Western Canada on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Western Canada, also referred to as the Western provinces, Canadian West, or Western provinces of Canada, and commonly known within Canada as the West, is a Canadian region that includes the four western
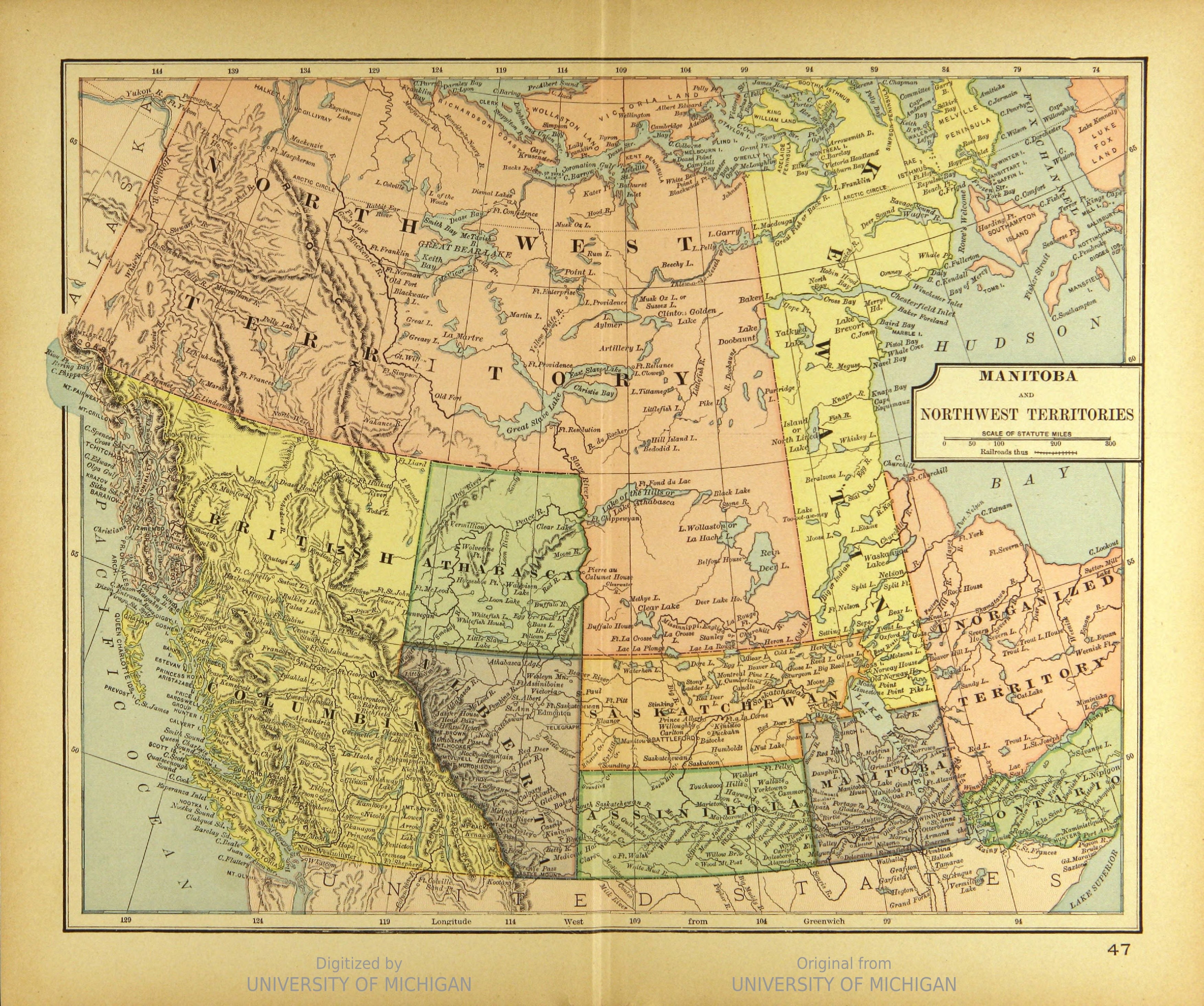 In 1858, the British government established the
In 1858, the British government established the
 As of the 2016 Census, the total population of Western Canada was nearly 11.1 million, including approximately 4.65 million in British Columbia, 4.07 million in Alberta, 1.1 million in Saskatchewan, and 1.28 million in Manitoba. This represents 31.5% of Canada's population.
As of the 2016 Census, the total population of Western Canada was nearly 11.1 million, including approximately 4.65 million in British Columbia, 4.07 million in Alberta, 1.1 million in Saskatchewan, and 1.28 million in Manitoba. This represents 31.5% of Canada's population.
 As of the 2016 Census,
As of the 2016 Census,
 Western Canada consists of the country's four westernmost provinces: British Columbia, Alberta, Saskatchewan and Manitoba. It covers 2.9 million square kilometres – almost 29% of Canada's land area. British Columbia adjoins the
Western Canada consists of the country's four westernmost provinces: British Columbia, Alberta, Saskatchewan and Manitoba. It covers 2.9 million square kilometres – almost 29% of Canada's land area. British Columbia adjoins the
 In Canadian politics, Western Canada is currently associated with a general Conservative Party lean, contrasted with a proportionally greater
In Canadian politics, Western Canada is currently associated with a general Conservative Party lean, contrasted with a proportionally greater
File:Legislative Assembly of British Columbia - Seating Chart by Party.svg, Legislative assembly of British Columbia. The Conservatives, Greens, and NDP are represented by blue, green, and orange respectively.
File:31st Alberta Legislature.svg, Legislative Assembly of Alberta. The NDP and United Conservatives are represented by orange and dark blue respectively.
File:Legislative Assembly of Saskatchewan - Seating Chart by Party.svg, Legislative Assembly of Saskatchewan. The NDP and Saskatchewan Party are represented by orange and green respectively.
File:Legislative Assembly of Manitoba - Party Layout Chart Jan 2017.svg, Legislative Assembly of Manitoba. The Liberals, NDP and Progressive Conservatives are represented by red, orange and blue respectively.
 Energy and agriculture are Western Canada's dominant industries – and this region, with only 11 million inhabitants, is one of the world's largest net exporters of both energy and agricultural commodities. Approximate breakdown:
Energy and agriculture are Western Canada's dominant industries – and this region, with only 11 million inhabitants, is one of the world's largest net exporters of both energy and agricultural commodities. Approximate breakdown:Enquirica Research – Canada's Bifurcated Economy
Energy:
* Oil (13% of world reserves; 4% of world production)
* Uranium (8% of world reserves; 20% of world production)
Agriculture:
* Potash (60% of world reserves; 30% of world production)
* Wheat, coarse grains, oilseeds (21% of the world export market for wheat; 10% for oilseeds)
* Farmland (80% of Canadian total)
Peel's Prairie Provinces: Sources for Canada and Western Canadian History
{{Authority control Regions of Canada
provinces
A province is an administrative division within a country or state. The term derives from the ancient Roman , which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire's territorial possessions outside Italy. The term ''provi ...
just north of the Canada–United States border
The international border between Canada and the United States is the longest in the world by total length. The boundary (including boundaries in the Great Lakes, Atlantic, and Pacific coasts) is long. The land border has two sections: Canada' ...
namely (from west to east) British Columbia
British Columbia is the westernmost Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada. Situated in the Pacific Northwest between the Pacific Ocean and the Rocky Mountains, the province has a diverse geography, with rugged landscapes that ...
, Alberta
Alberta is a Provinces and territories of Canada, province in Canada. It is a part of Western Canada and is one of the three Canadian Prairies, prairie provinces. Alberta is bordered by British Columbia to its west, Saskatchewan to its east, t ...
, Saskatchewan
Saskatchewan is a Provinces and territories of Canada, province in Western Canada. It is bordered on the west by Alberta, on the north by the Northwest Territories, on the east by Manitoba, to the northeast by Nunavut, and to the south by the ...
and Manitoba
Manitoba is a Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada at the Centre of Canada, longitudinal centre of the country. It is Canada's Population of Canada by province and territory, fifth-most populous province, with a population ...
. The people of the region are often referred to as "Western Canadians" or "Westerners", and though diverse from province to province are largely seen as being collectively distinct from other Canadians along cultural, linguistic, socioeconomic, geographic and political lines. They account for approximately 32% of Canada's total population.
The region is further subdivided geographically and culturally between British Columbia, which is mostly on the western side of the Canadian Rockies
The Canadian Rockies () or Canadian Rocky Mountains, comprising both the Alberta Rockies and the British Columbian Rockies, is the Canadian segment of the North American Rocky Mountains. It is the easternmost part of the Canadian Cordillera, w ...
and often referred to as the " west coast", and the "Prairie Provinces" (commonly known as "the Prairies"), which include those provinces on the eastern side of the Rockies yet west of Ontario - Alberta, Saskatchewan and Manitoba. Alberta and British Columbia are also sometimes subcategorized together, either as the "Rockie Provinces" or "mountain provinces" owing to both hosting large swathes of the mountain range, or due to shared socioeconomic factors such as their highly urbanized populations (three of Canada's five largest cities are Calgary
Calgary () is a major city in the Canadian province of Alberta. As of 2021, the city proper had a population of 1,306,784 and a metropolitan population of 1,481,806 making it the third-largest city and fifth-largest metropolitan area in C ...
, Edmonton
Edmonton is the capital city of the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian province of Alberta. It is situated on the North Saskatchewan River and is the centre of the Edmonton Metropolitan Region, which is surrounded by Central Alberta ...
, and Vancouver
Vancouver is a major city in Western Canada, located in the Lower Mainland region of British Columbia. As the List of cities in British Columbia, most populous city in the province, the 2021 Canadian census recorded 662,248 people in the cit ...
) and significant interprovincial mobility between the two. Alberta and Saskatchewan, are also sometimes subcategorized together due to shared political and economic histories, as well as similar historic migratory patterns from Eastern Europe.
Capital cities
The capital cities of the four western provinces, from west to east, are: * Victoria, British Columbia *Edmonton
Edmonton is the capital city of the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian province of Alberta. It is situated on the North Saskatchewan River and is the centre of the Edmonton Metropolitan Region, which is surrounded by Central Alberta ...
, Alberta
* Regina, Saskatchewan
* Winnipeg
Winnipeg () is the capital and largest city of the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian province of Manitoba. It is centred on the confluence of the Red River of the North, Red and Assiniboine River, Assiniboine rivers. , Winnipeg h ...
, Manitoba
With the exception of Winnipeg, which is the largest census metropolitan area
The census geographic units of Canada are the census subdivisions defined and used by Canada's federal government statistics bureau Statistics Canada to conduct the country's quinquennial census. These areas exist solely for the purposes of stat ...
in Manitoba, all other western provincial capitals are the second-largest metropolitan areas of their respective province.
Constitutional history
Western Canada is the traditional territory of Indigenous andFirst Nations
First nations are indigenous settlers or bands.
First Nations, first nations, or first peoples may also refer to:
Indigenous groups
*List of Indigenous peoples
*First Nations in Canada, Indigenous peoples of Canada who are neither Inuit nor Mé ...
predating the arrival of European colonization
The phenomenon of colonization is one that stretches around the globe and across time. Ancient and medieval colonialism was practiced by various civilizations such as the Phoenicians, Babylonians, Persians, Greeks, Romans, Han Chinese, and A ...
. As Britain colonized the West, it established treaties with various First Nations, took control of other areas without opposition and fought with other First Nations for control of Western Canada. Not all lands were ceded by the First Nations to British control and land claims are still ongoing.
 In 1858, the British government established the
In 1858, the British government established the Colony of British Columbia The Colony of British Columbia refers to one of two colonies of British North America, located on the Pacific coast of modern-day Canada:
* Colony of British Columbia (1858–1866)
* Colony of British Columbia (1866–1871)
See also
* History of ...
, governing that part of Canada still known as British Columbia. The English government established the Hudson's Bay Company, which controlled most of the current area of Western Canada, northern Ontario and northern Quebec, the area known as Rupert's Land
Rupert's Land (), or Prince Rupert's Land (), was a territory in British North America which comprised the Hudson Bay drainage basin. The right to "sole trade and commerce" over Rupert's Land was granted to Hudson's Bay Company (HBC), based a ...
and the North-Western Territory
The North-Western Territory was a region of British North America extant until 1870 and named for where it lay in relation to Rupert's Land.
Because of the lack of development, exploration, and cartographic limits of the time, the exact boun ...
. In 1870, the British government transferred the lands of the company to Canada. The area of Western Canada not within British Columbia was established as the Northwest Territories
The Northwest Territories is a federal Provinces and territories of Canada, territory of Canada. At a land area of approximately and a 2021 census population of 41,070, it is the second-largest and the most populous of Provinces and territorie ...
under Canadian control. The western provinces other than British Columbia were established from areas of the Northwest Territories:
*Manitoba
Manitoba is a Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada at the Centre of Canada, longitudinal centre of the country. It is Canada's Population of Canada by province and territory, fifth-most populous province, with a population ...
established as a province of Canada in 1870, following the enacting of the ''Manitoba Act
The ''Manitoba Act, 1870'' ()Originally entitled (until renamed in 1982) ''An Act to amend and continue the Act 32 and 33 Victoria, chapter 3; and to establish and provide for the Government of the Province of Manitoba.'' is an act of the Parli ...
''.
*British Columbia
British Columbia is the westernmost Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada. Situated in the Pacific Northwest between the Pacific Ocean and the Rocky Mountains, the province has a diverse geography, with rugged landscapes that ...
: Under terms that Canada would absorb the colony's debt, would begin to subsidize public work, and would begin to construct a railway allowing travel from British Columbia to Ontario
Ontario is the southernmost Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada. Located in Central Canada, Ontario is the Population of Canada by province and territory, country's most populous province. As of the 2021 Canadian census, it ...
, British Columbia agreed to join Canadian confederation
Canadian Confederation () was the process by which three British North American provinces—the Province of Canada, Nova Scotia, and New Brunswick—were united into one federation, called the Name of Canada#Adoption of Dominion, Dominion of Ca ...
in 1871.
*Saskatchewan
Saskatchewan is a Provinces and territories of Canada, province in Western Canada. It is bordered on the west by Alberta, on the north by the Northwest Territories, on the east by Manitoba, to the northeast by Nunavut, and to the south by the ...
: Established as province in 1905, with the implementation of the ''Saskatchewan Act
The ''Saskatchewan Act'' () is an Act of Parliament, act of the Parliament of Canada which established the new Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Saskatchewan, effective September 1, 1905. Its long title is ''An Act to establish a ...
''.
*Alberta
Alberta is a Provinces and territories of Canada, province in Canada. It is a part of Western Canada and is one of the three Canadian Prairies, prairie provinces. Alberta is bordered by British Columbia to its west, Saskatchewan to its east, t ...
: In 1905, the same year as Saskatchewan, Alberta also was established as province. Just like Saskatchewan had the ''Saskatchewan Act'', Alberta had the '' Alberta Act''.
Demographics
 As of the 2016 Census, the total population of Western Canada was nearly 11.1 million, including approximately 4.65 million in British Columbia, 4.07 million in Alberta, 1.1 million in Saskatchewan, and 1.28 million in Manitoba. This represents 31.5% of Canada's population.
As of the 2016 Census, the total population of Western Canada was nearly 11.1 million, including approximately 4.65 million in British Columbia, 4.07 million in Alberta, 1.1 million in Saskatchewan, and 1.28 million in Manitoba. This represents 31.5% of Canada's population. Vancouver
Vancouver is a major city in Western Canada, located in the Lower Mainland region of British Columbia. As the List of cities in British Columbia, most populous city in the province, the 2021 Canadian census recorded 662,248 people in the cit ...
is the largest metropolitan area in Western Canada at nearly 2.5 million people, while Calgary
Calgary () is a major city in the Canadian province of Alberta. As of 2021, the city proper had a population of 1,306,784 and a metropolitan population of 1,481,806 making it the third-largest city and fifth-largest metropolitan area in C ...
is largest city proper at over 1.2 million people.
Census metropolitan areas
 As of the 2016 Census,
As of the 2016 Census, Statistics Canada
Statistics Canada (StatCan; ), formed in 1971, is the agency of the Government of Canada commissioned with producing statistics to help better understand Canada, its population, resources, economy, society, and culture. It is headquartered in ...
recognized ten census metropolitan area
The census geographic units of Canada are the census subdivisions defined and used by Canada's federal government statistics bureau Statistics Canada to conduct the country's quinquennial census. These areas exist solely for the purposes of stat ...
s within Western Canada, including four in British Columbia, three in Alberta, two in Saskatchewan, and one in Manitoba. The following is a list of these areas and their populations as of 2016.
From 2011 to 2016, the fastest growing CMAs in the country were the five in Alberta and Saskatchewan: Calgary (+14.6%), Edmonton
Edmonton is the capital city of the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian province of Alberta. It is situated on the North Saskatchewan River and is the centre of the Edmonton Metropolitan Region, which is surrounded by Central Alberta ...
(+13.9%), Saskatoon
Saskatoon () is the largest city in the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian province of Saskatchewan. It straddles a bend in the South Saskatchewan River in the central region of the province. It is located along the Trans-Canada Hig ...
(+12.5%), Regina (+11.8%) and Lethbridge
Lethbridge ( ) is a city in the province of Alberta, Canada. With a population of 106,550 in the 2023 Alberta municipal censuses, 2023 municipal census, Lethbridge became the fourth Alberta city to surpass 100,000 people. The nearby Canadian ...
(+10.8%). These were the only CMAs in the country to register growth over 10%. The three fastest growing CMAs - Calgary, Edmonton, and Saskatoon - were unchanged from the previous intercensal period.
Geography
 Western Canada consists of the country's four westernmost provinces: British Columbia, Alberta, Saskatchewan and Manitoba. It covers 2.9 million square kilometres – almost 29% of Canada's land area. British Columbia adjoins the
Western Canada consists of the country's four westernmost provinces: British Columbia, Alberta, Saskatchewan and Manitoba. It covers 2.9 million square kilometres – almost 29% of Canada's land area. British Columbia adjoins the Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five Borders of the oceans, oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is ...
to the west, while Manitoba has a coastline on Hudson Bay
Hudson Bay, sometimes called Hudson's Bay (usually historically), is a large body of Saline water, saltwater in northeastern Canada with a surface area of . It is located north of Ontario, west of Quebec, northeast of Manitoba, and southeast o ...
in its northeast of the province. Both Alberta and Saskatchewan are landlocked
A landlocked country is a country that has no territory connected to an ocean or whose coastlines lie solely on endorheic basins. Currently, there are 44 landlocked countries, two of them doubly landlocked (Liechtenstein and Uzbekistan), and t ...
between British Columbia and Manitoba.
The Canadian Prairies
The Canadian Prairies (usually referred to as simply the Prairies in Canada) is a region in Western Canada. It includes the Canadian portion of the Great Plains and the Prairie provinces, namely Alberta, Saskatchewan, and Manitoba. These provin ...
are part of a vast sedimentary
Sedimentary rocks are types of rock formed by the cementation of sediments—i.e. particles made of minerals (geological detritus) or organic matter (biological detritus)—that have been accumulated or deposited at Earth's surface. Sedime ...
plain
In geography, a plain, commonly known as flatland, is a flat expanse of land that generally does not change much in elevation, and is primarily treeless. Plains occur as lowlands along valleys or at the base of mountains, as coastal plains, and ...
covering much of Alberta, southern Saskatchewan, and southwestern Manitoba. The prairies form a significant portion of the land area of Western Canada. The plains generally describes the expanses of largely flat, arable agricultural land which sustain extensive grain farming operations in the southern part of the provinces. Despite this, some areas such as the Cypress Hills and Alberta Badlands are quite hilly and the prairie provinces contain large areas of forest such as the Mid-Continental Canadian forests
The Mid-Canada Boreal Plains Forests is a taiga ecoregion of Western Canada, designated by One Earth. It was previously defined as the Mid-Continental Canadian Forests by the World Wildlife Fund (WWF) categorization system, before it was modified ...
.
In Alberta and British Columbia, the Canadian Cordillera The Pacific Cordillera, also known as the Western Cordillera or simply The Cordillera, is a top-level physiographic region of Canada, referring mainly to the extensive cordillera system in Western and Northwestern Canada that constitutes the northe ...
is bounded by the Rocky Mountains to the east and the Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five Borders of the oceans, oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is ...
to the west.
The Canadian Rockies
The Canadian Rockies () or Canadian Rocky Mountains, comprising both the Alberta Rockies and the British Columbian Rockies, is the Canadian segment of the North American Rocky Mountains. It is the easternmost part of the Canadian Cordillera, w ...
are part of a major continental divide
A continental divide is a drainage divide on a continent such that the drainage basin on one side of the divide feeds into one ocean or sea, and the basin on the other side either feeds into a different ocean or sea, or else is endorheic, not ...
that extends north and south through western North America and western South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a considerably smaller portion in the Northern Hemisphere. It can also be described as the southern Subregion#Americas, subregion o ...
. The continental divide also defines much of the border between Alberta and British Columbia. The Columbia and the Fraser River
The Fraser River () is the longest river within British Columbia, Canada, rising at Fraser Pass near Blackrock Mountain (Canada), Blackrock Mountain in the Rocky Mountains and flowing for , into the Strait of Georgia just south of the City of V ...
s have their headwaters in the Canadian Rockies and are the second- and third-largest rivers, respectively, to drain to the west coast of North America. To the west of their headwaters, across the Rocky Mountain Trench
The Rocky Mountain Trench, also known as the Valley of a Thousand Peaks or simply the Trench, is a large valley on the western side of the northern part of North America's Rocky Mountains. The Trench is both visually and cartographically a ...
, is a second belt of mountains, the Columbia Mountains
The Columbia Mountains are a group of mountain ranges along the Upper Columbia River in British Columbia, Montana, Idaho and Washington (state), Washington. The mountain range covers 135,952 km² (52,491 sq mi). The range is bounded by th ...
, comprising the Selkirk, Purcell
Henry Purcell (, rare: ; September 1659 – 21 November 1695) was an English composer of Baroque music, most remembered for his more than 100 songs; a tragic opera, ''Dido and Aeneas''; and his incidental music to a version of Shakespeare's ...
, Monashee and Cariboo Mountains sub-ranges.
Climate
The coast of British Columbia enjoys a moderateoceanic climate
An oceanic climate, also known as a marine climate or maritime climate, is the temperate climate sub-type in Köppen climate classification, Köppen classification represented as ''Cfb'', typical of west coasts in higher middle latitudes of co ...
because of the influence of the Pacific Ocean. Winters are typically wet and summers relatively dry. These areas enjoy the mildest winter weather in all of Canada, as temperatures rarely fall much below the freezing mark. The mountainous Interior of the province is drier and has colder winters, but experiences hotter summers than the more moderate coastal areas. Lytton, British Columbia
Lytton is a village of about 250 residents in southern British Columbia, Canada, on the east side of the Fraser River and primarily the south side of the Thompson River, where it flows southwesterly into the Fraser. The community includes the ...
, a small town that sits at the confluence of the Thompson River holds the record for the hottest temperature ever recorded in Canada at on 29 June 2021, and is regularly referred as Canada's hot spot in summer with temperatures easily reaching the mid to high 30 °C 's (upper 90s to low 100s °F) in July and August and sometimes top .
Alberta has a dry continental climate with warm summers and cold winters. The province is open to cold Arctic weather systems from the north, which often produce extremely cold conditions in winter. Winters are generally quite cold, though some areas can experience a phenomenon known as the "Chinook wind
Chinook winds, or simply Chinooks, are two types of prevailing warm, generally westerly winds in western North America: Coastal Chinooks and interior Chinooks. The coastal Chinooks are persistent seasonal, wet, southwesterly winds blowing in from ...
", wherein warm winds raise the winter temperatures temporarily. In contrast, summers can fluctuate from cool to hot and are generally wetter.
Saskatchewan
Saskatchewan is a Provinces and territories of Canada, province in Western Canada. It is bordered on the west by Alberta, on the north by the Northwest Territories, on the east by Manitoba, to the northeast by Nunavut, and to the south by the ...
and Manitoba
Manitoba is a Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada at the Centre of Canada, longitudinal centre of the country. It is Canada's Population of Canada by province and territory, fifth-most populous province, with a population ...
have a continental climate and experience extremes in weather. Winters in both provinces can be classified as harsh with Arctic
The Arctic (; . ) is the polar regions of Earth, polar region of Earth that surrounds the North Pole, lying within the Arctic Circle. The Arctic region, from the IERS Reference Meridian travelling east, consists of parts of northern Norway ( ...
winds and temperatures possible. Winter temperatures in both provinces average between . In contrast, summers can be hot with temperatures exceeding at least once per year in most locations.
Politics
Federal politics
 In Canadian politics, Western Canada is currently associated with a general Conservative Party lean, contrasted with a proportionally greater
In Canadian politics, Western Canada is currently associated with a general Conservative Party lean, contrasted with a proportionally greater Liberal Party
The Liberal Party is any of many political parties around the world.
The meaning of ''liberal'' varies around the world, ranging from liberal conservatism on the right to social liberalism on the left. For example, while the political systems ...
lean in Central and Atlantic Canada
Atlantic Canada, also called the Atlantic provinces (), is the list of regions of Canada, region of Eastern Canada comprising four provinces: New Brunswick, Newfoundland and Labrador, Nova Scotia, and Prince Edward Island. As of 2021, the landma ...
. Liberal Party strongholds exist particularly in Greater Vancouver and Winnipeg. The social democratic
Social democracy is a Social philosophy, social, Economic ideology, economic, and political philosophy within socialism that supports Democracy, political and economic democracy and a gradualist, reformist, and democratic approach toward achi ...
New Democratic Party
The New Democratic Party (NDP; , ) is a federal political party in Canada. Widely described as social democratic,The party is widely described as social democratic:
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
* The Editors of ''Encyclopædia Britann ...
had its origins on the Canadian Prairies and in the mining and pulp mill towns and railway camps of British Columbia and has a history of support in Manitoba and British Columbia.
The western provinces are represented in the Parliament of Canada
The Parliament of Canada () is the Canadian federalism, federal legislature of Canada. The Monarchy of Canada, Crown, along with two chambers: the Senate of Canada, Senate and the House of Commons of Canada, House of Commons, form the Bicameral ...
by 108 Members of Parliament (MPs) in the House of Commons
The House of Commons is the name for the elected lower house of the Bicameralism, bicameral parliaments of the United Kingdom and Canada. In both of these countries, the Commons holds much more legislative power than the nominally upper house of ...
(British Columbia 43, Alberta 37, Saskatchewan and Manitoba 14 each) and 24 senators (6 from each province). Currently, of the 108 western MPs in the Commons, 73 are Conservatives, Liberals hold 29 seats, the New Democrats hold 5 and the Greens hold 1.
Western alienation
Western alienation refers to the notion that Western Canada has been excluded economically and politically from the rest of Canada.Senate reform
The West has been the most vocal in calls for reform of theSenate
A senate is a deliberative assembly, often the upper house or chamber of a bicameral legislature. The name comes from the ancient Roman Senate (Latin: ''Senatus''), so-called as an assembly of the senior (Latin: ''senex'' meaning "the el ...
, in which Ontario, Quebec
Quebec is Canada's List of Canadian provinces and territories by area, largest province by area. Located in Central Canada, the province shares borders with the provinces of Ontario to the west, Newfoundland and Labrador to the northeast, ...
, and particularly Atlantic Canada
Atlantic Canada, also called the Atlantic provinces (), is the list of regions of Canada, region of Eastern Canada comprising four provinces: New Brunswick, Newfoundland and Labrador, Nova Scotia, and Prince Edward Island. As of 2021, the landma ...
are seen by some westerners as being over-represented. The population of Ontario alone (13.1 million) exceeds that of all the western provinces combined. The total population of Atlantic Canada, however, is 2.3 million, and this region is represented by 30 senators. Thus, Ontario is under-represented, Quebec has representation proportional to its population and the Atlantic provinces are over-represented. Westerners have advocated the so-called Triple-E Senate, which stands for "equal, elected, effective." They feel if all 10 provinces were allotted an equal number of senators, if those senators were elected instead of appointed, and if the Senate were a body that had more direct political power (for example via an arrangement more similar to the structure of the Australian Senate
The Senate is the upper house of the Bicameralism, bicameral Parliament of Australia, the lower house being the Australian House of Representatives, House of Representatives.
The powers, role and composition of the Senate are set out in Chap ...
or the United States Senate
The United States Senate is a chamber of the Bicameralism, bicameral United States Congress; it is the upper house, with the United States House of Representatives, U.S. House of Representatives being the lower house. Together, the Senate and ...
rather than the UK model), then their region would have more of its concerns addressed at the federal level. Other westerners find this approach simplistic and either advocate keeping the status quo or may support other models for senate reform. The combination of all of these issues has led to the concept known as Western alienation
Western alienation, in the context of Canadian politics, refers to the notion that the Western provinces—British Columbia, Alberta, Saskatchewan and Manitoba—have been marginalized within Confederation, particularly compared to Central Canada ...
, as well as calls for Western Canada independence by various fringe groups.
Provincial politics
Regarding provincial politics, from May 2001 to June 2017, theBritish Columbia Liberal Party
BC United (BCU), known from 1903 until 2023 as the British Columbia Liberal Party or BC Liberals, is a provincial political party in British Columbia, Canada. The party has been described as conservative, neoliberal, and occupying a centre-right ...
formed the provincial government in British Columbia, though despite the name is not formally allied with the federal Liberal Party and is widely seen as centre-right or conservative in nature. It is also composed of members from the federal Conservative Party's right-wing and many former Reform Party supporters. Following the 2017 provincial election in British Columbia, the British Columbia New Democratic Party
The New Democratic Party of British Columbia (BC NDP) is a social democratic political party in British Columbia, Canada. The party sits on the centre-left of the political spectrum and is one of the two major parties in British Columbia; since ...
formed a minority government with the support of the British Columbia Green Party, following the defeat of Christy Clark
Christina Joan Clark (born October 29, 1965) is a Canadian politician who served as the 35th premier of British Columbia from 2011 to 2017. Clark was the second woman to be premier of BC, after Rita Johnston in 1991, and the first female premi ...
's Liberal Party government by a vote of non-confidence. As of October 2020, the BC NDP hold a majority government in the legislature. The New Democratic Party
The New Democratic Party (NDP; , ) is a federal political party in Canada. Widely described as social democratic,The party is widely described as social democratic:
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
* The Editors of ''Encyclopædia Britann ...
holds a majority in the Manitoba legislature. The 2023 Alberta general election
The 2023 Alberta general election was held on May 29, 2023. Voters elected the members of the 31st Alberta Legislature. The United Conservative Party under Danielle Smith, the incumbent Premier of Alberta, was re-elected to a second term with a ...
reduced the United Conservative Party
The United Conservative Party of Alberta (UCP) is a conservative political party in the province of Alberta, Canada. It was established in July 2017 as a merger between the Progressive Conservative Association of Alberta and the Wildrose Party ...
's seat count, but they held on to a majority. The Saskatchewan Party
The Saskatchewan Party (SP or Sask Party) is a conservative political party in the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian province of Saskatchewan. The party was founded in 1997 by a coalition of former provincial Progressive Conservative ...
holds a supermajority
A supermajority is a requirement for a proposal to gain a specified level of support which is greater than the threshold of one-half used for a simple majority. Supermajority rules in a democracy can help to prevent a majority from eroding fun ...
government in its legislature.
Economy
 Energy and agriculture are Western Canada's dominant industries – and this region, with only 11 million inhabitants, is one of the world's largest net exporters of both energy and agricultural commodities. Approximate breakdown:
Energy and agriculture are Western Canada's dominant industries – and this region, with only 11 million inhabitants, is one of the world's largest net exporters of both energy and agricultural commodities. Approximate breakdown:See also
*History of the west coast of North America
The human history of the west coast of North America is believed to stretch back to the arrival of the earliest people over the Bering Strait, or alternately along the ice free coastal islands of British Columbia. This was followed by the develop ...
*American Old West
The American frontier, also known as the Old West, and popularly known as the Wild West, encompasses the geography, history, folklore, and culture associated with the forward wave of American expansion in mainland North America that bega ...
*Western United States
The Western United States (also called the American West, the Western States, the Far West, the Western territories, and the West) is List of regions of the United States, census regions United States Census Bureau.
As American settlement i ...
* Cascadia
References
Further reading
* *External links
* *Peel's Prairie Provinces: Sources for Canada and Western Canadian History
{{Authority control Regions of Canada