West Belarus on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Western Belorussia or Western Belarus ( be, Заходняя Беларусь, translit=Zachodniaja Bielaruś; pl, Zachodnia Białoruś; russian: Западная Белоруссия, translit=Zapadnaya Belorussiya) is a historical region of modern-day
 The territories of contemporary Belarus, Poland, Ukraine, and the Baltic states were a major theatre of operations during World War I; all the while, the
The territories of contemporary Belarus, Poland, Ukraine, and the Baltic states were a major theatre of operations during World War I; all the while, the
 As soon as the Soviet-German peace treaty was signed in March 1918, the newly formed
As soon as the Soviet-German peace treaty was signed in March 1918, the newly formed
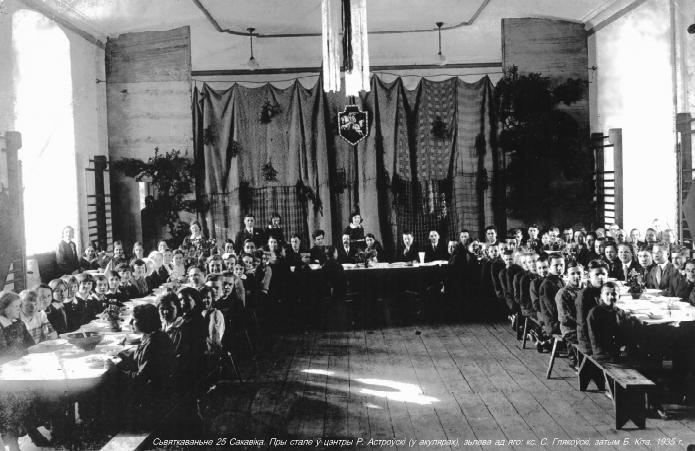 Compared to the (larger) Ukrainian minority living in Poland, Belarusians were much less politically aware and active. The largest Belarusian political organization was the
Compared to the (larger) Ukrainian minority living in Poland, Belarusians were much less politically aware and active. The largest Belarusian political organization was the
Belarus
Belarus,, , ; alternatively and formerly known as Byelorussia (from Russian ). officially the Republic of Belarus,; rus, Республика Беларусь, Respublika Belarus. is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by R ...
which belonged to the Second Polish Republic
The Second Polish Republic, at the time officially known as the Republic of Poland, was a country in Central and Eastern Europe that existed between 1918 and 1939. The state was established on 6 November 1918, before the end of the First Worl ...
during the interwar period
In the history of the 20th century, the interwar period lasted from 11 November 1918 to 1 September 1939 (20 years, 9 months, 21 days), the end of the First World War to the beginning of the Second World War. The interwar period was relati ...
. For twenty years before the 1939 invasion of Poland
The invasion of Poland (1 September – 6 October 1939) was a joint attack on the Republic of Poland by Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union which marked the beginning of World War II. The German invasion began on 1 September 1939, one week aft ...
, it was the northern part of the Polish Kresy
Eastern Borderlands ( pl, Kresy Wschodnie) or simply Borderlands ( pl, Kresy, ) was a term coined for the eastern part of the Second Polish Republic during the History of Poland (1918–1939), interwar period (1918–1939). Largely agricultural ...
macroregion A macroregion is a geopolitical subdivision that encompasses several traditionally or politically defined regions or countries. The meaning may vary, with the common denominator being cultural, economical, historical or social similarity within a ma ...
. Following the end of World War II in Europe
The final battle of the European Theatre of World War II continued after the definitive overall surrender of Nazi Germany to the Allies, signed by Field marshal Wilhelm Keitel on 8 May 1945 in Karlshorst, Berlin. After German dictator Adolf ...
, most of Western Belorussia was ceded to the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
by the Allies, while some of it, including Białystok
Białystok is the largest city in northeastern Poland and the capital of the Podlaskie Voivodeship. It is the tenth-largest city in Poland, second in terms of population density, and thirteenth in area.
Białystok is located in the Białystok U ...
, was given to the Polish People's Republic
The Polish People's Republic ( pl, Polska Rzeczpospolita Ludowa, PRL) was a country in Central Europe that existed from 1947 to 1989 as the predecessor of the modern Republic of Poland. With a population of approximately 37.9 million near ...
. Until the dissolution of the Soviet Union
The dissolution of the Soviet Union, also negatively connoted as rus, Разва́л Сове́тского Сою́за, r=Razvál Sovétskogo Soyúza, ''Ruining of the Soviet Union''. was the process of internal disintegration within the Sov ...
in 1991, Western Belorussia formed the western part of the Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic (BSSR). Today, it constitutes the west of modern Belarus.
Created by the USSR after the conquest of Poland, the new western provinces of Byelorussian SSR acquired from Poland included Baranavichy
Baranavichy ( ; be, Бара́навічы, Łacinka: , ; russian: Бара́новичи; yi, באַראַנאָוויטש; pl, Baranowicze) is a city in the Brest Region of western Belarus, with a population (as of 2019) of 179,000. It is no ...
, Belastok, Brest, Vileyka
Vileyka ( officially transliterated as Viliejka, be, Віле́йка , also ''Вялейка''; russian: Вилейка; lt, Vileika; pl, Wilejka) is a city in Belarus and the administrative center of the Vileyka District of Minsk Region. It i ...
and the Pinsk
Pinsk ( be, Пі́нск; russian: Пи́нск ; Polish: Pińsk; ) is a city located in the Brest Region of Belarus, in the Polesia region, at the confluence of the Pina River and the Pripyat River. The region was known as the Marsh of Pinsk a ...
Regions. They were reorganized one more time after the Soviet liberation of Belarus into the contemporary western provinces of Belarus which include all of Grodno
Grodno (russian: Гродно, pl, Grodno; lt, Gardinas) or Hrodna ( be, Гродна ), is a city in western Belarus. The city is located on the Neman River, 300 km (186 mi) from Minsk, about 15 km (9 mi) from the Polish b ...
and Brest voblasts, as well as parts of today's Minsk
Minsk ( be, Мінск ; russian: Минск) is the capital and the largest city of Belarus, located on the Svislach and the now subterranean Niamiha rivers. As the capital, Minsk has a special administrative status in Belarus and is the adm ...
and Vitsebsk
Vitebsk or Viciebsk (russian: Витебск, ; be, Ві́цебск, ; , ''Vitebsk'', lt, Vitebskas, pl, Witebsk), is a city in Belarus. The capital of the Vitebsk Region, it has 366,299 inhabitants, making it the country's fourth-largest ci ...
voblasts. Vilnius
Vilnius ( , ; see also other names) is the capital and largest city of Lithuania, with a population of 592,389 (according to the state register) or 625,107 (according to the municipality of Vilnius). The population of Vilnius's functional u ...
was returned by the USSR to the Republic of Lithuania
A republic () is a "state in which power rests with the people or their representatives; specifically a state without a monarchy" and also a "government, or system of government, of such a state." Previously, especially in the 17th and 18th ...
which soon after that became the Lithuanian SSR
The Lithuanian Soviet Socialist Republic (Lithuanian SSR; lt, Lietuvos Tarybų Socialistinė Respublika; russian: Литовская Советская Социалистическая Республика, Litovskaya Sovetskaya Sotsialistiche ...
.
Background
 The territories of contemporary Belarus, Poland, Ukraine, and the Baltic states were a major theatre of operations during World War I; all the while, the
The territories of contemporary Belarus, Poland, Ukraine, and the Baltic states were a major theatre of operations during World War I; all the while, the Bolshevik Coup
The October Revolution,. officially known as the Great October Socialist Revolution. in the Soviet Union, also known as the Bolshevik Revolution, was a revolution in Russia led by the Bolshevik Party of Vladimir Lenin that was a key mom ...
overturned the interim Russian Provisional Government
The Russian Provisional Government ( rus, Временное правительство России, Vremennoye pravitel'stvo Rossii) was a provisional government of the Russian Republic, announced two days before and established immediately ...
and formed Soviet Russia
The Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic, Russian SFSR or RSFSR ( rus, Российская Советская Федеративная Социалистическая Республика, Rossíyskaya Sovétskaya Federatívnaya Soci ...
. The Bolsheviks withdrew from the war with the Central Powers
The Central Powers, also known as the Central Empires,german: Mittelmächte; hu, Központi hatalmak; tr, İttifak Devletleri / ; bg, Централни сили, translit=Tsentralni sili was one of the two main coalitions that fought in ...
by signing the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk
The Treaty of Brest-Litovsk (also known as the Treaty of Brest in Russia) was a separate peace treaty signed on 3 March 1918 between Russia and the Central Powers (Germany, Austria-Hungary, Bulgaria, and the Ottoman Empire), that ended Russia ...
, and ceded Belarus to Germany for the next eight and a half months. The German high command used this window of opportunity to transfer its troops to the Western Front for the 1918 Spring Offensive, leaving behind a power vacuum
In political science and political history, the term power vacuum, also known as a power void, is an analogy between a physical vacuum to the political condition "when someone in a place of power, has lost control of something and no one has repla ...
. The non-Russians inhabiting the lands ceded by the Soviets to the German Empire, saw the treaty as an opportunity to set up independent states under the German umbrella. Three weeks after the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk was signed on 3 March 1918, the newly formed Belarusian Central Council founded the Belarusian People's Republic
The Belarusian People's Republic (BNR; be, Беларуская Народная Рэспубліка, Bielaruskaja Narodnaja Respublika, ), or Belarusian Democratic Republic, was a state proclaimed by the Council of the Belarusian Democratic R ...
. The idea was rejected by the Germans, the Bolsheviks
The Bolsheviks (russian: Большевики́, from большинство́ ''bol'shinstvó'', 'majority'),; derived from ''bol'shinstvó'' (большинство́), "majority", literally meaning "one of the majority". also known in English ...
and the Americans. Woodrow Wilson
Thomas Woodrow Wilson (December 28, 1856February 3, 1924) was an American politician and academic who served as the 28th president of the United States from 1913 to 1921. A member of the Democratic Party, Wilson served as the president of ...
rejected it, because the Americans intended to protect the territorial integrity
Territorial integrity is the principle under international law that gives the right to sovereign states to defend their borders and all territory in them of another state. It is enshrined in Article 2(4) of the UN Charter and has been recognized ...
of European Russia
European Russia (russian: Европейская Россия, russian: европейская часть России, label=none) is the western and most populated part of Russia. It is geographically situated in Europe, as opposed to the co ...
.
The fate of the region was not settled for the following three and a half years. The Polish–Soviet War
The Polish–Soviet War (Polish–Bolshevik War, Polish–Soviet War, Polish–Russian War 1919–1921)
* russian: Советско-польская война (''Sovetsko-polskaya voyna'', Soviet-Polish War), Польский фронт (' ...
which erupted in 1919, was particularly bitter; it ended with the Peace of Riga
The Peace of Riga, also known as the Treaty of Riga ( pl, Traktat Ryski), was signed in Riga on 18 March 1921, among Poland, Soviet Russia (acting also on behalf of Soviet Belarus) and Soviet Ukraine. The treaty ended the Polish–Soviet War. ...
of 1921. Poland and the Baltic states
The Baltic states, et, Balti riigid or the Baltic countries is a geopolitical term, which currently is used to group three countries: Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania. All three countries are members of NATO, the European Union, the Eurozone, ...
emerged as independent countries bordering the USSR
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nation ...
. The territory of modern-day Belarus was split by the treaty into Western Belorussia ruled by the Polish and the Soviet Eastern Belorussia
East Belarus usually refers to the part of Belarus that was part of the Soviet Union between 1919 and 1939, as opposed to West Belarus that was part of the Second Polish Republic at that time.
The region was known as the Socialist Soviet Republ ...
, with the border town in Mikaszewicze. Notably, the peace treaty was signed with the full active participation of the Belarusian delegation on the Soviet side. In paragraph 3, Poland abandoned all rights and claims to the territories of Soviet Belarus, while Soviet Russia abandoned all rights and claims to Polish Western Belarus.
Rada of the Belarusian Democratic Republic in Exile
 As soon as the Soviet-German peace treaty was signed in March 1918, the newly formed
As soon as the Soviet-German peace treaty was signed in March 1918, the newly formed Rada of the Belarusian Democratic Republic
The Rada of the Belarusian Democratic Republic ( be, Рада Беларускай Народнай Рэспублікі, Рада БНР, Rada BNR) was the governing body of the Belarusian Democratic Republic. Since 1919, the Rada BNR has be ...
laid territorial claims to Belarus based on areas specified in the Third Constituent Charter unilaterally as inhabited by the Belarusian majority. The same Rada charter also declared that the Treaty of Brest-Litowsk of March 1918 was invalid because it was signed by foreign governments partitioning territories that were not theirs.
In the Second Constituent Charter, the Rada abolished the right to private ownership of land (paragraph 7) in line with the Communist Manifesto
''The Communist Manifesto'', originally the ''Manifesto of the Communist Party'' (german: Manifest der Kommunistischen Partei), is a political pamphlet written by German philosophers Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels. Commissioned by the Commu ...
. Meanwhile, by 1919, the Bolsheviks took control over large parts of Belarus and forced the Belarusian Rada into exile in Germany. The Bolsheviks formed the Socialist Soviet Republic of Byelorussia
The Socialist Soviet Republic of Byelorussia or Soviet Socialist Republic of Belarus (SSRB; be, Савецкая Сацыялістычная Рэспубліка Беларусь, Savieckaja Sacyjalistyčnaja Respublika Biełaruś; russian: � ...
during the war with Poland on roughly the same territory claimed by the Belarusian Republic.
The League of Nations
The League of Nations (french: link=no, Société des Nations ) was the first worldwide intergovernmental organisation whose principal mission was to maintain world peace. It was founded on 10 January 1920 by the Paris Peace Conference th ...
ratified the new Polish-Soviet border. The peace agreement remained in place throughout the interwar period. The borders established between the two countries remained in force until World War II and 17 September 1939 Soviet invasion of Poland
The Soviet invasion of Poland was a military operation by the Soviet Union without a formal declaration of war. On 17 September 1939, the Soviet Union invaded Poland from the east, 16 days after Nazi Germany invaded Poland from the west. Subse ...
. On Joseph Stalin
Joseph Vissarionovich Stalin (born Ioseb Besarionis dze Jughashvili; – 5 March 1953) was a Georgian revolutionary and Soviet political leader who led the Soviet Union from 1924 until his death in 1953. He held power as General Secreta ...
's insistence, the borders were redrawn in the Conferences of Yalta
Yalta (: Я́лта) is a resort city on the south coast of the Crimean Peninsula surrounded by the Black Sea. It serves as the administrative center of Yalta Municipality, one of the regions within Crimea. Yalta, along with the rest of Crimea ...
and Potsdam
Potsdam () is the capital and, with around 183,000 inhabitants, largest city of the German state of Brandenburg. It is part of the Berlin/Brandenburg Metropolitan Region. Potsdam sits on the River Havel, a tributary of the Elbe, downstream of ...
.
Second Polish Republic
"Despite Soviet efforts at sealing the border ith Poland peasants – refugees from the BSSR – crossed into Poland in the tens of thousands, wrote Per Anders Rudling. According to thePolish census of 1921
The Polish census of 1921 or First General Census in Poland ( pl, Pierwszy Powszechny Spis Ludności) was the first census in the Second Polish Republic, performed on September 30, 1921 by the Main Bureau of Statistics ( Główny Urząd Statystycz ...
, there were around 1 million Belarusians in the country. Some estimated the number of Belarusians in Poland at that time to be perhaps 1.7 million,Żarnowski, p. 373. or even up to . Following the Peace of Riga, thousands of Poles settled in the area, many of them (including veterans of armed struggle for Poland's independence) were given land by the government.
In his negotiations with Belarusian leaders in Vilnius, Józef Piłsudski
), Vilna Governorate, Russian Empire (now Lithuania)
, death_date =
, death_place = Warsaw, Poland
, constituency =
, party = None (formerly PPS)
, spouse =
, children = Wa ...
rejected the call for Western Belorussian independence. In December 1919 the Rada was dissolved by Poland, while by early January 1920 a new body was formed, the ''Rada Najwyższa'', without aspirations for independence, but with proposed cultural, social and educational functions. Józef Piłsudski negotiated with the Western Belorussian leadership, but eventually abandoned the ideas of Intermarium
Intermarium ( pl, Międzymorze, ) was a post- World War I geopolitical plan conceived by Józef Piłsudski to unite former Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth lands within a single polity. The plan went through several iterations, some of which anti ...
, his own proposed federation of partially self-governing states on the lands of the former Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, formally known as the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and, after 1791, as the Commonwealth of Poland, was a bi-confederal state, sometimes called a federation, of Poland and Lithuania rul ...
.
In the 1922 Polish legislative election, the Belarusian party in the Bloc of National Minorities obtained 14 seats in the Polish parliament
The parliament of Poland is the bicameral legislature of Poland. It is composed of an upper house (the Senate) and a lower house (the Sejm). Both houses are accommodated in the ''Sejm'' complex in Warsaw. The Constitution of Poland does not re ...
(11 of them in the Sejm). In the spring of 1923, Polish prime minister
A prime minister, premier or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. Under those systems, a prime minister is ...
Władysław Sikorski
Władysław Eugeniusz Sikorski (; 20 May 18814 July 1943) was a Polish military and political leader.
Prior to the First World War, Sikorski established and participated in several underground organizations that promoted the cause for Polish i ...
ordered a report on the situation of the Belarusian minority in Poland. That summer, a new regulation was passed allowing for the Belarusian language
Belarusian ( be, беларуская мова, biełaruskaja mova, link=no, ) is an East Slavic language. It is the native language of many Belarusians and one of the two official state languages in Belarus. Additionally, it is spoken in some ...
to officially be used in courts and schools. Obligatory teaching of the Belarusian language was introduced in all Polish gymnasia in areas inhabited by Belarusians in 1927.
Polonization
The Belarusian population of West Belarus faced activePolonization
Polonization (or Polonisation; pl, polonizacja)In Polish historiography, particularly pre-WWII (e.g., L. Wasilewski. As noted in Смалянчук А. Ф. (Smalyanchuk 2001) Паміж краёвасцю і нацыянальнай ідэя� ...
by the central Polish authorities. The policy pressured Belarusian schooling, discriminated against the Belarusian language, and imposed the Polish national identity on Roman Catholics in Belarus.
In January 1921, the starosta from Wilejka wrote of the popular mood as being one of resignation and apathy among the Western Belorussian peasant
A peasant is a pre-industrial agricultural laborer or a farmer with limited land-ownership, especially one living in the Middle Ages under feudalism and paying rent, tax, fees, or services to a landlord. In Europe, three classes of peasants ...
s, impoverished by food requisitions by the Bolsheviks and the Polish military
The Armed Forces of the Republic of Poland ( pl, Siły Zbrojne Rzeczypospolitej Polskiej, abbreviated ''SZ RP''; popularly called ''Wojsko Polskie'' in Poland, abbreviated ''WP''—roughly, the "Polish Military") are the national armed forces of ...
. He insisted that, although the new Belorussian schools were 'springing up everywhere' in his county, they harbored anti-Polish attitudes.
In 1928 there were 69 schools with Belarusian language in Western Belorussia; the attendance was minimal due in part to lower quality of instruction. The first-ever textbook of Belarusian grammar was written only around 1918. In 1939, over 90% of children in Poland attended school. As elsewhere, the educational systems promoted Polish language there also. Meanwhile, the Belarusian agitators deported to the USSR from Poland were put in prison by the Soviet NKVD
The People's Commissariat for Internal Affairs (russian: Наро́дный комиссариа́т вну́тренних дел, Naródnyy komissariát vnútrennikh del, ), abbreviated NKVD ( ), was the interior ministry of the Soviet Union.
...
as bourgeois nationalists.
Most Polish inhabitants of the region supported the policy of cultural assimilation
Cultural assimilation is the process in which a minority group or culture comes to resemble a society's majority group or assume the values, behaviors, and beliefs of another group whether fully or partially.
The different types of cultural ass ...
of Belarusians as proposed by Dmowski. The polonization drive was inspired and influenced by Dmowski's Polish National Democracy, who advocated refusing Belarusians and Ukrainians the right of free national development. Władysław Studnicki, an influential Polish official, stated that Poland's engagement in the East amounts to a much needed economic colonization
Colonization, or colonisation, constitutes large-scale population movements wherein migrants maintain strong links with their, or their ancestors', former country – by such links, gain advantage over other inhabitants of the territory. When ...
. Belarusian nationalist media was pressured and censored
Censorship is the suppression of speech, public communication, or other information. This may be done on the basis that such material is considered objectionable, harmful, sensitive, or "inconvenient". Censorship can be conducted by governments ...
by the Polish authorities.
Belarusians were divided along religious lines with roughly 70% being Orthodox and 30% Roman Catholic. According to Russian sources, discrimination was targeting assimilation of Eastern Orthodox Belarusians. The Polish church authorities promoted Polish
Polish may refer to:
* Anything from or related to Poland, a country in Europe
* Polish language
* Poles, people from Poland or of Polish descent
* Polish chicken
*Polish brothers (Mark Polish and Michael Polish, born 1970), American twin scree ...
in Orthodox services, and initiated the creation of the ''Polish Orthodox Societies'' in four cities including Slonim
Slonim ( be, Сло́нім, russian: Сло́ним, lt, Slanimas, lv, Sloņima, pl, Słonim, yi, סלאָנים, ''Slonim'') is a city in Grodno Region, Belarus, capital of the Slonimski rajon. It is located at the junction of the Ščar ...
, Białystok
Białystok is the largest city in northeastern Poland and the capital of the Podlaskie Voivodeship. It is the tenth-largest city in Poland, second in terms of population density, and thirteenth in area.
Białystok is located in the Białystok U ...
, Vawkavysk
Vawkavysk ( be, Ваўкавы́ск, ; russian: Волковы́ск; pl, Wołkowysk; lt, Valkaviskas; yi, וואלקאוויסק; names in other languages) is one of the oldest towns in southwestern Belarus and the capital of the Vawkavysk ...
, and Novogrodek. The Belarusian Roman Catholic priest Fr. Vincent Hadleŭski who promoted Belarusian in church, and Belarusian national awareness, was under pressure by his Polish counterparts. The Polish Catholic Church in Western Belorussia issued documents to priests about the usage of the Belarusian language rather than Polish language in Churches and Catholic Sunday Schools. The Warsaw-published instruction of the Polish Catholic Church from 1921 criticized priests preaching in Belarusian at the Catholic masses.
''Hramada''
 Compared to the (larger) Ukrainian minority living in Poland, Belarusians were much less politically aware and active. The largest Belarusian political organization was the
Compared to the (larger) Ukrainian minority living in Poland, Belarusians were much less politically aware and active. The largest Belarusian political organization was the Belarusian Peasants' and Workers' Union
The Belarusian Peasants' and Workers' Union or the Hramada ( be, Беларуская Сялянска-Работніцкая Грамада ( Lacinka: ''Biełaruskaja Sialanska-Rabotnickaja Hramada''), pl, Białoruska Włościańsko-Robotnicza H ...
, also referred to as the ''Hramada''. Hramada received logistical help from the Soviet Union and the Communist International
The Communist International (Comintern), also known as the Third International, was a Soviet-controlled international organization founded in 1919 that advocated world communism. The Comintern resolved at its Second Congress to "struggle by ...
and served as a cover for the radical and subversive Communist Party of Western Belorussia. It was therefore banned by the Polish authorities, its leaders sentenced to various terms in prison and then deported to the USSR, where they were killed by the Soviet regime.
Tensions between the increasingly nationalistic Polish government and various increasingly separatist ethnic minorities continued to grow, and the Belarusian minority was no exception. Likewise, according to Marek Jan Chodakiewicz
Marek Jan Chodakiewicz (born July 15, 1962) is a Polish-American historian specializing in Central European history of the 19th and 20th centuries.Marek Jan Chodakiewicz, 2012, ''Intermarium: The Land between the Black and Baltic Seas'', Transaction Publishers, pp. 81–82. During the
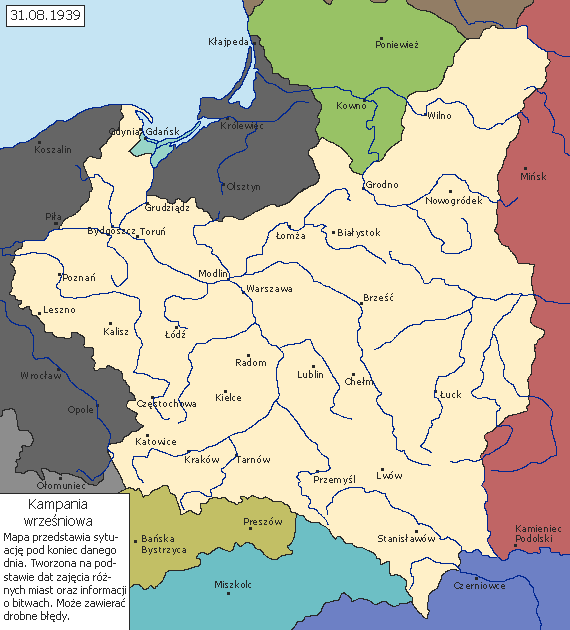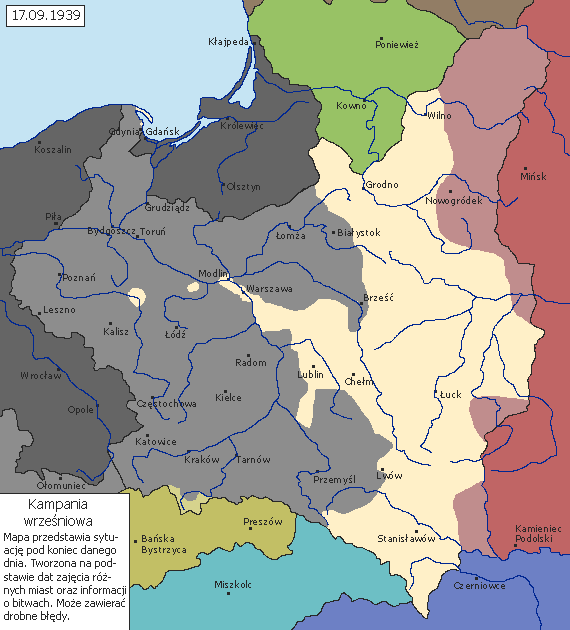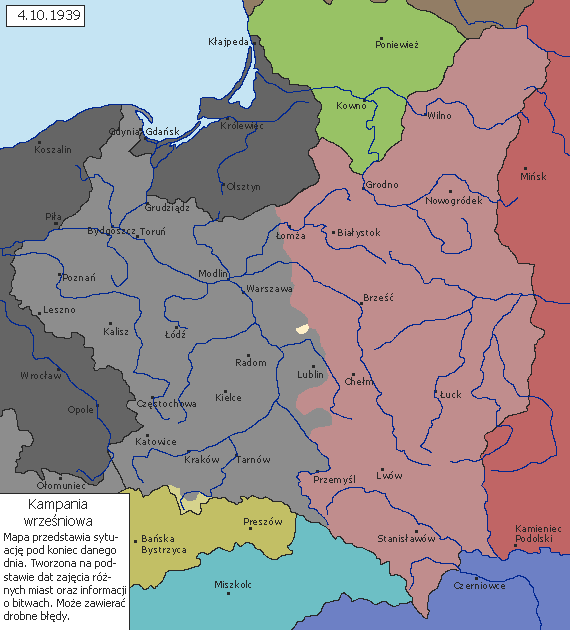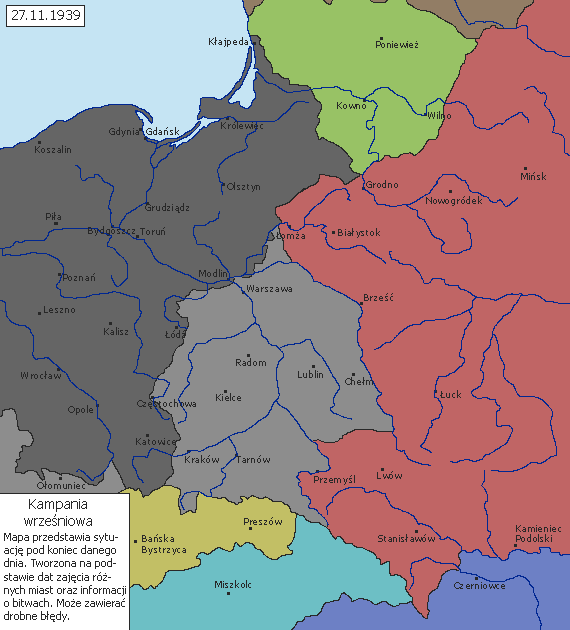 Soon after the Nazi-Soviet
Soon after the Nazi-Soviet
/ref>
 The Soviets quickly began confiscating, nationalizing, and redistributing all private and state-owned property. During the two years following the annexation, the Soviets arrested approximately 100,000 Polish citizens across Kresy. Due to a lack of access to the secret Soviet and Belorussian archives, for many years after the war, the estimates of the number of Polish citizens deported to Siberia from the areas of Western Belorussia, as well as the number who perished under Soviet rule, were only estimated. In August 2009, on the occasion of the 70th anniversary of the Soviet invasion, the authoritative Polish Institute of National Remembrance announced that its researchers reduced the estimate of the number of people deported to Siberia to 320,000 in total. Some 150,000 Polish citizens perished under the Soviet rule.
The Soviets quickly began confiscating, nationalizing, and redistributing all private and state-owned property. During the two years following the annexation, the Soviets arrested approximately 100,000 Polish citizens across Kresy. Due to a lack of access to the secret Soviet and Belorussian archives, for many years after the war, the estimates of the number of Polish citizens deported to Siberia from the areas of Western Belorussia, as well as the number who perished under Soviet rule, were only estimated. In August 2009, on the occasion of the 70th anniversary of the Soviet invasion, the authoritative Polish Institute of National Remembrance announced that its researchers reduced the estimate of the number of people deported to Siberia to 320,000 in total. Some 150,000 Polish citizens perished under the Soviet rule.
Participation of the local police in the extermination of Jews
(Участие местной полиции в уничтожении евреев, в акциях против партизан и местного населения.); (in) Местная вспомогательная полиция на территории Беларуси, июль 1941 — июль 1944 гг. (The auxiliary police in Belarus, July 1941 - July 1944). Known to the Germans as the ''
A Forgotten Odyssey
2001 Lest We Forget Productions.
Społeczeństwo Drugiej Rzeczypospolitej 1918-1939
' (in Polish), Warszawa. {{Authority control Generalbezirk Weißruthenien Geographic history of Poland Historical regions in Belarus Historical regions in Lithuania Second Polish Republic *
Great Purge
The Great Purge or the Great Terror (russian: Большой террор), also known as the Year of '37 (russian: 37-й год, translit=Tridtsat sedmoi god, label=none) and the Yezhovshchina ('period of Yezhov'), was Soviet General Secret ...
, the Polish National District at Dzyarzhynsk
Dzyarzhynsk or Dzerzhinsk, formerly Koidanova or Koydanava ( be, Дзяржы́нск, Dziaržynsk, formerly , ; russian: Дзержи́нск, Dzerzhinsk, formerly , ; pl, Kojdanów; yi, קוידאַנאָוו, Koydanov; lt, Kaidanava), in t ...
was disbanded and the Soviet NKVD undertook the so-called "Polish Operation" (from approximately August 25, 1937, to November 15, 1938) – where the Poles in East Belorussia,i.e. BSSR, were deported and executed. The operation caused the deaths of to 250,000 people – out of an official ethnic Polish population of 636,000 – as a result of political murder, disease
A disease is a particular abnormal condition that negatively affects the structure or function (biology), function of all or part of an organism, and that is not immediately due to any external injury. Diseases are often known to be medica ...
or starvation
Starvation is a severe deficiency in caloric energy intake, below the level needed to maintain an organism's life. It is the most extreme form of malnutrition. In humans, prolonged starvation can cause permanent organ damage and eventually, ...
. Amongst these, at least 111,091 members of the Polish minority were shot by NKVD troika
NKVD troika or Special troika (russian: особая тройка, osobaya troyka), in Soviet history, were the People's Commissariat of Internal Affairs (NKVD which would later be the beginning of the KGB) made up of three officials who issued ...
. According to Bogdan Musiał, many were murdered in prison executions. In addition, several hundred thousand ethnic Poles from Belarus and Ukraine were deported to other parts of the Soviet Union.
The Soviets also promoted the Soviet-controlled BSSR as formally autonomous to attract Belarusians living in Poland. This image was attractive to many Western Belorussian national leaders, and some of them, like Frantsishak Alyakhnovich or Uładzimir Žyłka emigrated from Poland to the BSSR, but very soon became victims of Soviet repression.
Soviet invasion of Poland, 1939
 Soon after the Nazi-Soviet
Soon after the Nazi-Soviet invasion of Poland
The invasion of Poland (1 September – 6 October 1939) was a joint attack on the Republic of Poland by Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union which marked the beginning of World War II. The German invasion began on 1 September 1939, one week aft ...
following the Nazi–Soviet Pact, the area of Western Belorussia was formally annexed into the Belarusian Soviet Socialist Republic
The Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic (BSSR, or Byelorussian SSR; be, Беларуская Савецкая Сацыялістычная Рэспубліка, Bielaruskaja Savieckaja Sacyjalistyčnaja Respublika; russian: Белор� ...
(BSSR). The Soviet secret police NKVD
The People's Commissariat for Internal Affairs (russian: Наро́дный комиссариа́т вну́тренних дел, Naródnyy komissariát vnútrennikh del, ), abbreviated NKVD ( ), was the interior ministry of the Soviet Union.
...
, aided by the Red Army, organized staged elections which were decided in the atmosphere of intimidation and state terror. The Soviet occupational administration held the elections on October 22, 1939, less than two weeks after the invasion. The citizens were threatened repeatedly that their deportations to Siberia were imminent. The ballot envelopes were numbered to remain traceable and usually handed over already sealed. The referendum was rigged. By design, the candidates were unknown to their constituencies which were brought to the voting stations by armed guards. The so-called Elections to the People's Assemblies of Western Ukraine and Western Belorussia were conducted in Russian.
On October 30, the People's Assembly session held in Belastok ( Polish Białystok) affirmed the Soviet decision to join the Belarusian Soviet Socialist Republic
The Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic (BSSR, or Byelorussian SSR; be, Беларуская Савецкая Сацыялістычная Рэспубліка, Bielaruskaja Savieckaja Sacyjalistyčnaja Respublika; russian: Белор� ...
(BSSR) with the USSR. The petition was officially accepted by the Supreme Soviet of the USSR
The Supreme Soviet of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics ( rus, Верховный Совет Союза Советских Социалистических Республик, r=Verkhovnyy Sovet Soyuza Sovetskikh Sotsialisticheskikh Respubl ...
on November 2 and by the Supreme Soviet of the BSSR on November 12, 1939. From then on, all citizens of Poland but also born in Poland would find themselves living in the Byelorussian SSR as the Soviet subjects, without the recognition of their Polish citizenship.
The Soviet propaganda portrayed the Soviet invasion of Poland
The Soviet invasion of Poland was a military operation by the Soviet Union without a formal declaration of war. On 17 September 1939, the Soviet Union invaded Poland from the east, 16 days after Nazi Germany invaded Poland from the west. Subse ...
as the "reunion of Western Belorussia and Ukraine". Many ethnic Belarusians and Jews welcomed unification with the BSSR. Mostly wealthy groups of citizens changed their attitude after experiencing firsthand the style of the Soviet system.Norman Davies
Ivor Norman Richard Davies (born 8 June 1939) is a Welsh-Polish historian, known for his publications on the history of Europe, Poland and the United Kingdom. He has a special interest in Central and Eastern Europe and is UNESCO Professor ...
, ''God's Playground
''God's Playground: A History of Poland'' is a history book in two volumes written by Norman Davies, covering a 1000-year history of Poland. Volume 1: ''The origins to 1795'', and Volume 2: ''1795 to the present'' first appeared as the Oxford Cl ...
'' (Polish edition), second tome, p.512-513.Stosunki polsko-białoruskie pod okupacją sowiecką (1939-1941)/ref>
Deportations, arrests, and the reign of terror
 The Soviets quickly began confiscating, nationalizing, and redistributing all private and state-owned property. During the two years following the annexation, the Soviets arrested approximately 100,000 Polish citizens across Kresy. Due to a lack of access to the secret Soviet and Belorussian archives, for many years after the war, the estimates of the number of Polish citizens deported to Siberia from the areas of Western Belorussia, as well as the number who perished under Soviet rule, were only estimated. In August 2009, on the occasion of the 70th anniversary of the Soviet invasion, the authoritative Polish Institute of National Remembrance announced that its researchers reduced the estimate of the number of people deported to Siberia to 320,000 in total. Some 150,000 Polish citizens perished under the Soviet rule.
The Soviets quickly began confiscating, nationalizing, and redistributing all private and state-owned property. During the two years following the annexation, the Soviets arrested approximately 100,000 Polish citizens across Kresy. Due to a lack of access to the secret Soviet and Belorussian archives, for many years after the war, the estimates of the number of Polish citizens deported to Siberia from the areas of Western Belorussia, as well as the number who perished under Soviet rule, were only estimated. In August 2009, on the occasion of the 70th anniversary of the Soviet invasion, the authoritative Polish Institute of National Remembrance announced that its researchers reduced the estimate of the number of people deported to Siberia to 320,000 in total. Some 150,000 Polish citizens perished under the Soviet rule.
The Soviet–German War 1941–1945
The terms of theMolotov–Ribbentrop Pact
The Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact was a non-aggression pact between Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union that enabled those powers to partition Poland between them. The pact was signed in Moscow on 23 August 1939 by German Foreign Minister Joachim von Ri ...
signed earlier in Moscow were soon broken, when the German Army
The German Army (, "army") is the land component of the armed forces of Germany. The present-day German Army was founded in 1955 as part of the newly formed West German ''Bundeswehr'' together with the ''Marine'' (German Navy) and the ''Luftwa ...
entered the Soviet occupation zone
The Soviet Occupation Zone ( or german: Ostzone, label=none, "East Zone"; , ''Sovetskaya okkupatsionnaya zona Germanii'', "Soviet Occupation Zone of Germany") was an area of Germany in Central Europe that was occupied by the Soviet Union as a ...
on June 22, 1941. After Operation Barbarossa
Operation Barbarossa (german: link=no, Unternehmen Barbarossa; ) was the invasion of the Soviet Union by Nazi Germany and many of its Axis allies, starting on Sunday, 22 June 1941, during the Second World War. The operation, code-named afte ...
, most of Western Belorussia became part of the German ''Reichskommissariat Ostland
The Reichskommissariat Ostland (RKO) was established by Nazi Germany in 1941 during World War II. It became the civilian occupation regime in Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, and the western part of Byelorussian SSR. German planning documents initia ...
'' (RKO), as the so-called ''Generalbezirk Weißruthenien
Generalbezirk Weissruthenien (General District White Ruthenia) was one of the four administrative subdivisions of ''Reichskommissariat Ostland'', the 1941-1945 civilian occupation regime established by Nazi Germany for the administration of the th ...
'' (General Region of White Ruthenia). Many ethnic Belarusians supported Nazi Germany. By the end of 1942, sworn Germanophile Ivan Yermachenka formed the pro-Nazi BNS organization with 30,000 members. The Belarusian Auxiliary Police was formed.Alexey Litvin (Алексей Літвін)Participation of the local police in the extermination of Jews
(Участие местной полиции в уничтожении евреев, в акциях против партизан и местного населения.); (in) Местная вспомогательная полиция на территории Беларуси, июль 1941 — июль 1944 гг. (The auxiliary police in Belarus, July 1941 - July 1944). Known to the Germans as the ''
Schutzmannschaft
The ''Schutzmannschaft'' or Auxiliary Police ( "protective, or guard units"; plural: ''Schutzmannschaften'', abbreviated as ''Schuma'') was the collaborationist auxiliary police of native policemen serving in those areas of the Soviet Union and ...
'', the ethnic Belarusian police played an indispensable role in the Holocaust in Belarus
The Holocaust in Belarus is the term that refers to the systematic discrimination and extermination of Jews living in the former Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic which was occupied by Nazi Germany after August 1941 during World War II. ...
, notably during the second wave of the ghetto liquidations, starting in February–March 1942.
In 1945, the Big Three, Great Britain, the United States and the Soviet Union, established new borders for Poland. Most of Western Belarus remained part of the BSSR after the end of World War II in Europe
The final battle of the European Theatre of World War II continued after the definitive overall surrender of Nazi Germany to the Allies, signed by Field marshal Wilhelm Keitel on 8 May 1945 in Karlshorst, Berlin. After German dictator Adolf ...
; only the region around Białystok
Białystok is the largest city in northeastern Poland and the capital of the Podlaskie Voivodeship. It is the tenth-largest city in Poland, second in terms of population density, and thirteenth in area.
Białystok is located in the Białystok U ...
(Belostok) was to be returned to Poland. The Polish population was soon forcibly resettled west. The Western Belorussia, in its entirety, was incorporated into the BSSR.
It was initially planned to move the capital of the BSSR to Vilna
Vilnius ( , ; see also #Etymology and other names, other names) is the capital and List of cities in Lithuania#Cities, largest city of Lithuania, with a population of 592,389 (according to the state register) or 625,107 (according to the munic ...
. However, the same year Joseph Stalin
Joseph Vissarionovich Stalin (born Ioseb Besarionis dze Jughashvili; – 5 March 1953) was a Georgian revolutionary and Soviet political leader who led the Soviet Union from 1924 until his death in 1953. He held power as General Secreta ...
ordered that the city and surrounding region be transferred to Lithuania
Lithuania (; lt, Lietuva ), officially the Republic of Lithuania ( lt, Lietuvos Respublika, links=no ), is a country in the Baltic region of Europe. It is one of three Baltic states and lies on the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea. Lithuania ...
, which some months later was annexed by the Soviet Union and became a new Soviet Republic. Minsk, therefore, remained the capital of the enlarged BSSR. The borders of the BSSR were again altered somewhat after the war (notably the area around the city of Białystok
Białystok is the largest city in northeastern Poland and the capital of the Podlaskie Voivodeship. It is the tenth-largest city in Poland, second in terms of population density, and thirteenth in area.
Białystok is located in the Białystok U ...
(Belastok Voblast
Belastok Voblast or Belostok Oblast ( be, Беластоцкая вобласць, Biełastockaja vobłasć, russian: Белостокская Область, pl, Obwód białostocki) was a short-lived territorial unit in the Belarusian Soviet ...
) was returned to Poland). Still, in general, they coincide with the borders of the modern Republic of Belarus.
Sovietization
The Belarusian political parties and the society in Western Belorussia often lacked information about repressions in the Soviet Union and was under a strong influence of Soviet propaganda. Because of bad economic conditions and national discrimination of Belarusian in Poland, much of the population of Western Belorussia welcomed the annexation by the USSR. However, soon after the annexation of Western Belorussia by the Soviet Union, the Belarusian political activists had no illusions as to the friendliness of the Soviet regime. The population grew less loyal as the economic conditions became even worse and as the new regime carried out mass repressions and deportations that targeted Belarusians as well as ethnic Poles. Immediately after the annexation, the Soviet authorities carried out the nationalization of agricultural land owned by large landowners in Western Belorussia.Collectivization
Collective farming and communal farming are various types of, "agricultural production in which multiple farmers run their holdings as a joint enterprise". There are two broad types of communal farms: agricultural cooperatives, in which member- ...
and the creation of collective farms (kolkhoz
A kolkhoz ( rus, колхо́з, a=ru-kolkhoz.ogg, p=kɐlˈxos) was a form of collective farm in the Soviet Union. Kolkhozes existed along with state farms or sovkhoz., a contraction of советское хозяйство, soviet ownership ...
) was planned to be carried out at a slower pace than in Eastern Belorussia in the 1920s. By 1941, in the western regions of the BSSR, the number of individual farms decreased only by 7%; 1115 collective farms were created. At the same time, pressure and even repressions against larger farmers (called by the Soviet propaganda, kulak
Kulak (; russian: кула́к, r=kulák, p=kʊˈlak, a=Ru-кулак.ogg; plural: кулаки́, ''kulakí'', 'fist' or 'tight-fisted'), also kurkul () or golchomag (, plural: ), was the term which was used to describe peasants who owned ove ...
i) began: the size of agricultural land for one individual farm was limited to 10ha, 12ha and 14ha depending on the quality of the land. It was forbidden to hire workers and lease land.
Under the Soviet occupation, the Western Belorussian citizenry, particularly the Poles, faced a "filtration" procedure by the NKVD apparatus, which resulted in over 100,000 people being forcibly deported to eastern parts of the Soviet Union (e.g. Siberia) in the very first wave of expulsions. In total, during the next two years some 1.7 million Polish citizens were put on freight trains and sent from the Polish Kresy
Eastern Borderlands ( pl, Kresy Wschodnie) or simply Borderlands ( pl, Kresy, ) was a term coined for the eastern part of the Second Polish Republic during the History of Poland (1918–1939), interwar period (1918–1939). Largely agricultural ...
to labour camps in the Gulag
The Gulag, an acronym for , , "chief administration of the camps". The original name given to the system of camps controlled by the GPU was the Main Administration of Corrective Labor Camps (, )., name=, group= was the government agency in ...
.2001 Lest We Forget Productions.
Republic of Belarus
The majority of Poles live in the Western regions, including 230,000 in the Grodno oblast. In addition, Sapotskin and itsselsoviet
Selsoviet ( be, сельсавет, r=sieĺsaviet, tr. ''sieĺsaviet''; rus, сельсовет, p=ˈsʲelʲsɐˈvʲɛt, r=selsovet; uk, сільрада, silrada) is a shortened name for a rural council and for the area governed by such a cou ...
have a Polish majority. The largest Polish organization in Belarus is the Union of Poles in Belarus (''Związek Polaków na Białorusi''), with over 20,000 members.
See also
*Western Ukraine
Western Ukraine or West Ukraine ( uk, Західна Україна, Zakhidna Ukraina or , ) is the territory of Ukraine linked to the former Kingdom of Galicia–Volhynia, which was part of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, the Austrian ...
* Soviet raid on Stołpce
* Border Protection Corps
* Siarhei Prytytski
Notes
References
* * * * * * * * * Żarnowski, Janusz (1973),Społeczeństwo Drugiej Rzeczypospolitej 1918-1939
' (in Polish), Warszawa. {{Authority control Generalbezirk Weißruthenien Geographic history of Poland Historical regions in Belarus Historical regions in Lithuania Second Polish Republic *