Action (firearms) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In firearms terminology, an action is the functional mechanism of a breech-loading firearm that handles (loads, locks, fires, extracts and ejects) the ammunition

 A revolver is a multi- chamber (but single- barrelled) firearm that houses cartridges in a rotary
A revolver is a multi- chamber (but single- barrelled) firearm that houses cartridges in a rotary
 In bolt-action firearms, the opening and closing of the breech is operated by direct manual manipulation of the bolt via a protruding bolt handle. Most bolt-actions utilize a rotating bolt ("turn-pull") design, where the bolt handle must be rotated upwards for unlocking before the bolt can be pulled back to opening the breech and eject any spent cartridge, and must be rotated back down for locking after the bolt closes the breech. The three predominant rotating bolt-action systems are the Mauser,
In bolt-action firearms, the opening and closing of the breech is operated by direct manual manipulation of the bolt via a protruding bolt handle. Most bolt-actions utilize a rotating bolt ("turn-pull") design, where the bolt handle must be rotated upwards for unlocking before the bolt can be pulled back to opening the breech and eject any spent cartridge, and must be rotated back down for locking after the bolt closes the breech. The three predominant rotating bolt-action systems are the Mauser,
 In the Mauser-style turn-bolt action, the bolt handle must be rotated upward, pull rearward, pushed forward, and finally rotated back downward into lock. In a straight-pull action, the bolt can be cycled without rotating, hence reducing the required range of motion by the shooter from four movements to two, with the goal of increasing the rate of fire. The Ross and Schmidt–Rubin rifles load via stripper clips, albeit of an unusual paperboard and steel design in the Schmidt–Rubin rifle, while the Mannlicher uses
In the Mauser-style turn-bolt action, the bolt handle must be rotated upward, pull rearward, pushed forward, and finally rotated back downward into lock. In a straight-pull action, the bolt can be cycled without rotating, hence reducing the required range of motion by the shooter from four movements to two, with the goal of increasing the rate of fire. The Ross and Schmidt–Rubin rifles load via stripper clips, albeit of an unusual paperboard and steel design in the Schmidt–Rubin rifle, while the Mannlicher uses
 In pump action or slide action firearms, a sliding grip at the fore-end beneath the barrel is manually operated by the user to eject and chamber a new round. Pump actions are predominantly found in shotguns. An example of firearms using the pump action are the Remington 870 and
In pump action or slide action firearms, a sliding grip at the fore-end beneath the barrel is manually operated by the user to eject and chamber a new round. Pump actions are predominantly found in shotguns. An example of firearms using the pump action are the Remington 870 and

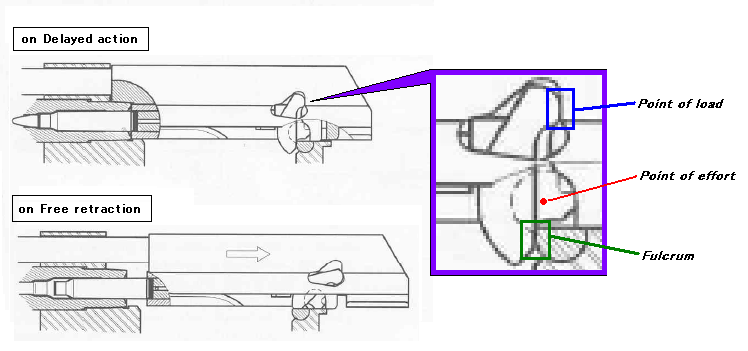 The blowback operation is a system in which semi-automatic firearm, semi-automatic and fully automatic firearms operate through the energy created by combustion in the chamber and bore acting directly on the bolt face through the cartridge. In blowback operation the bolt is not locked to the chamber, relying only on spring pressure and inertia from the weight of the bolt to keep the action from opening too quickly. Blowback operation is used for low-powered cartridges due to the weight of the bolt required.
Delayed blowback actions use some mechanism to slow down rearward travel of the bolt, allowing this action to handle more powerful ammunition and/or reduced weight of the bolt.
The blowback operation is a system in which semi-automatic firearm, semi-automatic and fully automatic firearms operate through the energy created by combustion in the chamber and bore acting directly on the bolt face through the cartridge. In blowback operation the bolt is not locked to the chamber, relying only on spring pressure and inertia from the weight of the bolt to keep the action from opening too quickly. Blowback operation is used for low-powered cartridges due to the weight of the bolt required.
Delayed blowback actions use some mechanism to slow down rearward travel of the bolt, allowing this action to handle more powerful ammunition and/or reduced weight of the bolt.
How Does It Work: Toggle Actions
Forgotten Weapons {{DEFAULTSORT:Firearm Action Firearm actions, Firearm terminology
cartridge
Cartridge may refer to:
Objects
* Cartridge (firearms), a type of modern ammunition
* ROM cartridge, a removable component in an electronic device
* Cartridge (respirator), a type of filter used in respirators
Other uses
* Cartridge (surname), a ...
s, or the method by which that mechanism works. Actions are technically not present on muzzleloaders, as all those are single-shot
Single-shot firearms are firearms that hold only a single round of ammunition, and must be reloaded manually after every shot. The history of firearms began with single-shot designs, then multi-barreled designs appeared, and eventually many cent ...
firearms with a closed off breech with the powder and projectile manually loaded from the muzzle. Instead, the muzzleloader ignition mechanism is referred to as the ''lock'' (e.g. matchlock
A matchlock or firelock is a historical type of firearm wherein the gunpowder is ignited by a burning piece of rope that is touched to the gunpowder by a mechanism that the musketeer activates by pulling a lever or trigger with his finger. Befor ...
, flintlock
Flintlock is a general term for any firearm that uses a flint-striking ignition mechanism, the first of which appeared in Western Europe in the early 16th century. The term may also apply to a particular form of the mechanism itself, also know ...
, caplock).
Actions can be categorized in several ways, including single action
A trigger is a mechanism that actuates the function of a ranged weapon such as a firearm, airgun, crossbow, or speargun. The word may also be used to describe a switch that initiates the operation of other non-shooting devices such as a trap ...
versus double action, break action
Break action is a type of firearm action in which the barrel or barrels are hinged much like a door and rotate perpendicularly to the bore axis to expose the breech and allow loading and unloading of cartridges. A separate operation may be requir ...
versus bolt action
Bolt-action is a type of manual firearm action that is operated by ''directly'' manipulating the bolt via a bolt handle, which is most commonly placed on the right-hand side of the weapon (as most users are right-handed).
Most bolt-actio ...
, and others. The term action can also include short, long, and magnum if it is in reference to the length of the rifle's receiver and the length of the bolt. The short action rifle usually can accommodate a cartridge length of or smaller. The long action rifle can accommodate a cartridge of , and the magnum action rifle can accommodate cartridges of .
Single-shot actions
Single-shot actions operate only to ignite acartridge
Cartridge may refer to:
Objects
* Cartridge (firearms), a type of modern ammunition
* ROM cartridge, a removable component in an electronic device
* Cartridge (respirator), a type of filter used in respirators
Other uses
* Cartridge (surname), a ...
that is separately set up ("in battery") for firing, and are incapable of moving the cartridge by itself. As the name implies, all single-shot long and short arms (unless multi-barreled) can only hold one round of ammunition and need to be manually reloaded after every firing. Historically, these are the earliest cartridge firearm actions to be invented.
Breechblock
Dropping block
The dropping block are actions wherein the breechblock lowers or "drops" into the receiver to open the breech, usually actuated by an underlever. There are two principal types of dropping block: the tilting block and the falling block.Tilting block
In a tilting block or pivoting block action, the breechblock is hinged on a pin mounted at the rear. When the lever is operated, the block tilts down and forward, exposing the chamber. The best-known pivoting block designs are the Peabody, the Peabody–Martini, and Ballard actions. The original Peabody rifles, manufactured by theProvidence Tool Company
The Rhode Island Tool Company is a historic industrial property at 146-148 West River Street in Providence, Rhode Island. It is a parcel located between West River Street and the channelized West River, on which stand two historic buildings. Th ...
, used a manually cocked side-hammer. Swiss gunsmith Friedrich Martini developed a pivoting block action by modifying the Peabody, that incorporated a hammerless striker which was cocked by the operating lever with the same single, efficient motion that also pivoted the block. The 1871 Martini–Henry which replaced the "trapdoor" Snider–Enfield
The British .577 Snider–Enfield was a breech-loading rifle. The American Jacob Snider invented this firearm action, and the Snider–Enfield was one of the most widely used of the Snider varieties. The British Army adopted it in 1866 as a con ...
was the standard British Army rifle of the later Victorian era, and the Martini is also a popular action for civilian rifles.
Charles H. Ballard's self-cocking tilting-block action was produced by the Marlin Firearms Company
Marlin Firearms Co. is an American manufacturer of semi-automatic, lever-action, and bolt-action rifles. In the past, the company, now based in Madison, North Carolina, and formerly based in North Haven, Connecticut, made shotguns, derringers, ...
from 1875, and earned a superlative reputation among long-range "Creedmoor" target shooters. Surviving Marlin Ballards are today highly prized by collectors, especially those mounted in the elaborate Swiss-style Schützen stocks of the day.
Falling block
A falling block action (also known as a sliding block action) is a single-shot firearm action in which a solid metal breechblock slides vertically in grooves cut into the breech of the firearm and actuated by a lever. Examples of firearms using the falling block action are theSharps rifle
Sharps rifles are a series of large-bore, single-shot, falling-block, breech-loading rifles, beginning with a design by Christian Sharps in 1848 and ceasing production in 1881. They were renowned for long-range accuracy. By 1874 the rifle wa ...
and Ruger No. 1.
Rolling block
In a rolling block action the breechblock takes the form of a part-cylinder, with a pivot pin through its axis. The operator rotates or "rolls" the block to open and close the breech; it is a simple, rugged and reliable design. Rolling blocks are most often associated with firearms made byRemington
Remington may refer to:
Organizations
* Remington Arms, American firearms manufacturer
* Remington Rand, American computer manufacturer
* Remington Products, American manufacturer of shavers and haircare products
* Remington College, American c ...
in the later 19th century; in the Remington action the hammer serves to lock the breech closed at the moment of firing, and the block in turn prevents the hammer from falling with the breech open.
Hinged block
The hinged block used in the earliest metallic-cartridge breechloaders designed for general military issue began as conversions of muzzle-loadingrifle-musket
A rifled musket, rifle musket, or rifle-musket is a type of firearm made in the mid-19th century. Originally the term referred only to muskets that had been produced as a smoothbore weapon and later had their barrels replaced with rifled barrels ...
s. The upper rear portion of the barrel was filed or milled away and replaced by a hinged breechblock which opened upward to permit loading. An internal angled firing pin allowed the re-use of the rifle's existing side-hammer. The Allin action made by Springfield Arsenal in the US hinged forward; the Snider–Enfield
The British .577 Snider–Enfield was a breech-loading rifle. The American Jacob Snider invented this firearm action, and the Snider–Enfield was one of the most widely used of the Snider varieties. The British Army adopted it in 1866 as a con ...
used by the British opened to the side. Whereas the British quickly replaced the Snider with a dropping-block Peabody-style Martini action, the US Army felt the trapdoor action to be adequate and followed its muzzleloader conversions with the new-production Springfield Model 1873, which was the principal longarm used as a weapon in the Indian Wars
The American Indian Wars, also known as the American Frontier Wars, and the Indian Wars, were fought by European governments and colonists in North America, and later by the United States and Canadian governments and American and Canadian settle ...
and was still in service with some units in the Spanish–American War
, partof = the Philippine Revolution, the decolonization of the Americas, and the Cuban War of Independence
, image = Collage infobox for Spanish-American War.jpg
, image_size = 300px
, caption = (cloc ...
.
Break-action
A break action is a type of firearm where the barrel(s) are hinged and can be "broken open" to expose the breech. Multi-barrel break action firearms are usually subdivided into over-and-under or side-by-side configurations for two barrel configurations or " combination gun" when mixed rifle and shotgun barrels are used.Bolt action
Although bolt-action guns are usually associated with fixed or detachable box magazines, in fact the first general-issue military breechloader was a single-shot bolt action: the paper-cartridge Prussian needle gun of 1841. France countered in 1866 with its superior Chassepot rifle, also a paper-cartridge bolt action. The first metallic-cartridge bolt actions in general military service were the Berdan Type II introduced by Russia in 1870, the Mauser Model 1871, and a modified Chassepot, the Gras rifle of 1874; all these were single-shots. Today most top-level smallbore match rifles are single-shot bolt actions. Single-shot bolt actions in .22 caliber were also widely manufactured as inexpensive "boys' guns" in the earlier 20th century; and there have been a few single-shot bolt-action shotguns, usually in .410 bore.Eccentric screw action
The eccentric screw action first seen on the M1867 Werndl–Holub and later on theMagnum Research
Magnum Research Inc. (MRI) was an American privately held corporation based in Fridley, Minnesota which manufactured and distributed firearms. The majority owners, Jim Skildum (President and CEO) and John Risdall (Chairman, COO), had been with ...
Lone Eagle pistol, the breech closure is a rotating drum with the same axis, but offset from the bore. When locked, a firing pin aligns with the primer and the breech is otherwise solid. When rotated open, a slot in the drum is exposed for extraction and feeding of a new round. Though first used on the Werndl-Holub, this action is commonly known as a cannon breech due to its association with the French 75mm Model of 1897 cannon. The French M1897 was, itself, based on William Hubbell's .
Other actions
*TheFerguson rifle
The Ferguson rifle was one of the first breech-loading rifles to be put into service by the British military. It fired a standard British carbine ball of .615" calibre and was used by the British Army in the American Revolutionary War at the Battle ...
: British Major Patrick Ferguson designed his rifle, considered to be the first military breechloader, in the 1770s. A plug-shaped breechblock was screw-threaded so that rotating the handle underneath would lower and raise it for loading with ball and loose powder; the flintlock action still required conventional priming.
*The Hall rifle: First U.S. cavalry breechloader, originally made in flint but later made-in and converted-to percussion in 1830s–1840s. The breech section tilts up to accept a paper cartridge. Excellent machine-made construction, but still tended to leak gas at the breech.
*The Kammerlader
The ''Kammerlader'', or "chamber loader", was the first Norwegian breech-loading rifle, and among the first breech loaders adopted for use by an armed force anywhere in the world. A single-shot black-powder rifle, the ''kammerlader'' was operate ...
: A crank-operated Norwegian firearm produced around the time of the Prussian Needle-gun. Originally used a paper cartridge. Later many were converted to rimfire; this was the first Norwegian breechloader.
*The Tarpley carbine {{infobox weapon
, name = Tarpley Carbine
, image = Tarpley breech-loading carbine.jpg
, image_size = 300
, caption = Tarpley carbine displayed at the National Museum of American History
, origin ...
: This is categorized into falling block action, but the breech block is hinged, unlike the others.
*The Morse Carbine: This mostly brass action is somewhat like the Hall rifle, except it was designed to take a special centerfire cartridge. Very few of these were actually made; all were constructed in the late 1850s.
*The Joslyn rifle
The term Joslyn Rifle refers to a series of rifles produced in the mid-19th century. The term is often used to refer specifically to the Joslyn Model 1861/1862, which was the first mass-produced breech-loading rifle produced at the Springfield Ar ...
:
* Rising Breech Carbine:
Repeating actions
Repeating actions are characterized by reciprocating/rotating
Rotation, or spin, is the circular movement of an object around a '' central axis''. A two-dimensional rotating object has only one possible central axis and can rotate in either a clockwise or counterclockwise direction. A three-dimensional ...
components that can move cartridge
Cartridge may refer to:
Objects
* Cartridge (firearms), a type of modern ammunition
* ROM cartridge, a removable component in an electronic device
* Cartridge (respirator), a type of filter used in respirators
Other uses
* Cartridge (surname), a ...
s in and out of battery from an ammunition-holding device ( magazine, cylinder
A cylinder (from ) has traditionally been a three-dimensional solid, one of the most basic of curvilinear geometric shapes. In elementary geometry, it is considered a prism with a circle as its base.
A cylinder may also be defined as an infin ...
or belt), which allows the gun to hold multiple rounds and shoot repeatedly before needing a manual ammunition reload.
Manual operation
Revolver
 A revolver is a multi- chamber (but single- barrelled) firearm that houses cartridges in a rotary
A revolver is a multi- chamber (but single- barrelled) firearm that houses cartridges in a rotary cylinder
A cylinder (from ) has traditionally been a three-dimensional solid, one of the most basic of curvilinear geometric shapes. In elementary geometry, it is considered a prism with a circle as its base.
A cylinder may also be defined as an infin ...
which indexes each round into alignment with the bore (with the help of a forcing cone) prior to each shot. Revolvers are most often handguns; however, examples of revolving rifle
A rifle is a long-barreled firearm designed for accurate shooting, with a barrel that has a helical pattern of grooves ( rifling) cut into the bore wall. In keeping with their focus on accuracy, rifles are typically designed to be held wit ...
s, shotguns and cannons have been made. The cylinder is most often rotated via linkage to a manually manipulated external hammer, although some revolvers are "double-action" and can use the manual pull of the trigger to drive both the cylinder rotation and hammer cocking.
Bolt action
 In bolt-action firearms, the opening and closing of the breech is operated by direct manual manipulation of the bolt via a protruding bolt handle. Most bolt-actions utilize a rotating bolt ("turn-pull") design, where the bolt handle must be rotated upwards for unlocking before the bolt can be pulled back to opening the breech and eject any spent cartridge, and must be rotated back down for locking after the bolt closes the breech. The three predominant rotating bolt-action systems are the Mauser,
In bolt-action firearms, the opening and closing of the breech is operated by direct manual manipulation of the bolt via a protruding bolt handle. Most bolt-actions utilize a rotating bolt ("turn-pull") design, where the bolt handle must be rotated upwards for unlocking before the bolt can be pulled back to opening the breech and eject any spent cartridge, and must be rotated back down for locking after the bolt closes the breech. The three predominant rotating bolt-action systems are the Mauser, Lee–Enfield
The Lee–Enfield or Enfield is a bolt-action, magazine-fed repeating rifle that served as the main firearm of the military forces of the British Empire and Commonwealth during the first half of the 20th century, and was the British Army's sta ...
and Mosin–Nagant systems, with the Mauser system emerging as the modern mainstream.
There are also straight-pull bolt-action systems that uses complex bolt head designs to facilitate locking instead of needing to rotate the bolt handle every time.
Straight-pull action
 In the Mauser-style turn-bolt action, the bolt handle must be rotated upward, pull rearward, pushed forward, and finally rotated back downward into lock. In a straight-pull action, the bolt can be cycled without rotating, hence reducing the required range of motion by the shooter from four movements to two, with the goal of increasing the rate of fire. The Ross and Schmidt–Rubin rifles load via stripper clips, albeit of an unusual paperboard and steel design in the Schmidt–Rubin rifle, while the Mannlicher uses
In the Mauser-style turn-bolt action, the bolt handle must be rotated upward, pull rearward, pushed forward, and finally rotated back downward into lock. In a straight-pull action, the bolt can be cycled without rotating, hence reducing the required range of motion by the shooter from four movements to two, with the goal of increasing the rate of fire. The Ross and Schmidt–Rubin rifles load via stripper clips, albeit of an unusual paperboard and steel design in the Schmidt–Rubin rifle, while the Mannlicher uses en-bloc clip
A clip is a device that is used to store multiple rounds of ammunition together as a unit for insertion into the magazine or cylinder of a firearm. This speeds up the process by loading the firearm with several rounds at once, rather than one at a ...
s. The Schmidt–Rubin series, which culminated in the K31
The Karabiner Modell 1931 (K. 31/Kar. 31/Mq. 31) is a magazine-fed, straight-pull bolt-action rifle. It was the standard issue rifle of the Swiss armed forces from 1933 until 1958 though examples remained in service into the 1970s. It has a 6-ro ...
, are also known for being among the most accurate military service rifles ever made. Yet another variant of the straight-pull bolt action, of which the M1895 Lee Navy is an example, is a camming action in which pulling the bolt handle causes the bolt to rock, freeing a stud from the receiver and unlocking the bolt.
In 1993 the German Blaser company introduced the Blaser R93, a new straight-pull action where locking is achieved by a series of concentric "claws" that protrude/retract from the bolthead, a design that is referred to as ''Radialbundverschluss'' ("radial connection"). As of 2017 the Rifle Shooter magazine listed its successor Blaser R8 as one of the three most popular straight pull rifles together with Merkel Helix and Browning Maral. Some other notable modern straight pull rifles are made by Chapuis, Heym Heym is a surname. Notable people with the surname include:
* Georg Heym (1887–1912), German author
* Stefan Heym (1913–2001), German author
See also
* Heym (gun manufacturer)
* Chayyim, the basis for this name
* Haim (disambiguation)
* Hei ...
, Lynx, Rößler Rößler is a surname and may refer to:
* Hole Rößler (born 1949), German modern pentathlete
* Matthias Rößler (born 1955), German politician (CDU)
* Robert Rößler (1838–1883), German poet
* Rößler firearms, an Austrian firearms manufa ...
, Strasser, and Steel Action.
In the sport of biathlon
The biathlon is a winter sport that combines cross-country skiing and rifle shooting. It is treated as a race, with contestants skiing through a cross-country trail whose distance is divided into shooting rounds. The shooting rounds are not time ...
, because shooting speed is an important performance factor and semi-automatic guns are illegal for race use, straight-pull actions are quite common, and are used almost exclusively on the Biathlon World Cup. The first company to make the straight-pull action for .22 caliber .22 caliber, or 5.6 mm caliber, refers to a common firearms bore diameter of 0.22 inch (5.6 mm).
Cartridges in this caliber include the very widely used .22 Long Rifle and .223 Remington / 5.56×45mm NATO.
.22 inch is also a popular ...
was J. G. Anschütz; the action is specifically the straight-pull ball bearing
A ball bearing is a type of rolling-element bearing that uses balls to maintain the separation between the bearing races.
The purpose of a ball bearing is to reduce rotational friction and support radial and axial loads. It achieves this ...
-lock action, which features spring-loaded ball bearings on the side of the bolt which lock into a groove inside the bolt's housing. With the new design came a new dry-fire method; instead of the bolt being turned up slightly, the action is locked back to catch the firing pin.
Pump-action
 In pump action or slide action firearms, a sliding grip at the fore-end beneath the barrel is manually operated by the user to eject and chamber a new round. Pump actions are predominantly found in shotguns. An example of firearms using the pump action are the Remington 870 and
In pump action or slide action firearms, a sliding grip at the fore-end beneath the barrel is manually operated by the user to eject and chamber a new round. Pump actions are predominantly found in shotguns. An example of firearms using the pump action are the Remington 870 and Winchester Model 1897
The Winchester Model 1897, also known as the Model 97, M97, or Trench Gun, is a pump-action shotgun with an external hammer and tube magazine manufactured by the Winchester Repeating Arms Company. The Model 1897 was an evolution of the Winchest ...
.
Lever-action
The lever-action firearms use a linked lever to eject and chamber cartridges. An example of firearms using lever action are the Winchester Repeating Rifle, the Henry rifle and the Marlin Model 1894.Bolt release
The bolt release or lever release action is a hybrid repeating action that uses the physical manipulation of a bolt release lever/button to complete the cartridge chambering process. However, unlike the lever action (which demands the shooter's hand to actually provide the force needed for cycling the action), bolt release firearms eject the used cartridge automatically without involving the lever, usually via blowback or gas operation, and often uses a spring-assisted mechanism to chamber the next round. However, after moving rearwards the bolt is stopped by a bolt catch and will not move back into battery position and chamber the new round, until the user manually disengage the catch by depressing a release lever/button. Due to the fact that the action cannot complete its loading cycle without manual input from the user, it is technically a manually operated action rather than a self-loading one. Whilst the basic principle can be traced back to other self-ejecting rifles, such as the single-shot Harrington & Richardson Model 755 rifle, this action has since been popularized in the United Kingdom by Southern Gun Company, who manufacture with "Manually Actuated Release System" (MARS) action rifles/pistol-caliber carbine
A carbine ( or ) is a long gun that has a barrel shortened from its original length. Most modern carbines are rifles that are compact versions of a longer rifle or are rifles chambered for less powerful cartridges.
The smaller size and lighter ...
s in .223
The .223 Remington (designated as the 223 Remington by the SAAMI and 223 Rem by the CIP) is a rimless, bottlenecked rifle cartridge. It was developed in 1957 by Remington Arms and Fairchild Industries for the U.S. Continental Army Command ...
, .308
The .308 Winchester is a smokeless powder rimless bottlenecked rifle cartridge widely used for hunting, target shooting, police, military, and personal protection applications globally. It is similar but not identical to the 7.62×51mm NATO ...
, 9mm and .45 ACP
The .45 ACP ( Automatic Colt Pistol) or .45 Auto (11.43×23mm) is a rimless straight-walled handgun cartridge designed by John Moses Browning in 1904, for use in his prototype Colt semi-automatic pistol. After successful military trials, it ...
calibers, as the interrupted mechanism complies with The Firearms (Amendment) Act 1988 which bans possession of self-loading centrefire
Two rounds of .357 Magnum, a centerfire cartridge; notice the circular primer in the center
A centerfire cartridge is a firearm metallic cartridge whose primer is located at the center of the base of its casing (i.e. "case head"). Unlike rim ...
rifles. The French company Verney-Carron makes and exports the ''Speedline'' hunting rifle and the ''Véloce'' shotgun, which has caused some moral concern in the mainstream media in Australia due to lobbying by the Greens and anti-gun groups such as Gun Control Australia, with David Shoebridge quoting the term "semi-semi-automatic". Similarly, Savage Arms
Savage Arms is an American gunmaker based in Westfield, Massachusetts, with operations in Canada. Savage makes a variety of rimfire and centerfire rifles, as well as Stevens single-shot rifles and shotguns. The company is best known for the ...
has introduced the A17R and A22R rimfire rifles (both modified from its new A-series rifles, with a bolt release lever in front of the trigger guard
A trigger guard is a protective loop surrounding the trigger of a firearm designed to prevent unwanted contact with the trigger, which may cause an accidental discharge. Other devices that use a trigger-like actuator mechanism, such as inhaler ...
), aiming at the Australian market, but law enforcement agencies such as the Northern Territory Police has attempted to unilaterally defining these rifles as "linear repeating firearms with assisted ejection" and reclassify them as semi-automatic rifle, semi-automatic, and hence prohibited without at least a Category C license, which is off-limit to most urban and rural residents who do not own farms. In 2020, Česká zbrojovka firearms, CZ also introduced CZ 515, a bolt-release modified version of the CZ 512, to the Australian market via its importer Winchester Repeating Arms Company, Winchester Australia. The Turkish manufacturer Pardus Arms also produces the 12-gauge shotgun, 12 gauge-caliber BRS17 shotgun, which uses a bolt release button on the back of the receiver (firearm), receiver to chamber rounds before firing.
Other actions
*Rotary cannon: Gatling gun, M134 Minigun *Chain gun: M230 chain gun, Hughes Chain Gun, Guycot chain rifle, Guycot Chain Rifle, Treeby chain gun *Kalthoff repeater *Cookson repeater *Belton flintlock *The Jennings Magazine Rifle *Meigs Sliding Guard Action Repeater *Roper repeater *The Orvill Robinson Model 2 rifle: Orvill Robinson, a New York-based firearms designer, developed two rifles. His first, patented in 1870 and commonly referred to by collectors as the "Model 1" though it has no official designation, was a precursor to straight-pull bolt actions like the Mannlicher M1886. The second rifle designed by Robinson, patented in 1872, was very different, employing a double hinged action that folded upward from the receiver to remove the spent casing and back down and forward to chamber a new round. Though hammer-fired, it is recognizable as a manually actuated ancestor of the toggle action found in firearms such as the Luger Parabellum 1908 pistol or Pedersen Rifle. *Krag–Petersson, Krag-Petersson Rifle Though frequently classified as only single-shot firearms, one tilting block rifle usually falls under the category of repeating firearms. The user, upon ejecting a round from the chamber, would load a round from the underbarrel magazine onto the loading surface of the tilting block, then raise it to the mouth of the chamber where the user could then easily push it forward into the chamber. Though this would not meet most standards of "repeating" for most modern users, the classification has been in use historically. *Remington-Rider Magazine Pistol has a manually-actuated rolling block action to pull a cartridge from a tubular magazine set below the barrel and simultaneously cock the firearm. The block was rolled back into battery, loading the cartridge into the chamber, by spring pressure while the hammer remained in the cocked position.Autoloading operation
Blowback operation
=Examples of blowback operation
= *Simple blowback: Halcón M-1943, Uzi submachine gun, Varan PMX-80 *Lever-delayed blowback: FAMAS (rifle), FAMAS, Sterling 7.62, AA-52, 2B-A-40, TKB-517 *Roller-delayed blowback: SIG 510, Heckler & Koch MP5, HK MP5, Heckler & Koch P9, HK P9, Heckler & Koch G3, HK G3 *Gas-delayed blowback: Volkssturmgewehr 1-5, Heckler & Koch P7, HK P7, Steyr GB *Toggle-delayed blowback: Schwarzlose MG M.07/12, Luger rifle and Pedersen rifle *Blish Lock: early Thompson submachine guns *Hesitation locked: Remington Model 51 and Remington R51, R51 pistols *Chamber-ring delayed blowback: Seecamp pistolBlow-forward operation
The blow-forward operation uses a fixed breech and moving barrel that is forced forward relative to the breech by the friction of the projectile against the bore as well as the breech recoiling away from the barrel. The barrel is spring loaded and returns automatically to chamber a fresh round from the magazine. Examples of this action are the Steyr Mannlicher M1894, Hino Komuro M1908 Pistol and the Schwarzlose Model 1908.Recoil operation
The recoil operation is a type of locked-breech action used in semi-automatic and fully automatic firearms. It also uses energy from the combustion in the chamber acting directly on the bolt through the cartridge head, but in this case the firearm has a reciprocating barrel and breech assembly, combined with a bolt that locks to the breech. The breech remains locked as the bolt and barrel travel rearward together for some distance, allowing pressure in the chamber to drop to a safe level before the breech is opened.=Examples of recoil operation
= *Short-recoil: M1911 Colt pistol, Colt M1911, MAB PA-15, Browning Hi-Power, Heckler & Koch USP, HK USP, Glock pistol, Glock, Mamba Pistol, M2 Browning machine gun, MG42, Vz. 52 (pistol), Vz 52 pistol, M82 Barrett rifle, M82 *Long-recoil: Browning Auto-5, Browning Auto 5, Frommer Stop, Femaru STOP Pistol, Mars Automatic Pistol, Chauchat *Inertia: Sjögren shotgun, Sjögren Inertial, certain Benelli (firearms), Benelli shotgunsGas operation
The gas operation is a system of operation mechanism used to provide energy to semi-automatic and fully automatic firearms. In gas-operation, a portion of high pressure gas from the cartridge being fired is tapped through a hole in the barrel and diverted to operate the action. There are three basic types: long stroke gas piston (where the gas piston goes the same distance as the operating stroke of the action parts, and is often attached to the action parts), short stroke gas piston (where the gas piston travels a shorter distance than the operating stroke of the action parts), and direct impingement (AKA "direct gas", "gas impingement", where there is no piston, and the gas acts directly on the action parts). A fourth type, now considered obsolete and ineffective, are those systems based on the Bang rifle that utilize a muzzle cap to capture gas after the bullet has left the barrel. While this system is successful in boosting the operating power of recoil operated guns, it is insufficient and too susceptible to fouling for use as the primary operating system.=Examples of gas operation
= *Short-stroke gas piston: FN FAL, Sterling SAR-87, SAR-87, Heckler & Koch G36, HK G36 *Long-stroke gas piston: M1 Garand, AK-47, FN FNC *Direct impingement: MAS 49, M16 rifle, M16, AG-42 *Gas trap: Gewehr 41, Bang M1922 rifleSee also
*Locked-breech *Lock (firearm) **Matchlock **Wheellock **Flintlock **Caplock mechanism, Caplock *Trigger (firearms), TriggerReferences
External links
*How Does It Work: Toggle Actions
Forgotten Weapons {{DEFAULTSORT:Firearm Action Firearm actions, Firearm terminology