anadromous on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
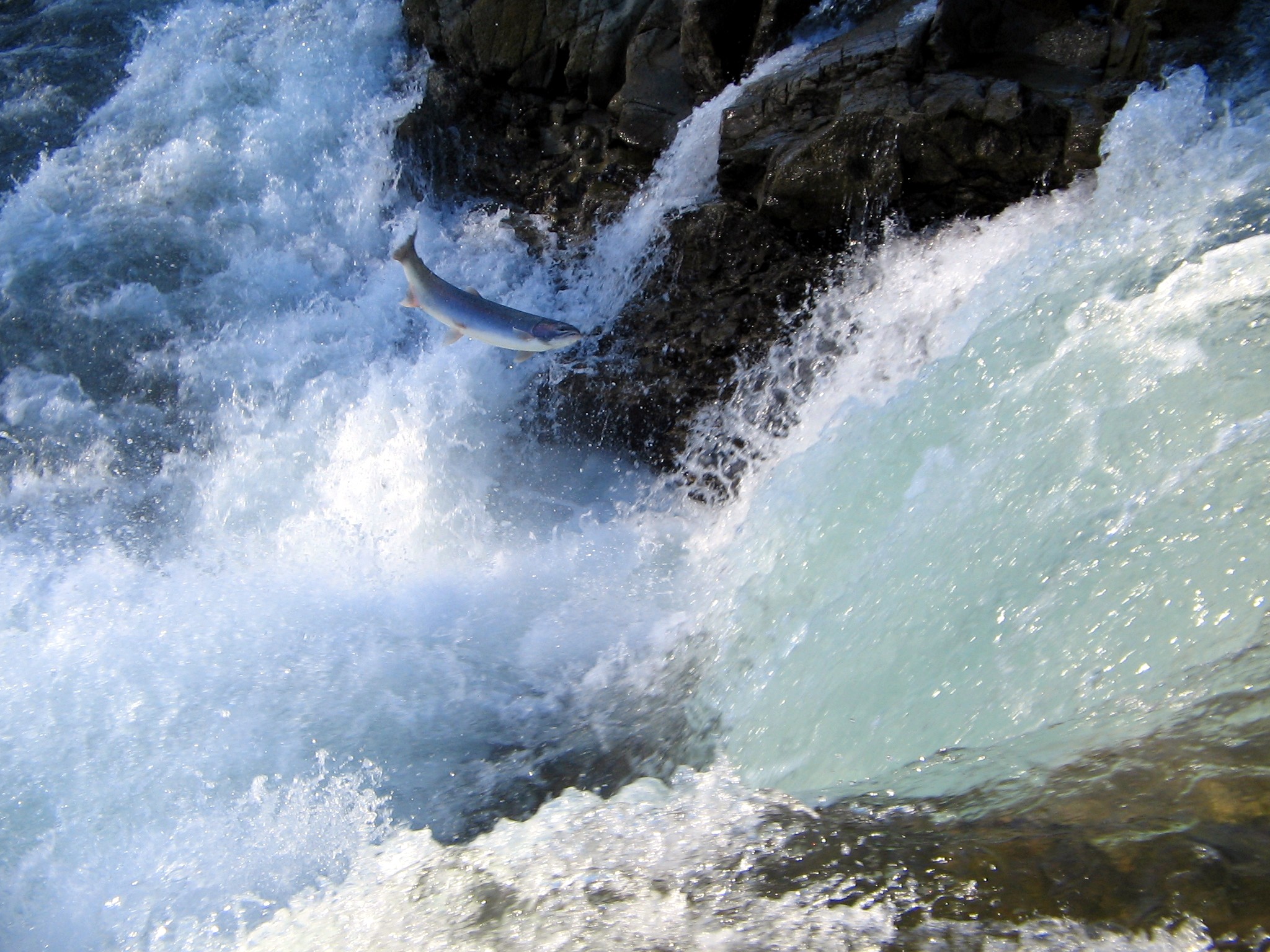 Fish migration is mass relocation by fish from one area or
Fish migration is mass relocation by fish from one area or
 As with various other aspects of fish life, zoologists have developed empirical classifications for fish migrations. The first two terms have been in long-standing wide usage while others are of more recent coinage:
* ''Anadromous'' fish migrate from the sea up (Greek: ἀνά ''aná'', "up" and δρόμος ''drómos'', "course") into fresh water to spawn, such as salmon, striped bass, and the sea lamprey.Silva, S., Araújo, M. J., Bao, M., Mucientes, G., & Cobo, F. (2014). "The haematophagous feeding stage of anadromous populations of sea lamprey Petromyzon marinus: low host selectivity and wide range of habitats". ''Hydrobiologia'', 734(1), 187–199.
* ''Catadromous'' fish migrate from fresh water down (Greek: κατά ''kata'', "down" and δρόμος ''dromos'', "course") into the sea to spawn, such as
As with various other aspects of fish life, zoologists have developed empirical classifications for fish migrations. The first two terms have been in long-standing wide usage while others are of more recent coinage:
* ''Anadromous'' fish migrate from the sea up (Greek: ἀνά ''aná'', "up" and δρόμος ''drómos'', "course") into fresh water to spawn, such as salmon, striped bass, and the sea lamprey.Silva, S., Araújo, M. J., Bao, M., Mucientes, G., & Cobo, F. (2014). "The haematophagous feeding stage of anadromous populations of sea lamprey Petromyzon marinus: low host selectivity and wide range of habitats". ''Hydrobiologia'', 734(1), 187–199.
* ''Catadromous'' fish migrate from fresh water down (Greek: κατά ''kata'', "down" and δρόμος ''dromos'', "course") into the sea to spawn, such as
 The term highly migratory species (HMS) has its origins in Article 64 of the
The term highly migratory species (HMS) has its origins in Article 64 of the
Report of the FAO workshop on vulnerable ecosystems and destructive fishing in deep sea fisheries
Rome, Fisheries Report No. 829
HTML
/ref> It can be challenging to determine the population structure of highly migratory species using physical tagging. Traditional genetic markers such as short-range PCR products, microsatellites and SNP-arrays have struggled to identify population structure and distinguish
 Remarkable catadromous migrations are made by freshwater eels. Examples are the
Remarkable catadromous migrations are made by freshwater eels. Examples are the
''Sacrificing the Salmon: A Legal and Policy History of the Decline of Columbia Basin Salmon''
Bookworld Publications. * Bond, C E (1996) ''Biology of Fishes'', 2nd ed. Saunders, pp. 599–605. * Hogan, C M (2008
''Morro Creek''
The Megalithic Portal, ed. by A. Burnham
in Carolsfield J, Harvey B, Ross C and Anton Baer A (2004) ''Migratory Fishes of South America'' World Fisheries Trust/World Bank/IDRC. .
''Physiology and Ecology of Fish Migration''
CRC Press. .
Introduction to the Convention on Migratory Species
Living North Sea
– International project on tackling fish migration problems in the North Sea Region
Fish Migration Network
– Worldwide network of specialist working on the theme fish migration {{DEFAULTSORT:Fish Migration Ichthyology Aquatic ecology Animal migration Articles containing video clips
 Fish migration is mass relocation by fish from one area or
Fish migration is mass relocation by fish from one area or body of water
A body of water or waterbody (often spelled water body) is any significant accumulation of water on the surface of Earth or another planet. The term most often refers to oceans, seas, and lakes, but it includes smaller pools of water such as ...
to another. Many types of fish migrate on a regular basis, on time scales ranging from daily to annually or longer, and over distances ranging from a few metres to thousands of kilometres. Such migrations are usually done for better feeding or to reproduce, but in other cases the reasons are unclear.
Fish migrations involve movements of schools of fish on a scale and duration larger than those arising during normal daily activities. Some particular types of migration are ''anadromous'', in which adult fish live in the sea and migrate into fresh water to spawn
Spawn or spawning may refer to:
* Spawn (biology), the eggs and sperm of aquatic animals
Arts, entertainment, and media
* Spawn (character), a fictional character in the comic series of the same name and in the associated franchise
** '' Spawn: A ...
; and ''catadromous'', in which adult fish live in fresh water and migrate into salt water to spawn.
Marine forage fish often make large migrations between their spawning, feeding and nursery grounds. Movements are associated with ocean currents and with the availability of food in different areas at different times of year. The migratory movements may partly be linked to the fact that the fish cannot identify their own offspring and moving in this way prevents cannibalism
Cannibalism is the act of consuming another individual of the same species as food. Cannibalism is a common ecological interaction in the animal kingdom and has been recorded in more than 1,500 species. Human cannibalism is well documented, bo ...
. Some species have been described by the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea
The United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS), also called the Law of the Sea Convention or the Law of the Sea Treaty, is an international agreement that establishes a legal framework for all marine and maritime activities. , 167 c ...
as highly migratory species. These are large pelagic fish
Pelagic fish live in the pelagic zone of ocean or lake waters—being neither close to the bottom nor near the shore—in contrast with demersal fish that do live on or near the bottom, and reef fish that are associated with coral reef ...
that move in and out of the exclusive economic zones of different nations, and these are covered differently in the treaty from other fish.
Salmon and striped bass are well-known anadromous fish, and freshwater eel
Eels are ray-finned fish belonging to the order Anguilliformes (), which consists of eight suborders, 19 families, 111 genera, and about 800 species. Eels undergo considerable development from the early larval stage to the eventual adult stage ...
s are catadromous fish that make large migrations. The bull shark
The bull shark (''Carcharhinus leucas''), also known as the Zambezi shark (informally zambi) in Africa and Lake Nicaragua shark in Nicaragua, is a species of requiem shark commonly found worldwide in warm, shallow waters along coasts and in ri ...
is a euryhaline
Euryhaline organisms are able to adapt to a wide range of salinities. An example of a euryhaline fish is the molly (''Poecilia sphenops'') which can live in fresh water, brackish water, or salt water.
The green crab (''Carcinus maenas'') is an e ...
species that moves at will from fresh to salt water, and many marine fish make a diel vertical migration, rising to the surface to feed at night and sinking to lower layers of the ocean by day. Some fish such as tuna move to the north and south at different times of year following temperature gradients. The patterns of migration are of great interest to the fishing industry. Movements of fish in fresh water also occur; often the fish swim upriver to spawn, and these traditional movements are increasingly being disrupted by the building of dams.
Classification
 As with various other aspects of fish life, zoologists have developed empirical classifications for fish migrations. The first two terms have been in long-standing wide usage while others are of more recent coinage:
* ''Anadromous'' fish migrate from the sea up (Greek: ἀνά ''aná'', "up" and δρόμος ''drómos'', "course") into fresh water to spawn, such as salmon, striped bass, and the sea lamprey.Silva, S., Araújo, M. J., Bao, M., Mucientes, G., & Cobo, F. (2014). "The haematophagous feeding stage of anadromous populations of sea lamprey Petromyzon marinus: low host selectivity and wide range of habitats". ''Hydrobiologia'', 734(1), 187–199.
* ''Catadromous'' fish migrate from fresh water down (Greek: κατά ''kata'', "down" and δρόμος ''dromos'', "course") into the sea to spawn, such as
As with various other aspects of fish life, zoologists have developed empirical classifications for fish migrations. The first two terms have been in long-standing wide usage while others are of more recent coinage:
* ''Anadromous'' fish migrate from the sea up (Greek: ἀνά ''aná'', "up" and δρόμος ''drómos'', "course") into fresh water to spawn, such as salmon, striped bass, and the sea lamprey.Silva, S., Araújo, M. J., Bao, M., Mucientes, G., & Cobo, F. (2014). "The haematophagous feeding stage of anadromous populations of sea lamprey Petromyzon marinus: low host selectivity and wide range of habitats". ''Hydrobiologia'', 734(1), 187–199.
* ''Catadromous'' fish migrate from fresh water down (Greek: κατά ''kata'', "down" and δρόμος ''dromos'', "course") into the sea to spawn, such as eel
Eels are ray-finned fish belonging to the order Anguilliformes (), which consists of eight suborders, 19 families, 111 genera, and about 800 species. Eels undergo considerable development from the early larval stage to the eventual adult stage ...
s.
* ''Diadromous'' fish — George S. Myers
George Sprague Myers (February 2, 1905 – November 4, 1985) was an American ichthyologist who spent most of his career at Stanford University. He served as the editor of ''Stanford Ichthyological Bulletin'' as well as president of the American So ...
coined the inclusive term ''diadromous'' in a 1949 journal article to refer to all fish that migrate between the sea and fresh water. Like the two well known terms, it was formed from classical Greek ( 'dia'' "through"; and 'dromous'' "running"). ''Diadromous'' proved a useful word, but terms proposed by Myers for other types of diadromous fish did not catch on. These included ''amphidromous'' (fish that migrate from fresh water to the seas, or vice versa, but not for the purpose of breeding), ''potamodromous'' (fish whose migrations occur wholly within fresh water), and ''oceanodromous'' (fish that live and migrate wholly in the sea).
Although these classifications were originated for fish, they are, in principle, applicable to any aquatic organism.
Forage fish
Forage fish often make great migrations between their spawning, feeding and nursery grounds. Schools of a particular stock usually travel in a triangle between these grounds. For example, one stock of herrings have their spawning ground in southern Norway, their feeding ground in Iceland and their nursery ground in northern Norway. Wide triangular journeys such as these may be important because forage fish, when feeding, cannot distinguish their own offspring.Capelin
The capelin or caplin (''Mallotus villosus'') is a small forage fish of the smelt family found in the North Atlantic, North Pacific and Arctic oceans. In summer, it grazes on dense swarms of plankton at the edge of the ice shelf. Larger capel ...
are a forage fish of the smelt
Smelt may refer to:
* Smelting, chemical process
* The common name of various fish:
** Smelt (fish), a family of small fish, Osmeridae
** Australian smelt in the family Retropinnidae and species ''Retropinna semoni''
** Big-scale sand smelt ''A ...
family found in the Atlantic and Arctic
The Arctic ( or ) is a polar region located at the northernmost part of Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean, adjacent seas, and parts of Canada (Yukon, Northwest Territories, Nunavut), Danish Realm (Greenland), Finland, Iceland, N ...
oceans. In summer, they graze on dense swarms of plankton at the edge of the ice shelf. Larger capelin also eat krill
Krill are small crustaceans of the order Euphausiacea, and are found in all the world's oceans. The name "krill" comes from the Norwegian word ', meaning "small fry of fish", which is also often attributed to species of fish.
Krill are cons ...
and other crustacean
Crustaceans (Crustacea, ) form a large, diverse arthropod taxon which includes such animals as decapods, seed shrimp, branchiopods, fish lice, krill, remipedes, isopods, barnacles, copepods, amphipods and mantis shrimp. The crustacean group ...
s. The capelin move inshore in large schools to spawn and migrate in spring and summer to feed in plankton rich areas between Iceland, Greenland and Jan Mayen. The migration is affected by ocean currents. Around Iceland maturing capelin make large northward feeding migrations in spring and summer. The return migration takes place in September to November. The spawning migration starts north of Iceland in December or January.
The diagram on the right shows the main spawning grounds and larval drift routes. Capelin on the way to feeding grounds is coloured green, capelin on the way back is blue, and the breeding grounds are red.
In a paper published in 2009, researchers from Iceland recount their application of an interacting particle model to the capelin stock around Iceland, successfully predicting the spawning migration route for 2008.
Highly migratory species
 The term highly migratory species (HMS) has its origins in Article 64 of the
The term highly migratory species (HMS) has its origins in Article 64 of the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea
The United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS), also called the Law of the Sea Convention or the Law of the Sea Treaty, is an international agreement that establishes a legal framework for all marine and maritime activities. , 167 c ...
(UNCLOS). The Convention does not provide an operational definition of the term, but in an annex (UNCLOS Annex 1) lists the species considered highly migratory by parties to the convention. The list includes: tuna and tuna-like species (albacore
The albacore (''Thunnus alalunga''), known also as the longfin tuna, is a species of tuna of the order Perciformes. It is found in temperate and tropical waters across the globe in the epipelagic and mesopelagic zones. There are six distinct st ...
, bluefin, bigeye tuna
The bigeye tuna (''Thunnus obesus'') is a species of true tuna of the genus ''Thunnus'', belonging to the wider mackerel family Scombridae. In Hawaiian, it is one of two species known as ahi, the other being the yellowfin tuna. Bigeye tuna are f ...
, skipjack, yellowfin, blackfin
The Blackfin is a family of 16-/32-bit microprocessors developed, manufactured and marketed by Analog Devices. The processors have built-in, fixed-point digital signal processor (DSP) functionality supplied by 16-bit multiply–accumulates (MA ...
, little tunny
The little tunny (''Euthynnus alletteratus''), also known as the false albacore, little tuna, bonita, bonito, or blue bonito, is a species of tuna in the family Scombridae. It can be found in the Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean and Blac ...
, southern bluefin and bullet
A bullet is a kinetic projectile, a component of firearm ammunition that is shot from a gun barrel. Bullets are made of a variety of materials, such as copper, lead, steel, polymer, rubber and even wax. Bullets are made in various shapes and co ...
), wahoo
Wahoo (''Acanthocybium solandri'') is a scombrid fish found worldwide in tropical and subtropical seas. It is best known to sports fishermen, as its speed and high-quality flesh makes it a prized and valued game fish. In Hawaii, the wahoo is ...
, pomfret
Pomfrets are perciform fishes belonging to the family Bramidae. The family currently includes 20 species across seven genera. Several species are important food sources for humans, especially ''Brama brama'' in South Asia. The earlier form of ...
, marlin, sailfish, swordfish, saury
The saury (''Cololabis adocetus'') is a species of fish (not to be confused with the Pacific saury, another species in the genus ''Cololabis'') which is a member of the family Scomberesocidae, or the saury family. It is widespread in the Eastern ...
and oceangoing sharks, dolphins and other cetaceans
Cetacea (; , ) is an infraorder of aquatic mammals that includes whales, dolphins, and porpoises. Key characteristics are their fully aquatic lifestyle, streamlined body shape, often large size and exclusively carnivorous diet. They propel them ...
.
These high trophic level
The trophic level of an organism is the position it occupies in a food web. A food chain is a succession of organisms that eat other organisms and may, in turn, be eaten themselves. The trophic level of an organism is the number of steps it i ...
oceanodromous species undertake migrations of significant but variable distances across oceans for feeding, often on forage fish, or reproduction, and also have wide geographic distributions. Thus, these species are found both inside the exclusive economic zones and in the high seas
The terms international waters or transboundary waters apply where any of the following types of bodies of water (or their drainage basins) transcend international boundaries: oceans, large marine ecosystems, enclosed or semi-enclosed region ...
outside these zones. They are pelagic species, which means they mostly live in the open ocean and do not live near the sea floor, although they may spend part of their life cycle in nearshore waters
The littoral zone or nearshore is the part of a sea, lake, or river that is close to the shore. In coastal ecology, the littoral zone includes the intertidal zone extending from the high water mark (which is rarely inundated), to coastal area ...
.
Highly migratory species can be compared with straddling stock Fish stock or stock fish may also refer to:
*Fish stocks are subpopulations of a particular species of fish.
* Fish stock (food), liquid made by boiling fish bones with vegetables, used as a base for fish soups and sauces
* Fish stocking, the practi ...
and transboundary stock. Straddling stock range both within an EEZ as well as in the high seas
The terms international waters or transboundary waters apply where any of the following types of bodies of water (or their drainage basins) transcend international boundaries: oceans, large marine ecosystems, enclosed or semi-enclosed region ...
. Transboundary stock range in the EEZs of at least two countries. A stock can be both transboundary and straddling. FAO (2007Report of the FAO workshop on vulnerable ecosystems and destructive fishing in deep sea fisheries
Rome, Fisheries Report No. 829
HTML
/ref> It can be challenging to determine the population structure of highly migratory species using physical tagging. Traditional genetic markers such as short-range PCR products, microsatellites and SNP-arrays have struggled to identify population structure and distinguish
fish stocks
Fish stocks are subpopulations of a particular species of fish, for which intrinsic parameters (growth, recruitment, mortality and fishing mortality) are traditionally regarded as the significant factors determining the stock's population dyna ...
from separate ocean basins. However, population genomic research using RAD sequencing in yellowfin tuna, albacore, and wahoo has been able to distinguish populations from different ocean basins and reveal fine-scale population structure. Similar population genomics methods have also provided improved insight towards population structure in striped marlin
The striped marlin (''Kajikia audax'') is a species of marlin found in tropical to temperate Indo-Pacific oceans not far from the surface. It is a desirable commercial and game fish. The striped marlin is a predator that hunts during the day in t ...
.
Other examples
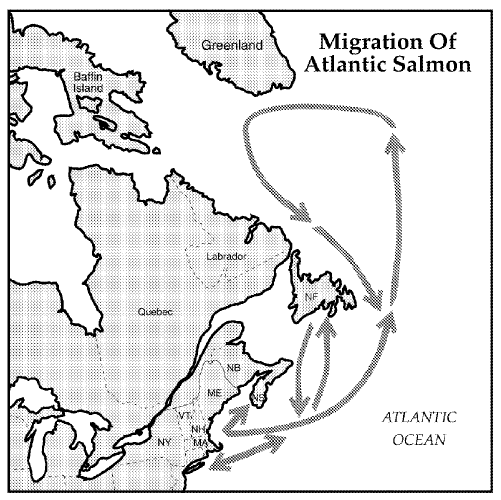
Some of the best-known anadromous fishes are thePacific salmon
''Oncorhynchus'' is a genus of fish in the family Salmonidae; it contains the Pacific salmon and Pacific trout. The name of the genus is derived from the Greek ὄγκος (ónkos, “lump, bend”) + ῥύγχος (rhúnkhos, “snout”), in r ...
species, such as Chinook (king), coho
The coho salmon (''Oncorhynchus kisutch;'' Karuk: achvuun) is a species of anadromous fish in the salmon family and one of the five Pacific salmon species. Coho salmon are also known as silver salmon or "silvers". The scientific species name i ...
(silver), chum
Chum may refer to:
Broadcasting
* CHUM Limited, a defunct Canadian media company
* CHUM Radio, now Bell Media Radio, a Canadian radio broadcasting company
* CHUM (AM), a Toronto radio station
* CHUM-FM, a Toronto radio station
* CHUM Chart, a C ...
(dog), pink (humpback) and sockeye
The sockeye salmon (''Oncorhynchus nerka''), also called red salmon, kokanee salmon, blueback salmon, or simply sockeye, is an anadromous species of salmon found in the Northern Pacific Ocean and rivers discharging into it. This species is a ...
(red) salmon. These salmon hatch in small freshwater streams. From there they migrate to the sea to mature, living there for two to six years. When mature, the salmon return to the same streams where they were hatched to spawn. Salmon are capable of going hundreds of kilometers upriver, and humans must install fish ladders in dam
A dam is a barrier that stops or restricts the flow of surface water or underground streams. Reservoirs created by dams not only suppress floods but also provide water for activities such as irrigation, human consumption, industrial use, a ...
s to enable the salmon to get past. Other examples of anadromous fishes are sea trout, three-spined stickleback, sea lamprey and shad.
Several Pacific salmon
''Oncorhynchus'' is a genus of fish in the family Salmonidae; it contains the Pacific salmon and Pacific trout. The name of the genus is derived from the Greek ὄγκος (ónkos, “lump, bend”) + ῥύγχος (rhúnkhos, “snout”), in r ...
(Chinook, coho and Steelhead) have been introduced into the US Great Lakes, and have become potamodromous, migrating between their natal waters to feeding grounds entirely within fresh water.
 Remarkable catadromous migrations are made by freshwater eels. Examples are the
Remarkable catadromous migrations are made by freshwater eels. Examples are the American eel
The American eel (''Anguilla rostrata'') is a facultative catadromous fish found on the eastern coast of North America. Freshwater eels are fish belonging to the elopomorph superorder, a group of phylogenetically ancient teleosts. The Amer ...
and the European eel
The European eel (''Anguilla anguilla'') is a species of eel, a snake-like, catadromous fish. They are normally around and rarely reach more than , but can reach a length of up to in exceptional cases.
Eels have been important sources of ...
which migrate huge distances from freshwater rivers to spawn in the Sargasso sea
The Sargasso Sea () is a region of the Atlantic Ocean bounded by four currents forming an ocean gyre. Unlike all other regions called seas, it has no land boundaries. It is distinguished from other parts of the Atlantic Ocean by its chara ...
, and whose subsequent larvae can drift in currents for months and even years before returning to their natal rivers and streams as glass eels or elvers.
An example of a euryhaline
Euryhaline organisms are able to adapt to a wide range of salinities. An example of a euryhaline fish is the molly (''Poecilia sphenops'') which can live in fresh water, brackish water, or salt water.
The green crab (''Carcinus maenas'') is an e ...
species is the bull shark
The bull shark (''Carcharhinus leucas''), also known as the Zambezi shark (informally zambi) in Africa and Lake Nicaragua shark in Nicaragua, is a species of requiem shark commonly found worldwide in warm, shallow waters along coasts and in ri ...
, which lives in Lake Nicaragua
Lake Nicaragua or Cocibolca or Granada ( es, Lago de Nicaragua, , or ) is a freshwater lake in Nicaragua. Of tectonic origin and with an area of , it is the largest lake in Central America, the 19th largest lake in the world (by area) and the t ...
of Central America and the Zambezi River of Africa. Both these habitats are fresh water, yet bull sharks will also migrate to and from the ocean. Specifically, Lake Nicaragua bull sharks migrate to the Atlantic Ocean and Zambezi bull sharks migrate to the Indian Ocean.
Diel vertical migration is a common behavior; many marine species move to the surface at night to feed, then return to the depths during daytime.
A number of large marine fishes, such as the tuna, migrate north and south annually, following temperature variations in the ocean. These are of great importance to fisheries
Fishery can mean either the enterprise of raising or harvesting fish and other aquatic life; or more commonly, the site where such enterprise takes place ( a.k.a. fishing ground). Commercial fisheries include wild fisheries and fish farms, bot ...
.
Freshwater (potamodromous) fish migrations are usually shorter, typically from lake to stream or vice versa, for spawning purposes. However, potamodromous migrations of the endangered Colorado pikeminnow
Pikeminnows, formerly squawfish, are cyprinid fish of the genus ''Ptychocheilus'' consisting of four species native to western North America. Voracious predators, they are considered an "undesirable" species in many waters, largely due to the spe ...
of the Colorado River system can be extensive. Migrations to natal spawning grounds can easily be 100 km, with maximum distances of 300 km reported from radiotagging studies. Colorado pikeminnow migrations also display a high degree of homing and the fish may make upstream or downstream migrations to reach very specific spawning locations in whitewater canyons.
Sometimes fish can be dispersed by birds that eat fish eggs. They carry eggs in the digestive tracts and then deposit them in their faeces in a new place. The survival rate for fish eggs that have passed through a bird's digestive tract is low.
Historic exploitation
Sinceprehistoric
Prehistory, also known as pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the use of the first stone tools by hominins 3.3 million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use o ...
times humans have exploited certain anadromous fishes during their migrations into freshwater streams, when they are more vulnerable to capture. Societies dating to the Millingstone Horizon
Millingstone Horizon is an archaeological period of Native American dominance denoting a period in California, United States involving extensive use of manos and other grinding technology. The interval is a subset of the Archaic Period; speci ...
are known which exploited the anadromous fishery of Morro Creek and other Pacific coast estuaries
An estuary is a partially enclosed coastal body of brackish water with one or more rivers or streams flowing into it, and with a free connection to the open sea. Estuaries form a transition zone between river environments and maritime environmen ...
. In Nevada the Paiute
Paiute (; also Piute) refers to three non-contiguous groups of indigenous peoples of the Great Basin. Although their languages are related within the Numic group of Uto-Aztecan languages, these three groups do not form a single set. The term "Paiu ...
tribe has harvested migrating Lahontan cutthroat trout
Lahontan cutthroat trout (''Oncorhynchus clarkii henshawi'') is the largest subspecies of cutthroat trout, and the state fish of Nevada. It is one of three subspecies of cutthroat trout that are listed as federally threatened.
Natural history
...
along the Truckee River
The Truckee River is a river in the U.S. states of California and Nevada. The river flows northeasterly and is long.U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map accessed October 20, 2012 Th ...
since prehistoric times. This fishing practice continues to current times, and the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency has supported research to assure the water quality in the Truckee can support suitable populations of the Lahontan cutthroat trout.
Myxovirus genes
Becausesalmonids
Salmonidae is a family of ray-finned fish that constitutes the only currently extant family in the order Salmoniformes . It includes salmon (both Atlantic and Pacific species), trout (both ocean-going and landlocked), chars, freshwater whitefi ...
live an anadromous lifestyle, they encounter a larger range of viruses from both freshwater and marine ecosystems. Myxovirus resistance (Mx) proteins are part of a GTP-ase family that aid in viral immunity, and previously, rainbow trout ('' Oncorhynchus mykiss'') have been shown to possess three different Mx genes to aid in viral defence in both environments. The number of Mx genes can differ among species of fish, with numbers ranging from 1 to 9 and some outliers like Gadiformes that have totally lost their Mx genes. A study was performed by Wang et al. (2019) to identify more potential Mx genes that resided in rainbow trout. An additional six Mx genes were identified in that study, now named Mx4-9. They also concluded that the trout Mx genes were "differentially expressed constitutively in tissues" and that this expression is increased during development. The Mx gene family is expressed at high levels in the blood and intestine during development, suggesting they are a key to immune defense for the growing fish. The idea that these genes play an important role in development against viruses suggests they are critical in the trout's success in an anadromous lifestyle.
See also
* * * * * * *Notes
References
* Blumm, M (2002''Sacrificing the Salmon: A Legal and Policy History of the Decline of Columbia Basin Salmon''
Bookworld Publications. * Bond, C E (1996) ''Biology of Fishes'', 2nd ed. Saunders, pp. 599–605. * Hogan, C M (2008
''Morro Creek''
The Megalithic Portal, ed. by A. Burnham
in Carolsfield J, Harvey B, Ross C and Anton Baer A (2004) ''Migratory Fishes of South America'' World Fisheries Trust/World Bank/IDRC. .
Further reading
* Ueda H and Tsukamoto K (eds) (2013''Physiology and Ecology of Fish Migration''
CRC Press. .
External links
*United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmonizi ...
Introduction to the Convention on Migratory Species
Living North Sea
– International project on tackling fish migration problems in the North Sea Region
Fish Migration Network
– Worldwide network of specialist working on the theme fish migration {{DEFAULTSORT:Fish Migration Ichthyology Aquatic ecology Animal migration Articles containing video clips