinogen, but more likely they used substances secreted by the Colorado River toad (''Bufo alvarius''). These contain bufotenin (5-MeO-DMT), a psychoactive drug, psychoactive compound that has been used in modern times as a recreational drug. Typically, the skin secretions are dried and then smoked. Illicit drug use by licking the skin of a toad has been reported in the media, but this may be an urban myth.
Exudations from the skin of the golden poison frog (''Phyllobates terribilis'') are traditionally used by native Colombians to poison the darts they use for hunting. The tip of the projectile is rubbed over the back of the frog and the dart is launched from a blowgun. The combination of the two alkaloid toxins batrachotoxin and homobatrachotoxin is so powerful, one frog contains enough poison to kill an estimated 22,000 mice. Two other species, the Kokoe poison dart frog (''Phyllobates aurotaenia'') and the black-legged dart frog (''Phyllobates bicolor'') are also used for this purpose. These are less toxic and less abundant than the golden poison frog. They are impaled on pointed sticks and may be heated over a fire to maximise the quantity of poison that can be transferred to the dart.
Because frog toxins are extraordinarily diverse, they have raised the interest of biochemists as a "natural pharmacy". The alkaloid epibatidine, a painkiller 200 times more potent than morphine, is made by some species of Poison dart frog, poison dart frogs. Other chemicals isolated from the skins of frogs may offer resistance to HIV infection. Dart poisons are under active investigation for their potential as therapeutic drugs.
It has long been suspected that pre-Columbian Mesoamericans used a toxic secretion produced by the cane toad as a hallucinogen, but more likely they used substances secreted by the Colorado River toad (''Bufo alvarius''). These contain bufotenin (5-MeO-DMT), a psychoactive drug, psychoactive compound that has been used in modern times as a recreational drug. Typically, the skin secretions are dried and then smoked. Illicit drug use by licking the skin of a toad has been reported in the media, but this may be an urban myth.
Exudations from the skin of the golden poison frog (''Phyllobates terribilis'') are traditionally used by native Colombians to poison the darts they use for hunting. The tip of the projectile is rubbed over the back of the frog and the dart is launched from a blowgun. The combination of the two alkaloid toxins batrachotoxin and homobatrachotoxin is so powerful, one frog contains enough poison to kill an estimated 22,000 mice. Two other species, the Kokoe poison dart frog (''Phyllobates aurotaenia'') and the black-legged dart frog (''Phyllobates bicolor'') are also used for this purpose. These are less toxic and less abundant than the golden poison frog. They are impaled on pointed sticks and may be heated over a fire to maximise the quantity of poison that can be transferred to the dart.

Cultural significance
Frogs have been featured in mythology, fairy tales and popular culture. In traditional Chinese myths, the world rests on a giant frog, who would try to swallow the moon, causing the lunar eclipse. Frogs have been featured in religion, folklore, and popular culture. The ancient Egyptians depicted the god Heqet, protector of newborns, with the head of a frog. For the Mayan civilization, Mayans, frogs represented water, crops, fertility and birth and were associated with the god Chaac. In the Bible, Moses unleashes a Plagues of Egypt, plague of frogs on the Egyptians. Medieval Europeans associated frogs and toads with evil and witchcraft. The Brothers Grimm fairy tale ''The Frog Prince'' features a princess taking in a frog and it turning into a handsome prince. In modern culture, frogs may take a comedic or hapless role, such as Mr. Toad of the 1908 novel ''The Wind in the Willows'', Michigan J. Frog of Warner Bros. Cartoons, the Muppet Kermit the Frog and in the game Frogger.See also
* *References
Further reading
* * * Estes, R., and O. A. Reig. (1973). "The early fossil record of frogs: a review of the evidence." pp. 11–63 In J. L. Vial (Ed.), ''Evolutionary Biology of the Anurans: Contemporary Research on Major Problems''. University of Missouri Press, Columbia. * * * *External links
AmphibiaWeb
Gallery of Frogs
nbsp;– Photography and images of various frog species
The Whole Frog Project
nbsp;– Virtual frog dissection and anatomy
''San Francisco Chronicle'', 20 April 1992
nbsp;– Features many unusual frogs
''Scientific American'': Researchers Pinpoint Source of Poison Frogs' Deadly Defenses
Media
Time-lapse video showing the egg's development until hatching
Frog vocalisations from around the world
nbsp;– From the British Library Sound Archive
Frog calls
nbsp;– From Manitoba, Canada {{Featured article Frogs, 01 Articles containing video clips Extant Hettangian first appearances