adrenal gland on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The adrenal glands (also known as suprarenal glands) are
 The adrenal glands are located on both sides of the body in the retroperitoneum, above and slightly medial to the
The adrenal glands are located on both sides of the body in the retroperitoneum, above and slightly medial to the
 The adrenal cortex is the outer region and also the largest part of an adrenal gland. It is divided into three separate zones: zona glomerulosa, zona fasciculata and zona reticularis. Each zone is responsible for producing specific hormones.
The adrenal cortex is the outermost layer of the adrenal gland. Within the cortex are three layers, called "zones". When viewed under a microscope each layer has a distinct appearance, and each has a different function. The adrenal cortex is devoted to production of
The adrenal cortex is the outer region and also the largest part of an adrenal gland. It is divided into three separate zones: zona glomerulosa, zona fasciculata and zona reticularis. Each zone is responsible for producing specific hormones.
The adrenal cortex is the outermost layer of the adrenal gland. Within the cortex are three layers, called "zones". When viewed under a microscope each layer has a distinct appearance, and each has a different function. The adrenal cortex is devoted to production of
 The adrenal gland secretes a number of different hormones which are metabolised by
The adrenal gland secretes a number of different hormones which are metabolised by
 All
All  Glucocorticoids are under the regulatory influence of the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis (HPA) axis. Glucocorticoid synthesis is stimulated by adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), a hormone released into the bloodstream by the
Glucocorticoids are under the regulatory influence of the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis (HPA) axis. Glucocorticoid synthesis is stimulated by adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), a hormone released into the bloodstream by the
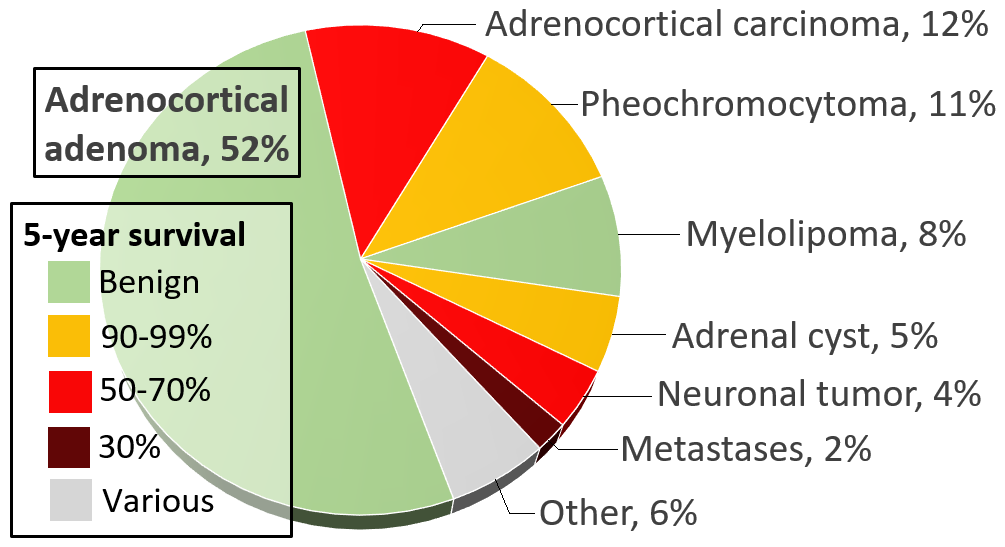 Adrenal tumors are commonly found as incidentalomas, unexpected
Adrenal tumors are commonly found as incidentalomas, unexpected
Adrenal gland at the Human Protein Atlas
*
Adrenal gland histology
* – "Adrenal Gland" * * – "Posterior Abdominal Wall: The Retroperitoneal Fat and Suprarenal Glands"
from Colorado State University * {{DEFAULTSORT:Adrenal Gland Adrenaline Endocrine system anatomy
endocrine gland
The endocrine system is a network of glands and organs located throughout the body. Along with the nervous system, it makes the neuroendocrine system, which controls and regulates many of the body's functions. Endocrine glands are ductless gland ...
s that produce a variety of hormones including adrenaline
Adrenaline, also known as epinephrine, is a hormone and medication which is involved in regulating visceral functions (e.g., respiration). It appears as a white microcrystalline granule. Adrenaline is normally produced by the adrenal glands a ...
and the steroids aldosterone
Aldosterone is the main mineralocorticoid steroid hormone produced by the zona glomerulosa of the adrenal cortex in the adrenal gland. It is essential for sodium conservation in the kidney, salivary glands, sweat glands, and colon. It plays ...
and cortisol
Cortisol is a steroid hormone in the glucocorticoid class of hormones and a stress hormone. When used as medication, it is known as hydrocortisone.
Cortisol is produced in many animals, mainly by the ''zona fasciculata'' of the adrenal corte ...
. They are found above the kidneys
In humans, the kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped blood-filtering organs that are a multilobar, multipapillary form of mammalian kidneys, usually without signs of external lobulation. They are located on the left and right in the retro ...
. Each gland has an outer cortex
Cortex or cortical may refer to:
Biology
* Cortex (anatomy), the outermost layer of an organ
** Cerebral cortex, the outer layer of the vertebrate cerebrum, part of which is the ''forebrain''
*** Motor cortex, the regions of the cerebral cortex i ...
which produces steroid hormone
A steroid hormone is a steroid that acts as a hormone. Steroid hormones can be grouped into two classes: corticosteroids (typically made in the adrenal cortex, hence ''cortico-'') and sex steroids (typically made in the gonads or placenta). Wit ...
s and an inner medulla. The adrenal cortex itself is divided into three main zones: the zona glomerulosa, the zona fasciculata and the zona reticularis.
The adrenal cortex produces three main types of steroid hormone
A steroid hormone is a steroid that acts as a hormone. Steroid hormones can be grouped into two classes: corticosteroids (typically made in the adrenal cortex, hence ''cortico-'') and sex steroids (typically made in the gonads or placenta). Wit ...
s: mineralocorticoid
Mineralocorticoids are a class of corticosteroids, which in turn are a class of steroid hormones. Mineralocorticoids are produced in the adrenal cortex and influence salt and water balances (electrolyte balance and fluid balance). The primary ...
s, glucocorticoid
Glucocorticoids (or, less commonly, glucocorticosteroids) are a class of corticosteroids, which are a class of steroid hormones. Glucocorticoids are corticosteroids that bind to the glucocorticoid receptor that is present in almost every vertebra ...
s, and androgen
An androgen (from Greek ''andr-'', the stem of the word meaning ) is any natural or synthetic steroid hormone that regulates the development and maintenance of male characteristics in vertebrates by binding to androgen receptors. This includes ...
s. Mineralocorticoids (such as aldosterone
Aldosterone is the main mineralocorticoid steroid hormone produced by the zona glomerulosa of the adrenal cortex in the adrenal gland. It is essential for sodium conservation in the kidney, salivary glands, sweat glands, and colon. It plays ...
) produced in the zona glomerulosa help in the regulation of blood pressure and electrolyte balance. The glucocorticoids cortisol
Cortisol is a steroid hormone in the glucocorticoid class of hormones and a stress hormone. When used as medication, it is known as hydrocortisone.
Cortisol is produced in many animals, mainly by the ''zona fasciculata'' of the adrenal corte ...
and cortisone
Cortisone is a pregnene (21-carbon) steroid hormone. It is a naturally-occurring corticosteroid metabolite that is also used as a pharmaceutical prodrug. Cortisol is converted by the action of the enzyme corticosteroid 11-beta-dehydrogenase ...
are synthesized in the zona fasciculata; their functions include the regulation of metabolism
Metabolism (, from ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cellular processes; the co ...
and immune system
The immune system is a network of biological systems that protects an organism from diseases. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to bacteria, as well as Tumor immunology, cancer cells, Parasitic worm, parasitic ...
suppression. The innermost layer of the cortex, the zona reticularis, produces androgens that are converted to fully functional sex hormones in the gonad
A gonad, sex gland, or reproductive gland is a Heterocrine gland, mixed gland and sex organ that produces the gametes and sex hormones of an organism. Female reproductive cells are egg cells, and male reproductive cells are sperm. The male gon ...
s and other target organs. The production of steroid hormones is called steroidogenesis, and involves a number of reactions and processes that take place in cortical cells. The medulla produces the catecholamines, which function to produce a rapid response throughout the body in stress situations.
A number of endocrine diseases involve dysfunctions of the adrenal gland. Overproduction of cortisol leads to Cushing's syndrome, whereas insufficient production is associated with Addison's disease. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH) is a group of Genetic disorder#Autosomal recessive, autosomal recessive disorders characterized by impaired cortisol synthesis. It results from the deficiency of one of the five enzymes required for the Biosy ...
is a genetic disease produced by dysregulation of endocrine control mechanisms. A variety of tumors
A neoplasm () is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists ...
can arise from adrenal tissue and are commonly found in medical imaging
Medical imaging is the technique and process of imaging the interior of a body for clinical analysis and medical intervention, as well as visual representation of the function of some organs or tissues (physiology). Medical imaging seeks to revea ...
when searching for other diseases.
Structure
 The adrenal glands are located on both sides of the body in the retroperitoneum, above and slightly medial to the
The adrenal glands are located on both sides of the body in the retroperitoneum, above and slightly medial to the kidney
In humans, the kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped blood-filtering organ (anatomy), organs that are a multilobar, multipapillary form of mammalian kidneys, usually without signs of external lobulation. They are located on the left and rig ...
s. In humans, the right adrenal gland is pyramidal in shape, whereas the left is semilunar or crescent shaped and somewhat larger. The adrenal glands measure approximately 5 cm in length, 3 cm in width, and up to 1 cm in thickness. Their combined weight in an adult human ranges from 7 to 10 grams. The glands are yellowish in colour.
The adrenal glands are surrounded by a fatty capsule and lie within the renal fascia, which also surrounds the kidneys. A weak septum
In biology, a septum (Latin language, Latin for ''something that encloses''; septa) is a wall, dividing a Body cavity, cavity or structure into smaller ones. A cavity or structure divided in this way may be referred to as septate.
Examples
Hum ...
(wall) of connective tissue
Connective tissue is one of the four primary types of animal tissue, a group of cells that are similar in structure, along with epithelial tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. It develops mostly from the mesenchyme, derived from the mesod ...
separates the glands from the kidneys. The adrenal glands are directly below the diaphragm, and are attached to the crura of the diaphragm by the renal fascia.
Each adrenal gland has two distinct parts, each with a unique function, the outer adrenal cortex and the inner medulla, both of which produce hormones.
Adrenal cortex
 The adrenal cortex is the outer region and also the largest part of an adrenal gland. It is divided into three separate zones: zona glomerulosa, zona fasciculata and zona reticularis. Each zone is responsible for producing specific hormones.
The adrenal cortex is the outermost layer of the adrenal gland. Within the cortex are three layers, called "zones". When viewed under a microscope each layer has a distinct appearance, and each has a different function. The adrenal cortex is devoted to production of
The adrenal cortex is the outer region and also the largest part of an adrenal gland. It is divided into three separate zones: zona glomerulosa, zona fasciculata and zona reticularis. Each zone is responsible for producing specific hormones.
The adrenal cortex is the outermost layer of the adrenal gland. Within the cortex are three layers, called "zones". When viewed under a microscope each layer has a distinct appearance, and each has a different function. The adrenal cortex is devoted to production of hormone
A hormone (from the Ancient Greek, Greek participle , "setting in motion") is a class of cell signaling, signaling molecules in multicellular organisms that are sent to distant organs or tissues by complex biological processes to regulate physio ...
s, namely aldosterone
Aldosterone is the main mineralocorticoid steroid hormone produced by the zona glomerulosa of the adrenal cortex in the adrenal gland. It is essential for sodium conservation in the kidney, salivary glands, sweat glands, and colon. It plays ...
, cortisol
Cortisol is a steroid hormone in the glucocorticoid class of hormones and a stress hormone. When used as medication, it is known as hydrocortisone.
Cortisol is produced in many animals, mainly by the ''zona fasciculata'' of the adrenal corte ...
, and androgen
An androgen (from Greek ''andr-'', the stem of the word meaning ) is any natural or synthetic steroid hormone that regulates the development and maintenance of male characteristics in vertebrates by binding to androgen receptors. This includes ...
s.
Zona glomerulosa
The outermost zone of the adrenal cortex is the zona glomerulosa. It lies immediately under the fibrous capsule of the gland. Cells in this layer form oval groups, separated by thin strands of connective tissue from the fibrous capsule of the gland and carry widecapillaries
A capillary is a small blood vessel, from 5 to 10 micrometres in diameter, and is part of the microcirculation system. Capillaries are microvessels and the smallest blood vessels in the body. They are composed of only the tunica intima (the in ...
.
This layer is the main site for production of aldosterone
Aldosterone is the main mineralocorticoid steroid hormone produced by the zona glomerulosa of the adrenal cortex in the adrenal gland. It is essential for sodium conservation in the kidney, salivary glands, sweat glands, and colon. It plays ...
, a mineralocorticoid
Mineralocorticoids are a class of corticosteroids, which in turn are a class of steroid hormones. Mineralocorticoids are produced in the adrenal cortex and influence salt and water balances (electrolyte balance and fluid balance). The primary ...
, by the action of the enzyme aldosterone synthase. Aldosterone plays an important role in the long-term regulation of blood pressure.
Zona fasciculata
The zona fasciculata is situated between the zona glomerulosa and zona reticularis. Cells in this layer are responsible for producingglucocorticoid
Glucocorticoids (or, less commonly, glucocorticosteroids) are a class of corticosteroids, which are a class of steroid hormones. Glucocorticoids are corticosteroids that bind to the glucocorticoid receptor that is present in almost every vertebra ...
s such as cortisol
Cortisol is a steroid hormone in the glucocorticoid class of hormones and a stress hormone. When used as medication, it is known as hydrocortisone.
Cortisol is produced in many animals, mainly by the ''zona fasciculata'' of the adrenal corte ...
. It is the largest of the three layers, accounting for nearly 80% of the volume of the cortex. In the zona fasciculata, cells are arranged in columns radially oriented towards the medulla. Cells contain numerous lipid droplets, abundant mitochondria
A mitochondrion () is an organelle found in the cells of most eukaryotes, such as animals, plants and fungi. Mitochondria have a double membrane structure and use aerobic respiration to generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is us ...
and a complex smooth endoplasmic reticulum.
Zona reticularis
The innermost cortical layer, the zona reticularis, lies directly adjacent to the medulla. It producesandrogen
An androgen (from Greek ''andr-'', the stem of the word meaning ) is any natural or synthetic steroid hormone that regulates the development and maintenance of male characteristics in vertebrates by binding to androgen receptors. This includes ...
s, mainly dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA), DHEA sulfate (DHEA-S), and androstenedione (the precursor to testosterone
Testosterone is the primary male sex hormone and androgen in Male, males. In humans, testosterone plays a key role in the development of Male reproductive system, male reproductive tissues such as testicles and prostate, as well as promoting se ...
) in humans. Its small cells form irregular cords and clusters, separated by capillaries and connective tissue. The cells contain relatively small quantities of cytoplasm and lipid droplets, and sometimes display brown lipofuscin pigment.
Medulla
The adrenal medulla is at the center of each adrenal gland, and is surrounded by the adrenal cortex. The chromaffin cells of the medulla are the body's main source of the catecholamines, such as adrenaline and noradrenaline, released by the medulla. Approximately 20% noradrenaline (norepinephrine) and 80% adrenaline (epinephrine) are secreted here. The adrenal medulla is driven by thesympathetic nervous system
The sympathetic nervous system (SNS or SANS, sympathetic autonomic nervous system, to differentiate it from the somatic nervous system) is one of the three divisions of the autonomic nervous system, the others being the parasympathetic nervous sy ...
via preganglionic fibers originating in the thoracic spinal cord, from vertebrae T5–T11. Because it is innervated by preganglionic nerve fibers, the adrenal medulla can be considered as a specialized sympathetic ganglion. Unlike other sympathetic ganglia, however, the adrenal medulla lacks distinct synapses and releases its secretions directly into the blood.
Blood supply
The adrenal glands have one of the greatest blood supply rates per gram of tissue of any organ: up to 60 small arteries may enter each gland. Three arteries usually supply each adrenal gland: * The superior suprarenal artery, a branch of the inferior phrenic artery * The middle suprarenal artery, a direct branch of the abdominal aorta * The inferior suprarenal artery, a branch of the renal artery These blood vessels supply a network of small arteries within the capsule of the adrenal glands. Thin strands of the capsule enter the glands, carrying blood to them. Venous blood is drained from the glands by the suprarenal veins, usually one for each gland: * The right suprarenal vein drains into theinferior vena cava
The inferior vena cava is a large vein that carries the deoxygenated blood from the lower and middle body into the right atrium of the heart. It is formed by the joining of the right and the left common iliac veins, usually at the level of the ...
.
* The left suprarenal vein drains into the left renal vein or the left inferior phrenic vein.
The central adrenomedullary vein, in the adrenal medulla, is an unusual type of blood vessel. Its structure is different from the other veins in that the smooth muscle
Smooth muscle is one of the three major types of vertebrate muscle tissue, the others being skeletal and cardiac muscle. It can also be found in invertebrates and is controlled by the autonomic nervous system. It is non- striated, so-called bec ...
in its tunica media
The tunica media (Neo-Latin "middle coat"), or media for short, is the middle tunica (layer) of an artery or vein. It lies between the internal elastic lamina of the tunica intima on the inside and the tunica externa on the outside.
Artery
The ...
(the middle layer of the vessel) is arranged in conspicuous, longitudinally oriented bundles.
Variability
The adrenal glands may not develop at all, or may be fused in the midline behind theaorta
The aorta ( ; : aortas or aortae) is the main and largest artery in the human body, originating from the Ventricle (heart), left ventricle of the heart, branching upwards immediately after, and extending down to the abdomen, where it splits at ...
. These are associated with other congenital abnormalities, such as failure of the kidneys to develop, or fused kidneys. The gland may develop with a partial or complete absence of the cortex, or may develop in an unusual location.
Function
 The adrenal gland secretes a number of different hormones which are metabolised by
The adrenal gland secretes a number of different hormones which are metabolised by enzyme
An enzyme () is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different mol ...
s either within the gland or in other parts of the body. These hormones are involved in a number of essential biological functions.
Corticosteroids
Corticosteroid
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates, as well as the synthetic analogues of these hormones. Two main classes of corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are invo ...
s are a group of steroid hormones produced from the cortex of the adrenal gland, from which they are named.
* Mineralocorticoids such as aldosterone
Aldosterone is the main mineralocorticoid steroid hormone produced by the zona glomerulosa of the adrenal cortex in the adrenal gland. It is essential for sodium conservation in the kidney, salivary glands, sweat glands, and colon. It plays ...
regulate salt ("mineral") balance and blood pressureMarieb Human Anatomy & Physiology 9th edition, chapter:16, page:629, question number:14
* Glucocorticoids such as cortisol
Cortisol is a steroid hormone in the glucocorticoid class of hormones and a stress hormone. When used as medication, it is known as hydrocortisone.
Cortisol is produced in many animals, mainly by the ''zona fasciculata'' of the adrenal corte ...
influence metabolism rates of proteins, fats and sugars ("glucose").
* Androgens such as dehydroepiandrosterone.
;Mineralocorticoids
The adrenal gland produces aldosterone
Aldosterone is the main mineralocorticoid steroid hormone produced by the zona glomerulosa of the adrenal cortex in the adrenal gland. It is essential for sodium conservation in the kidney, salivary glands, sweat glands, and colon. It plays ...
, a mineralocorticoid
Mineralocorticoids are a class of corticosteroids, which in turn are a class of steroid hormones. Mineralocorticoids are produced in the adrenal cortex and influence salt and water balances (electrolyte balance and fluid balance). The primary ...
, which is important in the regulation of salt ("mineral") balance and blood volume. In the kidneys, aldosterone acts on the distal convoluted tubules and the collecting ducts by increasing the reabsorption of sodium
Sodium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Na (from Neo-Latin ) and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal. Sodium is an alkali metal, being in group 1 element, group 1 of the peri ...
and the excretion of both potassium and hydrogen ions. Aldosterone is responsible for the reabsorption of about 2% of filtered glomerular filtrate. Sodium retention is also a response of the distal colon and sweat glands to aldosterone receptor stimulation. Angiotensin II
Angiotensin is a peptide hormone that causes vasoconstriction and an increase in blood pressure. It is part of the renin–angiotensin system, which regulates blood pressure. Angiotensin also stimulates the release of aldosterone from the ...
and extracellular potassium
Potassium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol K (from Neo-Latin ) and atomic number19. It is a silvery white metal that is soft enough to easily cut with a knife. Potassium metal reacts rapidly with atmospheric oxygen to ...
are the two main regulators of aldosterone production. The amount of sodium present in the body affects the extracellular volume, which in turn influences blood pressure
Blood pressure (BP) is the pressure of Circulatory system, circulating blood against the walls of blood vessels. Most of this pressure results from the heart pumping blood through the circulatory system. When used without qualification, the term ...
. Therefore, the effects of aldosterone in sodium retention are important for the regulation of blood pressure.
;Glucocorticoids
Cortisol
Cortisol is a steroid hormone in the glucocorticoid class of hormones and a stress hormone. When used as medication, it is known as hydrocortisone.
Cortisol is produced in many animals, mainly by the ''zona fasciculata'' of the adrenal corte ...
is the main glucocorticoid
Glucocorticoids (or, less commonly, glucocorticosteroids) are a class of corticosteroids, which are a class of steroid hormones. Glucocorticoids are corticosteroids that bind to the glucocorticoid receptor that is present in almost every vertebra ...
in humans. In species that do not create cortisol, this role is played by corticosterone instead. Glucocorticoids have many effects on metabolism
Metabolism (, from ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cellular processes; the co ...
. As their name suggests, they increase the circulating level of glucose
Glucose is a sugar with the Chemical formula#Molecular formula, molecular formula , which is often abbreviated as Glc. It is overall the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates. It is mainly made by plants and most algae d ...
. This is the result of an increase in the mobilization of amino acids
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although over 500 amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the Proteinogenic amino acid, 22 α-amino acids incorporated into p ...
from protein and the stimulation of synthesis of glucose from these amino acids in the liver. In addition, they increase the levels of free fatty acids, which cells can use as an alternative to glucose to obtain energy. Glucocorticoids also have effects unrelated to the regulation of blood sugar levels, including the suppression of the immune system and a potent anti-inflammatory
Anti-inflammatory is the property of a substance or treatment that reduces inflammation, fever or swelling. Anti-inflammatory drugs, also called anti-inflammatories, make up about half of analgesics. These drugs reduce pain by inhibiting mechan ...
effect. Cortisol reduces the capacity of osteoblast
Osteoblasts (from the Greek combining forms for " bone", ὀστέο-, ''osteo-'' and βλαστάνω, ''blastanō'' "germinate") are cells with a single nucleus that synthesize bone. However, in the process of bone formation, osteoblasts fu ...
s to produce new bone tissue and decreases the absorption of calcium in the gastrointestinal tract
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the Digestion, digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The tract is the largest of the body's systems, after the cardiovascula ...
.
The adrenal gland secretes a basal level of cortisol but can also produce bursts of the hormone in response to adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) from the anterior pituitary
The anterior pituitary (also called the adenohypophysis or pars anterior) is a major Organ (anatomy), organ of the endocrine system. The anterior pituitary is the glandular, Anatomical terms of location#Usage in human anatomy, anterior lobe that t ...
. Cortisol is not evenly released during the day – its concentrations in the blood are highest in the early morning and lowest in the evening as a result of the circadian rhythm
A circadian rhythm (), or circadian cycle, is a natural oscillation that repeats roughly every 24 hours. Circadian rhythms can refer to any process that originates within an organism (i.e., Endogeny (biology), endogenous) and responds to the env ...
of ACTH secretion. Cortisone
Cortisone is a pregnene (21-carbon) steroid hormone. It is a naturally-occurring corticosteroid metabolite that is also used as a pharmaceutical prodrug. Cortisol is converted by the action of the enzyme corticosteroid 11-beta-dehydrogenase ...
is an inactive product of the action of the enzyme 11β-HSD on cortisol. The reaction catalyzed by 11β-HSD is reversible, which means that it can turn administered cortisone into cortisol, the biologically active hormone.
;Formation
corticosteroid
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates, as well as the synthetic analogues of these hormones. Two main classes of corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are invo ...
hormones share cholesterol
Cholesterol is the principal sterol of all higher animals, distributed in body Tissue (biology), tissues, especially the brain and spinal cord, and in Animal fat, animal fats and oils.
Cholesterol is biosynthesis, biosynthesized by all anima ...
as a common precursor. Therefore, the first step in steroidogenesis is cholesterol uptake or synthesis. Cells that produce steroid hormones can acquire cholesterol through two paths. The main source is through dietary cholesterol transported via the blood as cholesterol esters within low density lipoproteins (LDL). LDL enters the cells through receptor-mediated endocytosis. The other source of cholesterol is synthesis in the cell's endoplasmic reticulum
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a part of a transportation system of the eukaryote, eukaryotic cell, and has many other important functions such as protein folding. The word endoplasmic means "within the cytoplasm", and reticulum is Latin for ...
. Synthesis can compensate when LDL levels are abnormally low. In the lysosome
A lysosome () is a membrane-bound organelle that is found in all mammalian cells, with the exception of red blood cells (erythrocytes). There are normally hundreds of lysosomes in the cytosol, where they function as the cell’s degradation cent ...
, cholesterol esters are converted to free cholesterol, which is then used for steroidogenesis or stored in the cell.
The initial part of conversion of cholesterol into steroid hormones involves a number of enzymes of the cytochrome P450
Cytochromes P450 (P450s or CYPs) are a Protein superfamily, superfamily of enzymes containing heme as a cofactor (biochemistry), cofactor that mostly, but not exclusively, function as monooxygenases. However, they are not omnipresent; for examp ...
family that are located in the inner membrane of mitochondria
A mitochondrion () is an organelle found in the cells of most eukaryotes, such as animals, plants and fungi. Mitochondria have a double membrane structure and use aerobic respiration to generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is us ...
. Transport of cholesterol from the outer to the inner membrane is facilitated by steroidogenic acute regulatory protein and is the rate-limiting step of steroid synthesis.
The layers of the adrenal gland differ by function, with each layer having distinct enzymes that produce different hormones from a common precursor. The first enzymatic step in the production of all steroid hormones is cleavage of the cholesterol side chain, a reaction that forms pregnenolone as a product and is catalyzed by the enzyme P450scc, also known as ''cholesterol desmolase''. After the production of pregnenolone, specific enzymes of each cortical layer further modify it. Enzymes involved in this process include both mitochondrial and microsomal P450s and hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases. Usually a number of intermediate steps in which pregnenolone is modified several times are required to form the functional hormones. Enzymes that catalyze reactions in these metabolic pathways are involved in a number of endocrine diseases. For example, the most common form of congenital adrenal hyperplasia
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH) is a group of Genetic disorder#Autosomal recessive, autosomal recessive disorders characterized by impaired cortisol synthesis. It results from the deficiency of one of the five enzymes required for the Biosy ...
develops as a result of deficiency of 21-hydroxylase, an enzyme involved in an intermediate step of cortisol production.
;Regulation
anterior pituitary
The anterior pituitary (also called the adenohypophysis or pars anterior) is a major Organ (anatomy), organ of the endocrine system. The anterior pituitary is the glandular, Anatomical terms of location#Usage in human anatomy, anterior lobe that t ...
. In turn, production of ACTH is stimulated by the presence of corticotropin-releasing hormone
Corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) (also known as corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF) or corticoliberin; corticotropin may also be spelled corticotrophin) is a peptide hormone involved in stress responses. It is a releasing hormone that b ...
(CRH), which is released by neurons of the hypothalamus
The hypothalamus (: hypothalami; ) is a small part of the vertebrate brain that contains a number of nucleus (neuroanatomy), nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions is to link the nervous system to the endocrin ...
. ACTH acts on the adrenal cells first by increasing the levels of StAR within the cells, and then of all steroidogenic P450 enzymes. The HPA axis is an example of a negative feedback
Feedback occurs when outputs of a system are routed back as inputs as part of a chain of cause and effect that forms a circuit or loop. The system can then be said to ''feed back'' into itself. The notion of cause-and-effect has to be handle ...
system, in which cortisol itself acts as a direct inhibitor of both CRH and ACTH synthesis. The HPA axis also interacts with the immune system through increased secretion of ACTH at the presence of certain molecules of the inflammatory response.
Mineralocorticoid secretion is regulated mainly by the renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system (RAAS), the concentration of potassium
Potassium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol K (from Neo-Latin ) and atomic number19. It is a silvery white metal that is soft enough to easily cut with a knife. Potassium metal reacts rapidly with atmospheric oxygen to ...
, and to a lesser extent the concentration of ACTH. Sensors of blood pressure in the juxtaglomerular apparatus of the kidneys release the enzyme renin into the blood, which starts a cascade of reactions that lead to formation of angiotensin II
Angiotensin is a peptide hormone that causes vasoconstriction and an increase in blood pressure. It is part of the renin–angiotensin system, which regulates blood pressure. Angiotensin also stimulates the release of aldosterone from the ...
. Angiotensin receptors in cells of the zona glomerulosa recognize the substance, and upon binding they stimulate the release of aldosterone
Aldosterone is the main mineralocorticoid steroid hormone produced by the zona glomerulosa of the adrenal cortex in the adrenal gland. It is essential for sodium conservation in the kidney, salivary glands, sweat glands, and colon. It plays ...
.
Androgens
Cells in zona reticularis of the adrenal glands produce male sex hormones, orandrogen
An androgen (from Greek ''andr-'', the stem of the word meaning ) is any natural or synthetic steroid hormone that regulates the development and maintenance of male characteristics in vertebrates by binding to androgen receptors. This includes ...
s, the most important of which is DHEA. In general, these hormones do not have an overall effect in the male body, and are converted to more potent androgens such as testosterone
Testosterone is the primary male sex hormone and androgen in Male, males. In humans, testosterone plays a key role in the development of Male reproductive system, male reproductive tissues such as testicles and prostate, as well as promoting se ...
and DHT or to estrogen
Estrogen (also spelled oestrogen in British English; see spelling differences) is a category of sex hormone responsible for the development and regulation of the female reproductive system and secondary sex characteristics. There are three ...
s (female sex hormones) in the gonad
A gonad, sex gland, or reproductive gland is a Heterocrine gland, mixed gland and sex organ that produces the gametes and sex hormones of an organism. Female reproductive cells are egg cells, and male reproductive cells are sperm. The male gon ...
s, acting in this way as a metabolic intermediate.
Catecholamines
Also calledepinephrine
Adrenaline, also known as epinephrine, is a hormone and medication which is involved in regulating visceral functions (e.g., respiration). It appears as a white microcrystalline granule. Adrenaline is normally produced by the adrenal glands a ...
and norepinephrine
Norepinephrine (NE), also called noradrenaline (NA) or noradrenalin, is an organic compound, organic chemical in the catecholamine family that functions in the brain and human body, body as a hormone, neurotransmitter and neuromodulator. The ...
, adrenaline
Adrenaline, also known as epinephrine, is a hormone and medication which is involved in regulating visceral functions (e.g., respiration). It appears as a white microcrystalline granule. Adrenaline is normally produced by the adrenal glands a ...
and noradrenaline, respectively, are catecholamines – water-soluble compounds that have a structure made of a catechol group and an amine group. The adrenal glands are responsible for most of the adrenaline that circulates in the body, but only for a small amount of circulating noradrenaline. These hormones are released by the adrenal medulla, which contains a dense network of blood vessels. Adrenaline and noradrenaline act by binding to adrenoreceptors throughout the body, with effects that include an increase in blood pressure and heart rate. Actions of adrenaline and noradrenaline are responsible for the fight or flight response, characterised by a quickening of breathing and heart rate, an increase in blood pressure, and constriction of blood vessels in many parts of the body.
Formation
Catecholamines are produced in chromaffin cells in the medulla of the adrenal gland, from tyrosine, a non-essential amino acid derived from food or produced fromphenylalanine
Phenylalanine (symbol Phe or F) is an essential α-amino acid with the chemical formula, formula . It can be viewed as a benzyl group substituent, substituted for the methyl group of alanine, or a phenyl group in place of a terminal hydrogen of ...
in the liver. The enzyme tyrosine hydroxylase converts tyrosine to L-DOPA
-DOPA, also known as -3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine and used medically as levodopa, is made and used as part of the normal biology of some plants and animals, including humans. Humans, as well as a portion of the other animals that utilize -DO ...
in the first step of catecholamine synthesis. L-DOPA is then converted to dopamine
Dopamine (DA, a contraction of 3,4-dihydroxyphenethylamine) is a neuromodulatory molecule that plays several important roles in cells. It is an organic chemical of the catecholamine and phenethylamine families. It is an amine synthesized ...
before it can be turned into noradrenaline. In the cytosol
The cytosol, also known as cytoplasmic matrix or groundplasm, is one of the liquids found inside cells ( intracellular fluid (ICF)). It is separated into compartments by membranes. For example, the mitochondrial matrix separates the mitochondri ...
, noradrenaline is converted to epinephrine by the enzyme phenylethanolamine N-methyltransferase (PNMT) and stored in granules. Glucocorticoids produced in the adrenal cortex stimulate the synthesis of catecholamines by increasing the levels of tyrosine hydroxylase and PNMT.
Catecholamine release is stimulated by the activation of the sympathetic nervous system
The sympathetic nervous system (SNS or SANS, sympathetic autonomic nervous system, to differentiate it from the somatic nervous system) is one of the three divisions of the autonomic nervous system, the others being the parasympathetic nervous sy ...
. Splanchnic nerves of the sympathetic nervous system
The sympathetic nervous system (SNS or SANS, sympathetic autonomic nervous system, to differentiate it from the somatic nervous system) is one of the three divisions of the autonomic nervous system, the others being the parasympathetic nervous sy ...
innervate the medulla of the adrenal gland. When activated, it evokes the release of catecholamines from the storage granules by stimulating the opening of calcium channels in the cell membrane.
Gene and protein expression
Thehuman genome
The human genome is a complete set of nucleic acid sequences for humans, encoded as the DNA within each of the 23 distinct chromosomes in the cell nucleus. A small DNA molecule is found within individual Mitochondrial DNA, mitochondria. These ar ...
includes approximately 20,000 protein coding genes and 70% of these genes are expressed in the normal adult adrenal glands. Only some 250 genes are more specifically expressed in the adrenal glands compared to other organs and tissues. The adrenal-gland-specific genes with the highest level of expression include members of the cytochrome P450
Cytochromes P450 (P450s or CYPs) are a Protein superfamily, superfamily of enzymes containing heme as a cofactor (biochemistry), cofactor that mostly, but not exclusively, function as monooxygenases. However, they are not omnipresent; for examp ...
superfamily of enzymes. Corresponding proteins are expressed in the different compartments of the adrenal gland, such as CYP11A1, HSD3B2 and FDX1 involved in steroid hormone
A steroid hormone is a steroid that acts as a hormone. Steroid hormones can be grouped into two classes: corticosteroids (typically made in the adrenal cortex, hence ''cortico-'') and sex steroids (typically made in the gonads or placenta). Wit ...
synthesis and expressed in cortical cell layers, and PNMT and DBH involved in noradrenaline and adrenaline
Adrenaline, also known as epinephrine, is a hormone and medication which is involved in regulating visceral functions (e.g., respiration). It appears as a white microcrystalline granule. Adrenaline is normally produced by the adrenal glands a ...
synthesis and expressed in the medulla.
Development
The adrenal glands are composed of two heterogenous types of tissue. In the center is the adrenal medulla, which producesadrenaline
Adrenaline, also known as epinephrine, is a hormone and medication which is involved in regulating visceral functions (e.g., respiration). It appears as a white microcrystalline granule. Adrenaline is normally produced by the adrenal glands a ...
and noradrenaline and releases them into the bloodstream, as part of the sympathetic nervous system
The sympathetic nervous system (SNS or SANS, sympathetic autonomic nervous system, to differentiate it from the somatic nervous system) is one of the three divisions of the autonomic nervous system, the others being the parasympathetic nervous sy ...
. Surrounding the medulla is the cortex
Cortex or cortical may refer to:
Biology
* Cortex (anatomy), the outermost layer of an organ
** Cerebral cortex, the outer layer of the vertebrate cerebrum, part of which is the ''forebrain''
*** Motor cortex, the regions of the cerebral cortex i ...
, which produces a variety of steroid hormone
A steroid hormone is a steroid that acts as a hormone. Steroid hormones can be grouped into two classes: corticosteroids (typically made in the adrenal cortex, hence ''cortico-'') and sex steroids (typically made in the gonads or placenta). Wit ...
s. These tissues come from different embryological
Embryology (from Greek ἔμβρυον, ''embryon'', "the unborn, embryo"; and -λογία, ''-logia'') is the branch of animal biology that studies the prenatal development of gametes (sex cells), fertilization, and development of embryos an ...
precursors and have distinct prenatal development
Prenatal development () involves the development of the embryo and of the fetus during a viviparous animal's gestation. Prenatal development starts with fertilization, in the germinal stage of embryonic development, and continues in fetal de ...
paths. The cortex of the adrenal gland is derived from mesoderm
The mesoderm is the middle layer of the three germ layers that develops during gastrulation in the very early development of the embryo of most animals. The outer layer is the ectoderm, and the inner layer is the endoderm.Langman's Medical ...
, whereas the medulla is derived from the neural crest
The neural crest is a ridge-like structure that is formed transiently between the epidermal ectoderm and neural plate during vertebrate development. Neural crest cells originate from this structure through the epithelial-mesenchymal transition, ...
, which is of ectoderm
The ectoderm is one of the three primary germ layers formed in early embryonic development. It is the outermost layer, and is superficial to the mesoderm (the middle layer) and endoderm (the innermost layer). It emerges and originates from the o ...
al origin.
The adrenal glands in a newborn baby are much larger as a proportion of the body size than in an adult. For example, at age three months the glands are four times the size of the kidneys. The size of the glands decreases relatively after birth, mainly because of shrinkage of the cortex. The cortex, which almost completely disappears by age 1, develops again from age 4–5. The glands weigh about at birth and develop to an adult weight of about each. In a fetus the glands are first detectable after the sixth week of development.
Cortex
Adrenal cortex tissue is derived from theintermediate mesoderm
Intermediate mesoderm or intermediate mesenchyme is a narrow section of the mesoderm (one of the three primary germ layers) located between the paraxial mesoderm and the lateral plate of the developing embryo. The intermediate mesoderm develops in ...
. It first appears 33 days after fertilisation
Fertilisation or fertilization (see spelling differences), also known as generative fertilisation, syngamy and impregnation, is the fusion of gametes to give rise to a zygote and initiate its development into a new individual organism or of ...
, shows steroid hormone production capabilities by the eighth week and undergoes rapid growth during the first trimester of pregnancy. The fetal adrenal cortex is different from its adult counterpart, as it is composed of two distinct zones: the inner "fetal" zone, which carries most of the hormone-producing activity, and the outer "definitive" zone, which is in a proliferative phase. The fetal zone produces large amounts of adrenal androgen
An androgen (from Greek ''andr-'', the stem of the word meaning ) is any natural or synthetic steroid hormone that regulates the development and maintenance of male characteristics in vertebrates by binding to androgen receptors. This includes ...
s (male sex hormones) that are used by the placenta
The placenta (: placentas or placentae) is a temporary embryonic and later fetal organ that begins developing from the blastocyst shortly after implantation. It plays critical roles in facilitating nutrient, gas, and waste exchange between ...
for estrogen
Estrogen (also spelled oestrogen in British English; see spelling differences) is a category of sex hormone responsible for the development and regulation of the female reproductive system and secondary sex characteristics. There are three ...
biosynthesis. Cortical development of the adrenal gland is regulated mostly by ACTH, a hormone produced by the pituitary gland
The pituitary gland or hypophysis is an endocrine gland in vertebrates. In humans, the pituitary gland is located at the base of the human brain, brain, protruding off the bottom of the hypothalamus. The pituitary gland and the hypothalamus contr ...
that stimulates cortisol
Cortisol is a steroid hormone in the glucocorticoid class of hormones and a stress hormone. When used as medication, it is known as hydrocortisone.
Cortisol is produced in many animals, mainly by the ''zona fasciculata'' of the adrenal corte ...
synthesis. During midgestation, the fetal zone occupies most of the cortical volume and produces 100–200 mg/day of DHEA-S, an androgen
An androgen (from Greek ''andr-'', the stem of the word meaning ) is any natural or synthetic steroid hormone that regulates the development and maintenance of male characteristics in vertebrates by binding to androgen receptors. This includes ...
and precursor of both androgens and estrogen
Estrogen (also spelled oestrogen in British English; see spelling differences) is a category of sex hormone responsible for the development and regulation of the female reproductive system and secondary sex characteristics. There are three ...
s (female sex hormones). Adrenal hormones, especially glucocorticoid
Glucocorticoids (or, less commonly, glucocorticosteroids) are a class of corticosteroids, which are a class of steroid hormones. Glucocorticoids are corticosteroids that bind to the glucocorticoid receptor that is present in almost every vertebra ...
s such as cortisol, are essential for prenatal development of organs, particularly for the maturation of the lung
The lungs are the primary Organ (biology), organs of the respiratory system in many animals, including humans. In mammals and most other tetrapods, two lungs are located near the Vertebral column, backbone on either side of the heart. Their ...
s. The adrenal gland decreases in size after birth because of the rapid disappearance of the fetal zone, with a corresponding decrease in androgen secretion.
Adrenarche
During early childhood androgen synthesis and secretion remain low, but several years before puberty (from 6–8 years of age) changes occur in both anatomical and functional aspects of cortical androgen production that lead to increased secretion of the steroids DHEA and DHEA-S. These changes are part of a process calledadrenarche
Adrenarche is an early stage in sexual maturation that happens in some higher primates (including humans), typically peaks at around 20 years of age, and is involved in the development of pubic hair, body odor, skin oiliness#Oily skin, skin oiline ...
, which has only been described in humans and some other primates. Adrenarche is independent of ACTH or gonadotropins and correlates with a progressive thickening of the zona reticularis layer of the cortex. Functionally, adrenarche provides a source of androgens for the development of axillary and pubic hair before the beginning of puberty.
Medulla
The adrenal medulla is derived fromneural crest cells
The neural crest is a ridge-like structure that is formed transiently between the epidermal ectoderm and neural plate during vertebrate development. Neural crest cells originate from this structure through the epithelial-mesenchymal transition, an ...
, which come from the ectoderm
The ectoderm is one of the three primary germ layers formed in early embryonic development. It is the outermost layer, and is superficial to the mesoderm (the middle layer) and endoderm (the innermost layer). It emerges and originates from the o ...
layer of the embryo
An embryo ( ) is the initial stage of development for a multicellular organism. In organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization of the female egg cell by the male sp ...
. These cells migrate from their initial position and aggregate in the vicinity of the dorsal aorta, a primitive blood vessel, which activates the differentiation of these cells through the release of proteins known as BMPs. These cells then undergo a second migration from the dorsal aorta to form the adrenal medulla and other organs of the sympathetic nervous system
The sympathetic nervous system (SNS or SANS, sympathetic autonomic nervous system, to differentiate it from the somatic nervous system) is one of the three divisions of the autonomic nervous system, the others being the parasympathetic nervous sy ...
. Cells of the adrenal medulla are called chromaffin cells because they contain granules that stain with chromium
Chromium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Cr and atomic number 24. It is the first element in Group 6 element, group 6. It is a steely-grey, Luster (mineralogy), lustrous, hard, and brittle transition metal.
Chromium ...
salts, a characteristic not present in all sympathetic organs. Glucocorticoid
Glucocorticoids (or, less commonly, glucocorticosteroids) are a class of corticosteroids, which are a class of steroid hormones. Glucocorticoids are corticosteroids that bind to the glucocorticoid receptor that is present in almost every vertebra ...
s produced in the adrenal cortex were once thought to be responsible for the differentiation of chromaffin cells. More recent research suggests that BMP-4 secreted in adrenal tissue is the main responsible for this, and that glucocorticoids only play a role in the subsequent development of the cells.
Clinical significance
The normal function of the adrenal gland may be impaired by conditions such as infections, tumors, genetic disorders and autoimmune diseases, or as aside effect
In medicine, a side effect is an effect of the use of a medicinal drug or other treatment, usually adverse but sometimes beneficial, that is unintended. Herbal and traditional medicines also have side effects.
A drug or procedure usually use ...
of medical therapy. These disorders affect the gland either directly (as with infections or autoimmune diseases) or as a result of the dysregulation of hormone production (as in some types of Cushing's syndrome) leading to an excess or insufficiency of adrenal hormones and the related symptoms.
Corticosteroid overproduction
Cushing's syndrome
Cushing's syndrome is the manifestation of glucocorticoid excess. It can be the result of a prolonged treatment with glucocorticoids or be caused by an underlying disease which produces alterations in the HPA axis or the production of cortisol. Causes can be further classified into ACTH-dependent or ACTH-independent. The most common cause ofendogenous
Endogeny, in biology, refers to the property of originating or developing from within an organism, tissue, or cell.
For example, ''endogenous substances'', and ''endogenous processes'' are those that originate within a living system (e.g. an ...
Cushing's syndrome is a pituitary adenoma which causes an excessive production of ACTH. The disease produces a wide variety of signs and symptoms which include obesity, diabetes, increased blood pressure, excessive body hair ( hirsutism), osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a systemic skeletal disorder characterized by low bone mass, micro-architectural deterioration of bone tissue leading to more porous bone, and consequent increase in Bone fracture, fracture risk.
It is the most common reason f ...
, depression, and most distinctively, stretch marks in the skin, caused by its progressive thinning.
Primary aldosteronism
When the zona glomerulosa produces excessaldosterone
Aldosterone is the main mineralocorticoid steroid hormone produced by the zona glomerulosa of the adrenal cortex in the adrenal gland. It is essential for sodium conservation in the kidney, salivary glands, sweat glands, and colon. It plays ...
, the result is primary aldosteronism
Primary aldosteronism (PA)'','' also known as primary hyperaldosteronism, refers to the excess production of the hormone aldosterone from the adrenal glands, resulting in low renin levels and high blood pressure. This abnormality is a paraneopl ...
. Causes for this condition are bilateral hyperplasia
Hyperplasia (from ancient Greek ὑπέρ ''huper'' 'over' + πλάσις ''plasis'' 'formation'), or hypergenesis, is an enlargement of an organ or tissue caused by an increase in the amount of Tissue (biology), organic tissue that results from ...
(excessive tissue growth) of the glands, or aldosterone-producing adenomas (a condition called Conn's syndrome). Primary aldosteronism produces hypertension and electrolyte
An electrolyte is a substance that conducts electricity through the movement of ions, but not through the movement of electrons. This includes most soluble Salt (chemistry), salts, acids, and Base (chemistry), bases, dissolved in a polar solven ...
imbalance, increasing potassium
Potassium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol K (from Neo-Latin ) and atomic number19. It is a silvery white metal that is soft enough to easily cut with a knife. Potassium metal reacts rapidly with atmospheric oxygen to ...
depletion sodium retention.
Adrenal insufficiency
Adrenal insufficiency (the deficiency ofglucocorticoid
Glucocorticoids (or, less commonly, glucocorticosteroids) are a class of corticosteroids, which are a class of steroid hormones. Glucocorticoids are corticosteroids that bind to the glucocorticoid receptor that is present in almost every vertebra ...
s) occurs in about 5 in 10,000 in the general population. Diseases classified as ''primary adrenal insufficiency'' (including Addison's disease and genetic causes) directly affect the adrenal cortex. If a problem that affects the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis
The hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis (HPA axis or HTPA axis) is a complex set of direct influences and feedback interactions among three components: the hypothalamus (a part of the brain located below the thalamus), the pituitary gland ( ...
arises outside the gland, it is a ''secondary adrenal insufficiency''.
Addison's disease
Addison's disease refers to primary hypoadrenalism, which is a deficiency in glucocorticoid and mineralocorticoid production by the adrenal gland. In the Western world, Addison's disease is most commonly an autoimmune condition, in which the body producesantibodies
An antibody (Ab) or immunoglobulin (Ig) is a large, Y-shaped protein belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily which is used by the immune system to identify and neutralize antigens such as bacteria and viruses, including those that caus ...
against cells of the adrenal cortex. Worldwide, the disease is more frequently caused by infection, especially from tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB), also known colloquially as the "white death", or historically as consumption, is a contagious disease usually caused by ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can al ...
. A distinctive feature of Addison's disease is hyperpigmentation
Hyperpigmentation, also known as the dark spots or circles on the skin, is the darkening of an area of Human skin, skin or nail (anatomy), nails caused by increased melanin.
Causes
Hyperpigmentation can be caused by sun damage, inflammation, or ...
of the skin, which presents with other nonspecific symptoms such as fatigue.
A complication seen in untreated Addison's disease and other types of primary adrenal insufficiency is the adrenal crisis, a medical emergency
A medical emergency is an acute injury or illness that poses an immediate risk to a person's life or long-term health, sometimes referred to as a situation risking "life or limb". These emergencies may require assistance from another, qualified ...
in which low glucocorticoid and mineralocorticoid levels result in hypovolemic shock
Hypovolemic shock is a form of Shock (circulatory), shock caused by severe hypovolemia (insufficient blood volume or extracellular fluid in the body). It can be caused by severe dehydration or blood loss. Hypovolemic shock is a medical emergency ...
and symptoms such as vomiting and fever. An adrenal crisis can progressively lead to stupor
Stupor is the lack of critical mental function and a level of consciousness, in which an affected person is almost entirely unresponsive and responds only to intense stimuli such as pain. The word derives from the Latin '' stupor'' ("numbness, in ...
and coma
A coma is a deep state of prolonged unconsciousness in which a person cannot be awakened, fails to Nociception, respond normally to Pain, painful stimuli, light, or sound, lacks a normal Circadian rhythm, sleep-wake cycle and does not initiate ...
. The management of adrenal crises includes the application of hydrocortisone
Hydrocortisone is the name for the hormone cortisol when supplied as a medication. It is a corticosteroid and works as an anti-inflammatory and by immune suppression. Uses include conditions such as adrenocortical insufficiency, adrenogenit ...
injections.
Secondary adrenal insufficiency
In secondary adrenal insufficiency, a dysfunction of thehypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis
The hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis (HPA axis or HTPA axis) is a complex set of direct influences and feedback interactions among three components: the hypothalamus (a part of the brain located below the thalamus), the pituitary gland ( ...
leads to decreased stimulation of the adrenal cortex. Apart from suppression of the axis by glucocorticoid therapy, the most common cause of secondary adrenal insufficiency are tumors that affect the production of adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) by the pituitary gland
The pituitary gland or hypophysis is an endocrine gland in vertebrates. In humans, the pituitary gland is located at the base of the human brain, brain, protruding off the bottom of the hypothalamus. The pituitary gland and the hypothalamus contr ...
. This type of adrenal insufficiency usually does not affect the production of mineralocorticoid
Mineralocorticoids are a class of corticosteroids, which in turn are a class of steroid hormones. Mineralocorticoids are produced in the adrenal cortex and influence salt and water balances (electrolyte balance and fluid balance). The primary ...
s, which are under regulation of the renin–angiotensin system
The renin–angiotensin system (RAS), or renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system (RAAS), is a hormone system that regulates blood pressure, fluid, and electrolyte balance, and systemic vascular resistance.
When renal blood flow is reduced, ...
instead.
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH) is a group of Genetic disorder#Autosomal recessive, autosomal recessive disorders characterized by impaired cortisol synthesis. It results from the deficiency of one of the five enzymes required for the Biosy ...
is a family of congenital diseases in which mutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, ...
s of enzymes that produce steroid hormones result in a glucocorticoid deficiency and malfunction of the negative feedback loop of the HPA axis. In the HPA axis, cortisol (a glucocorticoid) inhibits the release of CRH and ACTH, hormones that in turn stimulate corticosteroid synthesis. As cortisol cannot be synthesized, these hormones are released in high quantities and stimulate production of other adrenal steroids instead. The most common form of congenital adrenal hyperplasia is due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency. 21-hydroxylase is necessary for production of both mineralocorticoids and glucocorticoids, but not androgen
An androgen (from Greek ''andr-'', the stem of the word meaning ) is any natural or synthetic steroid hormone that regulates the development and maintenance of male characteristics in vertebrates by binding to androgen receptors. This includes ...
s. Therefore, ACTH stimulation of the adrenal cortex induces the release of excessive amounts of adrenal androgens, which can lead to the development of ambiguous genitalia and secondary sex characteristic
A secondary sex characteristic is a physical characteristic of an organism that is related to or derived from its sex, but not directly part of its reproductive system. In humans, these characteristics typically start to appear during pubert ...
s.
Adrenal tumors
 Adrenal tumors are commonly found as incidentalomas, unexpected
Adrenal tumors are commonly found as incidentalomas, unexpected asymptomatic
Asymptomatic (or clinically silent) is an adjective categorising the medical conditions (i.e., injuries or diseases) that patients carry but without experiencing their symptoms, despite an explicit diagnosis (e.g., a positive medical test).
P ...
tumors found during medical imaging
Medical imaging is the technique and process of imaging the interior of a body for clinical analysis and medical intervention, as well as visual representation of the function of some organs or tissues (physiology). Medical imaging seeks to revea ...
. They are seen in around 3.4% of CT scans, and in most cases they are benign adenomas. Adrenal carcinomas are very rare, with an incidence of 1 case per million per year.
Pheochromocytomas are tumors of the adrenal medulla that arise from chromaffin cells. They can produce a variety of nonspecific symptoms, which include headaches, sweating, anxiety and palpitations. Common signs include hypertension
Hypertension, also known as high blood pressure, is a Chronic condition, long-term Disease, medical condition in which the blood pressure in the artery, arteries is persistently elevated. High blood pressure usually does not cause symptoms i ...
and tachycardia
Tachycardia, also called tachyarrhythmia, is a heart rate that exceeds the normal resting rate. In general, a resting heart rate over 100 beats per minute is accepted as tachycardia in adults. Heart rates above the resting rate may be normal ...
. Surgery, especially adrenal laparoscopy, is the most common treatment for small pheochromocytomas.
History
Bartolomeo Eustachi, an Italian anatomist, is credited with the first description of the adrenal glands in 1563–4. However, these publications were part of the papal library and did not receive public attention, which was first received with Caspar Bartholin the Elder's illustrations in 1611. The adrenal glands are named for their location relative to the kidneys. The term "adrenal" comes fromLatin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
'' ad'', "near", and '' ren'', "kidney". Similarly, "suprarenal", as termed by Jean Riolan the Younger in 1629, is derived from the Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
'' supra'', "above", and ''ren'', "kidney", as well. The suprarenal nature of the glands was not truly accepted until the 19th century, as anatomists clarified the ductless nature of the glands and their likely secretory role – prior to this, there was some debate as to whether the glands were indeed suprarenal or part of the kidney.
One of the most recognized works on the adrenal glands came in 1855 with the publication of ''On the Constitutional and Local Effects of Disease of the Suprarenal Capsule'', by the English physician Thomas Addison. In his monography, Addison described what the French physician George Trousseau would later name Addison's disease, an eponym still used today for a condition of adrenal insufficiency and its related clinical manifestations. In 1894, English physiologists George Oliver and Edward Schafer studied the action of adrenal extracts and observed their pressor effects. In the following decades several physicians experimented with extracts from the adrenal cortex to treat Addison's disease. Edward Calvin Kendall, Philip Hench and Tadeusz Reichstein were then awarded the 1950 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine
The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine () is awarded yearly by the Nobel Assembly at the Karolinska Institute for outstanding discoveries in physiology or medicine. The Nobel Prize is not a single prize, but five separate prizes that, acco ...
for their discoveries on the structure and effects of the adrenal hormones.
See also
* Adrenopause * Adrenochrome * List of distinct cell types in the adult human body * Adrenal insufficiency * Adrenal gland disorderReferences
External links
Adrenal gland at the Human Protein Atlas
*
Adrenal gland histology
* – "Adrenal Gland" * * – "Posterior Abdominal Wall: The Retroperitoneal Fat and Suprarenal Glands"
from Colorado State University * {{DEFAULTSORT:Adrenal Gland Adrenaline Endocrine system anatomy