Zanzibar Town on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Stonetown of Zanzibar ( ar, مدينة زنجبار الحجرية), also known as Mji Mkongwe ( Swahili for "old town"), is the old part of
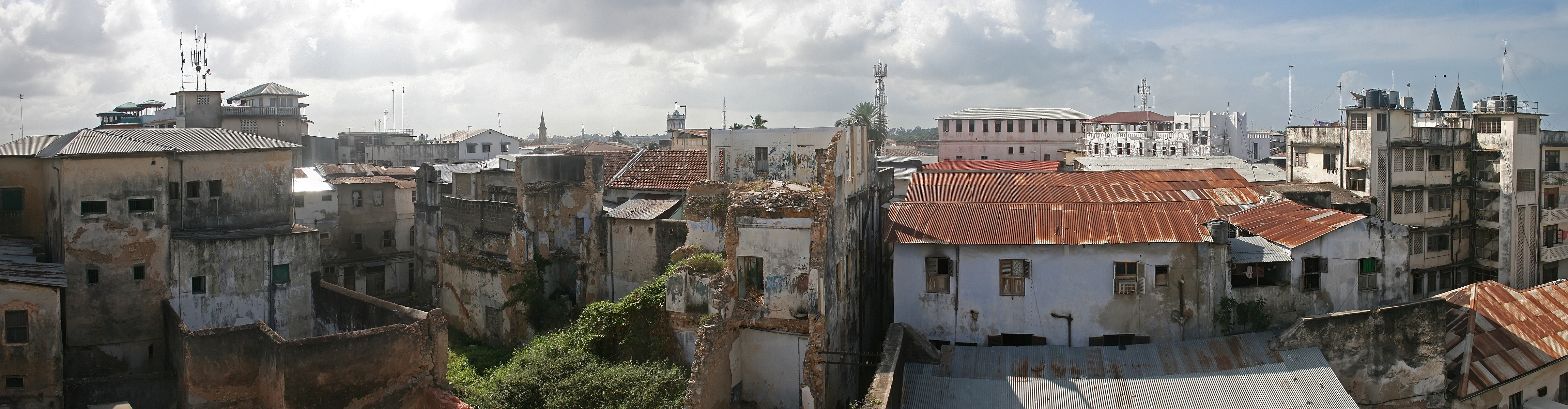 The heart of Stone Town mostly consists of a maze of narrow alleys lined by houses, shops, bazaars and
The heart of Stone Town mostly consists of a maze of narrow alleys lined by houses, shops, bazaars and
/ref> Traditional buildings have a ''baraza'', a long stone bench along the outside walls; this is used as an elevated sidewalk if heavy rains make the streets impracticable, or otherwise as benches to sit down, rest, socialize.Stone Town
at Overland Africa Another key feature of most buildings is large
 Stone Town is located along a natural harbour and the first Europeans to set foot on the island of
Stone Town is located along a natural harbour and the first Europeans to set foot on the island of
 In the last decades of the century, the Sultans of Zanzibar gradually lost their possessions in mainland
In the last decades of the century, the Sultans of Zanzibar gradually lost their possessions in mainland
 In 1964, Stone Town was the theatre of the
In 1964, Stone Town was the theatre of the

 #The House of Wonders (or "Palace of Wonders", also known as "Beit-al-Ajaib"), in located on the Mizingani Road along the Stone Town seafront, and is probably the most well-known landmarks of Stone Town. It was built in 1883 and restored after the
#The House of Wonders (or "Palace of Wonders", also known as "Beit-al-Ajaib"), in located on the Mizingani Road along the Stone Town seafront, and is probably the most well-known landmarks of Stone Town. It was built in 1883 and restored after the
/ref> It was built in late 19th century and now hosts a museum about the daily life of the Zanzibari royal family, including items that belonged to Sayyida Salme, a former Zanzibar princess who fled to relocate in Europe with her husband. #The
 The streets in Stone Town are very narrow and almost getting anywhere within the town must be done on foot. The narrow streets provide shade and almost everything is accessible from within the town. However, on slightly wider roads historically bicycles and now most recently motor cycles are used to transport people and goods. The town is accessible from Zanzibar and the rest of the region through three possible ports of entry.
The main form of public transport in Zanzibar are the
The streets in Stone Town are very narrow and almost getting anywhere within the town must be done on foot. The narrow streets provide shade and almost everything is accessible from within the town. However, on slightly wider roads historically bicycles and now most recently motor cycles are used to transport people and goods. The town is accessible from Zanzibar and the rest of the region through three possible ports of entry.
The main form of public transport in Zanzibar are the
/ref> For longer trips, "mabasi" (Swahili for "bus", singular "basi") are available, which are trucks adapted for passenger transport. The main "mabasi" station is also close to the Market and the "mabasi" network stretch across the entire island and is the cheapest form of long-distance transit. The main Zanzibar island harbour is in the heart of Stone Town and regular ferries from
File:Old dispensary front.jpg, The Old Dispensary
File:Shangani Post Office, Zanzibar.jpg, Shangani Post Office
File:Stone Town - Zanzibar - door.jpg, Traditional Zanzibar style door
File:Freddie Mercury's birthplace.jpg, Birth house of Freddie Mercury
File:Christ Church Stone Town Zanzibar.jpg, The
UNESCO Stone Town Site
Stone Town Conservation and Development Authority
{{Authority control Swahili city-states Swahili architecture Cities in Zanzibar Zanzibar City World Heritage Sites in Tanzania Aga Khan Trust for Culture projects Geography of Mjini Magharibi Region Archaeological sites of Eastern Africa
Zanzibar City
Zanzibar City or Mjini District, often simply referred to as Zanzibar (''Wilaya ya Zanzibar Mjini'' or ''Jiji la Zanzibar'' in Swahili) is one of two administrative districts of Mjini Magharibi Region in Tanzania. The district covers an area of ...
, the main city of Zanzibar
Zanzibar (; ; ) is an insular semi-autonomous province which united with Tanganyika in 1964 to form the United Republic of Tanzania. It is an archipelago in the Indian Ocean, off the coast of the mainland, and consists of many small islan ...
, in Tanzania
Tanzania (; ), officially the United Republic of Tanzania ( sw, Jamhuri ya Muungano wa Tanzania), is a country in East Africa within the African Great Lakes region. It borders Uganda to the north; Kenya to the northeast; Comoro Islands an ...
. The newer portion of the city is known as Ng'ambo
Ng'ambo (literally, "The Other Side"; sometimes also referred to as the "New City") is one of the two main parts comprising Zanzibar City, the capital of Zanzibar, the other being the historical Stone Town. Ng'ambo is much larger and more modern ...
, Swahili for 'the other side'. Stone Town is located on the western coast of Unguja
Unguja (also referred to as "Zanzibar Island" or simply "Zanzibar", in grc, Μενουθιάς, Menuthias – as mentioned in The ''Periplus of the Erythraean Sea'') is the largest and most populated island of the Zanzibar archipelago, in Tanza ...
, the main island of the Zanzibar Archipelago
The Zanzibar Archipelago ( ar, أرخبيل زنجبار, sw, Funguvisiwa la Zanzibar) consists of several islands lying off the coast of East Africa south of the Somali sea. The archipelago is also known as the Spice Islands. There are four ...
. Former capital of the Zanzibar Sultanate
The Sultanate of Zanzibar ( sw, Usultani wa Zanzibar, ar, سلطنة زنجبار , translit=Sulṭanat Zanjībār), also known as the Zanzibar Sultanate, was a state controlled by the Sultan of Zanzibar, in place between 1856 and 1964. The Sul ...
, and flourishing centre of the spice trade as well as the slave trade
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perf ...
in the 19th century, it retained its importance as the main city of Zanzibar during the period of the British protectorate. When Tanganyika and Zanzibar joined each other to form the United Republic of Tanzania, Zanzibar kept a semi-autonomous status, with Stone Town as its local government seat.
Stone Town is a city of prominent historical and artistic importance in East Africa
East Africa, Eastern Africa, or East of Africa, is the eastern subregion of the African continent. In the United Nations Statistics Division scheme of geographic regions, 10-11-(16*) territories make up Eastern Africa:
Due to the historica ...
. Its architecture, mostly dating back to the 19th century, reflects the diverse influences underlying the Swahili culture
Swahili culture is the culture of the Swahili people inhabiting the Swahili coast. This littoral area encompasses Tanzania, Kenya, and Mozambique, as well as the adjacent islands of Zanzibar and Comoros and some parts of Malawi. They speak Swah ...
, giving a unique mixture of Arab, Persian
Persian may refer to:
* People and things from Iran, historically called ''Persia'' in the English language
** Persians, the majority ethnic group in Iran, not to be conflated with the Iranic peoples
** Persian language, an Iranian language of the ...
, Indian and European elements. For this reason, the town was designated as a UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. It ...
World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for ...
in 2000.
Due to its heritage, Stone Town is also a major visitor attraction
A tourist attraction is a place of interest that tourists visit, typically for its inherent or an exhibited natural or cultural value, historical significance, natural or built beauty, offering leisure and amusement.
Types
Places of natural b ...
in Tanzania, and a large part of its economy depends on tourism
Tourism is travel for pleasure or business; also the theory and practice of touring (disambiguation), touring, the business of attracting, accommodating, and entertaining tourists, and the business of operating tour (disambiguation), tours. Th ...
-related activities.
Overview
 The heart of Stone Town mostly consists of a maze of narrow alleys lined by houses, shops, bazaars and
The heart of Stone Town mostly consists of a maze of narrow alleys lined by houses, shops, bazaars and mosque
A mosque (; from ar, مَسْجِد, masjid, ; literally "place of ritual prostration"), also called masjid, is a place of prayer for Muslims. Mosques are usually covered buildings, but can be any place where prayers (sujud) are performed, in ...
s. Since most streets are too narrow for cars, the town is crowded with bicycle
A bicycle, also called a pedal cycle, bike or cycle, is a human-powered or motor-powered assisted, pedal-driven, single-track vehicle, having two wheels attached to a frame, one behind the other. A is called a cyclist, or bicyclist.
Bic ...
s and motorbike
A motorcycle (motorbike, bike, or trike (if three-wheeled)) is a two or three-wheeled motor vehicle steered by a handlebar. Motorcycle design varies greatly to suit a range of different purposes: long-distance travel, commuting, cruising ...
s. The seafront has wider streets and larger, more regularly placed buildings.
Stone Town's architecture has a number of distinctive features, as a result of Arab, Persian, Indian, European, and African traditions mixing together. The name "Stone Town" comes from the ubiquitous use of coral stone as the main construction material; this stone gives the town a characteristic, reddish warm colour.Independent Travel Guide to Zanzibar/ref> Traditional buildings have a ''baraza'', a long stone bench along the outside walls; this is used as an elevated sidewalk if heavy rains make the streets impracticable, or otherwise as benches to sit down, rest, socialize.Stone Town
at Overland Africa Another key feature of most buildings is large
veranda
A veranda or verandah is a roofed, open-air gallery or porch, attached to the outside of a building. A veranda is often partly enclosed by a railing and frequently extends across the front and sides of the structure.
Although the form ''veran ...
s protected by carved wooden balustrade
A baluster is an upright support, often a vertical moulded shaft, square, or lathe-turned form found in stairways, parapets, and other architectural features. In furniture construction it is known as a spindle. Common materials used in its c ...
s. The best-known feature of Zanzibari houses are the finely decorated wooden doors, with rich carvings and bas-relief
Relief is a sculptural method in which the sculpted pieces are bonded to a solid background of the same material. The term ''relief'' is from the Latin verb ''relevo'', to raise. To create a sculpture in relief is to give the impression that the ...
s, sometimes with big brass studs of Indian tradition. Two main types of doors can be distinguished: those of Indian style have rounded tops, while those in the Omani Arab style are rectangular. Carvings are often Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God (or '' Allah'') as it was revealed to Muhammad, the ...
ic in content (for example, many consist of verses of the Qur'an
The Quran (, ; Standard Arabic: , Quranic Arabic: , , 'the recitation'), also romanized Qur'an or Koran, is the central religious text of Islam, believed by Muslims to be a revelation from God. It is organized in 114 chapters (pl.: , si ...
), but other symbolism is occasionally used, e.g., Indian lotus flowers as emblems of prosperity.
Stone Town is punctuated with major historical buildings, several of which are found on the seafront; these include former palaces of the sultans, fortifications, churches, mosques, and other institutional buildings.
While Stone Town was included in UNESCO's World Heritage Sites in 2000, this designation does not provide complete protection for the town's heritage. Despite the establishment of a Conservation Authority, about 80% of the 1,709 buildings of Stone Town are in a deteriorating condition. As coral stone is very friable, frequent maintenance is needed for most of these buildings. Some major restoration projects (especially on the seafront) have been done in recent times by the Aga Khan Trust for Culture
The Aga Khan Trust for Culture (AKTC) is an agency of the Aga Khan Development Network (AKDN), a family of institutions created by Aga Khan IV with distinct but complementary mandates to improve the welfare and prospects of people in the developi ...
(AKTC).
History
Medieval Zanzibar
A Greco-Roman text between the 1st and 3rd centuries, the ''Periplus of the Erythraean Sea
The ''Periplus of the Erythraean Sea'' ( grc, Περίπλους τῆς Ἐρυθρᾶς Θαλάσσης, ', modern Greek '), also known by its Latin name as the , is a Greco-Roman periplus written in Koine Greek that describes navigation an ...
'', mentioned the island of ''Menuthias'' ( grc, Μενουθιάς), which is probably Unguja
Unguja (also referred to as "Zanzibar Island" or simply "Zanzibar", in grc, Μενουθιάς, Menuthias – as mentioned in The ''Periplus of the Erythraean Sea'') is the largest and most populated island of the Zanzibar archipelago, in Tanza ...
. Zanzibar, like the nearby coast, was settled by Bantu-speakers at the outset of the first millennium. Archaeological finds at Fukuchani, on the north-west coast of Zanzibar, indicate a settled agricultural and fishing community from the 6th century CE at the latest. The considerable amount of daub found indicates timber buildings, and shell beads, bead grinders, and iron slag have been found at the site. There is evidence for limited engagement in long-distance trade: a small amount of imported pottery has been found, less than 1% of total pottery finds, mostly from the Gulf and dated to the 5th to 8th century. The similarity to contemporary sites such as Mkokotoni and Dar es Salaam indicate a unified group of communities that developed into the first center of coastal maritime culture. The coastal towns, including those on Zanzibar, appear to have been engaged in Indian Ocean trade at this early period. Trade rapidly increased in importance and quantity beginning in the mid-8th century and by the close of the 10th century Zanzibar was one of the central Swahili trading towns.
Shangani, the original fishing town that developed into Stone Town, was a small, largely unimportant Swahili site founded in the 11th century. Bigger towns at Unguja Ukuu
Unguja Ukuu (''Mji wa Kale wa Unguja Ukuu'' in Swahili) is a historic Swahili settlement on Unguja island (Zanzibar Island), in Zanzibar, Tanzania.
Background
Unguja Ukuu is an archaeological site on the island of Zanzibar. This site has yield ...
, Kizimkazi, and Tumbatu
Tumbatu (''eneo la kale wa Tumbatu'' in Swahili) is historic Swahili settlement located on Tumbatu Island, Kaskazini A District of Unguja North Region in Tanzania. This site is a significant archaeological site that contains a large number o ...
were the island's powers from the 8th to the 16th century. The Portuguese built a church at Shangani in the early 16th century, and the Queen of northern Unguja
Unguja (also referred to as "Zanzibar Island" or simply "Zanzibar", in grc, Μενουθιάς, Menuthias – as mentioned in The ''Periplus of the Erythraean Sea'') is the largest and most populated island of the Zanzibar archipelago, in Tanza ...
had a house built there in the mid-17th century. When the Portuguese were ousted by Zanzibaris and Pembans in the 17th century, local patricians invited the Sultan of Oman to wield political power in exchange for defense against Portuguese reprisals. Part of the Portuguese church was built into the Omani fort, which housed roughly fifty soldiers. The Sultan also appointed a local governor, but political authority was still largely vested in the Mwinyi Mkuu, at this time Queen Fatima.
Excavations at nearby Pemba Island, but especially at Shanga in the Lamu Archipelago, provide the clearest picture of architectural development. Houses were originally built with timber (c. 1050) and later in mud with coral walls (c. 1150). The houses were continually rebuilt with more permanent materials. By the 13th century, houses were built with stone, and bonded with mud, and the 14th century saw the use of lime to bond stone. Only the wealthier patricians would have had stone and lime built houses, the strength of the materials allowing for flat roofs, while the majority of the population lived in single-story thatched houses similar to those from the 11th and 12th centuries. According to Tom Middleton and Mark Horton, the architectural style of these stone houses have no Arab or Persian elements, and should be viewed as an entirely indigenous development of local vernacular architecture. While much of Zanzibar Town's architecture was rebuilt during Omani rule, nearby sites elucidate the general development of Swahili, and Zanzibari, architecture before the 15th century.
Omani Dominion
 Stone Town is located along a natural harbour and the first Europeans to set foot on the island of
Stone Town is located along a natural harbour and the first Europeans to set foot on the island of Zanzibar
Zanzibar (; ; ) is an insular semi-autonomous province which united with Tanganyika in 1964 to form the United Republic of Tanzania. It is an archipelago in the Indian Ocean, off the coast of the mainland, and consists of many small islan ...
were the Portuguese. The Portuguese ruled the island for over 2 centuries and began constructing Stone Town's first stone structure, the Old Fort. However, towards the end of the 17th century the Sultanate of Oman
Oman ( ; ar, عُمَان ' ), officially the Sultanate of Oman ( ar, سلْطنةُ عُمان ), is an Arabian country located in southwestern Asia. It is situated on the southeastern coast of the Arabian Peninsula, and spans the mouth of t ...
took over the island and completed the fort to prevent future attacks. The first stone houses in Stone Town probably began to be built in the 1830s, gradually replacing an earlier fishing village around the Old Fort. At the time the Sultanate of Oman
Oman ( ; ar, عُمَان ' ), officially the Sultanate of Oman ( ar, سلْطنةُ عُمان ), is an Arabian country located in southwestern Asia. It is situated on the southeastern coast of the Arabian Peninsula, and spans the mouth of t ...
controlled the Zanzibar Archipelago
The Zanzibar Archipelago ( ar, أرخبيل زنجبار, sw, Funguvisiwa la Zanzibar) consists of several islands lying off the coast of East Africa south of the Somali sea. The archipelago is also known as the Spice Islands. There are four ...
, Mombasa
Mombasa ( ; ) is a coastal city in southeastern Kenya along the Indian Ocean. It was the first capital of the British East Africa, before Nairobi was elevated to capital city status. It now serves as the capital of Mombasa County. The town is ...
and the Swahili coast.
In 1840, Sultan
Sultan (; ar, سلطان ', ) is a position with several historical meanings. Originally, it was an Arabic abstract noun meaning "strength", "authority", "rulership", derived from the verbal noun ', meaning "authority" or "power". Later, it ...
Said bin Sultan
Sayyid Saïd bin Sultan al-Busaidi ( ar, سعيد بن سلطان, , sw, Saïd bin Sultani) (5 June 1791 – 19 October 1856), was Sultan of Muscat and Oman, the fifth ruler of the Busaid dynasty from 1804 to 4 June 1856. His rule commenced fo ...
moved his seat from Muscat
Muscat ( ar, مَسْقَط, ) is the capital and most populated city in Oman. It is the seat of the Governorate of Muscat. According to the National Centre for Statistics and Information (NCSI), the total population of Muscat Governorate was ...
, Oman, to Stone Town, which thus entered an era of quick development as the new capital of the Sultanate of Oman and Zanzibar. With the British outlawing the slave trade in the Indian Ocean, the Sultanate's fortunes crashed. The Muscat economy was in shambles and many Omanis migrated to Zanzibar. The increase in the Arab population on the island facilitated further growth and more buildings began to spring up in the town. Furthermore, grand royal structures like the House of Wonders and the Sultan's Palace were also built. In 1861, as a consequence of a war of succession
A war of succession is a war prompted by a succession crisis in which two or more individuals claim the right of successor to a deceased or deposed monarch. The rivals are typically supported by factions within the royal court. Foreign pow ...
within the Omani royal family, Zanzibar and Oman were separated, with Zanzibar becoming an independent sultanate under Sultan Majid bin Said.
In the 19th century Stone Town flourished as a trading centre. It was especially renowned for the commerce of spices (mostly cloves
Cloves are the aromatic flower buds of a tree in the family Myrtaceae, ''Syzygium aromaticum'' (). They are native to the Maluku Islands (or Moluccas) in Indonesia, and are commonly used as a spice, flavoring or fragrance in consumer products, ...
) and slaves
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perf ...
. Around middle of the century, the sultanate had a close relationship with the British; David Livingstone
David Livingstone (; 19 March 1813 – 1 May 1873) was a Scottish physician, Congregationalist, and pioneer Christian missionary with the London Missionary Society, an explorer in Africa, and one of the most popular British heroes of ...
, for example, is known to have stayed in Stone Town in 1866 while he was preparing his final expedition into the interior of East Africa. In the same period, several immigrant communities from Oman
Oman ( ; ar, عُمَان ' ), officially the Sultanate of Oman ( ar, سلْطنةُ عُمان ), is an Arabian country located in southwestern Asia. It is situated on the southeastern coast of the Arabian Peninsula, and spans the mouth of t ...
, Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmen ...
and India formed as a consequence of the town's intense commercial activity. The Sultan of Zanzibar encouraged immigration of foreign traders who became very wealthy and settled in the city who brought diversity to the city's architecture.
Colonial Control
 In the last decades of the century, the Sultans of Zanzibar gradually lost their possessions in mainland
In the last decades of the century, the Sultans of Zanzibar gradually lost their possessions in mainland East Africa
East Africa, Eastern Africa, or East of Africa, is the eastern subregion of the African continent. In the United Nations Statistics Division scheme of geographic regions, 10-11-(16*) territories make up Eastern Africa:
Due to the historica ...
to the German Empire and the United Kingdom. In 1890, with the Heligoland-Zanzibar Treaty, Zanzibar itself became a British protectorate
A protectorate, in the context of international relations, is a state that is under protection by another state for defence against aggression and other violations of law. It is a dependent territory that enjoys autonomy over most of its int ...
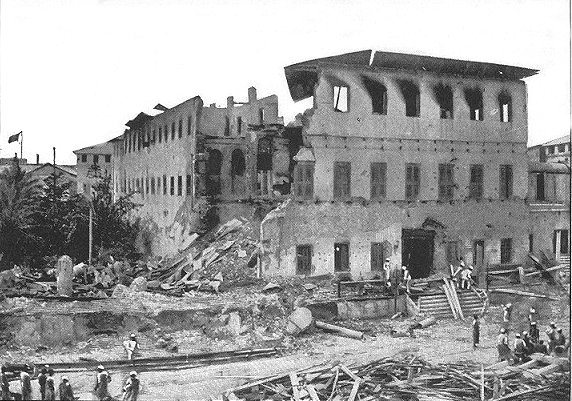
. In 1896, a sudden rebellion of the Zanzibari Omanis against the British rule led to the Anglo-Zanzibar War
The Anglo-Zanzibar War was a military conflict fought between the United Kingdom and the Zanzibar Sultanate on 27 August 1896. The conflict lasted between 38 and 45 minutes, marking it as the shortest recorded war in history. The immediate ca ...
, which is remembered as the shortest war in history: the Sultan surrendered after 45 minutes of naval bombardment of Stone Town by the Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against ...
.
During the period of British protection, the Sultan still retained some power and Stone Town remained a relatively important trading centre for the informal trade. Though the town previously had a small railway the British constructed a railway
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the vehicles run on a prep ...
from the Town to Bububu village. The British did not fund major developments in the town and allowed the sultan to manage the islands affairs from stone town. The British gave privileges to Mombasa
Mombasa ( ; ) is a coastal city in southeastern Kenya along the Indian Ocean. It was the first capital of the British East Africa, before Nairobi was elevated to capital city status. It now serves as the capital of Mombasa County. The town is ...
and Dar es Salaam
Dar es Salaam (; from ar, دَار السَّلَام, Dâr es-Selâm, lit=Abode of Peace) or commonly known as Dar, is the largest city and financial hub of Tanzania. It is also the capital of Dar es Salaam Region. With a population of over s ...
as their trading stations in East Africa.
Zanzibar Revolution
 In 1964, Stone Town was the theatre of the
In 1964, Stone Town was the theatre of the Zanzibar Revolution
The Zanzibar Revolution () occurred in January 1964 and led to the overthrow of the Sultan of Zanzibar and his mainly Arab government by local Africans.
Zanzibar was an ethnically diverse state consisting of a number of islands off the east c ...
, which brought about the removal of the sultan and the birth of a socialist government led by the Afro-Shirazi Party (ASP). More than 20,000 people were killed and refugees, especially Arabs and Indians, escaped the island as a consequence of the revolution. The Arabs and Indians left behind everything they had and the ASP quickly occupied old homes and converted them into public buildings. In 1964, when Tanganyika and Zanzibar combined to form Tanzania
Tanzania (; ), officially the United Republic of Tanzania ( sw, Jamhuri ya Muungano wa Tanzania), is a country in East Africa within the African Great Lakes region. It borders Uganda to the north; Kenya to the northeast; Comoro Islands an ...
, Stone Town kept its role as a capital and government seat for Zanzibar, which was declared a semi-autonomous part of the new nation.
Geography
Stone Town is located roughly in the middle of the west coast ofUnguja
Unguja (also referred to as "Zanzibar Island" or simply "Zanzibar", in grc, Μενουθιάς, Menuthias – as mentioned in The ''Periplus of the Erythraean Sea'') is the largest and most populated island of the Zanzibar archipelago, in Tanza ...
, on a small promontory
A promontory is a raised mass of land that projects into a lowland or a body of water (in which case it is a peninsula). Most promontories either are formed from a hard ridge of rock that has resisted the erosive forces that have removed the s ...
protruding into the Zanzibar Channel
The Zanzibar Channel is a strait in south-eastern Africa, separating the island of Unguja (also known as Zanzibar) from mainland Tanzania. The channel is 120 km long and 29–37 km wide, with depth varying from a few dozen metres (in the ...
. The closest major settlement on the Tanzanian coast, opposite Stone Town, is Bagamoyo
Bagamoyo, is a historic coastal town founded at the end of the 18th century, though it is an extension of a much older (8th century) Swahili settlement, Kaole. It was chosen as the capital of German East Africa by the German colonial administrat ...
(to the south-west). Stone Town is part of Zanzibar City
Zanzibar City or Mjini District, often simply referred to as Zanzibar (''Wilaya ya Zanzibar Mjini'' or ''Jiji la Zanzibar'' in Swahili) is one of two administrative districts of Mjini Magharibi Region in Tanzania. The district covers an area of ...
, which also includes the 'New City' of Ng'ambo
Ng'ambo (literally, "The Other Side"; sometimes also referred to as the "New City") is one of the two main parts comprising Zanzibar City, the capital of Zanzibar, the other being the historical Stone Town. Ng'ambo is much larger and more modern ...
("the Other Side"), which mostly extends in the interior of Unguja to the south-east. The dividing line between Stone Town and Ng'ambo is Creek Road.
Demographics
Landmarks
Historical buildings and sites


 #The House of Wonders (or "Palace of Wonders", also known as "Beit-al-Ajaib"), in located on the Mizingani Road along the Stone Town seafront, and is probably the most well-known landmarks of Stone Town. It was built in 1883 and restored after the
#The House of Wonders (or "Palace of Wonders", also known as "Beit-al-Ajaib"), in located on the Mizingani Road along the Stone Town seafront, and is probably the most well-known landmarks of Stone Town. It was built in 1883 and restored after the Anglo-Zanzibar War
The Anglo-Zanzibar War was a military conflict fought between the United Kingdom and the Zanzibar Sultanate on 27 August 1896. The conflict lasted between 38 and 45 minutes, marking it as the shortest recorded war in history. The immediate ca ...
of 1896. Formerly the Sultan
Sultan (; ar, سلطان ', ) is a position with several historical meanings. Originally, it was an Arabic abstract noun meaning "strength", "authority", "rulership", derived from the verbal noun ', meaning "authority" or "power". Later, it ...
's residence, it became the seat of the Afro-Shirazi Party after the revolution. It was the first building in Zanzibar to have electricity
Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and motion of matter that has a property of electric charge. Electricity is related to magnetism, both being part of the phenomenon of electromagnetism, as described ...
as well as the first building in East Africa to have a lift
Lift or LIFT may refer to:
Physical devices
* Elevator, or lift, a device used for raising and lowering people or goods
** Paternoster lift, a type of lift using a continuous chain of cars which do not stop
** Patient lift, or Hoyer lift, mobile ...
. Since 2000, its interior has been dedicated to a museum on Swahili and Zanzibar culture. In December 2020, during renovations, a large part of the building collapsed in a major accident.
#The Old Fort ("Ngome Kongwe" in Swahili), adjacent to the House of Wonders, is a heavy stone fortress that was built in the 17th century by the Omanis. Also known as the Omani fort it was built by the early rulers to protect the city from European invasions. It has a roughly square shape and the internal courtyard is now a cultural centre with shops, workshops, and a small arena where live dance and music shows are held daily. The fort location is also used for the Zanzibar International Film Festival.
#The Old Dispensary (or "Ithnashiri Dispensary") was built from 1887 to 1894 by a wealthy Indian trader, to serve as a charity hospital for the poor but was later used as a dispensary
A dispensary is an office in a school, hospital, industrial plant, or other organization that dispenses medications, medical supplies, and in some cases even medical and dental treatment. In a traditional dispensary set-up, a pharmacist dispense ...
. It is one of the most finely decorated buildings of Stone Town, with large carved wooden balconies, stained-glass windows, and neo-classical stucco
Stucco or render is a construction material made of aggregates, a binder, and water. Stucco is applied wet and hardens to a very dense solid. It is used as a decorative coating for walls and ceilings, exterior walls, and as a sculptural and a ...
adornments. After falling into decay in the 1970s and 1980s, the building was accurately restored by the AKTC.
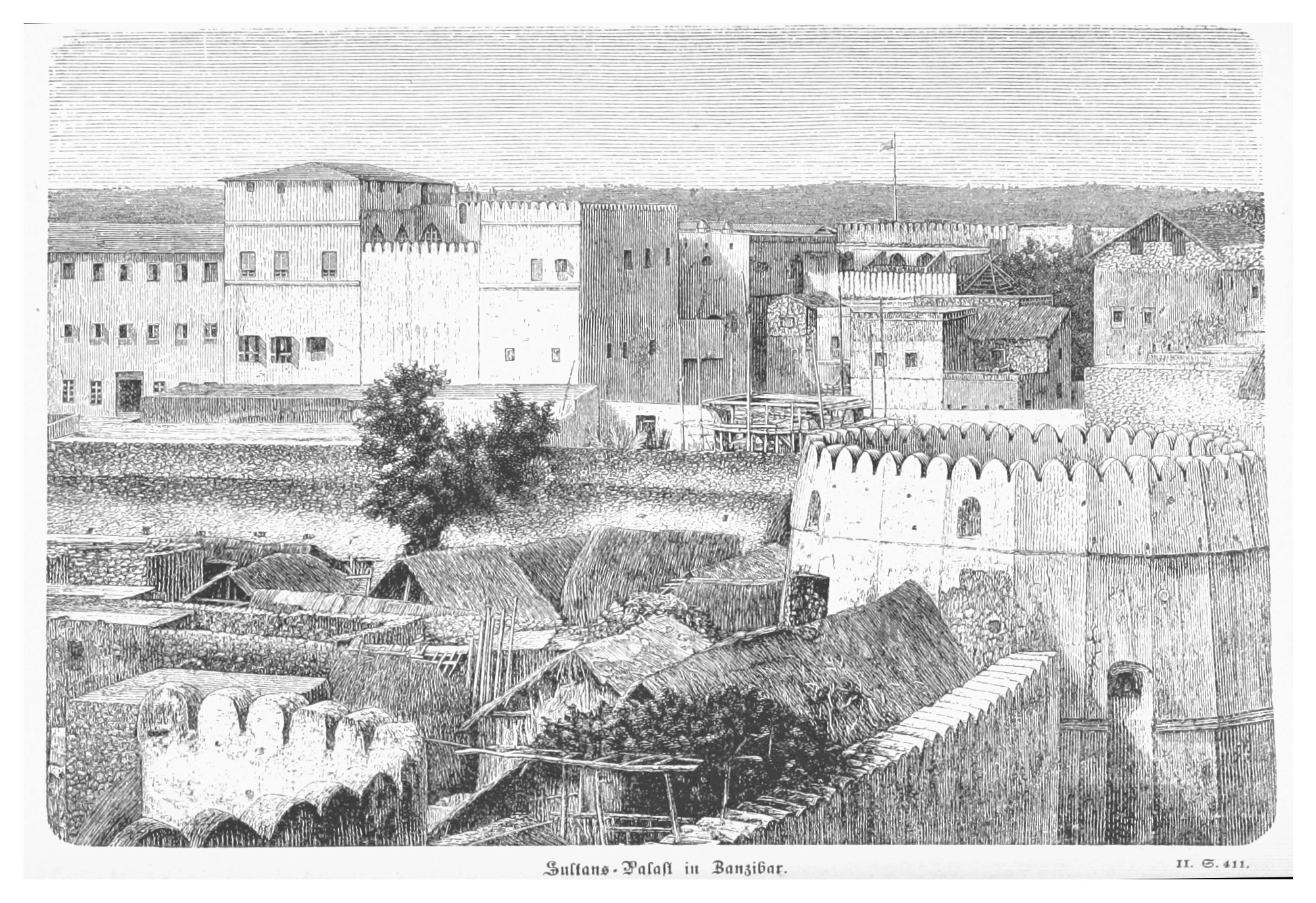
#The Palace Museum
The Palace Museum () is a huge national museum complex housed in the Forbidden City at the core of Beijing, China. With , the museum inherited the imperial royal palaces from the Ming and Qing dynasties of China and opened to the public in 192 ...
(also known as the "Sultan's Palace", "Beit el-Sahel" in Arab) is another former sultan's palace, on the seafront, to the north of the House of Wonders.Stone Town - Zanzibar Town/ref> It was built in late 19th century and now hosts a museum about the daily life of the Zanzibari royal family, including items that belonged to Sayyida Salme, a former Zanzibar princess who fled to relocate in Europe with her husband. #The
Anglican
Anglicanism is a Western Christianity, Western Christian tradition that has developed from the practices, liturgy, and identity of the Church of England following the English Reformation, in the context of the Protestant Reformation in Euro ...
cathedral
A cathedral is a church that contains the ''cathedra'' () of a bishop, thus serving as the central church of a diocese, conference, or episcopate. Churches with the function of "cathedral" are usually specific to those Christian denominat ...
of Christ Church, on Mkunazini Road, was built at the end of the 19th century by Edward Steere, third bishop
A bishop is an ordained clergy member who is entrusted with a position of Episcopal polity, authority and oversight in a religious institution.
In Christianity, bishops are normally responsible for the governance of dioceses. The role or offic ...
of Zanzibar. The cathedral was constructed in a large area at the centre of Stone Town that previously hosted the biggest slave market of Zanzibar; the place was deliberately chosen to celebrate the end of slavery, and the altar was in the exact spot where the main whipping post of the market used to be. A monument to the slaves, as well as a museum on the history of slavery, are besides the church.
#The Roman Catholic Cathedral
A cathedral is a church that contains the ''cathedra'' () of a bishop, thus serving as the central church of a diocese, conference, or episcopate. Churches with the function of "cathedral" are usually specific to those Christian denominat ...
of St. Joseph was built by French missionaries
A missionary is a member of a Religious denomination, religious group which is sent into an area in order to promote its faith or provide services to people, such as education, literacy, social justice, health care, and economic development.Tho ...
between 1893 and 1897. The design of the church was based on that of the Marseille Cathedral
Marseille Cathedral ( French: ''Cathédrale Sainte-Marie-Majeure de Marseille'' or ''Cathédrale de la Major'') is a Roman Catholic cathedral, and a national monument of France, located in Marseille. It has been a basilica minor since 1896. It i ...
, its façade, with two high spires, is one of the most well-known landmarks of Stone Town and can be seen from a distance when sailing into the harbor. The church is still operational today and holds regular mass on Sundays.
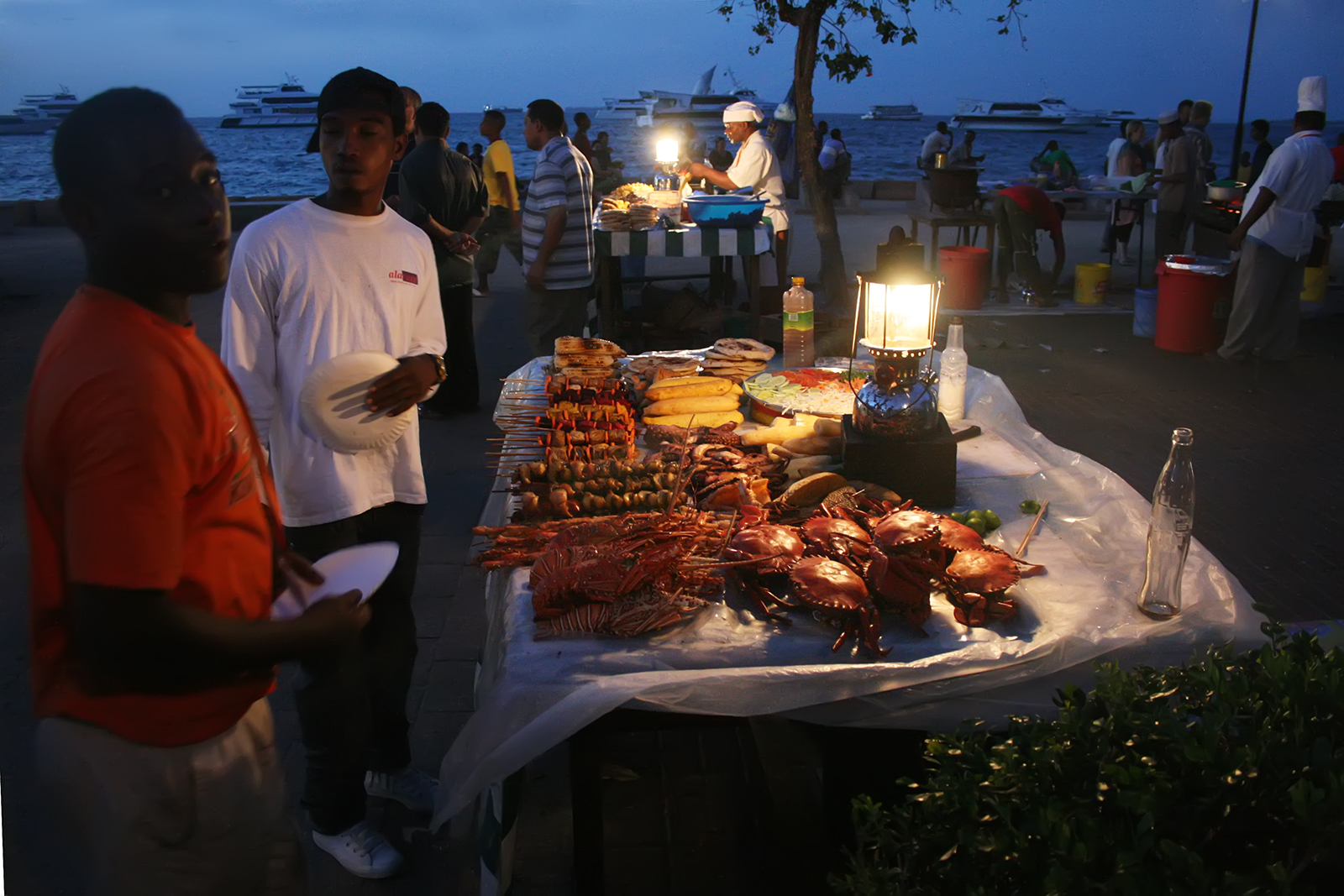
#The Forodhani Gardens are a small park in the main sea walk of Stone Town, right in front of the Old Fort and the House of Wonders. The garden was recently restored for 3 million dollars by the Aga Khan Trust for Culture
The Aga Khan Trust for Culture (AKTC) is an agency of the Aga Khan Development Network (AKDN), a family of institutions created by Aga Khan IV with distinct but complementary mandates to improve the welfare and prospects of people in the developi ...
. Every evening after sunset the gardens host a popular, tourist-oriented market selling grilled seafood and other Zanzibari recipes which attracts both tourists and locals
Transportation
 The streets in Stone Town are very narrow and almost getting anywhere within the town must be done on foot. The narrow streets provide shade and almost everything is accessible from within the town. However, on slightly wider roads historically bicycles and now most recently motor cycles are used to transport people and goods. The town is accessible from Zanzibar and the rest of the region through three possible ports of entry.
The main form of public transport in Zanzibar are the
The streets in Stone Town are very narrow and almost getting anywhere within the town must be done on foot. The narrow streets provide shade and almost everything is accessible from within the town. However, on slightly wider roads historically bicycles and now most recently motor cycles are used to transport people and goods. The town is accessible from Zanzibar and the rest of the region through three possible ports of entry.
The main form of public transport in Zanzibar are the daladala
Dala dala are minibus share taxis in Tanzania.Thoughts On Dala Dala Buse ...
share taxi
Share may refer to:
* Share, to make joint use of a resource (such as food, money, or space); see Sharing
* Share (finance), a stock or other financial security (such as a mutual fund)
* Share, Kwara, a town and LGA in Kwara State, Nigeria
Share ...
s; and the main station is located by the Darajani Market. Daladalas connect Stone Town to several island locations, such as Bububu (a village north of Stone Town), the airport, the Amaan Stadium, Jangombe, and Magomeni.Transportation on the island of Unguja/ref> For longer trips, "mabasi" (Swahili for "bus", singular "basi") are available, which are trucks adapted for passenger transport. The main "mabasi" station is also close to the Market and the "mabasi" network stretch across the entire island and is the cheapest form of long-distance transit. The main Zanzibar island harbour is in the heart of Stone Town and regular ferries from
Dar es Salaam
Dar es Salaam (; from ar, دَار السَّلَام, Dâr es-Selâm, lit=Abode of Peace) or commonly known as Dar, is the largest city and financial hub of Tanzania. It is also the capital of Dar es Salaam Region. With a population of over s ...
and Pemba Pemba may refer to:
__NOTOC__ Places
* Pemba Island, in Tanzania
* Pemba, Mozambique, the capital of Cabo Delgado Province
* Pemba, Zambia, a small town
Individuals
* George Pemba, South African painter
* Pemba (panda), a red panda
*Tsewang Yishey ...
connect the town to the mainland. The town is also in close proximity to the Island's major airport. Zanzibar Airport, south of Stone Town has flights to mainland Tanzania (especially Arusha
Arusha City is a Tanzanian city and the regional capital of the Arusha Region, with a population of 416,442 plus 323,198 in the surrounding Arusha District Council (2012 census).
Located below Mount Meru on the eastern edge of the eastern b ...
and Dar es Salaam
Dar es Salaam (; from ar, دَار السَّلَام, Dâr es-Selâm, lit=Abode of Peace) or commonly known as Dar, is the largest city and financial hub of Tanzania. It is also the capital of Dar es Salaam Region. With a population of over s ...
) as well as other African main airports such as Nairobi
Nairobi ( ) is the capital and largest city of Kenya. The name is derived from the Maasai phrase ''Enkare Nairobi'', which translates to "place of cool waters", a reference to the Nairobi River which flows through the city. The city proper ...
, Mombasa
Mombasa ( ; ) is a coastal city in southeastern Kenya along the Indian Ocean. It was the first capital of the British East Africa, before Nairobi was elevated to capital city status. It now serves as the capital of Mombasa County. The town is ...
, and Johannesburg
Johannesburg ( , , ; Zulu and xh, eGoli ), colloquially known as Jozi, Joburg, or "The City of Gold", is the largest city in South Africa, classified as a megacity, and is one of the 100 largest urban areas in the world. According to De ...
.
Climate
Stone Town along with the entireZanzibar Archipelago
The Zanzibar Archipelago ( ar, أرخبيل زنجبار, sw, Funguvisiwa la Zanzibar) consists of several islands lying off the coast of East Africa south of the Somali sea. The archipelago is also known as the Spice Islands. There are four ...
experiences a similar climate throughout the year. The island has a hot tropical
The tropics are the regions of Earth surrounding the Equator. They are defined in latitude by the Tropic of Cancer in the Northern Hemisphere at N and the Tropic of Capricorn in
the Southern Hemisphere at S. The tropics are also referred to ...
weather all year round with the hottest months being February and March and the cooler months being July and August. During most months of the year there is significant rainfall with a long rain season spanning from March–May and a shorter rain season from November–December. The lesser dry season occurs between December–February and May–August and consequently is the peak tourist season due to beach tourism on the island.
Notable residents
*Freddie Mercury
Freddie Mercury (born Farrokh Bulsara; 5 September 1946 – 24 November 1991) was a British singer and songwriter, who achieved worldwide fame as the lead vocalist of the rock band Queen. Regarded as one of the greatest singers in th ...
(Farrokh Bulsara), lead vocalist of British band Queen, was born in Stone Town.
* Ali Muhsin al-Barwani, first foreign minister of independent Zanzibar
* Bi Kidude, singer
* David Livingstone
David Livingstone (; 19 March 1813 – 1 May 1873) was a Scottish physician, Congregationalist, and pioneer Christian missionary with the London Missionary Society, an explorer in Africa, and one of the most popular British heroes of ...
, Scottish explorer and missionary
* Tippu Tip, slave trader
Gallery
Anglican
Anglicanism is a Western Christianity, Western Christian tradition that has developed from the practices, liturgy, and identity of the Church of England following the English Reformation, in the context of the Protestant Reformation in Euro ...
Cathedral of Zanzibar.
File:Stone Town of Zanzibar-108843.jpg, Old Fort
File:Stone Town of Zanzibar-108845.jpg, St. Joseph's Cathedral, Zanzibar
File:Stone Town of Zanzibar-108847.jpg, Traditional door
File:The_French_Post_Office_in_Malindi_(Road),_Zanzibar_Stone_Town,_19th_century.jpg, "Poste française". French post office with French flag in Stone Town, before 1900.
References
External links
UNESCO Stone Town Site
Stone Town Conservation and Development Authority
{{Authority control Swahili city-states Swahili architecture Cities in Zanzibar Zanzibar City World Heritage Sites in Tanzania Aga Khan Trust for Culture projects Geography of Mjini Magharibi Region Archaeological sites of Eastern Africa