Zebra Striped Surface on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Zebras (, ) (subgenus ''Hippotigris'') are African
 As with all wild equines, zebras have barrel-chested bodies with tufted tails, elongated faces and long necks with long, erect
As with all wild equines, zebras have barrel-chested bodies with tufted tails, elongated faces and long necks with long, erect
 * The confusion hypothesis states that the stripes confuse predators, be it by: making it harder to distinguish individuals in a group as well as determining the number of zebras in a group; making it difficult to determine an individual's outline when the group runs away; reducing a predator's ability to keep track of a target during a chase; dazzling an assailant so they have difficulty making contact; or making it difficult for a predator to deduce the zebra's size, speed and direction via motion dazzle. This theory has been proposed by several biologists since at least the 1970s. A 2014 computer study of zebra stripes found that they may create a
* The confusion hypothesis states that the stripes confuse predators, be it by: making it harder to distinguish individuals in a group as well as determining the number of zebras in a group; making it difficult to determine an individual's outline when the group runs away; reducing a predator's ability to keep track of a target during a chase; dazzling an assailant so they have difficulty making contact; or making it difficult for a predator to deduce the zebra's size, speed and direction via motion dazzle. This theory has been proposed by several biologists since at least the 1970s. A 2014 computer study of zebra stripes found that they may create a  * The fly protection hypothesis holds that the stripes deter blood-sucking flies. Horse flies, in particular, spread diseases that are lethal to equines such as African horse sickness, equine influenza,
* The fly protection hypothesis holds that the stripes deter blood-sucking flies. Horse flies, in particular, spread diseases that are lethal to equines such as African horse sickness, equine influenza,
 Zebra species have two basic social structures. Plains and mountain zebras live in stable, closed family groups or
Zebra species have two basic social structures. Plains and mountain zebras live in stable, closed family groups or
 For the
For the
 Zebras have been kept in captivity since at least the
Zebras have been kept in captivity since at least the  Attempts to
Attempts to
 As of 2016ŌĆō2019, the
As of 2016ŌĆō2019, the
The Quagga Project
ĆöAn organisation that selectively breeds zebras to recreate the hair coat pattern of the quagga {{Authority control * Equus (genus) Fauna of Sub-Saharan Africa Herbivorous mammals Mammals of Africa Extant Pleistocene first appearances Animal subgenera
equines
''Equus'' () is a genus of mammals in the perissodactyl family (biology), family Equidae, which includes wild horse, horses, Asinus, asses, and zebras. Within the Equidae, ''Equus'' is the only recognized Extant taxon, extant genus, comprising s ...
with distinctive black-and-white striped coat
A coat is typically an outer garment for the upper body, worn by any gender for warmth or fashion. Coats typically have long sleeves and are open down the front, and closing by means of buttons, zippers, hook-and-loop fasteners (AKA velcro), ...
s. There are three living
Living or The Living may refer to:
Common meanings
*Life, a condition that distinguishes organisms from inorganic objects and dead organisms
** Living species, one that is not extinct
*Personal life, the course of an individual human's life
* ...
species: Gr├®vy's zebra
Gr├®vy's zebra (''Equus grevyi)'', also known commonly as the imperial zebra, is the largest living species of wild equid and the most threatened of the three species of zebras, the other two being the plains zebra and the mountain zebra. Name ...
(''Equus grevyi''), the plains zebra
The plains zebra (''Equus quagga'', formerly ''Equus burchellii'') is the most common and geographically widespread species of zebra. Its range is fragmented, but spans much of southern and eastern Africa south of the Sahara. Six or seven subspec ...
(''E. quagga''), and the mountain zebra
The mountain zebra (''Equus zebra'') is a zebra species in the family Equidae, native to southwestern Africa. There are two subspecies, the Cape mountain zebra (''E. z. zebra'') found in South Africa and Hartmann's mountain zebra (''E. z. hartma ...
(''E. zebra''). Zebras share the genus '' Equus'' with horses
The horse (''Equus ferus caballus'') is a domesticated, one-toed, hoofed mammal. It belongs to the taxonomic family Equidae and is one of two extant subspecies of ''Equus ferus''. The horse has evolved over the past 45 to 55 milli ...
and asses
Ass most commonly refers to:
* Buttocks (in informal American English)
* Donkey or ass, ''Equus africanus asinus''
**any other member of the subgenus ''Asinus''
Ass or ASS may also refer to:
Art and entertainment
* ''Ass'' (album), 1973 alb ...
, the three groups being the only living members of the family Equidae
Equidae (commonly known as the horse family) is the Taxonomy (biology), taxonomic Family (biology), family of Wild horse, horses and related animals, including Asinus, asses, zebra, zebras, and many extinct species known only from fossils. The fa ...
. Zebra stripes come in different patterns, unique to each individual. Several theories have been proposed for the function of these patterns, with most evidence supporting them as a deterrent for biting flies. Zebras inhabit eastern
Eastern or Easterns may refer to:
Transportation
Airlines
*China Eastern Airlines, a current Chinese airline based in Shanghai
* Eastern Air, former name of Zambia Skyways
*Eastern Air Lines, a defunct American airline that operated from 192 ...
and southern Africa
Southern Africa is the southernmost region of Africa. No definition is agreed upon, but some groupings include the United Nations geoscheme for Africa, United Nations geoscheme, the intergovernmental Southern African Development Community, and ...
and can be found in a variety of habitats such as savannahs
A savanna or savannah is a mixed woodland-grassland (i.e. grassy woodland) biome and ecosystem characterised by the trees being sufficiently widely spaced so that the Canopy (forest), canopy does not close. The open canopy allows sufficient li ...
, grasslands
A grassland is an area where the vegetation is dominated by grasses (Poaceae). However, sedge ( Cyperaceae) and rush ( Juncaceae) can also be found along with variable proportions of legumes such as clover, and other herbs. Grasslands occur ...
, woodlands, shrubland
Shrubland, scrubland, scrub, brush, or bush is a plant community characterized by vegetation dominance (ecology), dominated by shrubs, often also including grasses, herbaceous plant, herbs, and geophytes. Shrubland may either occur naturally o ...
s, and mountainous areas.
Zebras are primarily grazers and can subsist on lower-quality vegetation. They are preyed on mainly by lion
The lion (''Panthera leo'') is a large Felidae, cat of the genus ''Panthera'', native to Sub-Saharan Africa and India. It has a muscular, broad-chested body (biology), body; a short, rounded head; round ears; and a dark, hairy tuft at the ...
s, and typically flee when threatened but also bite and kick. Zebra species differ in social behaviour
Social behavior is behavior among two or more organisms within the same species, it encompasses any behavior in which one member affects another. Social behavior can be seen as similar to an exchange of goods, with the expectation that when you ...
, with plains and mountain zebra living in stable harems
A harem is a domestic space that is reserved for the women of the house in a Muslim family. A harem may house a man's wife or wives, their pre-pubescent male children, unmarried daughters, female domestic Domestic worker, servants, and other un ...
consisting of an adult male or stallion
A stallion is an adult male horse that has not been gelded ( castrated). Stallions follow the conformation and phenotype of their breed, but within that standard, the presence of hormones such as testosterone may give stallions a thicker, "cre ...
, several adult females or mares
A mare is an adult female horse or other equine. In most cases, a mare is a female horse over the age of three, and a filly is a female horse three and younger. In Thoroughbred horse racing, a mare is defined as a female horse more than four y ...
, and their young or foals
A foal is an equine up to one year old; this term is used mainly for horses, but can be used for donkeys. More specific terms are colt for a male foal and filly for a female foal, and are used until the horse is three or four. When the foal is ...
; while Gr├®vy's zebra live alone or in loosely associated herds. In harem-holding species, adult females mate only with their harem stallion, while male Gr├®vy's zebras establish territories
A territory is an area of land, sea, or space, belonging or connected┬Āto a particular country, person, or animal.
In international politics, a territory is usually a geographic area which has not been granted the powers of self-government, ...
which attract females and the species is polygynandrous
Polygynandry is a mating system in which both males and females have multiple mating partners during a breeding season. In sexually reproducing diploid animals, different mating strategies are employed by males and females, because the cost of gam ...
. Zebras communicate with various vocalisations, body postures and facial expressions. Social grooming
Social grooming is a behavior in which social animals, including humans, clean or maintain one another's bodies or appearances. A related term, allogrooming, indicates social grooming between members of the same species. Grooming is a major s ...
strengthens social bonds in plains and mountain zebras.
Zebras' dazzling stripes make them among the most recognisable mammals. They have been featured in art and stories in Africa and beyond. Historically, they have been highly sought by exotic animal collectors, but unlike horses
The horse (''Equus ferus caballus'') is a domesticated, one-toed, hoofed mammal. It belongs to the taxonomic family Equidae and is one of two extant subspecies of ''Equus ferus''. The horse has evolved over the past 45 to 55 milli ...
and donkeys
The donkey or ass is a domesticated equine. It derives from the African wild ass, ''Equus africanus'', and may be classified either as a subspecies thereof, ''Equus africanus asinus'', or as a separate species, ''Equus asinus''. It was domes ...
, zebras have never been completely domesticated
Domestication is a multi-generational mutualistic relationship in which an animal species, such as humans or leafcutter ants, takes over control and care of another species, such as sheep or fungi, to obtain from them a steady supply of reso ...
. The International Union for Conservation of Nature
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) is an international organization working in the field of nature conservation and sustainable use of natural resources. Founded in 1948, IUCN has become the global authority on the stat ...
(IUCN) lists Gr├®vy's zebra as endangered
An endangered species is a species that is very likely to become extinct in the near future, either worldwide or in a particular political jurisdiction. Endangered species may be at risk due to factors such as habitat loss, poaching, inv ...
, the mountain zebra as vulnerable and the plains zebra as near-threatened
A near-threatened species is a species which has been categorized as "Near Threatened" (NT) by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) as that may be vulnerable to endangerment in the near future, but it does not currently qu ...
. The quagga
The quagga ( or ) (''Equus quagga quagga'') is an extinct subspecies of the plains zebra that was endemic to South Africa until it was hunted to extinction in the late 19th century. It was long thought to be a distinct species, but mtDNA ...
(''E. quagga quagga''), a type of plains zebra, was driven to extinction in the 19th century. Nevertheless, zebras can be found in numerous protected areas.
Etymology
The English name "zebra" derives fromItalian
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, a Romance ethnic group related to or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance languag ...
, Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many countries in the Americas
**Spanish cuisine
**Spanish history
**Spanish culture
...
or Portuguese. Its origins may lie in the Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
''equiferus'', meaning "wild horse". ''Equiferus'' appears to have entered into Portuguese as ''ezebro'' or ''zebro'', which was originally used for a legendary equine in the wilds of the Iberian Peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula ( ), also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in south-western Europe. Mostly separated from the rest of the European landmass by the Pyrenees, it includes the territories of peninsular Spain and Continental Portugal, comprisin ...
during the Middle Ages. In 1591, Italian explorer Filippo Pigafetta Filippo Pigafetta (1533ŌĆō1604) was an Italian mathematician and explorer.
Pigafetta's ''Relatione del reame del Congo'' (A Report of the Kingdom of Congo and of the Surrounding Countries) 1591 was translated into English language, English, Latin ...
recorded "zebra" being used to refer to the African animals by Portuguese visitors to the continent. In ancient times, the zebra was called ''hippotigris'' ("horse tiger") by the Greeks
Greeks or Hellenes (; , ) are an ethnic group and nation native to Greece, Greek Cypriots, Cyprus, Greeks in Albania, southern Albania, Greeks in Turkey#History, Anatolia, parts of Greeks in Italy, Italy and Egyptian Greeks, Egypt, and to a l ...
and Romans
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of Roman civilization
*Epistle to the Romans, shortened to Romans, a letter w ...
.
The word ''zebra'' was traditionally pronounced with a long initial vowel, but over the course of the 20th century the pronunciation with the short initial vowel became the norm in British English
British English is the set of Variety (linguistics), varieties of the English language native to the United Kingdom, especially Great Britain. More narrowly, it can refer specifically to the English language in England, or, more broadly, to ...
. The pronunciation with a long initial vowel remains standard in American English
American English, sometimes called United States English or U.S. English, is the set of variety (linguistics), varieties of the English language native to the United States. English is the Languages of the United States, most widely spoken lang ...
.
Taxonomy
Zebras are classified in the genus '' Equus'' (known as equines) along withhorses
The horse (''Equus ferus caballus'') is a domesticated, one-toed, hoofed mammal. It belongs to the taxonomic family Equidae and is one of two extant subspecies of ''Equus ferus''. The horse has evolved over the past 45 to 55 milli ...
and asses
Ass most commonly refers to:
* Buttocks (in informal American English)
* Donkey or ass, ''Equus africanus asinus''
**any other member of the subgenus ''Asinus''
Ass or ASS may also refer to:
Art and entertainment
* ''Ass'' (album), 1973 alb ...
. These three groups are the only living members of the family Equidae
Equidae (commonly known as the horse family) is the Taxonomy (biology), taxonomic Family (biology), family of Wild horse, horses and related animals, including Asinus, asses, zebra, zebras, and many extinct species known only from fossils. The fa ...
. The plains zebra
The plains zebra (''Equus quagga'', formerly ''Equus burchellii'') is the most common and geographically widespread species of zebra. Its range is fragmented, but spans much of southern and eastern Africa south of the Sahara. Six or seven subspec ...
and mountain zebra
The mountain zebra (''Equus zebra'') is a zebra species in the family Equidae, native to southwestern Africa. There are two subspecies, the Cape mountain zebra (''E. z. zebra'') found in South Africa and Hartmann's mountain zebra (''E. z. hartma ...
were traditionally placed in the subgenus
In biology, a subgenus ( subgenera) is a taxonomic rank directly below genus.
In the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature, a subgeneric name can be used independently or included in a species name, in parentheses, placed between the ge ...
''Hippotigris'' (C. H. Smith, 1841) in contrast to the Gr├®vy's zebra
Gr├®vy's zebra (''Equus grevyi)'', also known commonly as the imperial zebra, is the largest living species of wild equid and the most threatened of the three species of zebras, the other two being the plains zebra and the mountain zebra. Name ...
which was considered the sole species of subgenus ''Dolichohippus'' (Heller, 1912). Groves and Bell (2004) placed all three species in the subgenus ''Hippotigris''. A 2013 phylogenetic
In biology, phylogenetics () is the study of the evolutionary history of life using observable characteristics of organisms (or genes), which is known as phylogenetic inference. It infers the relationship among organisms based on empirical dat ...
study found that the plains zebra is more closely related to Gr├®vy's zebras than mountain zebras. The extinct quagga
The quagga ( or ) (''Equus quagga quagga'') is an extinct subspecies of the plains zebra that was endemic to South Africa until it was hunted to extinction in the late 19th century. It was long thought to be a distinct species, but mtDNA ...
was originally classified as a distinct species. Later genetic studies have placed it as the same species as the plains zebra, either a subspecies or just the southernmost population. Molecular evidence supports zebras as a monophyletic
In biological cladistics for the classification of organisms, monophyly is the condition of a taxonomic grouping being a clade ŌĆō that is, a grouping of organisms which meets these criteria:
# the grouping contains its own most recent co ...
lineage.
''Equus'' originated in North America and direct paleogenomic sequencing of a 700,000-year-old middle Pleistocene horse metapodial
Metapodials are long bone
The long bones are those that are longer than they are wide. They are one of five types of bones: long, short, flat, irregular and sesamoid. Long bones, especially the femur and tibia, are subjected to most of the l ...
bone from Canada implies a date of 4.07 million years ago (mya) for the most recent common ancestor
A most recent common ancestor (MRCA), also known as a last common ancestor (LCA), is the most recent individual from which all organisms of a set are inferred to have descended. The most recent common ancestor of a higher taxon is generally assu ...
of the equines within a range of 4.0 to 4.5 mya. Horses split
Split(s) or The Split may refer to:
Places
* Split, Croatia, the largest coastal city in Croatia
* Split Island, Canada, an island in the Hudson Bay
* Split Island, Falkland Islands
* Split Island, Fiji, better known as Hß║Īfliua
Arts, enter ...
from asses and zebras around this time and equines colonised Eurasia and Africa around 2.1ŌĆō3.4 mya. Zebras and asses diverged from each other close to 2 mya. The mountain zebra diverged from the other species around 1.6 mya and the plains and Gr├®vy's zebra split 1.4 mya.
A 2017 mitochondrial DNA study placed the Eurasian '' Equus ovodovi'' and the subgenus ''Sussemionus'' lineage as closer to zebras than to asses. However, other studies disputed this placement, finding the ''Sussemionus'' lineage basal to the zebra+asses group, but suggested that the ''Sussemionus'' lineage may have received gene flow from zebras.
The cladogram of ''Equus'' below is based on Vilstrup and colleagues (2013) and J├│nsson and colleagues (2014):
Extant species
Fossil record
In addition to the three living species, some fossil zebras and relatives have also been identified. ''E. oldowayensis'' is identified from remains in Olduvai Gorge dating to 1.8 mya. Fossil skulls of ''E. mauritanicus'' from Algeria which date to around 1 mya appears to show affinities with the plains zebra. '' E. capensis'', known as the Cape zebra, appeared around 2 mya and lived throughout southern and eastern Africa.Hybridisation
Fertile hybrids have been reported in the wild between plains and Gr├®vy's zebra. Hybridisation has also been recorded between the plains and mountain zebra, though it is possible that these are infertile due to the difference in chromosome numbers between the two species. Captive zebras have been bred with horses anddonkeys
The donkey or ass is a domesticated equine. It derives from the African wild ass, ''Equus africanus'', and may be classified either as a subspecies thereof, ''Equus africanus asinus'', or as a separate species, ''Equus asinus''. It was domes ...
; these are known as zebroids. A zorse is a cross between a zebra and a horse; a zonkey, between a zebra and a donkey; and a zoni, between a zebra and a pony
A pony is a type of small horse, usually measured under a specified height at maturity. Ponies often have thicker coats, manes and tails, compared to larger horses, and proportionally shorter legs, wider barrels, heavier , thicker necks and s ...
. Zebroids are often born sterile with dwarfism
Dwarfism is a condition of people and animals marked by unusually small size or short stature. In humans, it is sometimes defined as an adult height of less than , regardless of sex; the average adult height among people with dwarfism is . '' ...
.
Characteristics
manes
In ancient Roman religion, the ''Manes'' (, , ) or ''Di Manes'' are chthonic deities sometimes thought to represent souls of deceased loved ones. They were associated with the '' Lares'', '' Lemures'', '' Genii'', and '' Di Penates'' as deities ...
. Their thin legs are each supported by a spade-shaped toe covered in a hard hoof
The hoof (: hooves) is the tip of a toe of an ungulate mammal, which is covered and strengthened with a thick and horny keratin covering. Artiodactyls are even-toed ungulates, species whose feet have an even number of digits; the ruminants with ...
. Their dentition
Dentition pertains to the development of teeth and their arrangement in the mouth. In particular, it is the characteristic arrangement, kind, and number of teeth in a given species at a given age. That is, the number, type, and morpho-physiology ...
is adapted for grazing
In agriculture, grazing is a method of animal husbandry whereby domestic livestock are allowed outdoors to free range (roam around) and consume wild vegetations in order to feed conversion ratio, convert the otherwise indigestible (by human diges ...
; they have large incisors that clip grass blades and rough molars and premolars well suited for grinding. Males have spade-shaped canines, which can be used as weapons in fighting. The eyes of zebras are at the sides and far up the head, which allows them to look over the tall grass while feeding. Their moderately long, erect ears are movable and can locate the source of a sound.
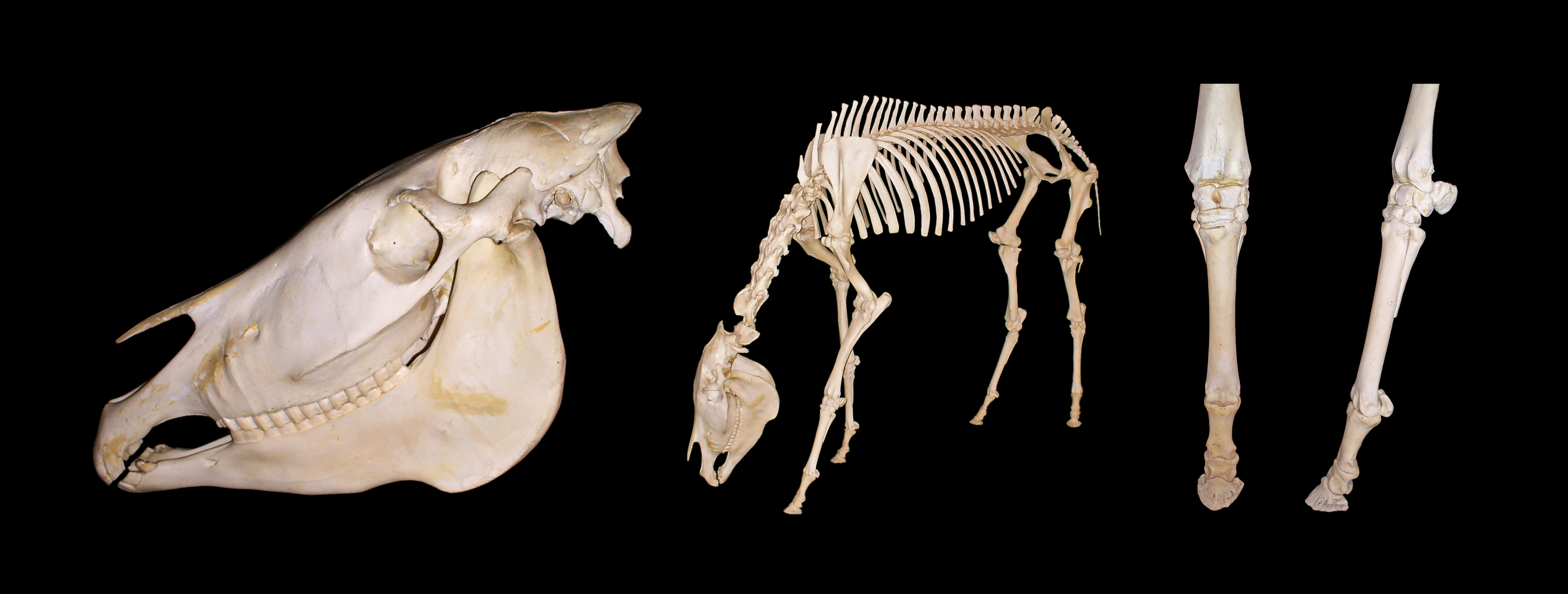
Unlike horses, zebras and asses have chestnut callosities present only on their front legs. In contrast to other living equines, zebras have longer front legs than back legs. Diagnostic traits of the zebra skull include: its relatively small size with a straight dorsal outline, protruding eye sockets, narrower rostrum, less conspicuous postorbital bar
The postorbital bar (or postorbital bone) is a bony arched structure that connects the frontal bone of the skull to the zygomatic arch, which runs laterally around the eye socket. It is a trait that only occurs in mammalian taxa, such as most strep ...
, separation of the metaconid
Many different terms have been proposed for features of the tooth crown in mammals.
The structures within the molars receive different names according to their position and morphology. This nomenclature was developed by Henry Fairfield Osborn i ...
and metastylid of the tooth by a V-shaped canal and rounded enamel wall.
Stripes
Zebras are easily recognised by their bold black-and-white striping patterns. Thecoat
A coat is typically an outer garment for the upper body, worn by any gender for warmth or fashion. Coats typically have long sleeves and are open down the front, and closing by means of buttons, zippers, hook-and-loop fasteners (AKA velcro), ...
appears to be white with black stripes, as indicated by the belly and legs when unstriped, but the skin is black. Young or foal
A foal is an equine up to one year old; this term is used mainly for horses, but can be used for donkeys. More specific terms are colt (horse), colt for a male foal and filly for a female foal, and are used until the horse is three or four. Whe ...
s are born with brown and white coats, and the brown darkens with age. A dorsal
Dorsal (from Latin ''dorsum'' ŌĆśbackŌĆÖ) may refer to:
* Dorsal (anatomy), an anatomical term of location referring to the back or upper side of an organism or parts of an organism
* Dorsal, positioned on top of an aircraft's fuselage
The fus ...
line acts as the backbone for vertical stripes along the sides, from the head to the rump. On the snout they curve toward the nostrils, while the stripes above the front legs split into two branches. On the rump, they develop into species-specific patterns. The stripes on the legs, ears and tail are separate and horizontal.
Striping patterns are unique to an individual and heritable. During embryonic development
In developmental biology, animal embryonic development, also known as animal embryogenesis, is the developmental stage of an animal embryo. Embryonic development starts with the fertilization of an egg cell (ovum) by a sperm, sperm cell (spermat ...
, the stripes appear at eight months, but the patterns may be determined at three to five weeks. For each species there is a point in embryonic development where the stripes are perpendicular to the dorsal line and spaced apart. However, this happens at three weeks of development for the plains zebra, four weeks for the mountain zebra, and five for Gr├®vy's zebra. The difference in timing is thought to be responsible for the differences in the striping patterns of the different species.
Various abnormalities of the patterns have been documented in plains zebras. In "melanistic
Melanism is the congenital excess of melanin in an organism resulting in dark pigment.
Pseudomelanism, also called abundism, is another variant of pigmentation, identifiable by dark spots or enlarged stripes, which cover a large part of the bod ...
" zebras, dark stripes are highly concentrated on the torso but the legs are whiter. "Spotted" individuals have broken up black stripes around the dorsal area. There have even been morphs with white spots on dark backgrounds. Striping abnormalities have been linked to inbreeding
Inbreeding is the production of offspring from the mating or breeding of individuals or organisms that are closely genetic distance, related genetically. By analogy, the term is used in human reproduction, but more commonly refers to the genet ...
. Albino
Albinism is the congenital absence of melanin in an animal or plant resulting in white hair, feathers, scales and skin and reddish pink or blue eyes. Individuals with the condition are referred to as albinos.
Varied use and interpretation of ...
zebras have been recorded in the forests of Mount Kenya
Mount Kenya (Meru people, Meru: ''K─®r─®maara,'' Kikuyu people, Kikuyu: ''K─®r─®nyaga'', Kamba language, Kamba: ''Ki nyaa'', Embu language, Embu: ''K─® nyaga'') is an extinct volcano in Kenya and the Highest mountain peaks of Africa, second-highe ...
, with the dark stripes being blonde. The quagga had brown and white stripes on the head and neck, brown upper parts and a white belly, tail and legs.
Function
The function of stripes in zebras has been discussed among biologists since at least the 19th century. Popular hypotheses include the following: * Thecrypsis
In ecology, crypsis is the ability of an animal or a plant to avoid observation or detection by other animals. It may be part of a predation strategy or an antipredator adaptation. Methods include camouflage, nocturnality, subterranean life ...
hypothesis suggests that the stripes allow the animal to blend in with its environment or break up its outline. This was the earliest hypothesis and proponents argued that the stripes were particularly suited for camouflage in tall grassland and woodland habitat. Alfred Wallace
Alfred Russel Wallace (8 January 1823 ŌĆō 7 November 1913) was an English naturalist, explorer, geographer, anthropologist, biologist and illustrator. He independently conceived the theory of evolution through natural selection; his 1858 pap ...
also wrote in 1896 that stripes make zebras less noticeable at night. Biologist Tim Caro
Timothy M. Caro (born 1951) is a British evolutionary ecologist known for his work on conservation biology, animal behaviour, anti-predator defences in animals, and the function of zebra stripes. He is the author of several textbooks on these su ...
notes that zebras graze in open habitat and do not behave cryptically, being noisy, fast, and social and do not freeze when a predator is near. In addition, the camouflaging stripes of woodland living ungulates like bongos
Bongos (Spanish language, Spanish: ''bong├│'') are an Afro-Cubans, Afro-Cuban percussion instrument consisting of a pair of small open bottomed hand drums of different sizes. The pair consists of the larger ''hembra'' () and the smaller ''macho'' ...
and bushbucks are much less vivid with less contrast with the background colour. A 1987 Fourier analysis
In mathematics, Fourier analysis () is the study of the way general functions may be represented or approximated by sums of simpler trigonometric functions. Fourier analysis grew from the study of Fourier series, and is named after Joseph Fo ...
study concluded that the spatial frequencies
In mathematics, physics, and engineering, spatial frequency is a characteristic of any structure that is periodic across position in space. The spatial frequency is a measure of how often sinusoidal components (as determined by the Fourier tran ...
of zebra stripes do not line up with their environment, while a 2014 study of wild equine species and subspecies could not find any correlations between striping patterns and woodland habitats. Melin and colleagues (2016) found that lion
The lion (''Panthera leo'') is a large Felidae, cat of the genus ''Panthera'', native to Sub-Saharan Africa and India. It has a muscular, broad-chested body (biology), body; a short, rounded head; round ears; and a dark, hairy tuft at the ...
s and hyenas do not appear to perceive the stripes when they are a certain distance away at daytime or nighttime, thus making the stripes useless in blending in except when the predators are close enough by which they could smell or hear their target. They also found that the stripes do not make the zebra less noticeable than solidly coloured herbivores on the open plains. They suggested that stripes may give zebras an advantage in woodlands, as the dark stripes could line up with the outlines of tree branches and other vegetation.
 * The confusion hypothesis states that the stripes confuse predators, be it by: making it harder to distinguish individuals in a group as well as determining the number of zebras in a group; making it difficult to determine an individual's outline when the group runs away; reducing a predator's ability to keep track of a target during a chase; dazzling an assailant so they have difficulty making contact; or making it difficult for a predator to deduce the zebra's size, speed and direction via motion dazzle. This theory has been proposed by several biologists since at least the 1970s. A 2014 computer study of zebra stripes found that they may create a
* The confusion hypothesis states that the stripes confuse predators, be it by: making it harder to distinguish individuals in a group as well as determining the number of zebras in a group; making it difficult to determine an individual's outline when the group runs away; reducing a predator's ability to keep track of a target during a chase; dazzling an assailant so they have difficulty making contact; or making it difficult for a predator to deduce the zebra's size, speed and direction via motion dazzle. This theory has been proposed by several biologists since at least the 1970s. A 2014 computer study of zebra stripes found that they may create a wagon-wheel effect
The wagon-wheel effect (alternatively called stagecoach-wheel effect) is an optical illusion in which a spoked wheel appears to rotate differently from its true rotation. The wheel can appear to rotate more slowly than the true rotation, it ca ...
and/or barber pole illusion when in motion. The researchers concluded that this could be used against mammalian predators or biting flies. The use of the stripes for confusing mammalian predators has been questioned. Caro suggests that the stripes of zebras could make groups seem smaller, and thus more likely to be attacked. Zebras also tend to scatter when fleeing from attackers and thus the stripes could not break up an individual's outline. Lions, in particular, appear to have no difficulty targeting and catching zebras when they get close and take them by ambush. In addition, no correlations have been found between the number of stripes and populations of mammal predators. Hughes and colleagues (2021) disputed the idea of motion dazzle and concluded that moving objects that are solidly grey or have less contrasted patterns are actually more likely to escape being caught.
* The aposematic
Aposematism is the Advertising in biology, advertising by an animal, whether terrestrial or marine, to potential predation, predators that it is not worth attacking or eating. This unprofitability may consist of any defenses which make the pr ...
hypothesis suggests that the stripes serve as warning colouration. This hypothesis was first suggested by Wallace in 1867 and discussed in more detail by Edward Bagnall Poulton
Sir Edward Bagnall Poulton, FRS HFRSE FLS (27 January 1856 ŌĆō 20 November 1943) was a British evolutionary biologist, a lifelong advocate of natural selection through a period in which many scientists such as Reginald Punnett doubted its ...
in 1890. As with known aposematic mammals, zebras are recognizable up close, live in more open environments, have a high risk of predation and do not hide or act inconspicuous. However, Caro notes that stripes do not work on lions because they frequently prey on zebras, though they may work on smaller predators, and zebras are not slow-moving enough to need to ward off threats. In addition, zebras do not possess adequate defenses to back up the warning pattern.
* The social function hypothesis states that stripes serve a role in intraspecific or individual recognition, social bonding, mutual grooming or a signal of fitness. Charles Darwin
Charles Robert Darwin ( ; 12 February 1809 ŌĆō 19 April 1882) was an English Natural history#Before 1900, naturalist, geologist, and biologist, widely known for his contributions to evolutionary biology. His proposition that all speci ...
wrote in 1871 that "a female zebra would not admit the addresses of a male ass until he was painted so as to resemble a zebra" while Wallace stated in 1871 that: "The stripes therefore may be of use by enabling stragglers to distinguish their fellows at a distance". Regarding species and individual identification, Caro notes that zebra species have limited range overlap with each other and horses can recognise each other using visual communication. In addition, no correlation has been found between striping and social behaviour or group numbers among equines, and no link has been found between fitness and striping.
* The thermoregulatory
Thermoregulation is the ability of an organism to keep its body temperature within certain boundaries, even when the surrounding temperature is very different. A thermoconforming organism, by contrast, simply adopts the surrounding temperature ...
hypothesis suggests that stripes help to control a zebra's body temperature. In 1971, biologist H. A. Baldwin noted that heat would be absorbed by the black stripes and reflected by the white ones and in 1990, zoologist Desmond Morris
Desmond John Morris FLS ''hon. caus.'' (born 24 January 1928) is an English zoologist, ethologist and surrealist painter, as well as a popular author in human sociobiology. He is known for his 1967 book ''The Naked Ape'', and for his televis ...
suggested that the stripes create cooling convection currents. A 2019 study supported this, finding that where the faster air currents of the warmer black stripes meet those of the white, air swirls form. The researchers also concluded that during the hottest times of the day, zebras erect their black hair to release heat from the skin and flatten it again when it gets cooler. Larison and colleagues (2015) determined that environmental temperature is a strong predictor for zebra striping patterns. Others have found no evidence that zebras have lower body temperatures than other ungulates whose habitat they share, or that striping correlates with temperature. A 2018 experimental study which dressed water-filled metal barrels in horse, zebra and cattle hides concluded that the zebra stripes had no effect on thermoregulation.
 * The fly protection hypothesis holds that the stripes deter blood-sucking flies. Horse flies, in particular, spread diseases that are lethal to equines such as African horse sickness, equine influenza,
* The fly protection hypothesis holds that the stripes deter blood-sucking flies. Horse flies, in particular, spread diseases that are lethal to equines such as African horse sickness, equine influenza, equine infectious anemia
Equine infectious anemia or equine infectious anaemia (EIA), also known by horsemen as swamp fever, is a horse disease caused by a retrovirus (Equine infectious anemia virus) and transmitted by bloodsucking insects. The virus (EIAV) is endemic in ...
and trypanosomiasis
Trypanosomiasis or trypanosomosis is the name of several diseases in vertebrates caused by parasitic protozoan trypanosomes of the genus ''Trypanosoma''. In humans this includes African trypanosomiasis and Chagas disease. A number of other disea ...
. In addition, zebra hair is about as long as the mouthparts of these flies. This hypothesis is the most strongly supported by the evidence. It was found that flies preferred landing on solidly coloured surfaces over those with black-and-white striped patterns in 1930 by biologist R. Harris, and this was proposed to have been a function of zebra stripes in a 1981 study. A 2014 study found a correlation between striping and overlap with horse and tsetse fly
Tsetse ( , or ) (sometimes spelled tzetze; also known as tik-tik flies) are large, biting flies that inhabit much of tropical Africa. Tsetse flies include all the species in the genus ''Glossina'', which are placed in their own family, Gloss ...
populations and activity. Other studies have found that zebras are rarely targeted by these insect species. Caro and colleagues (2019) studied captive zebras and horses and observed that neither could deter flies from a distance, but zebra stripes kept flies from landing, both on zebras and horses dressed in zebra print coats. There does not appear to be any difference in the effectiveness of repelling flies between the different zebra species; thus the difference in striping patterns may have evolved for other reasons. White or light stripes painted on dark bodies have also been found to reduce fly irritations in both cattle and humans. The effect even extends to pelts, with zebra pelts being less attractive to flies than unstriped impala
The impala or rooibok (''Aepyceros melampus'', lit. 'black-footed high-horn' in Ancient Greek) is a medium-sized antelope found in eastern and southern Africa. The only extant member of the genus '' Aepyceros'', and tribe Aepycerotini, it ...
pelts. How the stripes repel flies is less clear. A 2012 study concluded that they disrupt the polarised light patterns these insects use to locate water and habitat, though subsequent studies have refuted this. Stripes do not appear to work like a barber pole against flies since checkered pattern
Check (also checker, Brit: chequer, or dicing) is a pattern of modified stripes consisting of crossed horizontal and vertical lines which form squares. The pattern typically contains two colours where a single checker (that is a single square with ...
s also repel them. There is also little evidence that zebra stripes confuse the insects via visual distortion or aliasing
In signal processing and related disciplines, aliasing is a phenomenon that a reconstructed signal from samples of the original signal contains low frequency components that are not present in the original one. This is caused when, in the ori ...
. Tak├Īcs and colleagues (2022) suggest that, when the animal is in sunlight, temperature gradients between the warmer dark stripes and cooler white stripes prevent horseflies from detecting the warm blood vessels underneath. Caro and colleagues (2023) conclude that the insects are disoriented by the high colour contrast and relative thinness of the patterns.
Behaviour and ecology
Zebras may travel ormigrate
Migration, migratory, or migrate may refer to: Human migration
* Human migration, physical movement by humans from one region to another
** International migration, when peoples cross state boundaries and stay in the host state for some minimum le ...
to wetter areas during the dry season. Plains zebras have been recorded travelling between Namibia and Botswana, the longest land migration of mammals in Africa. When migrating, they appear to rely on some memory of the locations where foraging conditions were best and may predict conditions months after their arrival. Plains zebras are more water-dependent and live in moister environments than other species. They usually can be found from a water source. Gr├®vy's zebras can survive almost a week without water but will drink it every day when given the chance, and their bodies maintain water better than cattle. Mountain zebras can be found at elevations of up to . Zebras sleep up to seven hours a day, standing up during the day and lying down during the night. They regularly use various objects as rubbing posts and will roll on the ground.
A zebra's diet is mostly grass
Poaceae ( ), also called Gramineae ( ), is a large and nearly ubiquitous family (biology), family of monocotyledonous flowering plants commonly known as grasses. It includes the cereal grasses, bamboos, the grasses of natural grassland and spe ...
es and sedge
The Cyperaceae () are a family of graminoid (grass-like), monocotyledonous flowering plants known as wikt:sedge, sedges. The family (biology), family is large; botanists have species description, described some 5,500 known species in about 90 ...
s, but they will opportunistically consume bark
Bark may refer to:
Common meanings
* Bark (botany), an outer layer of a woody plant such as a tree or stick
* Bark (sound), a vocalization of some animals (which is commonly the dog)
Arts and entertainment
* ''Bark'' (Jefferson Airplane album), ...
, leaves, buds, fruits, and roots. Compared to ruminants
Ruminants are herbivorous grazing or browsing artiodactyls belonging to the suborder Ruminantia that are able to acquire nutrients from plant-based food by Enteric fermentation, fermenting it in a specialized stomach prior to digestion, principa ...
, zebras have a simpler and less efficient digestive system. Nevertheless, they can subsist on lower-quality vegetation. Zebras may spend 60ŌĆō80% of their time feeding, depending on the availability of vegetation. The plains zebra is a pioneer grazer, mowing down the upper, less nutritious grass canopy and preparing the way for more specialised grazers like wildebeest
Wildebeest ( , ,), also called gnu ( or ), are antelopes of the genus ''Connochaetes'' and native to Eastern and Southern Africa. They belong to the family Bovidae, which includes true antelopes, cattle, goats, sheep, and other even-toed ...
, which depend on shorter and more nutritious grasses below.
Zebras are preyed on mainly by lions. Leopards
The leopard (''Panthera pardus'') is one of the five extant cat species in the genus ''Panthera''. It has a pale yellowish to dark golden fur with dark spots grouped in rosettes. Its body is slender and muscular reaching a length of with a ...
, cheetahs
The cheetah (''Acinonyx jubatus'') is a large cat and the fastest land animal. It has a tawny to creamy white or pale buff fur that is marked with evenly spaced, solid black spots. The head is small and rounded, with a short snout and blac ...
, spotted hyenas
The spotted hyena (''Crocuta crocuta''), also known as the laughing hyena, is a hyena species, currently classed as the sole extant member of the genus ''Crocuta'', native to sub-Saharan Africa. It is listed as being of least concern by the IUC ...
, brown hyena
The brown hyena (''Parahyaena brunnea''), also called the strandwolf, is a species of hyena found in Namibia, Botswana, western and southern Zimbabwe, southern Mozambique and South Africa. It is the only extant species in the genus ''Parahyaena' ...
s and wild dogs pose less of a threat to adults. Biting and kicking are a zebra's defense tactics. When threatened by lions, zebras flee, and when caught they are rarely effective in fighting off the big cats. In one study, the maximum speed of a zebra was found to be while a lion was measured at . Zebras do not escape lions by speed alone but by sideways turning, especially when the cat is close behind. With smaller predators like hyenas and dogs, zebras may act more aggressively, especially in defense of their young.
Social behaviour
 Zebra species have two basic social structures. Plains and mountain zebras live in stable, closed family groups or
Zebra species have two basic social structures. Plains and mountain zebras live in stable, closed family groups or harems
A harem is a domestic space that is reserved for the women of the house in a Muslim family. A harem may house a man's wife or wives, their pre-pubescent male children, unmarried daughters, female domestic Domestic worker, servants, and other un ...
consisting of one stallion
A stallion is an adult male horse that has not been gelded ( castrated). Stallions follow the conformation and phenotype of their breed, but within that standard, the presence of hormones such as testosterone may give stallions a thicker, "cre ...
, several mares
A mare is an adult female horse or other equine. In most cases, a mare is a female horse over the age of three, and a filly is a female horse three and younger. In Thoroughbred horse racing, a mare is defined as a female horse more than four y ...
, and their offspring. These groups have their own home ranges
A home range is the area in which an animal lives and moves on a periodic basis. It is related to the concept of an animal's territory which is the area that is actively defended. The concept of a home range was introduced by W. H. Burt in 1943. ...
, which overlap, and they tend to be nomadic. Stallions form and expand their harems by herding young mares away from their birth harems. The stability of the group remains even when the family stallion is displaced. Plains zebras groups gather into large herds and may create temporarily stable subgroups within a herd, allowing individuals to interact with those outside their group. Females in harems can spend more time feeding, and gain protection both for them and their young. They have a linear dominance hierarchy
In the zoological field of ethology, a dominance hierarchy (formerly and colloquially called a pecking order) is a type of social hierarchy that arises when members of animal social animal, social groups interact, creating a ranking system. Dif ...
with the high-ranking females having lived in the group longest. While traveling, the most dominant females and their offspring lead the group, followed by the next most dominant; the family stallion trails behind. Young of both sexes leave their natal groups as they mature; females are usually herded by outside males to become part of their harems.
In the more arid-living Gr├®vy's zebras, adults have more fluid associations and adult males establish large territories
A territory is an area of land, sea, or space, belonging or connected┬Āto a particular country, person, or animal.
In international politics, a territory is usually a geographic area which has not been granted the powers of self-government, ...
, marked by dung piles, and mate with the females that enter them. Grazing and drinking areas tend to be separated in these environments and the most dominant males establish territories near watering holes, which attract females with dependent foals and those who simply want a drink, while less dominant males control territories away from water with more vegetation, and only attract mares without foals. Mares may travel through several territories but remain in one when they have young. Staying in a territory offers a female protection from harassment by outside males, as well as access to resources.
In all species, excess males gather in bachelor group A bachelor herd is a herd of (usually) juvenile male animals who are still sexually immature or 'harem'-forming animals who have been thrown out of their parent groups but not yet formed a new family group. It may also refer to a group of males who ...
s. These are typically young males that are not yet ready to establish a harem or territory. With the plains zebra, the oldest males are the most dominant and group membership is stable. Bachelor groups tend to be at the boundaries of herds and during group movements, the bachelors follow behind or along the sides. Mountain zebra bachelor groups may also include young females that have left their natal group early, as well as old, former harem males. A territorial Gr├®vy's zebra stallion may allow non-territorial bachelors in their territory, however when a mare in oestrous is present the territorial stallion keeps other stallions at bay. Bachelors prepare for their future harem roles with play fights and greeting/challenge rituals, which make up most of their activities.
Fights between males usually occur over mates and involve biting and kicking. In plains zebra, stallions fight each other over recently matured mares to bring into their group and her father will fight off other males trying to abduct her. As long as a harem stallion is healthy, he is not usually challenged. Only unhealthy stallions have their harems taken over, and even then, the new stallion slowly takes over, peacefully displacing the old one. Agonistic behaviour
Agonistic behaviour is any social behaviour related to fighting, which can include aggressive behaviour, but also threats, displays, retreats, placation, and conciliation. The term "agonistic behaviour" was first defined and used by J.P. Scott ...
between male Gr├®vy's zebras occurs at the border of their territories.
Communication
Zebras produce a number of vocalisations and noises. The plains zebra has a distinctive,barking
Barking may refer to:
Places
* Barking, London, a town in East London, England
** London Borough of Barking, 1965ŌĆō1980
** Municipal Borough of Barking, 1931ŌĆō1965
** Barking (UK Parliament constituency)
** Barking (electoral division), Greater ...
contact call heard as "a-''ha'', a-''ha'', a-''ha''" or "kwa-ha, kaw-ha, ha, ha". The mountain zebra may produce a similar sound while the call of Gr├®vy's zebra has been described as "something like a hippo
The hippopotamus (''Hippopotamus amphibius;'' ; : hippopotamuses), often shortened to hippo (: hippos), further qualified as the common hippopotamus, Nile hippopotamus and river hippopotamus, is a large semiaquatic Mammal, mammal native to su ...
's grunt combined with a donkey's wheeze". Loud snorting and rough "gasping" in zebras signals alarm. Squealing is usually made when in pain, but can also be heard in friendly interactions. Zebras also communicate with visual displays, and the flexibility of their lips allows them to make complex facial expressions. Visual displays also consist of head, ear, and tail postures. A zebra may signal an intention to kick by dropping back its ears and whipping its tail. Flattened ears, bared teeth and a waving head may be used as threatening gestures by stallions.
Individuals may greet each other by mutually touching and rubbing, sniffing their genitals and resting their heads on their shoulders. They then may caress their shoulders against each other and lay their heads on one another. This greeting usually occurs between harem or territorial males or among bachelor males playing. Plains and mountain zebras strengthen their social bonds with grooming
A groom (short for bridegroom) is a male participant in a wedding ceremony.
Groom or grooming may also refer to:
Occupations
* Groom (profession), a person responsible for the feeding and care of horses
* One of the competitors in combined drivi ...
. Members of a harem nibble and rake along the neck, shoulder, and back with their teeth and lips. Grooming usually occurs between mothers and foals and between stallions and mares. Grooming establishes social rank and eases aggressive behaviour, although Gr├®vy's zebras generally do not perform social grooming.
Reproduction and parenting
Among plains and mountain zebras, the adult females mate only with their harem stallion, while in Gr├®vy's zebras, mating is morepolygynandrous
Polygynandry is a mating system in which both males and females have multiple mating partners during a breeding season. In sexually reproducing diploid animals, different mating strategies are employed by males and females, because the cost of gam ...
and the males have larger testes for sperm competition
Sperm competition is the competitive process between Spermatozoon, spermatozoa of two or more different males to fertility, fertilize the same Egg cell, egg during sexual reproduction. Competition can occur when females have multiple potential m ...
. Female zebras have five to ten day long oestrous cycles; physical signs include a swollen, everted (inside out) labia and copious flows of urine and mucus. Upon reaching peak oestrous, mares spread-out their legs, lift their tails and open their mouths when in the presence of a male. Males assess the female's reproductive state with a curled lip and bared teeth (flehmen response
The flehmen response (; from German , and Upper Saxon German ), also called the flehmen position, flehmen reaction, flehmen grimace, flehming, or flehmening, is a behavior in which an animal curls back its upper lip exposing its front teeth, i ...
) and the female will solicit mating by backing in. Gestation is typically around a year. A few days to a month later, mares can return to oestrus. In harem-holding species, oestrus in a female becomes less noticeable to outside males as she gets older, hence competition for older females is virtually nonexistent.
Usually, a single foal is born, which is capable of running within an hour of birth. A newborn zebra will follow anything that moves, so new mothers prevent other mares from approaching their foals as they become more familiar with the mother's striping pattern, smell and voice. At a few weeks old, foals begin to graze, but may continue to nurse for eight to thirteen months. Living in an arid environment, Gr├®vy's zebras have longer nursing intervals and young only begin to drink water three months after birth.
In plains and mountain zebras, foals are cared for mostly by their mothers, but if threatened by pack-hunting hyenas and dogs, the entire group works together to protect all the young. The group forms a protective front with the foals in the centre, and the stallion will rush at predators that come too close. In Gr├®vy's zebras, young stay in "kindergartens
Kindergarten is a preschool educational approach based on playing, singing, practical activities such as drawing, and social interaction as part of the transition from home to school. Such institutions were originally made in the late 18th cent ...
" when their mothers leave for water. These groups are tended to by the territorial male. A stallion may look after a foal in his territory to ensure that the mother stays, though it may not be his. By contrast, plains zebra stallions are generally intolerant of foals that are not theirs and may practice infanticide
Infanticide (or infant homicide) is the intentional killing of infants or offspring. Infanticide was a widespread practice throughout human history that was mainly used to dispose of unwanted children, its main purpose being the prevention of re ...
and feticide
Foeticide (British English), or feticide (North American English), is the act of killing a fetus, or causing a miscarriage. Definitions differ between legal and medical applications, whereas in law, feticide frequently refers to a criminal offe ...
via violence to the pregnant mare.
Human relations
Cultural significance
With their distinctive black-and-white stripes, zebras are among the most recognizable mammals. They have been associated with beauty and grace, with naturalistThomas Pennant
Thomas Pennant (16 December 1798) was a Welsh natural history, naturalist, traveller, writer and antiquarian. He was born and lived his whole life at his family estate, Downing Hall, near Whitford, Flintshire, in Wales.
As a naturalist he had ...
describing them in 1781 as "the most elegant of quadrupeds". Zebras have been popular in photography, with some wildlife photographers describing them as the most photogenic animal. They have become staples in children's stories and wildlife-themed art, such as depictions of Noah's Ark. In children's alphabet book
An alphabet book is a type of children's book giving basic instruction in an alphabet. Intended for young children, alphabet books commonly use pictures, simple language and alliteration to aid language learning. Alphabet books are published ...
s, the animals are often used to represent the letter 'Z'. Zebra stripe patterns are popularly used for body paintings, dress, furniture and architecture.
Zebras have been featured in African art
African art encompasses modern and historical paintings, sculptures, installations, and other visual cultures originating from indigenous African diaspora, African communities across the African continent. The definition may also include the ar ...
and culture
Culture ( ) is a concept that encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and Social norm, norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, Social norm, customs, capabilities, Attitude (psychology), attitudes ...
for millennia. They are depicted in rock art
In archaeology, rock arts are human-made markings placed on natural surfaces, typically vertical stone surfaces. A high proportion of surviving historic and prehistoric rock art is found in caves or partly enclosed rock shelters; this type al ...
in Southern Africa dating from 28,000 to 20,000 years ago, though less often than antelope species like eland. How the zebra got its stripes has been the subject of folk tales, some of which involve it being scorched by fire. The Maasai Maasai may refer to:
*Maasai people
*Maasai language
*Maasai mythology
* MAASAI (band)
See also
* Masai (disambiguation)
Masai may refer to:
*Masai, Johor, a town in Malaysia
* Masai Plateau, a plateau in Kolhapur, Maharashtra, India
*Maasai peopl ...
proverb "a man without culture is like a zebra without stripes" has become popular in Africa. The San people
The San peoples (also Saan), or Bushmen, are the members of any of the indigenous hunter-gatherer cultures of southern Africa, and the oldest surviving cultures of the region. They are thought to have diverged from other humans 100,000 to 200 ...
connected zebra stripes with water, rain and lightning, and water spirit
A water spirit is a kind of supernatural being found in the folklore of many cultures:
African
Some water spirits in traditional African religion include:
* Mami Wata is a transcultural pantheon of water spirits and deities of the African ...
s were conceived of having these markings.
 For the
For the Shona people
The Shona people () also/formerly known as the Karanga are a Bantu peoples, Bantu ethnic group native to Southern Africa, primarily living in Zimbabwe where they form the majority of the population, as well as Mozambique, South Africa, and world ...
, the zebra is a totem
A totem (from or ''doodem'') is a spirit being, sacred object, or symbol that serves as an emblem of a group of people, such as a family, clan, lineage (anthropology), lineage, or tribe, such as in the Anishinaabe clan system.
While the word ...
animal and is glorified in a poem as an "iridescent and glittering creature". Its stripes have symbolised the union of male and female and at the ruined city of Great Zimbabwe
Great Zimbabwe was a city in the south-eastern hills of the modern country of Zimbabwe, near Masvingo. It was settled from 1000 AD, and served as the capital of the Kingdom of Great Zimbabwe from the 13th century. It is the largest stone struc ...
, zebra stripes decorate what is believed to be a ''domba'', a school meant to prepare girls for adulthood. In the Shona language
Shona ( ; ) is a Bantu language spoken by the Shona people of Zimbabwe and Mozambique. The term is variously used to collectively describe all the Central Shonic varieties (comprising Zezuru, Manyika, Korekore and Karanga or Ndau) or specifica ...
, the name ''madhuve'' means "woman/women of the zebra totem" and is a name for girls in Zimbabwe
file:Zimbabwe, relief map.jpg, upright=1.22, Zimbabwe, relief map
Zimbabwe, officially the Republic of Zimbabwe, is a landlocked country in Southeast Africa, between the Zambezi and Limpopo Rivers, bordered by South Africa to the south, Bots ...
. The plains zebra is the national animal
This is a list of countries that have officially designated one or more animals as their national animals. Most species in the list are officially designated. Some species hold only an "unofficial" status. Additionally, the list includes animals t ...
of Botswana and zebras have been depicted on stamps during colonial and post-colonial Africa. For people of the African diaspora
The African diaspora is the worldwide collection of communities descended from List of ethnic groups of Africa, people from Africa. The term most commonly refers to the descendants of the native West Africa, West and Central Africans who were ...
, the zebra represented the politics of race and identity, being both black and white.
In cultures outside of its range, the zebra has been thought of as a more exotic alternative to the horse; the comic book character Sheena, Queen of the Jungle
Sheena, Queen of the Jungle, is a fictional American comic book jungle girl heroine during the Golden Age of Comic Books. She originally debuted in the British magazine ''Wags'' #46 (January 1938). and later made her first American appearance i ...
, is depicted riding a zebra and explorer Osa Johnson
Martin Elmer Johnson (October 9, 1884 ŌĆō January 13, 1937) and Osa Helen Johnson (n├®e Leighty, March 14, 1894 ŌĆō January 7, 1953) were married American adventurers and documentary filmmakers. In the first half of the 20th century the couple ...
was photographed riding one. The film ''Racing Stripes
''Racing Stripes'' is a 2005 American sports comedy family film directed by Frederik Du Chau. The film was produced by Andrew A. Kosove, Broderick Johnson, Lloyd Phillips and Edward L. McDonnell, based on a script written by David Schmidt, S ...
'' features a captive zebra ostracised from the horses and ends up being ridden by a rebellious girl. Zebras have been featured as characters in animated films like ''Khumba
''Khumba'' is a 2013 South African animated comedy film directed and co-produced by Anthony Silverston and written by Silverston and Raffaella Delle Donne. The film stars the voices of Jake T. Austin, Steve Buscemi, Loretta Devine, Laurence Fish ...
'', ''The Lion King
''The Lion King'' is a 1994 American animated musical coming-of-age drama film directed by Roger Allers and Rob Minkoff, produced by Don Hahn, and written by Irene Mecchi, Jonathan Roberts, and Linda Woolverton. Produced by Walt Disney ...
'' and the ''Madagascar'' films and television series such as '' Zou''.
Zebras have been popular subjects for abstract, modernist
Modernism was an early 20th-century movement in literature, visual arts, and music that emphasized experimentation, abstraction, and Subjectivity and objectivity (philosophy), subjective experience. Philosophy, politics, architecture, and soc ...
and surrealist
Surrealism is an art movement, art and cultural movement that developed in Europe in the aftermath of World War I in which artists aimed to allow the unconscious mind to express itself, often resulting in the depiction of illogical or dreamlike s ...
artists. Such art includes Christopher Wood's ''Zebra and Parachute'', Lucian Freud
Lucian Michael Freud (; 8 December 1922 ŌĆō 20 July 2011) was a British painter and draughtsman, specialising in figurative art, and is known as one of the foremost 20th-century English portraitists.
His early career as a painter was inf ...
's ''The Painter's Room'' and ''Quince on a Blue Table'' and the various paintings of Mary Fedden and Sidney Nolan
Sir Sidney Robert Nolan (22 April 191728 November 1992) was one of the leading Australian artists of the 20th century. Working in a wide variety of media, his oeuvre is among the most diverse and prolific in all of modern art. He is best known ...
. Victor Vasarely
Victor Vasarely (; born Gy┼æz┼æ V├Īs├Īrhelyi, ; 9 April 1906 ŌĆō 15 March 1997) was a Hungarian-French artist, who is widely accepted as a "grandfather" and leader of the Op art movement.
His work titled ''Zebra'', created in 1937, i ...
depicted zebras as black and white lines and connected in a jigsaw puzzle
A jigsaw puzzle (with context, sometimes just jigsaw or just puzzle) is a tiling puzzle that requires the assembly of often irregularly shaped interlocking and mosaicked pieces. Typically each piece has a portion of a picture, which is comple ...
fashion. Carel Weight's ''Escape of the Zebra from the Zoo during an Air Raid'' was based on a real life incident of a zebra escaping during the bombing of London Zoo and consists of four comic book-like panels. Zebras have lent themselves to products and advertisements, notably for 'Zebra Grate Polish' cleaning supplies by British manufacturer Reckitt and Sons
Reckitt and Sons was a leading British manufacturer of household products, notably starch, black lead, laundry blue, and household polish, and based in Kingston upon Hull.
Isaac Reckitt began business in Hull in 1840, and his business bec ...
and Japanese pen manufacturer Zebra Co., Ltd.
Captivity
 Zebras have been kept in captivity since at least the
Zebras have been kept in captivity since at least the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ruled the Mediterranean and much of Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. The Roman people, Romans conquered most of this during the Roman Republic, Republic, and it was ruled by emperors following Octavian's assumption of ...
. In later times, captive zebras have been shipped around the world, often for diplomatic reasons. In 1261, Sultan Baibars
Al-Malik al-Zahir Rukn al-Din Baybars al-Bunduqdari (; 1223/1228 ŌĆō 1 July 1277), commonly known as Baibars or Baybars () and nicknamed Abu al-Futuh (, ), was the fourth Mamluk sultan of Egypt and Syria, of Turkic Kipchak origin, in the Ba ...
of Egypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northe ...
established an embassy with Alfonso X of Castile
Alfonso X (also known as the Wise, ; 23 November 1221 ŌĆō 4 April 1284) was King of Castile, Kingdom of Le├│n, Le├│n and Kingdom of Galicia, Galicia from 1 June 1252 until his death in 1284. During the April 1257 Imperial election, election of 1 ...
and sent a zebra and other exotic animals as gifts. In 1417, a zebra was gifted to the Chinese people by Somalia and displayed before the Yongle Emperor
The Yongle Emperor (2 May 1360 ŌĆō 12 August 1424), also known by his temple name as the Emperor Chengzu of Ming, personal name Zhu Di, was the third List of emperors of the Ming dynasty, emperor of the Ming dynasty, reigning from 1402 to 142 ...
. The fourth Mughal
Mughal or Moghul may refer to:
Related to the Mughal Empire
* Mughal Empire of South Asia between the 16th and 19th centuries
* Mughal dynasty
* Mughal emperors
* Mughal people, a social group of Central and South Asia
* Mughal architecture
* Mug ...
emperor Jahangir
Nur-ud-din Muhammad Salim (31 August 1569 ŌĆō 28 October 1627), known by his imperial name Jahangir (; ), was List of emperors of the Mughal Empire, Emperor of Hindustan from 1605 until his death in 1627, and the fourth Mughal emperors, Mughal ...
received a zebra from Ethiopia in 1620 and Ustad Mansur
Ustad Mansur (died 1624) was a seventeenth-century Indian painter and naturalist who served as a Mughal court artist. During which period he excelled at depicting plants and animals. He was the earliest artist to depict the dodo in colour, apart ...
made a painting of it. In the 1670s, Ethiopian Emperor
The emperor of Ethiopia (, "King of Kings"), also known as the Atse (, "emperor"), was the hereditary ruler of the Ethiopian Empire, from at least the 13th century until the abolition of the monarchy in 1975. The emperor was the head of state ...
Yohannes I
Yohannes I (), also known as Yohannes the Righteous (Ge'ez: ßī╗ßŗĄßēü ßŗ«ßłÉßŖĢßłĄ), throne name A'ilaf Sagad (Ge'ez: ßŖĀßŖźßłŗߏŹ ßł░ßīłßŗĄ; 1640 ŌĆō 19 July 1682) was Emperor of Ethiopia from 1667 to 1682, and a member of the Solomonic dynas ...
exported two zebras to the Dutch governor of Jakarta
Jakarta (; , Betawi language, Betawi: ''Jakart├©''), officially the Special Capital Region of Jakarta (; ''DKI Jakarta'') and formerly known as Batavia, Dutch East Indies, Batavia until 1949, is the capital and largest city of Indonesia and ...
. These animals would eventually be given by the Dutch to the Tokugawa Shogunate
The Tokugawa shogunate, also known as the was the military government of Japan during the Edo period from 1603 to 1868.
The Tokugawa shogunate was established by Tokugawa Ieyasu after victory at the Battle of Sekigahara, ending the civil wars ...
of Japan.
When Queen Charlotte
Charlotte of Mecklenburg-Strelitz (Sophia Charlotte; 19 May 1744 ŌĆō 17 November 1818) was Queen of Great Britain and Ireland as the wife of King George III from their marriage on 8 September 1761 until her death in 1818. The Acts of Un ...
received a zebra as a wedding gift in 1762, the animal became a source of fascination for the people of Britain. Many flocked to see it at its paddock
A paddock is a small enclosure for horses. In the United Kingdom, this term also applies to a field for a general automobile racing competition, particularly Formula 1.
Description
The most common design provides an area for exercise and is ofte ...
at Buckingham Palace
Buckingham Palace () is a royal official residence, residence in London, and the administrative headquarters of the monarch of the United Kingdom. Located in the City of Westminster, the palace is often at the centre of state occasions and r ...
. It soon became the subject of humour and satire, being referred to as "The Queen's Ass", and was the subject of an oil painting by George Stubbs
George Stubbs (25 August 1724 ŌĆō 10 July 1806) was an English painter, best known for his paintings of horses. Self-trained, Stubbs learnt his skills independently from other great artists of the 18th century such as Joshua Reynolds and Thoma ...
in 1763. The zebra also gained a reputation for being ill-tempered and kicked at visitors. In 1882, Ethiopia sent a zebra to French president Jules Gr├®vy
Fran├¦ois Judith Paul Gr├®vy (15 August 1807 ŌĆō 9 September 1891), known as Jules Gr├®vy (), was a French people, French lawyer and politician who served as President of France from 1879 to 1887. He was a leader of the Opportunist Republicans, M ...
, and the species it belonged to was named in his honour.
 Attempts to
Attempts to domesticate
Domestication is a multi-generational mutualistic relationship in which an animal species, such as humans or leafcutter ants, takes over control and care of another species, such as sheep or fungi, to obtain from them a steady supply of resou ...
zebras were largely unsuccessful. It is possible that having evolved under pressure from the many large predators of Africa, including early humans, they became more aggressive, thus making domestication more difficult. However, zebras have been trained throughout history. In Rome, zebras are recorded to have pulled chariots during amphitheatre
An amphitheatre (American English, U.S. English: amphitheater) is an open-air venue used for entertainment, performances, and sports. The term derives from the ancient Greek ('), from ('), meaning "on both sides" or "around" and ('), meani ...
games starting in the reign of Caracalla
Marcus Aurelius Antoninus (born Lucius Septimius Bassianus, 4 April 188 ŌĆō 8 April 217), better known by his nickname Caracalla (; ), was Roman emperor from 198 to 217 AD, first serving as nominal co-emperor under his father and then r ...
(198 to 217 AD). In the late 19th century, the zoologist Walter Rothschild
Lionel Walter Rothschild, 2nd Baron Rothschild, Baron de Rothschild, (8 February 1868 ŌĆō 27 August 1937) was a British banker, politician, zoologist, and soldier, who was a member of the Rothschild family. As a Zionist leader, he was present ...
trained some zebras to draw a carriage in England, which he drove to Buckingham Palace to demonstrate that it can be done. However, he did not ride on them knowing that they were too small and aggressive. In the early 20th century, German colonial officers in East Africa tried to use zebras for both driving and riding, with limited success.
Conservation
 As of 2016ŌĆō2019, the
As of 2016ŌĆō2019, the IUCN Red List
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List of Threatened Species, also known as the IUCN Red List or Red Data Book, founded in 1964, is an inventory of the global conservation status and extinction risk of biological ...
of mammals lists Gr├®vy's zebra as endangered
An endangered species is a species that is very likely to become extinct in the near future, either worldwide or in a particular political jurisdiction. Endangered species may be at risk due to factors such as habitat loss, poaching, inv ...
, the mountain zebra as vulnerable and the plains zebra as near-threatened
A near-threatened species is a species which has been categorized as "Near Threatened" (NT) by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) as that may be vulnerable to endangerment in the near future, but it does not currently qu ...
. Gr├®vy's zebra populations are estimated at less than 2,000 mature individuals, but they are stable. Mountain zebras number near 35,000 individuals and their population appears to be increasing. Plains zebra are estimated to number 150,000ŌĆō250,000 with a decreasing population trend. Human intervention has fragmented zebra ranges and populations. Zebras are threatened by hunting for their hide and meat, and habitat destruction
Habitat destruction (also termed habitat loss or habitat reduction) occurs when a natural habitat is no longer able to support its native species. The organisms once living there have either moved elsewhere, or are dead, leading to a decrease ...
. They also compete with livestock and have their travelling routes obstruct by fences. Civil wars in some countries have also caused declines in zebra populations. By the early 20th century, zebra skins were being used to make rugs and chairs. In the 21st century, zebras may be taken by trophy hunters as zebra skin rugs sell for $1,000 to $2,000. Trophy hunting was rare among African peoples though the San were known to hunt zebra for meat.
The quagga
The quagga ( or ) (''Equus quagga quagga'') is an extinct subspecies of the plains zebra that was endemic to South Africa until it was hunted to extinction in the late 19th century. It was long thought to be a distinct species, but mtDNA ...
(''E. quagga quagga'') population was hunted by early Dutch settlers and later by Afrikaner
Afrikaners () are a Southern African ethnic group descended from predominantly Dutch settlers who first arrived at the Cape of Good Hope in 1652.Entry: Cape Colony. ''Encyclop├”dia Britannica Volume 4 Part 2: Brain to Casting''. Encyclop├”d ...
s to provide meat or for their skins. The skins were traded or used locally. The quagga was probably vulnerable to extinction due to its restricted range, and because they were easy to find in large groups. The last known wild quagga died in 1878. The last captive quagga, a female in Amsterdam's Natura Artis Magistra
Natura Artis Magistra (Latin for "Nature is the teacher of art"), commonly known just as Artis (), is a zoo and botanical garden in the centre of Amsterdam. It is the oldest zoo in the Netherlands and fifth oldest zoo in the world.
In addition ...
zoo, lived there from 9 May 1867 until it died on 12 August 1883. The Cape mountain zebra
The Cape mountain zebra (''Equus zebra zebra'') is a nominate subspecies of mountain zebra that occurs in certain mountainous regions of the Western and Eastern Cape provinces of South Africa.
It is the smallest of all existing zebra species and ...
, a subspecies of mountain zebra, nearly went extinct due to hunting and habitat destruction, with less than 50 individuals left by the 1950s. Protections from South African National Parks
South African National Parks (SANParks) is the body responsible for managing South Africa's national parks. SANParks was formed in 1926, and currently manages 19 parks consisting of , over 3% of the total area of South Africa.
Many parks offer ...
allowed the population to rise to 2,600 by the 2010s.
Zebras can be found in numerous protected areas. Important areas for Gr├®vy's zebra include Yabelo Wildlife Sanctuary and Chelbi Sanctuary in Ethiopia and Buffalo Springs, Samburu and Shaba National Reserves in Kenya
Kenya, officially the Republic of Kenya, is a country located in East Africa. With an estimated population of more than 52.4 million as of mid-2024, Kenya is the 27th-most-populous country in the world and the 7th most populous in Africa. ...
. The plains zebra inhabits the Serengeti National Park
The Serengeti National Park is a large national park in northern Tanzania that stretches over . It is located in eastern Mara Region and northeastern Simiyu Region and contains over of virgin savanna. The park was established in 1940.
The Se ...
in Tanzania, Tsavo
Tsavo is a region of Kenya located at the crossing of the Uganda Railway over the Tsavo River, close to where it meets the Athi-Galana-Sabaki River. Two national parks, Tsavo East and Tsavo West are located in the area.
The meaning of the w ...
and Masai Mara
Maasai Mara, sometimes also spelt Masai Mara and locally known simply as The Mara, is a large national game reserve in Narok County, Kenya, contiguous with the Serengeti National Park in Tanzania. It is named in honour of the Maasai people, th ...
in Kenya, Hwange National Park
Hwange National Park (formerly Wankie Game Reserve) is the largest natural reserve in Zimbabwe. It is around 14,600 sq km in area. It lies in the northwest of the country, just off the main road between Bulawayo and Victoria Falls. The nearest ...
in Zimbabwe, Etosha National Park
Etosha National Park is a national park in northwestern Namibia and one of the largest national parks in Africa. It was proclaimed a game reserve in March 1907 in Ordinance 88 by the Governor of German South West Africa, Friedrich von Lindequist. ...
in Namibia
Namibia, officially the Republic of Namibia, is a country on the west coast of Southern Africa. Its borders include the Atlantic Ocean to the west, Angola and Zambia to the north, Botswana to the east and South Africa to the south; in the no ...
, and Kruger National Park
Kruger National Park () is a national park in South Africa covering an area of in the provinces of Limpopo and Mpumalanga in the country's northeast. It extends from north to south and from east to west. The administrative headquarters are i ...
in South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the Southern Africa, southernmost country in Africa. Its Provinces of South Africa, nine provinces are bounded to the south by of coastline that stretches along the Atlantic O ...
. Mountain zebras are protected in Mountain Zebra National Park
Mountain Zebra National Park is a national park in the Eastern Cape province of South Africa; established in July 1937 for the purpose of providing a nature reserve for the endangered Cape mountain zebra. It is surrounded by of the Mountain Z ...
, Karoo National Park
The Karoo National Park is a wildlife reserve in the Karoo, Great Karoo area of the Western Cape, South Africa#Geography, South Africa near Beaufort West. This semi-desert area covers an area of . The Nuweveld portion of the Great Escarpment, Sou ...
and Goegap Nature Reserve in South Africa as well as Etosha and Namib-Naukluft Park in Namibia.
Notes
See also
*Fauna of Africa
The fauna of Africa are all the animals living in Africa and its surrounding seas and islands. The more characteristic African fauna are found in the Afrotropical realm, Afro-tropical realm. Lying almost entirely within the tropics, and stretching ...
* Lord Morton's mare
* Primitive markings
Primitive markings are a group of equine coat color, hair coat markings and qualities seen in several equine species, including horses, donkey, donkeys, and asses. In horses, they are associated with primitive breeds, though not limited to such ...
ŌĆō markings found on other equines
* Zonkey (Tijuana)
Zonkeys in Tijuana, Mexico are donkeys (also known as burros in Mexico and the Southwestern United States; ''burro'' is the Spanish word for donkey) painted with fake zebra stripes, so that tourists will pay the owner to appear in souvenir photos ...
ŌĆō a donkey painted with zebra stripes
References
General bibliography
* *External links
The Quagga Project
ĆöAn organisation that selectively breeds zebras to recreate the hair coat pattern of the quagga {{Authority control * Equus (genus) Fauna of Sub-Saharan Africa Herbivorous mammals Mammals of Africa Extant Pleistocene first appearances Animal subgenera