West Point on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The United States Military Academy (USMA), also known
The United States Military Academy (USMA), also known


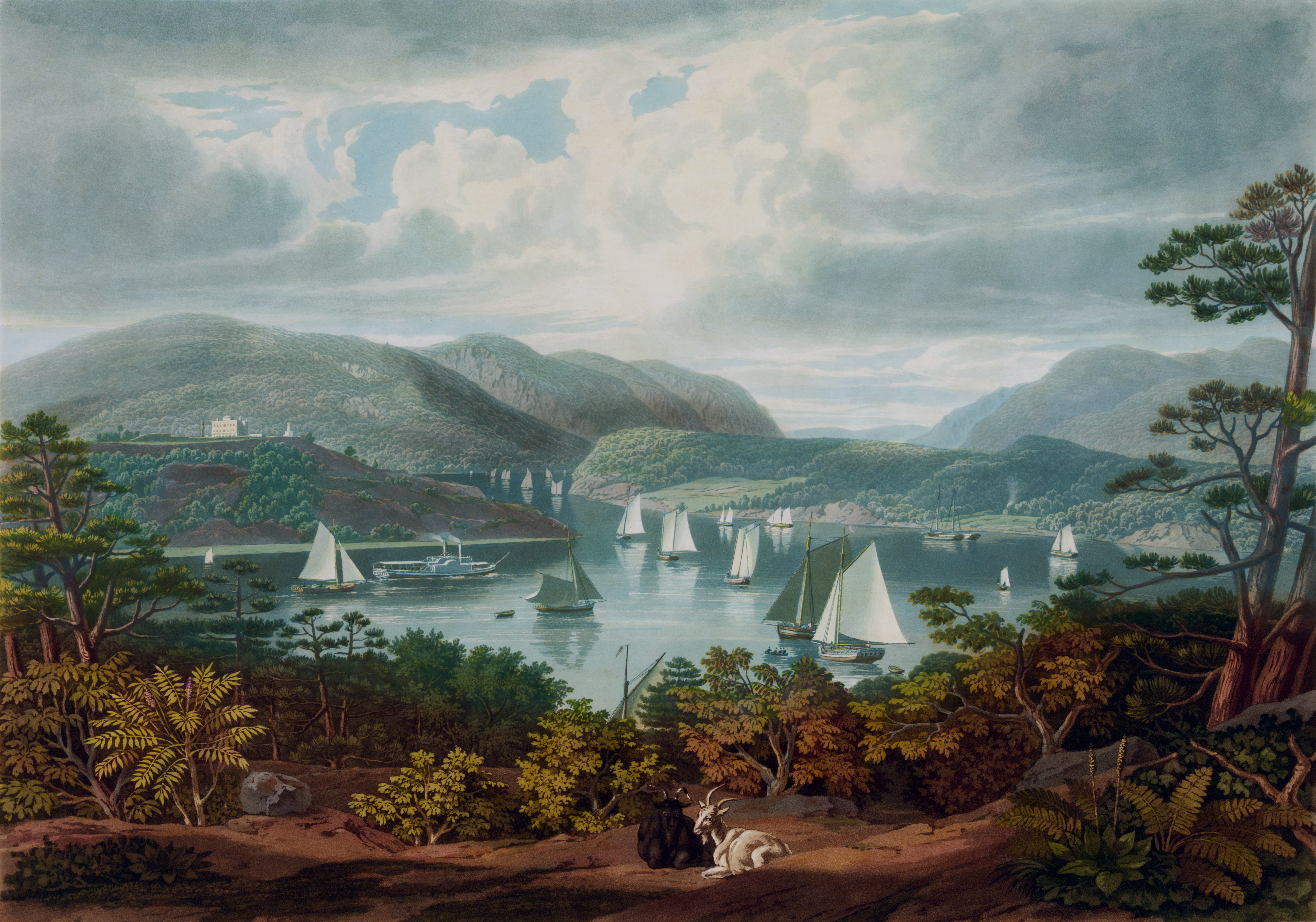

 In 1817,
In 1817,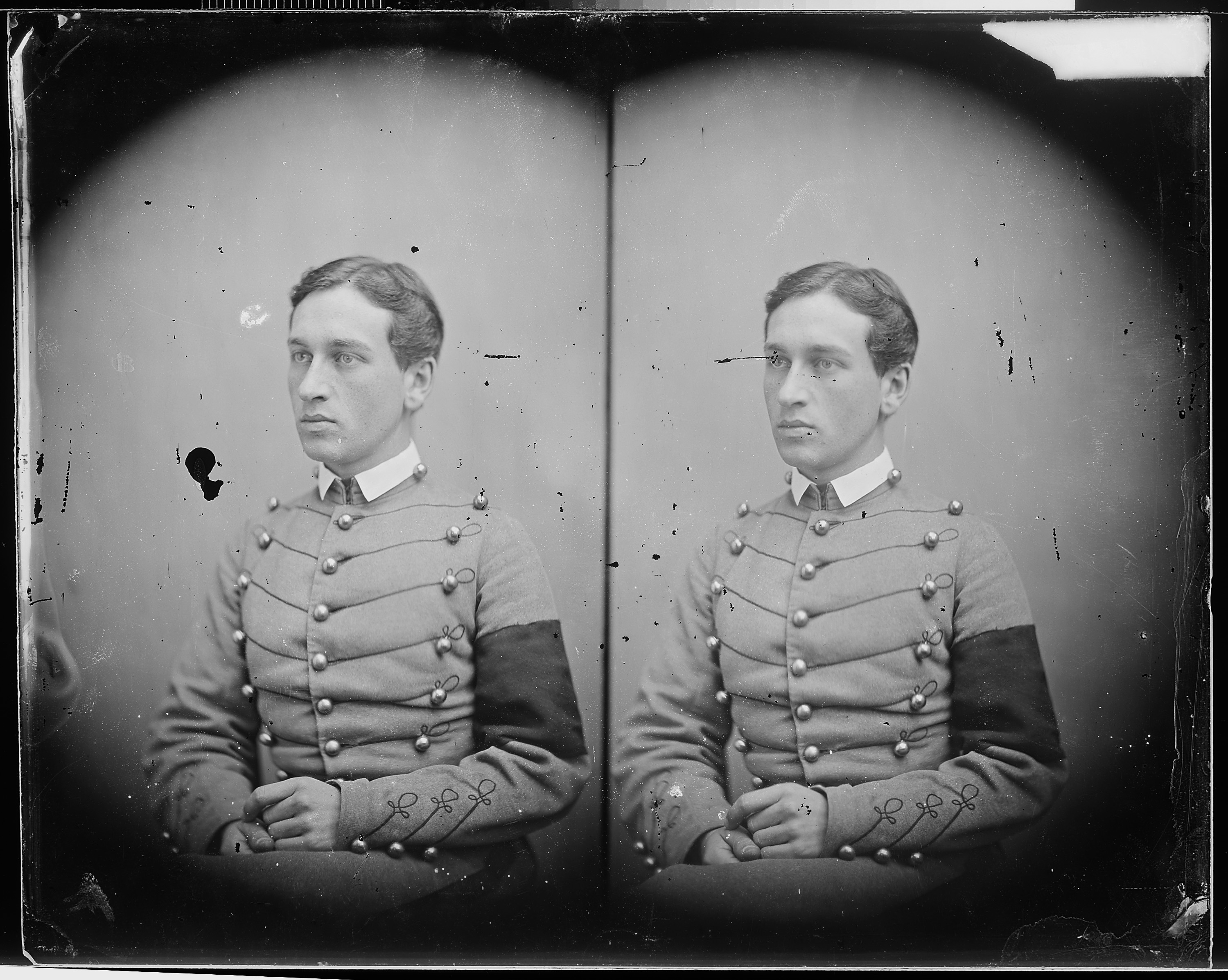 
 Immediately following the Civil War, the academy enjoyed unprecedented fame as a result of the role its graduates had played. However, the post-war years were a difficult time for the academy as it struggled to admit and reintegrate cadets from former confederate states. The first cadets from Southern states were re-admitted in 1868, and 1870 saw the admission of the first black cadet, James Webster Smith of
Immediately following the Civil War, the academy enjoyed unprecedented fame as a result of the role its graduates had played. However, the post-war years were a difficult time for the academy as it struggled to admit and reintegrate cadets from former confederate states. The first cadets from Southern states were re-admitted in 1868, and 1870 saw the admission of the first black cadet, James Webster Smith of  Besides the integration of southern-state and black cadets, the post-war academy also struggled with the issue of
Besides the integration of southern-state and black cadets, the post-war academy also struggled with the issue of 
 The demand for junior officers during the
The demand for junior officers during the
 Following the 1973 end of American involvement in Vietnam, the strain and stigma of earlier social unrest dissolved and West Point enjoyed surging enrollments. On 20 May 1975, an amendment to the Defense Authorization Bill of 1976 opening the service academies to women was approved by the House of Representatives, 303–96. The Senate followed suit on 6 June. President Ford signed the bill on 7 October 1975.
West Point admitted its first 119 female cadets in 1976.Barkalow (1990), p. 20. Also in 1976, physics professor James H. Stith became the first tenured African American Professor. In 1979, Cadet, later General,
Following the 1973 end of American involvement in Vietnam, the strain and stigma of earlier social unrest dissolved and West Point enjoyed surging enrollments. On 20 May 1975, an amendment to the Defense Authorization Bill of 1976 opening the service academies to women was approved by the House of Representatives, 303–96. The Senate followed suit on 6 June. President Ford signed the bill on 7 October 1975.
West Point admitted its first 119 female cadets in 1976.Barkalow (1990), p. 20. Also in 1976, physics professor James H. Stith became the first tenured African American Professor. In 1979, Cadet, later General,  In 1985, cadets were formally authorized to declare an academic major; all previous graduates had been awarded a general bachelor of science degree. Five years later there was a major revision of the ''Fourth Class System'', as the Cadet Leader Development System (CLDS) became the guidance for the development of all four classes. The class of 1990 was the first one to be issued a standard and mandatory computer to every member of the class at the beginning of Plebe year, the Zenith 248 SX. The academy was also an early adopter of the Internet in the mid-1990s, and was recognized in 2006 as one of the nation's "most wired" campuses.
At the height of the Cold War in October 1987, President Reagan visited the academy and delivered a speech about ending the Evil Empire.
During the
In 1985, cadets were formally authorized to declare an academic major; all previous graduates had been awarded a general bachelor of science degree. Five years later there was a major revision of the ''Fourth Class System'', as the Cadet Leader Development System (CLDS) became the guidance for the development of all four classes. The class of 1990 was the first one to be issued a standard and mandatory computer to every member of the class at the beginning of Plebe year, the Zenith 248 SX. The academy was also an early adopter of the Internet in the mid-1990s, and was recognized in 2006 as one of the nation's "most wired" campuses.
At the height of the Cold War in October 1987, President Reagan visited the academy and delivered a speech about ending the Evil Empire.
During the  Brig. Gen. Diana Holland became West Point's first woman Commandant of Cadets in January 2016.
In 2020, the campus confronted its first major pandemic in a century, with the
Brig. Gen. Diana Holland became West Point's first woman Commandant of Cadets in January 2016.
In 2020, the campus confronted its first major pandemic in a century, with the

 The academy is located approximately north of New York City on the western bank of the
The academy is located approximately north of New York City on the western bank of the  In 1902, the Boston architectural firm Cram, Goodhue, and Ferguson was awarded a major construction contract that set the predominantly neogothic architectural style still seen today.Palka (2008), p. 27. Most of the buildings of the central cadet area are in this style, as typified by the
In 1902, the Boston architectural firm Cram, Goodhue, and Ferguson was awarded a major construction contract that set the predominantly neogothic architectural style still seen today.Palka (2008), p. 27. Most of the buildings of the central cadet area are in this style, as typified by the  The academy grounds are home to numerous monuments and statues. The central cadet parade ground, the Plain, hosts the largest number, and includes the
The academy grounds are home to numerous monuments and statues. The central cadet parade ground, the Plain, hosts the largest number, and includes the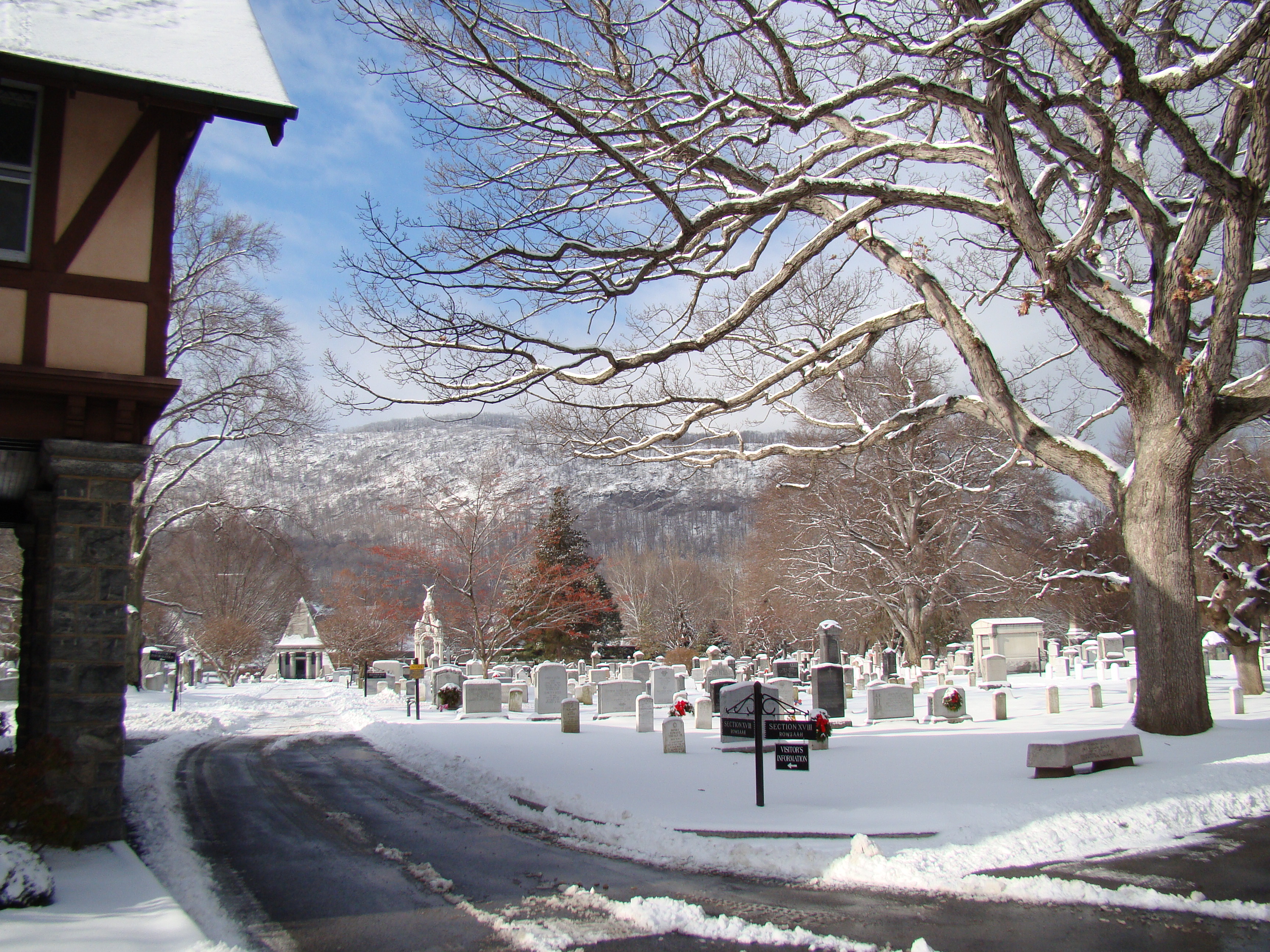  The
The
 The commanding officer at the USMA is the Superintendent, equivalent to the president or chancellor of a civilian university. In recent years, the position of superintendent has been held by a
The commanding officer at the USMA is the Superintendent, equivalent to the president or chancellor of a civilian university. In recent years, the position of superintendent has been held by a
''Congressional Research Service''. Retrieved 19 December 2008 Admission to West Point is selective: 7.74% of applicants were admitted (total of 1232) to the Class of 2024. Candidates may have previous college experience, but they may not transfer, meaning that regardless of previous college credit, they enter the academy as a fourth class cadet and undergo the entire four-year program. If a candidate is considered academically disqualified and not selected, he or she may receive an offer to attend to the United States Military Academy Preparatory School. Upon graduation from USMAPS, these candidates are appointed to the academy if they receive the recommendation of the USMAPS Commandant and meet medical admission requirements. The West Point Association of Graduates (WPAOG) also offers scholarship support to people who are qualified but not selected. The scholarships usually cover around $7,000 to civilian universities; the students who receive these scholarships do so under the stipulation that they will be admitted to and attend West Point a year later. Those who do not must repay the AOG. Marion Military Institute, New Mexico Military Institute,
 West Point is a medium-sized, highly residential baccalaureate college, with a full-time, four-year undergraduate program that emphasizes instruction in the arts, sciences, and professions with no graduate program. There are forty-five academic majors, the most popular of which are foreign languages, management information systems, history, economics, and mechanical engineering. West Point is accredited by the
West Point is a medium-sized, highly residential baccalaureate college, with a full-time, four-year undergraduate program that emphasizes instruction in the arts, sciences, and professions with no graduate program. There are forty-five academic majors, the most popular of which are foreign languages, management information systems, history, economics, and mechanical engineering. West Point is accredited by the
 As all cadets are commissioned as second lieutenants upon graduation, military and leadership education is nested with academic instruction. Military training and discipline fall under the purview of the Office of the Commandant of Cadets. Entering freshmen, or fourth class cadets, are referred to as New Cadets, and enter the academy on Reception Day or R-day, which marks the start of cadet basic training (CBT), known colloquially as Beast Barracks, or simply Beast. Most cadets consider Beast to be their most difficult time at the academy because of the transition from civilian to military life. Their second summer, cadets undergo cadet field training (CFT) at nearby Camp Buckner, where they train in more advanced field craft and military skills. During a cadet's third summer, they may serve as instructors for CBT or CFT. Rising Firstie (senior) cadets also spend one-month training at Camp Buckner, where they train for modern tactical situations that they will soon face as new platoon leaders. Cadets also have the opportunity during their second, third and fourth summers to serve in active army units and military schools around the world. The schools include Airborne, Air Assault, Sapper, Pathfinder, etc.
Active duty officers in the
As all cadets are commissioned as second lieutenants upon graduation, military and leadership education is nested with academic instruction. Military training and discipline fall under the purview of the Office of the Commandant of Cadets. Entering freshmen, or fourth class cadets, are referred to as New Cadets, and enter the academy on Reception Day or R-day, which marks the start of cadet basic training (CBT), known colloquially as Beast Barracks, or simply Beast. Most cadets consider Beast to be their most difficult time at the academy because of the transition from civilian to military life. Their second summer, cadets undergo cadet field training (CFT) at nearby Camp Buckner, where they train in more advanced field craft and military skills. During a cadet's third summer, they may serve as instructors for CBT or CFT. Rising Firstie (senior) cadets also spend one-month training at Camp Buckner, where they train for modern tactical situations that they will soon face as new platoon leaders. Cadets also have the opportunity during their second, third and fourth summers to serve in active army units and military schools around the world. The schools include Airborne, Air Assault, Sapper, Pathfinder, etc.
Active duty officers in the
 The Department of Physical Education (DPE) administers the physical program, which includes both physical education classes, physical fitness testing, and competitive athletics. The head of DPE holds the title of Master of the Sword, dating back to the 19th century when DPE taught swordsmanship as part of the curriculum.
All cadets take a prescribed series of physical fitness courses such as military movement (applied gymnastics), boxing, survival swimming, and beginning in 2009, advanced combatives. Cadets can also take elective physical activity classes such as
The Department of Physical Education (DPE) administers the physical program, which includes both physical education classes, physical fitness testing, and competitive athletics. The head of DPE holds the title of Master of the Sword, dating back to the 19th century when DPE taught swordsmanship as part of the curriculum.
All cadets take a prescribed series of physical fitness courses such as military movement (applied gymnastics), boxing, survival swimming, and beginning in 2009, advanced combatives. Cadets can also take elective physical activity classes such as
 Moral and ethical development occurs throughout the entirety of the cadet experience by living under the honor code and through formal leadership programs available at the academy. These include instruction in the values of the military profession through Professional Military Ethics Education (PME2), voluntary religious programs, interaction with staff and faculty role models, and an extensive guest-speaker program. The foundation of the ethical code at West Point is found in the academy's motto, "Duty, Honor, Country."
West Point's Cadet Honor Code reads simply that: "A cadet will not lie, cheat, steal, or tolerate those who do." Cadets accused of violating the Honor Code face an investigative and hearing process. If they are found guilty by a jury of their peers, they face severe consequences ranging from being "turned back" (repeating an academic year) to separation from the academy. Cadets previously enforced collective censure by an unofficial sanction known as "silencing" by not speaking to cadets accused of violating the honor code, but the practice ended in 1973 after national scrutiny.
Although the academy's honor code is well known and has been influential for many other colleges and universities, the academy has experienced several significant violations. For example, 151 junior cadets were found guilty of "violating the honor code" in their exams in 1976. In 2020, more than 70 cadets were also accused of cheating on exams.
Moral and ethical development occurs throughout the entirety of the cadet experience by living under the honor code and through formal leadership programs available at the academy. These include instruction in the values of the military profession through Professional Military Ethics Education (PME2), voluntary religious programs, interaction with staff and faculty role models, and an extensive guest-speaker program. The foundation of the ethical code at West Point is found in the academy's motto, "Duty, Honor, Country."
West Point's Cadet Honor Code reads simply that: "A cadet will not lie, cheat, steal, or tolerate those who do." Cadets accused of violating the Honor Code face an investigative and hearing process. If they are found guilty by a jury of their peers, they face severe consequences ranging from being "turned back" (repeating an academic year) to separation from the academy. Cadets previously enforced collective censure by an unofficial sanction known as "silencing" by not speaking to cadets accused of violating the honor code, but the practice ended in 1973 after national scrutiny.
Although the academy's honor code is well known and has been influential for many other colleges and universities, the academy has experienced several significant violations. For example, 151 junior cadets were found guilty of "violating the honor code" in their exams in 1976. In 2020, more than 70 cadets were also accused of cheating on exams.
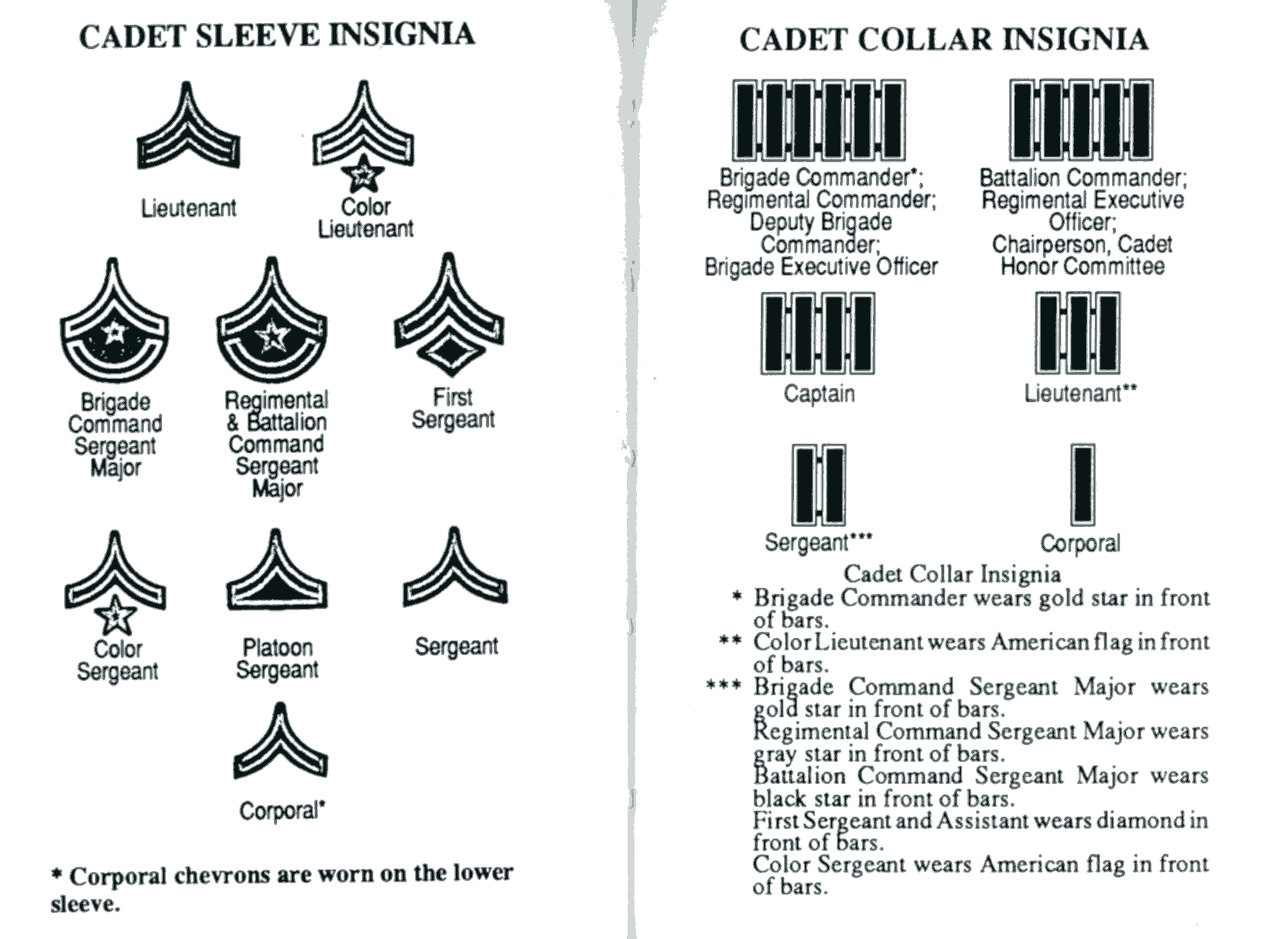
 Cadets are not referred to as freshmen, sophomores, juniors, or seniors. Instead they are officially called fourth class, third class, second class, and first class cadets. Colloquially, freshmen are ''plebes'', sophomores are ''yearlings'' or ''yuks'', juniors are ''cows'', and seniors are ''firsties''. Some of the origins of the class names are known, some are not.
Cadets are not referred to as freshmen, sophomores, juniors, or seniors. Instead they are officially called fourth class, third class, second class, and first class cadets. Colloquially, freshmen are ''plebes'', sophomores are ''yearlings'' or ''yuks'', juniors are ''cows'', and seniors are ''firsties''. Some of the origins of the class names are known, some are not.
 Because of the academy's congressional nomination process, students come from all 50 states, Puerto Rico, the District of Columbia, the Mariana Islands, Guam, American Samoa, and the US Virgin Islands. The academy is also authorized up to 60 international exchange cadets, who undergo the same four-year curriculum as fully integrated members of the Corps of Cadets. Cadets attend the United States Military Academy free of charge, with all tuition and board paid for by the Army in return for a service commitment of five years of active duty and three years of reserve status upon graduation. Starting on the first day of a cadet's second class year, non-graduates after that point are expected to fulfill their obligations in enlisted service. Cadets receive a monthly
Because of the academy's congressional nomination process, students come from all 50 states, Puerto Rico, the District of Columbia, the Mariana Islands, Guam, American Samoa, and the US Virgin Islands. The academy is also authorized up to 60 international exchange cadets, who undergo the same four-year curriculum as fully integrated members of the Corps of Cadets. Cadets attend the United States Military Academy free of charge, with all tuition and board paid for by the Army in return for a service commitment of five years of active duty and three years of reserve status upon graduation. Starting on the first day of a cadet's second class year, non-graduates after that point are expected to fulfill their obligations in enlisted service. Cadets receive a monthly  Each class of cadets elects representatives to serve as class president and fill several administrative positions. They also elect a ring and crest committee, which designs the class's crest, the emblem that signifies their class and is embossed upon their class rings. Each class crest is required to contain the initials ''USMA'' and their class motto. The class motto is proposed by the class during cadet basic training and voted on by the class prior to the beginning of their freshman academic year. Class mottos typically have wording that rhymes or is phonetically similar with their class year.
Cadets today live and work within the framework of the Cadet Leader Development System (CLDS), which specifies the roles that a cadet plays throughout their four years at the academy. Cadets begin their USMA careers as trainees (new cadets), then advance in rank, starting as CDT Privates (freshmen) and culminating as CDT Officers (seniors). Freshmen have no leadership responsibilities, but have a host of duties to perform as they learn how to follow orders and operate in an environment of rigid rank structure, while seniors have significant leadership responsibilities and significantly more privileges that correspond to their rank.
Each class of cadets elects representatives to serve as class president and fill several administrative positions. They also elect a ring and crest committee, which designs the class's crest, the emblem that signifies their class and is embossed upon their class rings. Each class crest is required to contain the initials ''USMA'' and their class motto. The class motto is proposed by the class during cadet basic training and voted on by the class prior to the beginning of their freshman academic year. Class mottos typically have wording that rhymes or is phonetically similar with their class year.
Cadets today live and work within the framework of the Cadet Leader Development System (CLDS), which specifies the roles that a cadet plays throughout their four years at the academy. Cadets begin their USMA careers as trainees (new cadets), then advance in rank, starting as CDT Privates (freshmen) and culminating as CDT Officers (seniors). Freshmen have no leadership responsibilities, but have a host of duties to perform as they learn how to follow orders and operate in an environment of rigid rank structure, while seniors have significant leadership responsibilities and significantly more privileges that correspond to their rank.
 Cadets have a host of extracurricular activities available, most run by the office of the Directorate of Cadet Activities (DCA). DCA sponsors or operates 113 athletic and non-sport clubs. Many cadets join several clubs during their time at the academy and find their time spent with their clubs a welcome respite from the rigors of cadet life. DCA is responsible for a wide range of activities that provide improved quality of life for cadets, including: three cadet-oriented restaurants, the Cadet Store, and the ''Howitzer'' and ''Bugle Notes''. ''The Howitzer'' is the annual yearbook, while ''Bugle Notes'', also known as the "plebe bible," is the manual of plebe knowledge. Plebe knowledge is a lengthy collection of traditions, songs, poems, anecdotes, and facts about the academy, the army, the ''Old Corps'', and the rivalry with Navy that all plebes must memorize during cadet basic training. During plebe year, plebes may be asked, and are expected to answer, any inquiry about plebe knowledge asked by upper class cadets. Other knowledge is historical in nature, including information as found in ''Bugle Notes''.Lipsky (2003), p. 9. However, some knowledge changes daily, such as "the days" (a running list of the number of days until important academy events), the menu in the mess hall for the day, or the lead stories in ''
Cadets have a host of extracurricular activities available, most run by the office of the Directorate of Cadet Activities (DCA). DCA sponsors or operates 113 athletic and non-sport clubs. Many cadets join several clubs during their time at the academy and find their time spent with their clubs a welcome respite from the rigors of cadet life. DCA is responsible for a wide range of activities that provide improved quality of life for cadets, including: three cadet-oriented restaurants, the Cadet Store, and the ''Howitzer'' and ''Bugle Notes''. ''The Howitzer'' is the annual yearbook, while ''Bugle Notes'', also known as the "plebe bible," is the manual of plebe knowledge. Plebe knowledge is a lengthy collection of traditions, songs, poems, anecdotes, and facts about the academy, the army, the ''Old Corps'', and the rivalry with Navy that all plebes must memorize during cadet basic training. During plebe year, plebes may be asked, and are expected to answer, any inquiry about plebe knowledge asked by upper class cadets. Other knowledge is historical in nature, including information as found in ''Bugle Notes''.Lipsky (2003), p. 9. However, some knowledge changes daily, such as "the days" (a running list of the number of days until important academy events), the menu in the mess hall for the day, or the lead stories in ''
 Since 1899, Army's mascot has officially been a mule because the animal symbolizes strength and perseverance. The academy's football team was nicknamed "The Black Knights of the Hudson" due to the black color of its uniforms. This nickname has since been officially shortened to the "Black Knights." U.S. sports media use "Army" as a synonym for the academy. "On Brave Old Army Team" is the school's
Since 1899, Army's mascot has officially been a mule because the animal symbolizes strength and perseverance. The academy's football team was nicknamed "The Black Knights of the Hudson" due to the black color of its uniforms. This nickname has since been officially shortened to the "Black Knights." U.S. sports media use "Army" as a synonym for the academy. "On Brave Old Army Team" is the school's
 Though football may receive a lot of media attention due to its annual rivalry game, West Point has a long history of athletics in other NCAA sports. Army is a member of the Division I
Though football may receive a lot of media attention due to its annual rivalry game, West Point has a long history of athletics in other NCAA sports. Army is a member of the Division I  Approximately 15% of cadets are members of a club sport team. West Point fields a total of 24 club sports teams that have been very successful in recent years, winning national championships in judo, boxing, orienteering, pistol, triathlon, crew, cycling, and team handball.
The majority of the student body, about 65%, competes in intramural sports, known at the academy as "company athletics." DPE's Competitive Sports committee runs the club and company athletics sports programs and was recently named one of the "15 Most Influential Sports Education Teams in America" by the Institute for International Sport. The fall season sees competition in basketball, flag-football, team handball, soccer, ultimate disc, and wrestling; while the spring season sees competition in combative grappling, floor hockey, orienteering, flicker ball, and swimming. In the spring, each company also fields a team entry into the annual Sandhurst Competition, a military skills event conducted by the Department of Military Instruction.
Approximately 15% of cadets are members of a club sport team. West Point fields a total of 24 club sports teams that have been very successful in recent years, winning national championships in judo, boxing, orienteering, pistol, triathlon, crew, cycling, and team handball.
The majority of the student body, about 65%, competes in intramural sports, known at the academy as "company athletics." DPE's Competitive Sports committee runs the club and company athletics sports programs and was recently named one of the "15 Most Influential Sports Education Teams in America" by the Institute for International Sport. The fall season sees competition in basketball, flag-football, team handball, soccer, ultimate disc, and wrestling; while the spring season sees competition in combative grappling, floor hockey, orienteering, flicker ball, and swimming. In the spring, each company also fields a team entry into the annual Sandhurst Competition, a military skills event conducted by the Department of Military Instruction.
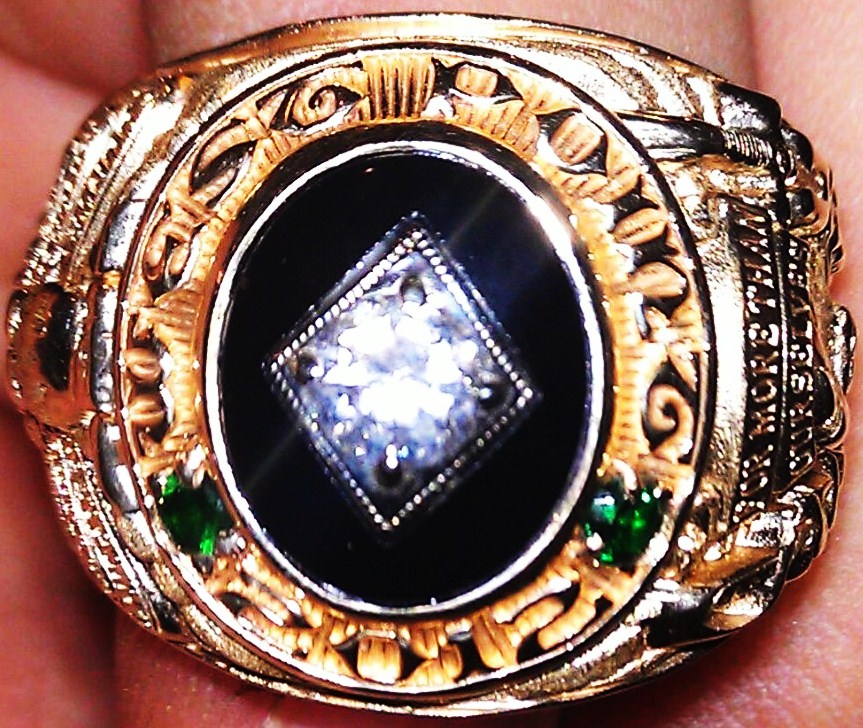 West Point began the collegiate tradition of the class ring, beginning with the class of 1835. The class of 1836 chose no rings, and the class of 1879 had cuff links in lieu of a class ring. Before 1917, cadets could design much of the ring individually, but now only the center stone can be individualized. One side of the ring bears the academy crest, while the other side bears the class crest and the center stone ring bears the words ''West Point'' and the class year. The academy library has a large collection of cadet rings on display. Senior cadets receive their rings during
West Point began the collegiate tradition of the class ring, beginning with the class of 1835. The class of 1836 chose no rings, and the class of 1879 had cuff links in lieu of a class ring. Before 1917, cadets could design much of the ring individually, but now only the center stone can be individualized. One side of the ring bears the academy crest, while the other side bears the class crest and the center stone ring bears the words ''West Point'' and the class year. The academy library has a large collection of cadet rings on display. Senior cadets receive their rings during
Army Athletics website
() {{authority control 1802 establishments in New York (state) Educational institutions established in 1802 Forts in New York (state) Forts on the National Register of Historic Places in New York (state) Historic Civil Engineering Landmarks Military academies Military academies of the United States Military and war museums in New York (state) National Historic Landmarks in New York (state) New York (state) in the American Revolution Patriot League Tourist attractions in Orange County, New York U.S. Route 9W United States Army Direct Reporting Units United States Army museums United States Army posts United States Army schools Universities and colleges in New York (state) National Register of Historic Places in Orange County, New York American Revolution on the National Register of Historic Places United States military service academies United States senior military colleges
 The United States Military Academy (USMA), also known
The United States Military Academy (USMA), also known metonymically
Metonymy () is a figure of speech in which a concept is referred to by the name of something closely associated with that thing or concept.
Etymology
The words ''metonymy'' and ''metonym'' come from grc, μετωνυμία, 'a change of name' ...
as West Point or simply as Army, is a United States service academy in West Point, New York
West Point is the oldest continuously occupied military post in the United States. Located on the Hudson River in New York, West Point was identified by General George Washington as the most important strategic position in America during the Ame ...
. It was originally established as a fort, since it sits on strategic high ground overlooking the Hudson River
The Hudson River is a river that flows from north to south primarily through eastern New York. It originates in the Adirondack Mountains of Upstate New York and flows southward through the Hudson Valley to the New York Harbor between Ne ...
with a scenic view, north of New York City. It is the oldest of the five American service academies and educates cadets for commissioning into the United States Army
The United States Army (USA) is the land service branch of the United States Armed Forces. It is one of the eight U.S. uniformed services, and is designated as the Army of the United States in the U.S. Constitution.Article II, section 2, ...
.
The academy was founded in 1802, one year after President Thomas Jefferson
Thomas Jefferson (April 13, 1743 – July 4, 1826) was an American statesman, diplomat, lawyer, architect, philosopher, and Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father who served as the third president of the United States from 18 ...
directed that plans be set in motion to establish it. It was constructed on site of Fort Clinton on West Point overlooking the Hudson, which Colonial General Benedict Arnold
Benedict Arnold ( Brandt (1994), p. 4June 14, 1801) was an American military officer who served during the Revolutionary War. He fought with distinction for the American Continental Army and rose to the rank of major general before defect ...
conspired to turn over to the British during the Revolutionary War. The entire central campus is a national landmark and home to scores of historic sites, buildings, and monuments. The majority of the campus's Norman-style buildings are constructed from gray and black granite. The campus is a popular tourist destination, with a visitor center and the oldest museum in the United States Army.
Candidates for admission must apply directly to the academy and receive a nomination, usually from a member of Congress. Other nomination sources include the president and vice president. Students are officers-in-training and are referred to as "cadets" or collectively as the "United States Corps of Cadets" (USCC). The Army fully funds tuition for cadets in exchange for an active duty service obligation upon graduation. About 1,300 cadets enter the academy each July, with about 1,000 cadets graduating.
The academic program grants a Bachelor of Science degree with a curriculum that grades cadets' performance upon a broad academic program, military leadership performance, and mandatory participation in competitive athletics. Cadets are required to adhere to the Cadet Honor Code, which states that "a cadet will not lie, cheat, steal, or tolerate those who do." The academy bases a cadet's leadership experience as a development of all four pillars of performance: academics, character, physical, and military.
Most graduates are commissioned as second lieutenant
Second lieutenant is a junior commissioned officer military rank in many armed forces, comparable to NATO OF-1 rank.
Australia
The rank of second lieutenant existed in the military forces of the Australian colonies and Australian Army unt ...
s in the Army. Foreign cadets are commissioned into the armies of their home countries. Since 1959, cadets have also been eligible for an interservice commission in one of the other armed services provided that they meet that service's eligibility standards. A small number of cadets do this.
The academy's traditions have influenced other institutions because of its age and unique mission. It was the first American college to have an accredited civil engineering program and the first to have class rings, and its technical curriculum became a model for engineering schools. West Point's student body has a unique rank structure and lexicon. All cadets reside on campus and dine together ''en masse'' on weekdays for lunch. The academy fields 15 men's and nine women's National Collegiate Athletic Association
The National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA) is a nonprofit organization that regulates student athletics among about 1,100 schools in the United States, Canada, and Puerto Rico. It also organizes the athletic programs of colleges ...
(NCAA) sports teams. Cadets compete in one sport every fall, winter, and spring season at the intramural, club, or intercollegiate level. Its football team
A football team is a group of players selected to play together in the various team sports known as football. Such teams could be selected to play in a match against an opposing team, to represent a football club, group, state or nation, an all-s ...
was a national power in the early and mid-20th century, winning three national championships. Among the country's public institutions, the academy is the top producer of Marshall and Rhodes
Rhodes (; el, Ρόδος , translit=Ródos ) is the largest and the historical capital of the Dodecanese islands of Greece. Administratively, the island forms a separate municipality within the Rhodes regional unit, which is part of the S ...
scholars. Its alumni and students are collectively referred to as "The Long Gray Line," the former include: U.S. Presidents Dwight D. Eisenhower and Ulysses S. Grant
Ulysses S. Grant (born Hiram Ulysses Grant ; April 27, 1822July 23, 1885) was an American military officer and politician who served as the 18th president of the United States from 1869 to 1877. As Commanding General, he led the Union A ...
; Jefferson Davis
Jefferson F. Davis (June 3, 1808December 6, 1889) was an American politician who served as the president of the Confederate States from 1861 to 1865. He represented Mississippi in the United States Senate and the House of Representatives as ...
of the Confederacy; Confederate general Robert E. Lee
Robert Edward Lee (January 19, 1807 – October 12, 1870) was a Confederate general during the American Civil War, towards the end of which he was appointed the overall commander of the Confederate States Army. He led the Army of Nor ...
; American poet Edgar Allen Poe; U.S. general George Patton
George Smith Patton Jr. (November 11, 1885 – December 21, 1945) was a general in the United States Army who commanded the Seventh United States Army in the Mediterranean Theater of World War II, and the Third United States Army in France ...
; presidents of Costa Rica
Costa Rica (, ; ; literally "Rich Coast"), officially the Republic of Costa Rica ( es, República de Costa Rica), is a country in the Central American region of North America, bordered by Nicaragua to the north, the Caribbean Sea to the no ...
, Nicaragua
Nicaragua (; ), officially the Republic of Nicaragua (), is the largest country in Central America, bordered by Honduras to the north, the Caribbean to the east, Costa Rica to the south, and the Pacific Ocean to the west. Managua is the coun ...
, and the Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
; and 76 Medal of Honor
The Medal of Honor (MOH) is the United States Armed Forces' highest military decoration and is awarded to recognize American soldiers, sailors, marines, airmen, guardians and coast guardsmen who have distinguished themselves by acts of val ...
recipients.
History


Colonial period, founding, and early years
TheContinental Army
The Continental Army was the army of the United Colonies (the Thirteen Colonies) in the Revolutionary-era United States. It was formed by the Second Continental Congress after the outbreak of the American Revolutionary War, and was establis ...
first occupied West Point, New York, on 27 January 1778, and it is the oldest continuously operating Army post in the United States. Between 1778 and 1780, the Polish engineer and military hero Tadeusz Kościuszko
Andrzej Tadeusz Bonawentura Kościuszko ( be, Andréj Tadévuš Banavientúra Kasciúška, en, Andrew Thaddeus Bonaventure Kosciuszko; 4 or 12 February 174615 October 1817) was a Polish military engineer, statesman, and military leader who ...
oversaw the construction of the garrison defenses. However, Kościuszko's plan of a system of small forts did not meet with the approval of New York Governor (and General) George Clinton or the other general officers. It was determined that a battery along the river to "annoy the shipping" was more appropriate, and Washington's chief engineer, Rufus Putnam
Brigadier-General Rufus Putnam (April 9, 1738 – May 4, 1824) was an American military officer who fought during the French and Indian War and the American Revolutionary War. As an organizer of the Ohio Company of Associates, he was instrumenta ...
, directed the construction of a major fortification on a hill above sea level that commanded the West Point plain. General Alexander McDougall named it Fort Putnam
Fort Putnam was a military garrison during the Revolutionary War at West Point, New York, United States. Built by a regiment of Colonel Rufus Putnam's 5th Massachusetts Regiment, it was completed in 1778 with the purpose of supporting Fort C ...
. The Great Hudson River Chain
The Hudson River Chains were a series of chain booms constructed across the Hudson River at West Point by Continental Army forces from 1776 to 1778 during the American Revolutionary War. These served as defenses preventing British naval vessels ...
and high ground above the narrow "S" curve in the river enabled the Continental Army
The Continental Army was the army of the United Colonies (the Thirteen Colonies) in the Revolutionary-era United States. It was formed by the Second Continental Congress after the outbreak of the American Revolutionary War, and was establis ...
to prevent British Royal Navy ships from sailing upriver and thus dividing the Colonies. While the fortifications at West Point were known as Fort Arnold during the war, as commander, Benedict Arnold
Benedict Arnold ( Brandt (1994), p. 4June 14, 1801) was an American military officer who served during the Revolutionary War. He fought with distinction for the American Continental Army and rose to the rank of major general before defect ...
committed his act of treason
Treason is the crime of attacking a state authority to which one owes allegiance. This typically includes acts such as participating in a war against one's native country, attempting to overthrow its government, spying on its military, its diplo ...
, attempting to sell the fort to the British. After Arnold betrayed the patriot cause, the Army changed the name of the fortifications at West Point, New York, to Fort Clinton. With the peace after the American Revolutionary War, various ordnance and military stores were left deposited at West Point.
"Cadets" underwent training in artillery and engineering studies at the garrison since 1794. During the Quasi-War
The Quasi-War (french: Quasi-guerre) was an undeclared naval war fought from 1798 to 1800 between the United States and the French First Republic, primarily in the Caribbean and off the East Coast of the United States. The ability of Congress ...
, Alexander Hamilton
Alexander Hamilton (January 11, 1755 or 1757July 12, 1804) was an American military officer, statesman, and Founding Father who served as the first United States secretary of the treasury from 1789 to 1795.
Born out of wedlock in Charle ...
laid out plans for the establishment of a military academy at West Point and introduced "A Bill for Establishing a Military Academy" in the House of Representatives. In 1801, shortly after his inauguration as president, Thomas Jefferson
Thomas Jefferson (April 13, 1743 – July 4, 1826) was an American statesman, diplomat, lawyer, architect, philosopher, and Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father who served as the third president of the United States from 18 ...
directed that plans be set in motion to establish at West Point the United States Military Academy. He selected Jonathan Williams to serve as its first superintendent. Congress formally authorized the establishment and funding of the school with the Military Peace Establishment Act of 1802, which Jefferson signed on 16 March.Ambrose (1966), p. 22. The academy officially commenced operations on 4 July 1802. The academy graduated Joseph Gardner Swift
Joseph Gardner Swift (December 31, 1783 – July 22, 1865) was an American soldier who, in 1802, became the first graduate of the newly instituted United States Military Academy in West Point, New York; he would later serve as its fourth Superin ...
, its first official graduate, in October 1802. He later returned as Superintendent from 1812 to 1814. In its tumultuous early years, the academy featured few standards for admission or length of study. Cadets ranged in age from 10 years to 37 years and attended between 6 months to 6 years. The impending War of 1812
The War of 1812 (18 June 1812 – 17 February 1815) was fought by the United States of America and its indigenous allies against the United Kingdom and its allies in British North America, with limited participation by Spain in Florida. It be ...
caused the United States Congress
The United States Congress is the legislature of the federal government of the United States. It is Bicameralism, bicameral, composed of a lower body, the United States House of Representatives, House of Representatives, and an upper body, ...
to authorize a more formal system of education at the academy and increased the size of the Corps of Cadets to 250.
 In 1817,
In 1817, Colonel
Colonel (abbreviated as Col., Col or COL) is a senior military officer rank used in many countries. It is also used in some police forces and paramilitary organizations.
In the 17th, 18th and 19th centuries, a colonel was typically in charge ...
Sylvanus Thayer became the Superintendent and established the curriculum, elements of which are still in use . Thayer instilled strict disciplinary standards, set a standard course of academic study, and emphasized honorable conduct. He was very much inspired by the curriculum of the French École Polytechnique
École may refer to:
* an elementary school in the French educational stages normally followed by secondary education establishments (collège and lycée)
* École (river), a tributary of the Seine flowing in région Île-de-France
* École, Savoi ...
where he had been sent upon his demand for two years in order to study the scientific and technological achievements developed by the French Republican faction and bring them back to the United States. Known as the "Father of the Military Academy," he is honored with a monument on campus for the profound impact he had upon the academy. Founded as a school of engineering, for the first half of the 19th century, USMA produced graduates who gained recognition for engineering the bulk of the nation's initial railway lines, bridges, harbors and roads.McMaster (1952), p. 6.Endler 19980, p. 12. The academy was the only engineering school in the country until the founding of Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute
Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute () (RPI) is a private research university in Troy, New York, with an additional campus in Hartford, Connecticut. A third campus in Groton, Connecticut closed in 2018. RPI was established in 1824 by Stephen Van ...
in 1824. It was so successful in its engineering curriculum that it significantly influenced every American engineering school founded prior to the Civil War
A civil war or intrastate war is a war between organized groups within the same state (or country).
The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government polici ...
.
In 1835, during the Army's first year of the Second Seminole War
The Second Seminole War, also known as the Florida War, was a conflict from 1835 to 1842 in Florida between the United States and groups collectively known as Seminoles, consisting of Native Americans and Black Indians. It was part of a ser ...
, they had only three generals: Winfield Scott
Winfield Scott (June 13, 1786May 29, 1866) was an American military commander and political candidate. He served as a general in the United States Army from 1814 to 1861, taking part in the War of 1812, the Mexican–American War, the early s ...
, Edmund P. Gaines, and Thomas S. Jesup
Thomas Sidney Jesup (December 16, 1788 – June 10, 1860) was a United States Army officer known as the "Father of the Modern Quartermaster Corps". His 52-year (1808–1860) military career was one of the longest in the history of the United St ...
. The Army's remaining fourteen generals "held their rank by brevet only," and none of them were West Point graduates. Nearly the only way to obtain a commission up to 1835, was thru the academy, "which created loud complaint", and added to the "Jacksonian Democracy...a deep desire to get rid of the Academy, where, Jacksonians were sure, an aristocratic tradition was being bred."
The Mexican–American War
The Mexican–American War, also known in the United States as the Mexican War and in Mexico as the (''United States intervention in Mexico''), was an armed conflict between the United States and Mexico from 1846 to 1848. It followed the ...
brought the academy to prominence as graduates proved themselves in battle for the first time. Future Civil War
A civil war or intrastate war is a war between organized groups within the same state (or country).
The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government polici ...
commanders Ulysses S. Grant
Ulysses S. Grant (born Hiram Ulysses Grant ; April 27, 1822July 23, 1885) was an American military officer and politician who served as the 18th president of the United States from 1869 to 1877. As Commanding General, he led the Union A ...
and Robert E. Lee
Robert Edward Lee (January 19, 1807 – October 12, 1870) was a Confederate general during the American Civil War, towards the end of which he was appointed the overall commander of the Confederate States Army. He led the Army of Nor ...
, who also later became the superintendent of the academy, first distinguished themselves in battle in Mexico. In all, 452 of 523 graduates who served in the war received battlefield promotions or awards for bravery. The school experienced a rapid modernization during the 1850s, often romanticized by the graduates who led both sides of the Civil War as the "end of the Old West Point era." New barracks brought better heat and gas lighting
Gas lighting is the production of artificial light from combustion of a gaseous fuel, such as hydrogen, methane, carbon monoxide, propane, butane, acetylene, ethylene, coal gas (town gas) or natural gas. The light is produced either directly ...
, while new ordnance and tactics training incorporated new rifle and musket
A musket is a muzzle-loaded long gun that appeared as a smoothbore weapon in the early 16th century, at first as a heavier variant of the arquebus, capable of penetrating plate armour. By the mid-16th century, this type of musket gradually di ...
technology and accommodated transportation advances created by the steam engine. With the outbreak of the Civil War, West Point graduates filled the general officer
A general officer is an officer of high rank in the armies, and in some nations' air forces, space forces, and marines or naval infantry.
In some usages the term "general officer" refers to a rank above colonel."general, adj. and n.". OED ...
ranks of the rapidly expanding Union and Confederate armies.Crackel (2002), p. 135. 294 graduates served as general officers for the Union, and 151 served as general officers for the Confederacy. Of all living graduates at the time of the war, 105 (10%) were killed, and another 151 (15%) were wounded. Nearly every general officer of note from either army during the Civil War was a graduate of West Point and a West Point graduate commanded the forces of one or both sides in every one of the 60 major battles of the war.

After the Civil War
 Immediately following the Civil War, the academy enjoyed unprecedented fame as a result of the role its graduates had played. However, the post-war years were a difficult time for the academy as it struggled to admit and reintegrate cadets from former confederate states. The first cadets from Southern states were re-admitted in 1868, and 1870 saw the admission of the first black cadet, James Webster Smith of
Immediately following the Civil War, the academy enjoyed unprecedented fame as a result of the role its graduates had played. However, the post-war years were a difficult time for the academy as it struggled to admit and reintegrate cadets from former confederate states. The first cadets from Southern states were re-admitted in 1868, and 1870 saw the admission of the first black cadet, James Webster Smith of South Carolina
)''Animis opibusque parati'' ( for, , Latin, Prepared in mind and resources, links=no)
, anthem = " Carolina";" South Carolina On My Mind"
, Former = Province of South Carolina
, seat = Columbia
, LargestCity = Charleston
, LargestMetro = ...
. Smith endured harsh treatment and was eventually dismissed for academic deficiency under controversial circumstances in 1874. As a result, Henry O. Flipper
Henry Ossian Flipper (March 21, 1856 – April 26, 1940) was an American soldier, engineer, former slave and in 1877, the first African American to graduate from the United States Military Academy at West Point, earning a commission as ...
of Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the Southeast United States
Georgia may also refer to:
Places
Historical states and entities
* Related to the ...
became the first black graduate in 1877, graduating 50th in a class of 76. Two of the most notable graduates during this period were George Washington Goethals from the class of 1880, and John J. Pershing from the class of 1886. Goethals gained prominence as the chief engineer of the Panama Canal
The Panama Canal ( es, Canal de Panamá, link=no) is an artificial waterway in Panama that connects the Atlantic Ocean with the Pacific Ocean and divides North and South America. The canal cuts across the Isthmus of Panama and is a condui ...
, and Pershing would become famous for his exploits against the famed Pancho Villa
Francisco "Pancho" Villa (, Orozco rebelled in March 1912, both for Madero's continuing failure to enact land reform and because he felt insufficiently rewarded for his role in bringing the new president to power. At the request of Madero's c ...
in Mexico and later for leading American Forces during World War I.
 Besides the integration of southern-state and black cadets, the post-war academy also struggled with the issue of
Besides the integration of southern-state and black cadets, the post-war academy also struggled with the issue of hazing
Hazing (American English), initiation, beasting (British English), bastardisation (Australian English), ragging (South Asian English) or deposition refers to any activity expected of someone in joining or participating in a group that humiliates, ...
. In its first 65 years, hazing was uncommon or non-existent beyond small pranks played upon the incoming freshmen, but took a harsher tone as Civil War veterans began to fill the incoming freshman classes. The upper class cadets saw it as their duty to "teach the plebes their manners." Hazing at the academy entered the national spotlight with the death of former cadet Oscar L. Booz on 3 December 1900. Congressional hearings, which included testimony by cadet Douglas MacArthur
Douglas MacArthur (26 January 18805 April 1964) was an American military leader who served as General of the Army for the United States, as well as a field marshal to the Philippine Army. He had served with distinction in World War I, was ...
, investigated his death and the pattern of freshmen's systemic hazing. When MacArthur returned as superintendent, he made an effort to end the practice of hazing the incoming freshmen by placing Army sergeants in charge of training new cadets during freshman summer. The practice of hazing continued on some levels well into the late 20th century, but is no longer allowed in the present day.

 The demand for junior officers during the
The demand for junior officers during the Spanish–American War
, partof = the Philippine Revolution, the decolonization of the Americas, and the Cuban War of Independence
, image = Collage infobox for Spanish-American War.jpg
, image_size = 300px
, caption = (clock ...
caused the class of 1899 to graduate early, and the Philippine–American War
The Philippine–American War or Filipino–American War ( es, Guerra filipina-estadounidense, tl, Digmaang Pilipino–Amerikano), previously referred to as the Philippine Insurrection or the Tagalog Insurgency by the United States, was an arm ...
did the same for the class of 1901. This increased demand for officers led Congress to increase the Corps of Cadets' size to 481 cadets in 1900. The period between 1900 and 1915 saw a construction boom as much of West Point's old infrastructure was rebuilt. Many of the academy's most famous graduates graduated during the 15-year period between 1900 and 1915: Douglas MacArthur
Douglas MacArthur (26 January 18805 April 1964) was an American military leader who served as General of the Army for the United States, as well as a field marshal to the Philippine Army. He had served with distinction in World War I, was ...
(1903), Joseph Stilwell
Joseph Warren "Vinegar Joe" Stilwell (March 19, 1883 – October 12, 1946) was a United States Army general who served in the China Burma India Theater during World War II. An early American popular hero of the war for leading a column walking ...
(1904), Henry "Hap" Arnold
Henry Harley Arnold (June 25, 1886 – January 15, 1950) was an American General officers in the United States, general officer holding the ranks of General of the Army (United States), General of the Army and later, General of the Air For ...
(1907), George S. Patton
George Smith Patton Jr. (November 11, 1885 – December 21, 1945) was a general in the United States Army who commanded the Seventh United States Army in the Mediterranean Theater of World War II, and the Third United States Army in France ...
(1909), Dwight D. Eisenhower, and Omar Bradley (both 1915). The class of 1915 is known as " the class the stars fell on" for the exceptionally high percentage of general officers that rose from that class (59 of 164).
The outbreak of America's involvement in World War I caused a sharp increase in the demand for army officers, and the academy accelerated graduation of all four classes then in attendance to meet this requirement, beginning with the early graduation of the First Class on 20 April 1917, the Second Class in August 1917, and both the Third and Fourth Classes just before the Armistice of 11 November 1918, when only freshman cadets remained (those who had entered in the summer of 1918). In all, wartime contingencies and post-war adjustments resulted in ten classes, varying in length of study from two to four years, within a seven-year period before the regular course of study was fully resumed.. See class introductions for each class from 1917 to 1923.
Douglas MacArthur became superintendent in 1919, instituting sweeping reforms to the academic process, including introducing a greater emphasis on history and humanities
Humanities are academic disciplines that study aspects of human society and culture. In the Renaissance, the term contrasted with divinity and referred to what is now called classics, the main area of secular study in universities at t ...
. He made major changes to the field training regimen and the Cadet Honor Committee was formed under his watch in 1922. MacArthur was a firm supporter of athletics at the academy, as he famously said "Upon the fields of friendly strife are sown the seeds that, upon other fields, on other days, will bear the fruits of victory."Ambrose (1966), p. 275. West Point was first officially accredited in 1925, and in 1933 began granting Bachelor of Science degrees to all graduates. In 1935, the academy's authorized strength increased to 1,960 cadets.
World War II and Cold War
AsWorld War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
engulfed Europe, Congress authorized an increase to 2,496 cadets in 1942 and began graduating classes early. The class of 1943 graduated six months early in January 1943, and the next four classes graduated after only three years. To accommodate this accelerated schedule, summer training was formally moved to a recently acquired piece of land southwest of main post. The site would later become Camp Buckner. The academy had its last serious brush with abolition or major reform during the war, when some members of Congress charged that even the accelerated curriculum allowed young men to "hide out" at West Point and avoid combat duty. A proposal was put forth to convert the academy to an officer's training school with a six-month schedule, but this was not adopted. West Point played a prominent role in WWII; four of the five five-star generals were alumni and nearly 500 graduates died. Immediately following the war in 1945, Maxwell Taylor (class of 1922) became superintendent. He expanded and modernized the academic program and abolished antiquated courses in fencing and horsemanship.
Unlike previous conflicts, the Korean War
{{Infobox military conflict
, conflict = Korean War
, partof = the Cold War and the Korean conflict
, image = Korean War Montage 2.png
, image_size = 300px
, caption = Clockwise from top:{ ...
did not disrupt class graduation schedules. More than half of the Army leadership during the war was composed of West Point graduates. The Class of 1950, which graduated only two weeks prior to the war's outbreak, suffered some of the heaviest casualties of any 20th century class and became known sourly as "the class the crosses fell on." A total of 157 alumni perished in the conflict. Garrison H. Davidson became superintendent in 1956 and instituted several reforms that included refining the admissions process, changing the core curriculum to include electives, and increasing the academic degree standards for academy instructors. The 1960s saw the size of the Corps expand to 4,400 cadets while the barracks and academic support structure grew proportionally.
West Point was not immune to the social upheaval of American society during the Vietnam War
The Vietnam War (also known by #Names, other names) was a conflict in Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia from 1 November 1955 to the fall of Saigon on 30 April 1975. It was the second of the Indochina Wars and was officially fought between North Vie ...
. The first woman joined the faculty of the all-male institution amidst controversy in 1968. West Point granted its first honorable discharge
A military discharge is given when a member of the armed forces is released from their obligation to serve. Each country's military has different types of discharge. They are generally based on whether the persons completed their training and the ...
in 1971 to an African-American West Point cadet, Cornelius M. Cooper, of California, who applied for conscientious objector
A conscientious objector (often shortened to conchie) is an "individual who has claimed the right to refuse to perform military service" on the grounds of freedom of thought, conscience, or religion. The term has also been extended to objec ...
status in 1969. The academy struggled to fill its incoming classes as its graduates led troops in Southeast Asia, where 333 graduates died.
Modern era
 Following the 1973 end of American involvement in Vietnam, the strain and stigma of earlier social unrest dissolved and West Point enjoyed surging enrollments. On 20 May 1975, an amendment to the Defense Authorization Bill of 1976 opening the service academies to women was approved by the House of Representatives, 303–96. The Senate followed suit on 6 June. President Ford signed the bill on 7 October 1975.
West Point admitted its first 119 female cadets in 1976.Barkalow (1990), p. 20. Also in 1976, physics professor James H. Stith became the first tenured African American Professor. In 1979, Cadet, later General,
Following the 1973 end of American involvement in Vietnam, the strain and stigma of earlier social unrest dissolved and West Point enjoyed surging enrollments. On 20 May 1975, an amendment to the Defense Authorization Bill of 1976 opening the service academies to women was approved by the House of Representatives, 303–96. The Senate followed suit on 6 June. President Ford signed the bill on 7 October 1975.
West Point admitted its first 119 female cadets in 1976.Barkalow (1990), p. 20. Also in 1976, physics professor James H. Stith became the first tenured African American Professor. In 1979, Cadet, later General, Vincent K. Brooks
Vincent Keith Brooks (born October 24, 1958) is a retired United States Army general who last commanded United States Forces Korea, United Nations Command, and ROK-U.S. Combined Forces Command. He previously served as the commanding general of Un ...
became the first African American
African Americans (also referred to as Black Americans and Afro-Americans) are an ethnic group consisting of Americans with partial or total ancestry from sub-Saharan Africa. The term "African American" generally denotes descendants of ens ...
to lead the Corp of Cadets. Kristin Baker, ten years later, became the first female First Captain (a depiction of her is now on display in the Museum), the highest ranking senior cadet at the academy in 1989. Six other women have been appointed as First Captain: Grace H. Chung in 2003, Stephanie Hightower in 2005, Lindsey Danilack in 2013, Simone Askew in 2017, Reilly McGinnis in 2020, and Lauren Drysdale in 2022. Simone Askew was the first African American woman to lead the Corps. In the 21st century, women comprise approximately 20% of entering new cadets.
 In 1985, cadets were formally authorized to declare an academic major; all previous graduates had been awarded a general bachelor of science degree. Five years later there was a major revision of the ''Fourth Class System'', as the Cadet Leader Development System (CLDS) became the guidance for the development of all four classes. The class of 1990 was the first one to be issued a standard and mandatory computer to every member of the class at the beginning of Plebe year, the Zenith 248 SX. The academy was also an early adopter of the Internet in the mid-1990s, and was recognized in 2006 as one of the nation's "most wired" campuses.
At the height of the Cold War in October 1987, President Reagan visited the academy and delivered a speech about ending the Evil Empire.
During the
In 1985, cadets were formally authorized to declare an academic major; all previous graduates had been awarded a general bachelor of science degree. Five years later there was a major revision of the ''Fourth Class System'', as the Cadet Leader Development System (CLDS) became the guidance for the development of all four classes. The class of 1990 was the first one to be issued a standard and mandatory computer to every member of the class at the beginning of Plebe year, the Zenith 248 SX. The academy was also an early adopter of the Internet in the mid-1990s, and was recognized in 2006 as one of the nation's "most wired" campuses.
At the height of the Cold War in October 1987, President Reagan visited the academy and delivered a speech about ending the Evil Empire.
During the Gulf War
The Gulf War was a 1990–1991 armed campaign waged by a 35-country military coalition in response to the Iraqi invasion of Kuwait. Spearheaded by the United States, the coalition's efforts against Iraq were carried out in two key phases: ...
, alumnus General Schwarzkopf was the commander of Allied Forces, and the American senior generals in Iraq
Iraq,; ku, عێراق, translit=Êraq officially the Republic of Iraq, '; ku, کۆماری عێراق, translit=Komarî Êraq is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Turkey to Iraq–Turkey border, the north, Iran to Iran–Iraq ...
, Generals Petraeus, Odierno and Austin
Austin is the capital city of the U.S. state of Texas, as well as the seat and largest city of Travis County, with portions extending into Hays and Williamson counties. Incorporated on December 27, 1839, it is the 11th-most-populous city ...
, and Afghanistan, retired General Stanley McChrystal and General David Rodriguez, are also alumni. Following the September 11 attacks
The September 11 attacks, commonly known as 9/11, were four coordinated suicide terrorist attacks carried out by al-Qaeda against the United States on Tuesday, September 11, 2001. That morning, nineteen terrorists hijacked four commer ...
, applications for admission to the academy increased dramatically, security on campus was increased, and the curriculum was revamped to include coursework on terrorism and military drills in civilian environments. One graduate was killed during the 9/11 terrorist attacks and ninety graduates have died during operations in Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan,; prs, امارت اسلامی افغانستان is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is borde ...
, Iraq
Iraq,; ku, عێراق, translit=Êraq officially the Republic of Iraq, '; ku, کۆماری عێراق, translit=Komarî Êraq is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Turkey to Iraq–Turkey border, the north, Iran to Iran–Iraq ...
, and the ongoing Global War on Terror
The war on terror, officially the Global War on Terrorism (GWOT), is an ongoing international counterterrorism military campaign initiated by the United States following the September 11 attacks. The main targets of the campaign are militant ...
. The Class of 2005 has been referred to as The Class of 9/11 as the attacks occurred during their first year at the academy, and they graduated 911 students. In 2008 gender-neutral lyrics were incorporated into West Point's "Alma Mater" and "The Corps" – replacing lines like "The men of the Corps" with "The ranks of the Corps." In December 2009, President Barack Obama
Barack Hussein Obama II ( ; born August 4, 1961) is an American politician who served as the 44th president of the United States from 2009 to 2017. A member of the Democratic Party (United States), Democratic Party, Obama was the first Af ...
delivered a major speech in Eisenhower Hall Theater outlining his policy for deploying 30,000 additional troops to Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan,; prs, امارت اسلامی افغانستان is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is borde ...
as well as setting a timetable for withdrawal. President Obama also provided the commencement address in 2014.
After the Don't Ask, Don't Tell
"Don't ask, don't tell" (DADT) was the official United States policy on military service of non-heterosexual people, instituted during the Clinton administration. The policy was issued under Department of Defense Directive 1304.26 on Decembe ...
policy was lifted 20 September 2011, the academy began admitting and retaining openly gay cadets. By March 2012, cadets were forming a gay-straight alliance group called Spectrum. By March 2015, Spectrum had two faculty and 40 cadet members, a mixture of gay, straight, bi, and undecided. According to a Vanity Fair essay, the LGBT cadets were well accepted. After the ban on transgender service members was lifted in 2016, the Class of 2017 saw the first openly transgender graduate. However, she was denied a commission and was honorably discharged.
 Brig. Gen. Diana Holland became West Point's first woman Commandant of Cadets in January 2016.
In 2020, the campus confronted its first major pandemic in a century, with the
Brig. Gen. Diana Holland became West Point's first woman Commandant of Cadets in January 2016.
In 2020, the campus confronted its first major pandemic in a century, with the COVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic, also known as the coronavirus pandemic, is an ongoing global pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The novel virus was first identi ...
causing limitations on classes, and the relocation of the traditional Army-Navy football game to ensure social distancing
In public health, social distancing, also called physical distancing, (NB. Regula Venske is president of the PEN Centre Germany.) is a set of non-pharmaceutical interventions or measures intended to prevent the spread of a contagious dis ...
. For the first time in many years, the 121st iteration of the game was held at West Point rather than the traditional Lincoln Financial Field
Lincoln Financial Field is an American football stadium located in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. It serves as the home stadium of the Philadelphia Eagles of the National Football League (NFL) and the Temple Owls football team of Temple University. ...
in Philadelphia
Philadelphia, often called Philly, is the largest city in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, the sixth-largest city in the U.S., the second-largest city in both the Northeast megalopolis and Mid-Atlantic regions after New York City. Since ...
. Ultimately, West Point beat Navy 15–0.
Campus

 The academy is located approximately north of New York City on the western bank of the
The academy is located approximately north of New York City on the western bank of the Hudson River
The Hudson River is a river that flows from north to south primarily through eastern New York. It originates in the Adirondack Mountains of Upstate New York and flows southward through the Hudson Valley to the New York Harbor between Ne ...
. West Point, New York
West Point is the oldest continuously occupied military post in the United States. Located on the Hudson River in New York, West Point was identified by General George Washington as the most important strategic position in America during the Ame ...
, is incorporated as a federal military reservation in Orange County and is adjacent to Highland Falls. Based on the significance both of the Revolutionary War fort ruins and of the military academy itself, the majority of the academy area was declared a National Historic Landmark
A National Historic Landmark (NHL) is a building, district, object, site, or structure that is officially recognized by the United States government for its outstanding historical significance. Only some 2,500 (~3%) of over 90,000 places liste ...
in 1960. In 1841, Charles Dickens
Charles John Huffam Dickens (; 7 February 1812 – 9 June 1870) was an English writer and social critic. He created some of the world's best-known fictional characters and is regarded by many as the greatest novelist of the Victorian er ...
visited the academy and said "It could not stand on more appropriate ground, and any ground more beautiful can hardly be." One of the most visited and scenic sites on post, Trophy Point, overlooks the Hudson River to the north, and is home to many captured cannon from past wars as well as the Stanford White
Stanford White (November 9, 1853 – June 25, 1906) was an American architect. He was also a partner in the architectural firm McKim, Mead & White, one of the most significant Beaux-Arts firms. He designed many houses for the rich, in addition ...
-designed Battle Monument. Though the entire military reservation encompasses , the academic area of the campus, known as "central area" or "the cadet area", is entirely accessible to cadets or visitors by foot.
Cadet Chapel
A cadet is an officer trainee or candidate. The term is frequently used to refer to those training to become an officer in the military, often a person who is a junior trainee. Its meaning may vary between countries which can include youths in ...
, completed in 1910. These buildings are nearly all constructed from granite that has a predominantly gray and black hue. The barracks that were built in the 1960s were designed to mimic this style. Other buildings on post, notably the oldest private residences for the faculty, are built in the Federal, Georgian, or English Tudor styles. A few buildings, such as Cullum Hall and the Old Cadet Chapel, are built in the Neoclassical style.
 The academy grounds are home to numerous monuments and statues. The central cadet parade ground, the Plain, hosts the largest number, and includes the
The academy grounds are home to numerous monuments and statues. The central cadet parade ground, the Plain, hosts the largest number, and includes the Washington Monument
The Washington Monument is an obelisk shaped building within the National Mall in Washington, D.C., built to commemorate George Washington, once commander-in-chief of the Continental Army (1775–1784) in the American Revolutionary War and ...
, Thayer Monument, Eisenhower Monument, MacArthur Monument, Kosciuszko Monument, and Sedgwick Monument. Patton Monument was first dedicated in front of the cadet library in 1950, but in 2004 it was placed in storage to make room for the construction of Jefferson Hall. With the completion of Jefferson Hall, Patton
George Smith Patton Jr. (November 11, 1885 – December 21, 1945) was a general in the United States Army who commanded the Seventh United States Army in the Mediterranean Theater of World War II, and the Third United States Army in France ...
's statue was relocated and unveiled at a temporary location on 15 May 2009, where it will remain until the completion of the renovation of the old cadet library and Bartlett Hall. There is also a statue commemorating brotherhood and friendship from the École Polytechnique
École may refer to:
* an elementary school in the French educational stages normally followed by secondary education establishments (collège and lycée)
* École (river), a tributary of the Seine flowing in région Île-de-France
* École, Savoi ...
in the cadet central area just outside Nininger Hall. The remaining campus area is home to 27 other monuments and memorials.
West Point Cemetery
West Point Cemetery is a historic cemetery in the eastern United States, on the grounds of the U.S. Military Academy in West Point, New York. It overlooks the Hudson River, and served as a burial ground for Revolutionary War soldiers and ear ...
is the final resting place of many notable graduates and faculty, including George Armstrong Custer
George Armstrong Custer (December 5, 1839 – June 25, 1876) was a United States Army officer and cavalry commander in the American Civil War and the American Indian Wars.
Custer graduated from West Point in 1861 at the bottom of his class, b ...
, Winfield Scott
Winfield Scott (June 13, 1786May 29, 1866) was an American military commander and political candidate. He served as a general in the United States Army from 1814 to 1861, taking part in the War of 1812, the Mexican–American War, the early s ...
, William Westmoreland, Earl Blaik, Margaret Corbin, and eighteen Medal of Honor
The Medal of Honor (MOH) is the United States Armed Forces' highest military decoration and is awarded to recognize American soldiers, sailors, marines, airmen, guardians and coast guardsmen who have distinguished themselves by acts of val ...
recipients.Poughkeepsie (2003), p. 16. The cemetery is also the burial place of several recent graduates who have died during the ongoing conflict in Iraq and Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan,; prs, امارت اسلامی افغانستان is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is borde ...
. Many of the older grave sites have large and ornate grave markers, the largest belonging to Egbert Viele (class of 1847), chief engineer of Brooklyn
Brooklyn () is a borough of New York City, coextensive with Kings County, in the U.S. state of New York. Kings County is the most populous county in the State of New York, and the second-most densely populated county in the United States, be ...
's Prospect Park. The cemetery is also home to a monument to Revolutionary War heroine Margaret Corbin.
Athletic facilities
West Point is home to historic athletic facilities like Michie Stadium and Gillis Field House as well as modern facilities such as the Lichtenberg Tennis Center, Anderson Rugby Complex, and the Lou Gross Gymnastics Facility. Michie Stadium recently underwent a significant upgrade in facilities for the football team, and the academy installed a new artificial turf field in the summer of 2008.West Point Museum
The visitor's center is just outside the Thayer Gate in the village of Highland Falls and offers the opportunity to arrange for a guided tour. These tours, which are the only way the general public can access the academy grounds, leave the visitor's center several times a day. The old West Point Visitor's Center was housed in the now-demolished Ladycliff College library building. On 9 September 2016, West Point broke ground in order to begin construction of the new 31,000 square foot Malek West Point Visitors Center. It is being built on the location of the former visitor's center. The Malek West Point Visitors Center is named after Frederic Malek, USMA Class of 1959 and a 2014 Distinguished Graduate. The West Point Museum is directly adjacent to the visitor's center, in the renovated Olmsted Hall on the grounds of the former Ladycliff College. Originally opened to the public in 1854, the West Point Museum is the oldest military museum in the country.Poughkeepsie (2003), p. 7. During the summer months, the museum operates access to theFort Putnam
Fort Putnam was a military garrison during the Revolutionary War at West Point, New York, United States. Built by a regiment of Colonel Rufus Putnam's 5th Massachusetts Regiment, it was completed in 1778 with the purpose of supporting Fort C ...
historic site on main post and access to the 282 acre Constitution Island
Constitution Island is in the northeastern United States, located in New York on the east side of the Hudson River, north of New York City. It is directly opposite the U.S. Military Academy Reservation at West Point and is connected to ...
. Some of the most notable items on display at the museum are George Washington
George Washington (February 22, 1732, 1799) was an American military officer, statesman, and Founding Father who served as the first president of the United States from 1789 to 1797. Appointed by the Continental Congress as commander of ...
's pistols, Napoleon's sword, a dagger carried by Hermann Göring
Hermann Wilhelm Göring (or Goering; ; 12 January 1893 – 15 October 1946) was a German politician, military leader and convicted war criminal. He was one of the most powerful figures in the Nazi Party, which ruled Germany from 1933 to 1 ...
when he was captured, a revolver that belonged to Göring, and a silver-plated party book, signed by Charles Lindbergh, Herbert Hoover and Mussolini, among others. Arguably, the most prized artifact on display is a gold-plated pistol that belonged to Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler (; 20 April 188930 April 1945) was an Austrian-born German politician who was dictator of Germany from 1933 until his death in 1945. He rose to power as the leader of the Nazi Party, becoming the chancellor in 1933 and the ...
.
Administration
Academy leadership
 The commanding officer at the USMA is the Superintendent, equivalent to the president or chancellor of a civilian university. In recent years, the position of superintendent has been held by a
The commanding officer at the USMA is the Superintendent, equivalent to the president or chancellor of a civilian university. In recent years, the position of superintendent has been held by a lieutenant general
Lieutenant general (Lt Gen, LTG and similar) is a three-star military rank (NATO code OF-8) used in many countries. The rank traces its origins to the Middle Ages, where the title of lieutenant general was held by the second-in-command on th ...
(three star general). The 61st Superintendent, Lieutenant General Steven W. Gilland, took command on 27 June 2022, replacing Darryl A. Williams. The academy is a direct reporting unit, and as such, the Superintendent reports directly to the Army Chief of Staff (CSA).
There are two other general officer positions at the academy. Brigadier General
Brigadier general or Brigade general is a military rank used in many countries. It is the lowest ranking general officer in some countries. The rank is usually above a colonel, and below a major general or divisional general. When appointe ...
Mark C. Quander is the Commandant of Cadets, equivalent to a dean of students at the civilian level. Brigadier General
Brigadier general or Brigade general is a military rank used in many countries. It is the lowest ranking general officer in some countries. The rank is usually above a colonel, and below a major general or divisional general. When appointe ...
Shane Reeves is the Dean of the Academic Board, equivalent to a provost at the civilian level. Brigadier General Diana Holland was the first female commandant. Brigadier General Jebb is the first female Dean. There are 13 academic departments at USMA, each with a colonel as the head of department. These 13 tenured colonels comprise the core of the Academic Board. These officers are titled "Professors USMA" or PUSMA. The academy is also overseen by the Board of Visitors (BOV). The BOV is a panel of Senators, Congressional Representatives, and presidential appointees who "shall inquire into the morale and discipline, curriculum, instruction, physical equipment, fiscal affairs, academic methods, and other matters relating to the academy that the board decides to consider." Currently the BOV is chaired by Representative John Shimkus and is composed of three Senators, five Representatives and six presidential appointees.
Admission requirements
Candidates must be between 17 and 23 years old (waivers have been accepted for 24-year olds in rare cases where the candidate is in the military and deployed and therefore unable to attend before his or her 24th birthday), unmarried, and with no legal obligation to support a child. Above average high school and/or previous college grades, and strong performance on standardized testing is expected. The interquartile range on the old SAT was 1100–1360 and 68% ranked in the top fifth of their high school class. To be eligible for appointment, candidates must also undergo a Candidate Fitness Assessment and a complete physical exam. Up to 60 students from foreign countries are present at USMA, educated at the expense of the sponsoring nation, with tuition assistance based on the GNP of their country. Of these foreign cadets theCode of Federal Regulations
In the law of the United States, the ''Code of Federal Regulations'' (''CFR'') is the codification of the general and permanent regulations promulgated by the executive departments and agencies of the federal government of the United States. ...
specifically permits one Filipino cadet designated by the President of the Philippines
The president of the Philippines ( fil, Pangulo ng Pilipinas, sometimes referred to as ''Presidente ng Pilipinas'') is the head of state, head of government and chief executive of the Philippines. The president leads the executive branch of ...
.
The actual application process consists of two main requirements: candidates apply to USMA for admission and separately provide a nomination. The majority of candidates receive a nomination from their United States Representative
The United States House of Representatives, often referred to as the House of Representatives, the U.S. House, or simply the House, is the lower chamber of the United States Congress, with the Senate being the upper chamber. Together they ...
or Senator
A senate is a deliberative assembly, often the upper house or chamber of a bicameral legislature. The name comes from the ancient Roman Senate (Latin: ''Senatus''), so-called as an assembly of the senior (Latin: ''senex'' meaning "the el ...
. Some receive a nomination from the Vice President or even the President of the United States.
The nomination process is not political. Applicants do not have to know their congressman to be nominated. The academy applicant typically provides written essays and letters of recommendation. The applicant then submits to a formal interview.Congressional Nominations to U.S. Service Academies: An Overview and Resources for Outreach and Management''Congressional Research Service''. Retrieved 19 December 2008 Admission to West Point is selective: 7.74% of applicants were admitted (total of 1232) to the Class of 2024. Candidates may have previous college experience, but they may not transfer, meaning that regardless of previous college credit, they enter the academy as a fourth class cadet and undergo the entire four-year program. If a candidate is considered academically disqualified and not selected, he or she may receive an offer to attend to the United States Military Academy Preparatory School. Upon graduation from USMAPS, these candidates are appointed to the academy if they receive the recommendation of the USMAPS Commandant and meet medical admission requirements. The West Point Association of Graduates (WPAOG) also offers scholarship support to people who are qualified but not selected. The scholarships usually cover around $7,000 to civilian universities; the students who receive these scholarships do so under the stipulation that they will be admitted to and attend West Point a year later. Those who do not must repay the AOG. Marion Military Institute, New Mexico Military Institute,
Georgia Military College
Georgia Military College (GMC) is a public military junior college in Milledgeville, Georgia. It is divided into the junior college, a military junior college program, high school, middle school, and elementary school. It was originally known as M ...
, Hargrave Military Academy
Hargrave Military Academy (HMA) is a private, all-male, military boarding school located in the town of Chatham, Virginia. Hargrave is affiliated with the Baptist General Association of Virginia emphasizing Christian values that focuses on a col ...
, Greystone Preparatory School at Schreiner University
Schreiner University is a private Presbyterian university in Kerrville, Texas. The university enrolls an estimated 1,300 undergraduate and graduate students. It offers over 40 four-year undergraduate programs, an MBA and a master of education. ...
, and Northwestern Preparatory School are approved programs that students attend on the AOG scholarship prior to admission to West Point.
Curriculum
 West Point is a medium-sized, highly residential baccalaureate college, with a full-time, four-year undergraduate program that emphasizes instruction in the arts, sciences, and professions with no graduate program. There are forty-five academic majors, the most popular of which are foreign languages, management information systems, history, economics, and mechanical engineering. West Point is accredited by the
West Point is a medium-sized, highly residential baccalaureate college, with a full-time, four-year undergraduate program that emphasizes instruction in the arts, sciences, and professions with no graduate program. There are forty-five academic majors, the most popular of which are foreign languages, management information systems, history, economics, and mechanical engineering. West Point is accredited by the Middle States Commission on Higher Education
The Middle States Commission on Higher Education (abbreviated as MSCHE and legally incorporated as the Mid-Atlantic Region Commission on Higher Education) is a voluntary, peer-based, non-profit membership organization that performs peer evalua ...
. Military officers compose 75% of the faculty, while civilian professors make up the remaining 25%.
A cadet's class rank, which determines his or her Army branch and assignment upon graduation, is calculated as a combination of academic performance (55%), military leadership performance (30%), and physical fitness and athletic performance (15%).
Academics
The academy's teaching style forms part of the Thayer method, which was implemented by Sylvanus Thayer during his tour as Superintendent. This form of instruction emphasizes small classes with daily homework, and strives to make students actively responsible for their own learning by completing homework assignments prior to class and bringing the work to class to discuss collaboratively. The academic program consists of a structured core of thirty-one courses balanced between the arts and sciences. The academy operates on the semester system, which it labels as "terms" (Term 1 is the fall semester; Term 2 is the spring semester). Although cadets choose their majors in the spring of their freshmen year, all cadets take the same course of instruction until the beginning of their second year. This core course of instruction consists of mathematics, information technology, chemistry, physics, engineering, history, physical geography, philosophy, leadership and general psychology, English composition and literature, foreign language, political science, international relations, economics, and constitutional law. Some advanced cadets may "validate" out of the base-level classes and take advanced or accelerated courses earlier as freshmen or sophomores. Regardless of major, all cadets graduate with a Bachelor of Science degree.Military
 As all cadets are commissioned as second lieutenants upon graduation, military and leadership education is nested with academic instruction. Military training and discipline fall under the purview of the Office of the Commandant of Cadets. Entering freshmen, or fourth class cadets, are referred to as New Cadets, and enter the academy on Reception Day or R-day, which marks the start of cadet basic training (CBT), known colloquially as Beast Barracks, or simply Beast. Most cadets consider Beast to be their most difficult time at the academy because of the transition from civilian to military life. Their second summer, cadets undergo cadet field training (CFT) at nearby Camp Buckner, where they train in more advanced field craft and military skills. During a cadet's third summer, they may serve as instructors for CBT or CFT. Rising Firstie (senior) cadets also spend one-month training at Camp Buckner, where they train for modern tactical situations that they will soon face as new platoon leaders. Cadets also have the opportunity during their second, third and fourth summers to serve in active army units and military schools around the world. The schools include Airborne, Air Assault, Sapper, Pathfinder, etc.
Active duty officers in the
As all cadets are commissioned as second lieutenants upon graduation, military and leadership education is nested with academic instruction. Military training and discipline fall under the purview of the Office of the Commandant of Cadets. Entering freshmen, or fourth class cadets, are referred to as New Cadets, and enter the academy on Reception Day or R-day, which marks the start of cadet basic training (CBT), known colloquially as Beast Barracks, or simply Beast. Most cadets consider Beast to be their most difficult time at the academy because of the transition from civilian to military life. Their second summer, cadets undergo cadet field training (CFT) at nearby Camp Buckner, where they train in more advanced field craft and military skills. During a cadet's third summer, they may serve as instructors for CBT or CFT. Rising Firstie (senior) cadets also spend one-month training at Camp Buckner, where they train for modern tactical situations that they will soon face as new platoon leaders. Cadets also have the opportunity during their second, third and fourth summers to serve in active army units and military schools around the world. The schools include Airborne, Air Assault, Sapper, Pathfinder, etc.
Active duty officers in the rank
Rank is the relative position, value, worth, complexity, power, importance, authority, level, etc. of a person or object within a ranking, such as:
Level or position in a hierarchical organization
* Academic rank
* Diplomatic rank
* Hierarchy
* ...
of captain
Captain is a title, an appellative for the commanding officer of a military unit; the supreme leader of a navy ship, merchant ship, aeroplane, spacecraft, or other vessel; or the commander of a port, fire or police department, election precinct, e ...
or major
Major ( commandant in certain jurisdictions) is a military rank of commissioned officer status, with corresponding ranks existing in many military forces throughout the world. When used unhyphenated and in conjunction with no other indicato ...
serve as Company Tactical Officers (TAC Officers). The role of the TAC is to mentor, train, and teach the cadets proper standards of good order and discipline and be a good role model. There is one TAC for every cadet company. There is also one senior Non-Commissioned Officer to assist each TAC, known as TAC-NCOs.
The Department of Military Instruction (DMI) is responsible for all military arts and sciences education as well as planning and executing the cadet summer training. Within DMI there is a representative from each of the Army's branches. These "branch reps" serve as proponents for their respective branches and liaise with cadets as they prepare for branch selection and graduation. Within DMI sits the Modern War Institute, a research center devoted to the study of contemporary conflict and the evolving character of war.
Physical
scuba
Scuba may refer to:
* Scuba diving
** Scuba set, the equipment used for scuba (Self-Contained Underwater Breathing Apparatus) diving
* Scuba, an in-memory database developed by Facebook
* Submillimetre Common-User Bolometer Array, either of two in ...
, rock climbing, and aerobic fitness.
As with all soldiers in the Army, cadets also must pass the Army Physical Fitness Test twice per year. Additionally, every year, cadets must pass the Indoor Obstacle Course Test
The Indoor Obstacle Course Test (IOCT) is a test of full-body functional physical fitness administered by the Department of Physical Education (DPE) at the United States Military Academy at West Point, NY. DPE considers the IOCT to be one of ...
(IOCT), which DPE has administered in Hayes Gymnasium
Hayes Gymnasium, completed in 1910, is the oldest section of the current Arvin Cadet Physical Development Center at the United States Military Academy. Originally built as an independent structure to replace the academy's previous Richard Mor ...
since 1944.
Since Douglas MacArthur
Douglas MacArthur (26 January 18805 April 1964) was an American military leader who served as General of the Army for the United States, as well as a field marshal to the Philippine Army. He had served with distinction in World War I, was ...
's tenure as superintendent, every cadet has been required to participate in either an intercollegiate sport, a club sport, or an intramural (referred to as "company athletics") sport each semester.
Moral and ethical training
Cadet life
Rank and organization

 Cadets are not referred to as freshmen, sophomores, juniors, or seniors. Instead they are officially called fourth class, third class, second class, and first class cadets. Colloquially, freshmen are ''plebes'', sophomores are ''yearlings'' or ''yuks'', juniors are ''cows'', and seniors are ''firsties''. Some of the origins of the class names are known, some are not.
Cadets are not referred to as freshmen, sophomores, juniors, or seniors. Instead they are officially called fourth class, third class, second class, and first class cadets. Colloquially, freshmen are ''plebes'', sophomores are ''yearlings'' or ''yuks'', juniors are ''cows'', and seniors are ''firsties''. Some of the origins of the class names are known, some are not. Plebeians
In ancient Rome, the plebeians (also called plebs) were the general body of free Roman citizens who were not patricians, as determined by the census, or in other words " commoners". Both classes were hereditary.
Etymology
The precise origins ...
were the lower class of ancient Roman society, while yearling is a euphemism for a year-old animal. The origin of cow is less known. There are a number of theories for the origin of the term ''cow''; however the most prevalent and probably accurate one is that cadets in years past had no leave until the end of their yearling year, when they were granted a summer-long furlough. Their return as second classmen was heralded as "the cows coming home."
The Corps of Cadets is officially organized into a brigade. The senior ranking cadet, the Brigade Commander, is known traditionally as the ''First Captain''. The brigade is organized into four regiments. Within each regiment there are three battalions, each consisting of three companies. Companies are lettered A through I, with a number signifying which regiment it belongs to. For example, there are four "H" companies: H1, H2, H3, and H4. First class cadets hold the leadership positions within the brigade from the First Captain down to platoon leaders within the companies. Leadership responsibility decreases with the lower classes, with second class cadets holding the rank of cadet sergeant, third class cadets holding the rank of cadet corporal, and fourth class cadets as cadet privates.
Life in the corps
 Because of the academy's congressional nomination process, students come from all 50 states, Puerto Rico, the District of Columbia, the Mariana Islands, Guam, American Samoa, and the US Virgin Islands. The academy is also authorized up to 60 international exchange cadets, who undergo the same four-year curriculum as fully integrated members of the Corps of Cadets. Cadets attend the United States Military Academy free of charge, with all tuition and board paid for by the Army in return for a service commitment of five years of active duty and three years of reserve status upon graduation. Starting on the first day of a cadet's second class year, non-graduates after that point are expected to fulfill their obligations in enlisted service. Cadets receive a monthly
Because of the academy's congressional nomination process, students come from all 50 states, Puerto Rico, the District of Columbia, the Mariana Islands, Guam, American Samoa, and the US Virgin Islands. The academy is also authorized up to 60 international exchange cadets, who undergo the same four-year curriculum as fully integrated members of the Corps of Cadets. Cadets attend the United States Military Academy free of charge, with all tuition and board paid for by the Army in return for a service commitment of five years of active duty and three years of reserve status upon graduation. Starting on the first day of a cadet's second class year, non-graduates after that point are expected to fulfill their obligations in enlisted service. Cadets receive a monthly stipend
A stipend is a regular fixed sum of money paid for services or to defray expenses, such as for scholarship, internship, or apprenticeship. It is often distinct from an income or a salary because it does not necessarily represent payment for work p ...
of $1,017.00 for books, uniforms, and other necessities, as of 2015. From this amount, pay is automatically deducted for the cost of uniforms, books, supplies, services, meals, and other miscellaneous expenses. All remaining money after deductions is used at the individual cadets' discretion. All cadets receive meals in the dining halls and have access to internet on approved, issued devices. The student population was 4,389 cadets for the 2016–2017 academic year. The student body has recently been around 20% female.
All cadets reside on campus for their entire four years in one of the nine barracks buildings. Most cadets are housed with one roommate, but some rooms are designed for three cadets. Cadets are grouped into ''companies'' identified by alpha-numeric codes. All companies live together in the same barracks area. The commandant may decide to have cadets change companies at some point in their cadet career. This process is known as scrambling and the method of scrambling has changed several times in recent years.Murphy (2008), p. 10. All 4,000 cadets dine together at breakfast and lunch in the Washington Hall during the weekdays. The cadet fitness center, Arvin Cadet Physical Development Center (usually just called "Arvin" by cadets and faculty), which was rebuilt in 2004, houses extensive physical fitness facilities and equipment for student use.
Activities
 Cadets have a host of extracurricular activities available, most run by the office of the Directorate of Cadet Activities (DCA). DCA sponsors or operates 113 athletic and non-sport clubs. Many cadets join several clubs during their time at the academy and find their time spent with their clubs a welcome respite from the rigors of cadet life. DCA is responsible for a wide range of activities that provide improved quality of life for cadets, including: three cadet-oriented restaurants, the Cadet Store, and the ''Howitzer'' and ''Bugle Notes''. ''The Howitzer'' is the annual yearbook, while ''Bugle Notes'', also known as the "plebe bible," is the manual of plebe knowledge. Plebe knowledge is a lengthy collection of traditions, songs, poems, anecdotes, and facts about the academy, the army, the ''Old Corps'', and the rivalry with Navy that all plebes must memorize during cadet basic training. During plebe year, plebes may be asked, and are expected to answer, any inquiry about plebe knowledge asked by upper class cadets. Other knowledge is historical in nature, including information as found in ''Bugle Notes''.Lipsky (2003), p. 9. However, some knowledge changes daily, such as "the days" (a running list of the number of days until important academy events), the menu in the mess hall for the day, or the lead stories in ''
Cadets have a host of extracurricular activities available, most run by the office of the Directorate of Cadet Activities (DCA). DCA sponsors or operates 113 athletic and non-sport clubs. Many cadets join several clubs during their time at the academy and find their time spent with their clubs a welcome respite from the rigors of cadet life. DCA is responsible for a wide range of activities that provide improved quality of life for cadets, including: three cadet-oriented restaurants, the Cadet Store, and the ''Howitzer'' and ''Bugle Notes''. ''The Howitzer'' is the annual yearbook, while ''Bugle Notes'', also known as the "plebe bible," is the manual of plebe knowledge. Plebe knowledge is a lengthy collection of traditions, songs, poems, anecdotes, and facts about the academy, the army, the ''Old Corps'', and the rivalry with Navy that all plebes must memorize during cadet basic training. During plebe year, plebes may be asked, and are expected to answer, any inquiry about plebe knowledge asked by upper class cadets. Other knowledge is historical in nature, including information as found in ''Bugle Notes''.Lipsky (2003), p. 9. However, some knowledge changes daily, such as "the days" (a running list of the number of days until important academy events), the menu in the mess hall for the day, or the lead stories in ''The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''the Times'', ''NYT'', or the Gray Lady) is a daily newspaper based in New York City with a worldwide readership reported in 2020 to comprise a declining 840,000 paid print subscribers, and a growing 6 million paid ...
''.
Each cadet class celebrates at least one special "class weekend" per academic year. Fourth class cadets participate in Plebe Parent Weekend during the first weekend of spring break. In February, third class cadets celebrate the winter season with Yearling Winter Weekend. In late January the second class cadets celebrate 500th Night, marking the remaining 500 days before graduation. First class cadets celebrate three different formal occasions. In late August, first class cadets celebrate Ring Weekend
The cadets of the United States Military Academy first began the practice of wearing class rings in 1835. The United States Military Academy class ring has traditionally been worn on the left hand, but most recent graduates choose to wear it on ...
, in February they mark their last 100 days with 100th Night, and in May they have a full week of events culminating in their graduation. All of the "class weekends" involve a formal dinner and social dance, known in old cadet slang as a "hop," held at Eisenhower Hall. Grant Hall, formerly the cadet mess hall at West Point, is now a social center.
Athletics
 Since 1899, Army's mascot has officially been a mule because the animal symbolizes strength and perseverance. The academy's football team was nicknamed "The Black Knights of the Hudson" due to the black color of its uniforms. This nickname has since been officially shortened to the "Black Knights." U.S. sports media use "Army" as a synonym for the academy. "On Brave Old Army Team" is the school's
Since 1899, Army's mascot has officially been a mule because the animal symbolizes strength and perseverance. The academy's football team was nicknamed "The Black Knights of the Hudson" due to the black color of its uniforms. This nickname has since been officially shortened to the "Black Knights." U.S. sports media use "Army" as a synonym for the academy. "On Brave Old Army Team" is the school's fight song
A fight song is a rousing short song associated with a sports team. The term is most common in the United States and Canada. In Australia, Mexico, and New Zealand these songs are called the team anthem, team song, or games song. First associated ...
. Army's chief sports rival is the Naval Academy
A naval academy provides education for prospective naval officers.
See also
* Military academy
A military academy or service academy is an educational institution which prepares candidates for service in the officer corps. It normally pr ...
due to its long-standing football rivalry and the interservice rivalry with the Navy
A navy, naval force, or maritime force is the branch of a nation's armed forces principally designated for naval and amphibious warfare; namely, lake-borne, riverine, littoral, or ocean-borne combat operations and related functions. It in ...
in general. Fourth class cadets verbally greet upper-class cadets and faculty with "Beat Navy," while the tunnel that runs under Washington Road is named the "Beat Navy" tunnel. Army also plays the U.S. Air Force Academy for the Commander-in-Chief's Trophy
The Commander-in-Chief's Trophy is awarded to each season's winner of the American college football series among the teams of the U.S. Military Academy (Army Black Knights), the U.S. Naval Academy (Navy Midshipmen), and the U.S. Air Force A ...
. In the first half of the 20th century, Army and Notre Dame were football rivals, but that rivalry has since died out. Notre Dame beat Army 44 – 6 in 2016.
Football
Armyfootball
Football is a family of team sports that involve, to varying degrees, kicking a ball to score a goal. Unqualified, the word ''football'' normally means the form of football that is the most popular where the word is used. Sports commonly ...
began in 1890, when Navy
A navy, naval force, or maritime force is the branch of a nation's armed forces principally designated for naval and amphibious warfare; namely, lake-borne, riverine, littoral, or ocean-borne combat operations and related functions. It in ...
challenged the cadets to a game of the relatively new sport. Navy defeated Army at West Point that year, but Army avenged the loss in Annapolis
Annapolis ( ) is the capital city of the U.S. state of Maryland and the county seat of, and only incorporated city in, Anne Arundel County. Situated on the Chesapeake Bay at the mouth of the Severn River, south of Baltimore and about east ...
the following year.Ambrose (1966), pp. 305–306. The rival academies still clash every December in what is traditionally the last regular-season Division I college-football game. The 2015 football season marked Navy's fourteenth consecutive victory over Army, the longest streak in the series since inception. The following year, Army won 21–17. Army's football team reached its pinnacle of success under coach Earl Blaik when Army won consecutive national championships in 1944, 1945 and 1946, and produced three Heisman trophy
The Heisman Memorial Trophy (usually known colloquially as the Heisman Trophy or The Heisman) is awarded annually to the most outstanding player in college football. Winners epitomize great ability combined with diligence, perseverance, and har ...
winners: Doc Blanchard (1945), Glenn Davis (1946) and Pete Dawkins (1958). Past NFL coaches Vince Lombardi
Vincent Thomas Lombardi (June 11, 1913 – September 3, 1970) was an American football coach and executive in the National Football League (NFL). Lombardi is considered by many to be the greatest coach in football history, and he is recognized a ...
and Bill Parcells were Army assistant coaches early in their careers. The football team plays its home games at Michie Stadium, where the playing field is named after Earl Blaik. Cadets' attendance is mandatory at football games and the Corps stands for the duration of the game. At all home games, one of the four regiments marches onto the field in formation before the team takes the field and leads the crowd in traditional Army cheers. From 1992 through 1996, Army won all of the games against Navy for the first time since the legendary days of Blanchard and Davis, and it introduced the fraternal group of players identifying themselves as the Fat Man Club, initiated by the offensive linemen of the Class of 1996. Between the 1998 and 2004 seasons, Army's football program was a member of Conference USA
Conference USA (C-USA or CUSA) is an intercollegiate athletic conference whose current member institutions are located within the Southern United States. The conference participates in the NCAA's Division I in all sports. C-USA's offices are ...
, but has since reverted to its former independent status.
Other sports
Patriot League
The Patriot League is a collegiate athletic conference comprising private institutions of higher education and two United States service academies based in the Northeastern United States. Outside the Ivy League, it is among the most selective g ...
in most sports, while its men's ice hockey
Ice hockey (or simply hockey) is a team sport played on ice skates, usually on an ice skating rink with lines and markings specific to the sport. It belongs to a family of sports called hockey. In ice hockey, two opposing teams use ice ...
program competes in Atlantic Hockey
The Atlantic Hockey Association (AHA) is an NCAA Men's Division I Ice Hockey conference which operates primarily in the northeastern United States. It participates in the NCAA's Division I as an ice hockey-only conference. Unlike several othe ...
. John P. Riley Jr.
John Patrick Riley (June 15, 1920 – February 3, 2016) was an American ice hockey player and coach. The hockey coach at West Point for more than 35 years, Riley coached the United States to the gold medal at the 1960 Squaw Valley Olympics. He ...
was the hockey coach at West Point for more than 35 years. Every year, Army faces the Royal Military College of Canada
'')
, established = 1876
, type = Military academy
, chancellor = Anita Anand ('' la, ex officio, label=none'' as Defence Minister)
, principal = Harry Kowal
, head_label ...
(RMC) Paladins
The Paladins, also called the Twelve Peers, are twelve legendary knights, the foremost members of Charlemagne's court in the 8th century. They first appear in the medieval (12th century) ''chanson de geste'' cycle of the Matter of France, whe ...
in the annual West Point Weekend hockey game. This series was first conceived in 1923.
The men's lacrosse team has won eight national championships and appeared in the NCAA tournament sixteen times. In its early years, lacrosse was used by football players, like the "Lonesome End" Bill Carpenter, to stay in shape during the off-season. The 2005–06 women's basketball team went 20–11 and won the Patriot League tournament. They went to the 2006 NCAA Women's Division I Basketball Tournament
The 2006 NCAA Division I women's basketball tournament was held from March 18 to April 4, 2006, at several sites, with the championship game held in Boston. The Maryland Terrapins, coached by Brenda Frese, won their first National Championship, b ...
as a 15th-ranked seed
A seed is an embryonic plant enclosed in a protective outer covering, along with a food reserve. The formation of the seed is a part of the process of reproduction in seed plants, the spermatophytes, including the gymnosperm and angiosper ...
, where they lost to Tennessee
Tennessee ( , ), officially the State of Tennessee, is a landlocked U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. Tennessee is the List of U.S. states and territories by area, 36th-largest by ...
, 102–54. It was the first March Madness tournament appearance for any Army basketball team. The head coach of that team, Maggie Dixon
Margaret Mary Dixon (May 9, 1977 – April 6, 2006) was an American collegiate women's basketball coach.
Life
Dixon was born in North Hollywood, California, and played basketball at Notre Dame High School. Dixon graduated in 1999 with a bac ...
, died soon after the season at only 28 years of age. Bob Knight
Robert Montgomery Knight (born October 25, 1940) is an American former basketball coach. Nicknamed "the General", Knight won 902 NCAA Division I men's college basketball games, a record at the time of his retirement, and currently fourth all-ti ...
, formerly the winningest men's basketball coach in NCAA history, began his head coaching career at Army in the late 1960s before moving on to Indiana
Indiana () is a U.S. state in the Midwestern United States. It is the 38th-largest by area and the 17th-most populous of the 50 States. Its capital and largest city is Indianapolis. Indiana was admitted to the United States as the 19th ...
and Texas Tech
Texas Tech University (Texas Tech, Tech, or TTU) is a public research university in Lubbock, Texas. Established on , and called Texas Technological College until 1969, it is the main institution of the five-institution Texas Tech University Sys ...
. One of Knight's players at Army was Mike Krzyzewski, who later was head coach at Army before moving on to Duke
Duke is a male title either of a monarch ruling over a duchy, or of a member of royalty, or nobility. As rulers, dukes are ranked below emperors, kings, grand princes, grand dukes, and sovereign princes. As royalty or nobility, they are r ...
, where he has won five national championships.
 Approximately 15% of cadets are members of a club sport team. West Point fields a total of 24 club sports teams that have been very successful in recent years, winning national championships in judo, boxing, orienteering, pistol, triathlon, crew, cycling, and team handball.
The majority of the student body, about 65%, competes in intramural sports, known at the academy as "company athletics." DPE's Competitive Sports committee runs the club and company athletics sports programs and was recently named one of the "15 Most Influential Sports Education Teams in America" by the Institute for International Sport. The fall season sees competition in basketball, flag-football, team handball, soccer, ultimate disc, and wrestling; while the spring season sees competition in combative grappling, floor hockey, orienteering, flicker ball, and swimming. In the spring, each company also fields a team entry into the annual Sandhurst Competition, a military skills event conducted by the Department of Military Instruction.
Approximately 15% of cadets are members of a club sport team. West Point fields a total of 24 club sports teams that have been very successful in recent years, winning national championships in judo, boxing, orienteering, pistol, triathlon, crew, cycling, and team handball.
The majority of the student body, about 65%, competes in intramural sports, known at the academy as "company athletics." DPE's Competitive Sports committee runs the club and company athletics sports programs and was recently named one of the "15 Most Influential Sports Education Teams in America" by the Institute for International Sport. The fall season sees competition in basketball, flag-football, team handball, soccer, ultimate disc, and wrestling; while the spring season sees competition in combative grappling, floor hockey, orienteering, flicker ball, and swimming. In the spring, each company also fields a team entry into the annual Sandhurst Competition, a military skills event conducted by the Department of Military Instruction.
Traditions
Due to West Point's age and its unique mission of producing Army officers, it has many time-honored traditions. The list below are some of the traditions unique to or started by the academy.Cullum number
The Cullum number is a reference and identification number assigned to each graduate. It was created by brevet Major GeneralGeorge W. Cullum
George Washington Cullum (25 February 1809 – 28 February 1892) was an American soldier, engineer and writer. He worked as the supervising engineer on the building and repair of many fortifications across the country. Cullum served as a general ...
(USMA Class of 1833) who, in 1850, began the monumental work of chronicling the biographies of every graduate. He assigned number one to the first West Point graduate, Joseph Gardner Swift
Joseph Gardner Swift (December 31, 1783 – July 22, 1865) was an American soldier who, in 1802, became the first graduate of the newly instituted United States Military Academy in West Point, New York; he would later serve as its fourth Superin ...
, and then numbered all successive graduates in sequence. Before his death in 1892, General Cullum completed the first three volumes of a work that eventually comprised 10 volumes, titled ''General Cullum's Biographical Register of the Officers and Graduates of the United States Military Academy, and covering USMA classes from 1802 through 1850''. From 1802 through the Class of 1977, graduates were listed by general order of Merit. Beginning with the Class of 1978, graduates were listed alphabetically, and then by date of graduation. Seven graduates have an "A" suffix after their Cullum Number. For various reasons these graduates were omitted from the original class roster, and a suffix letter was added to avoid renumbering the entire class and subsequent classes.
Class ring
Ring Weekend
The cadets of the United States Military Academy first began the practice of wearing class rings in 1835. The United States Military Academy class ring has traditionally been worn on the left hand, but most recent graduates choose to wear it on ...
in the early fall of their senior year. Immediately after senior cadets return to the barracks after receiving their rings, fourth class cadets take the opportunity to surround senior cadets from their company and ask to touch their rings. After the cadets recite a poem known as the ''Ring Poop'', the senior usually grants the freshmen permission to touch the ring. In 2002, the Memorial Class ring donor program began. Donations of class rings are melted and merged. A portion of the original gold is infused with gold from preceding melts to become part of the rings for each 'Firstie' class.
Thayer Award
West Point is home to the Sylvanus Thayer Award. Given annually by the academy since 1958, the award honors an outstanding citizen whose service and accomplishments in the national interest exemplify the academy's motto, "Duty, Honor, Country." Currently, the award guidelines state that the recipient not be a graduate of the academy. The award has been awarded to many notable American citizens, to include George H. W. Bush,Colin Powell
Colin Luther Powell ( ; April 5, 1937 – October 18, 2021) was an American politician, statesman, diplomat, and United States Army officer who served as the 65th United States Secretary of State from 2001 to 2005. He was the first Africa ...
, Tom Brokaw
Thomas John Brokaw (; born February 6, 1940) is an American retired network television journalist and author. He first served as the co-anchor of ''The Today Show'' from 1976 to 1981 with Jane Pauley, then as the anchor and managing editor of '' ...
, Sandra Day O'Connor
Sandra Day O'Connor (born March 26, 1930) is an American retired attorney and politician who served as the first female associate justice of the Supreme Court of the United States from 1981 to 2006. She was both the first woman nominated and th ...
, Henry Kissinger
Henry Alfred Kissinger (; ; born Heinz Alfred Kissinger, May 27, 1923) is a German-born American politician, diplomat, and geopolitical consultant who served as United States Secretary of State and National Security Advisor under the presid ...
, Ronald Reagan
Ronald Wilson Reagan ( ; February 6, 1911June 5, 2004) was an American politician, actor, and union leader who served as the 40th president of the United States from 1981 to 1989. He also served as the 33rd governor of California from 1967 ...
, Barry Goldwater
Barry Morris Goldwater (January 2, 1909 – May 29, 1998) was an American politician and United States Air Force officer who was a five-term U.S. Senator from Arizona (1953–1965, 1969–1987) and the Republican Party nominee for president ...
, Carl Vinson
Carl Vinson (November 18, 1883 – June 1, 1981) was an American politician who served in the U.S. House of Representatives for over 50 years and was influential in the 20th century expansion of the U.S. Navy. He was a member of the Democratic ...
, Barbara Jordan, William J. Perry, Bob Hope
Leslie Townes "Bob" Hope (May 29, 1903 – July 27, 2003) was a British-American comedian, vaudevillian, actor, singer and dancer. With a career that spanned nearly 80 years, Hope appeared in more than 70 short and feature films, with ...
, Condoleezza Rice
Condoleezza Rice ( ; born November 14, 1954) is an American diplomat and political scientist who is the current director of the Hoover Institution at Stanford University. A member of the Republican Party, she previously served as the 66th Un ...
and Leon E. Panetta
Leon Edward Panetta (born June 28, 1938) is an American Democratic Party politician who has served in several different public office positions, including Secretary of Defense, CIA Director, White House Chief of Staff, Director of the Office o ...
.
Sedgwick's spurs
A monument to Civil War Union General John Sedgwick stands on the outskirts of thePlain
In geography, a plain is a flat expanse of land that generally does not change much in elevation, and is primarily treeless. Plains occur as lowlands along valleys or at the base of mountains, as coastal plains, and as plateaus or uplands ...
. Sedgwick's bronze statue has spur
A spur is a metal tool designed to be worn in pairs on the heels of riding boots for the purpose of directing a horse or other animal to move forward or laterally while riding. It is usually used to refine the riding aids (commands) and to ba ...
s with rowels that freely rotate. Legend states that if a cadet is in danger of failing a class, they are to don their full-dress parade uniform the night before the final exam. The cadet visits the statue and spins the rowels at the stroke of midnight. Then the cadet runs back to the barracks as fast as he or she can. According to legend, if Sedgwick's ghost catches them, they will fail the exam. Otherwise the cadet will pass the exam and the course. Although being out of their rooms after midnight is officially against regulations, violations have been known to be overlooked for the sake of tradition.
Goat-Engineer game
As part of the run-up to the Navy football game, the Corps of Cadets plays the Goat-Engineer game. First played in 1907, it is a game between the "Goats" (the bottom half of the senior (Firstie) class academically), and the "Engineers" (the top half). The game is played with full pads and helmets using eight-man football rules. The location has changed over the years, with recent venues being Richard Shea Stadium/Doubleday Field, Michie Stadium, and Daly Field. Legend states that Army will beat Navy if the goats win, and the opposite if the engineers win. In recent years, female cadets have begun playing aflag football
Flag football is a variant of American football where, instead of tackling players to the ground, the defensive team must remove a flag or flag belt from the ball carrier ("deflagging") to end a down. The sport has a strong amateur following ...
contest, so there are now two Goat-Engineer games, played consecutively the same night.
Walking the area
From the earliest days of the academy, one form of punishment for cadets who commit regulatory infractions has been a process officially known as ''punishment tours''. This process is better known to the cadets as "hours" because as punishment, cadets must walk a specified number of hours in penalty. Cadets are "awarded" punishment tours based upon the severity of the infraction. Being late to class or having an unkempt room may result in as little as 5 hours while more severe misconduct infractions may result in upwards of 60 to 80 hours. In its most traditional form, punishment tours are "walked off" by wearing the dress gray uniform under arms and walking back and forth in a designated area of the cadet barracks courtyard, known as "Central Area." Cadets who get into trouble frequently and spend many weekends "walking off their hours" are known as "area birds." Cadets who walk more than 100 total hours in their career are affectionately known as "Century Men." An alternate form of punishment to walking hours is known as "fatigue tours," where assigned hours may be "worked off" by manual labor, such as cleaning the barracks. Certain cadets whose academics are deficient may also conduct "sitting tours," where they have to "sit hours" in a designated academic room in a controlled study environment, for which they receive half credit towards their reduction of tours. Cadets' uniforms are inspected before their tours begin each day. The inspection process is arduous and considered part of the punishment, but the time spent does not count against the awarded number of tours. A small number of cadets may be relieved of their tours that day if their uniforms are exceptionally presentable. Another tradition associated with punishment tours is that any visiting head of state has the authority to grant "amnesty," releasing all cadets with outstanding hours from the remainder of their assigned tours.Sandhurst Military Skills Competition
In 1967 theRoyal Military Academy Sandhurst
The Royal Military Academy Sandhurst (RMAS or RMA Sandhurst), commonly known simply as Sandhurst, is one of several military academies of the United Kingdom and is the British Army's initial officer training centre. It is located in the town o ...
presented West Point with a British Army
The British Army is the principal land warfare force of the United Kingdom, a part of the British Armed Forces along with the Royal Navy and the Royal Air Force. , the British Army comprises 79,380 regular full-time personnel, 4,090 Gurkha ...
officer's sword for use as a trophy in a military skills competition at West Point. In 2019 the Sandhurst competition spans two days, 12 and 13 April, with teams from USMA, the ROTC programs, the Naval, Coast Guard, and the Air Force academies. International academies including the UK, Canada, Australia and Ireland have won the Sandhurst Military Skills Competition.
Education of dependents
TheDepartment of Defense Education Activity
The Department of Defense Education Activity (DoDEA) is a federal school system headquartered in Alexandria, Virginia, responsible for planning, directing, coordinating, and managing prekindergarten through 12th grade educational programs on behal ...
(DoDEA) maintains, for children of military personnel, West Point Elementary School and West Point Middle School on the academy grounds.
The academy is physically in the Highland Falls Central School District. USMA sends high school aged students who are dependents of on-base military personnel to James I. O'Neill High School
James I. O'Neill High School is a public high school in Highland Falls, New York and a part of the Highland Falls-Fort Montgomery Central School District.
History
James I. O'Neill High School opened in 1971, replacing the existing Highland Falls ...
of Highland Falls schools under contract. In 2021, 190 children living on West Point attended O'Neill. In 2021 the agency at West Point announced that the bid to educate West Point High School students would be competitive. In March 2022 the O'Neill contract was renewed.
Notable alumni
An unofficial motto of the academy's history department is "Much of the history we teach was made by people we taught." Graduates of the academy refer to themselves as "The Long Gray Line," a phrase taken from the academy's traditional hymn " The Corps." The academy has produced just under 65,000 alumni, including twoPresidents of the United States
The president of the United States is the head of state and head of government of the United States, indirectly elected to a four-year term via the Electoral College. The officeholder leads the executive branch of the federal government and ...
: Ulysses S. Grant
Ulysses S. Grant (born Hiram Ulysses Grant ; April 27, 1822July 23, 1885) was an American military officer and politician who served as the 18th president of the United States from 1869 to 1877. As Commanding General, he led the Union A ...
and Dwight D. Eisenhower; the president of the Confederate States of America
The Confederate States of America (CSA), commonly referred to as the Confederate States or the Confederacy was an unrecognized breakaway republic in the Southern United States that existed from February 8, 1861, to May 9, 1865. The Confeder ...
, Jefferson Davis
Jefferson F. Davis (June 3, 1808December 6, 1889) was an American politician who served as the president of the Confederate States from 1861 to 1865. He represented Mississippi in the United States Senate and the House of Representatives as ...
; and three foreign heads of state: Anastasio Somoza Debayle
Anastasio "Tachito" Somoza Debayle (; 5 December 1925 – 17 September 1980) was the President of Nicaragua from 1 May 1967 to 1 May 1972 and from 1 December 1974 to 17 July 1979. As head of the National Guard, he was ''de facto'' ruler of t ...
of Nicaragua
Nicaragua (; ), officially the Republic of Nicaragua (), is the largest country in Central America, bordered by Honduras to the north, the Caribbean to the east, Costa Rica to the south, and the Pacific Ocean to the west. Managua is the coun ...
, Fidel V. Ramos of the Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
, and José María Figueres
José María Figueres Olsen (born 24 December 1954 in San José, Costa Rica) is a Costa Rican businessman and politician, who served as President of Costa Rica from 1994 to 1998. He also ran for president in the 2022 presidential election bu ...
of Costa Rica
Costa Rica (, ; ; literally "Rich Coast"), officially the Republic of Costa Rica ( es, República de Costa Rica), is a country in the Central American region of North America, bordered by Nicaragua to the north, the Caribbean Sea to the no ...
. Alumni currently serving in public office include Senator
A senate is a deliberative assembly, often the upper house or chamber of a bicameral legislature. The name comes from the ancient Roman Senate (Latin: ''Senatus''), so-called as an assembly of the senior (Latin: ''senex'' meaning "the el ...
Jack Reed, Governor of Nebraska David Heineman, Governor of Louisiana
A governor is an administrative leader and head of a polity or political region, ranking under the head of state and in some cases, such as governors-general, as the head of state's official representative. Depending on the type of political ...
John Bel Edwards
John Bel Edwards (born September 16, 1966) is an American politician and attorney serving as the 56th governor of Louisiana since 2016. A member of the Democratic Party, he previously served as the Democratic leader of the Louisiana House of ...
, Congressmen Warren Davidson, Mark Green, Brett Guthrie, John Shimkus and Steve Watkins
Steven Charles Watkins Jr. (born September 18, 1976) is an American politician and former military officer. He served as the U.S. representative for Kansas's from 2019 to 2021. He is a member of the Republican Party, and was succeeded by Ja ...
.
The academy has produced many notable generals during its 212 years. During the Civil War, graduates included John Bell Hood, Stonewall Jackson
Thomas Jonathan "Stonewall" Jackson (January 21, 1824 – May 10, 1863) was a Confederate general during the American Civil War, considered one of the best-known Confederate commanders, after Robert E. Lee. He played a prominent role in nearl ...
, Ulysses S. Grant
Ulysses S. Grant (born Hiram Ulysses Grant ; April 27, 1822July 23, 1885) was an American military officer and politician who served as the 18th president of the United States from 1869 to 1877. As Commanding General, he led the Union A ...
, Robert E. Lee
Robert Edward Lee (January 19, 1807 – October 12, 1870) was a Confederate general during the American Civil War, towards the end of which he was appointed the overall commander of the Confederate States Army. He led the Army of Nor ...
, George McClellan, Simon Bolivar Buckner, James Longstreet
James Longstreet (January 8, 1821January 2, 1904) was one of the foremost General officers in the Confederate States Army, Confederate generals of the American Civil War and the principal subordinate to General Robert E. Lee, who called him his ...
, George G. Meade, Phillip Sheridan
General of the Army Philip Henry Sheridan (March 6, 1831 – August 5, 1888) was a career United States Army officer and a Union general in the American Civil War. His career was noted for his rapid rise to major general and his close a ...
, William Tecumseh Sherman
William Tecumseh Sherman ( ; February 8, 1820February 14, 1891) was an American soldier, businessman, educator, and author. He served as a general in the Union Army during the American Civil War (1861–1865), achieving recognition for his com ...
, J.E.B. Stuart and Oliver O. Howard
Oliver Otis Howard (November 8, 1830 – October 26, 1909) was a career United States Army officer and a Union general in the Civil War. As a brigade commander in the Army of the Potomac, Howard lost his right arm while leading his men against ...
. George Armstrong Custer
George Armstrong Custer (December 5, 1839 – June 25, 1876) was a United States Army officer and cavalry commander in the American Civil War and the American Indian Wars.
Custer graduated from West Point in 1861 at the bottom of his class, b ...
graduated last in his class of 1861. The Spanish–American War
, partof = the Philippine Revolution, the decolonization of the Americas, and the Cuban War of Independence
, image = Collage infobox for Spanish-American War.jpg
, image_size = 300px
, caption = (clock ...
saw the first combat service of Lt. (later, Brigadier General) John "Gatling Gun" Parker, the first Army officer to employ machine guns in offensive fire support of infantry.
During World War I, the academy produced General of the Armies
General of the Armies of the United States, more commonly referred to as General of the Armies, is the highest military rank in the United States Army. The rank has been conferred three times: to John J. Pershing in 1919, as a personal accola ...
John J. Pershing, and Major Generals Charles T. Menoher
Major General Charles Thomas Menoher (March 20, 1862 – August 11, 1930) was a U.S. Army general, first Chief of the United States Army Air Service from 1918 to 1921, and commanded the U.S. Army Hawaiian Department from 1924 to 1925.
Early life ...
and Mason Patrick. West Point was the alma mater of many notable World War II generals, Henry H. Arnold, Omar Bradley, Mark Wayne Clark
Mark Wayne Clark (May 1, 1896 – April 17, 1984) was a United States Army officer who saw service during World War I, World War II, and the Korean War. He was the youngest four-star general in the US Army during World War II.
During World War I ...
, Robert L. Eichelberger
Robert Lawrence Eichelberger (9 March 1886 – 26 September 1961) was a general officer in the United States Army who commanded the Eighth United States Army in the Southwest Pacific Area during World War II.
A 1909 graduate of the Unite ...
, James M. Gavin, Leslie Groves, Douglas MacArthur
Douglas MacArthur (26 January 18805 April 1964) was an American military leader who served as General of the Army for the United States, as well as a field marshal to the Philippine Army. He had served with distinction in World War I, was ...
, George S. Patton
George Smith Patton Jr. (November 11, 1885 – December 21, 1945) was a general in the United States Army who commanded the Seventh United States Army in the Mediterranean Theater of World War II, and the Third United States Army in France ...
, Joseph Stilwell
Joseph Warren "Vinegar Joe" Stilwell (March 19, 1883 – October 12, 1946) was a United States Army general who served in the China Burma India Theater during World War II. An early American popular hero of the war for leading a column walking ...
, Maxwell D. Taylor
Maxwell Davenport Taylor (August 26, 1901 – April 19, 1987) was a senior United States Army officer and diplomat of the mid-20th century. He served with distinction in World War II, most notably as commander of the 101st Airborne Division, n ...
, James Van Fleet, Jonathan Mayhew Wainwright IV, and Simon Bolivar Buckner, Jr. the highest ranking General to be killed in combat during World War II, with many of these graduates also serving in commanding roles in the Korean War
{{Infobox military conflict
, conflict = Korean War
, partof = the Cold War and the Korean conflict
, image = Korean War Montage 2.png
, image_size = 300px
, caption = Clockwise from top:{ ...
. During the Vietnam War
The Vietnam War (also known by #Names, other names) was a conflict in Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia from 1 November 1955 to the fall of Saigon on 30 April 1975. It was the second of the Indochina Wars and was officially fought between North Vie ...
, notable graduates general officers included Creighton Abrams, Hal Moore, and William Westmoreland. West Point also produced some famous generals and statesmen of recent note including John Abizaid, Stanley A. McChrystal, Wesley Clark, Alexander Haig, Barry McCaffrey
Barry Richard McCaffrey (born November 17, 1942) is a retired United States Army general and current news commentator, professor and business consultant who served in President Bill Clinton's Cabinet as the Director of the Office of National ...
, Norman Schwarzkopf, Jr., Brent Scowcroft
Brent Scowcroft (; March 19, 1925August 6, 2020) was a United States Air Force officer who was a two-time United States National Security Advisor, first under U.S. President Gerald Ford and then under George H. W. Bush. He served as Military A ...
, Lloyd Austin, and former Director of the Central Intelligence Agency
The director of the Central Intelligence Agency (D/CIA) is a statutory office () that functions as the head of the Central Intelligence Agency, which in turn is a part of the United States Intelligence Community.
Beginning February 2017, the ...
, retired General David Petraeus
David Howell Petraeus (; born November 7, 1952) is a retired United States Army general and public official. He served as Director of the Central Intelligence Agency from September 6, 2011, until his resignation on November 9, 2012. Prior to ...
.
A total of 76 graduates have been awarded the Medal of Honor
The Medal of Honor (MOH) is the United States Armed Forces' highest military decoration and is awarded to recognize American soldiers, sailors, marines, airmen, guardians and coast guardsmen who have distinguished themselves by acts of val ...
.
West Point has produced 18 NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research.
NASA was established in 1958, succeedin ...
astronauts, including five who went to the Moon. Other noted alumni include Jim Kimsey
James Verlin Kimsey (September 15, 1939 – March 1, 2016) was the co-founder of AOL. He was the first chairman of the company and served as CEO until 1995. Although Kimsey is best known for having helped to create AOL, he also spearheaded many o ...
, founder of AOL
AOL (stylized as Aol., formerly a company known as AOL Inc. and originally known as America Online) is an American web portal and online service provider based in New York City. It is a brand marketed by the current incarnation of Yahoo! Inc. ...
; Bob McDonald, CEO of Procter & Gamble
The Procter & Gamble Company (P&G) is an American multinational consumer goods corporation headquartered in Cincinnati, Ohio, founded in 1837 by William Procter and James Gamble. It specializes in a wide range of personal health/consumer he ...
who was later nominated to be the Secretary of Veteran Affairs; Alex Gorsky, CEO of Johnson & Johnson; Keith McLoughlin, President and CEO of Electrolux
Electrolux AB () is a Swedish multinational home appliance manufacturer, headquartered in Stockholm. It is consistently ranked the world's second largest appliance maker by units sold, after Whirlpool.
Electrolux products sell under a variety ...
, Jeffrey W. Martin, CEO of Sempra Energy
Sempra is a North American energy infrastructure company based in San Diego, California. The company is one of the largest utility holding companies in the United States with roughly 40 million consumers. Sempra's focus is on electric and natura ...
, and Alden Partridge
Alden Partridge, (February 12, 1785 - January 17, 1854) was an American author, legislator, officer, surveyor, an early superintendent of the United States Military Academy at West Point, New York and a controversial pioneer in U.S. military ...
, founder of Norwich University
Norwich University – The Military College of Vermont is a private senior military college in Northfield, Vermont. It is the oldest private and senior military college in the United States and offers bachelor's and master's degrees on-campu ...
. West Point's contributions to sport include three Heisman Trophy
The Heisman Memorial Trophy (usually known colloquially as the Heisman Trophy or The Heisman) is awarded annually to the most outstanding player in college football. Winners epitomize great ability combined with diligence, perseverance, and har ...
winners: Glenn Davis, Doc Blanchard, and Pete Dawkins. West Point has produced many high government officials, including Brent Scowcroft, the National Security Advisor A national security advisor serves as the chief advisor to a national government on matters of security. The advisor is not usually a member of the government's cabinet but is usually a member of various military or security councils.
National sec ...
under presidents Gerald Ford
Gerald Rudolph Ford Jr. ( ; born Leslie Lynch King Jr.; July 14, 1913December 26, 2006) was an American politician who served as the 38th president of the United States from 1974 to 1977. He was the only president never to have been elected ...
and George H. W. Bush, and Eric Shinseki
Eric Ken Shinseki (; born November 28, 1942) is a retired United States Army general who served as the seventh United States Secretary of Veterans Affairs (2009–2014). His final United States Army post was as the 34th Chief of Staff of the Arm ...
, former Secretary of Veterans Affairs under President Barack Obama
Barack Hussein Obama II ( ; born August 4, 1961) is an American politician who served as the 44th president of the United States from 2009 to 2017. A member of the Democratic Party (United States), Democratic Party, Obama was the first Af ...
. West Point graduate Frank Medina organized and led the nationwide campaign that brought the Congressional Gold Medal
The Congressional Gold Medal is an award bestowed by the United States Congress. It is Congress's highest expression of national appreciation for distinguished achievements and contributions by individuals or institutions. The congressional pract ...
to the 65th Infantry Regiment, also known as the Borinqueneers.
Among American universities, the academy is fifth on the list of total winners for Rhodes Scholarships, seventh for Marshall Scholarships
The Marshall Scholarship is a postgraduate scholarship for "intellectually distinguished young Americans ndtheir country's future leaders" to study at any university in the United Kingdom. It is widely considered one of the most prestigious ...
and fourth on the list of Hertz Fellowships. The official alumni association of West Point is the West Point Association of Graduates (WPAOG or AOG), headquartered at Herbert Hall.
West Point Garrison and Stewart Army Subpost
As an active-duty U.S. Army installation, there are several regular Army units that provide support for the USMA and the West Point installation. The U.S. Army Garrison includes a Headquarters and Headquarters Company, Provost Marshal and Military Police, Religious Program Support, Keller Army Community Hospital, the West Point Dental Activity, the USMA Band (a regular Army band—USMA cadets are not members of the USMA band), and the Directorate of Human Resources (DHR). The DHR is the higher headquarters for: Military Personnel Division (MPD), Army Continuing Education System (ACES), Administrative Services Division (ASD) and the Army Substance Abuse Program (ASAP). The 1st Battalion, 1st Infantry Regiment (1–1 INF) and the 2d Army Aviation Detachment, both stationed on nearby Stewart Army Subpost, provide military training and aviation support to the USMA and the West Point Garrison. Additionally, active duty Army support, such as recent field artillery training conducted at Camp Buckner in July 2017, is sometimes provided by the10th Mountain Division
The 10th Mountain Division (Light Infantry) is a light infantry division in the United States Army based at Fort Drum, New York. Formerly designated as a mountain warfare unit, the division was the only one of its size in the US military to rec ...
, based at Fort Drum, NY.
See also
*United States Military Academy grounds and facilities
The United States Military Academy (West Point) and grounds were declared a National Historic Landmark in 1960 and due to the Revolutionary War history and the age and historic significance of the academy itself. The majority of the buildi ...
*List of monuments at the United States Military Academy
The United States Military Academy (USMA) is a federal service academy located at West Point, New York that educates and commissions officers for the United States Army. The Academy was formally founded in 1802 and graduated its first class in ...
*Kosciuszko's Garden
Kosciuszko's Garden is a small retreat garden built by Tadeusz Kosciuszko on the side of a cliff overlooking the Hudson River at West Point, New York. First constructed in 1778, it still offers visitors and cadets a place of quiet tranquility dur ...
*Army University
The Army University is a professional military education university system of the United States Army
The United States Army (USA) is the land service branch of the United States Armed Forces. It is one of the eight U.S. uniformed ser ...
*U.S. Naval Academy
The United States Naval Academy (US Naval Academy, USNA, or Navy) is a federal service academy in Annapolis, Maryland. It was established on 10 October 1845 during the tenure of George Bancroft as Secretary of the Navy. The Naval Academy is ...
* U.S. Air Force Academy
* U.S. Coast Guard Academy
* U.S. Merchant Marine Academy
*Redoubt Four (West Point)
Redoubt Four was a supporting defensive position of Fort Putnam during the Revolutionary War defensive network at West Point. It was constructed under the command of Tadeusz Kosciuszko in 1778-1779. During the war, it was a key defensive overwa ...
*West Point Cadets' Sword
The West Point Cadets' Sword is issued to cadet officers of the United States Military Academy at West Point, New York for wear when the uniform is designated as "under arms," to include formal functions, drill, parades, inspections and graduatio ...
*West Point Band
The West Point Band (also known as the U.S. Military Academy Band or USMA Band) is the U.S. Army's oldest active band and the oldest unit at the United States Military Academy, traces its roots to the American Revolutionary War. At that time, fif ...
* The Jazz Knights
Notes
References
Citations
Sources
* * * On integrating women * Betros, Lance. ''Carved from Granite: West Point since 1902'' (Texas A&M University Press, 2012), 458 pp. * * * * * * * *Mahon, John K. (1967). ''History of the Second Seminole War 1835–1842, Revised Edition''. University of Florida Press * * * * * * * *External links
*Army Athletics website
() {{authority control 1802 establishments in New York (state) Educational institutions established in 1802 Forts in New York (state) Forts on the National Register of Historic Places in New York (state) Historic Civil Engineering Landmarks Military academies Military academies of the United States Military and war museums in New York (state) National Historic Landmarks in New York (state) New York (state) in the American Revolution Patriot League Tourist attractions in Orange County, New York U.S. Route 9W United States Army Direct Reporting Units United States Army museums United States Army posts United States Army schools Universities and colleges in New York (state) National Register of Historic Places in Orange County, New York American Revolution on the National Register of Historic Places United States military service academies United States senior military colleges