Zhuge Liang's Northern Expeditions on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Zhuge Liang's Northern Expeditions were a series of five military campaigns launched by the state of Shu Han against the rival state of
 In 220, following the
In 220, following the
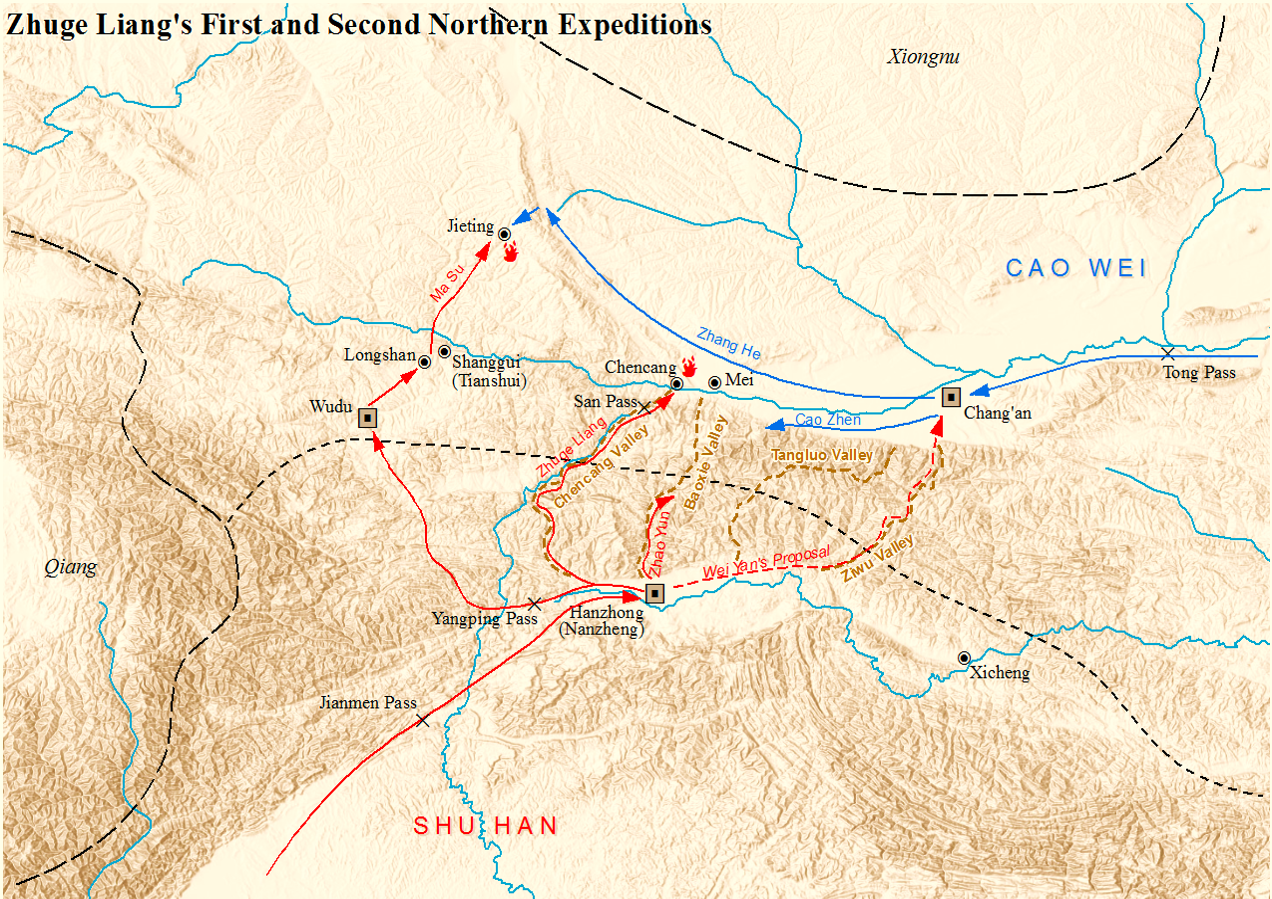 In the spring of 228, Zhuge Liang launched the first Northern Expedition and led the Shu forces to Mount Qi (祁山; the mountainous regions around present-day Li County, Gansu). At the same time, he ordered Zhao Yun and Deng Zhi to lead a decoy force to Ji Valley (箕谷) and pretend to be ready to attack Mei County, so as to divert the Wei forces' attention away from Mount Qi. News of the Shu invasion sent shock waves throughout the Guanzhong region. Three Wei-controlled commanderies – Nan'an (南安), Tianshui and Anding (安定) – defected to the Shu side.
In response to the Shu invasion, Cao Rui moved from
In the spring of 228, Zhuge Liang launched the first Northern Expedition and led the Shu forces to Mount Qi (祁山; the mountainous regions around present-day Li County, Gansu). At the same time, he ordered Zhao Yun and Deng Zhi to lead a decoy force to Ji Valley (箕谷) and pretend to be ready to attack Mei County, so as to divert the Wei forces' attention away from Mount Qi. News of the Shu invasion sent shock waves throughout the Guanzhong region. Three Wei-controlled commanderies – Nan'an (南安), Tianshui and Anding (安定) – defected to the Shu side.
In response to the Shu invasion, Cao Rui moved from
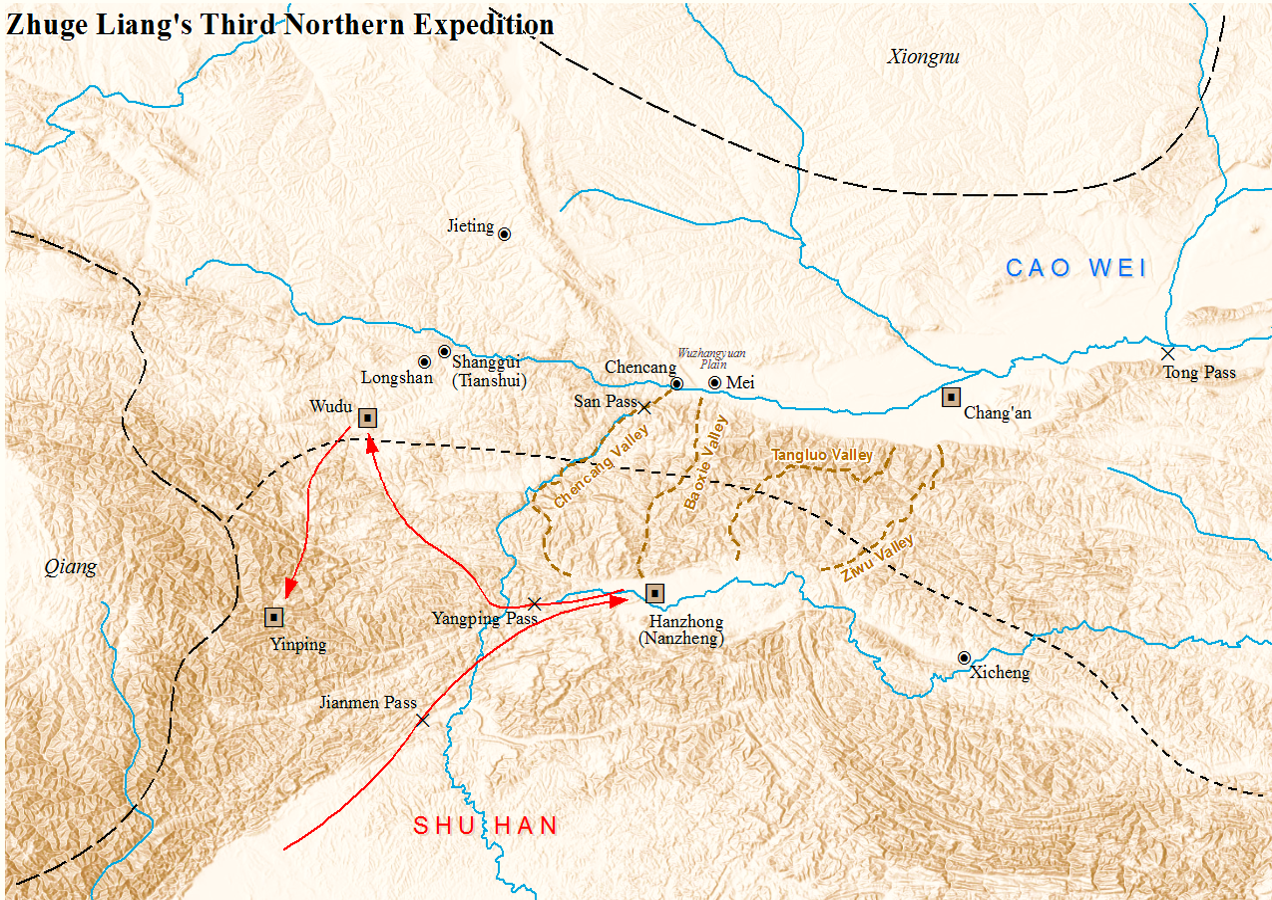 In the spring of 229, Zhuge Liang launched the third Northern Expedition and ordered Chen Shi to lead Shu forces to attack the Wei-controlled Wudu (武都) and Yinping (陰平) commanderies. The Wei general Guo Huai led his troops to resist Chen Shi. He retreated after Zhuge Liang led a Shu army to Jianwei (建威; in present-day Longnan, Gansu). The Shu forces then conquered Wudu and Yinping commanderies.
When Zhuge Liang returned from the campaign, the Shu emperor
In the spring of 229, Zhuge Liang launched the third Northern Expedition and ordered Chen Shi to lead Shu forces to attack the Wei-controlled Wudu (武都) and Yinping (陰平) commanderies. The Wei general Guo Huai led his troops to resist Chen Shi. He retreated after Zhuge Liang led a Shu army to Jianwei (建威; in present-day Longnan, Gansu). The Shu forces then conquered Wudu and Yinping commanderies.
When Zhuge Liang returned from the campaign, the Shu emperor
 In 230, during the
In 230, during the
Cao Wei
Wei ( Hanzi: 魏; pinyin: ''Wèi'' < : *''ŋjweiC'' < Three Kingdoms
The Three Kingdoms () from 220 to 280 AD was the tripartite division of China among the dynastic states of Cao Wei, Shu Han, and Eastern Wu. The Three Kingdoms period was preceded by the Eastern Han dynasty and was followed by the West ...
period in China. All five expeditions were led by Zhuge Liang, the Imperial Chancellor and regent of Shu. Although they proved unsuccessful and ended up as a stalemate, the expeditions have become some of the best known conflicts of the Three Kingdoms period and one of the few battles during it where each side (Shu and Wei) fought against each other with hundreds of thousands of troops, as opposed to other battles where one side had a huge numerical advantage.
The expeditions are dramatised and romanticised in the 14th-century historical novel ''Romance of the Three Kingdoms
''Romance of the Three Kingdoms'' () is a 14th-century historical novel attributed to Luo Guanzhong. It is set in the turbulent years towards the end of the Han dynasty and the Three Kingdoms period in Chinese history, starting in 184 AD ...
'', where they are referred to as the "six campaigns from Mount Qi" (). This term is inaccurate, since Zhuge Liang only launched two of his expeditions (the first and the fourth) from Mount Qi.
Background
 In 220, following the
In 220, following the end of the Han dynasty
The end of the Han dynasty was the period of Chinese history from 189 to 220 CE, roughly coinciding with the tumultuous reign of the Han dynasty's last ruler, Emperor Xian. During this period, the country was thrown into turmoil by the Yellow ...
, China was divided into three competing regimes – Cao Wei (or Wei), Shu Han (or Shu) and Eastern Wu (or Wu) – with each of them trying to unify the country under its rule.
In Shu, the strategic thinking behind the Northern Expeditions came from Zhuge Liang's Longzhong Plan
The Longzhong Plan is the name given to a strategic plan by Zhuge Liang, a statesman of the Shu Han state in the Three Kingdoms period (220–280) of China. Zhuge Liang presented the plan to Liu Bei, a warlord who became the founding emperor of ...
, which he presented to the warlord Liu Bei
Liu Bei (, ; ; 161 – 10 June 223), courtesy name Xuande (), was a warlord in the late Eastern Han dynasty who founded the state of Shu Han in the Three Kingdoms period and became its first ruler. Although he was a distant relative of the ...
in 207. In essence, the plan envisaged a tripartite division of China between the domains of the warlords Liu Bei, Cao Cao and Sun Quan
Sun Quan (, Chinese: 孫權) (183 – 21 May 252), courtesy name Zhongmou (), posthumously known as Emperor Da of Wu, was the founder of the Eastern Wu dynasty, one of the Three Kingdoms of China. He inherited control of the warlord regime ...
. According to the plan, Liu Bei would seize control of Jing Province
Jingzhou or Jing Province was one of the Nine Provinces of ancient China referenced in Chinese historical texts such as the '' Tribute of Yu'', ''Erya'' and '' Rites of Zhou''.
Jingzhou became an administrative division during the reign of Empe ...
and Yi Province from their respective governors, Liu Biao
Liu Biao () () (151 – September 208), courtesy name Jingsheng, was a Chinese military general, politician, and warlord who lived in the late Eastern Han dynasty of China. He is best known for serving as the Governor of Jing Province (coveri ...
and Liu Zhang, and establish a solid foothold in southern and western China. Liu Bei would then form an alliance with Sun Quan, who ruled eastern China, and wage war against Cao Cao, who controlled northern China and the political centre of the Han dynasty in central China. Liu Bei would then lead one army from Yi Province to attack Chang'an
Chang'an (; ) is the traditional name of Xi'an. The site had been settled since Neolithic times, during which the Yangshao culture was established in Banpo, in the city's suburbs. Furthermore, in the northern vicinity of modern Xi'an, Qin ...
via the Qin Mountains
The Qinling () or Qin Mountains, formerly known as the Nanshan ("Southern Mountains"), are a major east–west mountain range in southern Shaanxi Province, China. The mountains mark the divide between the drainage basins of the Yangtze and Yellow ...
and Wei River valley; one of Liu Bei's top generals would lead another army from Jing Province to attack Luoyang
Luoyang is a city located in the confluence area of Luo River and Yellow River in the west of Henan province. Governed as a prefecture-level city, it borders the provincial capital of Zhengzhou to the east, Pingdingshan to the southeast, Nanyan ...
.
The first phase of the plan was completed in 214 when Liu Bei gained control of southern Jing Province and Yi Province. Between 217 and 219, Liu Bei launched a campaign to seize control of Hanzhong Commandery, the "northern gateway" into Yi Province, and succeeded in capturing it from Cao Cao's forces. In 219, Liu Bei's general Guan Yu, whom Liu Bei had left in charge of Jing Province, started the Battle of Fancheng
The Battle of Fancheng or the Battle of Fan Castle was fought between the warlords Liu Bei and Cao Cao in 219 in the late Eastern Han dynasty. It is named after Fancheng in present-day Xiangyang, Hubei, a fortress that played a significant ro ...
against Cao Cao's forces. However, the Sun Quan–Liu Bei alliance ("Sun–Liu alliance"), which Zhuge Liang played an instrumental role in creating, broke down when Sun Quan sent his forces to attack and seize Liu Bei's territories in Jing Province while Guan Yu was away at the Battle of Fancheng. Guan Yu was captured and executed by Sun Quan's forces. Between 221 and 222, Liu Bei started the Battle of Xiaoting/Yiling against Sun Quan in an attempt to retake Jing Province, but failed and suffered a disastrous defeat. After Liu Bei died in 223, his son Liu Shan
Liu Shan () (207–271), courtesy name Gongsi, was the second and last emperor of the state of Shu Han during the Three Kingdoms period. As he ascended the throne at the age of 16, Liu Shan was entrusted to the care of the Chancellor Zhuge ...
succeeded him as emperor of Shu, with Zhuge Liang serving as regent. In the same year, Zhuge Liang made peace with Sun Quan's Eastern Wu regime and reestablished the Sun–Liu alliance (now the Wu–Shu alliance) against Wei, the regime established by Cao Cao's son and successor, Cao Pi
Cao Pi () ( – 29 June 226), courtesy name Zihuan, was the first emperor of the state of Cao Wei in the Three Kingdoms period of China. He was the second son of Cao Cao, a warlord who lived in the late Eastern Han dynasty, but the eldest s ...
.
In 227, Zhuge Liang ordered troops from throughout Shu to mobilise and assemble in Hanzhong Commandery in preparation for a large-scale military campaign against Wei. Before leaving, he wrote a memorial
A memorial is an object or place which serves as a focus for the memory or the commemoration of something, usually an influential, deceased person or a historical, tragic event. Popular forms of memorials include landmark objects or works of ...
, called ''Chu Shi Biao
The ''Chu Shi Biao'' refers to either of two memorials written by Zhuge Liang, the Imperial Chancellor of the state of Shu during the Three Kingdoms period of China. He presented them to Liu Shan, the second emperor of Shu. The first ''Chu Shi ...
'' (literally "memorial on the case to go to war"), and submitted it to Liu Shan. Among other things, the memorial contained Zhuge Liang's reasons for the campaign against Wei and his personal advice to Liu Shan on governance issues. After Liu Shan approved, Zhuge Liang ordered the Shu forces to garrison at Mianyang (沔陽; present-day Mian County, Shaanxi
Shaanxi (alternatively Shensi, see § Name) is a landlocked province of China. Officially part of Northwest China, it borders the province-level divisions of Shanxi (NE, E), Henan (E), Hubei (SE), Chongqing (S), Sichuan (SW), Gansu (W), N ...
).
Geography
Zhuge Liang's plan called for a march north from Hanzhong Commandery (what is now southernShaanxi
Shaanxi (alternatively Shensi, see § Name) is a landlocked province of China. Officially part of Northwest China, it borders the province-level divisions of Shanxi (NE, E), Henan (E), Hubei (SE), Chongqing (S), Sichuan (SW), Gansu (W), N ...
province), the main population centre in northern Yi Province. In the third century, Hanzhong Commandery was a sparsely populated area surrounded by wild virgin forest. Its importance lay in its strategic placement in a long and fertile plain along the Han River, between two massive mountain ranges, the Qin Mountains
The Qinling () or Qin Mountains, formerly known as the Nanshan ("Southern Mountains"), are a major east–west mountain range in southern Shaanxi Province, China. The mountains mark the divide between the drainage basins of the Yangtze and Yellow ...
in the north and the Micang Mountains in the south. It was the major administrative centre of the mountainous frontier district between the rich Sichuan Basin
The Sichuan Basin (), formerly transliterated as the Szechwan Basin, sometimes called the Red Basin, is a lowland region in southwestern China. It is surrounded by mountains on all sides and is drained by the upper Yangtze River and its tributar ...
in the south and the Wei River valley in the north. The area also afforded access to the dry northwest and the Gansu
Gansu (, ; alternately romanized as Kansu) is a province in Northwest China. Its capital and largest city is Lanzhou, in the southeast part of the province.
The seventh-largest administrative district by area at , Gansu lies between the Tibe ...
panhandle.
Geographically, the rugged barrier of the Qin Mountains provided the greatest obstacle to Chang'an
Chang'an (; ) is the traditional name of Xi'an. The site had been settled since Neolithic times, during which the Yangshao culture was established in Banpo, in the city's suburbs. Furthermore, in the northern vicinity of modern Xi'an, Qin ...
. The mountain range consists of a series of parallel ridges, all running slightly south of east, separated by a maze of ramifying valleys whose canyon walls often rise sheer above the valley streams. As a result of local dislocations from earthquakes, the topographical features are extremely complicated. Access from the south was limited to a few mountain routes called " gallery roads". These crossed major passes and were remarkable for their engineering skill and ingenuity. The oldest of these was to the northwest of Hanzhong Commandery and it crossed the San Pass. The Lianyun "Linked Cloud" Road was constructed there to take carriage traffic during the Qin dynasty
The Qin dynasty ( ; zh, c=秦朝, p=Qín cháo, w=), or Ch'in dynasty in Wade–Giles romanization ( zh, c=, p=, w=Ch'in ch'ao), was the first dynasty of Imperial China. Named for its heartland in Qin state (modern Gansu and Shaanxi), ...
in the third century BCE. Following the Jialing Valley, the route emerges in the north where the Wei River widens considerably near Chencang (in present-day Baoji
() is a prefecture-level city in western Shaanxi province, People's Republic of China. Since the early 1990s, Baoji has been the second largest city in Shaanxi.
Geography
The prefecture-level city of Baoji had a population of 3,321,853 accor ...
, Shaanxi). Another important route was the Baoye route, which transverses the Yegu Pass and ends south of Mei County. A few more minor and difficult routes lay to the east, notably the Ziwu Valley, which leads directly to the south of Chang'an.
Xincheng Rebellion
Meng Da, a former Shu general who defected to Wei in 220, served as the Administrator of Xincheng Commandery (新城郡; in present-day northwesternHubei
Hubei (; ; alternately Hupeh) is a landlocked province of the People's Republic of China, and is part of the Central China region. The name of the province means "north of the lake", referring to its position north of Dongting Lake. The p ...
) near Shu's northeastern border. Zhuge Liang hated Meng Da for his capricious behaviour and worried that he would become a threat to Shu. Around 227, when he heard that Meng Da had a quarrel with his colleague Shen Yi (申儀), he sent spies to stir up greater suspicions between them and spread news that Meng Da was plotting a rebellion against Wei. Meng Da became fearful and decided to rebel. However, he was stuck in a dilemma after receiving a letter from the Wei general Sima Yi
Sima Yi ( ; 179 CE – 7 September 251 CE), courtesy name Zhongda, was a Chinese military general, politician, and regent of the state of Cao Wei during the Three Kingdoms period of China.
He formally began his political career in 208 un ...
, who was stationed at Wancheng
Wancheng District () is one of two districts of the city of Nanyang, in the southwest of Henan province, People's Republic of China.
Administrative divisions
As 2012, this district is divided to 6 subdistricts, 4 towns and 6 townships.
;Subdist ...
. In the meantime, Sima Yi quickly assembled an army, headed towards Xincheng, and reached there within eight days.
Wei's rival states, Shu and Wu, sent forces to support Meng Da, but were defeated and driven back by Wei forces led by Sima Yi's subordinates. Sima Yi ordered his troops to surround Shangyong (上庸), Meng Da's base, and attack from eight directions. At the same time, he also successfully induced Meng Da's nephew Deng Xian (鄧賢) and subordinate Li Fu (李輔) to betray Meng Da. After 16 days of siege, Deng Xian and Li Fu opened Shangyong's gates and surrendered to Sima Yi. Meng Da was captured and executed. Sima Yi and his troops headed back to Wancheng after suppressing the rebellion. He then went to the Wei capital, Luoyang
Luoyang is a city located in the confluence area of Luo River and Yellow River in the west of Henan province. Governed as a prefecture-level city, it borders the provincial capital of Zhengzhou to the east, Pingdingshan to the southeast, Nanyan ...
, to report to the Wei emperor Cao Rui and returned to Wancheng after that.
First expedition
 In the spring of 228, Zhuge Liang launched the first Northern Expedition and led the Shu forces to Mount Qi (祁山; the mountainous regions around present-day Li County, Gansu). At the same time, he ordered Zhao Yun and Deng Zhi to lead a decoy force to Ji Valley (箕谷) and pretend to be ready to attack Mei County, so as to divert the Wei forces' attention away from Mount Qi. News of the Shu invasion sent shock waves throughout the Guanzhong region. Three Wei-controlled commanderies – Nan'an (南安), Tianshui and Anding (安定) – defected to the Shu side.
In response to the Shu invasion, Cao Rui moved from
In the spring of 228, Zhuge Liang launched the first Northern Expedition and led the Shu forces to Mount Qi (祁山; the mountainous regions around present-day Li County, Gansu). At the same time, he ordered Zhao Yun and Deng Zhi to lead a decoy force to Ji Valley (箕谷) and pretend to be ready to attack Mei County, so as to divert the Wei forces' attention away from Mount Qi. News of the Shu invasion sent shock waves throughout the Guanzhong region. Three Wei-controlled commanderies – Nan'an (南安), Tianshui and Anding (安定) – defected to the Shu side.
In response to the Shu invasion, Cao Rui moved from Luoyang
Luoyang is a city located in the confluence area of Luo River and Yellow River in the west of Henan province. Governed as a prefecture-level city, it borders the provincial capital of Zhengzhou to the east, Pingdingshan to the southeast, Nanyan ...
to Chang'an
Chang'an (; ) is the traditional name of Xi'an. The site had been settled since Neolithic times, during which the Yangshao culture was established in Banpo, in the city's suburbs. Furthermore, in the northern vicinity of modern Xi'an, Qin ...
to oversee the defences and provide backup. He ordered Zhang He to attack Zhuge Liang at Mount Qi, and Cao Zhen to attack Zhao Yun and Deng Zhi at Ji Valley. Zhao Yun and Deng Zhi lost the Battle of Ji Valley because their decoy force, composed of the weaker soldiers in the Shu army, were no match for Cao Zhen and his well-trained troops. (Zhuge Liang had reserved the better troops for the attack on Mount Qi.) In the meantime, Zhuge Liang sent Ma Su to lead the vanguard force to engage Zhang He at Jieting (街亭; located east of present-day Qin'an County, Gansu). Ma Su not only disobeyed Zhuge Liang's orders, but also made the wrong moves, resulting in the Shu vanguard suffering a disastrous defeat. After his victory at the Battle of Jieting, Zhang He seized the opportunity to attack and recapture the three commanderies.
Upon learning of the Shu defeats at Ji Valley and Jieting, Zhuge Liang pulled back all his forces and retreated to Hanzhong
Hanzhong (; abbreviation: Han) is a prefecture-level city in the southwest of Shaanxi province, China, bordering the provinces of Sichuan to the south and Gansu to the west.
The founder of the Han dynasty, Liu Bang, was once enfeoffed as ...
. Although the first Northern Expedition was an overall failure, Zhuge Liang still made some small gains for Shu. The first gain was the capture of some Wei civilian families, who were then registered as Shu citizens and resettled in Hanzhong. The second gain was the defection of Jiang Wei, a low-ranking Wei officer who later became a prominent Shu general. After returning to Hanzhong, Zhuge Liang executed Ma Su to appease public anger and then wrote a memorial
A memorial is an object or place which serves as a focus for the memory or the commemoration of something, usually an influential, deceased person or a historical, tragic event. Popular forms of memorials include landmark objects or works of ...
to Liu Shan
Liu Shan () (207–271), courtesy name Gongsi, was the second and last emperor of the state of Shu Han during the Three Kingdoms period. As he ascended the throne at the age of 16, Liu Shan was entrusted to the care of the Chancellor Zhuge ...
, taking full responsibility for the failure of the first Northern Expedition and requesting to be punished by demotion. Liu Shan approved and symbolically demoted Zhuge Liang from Imperial Chancellor (丞相) to General of the Right (右將軍), but allowed him to remain as acting Imperial Chancellor.
Second expedition
In the winter of 228–229, Zhuge Liang launched the second Northern Expedition and led Shu forces to attack the Wei fortress at Chencang via San Pass. When he showed up at Chencang, he was surprised to see that it was much more heavily fortified and well-defended than he expected. That was because after the first Northern Expedition, the Wei general Cao Zhen had predicted that Shu forces would attack Chencang the next time, so he put Hao Zhao in charge of defending Chencang and strengthening its defences. Zhuge Liang first ordered his troops to surround Chencang, then sent Jin Xiang (靳詳), an old friend of Hao Zhao, to persuade Hao Zhao to surrender. Hao Zhao refused twice. Although Hao Zhao had only 1,000 men with him to defend Chencang, he successfully held his ground against the Shu forces. During the 20-day-long siege of Chencang, Zhuge Liang used an array of tactics to attack the fortress –siege ladders
{{Unreferenced, date=May 2007
Escalade is the act of scaling defensive walls or ramparts with the aid of ladders. Escalade was a prominent feature of sieges in ancient and medieval warfare, and though it is no longer common in modern warfare, ...
, battering rams, siege towers and tunnels – but Hao Zhao successfully countered each of them in turn. Upon learning that Wei reinforcements were approaching Chencang, Zhuge Liang immediately pulled back all his troops and returned to Hanzhong. A Wei officer, Wang Shuang, led his men to attack the retreating Shu forces, but was killed in an ambush.
Third expedition
 In the spring of 229, Zhuge Liang launched the third Northern Expedition and ordered Chen Shi to lead Shu forces to attack the Wei-controlled Wudu (武都) and Yinping (陰平) commanderies. The Wei general Guo Huai led his troops to resist Chen Shi. He retreated after Zhuge Liang led a Shu army to Jianwei (建威; in present-day Longnan, Gansu). The Shu forces then conquered Wudu and Yinping commanderies.
When Zhuge Liang returned from the campaign, the Shu emperor
In the spring of 229, Zhuge Liang launched the third Northern Expedition and ordered Chen Shi to lead Shu forces to attack the Wei-controlled Wudu (武都) and Yinping (陰平) commanderies. The Wei general Guo Huai led his troops to resist Chen Shi. He retreated after Zhuge Liang led a Shu army to Jianwei (建威; in present-day Longnan, Gansu). The Shu forces then conquered Wudu and Yinping commanderies.
When Zhuge Liang returned from the campaign, the Shu emperor Liu Shan
Liu Shan () (207–271), courtesy name Gongsi, was the second and last emperor of the state of Shu Han during the Three Kingdoms period. As he ascended the throne at the age of 16, Liu Shan was entrusted to the care of the Chancellor Zhuge ...
issued an imperial decree to congratulate him on his successes in defeating Wang Shuang during the second Northern Expedition, forcing Guo Huai to flee, winning back the trust of the local tribes and capturing Wudu and Yinping commanderies during the third Northern Expedition. He also restored Zhuge Liang to the position of Imperial Chancellor (丞相).
Fourth expedition
 In 230, during the
In 230, during the Ziwu Campaign
The Ziwu Campaign was a military counter offensive launched in 230 by the state of Cao Wei against his rival state Shu Han during the Three Kingdoms period of China. The campaign was initiated by Wei's Grand Marshal, Cao Zhen following the num ...
Shu forces led by Wei Yan defeated Wei forces under Fei Yao
Fei Yao ( 220–231) was a military general of the state of Cao Wei during the Three Kingdoms period of China.
Life
Little information about Fei Yao is recorded in history; unlike other notable figures of the late Eastern Han dynasty and Three ...
and Guo Huai at Yangxi (陽谿; southwest of present-day Wushan County, Gansu).
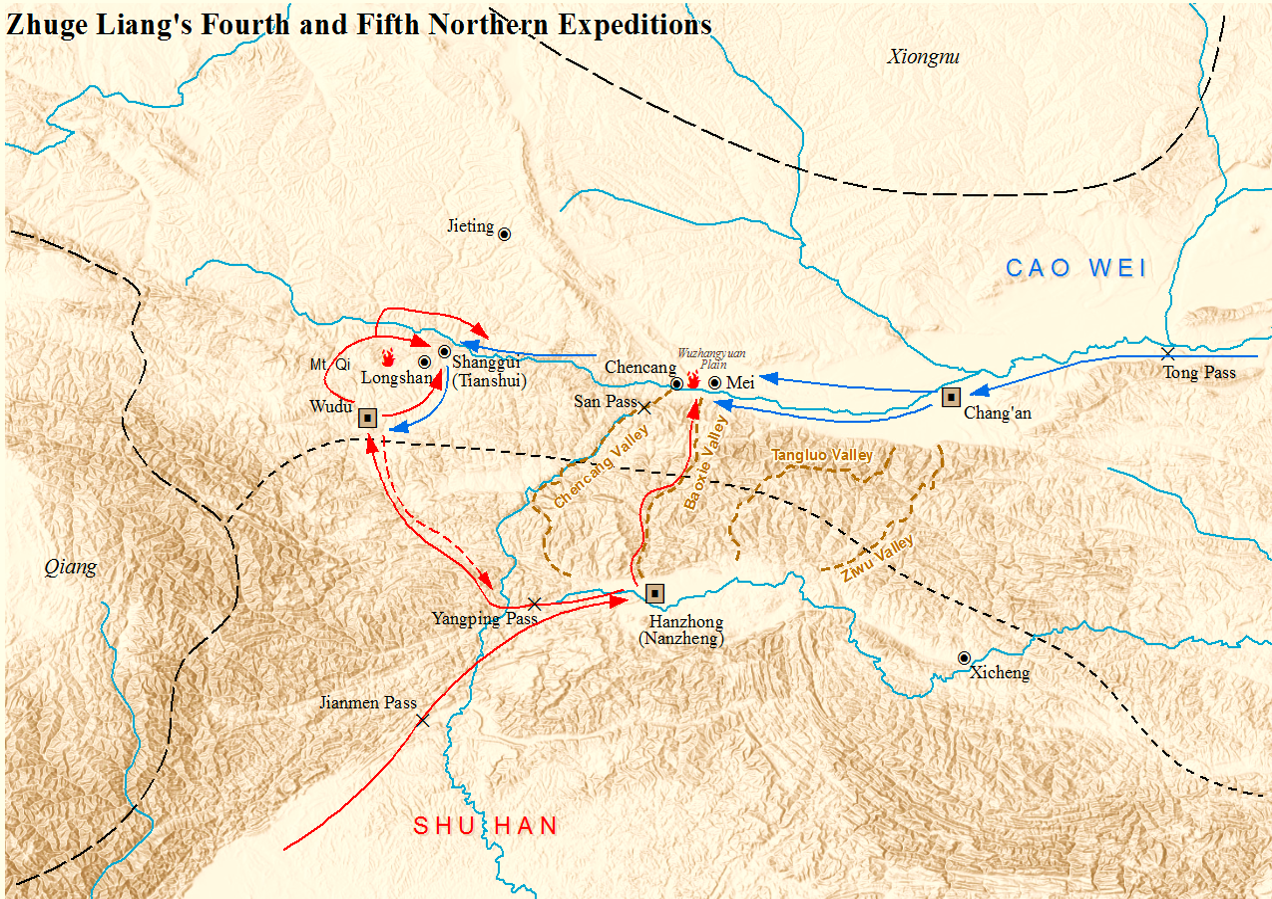
In 231, Zhuge Liang launched the fourth Northern Expedition and attacked Mount Qi again. He used the wooden ox, a mechanical device he invented, to transport food supplies to the frontline. The Shu forces attacked Tianshui Commandery and surrounded Mount Qi, which was defended by the Wei officers Jia Si (賈嗣) and Wei Ping (魏平). At Mount Qi, Zhuge Liang managed to convince Kebineng
Kebineng (died 235) was a Xianbei chieftain who lived during the late Eastern Han dynasty and Three Kingdoms period of China. He rose to power during the late Eastern Han dynasty after the warlord Cao Cao defeated the Wuhuan tribes in northern Chi ...
, a Xianbei tribal leader, to support Shu in the war against Wei. Kebineng went to Beidi Commandery and rallied the locals to support Shu.
At the time, as Cao Zhen, the Wei grand marshal, was ill, the Wei emperor Cao Rui ordered the general Sima Yi
Sima Yi ( ; 179 CE – 7 September 251 CE), courtesy name Zhongda, was a Chinese military general, politician, and regent of the state of Cao Wei during the Three Kingdoms period of China.
He formally began his political career in 208 un ...
to move to Chang'an
Chang'an (; ) is the traditional name of Xi'an. The site had been settled since Neolithic times, during which the Yangshao culture was established in Banpo, in the city's suburbs. Furthermore, in the northern vicinity of modern Xi'an, Qin ...
to supervise the Wei defences in the Guanzhong region against the Shu invasion. After making preparations for battle, Sima Yi, with Zhang He, Fei Yao
Fei Yao ( 220–231) was a military general of the state of Cao Wei during the Three Kingdoms period of China.
Life
Little information about Fei Yao is recorded in history; unlike other notable figures of the late Eastern Han dynasty and Three ...
, Dai Ling (戴陵) and Guo Huai serving as his subordinates, led Wei forces to Yumi County (隃麋縣; east of present-day Qianyang County
Qianyang County () is a county in the west of Shaanxi province, China, bordering Gansu province to the north. It is under the administration of the prefecture-level city of Baoji
() is a prefecture-level city in western Shaanxi province, Peopl ...
, Shaanxi) and stationed there. He then left Fei Yao and Dai Ling with 4,000 troops to guard Shanggui County (上邽縣; in present-day Tianshui, Gansu), while he led the others to Mount Qi to help Jia Si and Wei Ping.
When Zhuge Liang learnt of the Wei forces' approach, he split his forces into two groups – one group to remain at Mount Qi while he led the other group to attack Shanggui County. He defeated Guo Huai, Fei Yao and Dai Ling in battle and ordered his troops to collect the harvest in Shanggui County. In response, Sima Yi turned back from Mount Qi, headed to Shanggui County, and reached there within two days. By then, Zhuge Liang and his men had finished harvesting the wheat and were preparing to leave. Zhuge Liang encountered Sima Yi at Hanyang (漢陽) to the east of Shanggui County, but they did not engage in battle: Zhuge Liang ordered his troops to make use of the terrain and get into defensive positions; Sima Yi ordered his troops to get into formation, while sending Niu Jin
Niu Jin () ( 208–238) was a military general serving under the warlord Cao Cao during the late Eastern Han dynasty of China. He continued serving in the state of Cao Wei, founded by Cao Cao's successor Cao Pi, during the Three Kingdoms period ...
to lead a lightly armed cavalry detachment to Mount Qi. The stand off ended when Zhuge Liang and the Shu forces retreated to Lucheng (鹵城), took control of the hills in the north and south, and used the river as a natural barrier.
Although his subordinates repeatedly urged him to attack the enemy, Sima Yi was hesitant to do so after seeing the layout of the Shu camps in the hills. However, he eventually relented when Jia Si and Wei Ping mocked him and said he would become a laughing stock if he refused to attack. Sima Yi then sent Zhang He to attack the Shu camp in the south, guarded by Wang Ping, while he led the others to attack Lucheng head-on. In response, Zhuge Liang ordered Wei Yan, Wu Ban and Gao Xiang to resist the enemy outside Lucheng, where the Wei forces suffered an unexpected and tremendous defeat: 3,000 soldiers were killed, and 5,000 suits of armour and 3,100 sets of hornbeam crossbows were seized by Shu forces. Even though the losses were heavy, Sima Yi still retained a sizeable army, which he led back to his camp.
Despite the victory, Zhuge Liang could not press his advantage with a major offensive due to a dwindling food supply. Adverse weather prevented Shu's logistics from delivering matériel on schedule. Li Yan, the Shu general responsible for overseeing the transportation of food supplies to the frontline, falsely claimed that the emperor Liu Shan
Liu Shan () (207–271), courtesy name Gongsi, was the second and last emperor of the state of Shu Han during the Three Kingdoms period. As he ascended the throne at the age of 16, Liu Shan was entrusted to the care of the Chancellor Zhuge ...
had ordered a withdrawal. The ''Book of Jin
The ''Book of Jin'' is an official Chinese historical text covering the history of the Jin dynasty from 266 to 420. It was compiled in 648 by a number of officials commissioned by the imperial court of the Tang dynasty, with chancellor Fang ...
'' claimed that Sima Yi launched an attack on Shu garrisons at this juncture and succeeded in capturing the Shu "covering camps". Zhuge Liang abandoned Lucheng and retreated under the cover of night, but Sima Yi pursued him and inflicted roughly 10,000 casualties on the Shu army. This account from the ''Book of Jin'' is disputed by historians and is not included in the 11th-century outstanding chronological historical text ''Zizhi Tongjian
''Zizhi Tongjian'' () is a pioneering reference work in Chinese historiography, published in 1084 AD during the Northern Song dynasty in the form of a chronicle recording Chinese history from 403 BC to 959 AD, covering 16 dynast ...
''.
In any case, according to ''Records of the Three Kingdoms
The ''Records or History of the Three Kingdoms'', also known by its Chinese name as the Sanguo Zhi, is a Chinese historical text which covers the history of the late Eastern Han dynasty (c. 184–220 AD) and the Three Kingdoms period (220� ...
'' and ''Zizhi Tongjian
''Zizhi Tongjian'' () is a pioneering reference work in Chinese historiography, published in 1084 AD during the Northern Song dynasty in the form of a chronicle recording Chinese history from 403 BC to 959 AD, covering 16 dynast ...
'', Zhuge Liang retreated to the Shu, because of lack of supply, not defeat. and the Wei forces pursued him. The pursuit did not go completely smoothly for Wei. Sima Yi ordered Zhang He to further pursue the enemy in an attempt to capitalise on their momentum. The '' Weilüe'' mentioned that Zhang He refused to obey Sima Yi's order and argued that, according to classical military doctrine, one should refrain from pursuing an enemy force retreating to its home territory. However, Sima Yi refused to listen and forced Zhang He to carry out this order. Indeed, Zhang He fell into an ambush at Mumen Trail (木門道; near present-day Qinzhou District, Tianshui, Gansu), where Zhuge Liang had ordered crossbowmen to hide on high ground and fire at approaching enemy forces when they entered a narrow defile. Zhang He died after a stray arrow hit him in the right knee. Unlike ''book of Jin'' records, Wei's army suffered a great deal of damage from pursuing Shu's retreating army.
Fifth expedition
In the spring of 234, Zhuge Liang led more than 100,000 Shu troops out of Xie Valley (斜谷) and camped at theWuzhang Plains
The Wuzhang Plains (五丈原) are plateaus near the Wei River in China. They are now in the Shaanxi province, 56 kilometres from Baoji. The name "Wuzhang" means "five '' zhang''", where ''zhang'' (丈) is a Chinese unit of measurement which conv ...
on the south bank of the Wei River near Mei County. Aside from using the flowing horse to transport food supplies to the frontline, he implemented a '' tuntian'' plan by ordering his troops to grow crops alongside civilians at the south bank of the Wei River. He also forbid his troops from taking the civilians' crops.
In response to the Shu invasion, the Wei general Sima Yi
Sima Yi ( ; 179 CE – 7 September 251 CE), courtesy name Zhongda, was a Chinese military general, politician, and regent of the state of Cao Wei during the Three Kingdoms period of China.
He formally began his political career in 208 un ...
led his forces and another 20,000 reinforcements to the Wuzhang Plains to engage the enemy. After an initial skirmish and a night raid on the Shu camp, Sima Yi received orders from the Wei emperor Cao Rui to hold his ground and refrain from engaging the Shu forces. The battle became a stalemate. During this time, Zhuge Liang made several attempts to lure Sima Yi to attack him. On one occasion, he sent women's ornaments to Sima Yi to taunt him. An apparently angry Sima Yi sought permission from Cao Rui to attack the enemy but was denied. Cao Rui even sent Xin Pi as his special representative to the frontline to ensure that Sima Yi followed orders and remained in camp. Zhuge Liang knew that Sima Yi was pretending to be angry because he wanted to show the Wei soldiers that he would not put up with Zhuge Liang's taunting and to ensure that his men were ready for battle.
During the stalemate, when Zhuge Liang sent a messenger to meet Sima Yi, Sima Yi asked the messenger about Zhuge Liang's daily routine and living conditions. The messenger said that Zhuge Liang consumed three to four ''sheng'' of grain a day and that he micromanaged almost everything, except trivial issues like punishments for minor offences. After hearing that, Sima Yi remarked, "How can Zhuge Kongming expect to last long? He's going to die soon."
The stalemate at the Wuzhang Plains lasted for over 100 days. Sometime between 11 September and 10 October 234, Zhuge Liang became critically ill and died in camp. He was 54 (by East Asian age reckoning) at the time of his death.(其年八月,亮疾病,卒于軍,時年五十四。) ''Sanguozhi'' vol. 35.
When Sima Yi heard from civilians that Zhuge Liang had died from illness and that the Shu army had burnt down their camp and retreated, he led his troops in pursuit and caught up with them. The Shu forces, on Yang Yi and Jiang Wei's command, turned around and readied themselves for battle. Sima Yi pulled back his troops and retreated. Some days later, while surveying the remains of the Shu camp, Sima Yi remarked, "What a genius he was!" Based on his observations that the Shu army made a hasty retreat, he concluded that Zhuge Liang had indeed died and so he led his troops in pursuit again. When Sima Yi reached Chi'an (赤岸), he asked the civilians living there about Zhuge Liang and heard that there was a recent popular saying: "A dead Zhuge (Liang) scares away a living Zhongda" He laughed and said, "I can predict the thoughts of the living but I can't predict those of the dead."(與之對壘百餘日,會亮病卒,諸將燒營遁走,百姓奔告,帝出兵追之。亮長史楊儀反旗鳴皷,若將距帝者。帝以窮寇不之逼,於是楊儀結陣而去。經日,乃行其營壘,觀其遺事,獲其圖書、糧穀甚衆。帝審其必死, ... 追到赤岸,乃知亮死審問。時百姓為之諺曰:「死諸葛走生仲達。」帝聞而笑曰:「吾便料生,不便料死故也。」) ''Jin Shu'' vol. 1.
Results
Zhuge Liang's expeditions managed to inflict damage to the Wei army, killed several notable Wei commanders, and captured two small commanderies, but he failed to fulfil his strategic goal. After Zhuge Liang's death, his successor, Jiang Wan, changed the policy and turned to a defensive stance. Some people inEastern Wu
Wu (Chinese: 吳; pinyin: ''Wú''; Middle Chinese *''ŋuo'' < : ''*ŋuɑ''), known in hi ...
suspected that Shu Han wanted to renege on the Shu-Wu alliance, but Sun Quan commented that it was simply a sign of fatigue and exhaustion.
Yi Zhongtian listed three reasons for Zhuge Liang's failures:Yi Zhongtian. Analysis of the Three Kingdoms, Vol. 2, Vietnamese translation. Publisher of People's Public Security, 2010. Chapter 41: Attacks for Defenses
#Strong enemy: Cao Wei regime was robust and stable and had many talents (such as Sima Yi) and so could not be easily tackled by Shu Han.
#Rough terrain: Cao Wei and Shu Han were separated by natural barriers, which put extremely heavy logistical burdens on the Shu Han army including providing adequate food supply. This was a key reason for the failure of the expeditions.
#Zhuge Liang's own limitations: Zhuge Liang was an excellent military organizer but not an outstanding military commander. Zhuge Liang lacked the cleverness and decisiveness of a military general since he could properly lead an army but could not conduct complex and deceptive moves.
Yi Zhongtian argued that Zhuge Liang knew full well of all of the difficulties, including his own weaknesses, but Liang still pressed on with the Northern Expeditions for three reasons:
# Han restoration: Zhuge Liang was sincere and faithful to his goal of restoring the Han dynasty. He could change the tactics depended on the situation but never deviated from his ultimate goal.
#Waging war for internal stability: The expeditions also served as a means to maintain the "state of war" and hence "martial rule" over Shu Han. Zhuge Liang wanted to use "martial rule" to tighten control over the local nobility and the privileged classes, which were not always happy with Zhuge Liang's legalist
Legalist, Inc. is an investment firm that specializes in alternative assets in the private credit industry. Today the firm manages approximately $750 million across three separate strategies: litigation finance, bankruptcy ( debtor-in-possession ...
policies.
#Pre-emptive strike: Being the weakest of the three kingdoms, Shu Han would be the first one to be preyed upon. The only solution for that was making pre-emptive strikes to intimidate the enemy and to enlarge Shu Han's own power base. The pre-emptive moves did not guarantee a 100% success rate, but the option was better than doing nothing and withering away
In other words, Shu Han's relentless attacks against stronger enemy were from Zhuge Liang's point of view actually necessary for its own survival. Zhuge Liang was praised for being far-sighted in recognising this issue.
In ''Romance of the Three Kingdoms''
The Northern Expeditions are featured prominently in the 14th-century historical novel ''Romance of the Three Kingdoms
''Romance of the Three Kingdoms'' () is a 14th-century historical novel attributed to Luo Guanzhong. It is set in the turbulent years towards the end of the Han dynasty and the Three Kingdoms period in Chinese history, starting in 184 AD ...
'', covering 15 chapters (Chapters 91 to 105) out of a total of 120 chapters. Many actual events were largely romanticised or highly exaggerated, while some fictitious stories were also included, for dramatic effect. See the following for some fictitious stories in the novel that are related to the Northern Expeditions:
* Xincheng Rebellion#In Romance of the Three Kingdoms
* Empty Fort Strategy#Zhuge Liang
In popular culture
The Northern Expeditions are featured as playable stages inKoei
Koei Co., Ltd. was a Japanese video game publisher, developer, and distributor founded in 1978. The company is known for its ''Dynasty Warriors'' games based on the novel ''Romance of the Three Kingdoms'', as well as simulation games based on p ...
's video game series ''Dynasty Warriors
is a series of Japanese hack and slash action video games created by Omega Force and Koei (now is Koei Tecmo). The series is a spin-off of Koei's turn-based strategy ''Romance of the Three Kingdoms'' series, based upon the Chinese novel o ...
''. As of the sixth instalment in the franchise, all of the five expeditions are playable stages in some form. In the sixth game, the Battle of Wuzhang Plains is depicted as taking place shortly after the Battle of Yiling – with the battle serving as a final victory for the Shu forces in some cases –
while its proper point in time is restored with the seventh instalment. In the seventh and eighth games, the Battle of Wuzhang Plains is portrayed as a deadlock just as in history.
See also
* Zhuge Liang's Southern Campaign *Jiang Wei's Northern Expeditions
Jiang Wei's Northern Expeditions refer to a series of eleven military campaigns launched by the state of Shu Han against its rival state, Cao Wei, between 240 and 262 CE during the Three Kingdoms period in China. The campaigns were led by Jia ...
Notes
References
* Chen, Shou (3rd century). ''Records of the Three Kingdoms
The ''Records or History of the Three Kingdoms'', also known by its Chinese name as the Sanguo Zhi, is a Chinese historical text which covers the history of the late Eastern Han dynasty (c. 184–220 AD) and the Three Kingdoms period (220� ...
'' (''Sanguozhi'').
* Fang, Xuanling (648). ''Book of Jin
The ''Book of Jin'' is an official Chinese historical text covering the history of the Jin dynasty from 266 to 420. It was compiled in 648 by a number of officials commissioned by the imperial court of the Tang dynasty, with chancellor Fang ...
'' (''Jin Shu'').
* Luo, Guanzhong (14th century). ''Romance of the Three Kingdoms
''Romance of the Three Kingdoms'' () is a 14th-century historical novel attributed to Luo Guanzhong. It is set in the turbulent years towards the end of the Han dynasty and the Three Kingdoms period in Chinese history, starting in 184 AD ...
'' (''Sanguo Yanyi'').
* Pei, Songzhi (5th century). ''Annotations to Records of the Three Kingdoms
Annotations to Records of the Three Kingdoms () by Pei Songzhi (372-451) is an annotation completed in the 5th century of the 3rd century historical text ''Records of the Three Kingdoms'', compiled by Chen Shou. After leaving his native land, Pei ...
'' (''Sanguozhi zhu'').
* {{cite book , author-link=Sima Guang, last=Sima , first= Guang , year=1084 , title=Zizhi Tongjian
''Zizhi Tongjian'' () is a pioneering reference work in Chinese historiography, published in 1084 AD during the Northern Song dynasty in the form of a chronicle recording Chinese history from 403 BC to 959 AD, covering 16 dynast ...
Campaigns of the Three Kingdoms