altocumulus cloud on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Altocumulus (From Latin ''Altus'', "high", ''cumulus'', "heaped") is a middle-altitude
 :*Species: Altocumulus has four species. The stratiformis species (Ac str) is composed of sheets or relatively flat patches of stratocumuliform cloud. The synoptic coding is determined by the predominant variety or occasionally by the genitus mother cloud. Altocumulus lenticularis (Ac len
:*Species: Altocumulus has four species. The stratiformis species (Ac str) is composed of sheets or relatively flat patches of stratocumuliform cloud. The synoptic coding is determined by the predominant variety or occasionally by the genitus mother cloud. Altocumulus lenticularis (Ac len
Image:Ac perlucidus.JPG, Altocumulus perlucidus
Image:Lenticular clouds and Mount Hotaka from Mount Otensho 1994-06-25.jpg, Altocumulus lenticularis
Image:Partially illuminated Ac with shadows.JPG, Altocumulus at sunset
Image:Hiranandani-Gardens-3.jpg, Altocumulus floccus with line of castellanus
Image:Altocumulus1.jpg, Altocumulus during the day
Image:AltocumulusUndulatusClouds.png, Altocumulus undulatus during a cold front
File:Altocumulus-mamma.jpg, Altocumulus mamma
File:Altocumulus radiatus clouds 1.jpg, Altocumulus stratiformis radiatus
International Cloud Atlas – Altocumulus
Clouds-Online.com Cloud Atlas with many photos and description of the different cloud genusNational Science Digital Library – Altocumulus
WW2010: University of Illinois
{{Cloud types Cumulus
cloud
In meteorology, a cloud is an aerosol consisting of a visible mass of miniature liquid droplets, frozen crystals, or other particles suspended in the atmosphere of a planetary body or similar space. Water or various other chemicals may ...
genus that belongs mainly to the ''stratocumuliform'' physical category characterized by globular masses or rolls in layers or patches, the individual elements being larger and darker than those of cirrocumulus and smaller than those of stratocumulus
A stratocumulus cloud, occasionally called a cumulostratus, belongs to a genus-type of clouds characterized by large dark, rounded masses, usually in groups, lines, or waves, the individual elements being larger than those in altocumulus, and th ...
. However, if the layers become tufted in appearance due to increased airmass instability, then the altocumulus clouds become more purely ''cumuliform'' in structure. Like other cumuliform and stratocumuliform clouds, altocumulus signifies convection
Convection is single or multiphase fluid flow that occurs spontaneously due to the combined effects of material property heterogeneity and body forces on a fluid, most commonly density and gravity (see buoyancy). When the cause of the c ...
. A sheet of partially conjoined altocumulus perlucidus is sometimes found preceding a weakening warm front, where the altostratus is starting to fragment, resulting in patches of altocumulus perlucidus between the areas of altostratus. Altocumulus is also commonly found between the warm and cold fronts in a depression, although this is often hidden by lower clouds.
Towering altocumulus, known as altocumulus castellanus, frequently signals the development of thunderstorms
A thunderstorm, also known as an electrical storm or a lightning storm, is a storm characterized by the presence of lightning and its acoustic effect on the Earth's atmosphere, known as thunder. Relatively weak thunderstorms are somet ...
later in the day, as it shows instability and convection in the middle levels of the troposphere (the lowest layer of the atmosphere), the area where towering cumulus clouds can turn into cumulonimbus
Cumulonimbus (from Latin ''cumulus'', "heaped" and ''nimbus'', "rainstorm") is a dense, towering vertical cloud, typically forming from water vapor condensing in the lower troposphere that builds upward carried by powerful buoyant air currents. ...
. It is therefore one of three warning clouds often recorded by the aviation industry, the other two being towering cumulus and cumulonimbus. Altocumulus generally forms about above ground level, a similar level to altostratus formations, and satellite photography has revealed that the two types of cloud can create formations that can stretch for thousands of square miles. Extensive altocumulus formations, particularly if they take the form of undulatus are often referred to as altocumulus mackerel sky.
Subtypes
 :*Species: Altocumulus has four species. The stratiformis species (Ac str) is composed of sheets or relatively flat patches of stratocumuliform cloud. The synoptic coding is determined by the predominant variety or occasionally by the genitus mother cloud. Altocumulus lenticularis (Ac len
:*Species: Altocumulus has four species. The stratiformis species (Ac str) is composed of sheets or relatively flat patches of stratocumuliform cloud. The synoptic coding is determined by the predominant variety or occasionally by the genitus mother cloud. Altocumulus lenticularis (Ac len lenticular cloud
Lenticular clouds (Latin: ''Lenticularis'' lentil-shaped, from ''lenticula'' lentil) are stationary clouds that form mostly in the troposphere, typically in parallel alignment to the wind direction. They are often comparable in appearance to a ...
) is a lens-shaped middle cloud which can resemble flying saucers and may occasionally be mistaken for "unidentified flying object
An unidentified flying object (UFO), more recently renamed by US officials as a UAP (unidentified aerial phenomenon), is any perceived aerial phenomenon that cannot be immediately identified or explained. On investigation, most UFOs are Ide ...
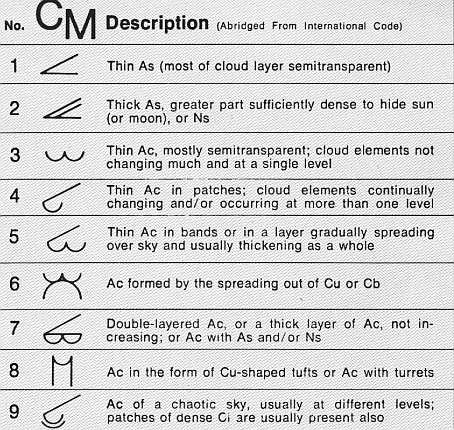
s". This is formed by uplift usually associated with mountains. but usually with at least some grey shading. It is coded CM4 on the SYNOP weather observation. Grey shading is also seen with altocumulus castellanus (Ac cas), a turreted middle cloud that can achieve significant vertical development and signals increasing air mass instability. It is nevertheless usually classified as middle rather than vertical and is coded CM8. The floccus species (Ac flo) is a tufted middle cloud which is also associated with greater instability. It shares the same code CM8. Chaotic altocumulus, which is typically poorly defined with multiple species or transitional forms arranged in several layers, is coded CM9.
::*Opacity-based varieties: Altocumulus stratiformis has three opacity-based varieties; ''Translucidus'' (CM3), ''perlucidus'' (CM3 or 7 depending on predominant opacity), and ''opacus'' (CM7). Varieties based on opacity are not commonly associated with the species lenticularis, castellanus, or floccus.
::*Pattern-based varieties: ''Radiatus'' (arranged in parallel bands) is sometimes seen with the stratformis and castellanus species. Altocumulus stratiformis radiatus of any opacity is coded CM5 if it is increasing in amount. The ''duplicatus'' or ''undulatus'' varieties are occasionally seen with the stratiformis and lenticularis species. Altocumulus stratiformis duplicatus is coded CM7 if it is not overridden by another coding of higher importance. ''Lacunosus'' is very occasionally associated with altocumulus of the species stratiformis, castellanus, or floccus.
:::*Precipitation-based supplementary feature: Altocumulus often produces virga but usually not precipitation that reaches the ground.
:::*Cloud-based supplementary feature: Mamma caused by localized downdrafts in the cloud layer are occasionally seen with altocumulus. A newly recognized type is the asperitas feature that is characterized by chaotic undulations caused by severe wind shear.
:::*Genitus Mother clouds: Altocumulus stratiformis cumulogenitus or cumulonimbogenitus can form when the middle or upper part of a towering free convective cloud begins to spread horizontally due to a loss of convective lift. It is coded CM6.
:::*Mutatus mother clouds: Altocumulus can form due to the complete transformation of cirrocumulus, altostratus, nimbostratus, or stratocumulus.
Gallery
See also
*Atmospheric convection
Atmospheric convection is the result of a parcel-environment instability, or temperature difference layer in the atmosphere. Different lapse rates within dry and moist air masses lead to instability. Mixing of air during the day which expands the ...
* Mackerel sky
References
External links
International Cloud Atlas – Altocumulus
Clouds-Online.com Cloud Atlas with many photos and description of the different cloud genus
WW2010: University of Illinois
{{Cloud types Cumulus