
Water supply is the provision of
water
Water (chemical formula ) is an Inorganic compound, inorganic, transparent, tasteless, odorless, and Color of water, nearly colorless chemical substance, which is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living ...
by
public utilities
A public utility company (usually just utility) is an organization that maintains the infrastructure for a public service (often also providing a service using that infrastructure). Public utilities are subject to forms of public control and ...
, commercial organisations, community endeavors or by individuals, usually via a system of pumps and
pipes
Pipe(s), PIPE(S) or piping may refer to:
Objects
* Pipe (fluid conveyance), a hollow cylinder following certain dimension rules
** Piping, the use of pipes in industry
* Smoking pipe
** Tobacco pipe
* Half-pipe and quarter pipe, semi-circula ...
. Public water supply systems are crucial to properly functioning societies. These systems are what supply drinking water to populations around the globe. Aspects of service quality include continuity of supply, water quality and water pressure. The institutional responsibility for water supply is arranged differently in different countries and regions (urban versus rural). It usually includes issues surrounding policy and regulation, service provision and standardization.
The cost of supplying water consists, to a very large extent, of fixed costs (capital costs and personnel costs) and only to a small extent of variable costs that depend on the amount of water consumed (mainly energy and chemicals). Almost all service providers in the world charge tariffs to recover part of their costs.
Water supply is a separate topic from
irrigation
Irrigation (also referred to as watering) is the practice of applying controlled amounts of water to land to help grow crops, landscape plants, and lawns. Irrigation has been a key aspect of agriculture for over 5,000 years and has been devel ...
, the practice and systems of water supply on a larger scale, for a wider variety of purposes, primarily
agriculture
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people t ...
.
Technical overview
Water supply systems get water from a variety of locations after appropriate treatment, including
groundwater
Groundwater is the water present beneath Earth's surface in rock and soil pore spaces and in the fractures of rock formations. About 30 percent of all readily available freshwater in the world is groundwater. A unit of rock or an unconsolidated ...
(
aquifers),
surface water (
lake
A lake is an area filled with water, localized in a basin, surrounded by land, and distinct from any river or other outlet that serves to feed or drain the lake. Lakes lie on land and are not part of the ocean, although, like the much large ...
s and
river
A river is a natural flowing watercourse, usually freshwater, flowing towards an ocean, sea, lake or another river. In some cases, a river flows into the ground and becomes dry at the end of its course without reaching another body of w ...
s), and the sea through
desalination. The
water treatment
Water treatment is any process that improves the quality of water to make it appropriate for a specific end-use. The end use may be drinking, industrial water supply, irrigation, river flow maintenance, water recreation or many other uses, inc ...
steps include, in most cases,
purification, disinfection through
chlorination Chlorination may refer to:
* Chlorination reaction
In chemistry, halogenation is a chemical reaction that entails the introduction of one or more halogens into a compound. Halide-containing compounds are pervasive, making this type of transform ...
and sometimes
fluoridation
Water fluoridation is the controlled adjustment of fluoride to a public water supply solely to reduce tooth decay. Fluoridated water contains fluoride at a level that is effective for preventing cavities; this can occur naturally or by addin ...
. Treated water then either flows by gravity or is pumped to
reservoirs
A reservoir (; from French ''réservoir'' ) is an enlarged lake behind a dam. Such a dam may be either artificial, built to store fresh water or it may be a natural formation.
Reservoirs can be created in a number of ways, including control ...
, which can be elevated such as
water towers or on the ground (for indicators related to the efficiency of
drinking water
Drinking water is water that is used in drink or food preparation; potable water is water that is safe to be used as drinking water. The amount of drinking water required to maintain good health varies, and depends on physical activity level, a ...
distribution see
non-revenue water
Non revenue water (NRW) is water that has been produced and is "lost" before it reaches the customer. Losses can be real losses (through leaks, sometimes also referred to as physical losses) or apparent losses (for example through theft or meteri ...
). Once water is used,
wastewater
Wastewater is water generated after the use of freshwater, raw water, drinking water or saline water in a variety of deliberate applications or processes. Another definition of wastewater is "Used water from any combination of domestic, industrial ...
is typically discharged in a
sewer system and treated in a
sewage treatment plant before being discharged into a river, lake, or the sea or reused for
landscaping or
irrigation
Irrigation (also referred to as watering) is the practice of applying controlled amounts of water to land to help grow crops, landscape plants, and lawns. Irrigation has been a key aspect of agriculture for over 5,000 years and has been devel ...
.
Use
In the
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
, the typical
single family home
A stand-alone house (also called a single-detached dwelling, detached residence or detached house) is a free-standing residential building. It is sometimes referred to as a single-family home, as opposed to a multi-family residential dwellin ...
uses about of water per day (2016 estimate) or per capita per day. This includes several common
residential end use purposes (in decreasing order) like
toilet use,
showers,
tap (faucet) use,
washing machine
A washing machine (laundry machine, clothes washer, washer, or simply wash) is a home appliance used to wash laundry. The term is mostly applied to machines that use water as opposed to dry cleaning (which uses alternative cleaning fluids and ...
use,
leak
A leak is a way (usually an opening) for fluid to escape a container or fluid-containing system, such as a tank or a ship's hull, through which the contents of the container can escape or outside matter can enter the container. Leaks are usually ...
s, other (unidentified),
baths, and
dishwasher
A dishwasher is a machine that is used to clean dishware, cookware, and cutlery automatically. Unlike manual dishwashing, which relies heavily on physical scrubbing to remove soiling, the mechanical dishwasher cleans by spraying hot water, ty ...
use.
Trends
During the beginning of the 21st Century, especially in areas of urban and suburban population centers, traditional centralized infrastructure have not been able to supply sufficient quantities of water to keep up with growing demand. Among several options that have been managed are the extensive use of desalination technology, this is especially prevalent in coastal areas and in "dry" countries like
Australia. Decentralization of water infrastructure has grown extensively as a viable solution including
Rainwater harvesting
Rainwater harvesting (RWH) is the collection and storage of rain, rather than allowing it to run off. Rainwater is collected from a roof-like surface and redirected to a tank, cistern, deep pit (well, shaft, or borehole), aquifer, or a reservoir ...
and
Stormwater harvesting Stormwater harvesting or Stormwater reuse is the collection, accumulation, treatment or purification, and storage of stormwater for its eventual reuse. While rainwater harvesting collects precipitation primarily from rooftops, stormwater harvesting ...
where policies are eventually tending towards a more rational use and sourcing of water incorporation concepts such as "Fit for Purpose".
Service quality
Water supply
service quality has many dimensions: continuity;
water quality; pressure; and the degree of responsiveness of service providers to customer complaints. Many people in
developing countries
A developing country is a sovereign state with a lesser developed industrial base and a lower Human Development Index (HDI) relative to other countries. However, this definition is not universally agreed upon. There is also no clear agreem ...
receive a poor or very poor quality of service.
[WHO and UNICEF (2017]
Progress on Drinking Water, Sanitation and Hygiene: 2017 Update and SDG Baselines
Geneva: World Health Organization (WHO) and the United Nations Children's Fund (UNICEF), 2017 Water quality is also dependant of the quality and level of
pollution of the water source.
Continuity of supply
Continuity of water supply is taken for granted in most developed countries, but is a severe problem in many developing countries, where sometimes water is only provided for a few hours every day or a few days a week. This is especially problematic for
informal settlements who are often poorly connected to the
water supply network and who have no means of procuring alternative sources such as private
borehole
A borehole is a narrow shaft bored in the ground, either vertically or horizontally. A borehole may be constructed for many different purposes, including the extraction of water ( drilled water well and tube well), other liquids (such as petrol ...
s. It is estimated that about half of the population of developing countries receives water on an intermittent basis.
Water quality
Drinking
water quality has a micro-biological and a physico-chemical dimension. There are thousands of parameters of water quality. In public water supply systems water should, at a minimum, be disinfected—most commonly through the use of
chlorination Chlorination may refer to:
* Chlorination reaction
In chemistry, halogenation is a chemical reaction that entails the introduction of one or more halogens into a compound. Halide-containing compounds are pervasive, making this type of transform ...
or the use of
ultraviolet
Ultraviolet (UV) is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelength from 10 nm (with a corresponding frequency around 30 PHz) to 400 nm (750 THz), shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation ...
light—or it may need to undergo treatment, especially in the case of
surface water. For more details, please see the separate entries on
water quality,
water treatment
Water treatment is any process that improves the quality of water to make it appropriate for a specific end-use. The end use may be drinking, industrial water supply, irrigation, river flow maintenance, water recreation or many other uses, inc ...
and
drinking water
Drinking water is water that is used in drink or food preparation; potable water is water that is safe to be used as drinking water. The amount of drinking water required to maintain good health varies, and depends on physical activity level, a ...
.
Water pressure
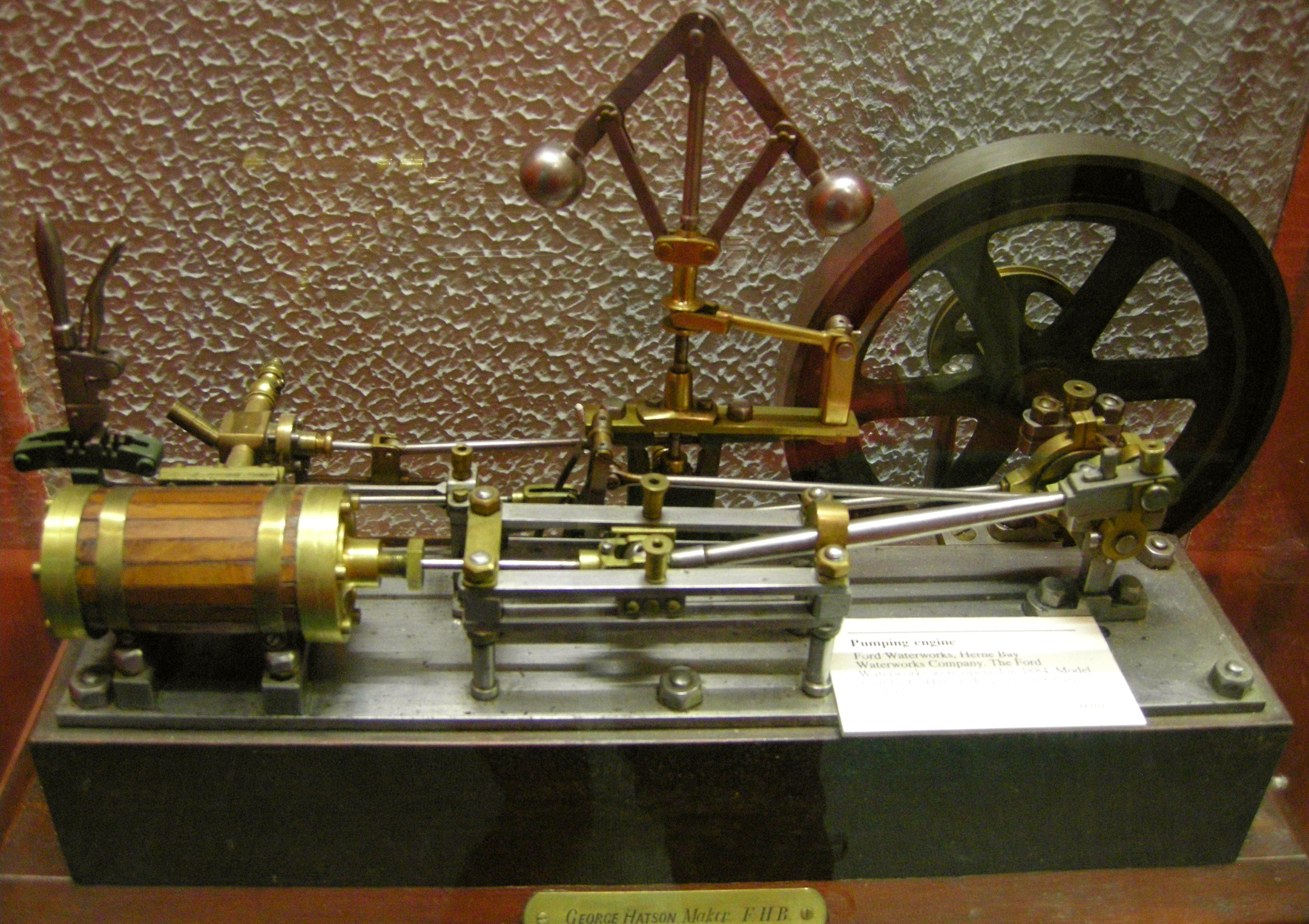
Water pressures vary in different locations of a distribution system. Water mains below the street may operate at higher pressures, with a
pressure reducer located at each point where the water enters a building or a house. In poorly managed systems, water pressure can be so low as to result only in a trickle of water or so high that it leads to damage to plumbing fixtures and waste of water. Pressure in an urban water system is typically maintained either by a pressurised water tank serving an urban area, by pumping the water up into a
water tower and relying on gravity to maintain a constant pressure in the system or solely by pumps at the
water treatment
Water treatment is any process that improves the quality of water to make it appropriate for a specific end-use. The end use may be drinking, industrial water supply, irrigation, river flow maintenance, water recreation or many other uses, inc ...
plant and repeater pumping stations.
Typical UK pressures are 4–5
bar (60–70
PSI) for an urban supply. However, some people can get over eight bars or below one bar. A single iron main pipe may cross a deep valley, it will have the same nominal pressure, however each consumer will get a bit more or less because of the
hydrostatic pressure (about 1 bar/10 m height). So people at the bottom of a hill will get about 3 bars more than those at the top.
The effective pressure also varies because of the pressure loss due to supply resistance even for the same static pressure. An urban consumer may have 5 metres of 15 mm pipe running from the iron main, so the kitchen tap flow will be fairly unrestricted, so high flow. A rural consumer may have a kilometre of rusted and
limed 22 mm iron pipe, so their kitchen tap flow will be small.
For this reason, the UK domestic water system has traditionally (prior to 1989) employed a "cistern feed" system, where the incoming supply is connected to the kitchen sink and also a header/storage tank in the
attic. Water can dribble into this tank through a 12 mm pipe, plus ball valve, and then supply the house on 22 or 28 mm pipes. Gravity water has a small pressure (say bar in the bathroom) so needs wide pipes to allow for higher flows. This is fine for baths and toilets but is frequently inadequate for showers. A
booster pump or a
hydrophore is installed to increase and maintain pressure. For this reason urban houses are increasingly using mains pressure boilers ("combies") which take a long time to fill a bath but suit the high back pressure of a shower.
Institutional responsibility and governance
A great variety of
institutions have responsibilities in water supply. A basic distinction is between institutions responsible for policy and regulation on the one hand; and institutions in charge of providing services on the other hand.
Policy and regulation

Water supply policies and regulation are usually defined by one or several Ministries, in consultation with the legislative branch. In the
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
the
United States Environmental Protection Agency
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) is an independent executive agency of the United States federal government tasked with environmental protection matters. President Richard Nixon proposed the establishment of EPA on July 9, 1970; it ...
, whose administrator reports directly to the President, is responsible for water and sanitation policy and standard setting within the executive branch. In other countries responsibility for sector policy is entrusted to a Ministry of Environment (such as in
Mexico
Mexico (Spanish: México), officially the United Mexican States, is a country in the southern portion of North America. It is bordered to the north by the United States; to the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; to the southeast by Guatema ...
and
Colombia), to a Ministry of Health (such as in
Panama
Panama ( , ; es, link=no, Panamá ), officially the Republic of Panama ( es, República de Panamá), is a transcontinental country spanning the southern part of North America and the northern part of South America. It is bordered by Co ...
,
Honduras and
Uruguay
Uruguay (; ), officially the Oriental Republic of Uruguay ( es, República Oriental del Uruguay), is a country in South America. It shares borders with Argentina to its west and southwest and Brazil to its north and northeast; while bordering ...
), a Ministry of Public Works (such as in
Ecuador
Ecuador ( ; ; Quechua: ''Ikwayur''; Shuar: ''Ecuador'' or ''Ekuatur''), officially the Republic of Ecuador ( es, República del Ecuador, which literally translates as "Republic of the Equator"; Quechua: ''Ikwadur Ripuwlika''; Shuar: ' ...
and
Haiti), a Ministry of Economy (such as in German states) or a Ministry of Energy (such as in
Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
). A few countries, such as
Jordan
Jordan ( ar, الأردن; tr. ' ), officially the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan,; tr. ' is a country in Western Asia. It is situated at the crossroads of Asia, Africa, and Europe, within the Levant region, on the East Bank of the Jordan Rive ...
and
Bolivia, even have a Ministry of Water. Often several Ministries share responsibilities for water supply.
In the European Union, important policy functions have been entrusted to the
supranational level. Policy and regulatory functions include the setting of tariff rules and the approval of tariff increases; setting, monitoring and enforcing norms for quality of service and environmental protection;
benchmarking the performance of service providers; and reforms in the structure of institutions responsible for service provision. The distinction between policy functions and regulatory functions is not always clear-cut. In some countries they are both entrusted to Ministries, but in others regulatory functions are entrusted to agencies that are separate from Ministries.
Regulatory agencies
Dozens of countries around the world have established regulatory agencies for infrastructure services, including often water supply and sanitation, in order to better protect consumers and to improve efficiency. Regulatory agencies can be entrusted with a variety of responsibilities, including in particular the approval of tariff increases and the management of sector information systems, including
benchmarking systems. Sometimes they also have a mandate to settle complaints by consumers that have not been dealt with satisfactorily by service providers. These specialized entities are expected to be more competent and objective in regulating service providers than departments of government Ministries. Regulatory agencies are supposed to be autonomous from the executive branch of government, but in many countries have often not been able to exercise a great degree of autonomy.
In the
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
regulatory agencies for utilities have existed for almost a century at the level of states, and in
Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot ...
at the level of provinces. In both countries they cover several infrastructure sectors. In many U.S. states they are called
Public Utility Commissions. For England and Wales, a regulatory agency for water (
OFWAT
The Water Services Regulation Authority, or Ofwat, is the body responsible for economic regulation of the privatised water and sewerage industry in England and Wales. Ofwat's main statutory duties include protecting the interests of consumers, secu ...
) was created as part of the privatization of the
water industry
The water industry provides drinking water and wastewater services (including sewage treatment) to residential, commercial, and industrial sectors of the economy. Typically public utilities operate water supply networks. The water industry doe ...
in 1989. In many developing countries, water regulatory agencies were created during the 1990s in parallel with efforts at increasing private sector participation. (for more details on regulatory agencies in Latin America, for example, please see
Water and sanitation in Latin America and the regional association of water regulatory agencies ADERASA.)
Many countries do not have regulatory agencies for water. In these countries service providers are regulated directly by local government, or the national government. This is, for example, the case in the countries of continental Europe, in China and India.
Service provision
Water supply service providers, which are often
utilities, differ from each other in terms of their geographical coverage relative to administrative boundaries; their sectoral coverage; their ownership structure; and their governance arrangements.
Geographical coverage

Many water utilities provide services in a single city, town or
municipality
A municipality is usually a single administrative division having corporate status and powers of self-government or jurisdiction as granted by national and regional laws to which it is subordinate.
The term ''municipality'' may also mean the go ...
. However, in many countries municipalities have associated in regional or inter-municipal or multi-jurisdictional utilities to benefit from
economies of scale
In microeconomics, economies of scale are the cost advantages that enterprises obtain due to their scale of operation, and are typically measured by the amount of output produced per unit of time. A decrease in cost per unit of output enables ...
. In the United States these can take the form of
special-purpose district
Special districts (also known as special service districts, special district governments, limited purpose entities, or special-purpose districts) are independent, special-purpose governmental units that exist separately from local governments such ...
s which may have independent taxing authority. An example of a multi-jurisdictional water utility in the United States is
WASA, a utility serving
Washington, D.C.
)
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from top left: the Washington Monument and Lincoln Memorial on the National Mall, United States Capitol, Logan Circle, Jefferson Memorial, White House, Adams Morgan, ...
and various localities in the state of
Maryland
Maryland ( ) is a state in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. It shares borders with Virginia, West Virginia, and the District of Columbia to its south and west; Pennsylvania to its north; and Delaware and the Atlantic Ocean to ...
. Multi-jurisdictional utilities are also common in Germany, where they are known as "Zweckverbaende", in France and in Italy.
In some federal countries, there are water service providers covering most or all cities and towns in an entire state, such as in all states of
Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area ...
and some states in
Mexico
Mexico (Spanish: México), officially the United Mexican States, is a country in the southern portion of North America. It is bordered to the north by the United States; to the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; to the southeast by Guatema ...
(see
Water supply and sanitation in Mexico). In
England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe b ...
and
Wales
Wales ( cy, Cymru ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by England to the east, the Irish Sea to the north and west, the Celtic Sea to the south west and the Bristol Channel to the south. It had a population in ...
, water supply and sewerage is supplied almost entirely through ten regional companies. Some smaller countries, especially developed countries, have established service providers that cover the entire country or at least most of its cities and major towns. Such national service providers are especially prevalent in West Africa and Central America, but also exist, for example, in
Tunisia
)
, image_map = Tunisia location (orthographic projection).svg
, map_caption = Location of Tunisia in northern Africa
, image_map2 =
, capital = Tunis
, largest_city = capital
, ...
,
Jordan
Jordan ( ar, الأردن; tr. ' ), officially the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan,; tr. ' is a country in Western Asia. It is situated at the crossroads of Asia, Africa, and Europe, within the Levant region, on the East Bank of the Jordan Rive ...
and
Uruguay
Uruguay (; ), officially the Oriental Republic of Uruguay ( es, República Oriental del Uruguay), is a country in South America. It shares borders with Argentina to its west and southwest and Brazil to its north and northeast; while bordering ...
(see also
water supply and sanitation in Uruguay). In rural areas, where about half the world population lives, water services are often not provided by utilities, but by community-based organizations which usually cover one or sometimes several villages.
Sector coverage
Some water utilities provide only water supply services, while
sewerage is under the responsibility of a different entity. This is for example the case in
Tunisia
)
, image_map = Tunisia location (orthographic projection).svg
, map_caption = Location of Tunisia in northern Africa
, image_map2 =
, capital = Tunis
, largest_city = capital
, ...
. However, in most cases water utilities also provide
sewer and
sewage treatment
Sewage treatment (or domestic wastewater treatment, municipal wastewater treatment) is a type of wastewater treatment which aims to remove contaminants from sewage to produce an effluent that is suitable for discharge to the surrounding e ...
services. In some cities or countries utilities also distribute electricity. In a few cases such multi-utilities also collect solid waste and provide local telephone services. An example of such an integrated utility can be found in the Colombian city of
Medellín. Utilities that provide water, sanitation and electricity can be found in
Frankfurt
Frankfurt, officially Frankfurt am Main (; Hessian: , " Frank ford on the Main"), is the most populous city in the German state of Hesse. Its 791,000 inhabitants as of 2022 make it the fifth-most populous city in Germany. Located on it ...
,
Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
(Mainova), in
Casablanca,
Morocco
Morocco (),, ) officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is the westernmost country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It overlooks the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria t ...
and in
Gabon
Gabon (; ; snq, Ngabu), officially the Gabonese Republic (french: République gabonaise), is a country on the west coast of Central Africa. Located on the equator, it is bordered by Equatorial Guinea to the northwest, Cameroon to the nort ...
in West Africa. Multi-utilities provide certain benefits such as common billing and the option to cross-subsidize water services with revenues from electricity sales, if permitted by law.
Ownership and governance arrangements
Water supply providers can be either public, private,
mixed or cooperative. Most urban water supply services around the world are provided by public entities. As Willem-Alexander, Prince of Orange (2002) stated, "The water crisis that is affecting so many people is mainly a crisis of governance—not of
water scarcity
Water scarcity (closely related to water stress or water crisis) is the lack of fresh water resources to meet the standard water demand. There are two types of water scarcity: physical or economic water scarcity. Physical water scarcity is whe ...
." The introduction of cost-reflective tariffs together with
cross-subsidization between richer and poorer consumers is an essential governance reform in order to reduce the high levels of
Unaccounted-for Water (UAW) and to provide the finance needed to extend the network to those poorest households who remain unconnected. Partnership arrangements between the public and private sector can play an important role in order to achieve this objective.
= Private sector participation
=
An estimated 10 percent of urban water supply is provided by
private or mixed public-private companies, usually under
concessions,
lease
A lease is a contractual arrangement calling for the user (referred to as the ''lessee'') to pay the owner (referred to as the ''lessor'') for the use of an asset. Property, buildings and vehicles are common assets that are leased. Industrial ...
s or
management contracts. Under these
water service contract arrangements the public entity that is legally responsible for service provision delegates certain or all aspects of service provision to the private service provider for a period typically ranging from 4 to 30 years. The public entity continues to own the assets. These arrangements are common in
France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan area ...
and in
Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
. Only in few parts of the world water supply systems have been completely sold to the private sector (
privatization
Privatization (also privatisation in British English) can mean several different things, most commonly referring to moving something from the public sector into the private sector. It is also sometimes used as a synonym for deregulation when ...
), such as in
England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe b ...
and
Wales
Wales ( cy, Cymru ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by England to the east, the Irish Sea to the north and west, the Celtic Sea to the south west and the Bristol Channel to the south. It had a population in ...
as well as in
Chile
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in the western part of South America. It is the southernmost country in the world, and the closest to Antarctica, occupying a long and narrow strip of land between the Andes to the east a ...
. The largest private water companies in the world are
Suez
Suez ( ar, السويس '; ) is a seaport city (population of about 750,000 ) in north-eastern Egypt, located on the north coast of the Gulf of Suez (a branch of the Red Sea), near the southern terminus of the Suez Canal, having the same bou ...
and
Veolia Environnement from France; ''Aguas de Barcelona'' from Spain; and
Thames Water from the UK, all of which are engaged internationally (see links to website of these companies below). In recent years, a number of cities have reverted to the public sector in a process called "
remunicipalization Remunicipalisation commonly refers to the return of previously privatised water supply and sanitation services to municipal authorities. It also encompasses regional or national initiatives.
Overview
The concept is broadly used to cover:
* Chang ...
".
= Public water service provision
=
90% of urban water supply and sanitation services are currently in the public sector. They are owned by the state or local authorities, or also by collectives or cooperatives. They run without an aim for profit but are based on the ethos of providing a common good considered to be of public interest. In most middle and low-income countries, these publicly owned and managed water providers can be inefficient as a result of political interference, leading to over-staffing and low labor productivity.
Ironically, the main losers from this institutional arrangement are the urban poor in these countries. Because they are not connected to the
water supply network, they end up paying far more per liter of water than do more well-off households connected to the network who benefit from the implicit subsidies that they receive from loss-making utilities.
The fact that we are still so far from achieving universal access to clean water and sanitation shows that public water authorities, in their current state, are not working well enough.
Yet some are being very successful and are modelling the best forms of public management. As
Ryutaro Hashimoto
was a Japanese politician who served as the Prime Minister of Japan from 1996 to 1998. He was the leader of one of the largest factions within the ruling LDP through most of the 1990s and remained a powerful back-room player in Japanese politi ...
, former Japanese Prime Minister, notes: "Public water services currently provide more than 90 percent of water supply in the world. Modest improvement in public water operators will have immense impact on global provision of services."
= Governance arrangements
=
Governance arrangements for both public and private utilities can take many forms (Kurian and McCarney, 2010). Governance arrangements define the relationship between the service provider, its owners, its customers and regulatory entities. They determine the financial autonomy of the service provider and thus its ability to maintain its assets, expand services, attract and retain qualified staff, and ultimately to provide high-quality services. Key aspects of governance arrangements are the extent to which the entity in charge of providing services is insulated from arbitrary political intervention; and whether there is an explicit mandate and political will to allow the service provider to recover all or at least most of its costs through tariffs and retain these revenues. If water supply is the responsibility of a department that is integrated in the administration of a city, town or municipality, there is a risk that tariff revenues are diverted for other purposes. In some cases, there is also a risk that staff are appointed mainly on political grounds rather than based on their professional credentials.
Standardization
International standards for water supply system are covered by International Classification of Standards (ICS) 91.140.60.
Comparing the performance of water and sanitation service providers
Comparing the performance of water and sanitation service providers (
utilities) is needed, because the sector offers limited scope for direct competition (
natural monopoly
A natural monopoly is a monopoly in an industry in which high infrastructural costs and other barriers to entry relative to the size of the market give the largest supplier in an industry, often the first supplier in a market, an overwhelming adv ...
). Firms operating in competitive markets are under constant pressure to out perform each other. Water utilities are often sheltered from this pressure, and it frequently shows: some utilities are on a sustained improvement track, but many others keep falling further behind best practice.
Benchmarking the performance of utilities allows the stimulation of competition, establish realistic targets for improvement and create pressure to catch up with better utilities. Information on benchmarks for water and sanitation utilities is provided by the International Benchmarking Network for Water and Sanitation Utilities.
Financial aspects
Costs and financing
The cost of supplying water consists, to a very large extent, of fixed costs (capital costs and personnel costs) and only to a small extent of variable costs that depend on the amount of water consumed (mainly energy and chemicals). The full cost of supplying water in urban areas in developed countries is about US$1–2 per cubic meter depending on local costs and local
water consumption levels. The cost of sanitation (sewerage and
wastewater treatment) is another US$1–2 per cubic meter. These costs are somewhat lower in developing countries. Throughout the world, only part of these costs is usually billed to consumers, the remainder being financed through direct or indirect
subsidies
A subsidy or government incentive is a form of financial aid or support extended to an economic sector (business, or individual) generally with the aim of promoting economic and social policy. Although commonly extended from the government, the ter ...
from local, regional or national governments (see section on tariffs).
Besides subsidies water supply investments are financed through internally generated revenues as well as through debt. Debt financing can take the form of credits from commercial Banks, credits from international financial institutions such as the World Bank and regional development banks (in the case of developing countries), and
bonds (in the case of some developed countries and some upper middle-income countries).
Tariffs
Almost all service providers in the world charge tariffs to recover part of their costs. According to estimates by the World Bank the average (
mean) global water tariff is US$0.53 per cubic meter. In developed countries the average tariff is US$1.04, while it is only U$0.11 in the poorest developing countries. The lowest tariffs in developing countries are found in South Asia (mean of US$0.09/m3), while the highest are found in Latin America (US$0.41/m3). Data for 132 cities were assessed. The tariff is estimate for a consumption level of 15 cubic meters per month. Few utilities do recover all their costs. According to the same World Bank study only 30% of utilities globally, and only 50% of utilities in developed countries, generate sufficient revenue to cover operation, maintenance and partial capital costs.
According to another study undertaken in 2006 by NUS Consulting, the average water and sewerage tariff in 14 mainly
OECD
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD; french: Organisation de coopération et de développement économiques, ''OCDE'') is an intergovernmental organisation with 38 member countries, founded in 1961 to stimulate e ...
countries excluding
VAT varied between US$0.66 per cubic meter in the United States and the equivalent of US$2.25 per cubic meter in Denmark. However, water consumption is much higher in the US than in Europe. Therefore, residential water bills may be very similar, even if the tariff per unit of consumption tends to be higher in Europe than in the US.
A typical family on the US East Coast paid between US$30 and US$70 per month for water and sewer services in 2005.
In developing countries, tariffs are usually much further from covering costs. Residential water bills for a typical consumption of 15 cubic meters per month vary between less than US$1 and US$12 per month.
Water and sanitation tariffs, which are almost always billed together, can take many different forms. Where meters are installed, tariffs are typically volumetric (per usage), sometimes combined with a small monthly fixed charge. In the absence of meters, flat or fixed rates—which are independent of actual consumption—are being charged. In developed countries, tariffs are usually the same for different categories of users and for different levels of consumption.
In developing countries, the situation is often characterized by cross-subsidies with the intent to make water more affordable for residential low-volume users that are assumed to be poor. For example, industrial and commercial users are often charged higher tariffs than public or residential users. Also, metered users are often charged higher tariffs for higher levels of consumption (increasing-block tariffs). However, cross-subsidies between residential users do not always reach their objective. Given the overall low level of water tariffs in developing countries even at higher levels of consumption, most consumption subsidies benefit the wealthier segments of society. Also, high industrial and commercial tariffs can provide an incentive for these users to supply water from other sources than the utility (own wells, water tankers) and thus actually erode the utility's revenue base.
Investments needed in developing countries
Water supply and
sanitation
Sanitation refers to public health conditions related to clean drinking water and treatment and disposal of human excreta and sewage. Preventing human contact with feces is part of sanitation, as is hand washing with soap. Sanitation syste ...
require a huge amount of capital
investment in infrastructure such as pipe networks, pumping stations and
water treatment works. It is estimated that in developing countries investments of at least US$200 billion have to be made per year to replace aging water infrastructure to guarantee supply, reduce leakage rates and protect water quality.
International attention has focused upon the needs of
developing countries
A developing country is a sovereign state with a lesser developed industrial base and a lower Human Development Index (HDI) relative to other countries. However, this definition is not universally agreed upon. There is also no clear agreem ...
. To meet the
Millennium Development Goals
The Millennium Development Goals (MDGs) were eight international development goals for the year 2015 that had been established following the Millennium Summit of the United Nations in 2000, following the adoption of the United Nations Millenn ...
targets of halving the proportion of the population lacking access to safe drinking water and basic sanitation by 2015, current annual investment on the order of US$10 to US$15 billion would need to be roughly doubled. This does not include investments required for the maintenance of existing infrastructure.
Once infrastructure is in place, operating water supply and sanitation systems entails significant ongoing costs to cover personnel, energy, chemicals, maintenance and other expenses. The sources of money to meet these capital and operational costs are essentially either user fees, public funds or some combination of the two. It is also important to consider is the flexibility of the water supply system.
Metering

Metering of water supply is usually motivated by one or several of four objectives. First, it provides an incentive to conserve water which protects
water resources (environmental objective). Second, it can postpone costly system expansion and saves energy and chemical costs (economic objective). Third, it allows a utility to better locate distribution losses (technical objective). Fourth, it allows suppliers to charge for water based on use, which is perceived by many as the fairest way to allocate the costs of water supply to users. Metering is considered good practice in water supply and is widespread in developed countries, except for the
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the European mainland, continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
. In developing countries it is estimated that half of all urban water supply systems are metered and the tendency is increasing.
Water meters
Water metering is the practice of measuring water use. Water meters measure the volume of water used by residential and commercial building units that are supplied with water by a public water supply system. They are also used to determine flow ...
are read by one of several methods:
* the water customer writes down the meter reading and mails in a postcard with this info to the water department;
* the water customer writes down the meter reading and uses a phone dial-in system to transfer this info to the water department;
* the water customer logs into the
website
A website (also written as a web site) is a collection of web pages and related content that is identified by a common domain name and published on at least one web server. Examples of notable websites are Google, Facebook, Amazon, and Wi ...
of the water supply company, enters the address, meter ID and meter reading
* a meter reader comes to the premises and enters the meter reading into a handheld computer;
* the meter reading is echoed on a display unit mounted to the outside of the premises, where a meter reader records them;
* a small radio is hooked up to the meter to automatically transmit readings to corresponding receivers in handheld computers, utility vehicles or distributed collectors
* a small computer is hooked up to the meter that can either dial out or receive automated phone calls that give the reading to a central computer system.
Most cities are increasingly installing
automatic meter reading (AMR) systems to prevent fraud, to lower ever-increasing labor and liability costs and to improve customer service and satisfaction.
Global access


Health aspects
Outbreaks of diseases due to contaminated water supply
Water supply can get contaminated by
pathogens
In biology, a pathogen ( el, πάθος, "suffering", "passion" and , "producer of") in the oldest and broadest sense, is any organism or agent that can produce disease. A pathogen may also be referred to as an infectious agent, or simply a ger ...
which may originate from
human excreta, for example due to a break-down or design fault in the
sanitation
Sanitation refers to public health conditions related to clean drinking water and treatment and disposal of human excreta and sewage. Preventing human contact with feces is part of sanitation, as is hand washing with soap. Sanitation syste ...
system, or by chemical contaminants.
Examples of contamination include:
* In 1854, a
cholera outbreak in London's Soho district was identified by
Dr. John Snow as originating from contaminated water from the Broad Street pump. This can be regarded as a founding event of the science of
epidemiology
Epidemiology is the study and analysis of the distribution (who, when, and where), patterns and determinants of health and disease conditions in a defined population.
It is a cornerstone of public health, and shapes policy decisions and evide ...
.
* In 1987, a
cryptosporidiosis
Cryptosporidiosis, sometimes informally called crypto, is a parasitic disease caused by '' Cryptosporidium'', a genus of protozoan parasites in the phylum Apicomplexa. It affects the distal small intestine and can affect the respiratory tra ...
outbreak is caused by the public water supply of which the filtration was contaminated, in western Georgia
* In 1993,
Milwaukee Cryptosporidium outbreak
* In 1998, an outbreak of
typhoid fever
Typhoid fever, also known as typhoid, is a disease caused by '' Salmonella'' serotype Typhi bacteria. Symptoms vary from mild to severe, and usually begin six to 30 days after exposure. Often there is a gradual onset of a high fever over several ...
in northern Israel, which was associated with the contaminated municipal water supply
* In 1997, 369 cases of
cryptosporidiosis
Cryptosporidiosis, sometimes informally called crypto, is a parasitic disease caused by '' Cryptosporidium'', a genus of protozoan parasites in the phylum Apicomplexa. It affects the distal small intestine and can affect the respiratory tra ...
occurred, caused by a contaminated fountain in the Minnesota zoo. Most of the sufferers were children
* In 1998, a non-chlorinated municipal water supply was blamed for a
campylobacteriosis outbreak in northern Finland
* In 2000, a
gastroenteritis outbreak that was brought by a non-chlorinated community water supply, in southern Finland
* In 2000, an
E. coli outbreak occurred in
Walkerton, Ontario, Canada.
Seven people died from drinking contaminated water. Hundreds suffered from the symptoms of the disease, not knowing if they too would die.
* In 2004, contamination of the community water supply, serving the Bergen city centre of Norway, was later reported after the outbreak of waterborne
giardiasis
* In 2007, contaminated drinking water was pinpointed which had led to the outbreak of gastroenteritis with multiple
aetiologies in Denmark
Examples of chemical contamination include:
* In 1988, many people were poisoned in
Camelford
Camelford ( kw, Reskammel) is a town and civil parish in north Cornwall, England, United Kingdom, situated in the River Camel valley northwest of Bodmin Moor. The town is approximately ten miles (16 km) north of Bodmin and is governed ...
, when a worker put 20 tonnes of aluminium sulphate in the wrong tank.
* In 1993, a fluoride poisoning outbreak resulting from overfeeding of fluoride, in Mississippi
* In 2019 oil for an electric transformer oil entered the water supply for the city of
Uummannaq
Uummannaq is a town in the Avannaata municipality, in central-western Greenland. With 1,407 inhabitants in 2020, it is the eighth-largest town in Greenland, and is home to the country's most northerly ferry terminal. Founded in 1763 as Omenak, t ...
in Greenland. A cargo ship in harbour was able to maintain a minimum supply the city for two days until the mains supply was restored and flushing of all the pipework was started.
History

Throughout history, people have devised systems to make getting and using water more convenient. Living in semi-arid regions, ancient
Persians
The Persians are an Iranian ethnic group who comprise over half of the population of Iran. They share a common cultural system and are native speakers of the Persian language as well as of the languages that are closely related to Persian.
...
in the 1st millennium BC used
qanat
A qanat or kārīz is a system for transporting water from an aquifer or water well to the surface, through an underground aqueduct; the system originated approximately 3,000 BC in what is now Iran. The function is essentially the same across ...
system to gain access to water in the mountains. Early
Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus (legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
had indoor plumbing, meaning a system of
aqueducts
Aqueduct may refer to:
Structures
*Aqueduct (bridge), a bridge to convey water over an obstacle, such as a ravine or valley
*Navigable aqueduct, or water bridge, a structure to carry navigable waterway canals over other rivers, valleys, railw ...
and pipes that terminated in homes and at public wells and fountains for people to use.
Until the
Enlightenment era
The Age of Enlightenment or the Enlightenment; german: Aufklärung, "Enlightenment"; it, L'Illuminismo, "Enlightenment"; pl, Oświecenie, "Enlightenment"; pt, Iluminismo, "Enlightenment"; es, La Ilustración, "Enlightenment" was an intel ...
, little progress was made in water supply and sanitation and the engineering skills of the Romans were largely neglected throughout Europe. It was in the 18th century that a rapidly growing population fueled a boom in the establishment of private
water supply networks in
London
London is the capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary dow ...
.
developed over many centuries from early mediaeval conduits, through major 19th-century treatment works built in response to
cholera threats, to modern, large-scale reservoirs. The first screw-down
water tap
A tap (also spigot or faucet: see usage variations) is a valve controlling the release of a liquid or gas.
Nomenclature
United Kingdom
* Tap is used in the United Kingdom and most of the Commonwealth for any everyday type of valve, parti ...
was patented in 1845 by Guest and Chrimes, a brass foundry in
Rotherham
Rotherham () is a large minster and market town in South Yorkshire, England. The town takes its name from the River Rother which then merges with the River Don. The River Don then flows through the town centre. It is the main settlement of ...
.
The first documented use of
sand filters to purify the water supply dates to 1804, when the owner of a bleachery in
Paisley, Scotland
Paisley ( ; sco, Paisley, gd, Pàislig ) is a large town situated in the west central Lowlands of Scotland. Located north of the Gleniffer Braes, the town borders the city of Glasgow to the east, and straddles the banks of the White Cart Wate ...
, John Gibb, installed an experimental filter, selling his unwanted surplus to the public. The first treated public water supply in the world was installed by engineer
James Simpson for the
Chelsea Waterworks Company
The Chelsea Waterworks Company was a London waterworks
Water supply is the provision of water by public utilities, commercial organisations, community endeavors or by individuals, usually via a system of pumps and pipes. Public water sup ...
in London in 1829.
[History of the Chelsea Waterworks](_blank)
/ref> The practice of water treatment soon became mainstream, and the virtues of the system were made starkly apparent after the investigations of the physician John Snow during the 1854 Broad Street cholera outbreak demonstrated the role of the water supply in spreading the cholera epidemic.''Concepts and practice of humanitarian medicine'' (2008) Par S. William Gunn, M. Masellis
/ref>
By country
Society and culture
Lawsuits
*'' Arizona v. California''
*''Colorado River Water Conservation District v. United States
''Colorado River Water Conservation District v. United States'', 424 U.S. 800 (1976), was a case in which the Supreme Court of the United States extensively refined the abstention doctrine to prevent duplicative litigation between state and federal ...
''
*'' Kansas v. Colorado''
*'' Tahoe-Sierra Preservation Council, Inc. v. Tahoe Regional Planning Agency''
*'' Wisconsin v. Illinois''
*'' Wyoming v. Colorado''
See also
*Human right to water and sanitation
The human right to water and sanitation (HRWS) is a principle stating that clean drinking water and sanitation are a universal human right because of their high importance in sustaining every person's life. It was recognized as a human right b ...
* Nonresidential water use in the U.S.
* Residential water use in the U.S. and Canada
*Water efficiency
Water efficiency is the practice of reducing water consumption by measuring the amount of water required for a particular purpose and is proportionate to the amount of essential water used.Vickers, Amy. “Water use and conservation." Amherst, MA ...
* Water resources
*Water scarcity
Water scarcity (closely related to water stress or water crisis) is the lack of fresh water resources to meet the standard water demand. There are two types of water scarcity: physical or economic water scarcity. Physical water scarcity is whe ...
*Water security
Water security is the focused goal of water policy and water management. A society with a high level of water security makes the most of water's benefits for humans and ecosystems and limits the risk of destructive impacts associated with water. T ...
* Water supply terrorism
References
External links
The World Bank on private water operations in rural communities
The World Bank on water utility subsidies
The WHO's site on water
The OECD's site on water
{{DEFAULTSORT:Water Supply
Water management
 Water supply is the provision of
Water supply is the provision of  Water pressures vary in different locations of a distribution system. Water mains below the street may operate at higher pressures, with a pressure reducer located at each point where the water enters a building or a house. In poorly managed systems, water pressure can be so low as to result only in a trickle of water or so high that it leads to damage to plumbing fixtures and waste of water. Pressure in an urban water system is typically maintained either by a pressurised water tank serving an urban area, by pumping the water up into a water tower and relying on gravity to maintain a constant pressure in the system or solely by pumps at the
Water pressures vary in different locations of a distribution system. Water mains below the street may operate at higher pressures, with a pressure reducer located at each point where the water enters a building or a house. In poorly managed systems, water pressure can be so low as to result only in a trickle of water or so high that it leads to damage to plumbing fixtures and waste of water. Pressure in an urban water system is typically maintained either by a pressurised water tank serving an urban area, by pumping the water up into a water tower and relying on gravity to maintain a constant pressure in the system or solely by pumps at the  Water supply policies and regulation are usually defined by one or several Ministries, in consultation with the legislative branch. In the
Water supply policies and regulation are usually defined by one or several Ministries, in consultation with the legislative branch. In the  Many water utilities provide services in a single city, town or
Many water utilities provide services in a single city, town or  Metering of water supply is usually motivated by one or several of four objectives. First, it provides an incentive to conserve water which protects water resources (environmental objective). Second, it can postpone costly system expansion and saves energy and chemical costs (economic objective). Third, it allows a utility to better locate distribution losses (technical objective). Fourth, it allows suppliers to charge for water based on use, which is perceived by many as the fairest way to allocate the costs of water supply to users. Metering is considered good practice in water supply and is widespread in developed countries, except for the
Metering of water supply is usually motivated by one or several of four objectives. First, it provides an incentive to conserve water which protects water resources (environmental objective). Second, it can postpone costly system expansion and saves energy and chemical costs (economic objective). Third, it allows a utility to better locate distribution losses (technical objective). Fourth, it allows suppliers to charge for water based on use, which is perceived by many as the fairest way to allocate the costs of water supply to users. Metering is considered good practice in water supply and is widespread in developed countries, except for the 
 Throughout history, people have devised systems to make getting and using water more convenient. Living in semi-arid regions, ancient
Throughout history, people have devised systems to make getting and using water more convenient. Living in semi-arid regions, ancient