When Humans Transcend Biology on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''The Singularity Is Near: When Humans Transcend Biology'' is a 2005 non-fiction book about
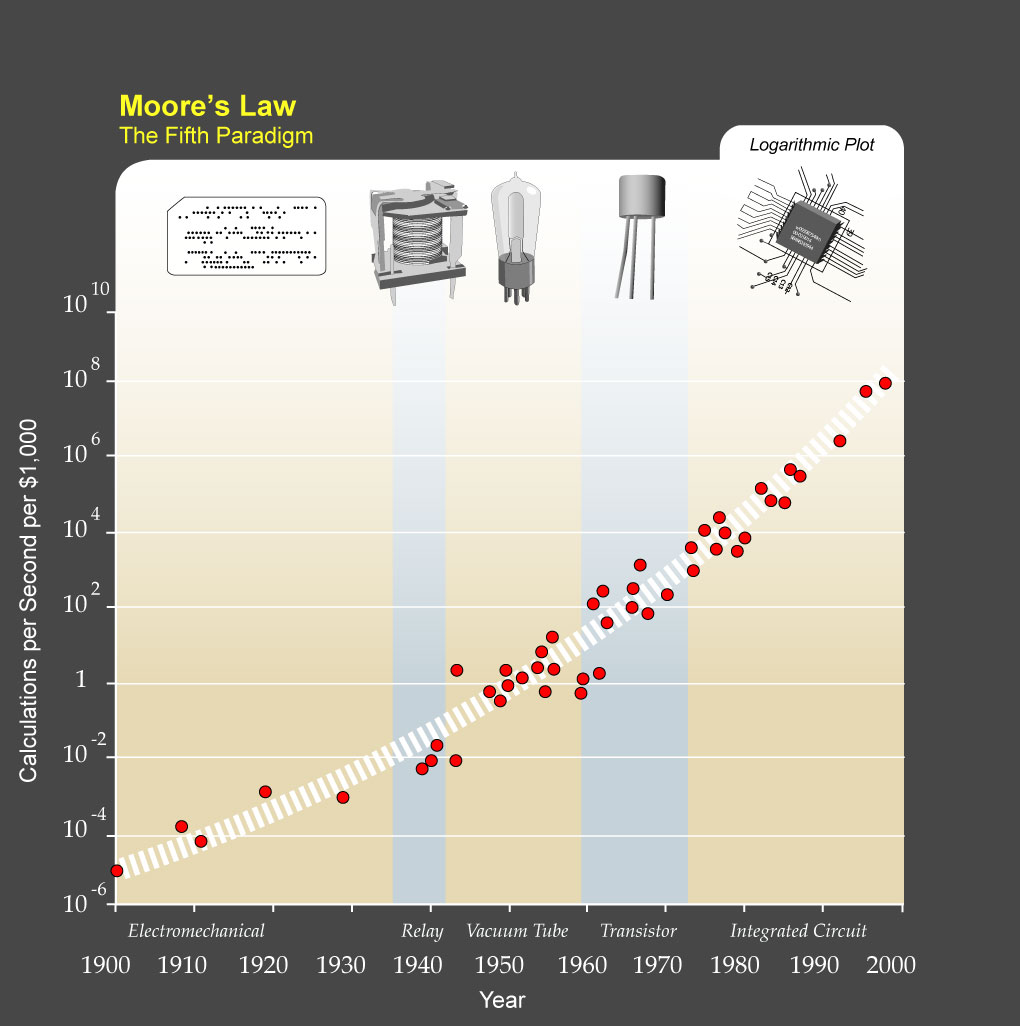 A fundamental pillar of Kurzweil's argument is that to get to the singularity, computational capacity is as much of a bottleneck as other things like quality of algorithms and understanding of the human brain.
A fundamental pillar of Kurzweil's argument is that to get to the singularity, computational capacity is as much of a bottleneck as other things like quality of algorithms and understanding of the human brain.
 Kurzweil notes that computational capacity alone will not create artificial intelligence. He asserts that the best way to build machine intelligence is to first understand human intelligence. The first step is to image the brain, to peer inside it. Kurzweil claims imaging technologies such as
Kurzweil notes that computational capacity alone will not create artificial intelligence. He asserts that the best way to build machine intelligence is to first understand human intelligence. The first step is to image the brain, to peer inside it. Kurzweil claims imaging technologies such as
 Kurzweil touches on the history of the singularity concept, tracing it back to
Kurzweil touches on the history of the singularity concept, tracing it back to
PDF
*
Singularity.com, official website for the book
''Vice'' Magazine interview with Ray Kurzweil
- Link down, 5/11/15
Documentary- ''The Singularity of Ray Kurzweil'' on YouTube
''Wall Street Journal'' review by Glenn Harlan Reynolds
* * ttps://web.archive.org/web/20080604004706/http://www.spectrum.ieee.org/singularity ''IEEE Spectrum special report on the Singularity''
Ray Kurzweil: The Coming Singularity - Big Think
YouTube {{DEFAULTSORT:Singularity Is Near Books by Ray Kurzweil 2005 non-fiction books Futurology books Singularitarianism Transhumanist books Futurology documentaries Non-fiction books about artificial intelligence
artificial intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) is the capability of computer, computational systems to perform tasks typically associated with human intelligence, such as learning, reasoning, problem-solving, perception, and decision-making. It is a field of re ...
and the future of humanity by inventor and futurist
Futurists (also known as futurologists, prospectivists, foresight practitioners and horizon scanners) are people whose specialty or interest is futures studies or futurology or the attempt to systematically explore predictions and possibilities ...
Ray Kurzweil
Raymond Kurzweil ( ; born February 12, 1948) is an American computer scientist, author, entrepreneur, futurist, and inventor. He is involved in fields such as optical character recognition (OCR), speech synthesis, text-to-speech synthesis, spee ...
. A sequel book, '' The Singularity Is Nearer'', was released on June 25, 2024.
The book builds on the ideas introduced in Kurzweil's previous books, '' The Age of Intelligent Machines'' (1990) and '' The Age of Spiritual Machines'' (1999). In the book, Kurzweil embraces the term " the singularity", which was popularized by Vernor Vinge
Vernor Steffen Vinge (; October 2, 1944 – March 20, 2024) was an American science fiction author and professor. He taught mathematics and computer science at San Diego State University. He was the first wide-scale popularizer of the technolo ...
in his 1993 essay "The Coming Technological Singularity."
Kurzweil describes his '' Law of Accelerating Returns'', which predicts an exponential increase in technologies like computer
A computer is a machine that can be Computer programming, programmed to automatically Execution (computing), carry out sequences of arithmetic or logical operations (''computation''). Modern digital electronic computers can perform generic set ...
s, genetics
Genetics is the study of genes, genetic variation, and heredity in organisms.Hartl D, Jones E (2005) It is an important branch in biology because heredity is vital to organisms' evolution. Gregor Mendel, a Moravian Augustinians, Augustinian ...
, nanotechnology
Nanotechnology is the manipulation of matter with at least one dimension sized from 1 to 100 nanometers (nm). At this scale, commonly known as the nanoscale, surface area and quantum mechanical effects become important in describing propertie ...
, robotics
Robotics is the interdisciplinary study and practice of the design, construction, operation, and use of robots.
Within mechanical engineering, robotics is the design and construction of the physical structures of robots, while in computer s ...
and artificial intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) is the capability of computer, computational systems to perform tasks typically associated with human intelligence, such as learning, reasoning, problem-solving, perception, and decision-making. It is a field of re ...
. Once the singularity has been reached, Kurzweil says that machine intelligence will be infinitely more powerful than all human intelligence combined. The singularity is also the point at which machines' intelligence and humans would merge; Kurzweil predicts this date: "I set the date for the Singularity—representing a profound and disruptive transformation in human capability—as 2045".
Content
Exponential growth
Kurzweil characterizesevolution
Evolution is the change in the heritable Phenotypic trait, characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. It occurs when evolutionary processes such as natural selection and genetic drift act on genetic variation, re ...
throughout all time as progressing through six epochs, each one building on the one before. He says the four epochs which have occurred so far are ''Physics and Chemistry'', ''Biology and DNA'', ''Brains'', and ''Technology''. Kurzweil predicts the singularity will coincide with the next epoch, ''The Merger of Human Technology with Human Intelligence''. After the singularity he says the final epoch will occur, ''The Universe Wakes Up''.
Kurzweil explains that evolutionary progress is exponential
Exponential may refer to any of several mathematical topics related to exponentiation, including:
* Exponential function, also:
**Matrix exponential, the matrix analogue to the above
*Exponential decay, decrease at a rate proportional to value
* Ex ...
because of positive feedback
Positive feedback (exacerbating feedback, self-reinforcing feedback) is a process that occurs in a feedback loop where the outcome of a process reinforces the inciting process to build momentum. As such, these forces can exacerbate the effects ...
; the results of one stage are used to create the next stage. Exponential growth is deceptive, nearly flat at first until it hits what Kurzweil calls "the knee in the curve" then rises almost vertically. In fact Kurzweil believes evolutionary progress is super-exponential because more resources are deployed to the winning process. As an example of super-exponential growth Kurzweil cites the computer chip business. The overall budget for the whole industry increases over time, since the fruits of exponential growth make it an attractive investment; meanwhile the additional budget fuels more innovation which makes the industry grow even faster, effectively an example of "double" exponential growth.
Kurzweil dictates evolutionary progress looks smooth, but that really it is divided into paradigms, specific methods of solving problems. Each paradigm starts with slow growth, builds to rapid growth, and then levels off. As one paradigm levels off, pressure builds to find or develop a new paradigm. So what looks like a single smooth curve is really series of smaller S curves. For example, Kurzweil notes that when vacuum tube
A vacuum tube, electron tube, thermionic valve (British usage), or tube (North America) is a device that controls electric current flow in a high vacuum between electrodes to which an electric voltage, potential difference has been applied. It ...
s stopped getting faster, cheaper transistor
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to Electronic amplifier, amplify or electronic switch, switch electrical signals and electric power, power. It is one of the basic building blocks of modern electronics. It is composed of semicondu ...
s became popular and continued the overall exponential growth.
Kurzweil calls this exponential growth the law of accelerating returns, and he believes it applies to many human-created technologies such as computer memory
Computer memory stores information, such as data and programs, for immediate use in the computer. The term ''memory'' is often synonymous with the terms ''RAM,'' ''main memory,'' or ''primary storage.'' Archaic synonyms for main memory include ...
, transistor
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to Electronic amplifier, amplify or electronic switch, switch electrical signals and electric power, power. It is one of the basic building blocks of modern electronics. It is composed of semicondu ...
s, microprocessor
A microprocessor is a computer processor (computing), processor for which the data processing logic and control is included on a single integrated circuit (IC), or a small number of ICs. The microprocessor contains the arithmetic, logic, a ...
s, DNA sequencing
DNA sequencing is the process of determining the nucleic acid sequence – the order of nucleotides in DNA. It includes any method or technology that is used to determine the order of the four bases: adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine. The ...
, magnetic storage
Magnetic storage or magnetic recording is the storage of data on a magnetized medium. Magnetic storage uses different patterns of magnetisation in a magnetizable material to store data and is a form of non-volatile memory. The information is acc ...
, the number of Internet hosts, Internet traffic
Internet traffic is the flow of data within the entire Internet, or in certain network links of its constituent networks. Common traffic measurements are total volume, in units of multiples of the byte, or as transmission rates in bytes per cert ...
, decrease in device size, and nanotech citations and patents. Kurzweil cites two historical examples of exponential growth: the Human Genome Project
The Human Genome Project (HGP) was an international scientific research project with the goal of determining the base pairs that make up human DNA, and of identifying, mapping and sequencing all of the genes of the human genome from both a ...
and the growth of the Internet. Kurzweil claims the whole world economy is in fact growing exponentially, although short term booms and busts tend to hide this trend.
Computational capacity
 A fundamental pillar of Kurzweil's argument is that to get to the singularity, computational capacity is as much of a bottleneck as other things like quality of algorithms and understanding of the human brain.
A fundamental pillar of Kurzweil's argument is that to get to the singularity, computational capacity is as much of a bottleneck as other things like quality of algorithms and understanding of the human brain. Moore's Law
Moore's law is the observation that the Transistor count, number of transistors in an integrated circuit (IC) doubles about every two years. Moore's law is an observation and Forecasting, projection of a historical trend. Rather than a law of ...
predicts the capacity of integrated circuits grows exponentially, but not indefinitely. Kurzweil feels the increase in the capacity of integrated circuits will probably slow by the year 2020. He feels confident that a new paradigm will debut at that point to carry on the exponential growth predicted by his law of accelerating returns. Kurzweil describes four paradigms of computing that came before integrated circuits: electromechanical, relay, vacuum tube, and transistors. What technology will follow integrated circuits, to serve as the sixth paradigm, is unknown, but Kurzweil believes nanotubes are the most likely alternative among a number of possibilities:
nanotubes and nanotube circuitry, molecular computing, self-assembly in nanotube circuits, biological systems emulating circuit assembly, computing with DNA,Since Kurzweil believes computational capacity will continue to grow exponentially long after Moore's Law ends it will eventually rival the raw computing power of the human brain. Kurzweil looks at several different estimates of how much computational capacity is in the brain and settles on 1016 calculations per second and 1013 bits of memory. He writes that $1,000 will buy computer power equal to a single brain "by around 2020" while by 2045, the onset of the singularity, he says the same amount of money will buy one billion times more power than all human brains combined today. Kurzweil admits the exponential trend in increased computing power will hit a limit eventually, but he calculates that limit to be trillions of times beyond what is necessary for the singularity.spintronics Spintronics (a portmanteau meaning spin transport electronics), also known as spin electronics, is the study of the intrinsic spin of the electron and its associated magnetic moment, in addition to its fundamental electronic charge, in solid-st ...(computing with the spin of electrons), computing with light, andquantum computing A quantum computer is a computer that exploits quantum mechanical phenomena. On small scales, physical matter exhibits properties of wave-particle duality, both particles and waves, and quantum computing takes advantage of this behavior using s ....
The brain
 Kurzweil notes that computational capacity alone will not create artificial intelligence. He asserts that the best way to build machine intelligence is to first understand human intelligence. The first step is to image the brain, to peer inside it. Kurzweil claims imaging technologies such as
Kurzweil notes that computational capacity alone will not create artificial intelligence. He asserts that the best way to build machine intelligence is to first understand human intelligence. The first step is to image the brain, to peer inside it. Kurzweil claims imaging technologies such as PET
A pet, or companion animal, is an animal kept primarily for a person's company or entertainment rather than as a working animal, livestock, or a laboratory animal. Popular pets are often considered to have attractive/ cute appearances, inte ...
and fMRI
Functional magnetic resonance imaging or functional MRI (fMRI) measures brain activity by detecting changes associated with blood flow. This technique relies on the fact that cerebral blood flow and neuronal activation are coupled. When an area o ...
are increasing exponentially in resolution while he predicts even greater detail will be obtained during the 2020s when it becomes possible to scan the brain from the inside using nanobots. Once the physical structure and connectivity information are known, Kurzweil says researchers will have to produce functional models of sub-cellular components and synapses all the way up to whole brain regions. The human brain is "a complex hierarchy of complex systems, but it does not represent a level of complexity beyond what we are already capable of handling".
Beyond reverse engineering the brain in order to understand and emulate it, Kurzweil introduces the idea of "uploading" a specific brain with every mental process intact, to be instantiated on a "suitably powerful computational substrate". He writes that general modeling requires 1016 calculations per second and 1013 bits of memory, but then explains uploading requires additional detail, perhaps as many as 1019 cps and 1018 bits. Kurzweil says the technology to do this will be available by 2040. Rather than an instantaneous scan and conversion to digital form, Kurzweil feels humans will most likely experience gradual conversion as portions of their brain are augmented with neural implants, increasing their proportion of non-biological intelligence slowly over time.
Kurzweil believes there is "no objective test that can conclusively determine" the presence of consciousness. Therefore, he says nonbiological intelligences will claim to have consciousness and "the full range of emotional and spiritual experiences that humans claim to have"; he feels such claims will generally be accepted.
Genetics, nanotechnology and robotics (AI)
Kurzweil says revolutions ingenetics
Genetics is the study of genes, genetic variation, and heredity in organisms.Hartl D, Jones E (2005) It is an important branch in biology because heredity is vital to organisms' evolution. Gregor Mendel, a Moravian Augustinians, Augustinian ...
, nanotechnology
Nanotechnology is the manipulation of matter with at least one dimension sized from 1 to 100 nanometers (nm). At this scale, commonly known as the nanoscale, surface area and quantum mechanical effects become important in describing propertie ...
and robotics
Robotics is the interdisciplinary study and practice of the design, construction, operation, and use of robots.
Within mechanical engineering, robotics is the design and construction of the physical structures of robots, while in computer s ...
will usher in the beginning of the singularity. Kurzweil feels with sufficient genetic technology it should be possible to maintain the body indefinitely, reversing aging while curing cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving Cell growth#Disorders, abnormal cell growth with the potential to Invasion (cancer), invade or Metastasis, spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Po ...
, heart disease
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is any disease involving the heart or blood vessels. CVDs constitute a class of diseases that includes: coronary artery diseases (e.g. angina pectoris, angina, myocardial infarction, heart attack), heart failure, ...
and other illnesses. Much of this will be possible thanks to nanotechnology, the second revolution, which entails the molecule by molecule construction of tools which themselves can "rebuild the physical world". Finally, the revolution in robotics will really be the development of strong AI, defined as machines which have human-level intelligence or greater. This development will be the most important of the century, "comparable in importance to the development of biology itself".
Kurzweil concedes that every technology carries with it the risk of misuse or abuse, from viruses and nanobots to out-of-control AI machines. He believes the only countermeasure is to invest in defensive technologies, for example by allowing new genetics and medical treatments, monitoring for dangerous pathogens, and creating limited moratoriums on certain technologies. As for artificial intelligence Kurzweil feels the best defense is to increase the "values of liberty, tolerance, and respect for knowledge and diversity" in society, because "the nonbiological intelligence will be embedded in our society and will reflect our values".
The singularity
John von Neumann
John von Neumann ( ; ; December 28, 1903 – February 8, 1957) was a Hungarian and American mathematician, physicist, computer scientist and engineer. Von Neumann had perhaps the widest coverage of any mathematician of his time, in ...
in the 1950s and I. J. Good in the 1960s. He compares his singularity to that of a mathematical or astrophysical singularity. While his ideas of a singularity is not actually infinite, he says it looks that way from any limited perspective.
During the singularity, Kurzweil predicts that "human life will be irreversibly transformed" and that humans will transcend the "limitations of our biological bodies and brain". He looks beyond the singularity to say that "the intelligence that will emerge will continue to represent the human civilization." Further, he feels that "future machines will be human-like, even if they are not biological".
Kurzweil claims once nonbiological intelligence predominates the nature of human life will be radically altered: there will be radical changes in how humans learn, work and play. Kurzweil envisions nanobots which allow people to eat whatever they want while remaining thin and fit, provide copious energy, fight off infections or cancer, replace organs and augment their brains. Eventually people's bodies will contain so much augmentation they'll be able to alter their "physical manifestation at will".
Kurzweil says the law of accelerating returns suggests that once a civilization develops primitive mechanical technologies, it is only a few centuries before they achieve everything outlined in the book, at which point it will start expanding outward, saturating the universe with intelligence. Since people have found no evidence of other civilizations, Kurzweil believes humans are likely alone in the universe. Thus Kurzweil concludes it is humanity's destiny to do the saturating, enlisting all matter and energy in the process.
As for individual identities during these radical changes, Kurzweil suggests people think of themselves as an evolving pattern rather than a specific collection of molecules. Kurzweil says evolution moves towards "greater complexity, greater elegance, greater knowledge, greater intelligence, greater beauty, greater creativity, and greater levels of subtle attributes such as love". He says that these attributes, in the limit, are generally used to describe God. That means, he continues, that evolution is moving towards a conception of God and that the transition away from biological roots is in fact a spiritual undertaking.
Predictions
Kurzweil does not include an actual written timeline of the past and future, as he did in ''The Age of Intelligent Machines'' and ''The Age of Spiritual Machines'', however he still makes many specific predictions. Kurzweil writes that by 2010 a supercomputer will have the computational capacity to emulate human intelligence and "by around 2020" this same capacity will be available "for one thousand dollars". After that milestone he expects human brain scanning to contribute to an effective model of human intelligence "by the mid-2020s". These two elements will culminate in computers that can pass theTuring test
The Turing test, originally called the imitation game by Alan Turing in 1949,. Turing wrote about the ‘imitation game’ centrally and extensively throughout his 1950 text, but apparently retired the term thereafter. He referred to ‘ iste ...
by 2029. By the early 2030s the amount of non-biological computation will exceed the "capacity of all living biological human intelligence". Finally the exponential growth in computing capacity will lead to the singularity. Kurzweil spells out the date very clearly: "I set the date for the Singularity—representing a profound and disruptive transformation in human capability—as 2045".
Reception
Analysis
A common criticism of the book relates to the "exponential growth fallacy". As an example, in 1969, humans landed on the moon. Extrapolating exponential growth from there one would expect huge lunar bases and crewed missions to distant planets. Instead, exploration stalled or even regressed after that.Paul Davies
Paul Charles William Davies (born 22 April 1946) is an English physicist, writer and broadcaster, a professor in Arizona State University and director of BEYOND: Center for Fundamental Concepts in Science. He is affiliated with the Institute ...
writes "the key point about exponential growth is that it never lasts" often due to resource constraints. On the other hand, it has been shown that the global acceleration until recently followed a hyperbolic rather than exponential pattern.
Theodore Modis says "nothing in nature follows a pure exponential" and suggests the logistic function
A logistic function or logistic curve is a common S-shaped curve ( sigmoid curve) with the equation
f(x) = \frac
where
The logistic function has domain the real numbers, the limit as x \to -\infty is 0, and the limit as x \to +\infty is L.
...
is a better fit for "a real growth process". The logistic function looks like an exponential at first but then tapers off and flattens completely. For example, world population and the United States's oil production both appeared to be rising exponentially, but both have leveled off because they were logistic. Kurzweil says "the knee in the curve" is the time when the exponential trend is going to explode, while Modis claims if the process is logistic when you hit the "knee" the quantity you are measuring is only going to increase by a factor of 100 more.
While some critics complain that the law of accelerating returns is not a law of nature others question the religious motivations or implications of Kurzweil's singularity. The buildup towards the singularity is compared with Judeo-Christian end-of-time scenarios. Beam calls it "a Buck Rogers
Buck Rogers is a science fiction adventure hero and feature comic strip created by Philip Francis Nowlan first appearing in daily American newspapers on January 7, 1929, and subsequently appearing in Sunday newspapers, international newspapers, b ...
vision of the hypothetical Christian Rapture". John Gray says "the Singularity echoes apocalyptic myths in which history is about to be interrupted by a world-transforming event".
The radical nature of Kurzweil's predictions is often discussed. Anthony Doerr says that before you "dismiss it as techno-zeal" consider that "every day the line between what is human and what is not quite human blurs a bit more". He lists technology of the day, in 2006, like computers that land supersonic airplanes or in vitro fertility treatments and asks whether brain implants that access the internet or robots in our blood really are that unbelievable.
In regard to reverse engineering the brain, neuroscientist David J. Linden writes that "Kurzweil is conflating biological data collection with biological insight". He feels that data collection might be growing exponentially, but insight is increasing only linearly. For example, the speed and cost of sequencing genomes is also improving exponentially, but our understanding of genetics is growing very slowly. As for nanobots Linden believes the spaces available in the brain for navigation are simply too small. He acknowledges that someday humans will fully understand the brain, except not on Kurzweil's mythical timetable.
Reviews
Paul Davies
Paul Charles William Davies (born 22 April 1946) is an English physicist, writer and broadcaster, a professor in Arizona State University and director of BEYOND: Center for Fundamental Concepts in Science. He is affiliated with the Institute ...
wrote in ''Nature
Nature is an inherent character or constitution, particularly of the Ecosphere (planetary), ecosphere or the universe as a whole. In this general sense nature refers to the Scientific law, laws, elements and phenomenon, phenomena of the physic ...
'' that ''The Singularity is Near'' is a "breathless romp across the outer reaches of technological possibility" while warning that the "exhilarating speculation is great fun to read, but needs to be taken with a huge dose of salt."
Anthony Doerr in ''The Boston Globe
''The Boston Globe,'' also known locally as ''the Globe'', is an American daily newspaper founded and based in Boston, Massachusetts. The newspaper has won a total of 27 Pulitzer Prizes. ''The Boston Globe'' is the oldest and largest daily new ...
'' wrote "Kurzweil's book is surprisingly elaborate, smart, and persuasive. He writes clean methodical sentences, includes humorous dialogues with characters in the future and past, and uses graphs that are almost always accessible." while his colleague Alex Beam points out that "Singularitarians have been greeted with hooting skepticism". Janet Maslin
Janet R. Maslin (born August 12, 1949) is an American journalist, who served as a film critic for ''The New York Times'' from 1977 to 1999, serving as chief critic for the last six years, and then a literary critic from 2000 to 2015. In 2000, M ...
in ''The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''NYT'') is an American daily newspaper based in New York City. ''The New York Times'' covers domestic, national, and international news, and publishes opinion pieces, investigative reports, and reviews. As one of ...
'' wrote "''The Singularity is Near'' is startling in scope and bravado", but says "much of his thinking tends to be pie in the sky". She observes that he's more focused on optimistic outcomes rather than the risks.
Film adaptations
In 2006, Barry Ptolemy and his production company Ptolemaic Productions licensed the rights to ''The Singularity Is Near'' from Kurzweil. Inspired by the book, Ptolemy directed and produced the film '' Transcendent Man'', which went on to bring more attention to the book. Kurzweil also directed his own film adaptation, produced in partnership with Terasem; ''The Singularity is Near'' mixes documentary interviews with a science-fiction story involving his robotic avatar Ramona's transformation into anartificial general intelligence
Artificial general intelligence (AGI)—sometimes called human‑level intelligence AI—is a type of artificial intelligence that would match or surpass human capabilities across virtually all cognitive tasks.
Some researchers argue that sta ...
. Screened at the World Film Festival, the Woodstock Film Festival, the Warsaw International FilmFest, the San Antonio Film Festival in 2010 and the San Francisco Indie Film Festival in 2011, the movie was released generally on July 20, 2012. It is available on DVD or digital download.
Translations
* 奇点迫近 ��点临近 Translator: Zhenhua Dong. * Dutch: De singulariteit is nabij * French: L'humanité 2.0 * Hungarian: A szingularitás küszöbén * Italian: La singolarità è vicina * Korean: 특이점이 온다 * Spanish: La Singularidad está cerca * German: Menschheit 2.0. Die Singularität naht * Turkish: İnsanlık 2.0: Tekilliğe Doğru Biyolojisini Aşan İnsan * Polish: Nadchodzi Osobliwość * Hebrew: Kineret הסינגולריות מתקרבת 2012See also
* Limits to computation *Paradigm shift
A paradigm shift is a fundamental change in the basic concepts and experimental practices of a scientific discipline. It is a concept in the philosophy of science that was introduced and brought into the common lexicon by the American physicist a ...
* Simulated reality
A simulated reality is an approximation of reality created in a simulation, usually in a set of circumstances in which something is engineered to appear real when it is not.
Most concepts invoking a simulated reality relate to some form of compu ...
* Singularitarianism
Singularitarianism is a Social movement, movement defined by the belief that a technological singularity—the creation of superintelligence—will likely happen in the medium future, and that deliberate action ought to be taken to ensure that t ...
* Technological singularity
The technological singularity—or simply the singularity—is a hypothetical point in time at which technological growth becomes uncontrollable and irreversible, resulting in unforeseeable consequences for human civilization. According to the ...
* Transcendent Man
* Transhumanism
Transhumanism is a philosophical and intellectual movement that advocates the human enhancement, enhancement of the human condition by developing and making widely available new and future technologies that can greatly enhance longevity, cogni ...
References
Sources
**
External links
Singularity.com, official website for the book
''Vice'' Magazine interview with Ray Kurzweil
- Link down, 5/11/15
Documentary- ''The Singularity of Ray Kurzweil'' on YouTube
''Wall Street Journal'' review by Glenn Harlan Reynolds
* * ttps://web.archive.org/web/20080604004706/http://www.spectrum.ieee.org/singularity ''IEEE Spectrum special report on the Singularity''
Ray Kurzweil: The Coming Singularity - Big Think
YouTube {{DEFAULTSORT:Singularity Is Near Books by Ray Kurzweil 2005 non-fiction books Futurology books Singularitarianism Transhumanist books Futurology documentaries Non-fiction books about artificial intelligence