Wars of the Delian League on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Wars of the Delian League (477–449 BC) were a series of campaigns fought between the
 The military history of Greece between the end of the second Persian invasion of Greece and the
The military history of Greece between the end of the second Persian invasion of Greece and the
XI, 62
/ref> There is also a reasonable body of archaeological evidence for the period, of which inscriptions detailing probable tribute lists of the Delian League are particularly important.
I, 135–137
/ref> The three events, Pausanias's treason, Themistocles's flight and the siege of Naxos therefore occurred in close temporal sequence. These events certainly happened after 474 BC (the earliest possible date for Themistocles's
I, 112
/ref>
pp. 269–277.
/ref> By 500 BC, Ionia appears to have been ripe for rebellion against these Persian place-men. The simmering tension finally broke into open revolt due to the actions of the tyrant of
V, 35
/ref> This triggered similar revolutions across Ionia, and indeed Doris and The Greek states of Athens and
The Greek states of Athens and
I, 89
/ref> The Allied fleet then sailed to the
IX, 114
/ref> The following year, 478 BC, the Allies sent a force to capture the city of
I, 95
/ref> The siege of Byzantium was the last action of the Hellenic alliance which had defeated the Persian invasion.
 After Byzantium, Sparta was eager to end her involvement in the war. The Spartans were of the view that, with the liberation of mainland Greece, and the Greek cities of Asia Minor, the war's purpose had already been reached. There was also perhaps a feeling that obtaining long-term security for the Asian Greeks would prove impossible. In the aftermath of Mycale, the Spartan king
After Byzantium, Sparta was eager to end her involvement in the war. The Spartans were of the view that, with the liberation of mainland Greece, and the Greek cities of Asia Minor, the war's purpose had already been reached. There was also perhaps a feeling that obtaining long-term security for the Asian Greeks would prove impossible. In the aftermath of Mycale, the Spartan king
I, 96
/ref> In reality, this goal was divided into three main efforts - to prepare against any future invasion, to seek revenge against Persia, and to organize a means of dividing spoils of war. The members were given a choice of either offering armed forces or paying a tax to the joint treasury; most states chose the tax.Thucydide
I, 99
/ref> League members swore to have the same friends and enemies, and dropped ingots of iron into the sea to symbolize the permanence of their alliance. The ingots of iron were cast into the ocean because the oath the league members swore stipulated that their allegiance would not end, or be otherwise broken, until the iron floated to the surface. In other words, that they had made a pact perceived to be eternal. The Athenian politician
I, 100
/ref> Thucydides does not provide more examples, but from archaeological sources it is possible to deduce that there were further rebellions in the following years.Fine, p. 359. Thucydides leaves us under no illusions that the behaviour of the Athenians in crushing such rebellions led firstly to the hegemony of Athens over the league, and eventually to the transition from the Delian League to the
 Athens sent troops in 462 BC to aid Sparta with the Messenian Revolt (c. 465–461 BC), under the terms of the old Hellenic alliance.Thucydide
Athens sent troops in 462 BC to aid Sparta with the Messenian Revolt (c. 465–461 BC), under the terms of the old Hellenic alliance.Thucydide
I, 102
/ref> The Spartans however, in the fear that Athens might interfere in the political situation between the Spartans and their
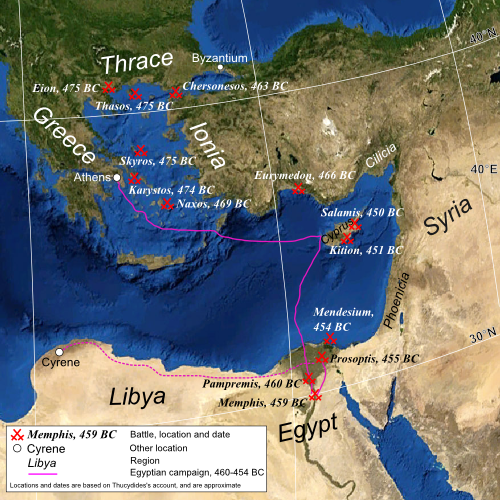 According to Thucydides, the League's opening campaign was against the city of
According to Thucydides, the League's opening campaign was against the city of
I, 98
/ref> Since Thucydides does not provide a detailed chronology for his history of the league, the year in which this campaign took place is uncertain. The siege seems to have lasted from autumn of one year into the summer of the next, with historians supporting either 477–476 BC or 476–475 BC.Fine, p. 343. Eion seems to have been one of the Persian garrisons left in Thrace during and after the second Persian invasion, along with
VII, 107
/ref> The campaign against Eion should probably be seen as part of a general campaign aimed at removing the Persian presence from Thrace.Sealey, p. 250. Even though he does not directly cover this period, Herodotus alludes to several failed attempts, presumably Athenian, to dislodge the Persian governor of Doriskos, The force which attacked Eion was under the command of Cimon. Plutarch says that Cimon first defeated the Persians in battle, whereupon they retreated to the city, and were besieged there.Plutarch, Cimon, 7 Cimon then expelled all Thracian collaborators from the region in order to starve the Persians into submission. Herodotus indicates that the Persian commander,
The force which attacked Eion was under the command of Cimon. Plutarch says that Cimon first defeated the Persians in battle, whereupon they retreated to the city, and were besieged there.Plutarch, Cimon, 7 Cimon then expelled all Thracian collaborators from the region in order to starve the Persians into submission. Herodotus indicates that the Persian commander,
 Once the Persian forces in Europe had largely been neutralised, the Athenians seem to have gone about starting to extend the League in Asia Minor.Plutarch, Cimon, 12Cawkwell, p. 133. The islands of Samos, Chios and Lesbos seem to have become members of the original Hellenic alliance after Mycale, and presumably were also therefore original members of the Delian League. However, it is unclear exactly when the other Ionian cities, or indeed the other Greek cities of Asia Minor, joined the league, though they certainly did at some point.Sealey, p. 247.
Cimon's Eurymedon campaign itself seems to have begun in response to the assembly of a large Persian fleet and army at
Once the Persian forces in Europe had largely been neutralised, the Athenians seem to have gone about starting to extend the League in Asia Minor.Plutarch, Cimon, 12Cawkwell, p. 133. The islands of Samos, Chios and Lesbos seem to have become members of the original Hellenic alliance after Mycale, and presumably were also therefore original members of the Delian League. However, it is unclear exactly when the other Ionian cities, or indeed the other Greek cities of Asia Minor, joined the league, though they certainly did at some point.Sealey, p. 247.
Cimon's Eurymedon campaign itself seems to have begun in response to the assembly of a large Persian fleet and army at
 Thucydides gives only the barest of details for this battle; the most reliable detailed account is given by Plutarch. According to Plutarch, the Persian fleet was anchored off the mouth of the Eurymedon, awaiting the arrival of 80 Phoenician ships from Cyprus. Several different estimates for the size of the Persian fleet are given. Thucydides says that there was a fleet of 200 Phoenician ships, and is generally considered the most reliable source.Cawkwell, p. 134. Plutarch gives numbers of 350 from Ephorus and 600 from Phanodemus.
Cimon, sailing from Phaselis, made to attack the Persians before the reinforcements arrived, whereupon the Persian fleet, eager to avoid fighting, retreated into the river itself. However, when Cimon continued to bear down on the Persians, they accepted battle. Regardless of their numbers, the Persian battle line was quickly breached, and the Persian ships then turned about, and made for the river bank. Grounding their ships, the crews sought sanctuary with the army waiting nearby. Despite the weariness of his troops after this first battle, Cimon landed the marines and proceeded to attack the Persian army. Initially the Persian line held the Athenian assault, but eventually, as at
Thucydides gives only the barest of details for this battle; the most reliable detailed account is given by Plutarch. According to Plutarch, the Persian fleet was anchored off the mouth of the Eurymedon, awaiting the arrival of 80 Phoenician ships from Cyprus. Several different estimates for the size of the Persian fleet are given. Thucydides says that there was a fleet of 200 Phoenician ships, and is generally considered the most reliable source.Cawkwell, p. 134. Plutarch gives numbers of 350 from Ephorus and 600 from Phanodemus.
Cimon, sailing from Phaselis, made to attack the Persians before the reinforcements arrived, whereupon the Persian fleet, eager to avoid fighting, retreated into the river itself. However, when Cimon continued to bear down on the Persians, they accepted battle. Regardless of their numbers, the Persian battle line was quickly breached, and the Persian ships then turned about, and made for the river bank. Grounding their ships, the crews sought sanctuary with the army waiting nearby. Despite the weariness of his troops after this first battle, Cimon landed the marines and proceeded to attack the Persian army. Initially the Persian line held the Athenian assault, but eventually, as at
 The Egyptian campaign, as discussed above, is generally thought to have begun in 460 BC. Even this date is subject to some debate however, since at this time Athens was already at war with Sparta in the First Peloponnesian War. It has been questioned whether Athens would really commit to an Egyptian campaign under these circumstances, and therefore suggested that this campaign began ''before'' the war with Sparta, in 462 BC.Kagan, p. 82. However, this date is generally rejected, and it seems that the Egyptian campaign was, on the part of Athens, simply a piece of political opportunism.Fine, p. 352.
The Egyptian campaign, as discussed above, is generally thought to have begun in 460 BC. Even this date is subject to some debate however, since at this time Athens was already at war with Sparta in the First Peloponnesian War. It has been questioned whether Athens would really commit to an Egyptian campaign under these circumstances, and therefore suggested that this campaign began ''before'' the war with Sparta, in 462 BC.Kagan, p. 82. However, this date is generally rejected, and it seems that the Egyptian campaign was, on the part of Athens, simply a piece of political opportunism.Fine, p. 352.
 The
The
I, 104
/ref> Inaros now appealed to the Delian League for assistance in their fight against the Persians. There was a League fleet of 200 ships under Admiral
Persica, 36
(from Photius's Epitome)Diodoru
XI, 74
/ref> Fine suggests a number of reasons that the Athenians may have been willing to engage themselves in Egypt, despite the ongoing war elsewhere; the opportunity to weaken Persia, the desire for a naval base in Egypt, the access to the
 The Athenians and Egyptians thus settled down to besiege the White Castle. The siege evidently did not progress well, and probably lasted for at least four years, since Thucydides says that their whole expedition lasted 6 years,Thucydide
The Athenians and Egyptians thus settled down to besiege the White Castle. The siege evidently did not progress well, and probably lasted for at least four years, since Thucydides says that their whole expedition lasted 6 years,Thucydide
I, 110
/ref> and of this time the final 18 months was occupied with the Siege of Prosoptis.Thucydide
I, 109
/ref> According to Thucydides, at first Artaxerxes sent Megabazus to try and bribe the Spartans into invading
XI, 77
/ref>
 In 478 BC the Allies had, according to Thucydides, sailed to Cyprus and "subdued most of the island".Thucydide
In 478 BC the Allies had, according to Thucydides, sailed to Cyprus and "subdued most of the island".Thucydide
I, 94
/ref> Exactly what Thucydides means by this is unclear. Sealey suggests that this was essentially a raid to gather as much booty as possible from the Persian garrisons on Cyprus.Sealey, p. 242 There is no indication that the Allies made any attempt to actually take possession of the island, and shortly after they sailed to Byzantium. Certainly, the fact that the Delian League repeatedly campaigned in Cyprus suggests that the island was not garrisoned by the Allies in 478 BC, or that the garrisons were quickly expelled. The next time Cyprus is mentioned is in relation to c. 460 BC, when a League fleet was campaigning there, before being instructed to head to Egypt to support Inaros's rebellion, with the fateful consequences discussed above. The Egyptian disaster would eventually lead the Athenians to sign a five-year truce with Sparta in 451 BC. Thereby freed from fighting in Greece, the League was again able to dispatch a fleet to campaign in Cyprus in 451 BC, under the recently recalled Cimon.
 Cimon's death was kept a secret from the Athenian army. 30 days after leaving Kition, the Athenians and their allies were attacked by a Persian force composed of Cilicians, Phoenicians, and Cyprians, whilst sailing off Salamis-in-Cyprus. Under the 'command' of the deceased Cimon, they defeated this force at sea, and also in a land battle. Having thus successfully extricated themselves, the Athenians sailed back to Greece, joined by the detachment which had been sent to Egypt.
These battles formed the end of the Greco-Persian Wars.
Cimon's death was kept a secret from the Athenian army. 30 days after leaving Kition, the Athenians and their allies were attacked by a Persian force composed of Cilicians, Phoenicians, and Cyprians, whilst sailing off Salamis-in-Cyprus. Under the 'command' of the deceased Cimon, they defeated this force at sea, and also in a land battle. Having thus successfully extricated themselves, the Athenians sailed back to Greece, joined by the detachment which had been sent to Egypt.
These battles formed the end of the Greco-Persian Wars.
XII, 4
/ref> Diodorus was probably following the history of Ephorus at this point, who in turn was presumably influenced by his teacher
''The Histories''
*
''History of the Peloponnesian War''
*
''Biblioteca Historica''
*
Persica
' (from
Delian League
The Delian League, founded in 478 BC, was an association of Greek city-states, numbering between 150 and 330, under the leadership of Athens, whose purpose was to continue fighting the Persian Empire after the Greek victory in the Battle of Pla ...
of Athens
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital and largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh largest city in the European Union. Athens dominates a ...
and her allies (and later subjects), and the Achaemenid Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire (; peo, 𐎧𐏁𐏂, , ), also called the First Persian Empire, was an ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC. Based in Western Asia, it was contemporarily the largest em ...
of Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
. These conflicts represent a continuation of the Greco-Persian Wars
The Greco-Persian Wars (also often called the Persian Wars) were a series of conflicts between the Achaemenid Empire and Greek city-states that started in 499 BC and lasted until 449 BC. The collision between the fractious political world of th ...
, after the Ionian Revolt
The Ionian Revolt, and associated revolts in Aeolis, Doris, Cyprus and Caria, were military rebellions by several Greek regions of Asia Minor against Persian rule, lasting from 499 BC to 493 BC. At the heart of the rebellion was the dissatisf ...
and the first and second
The second (symbol: s) is the unit of time in the International System of Units (SI), historically defined as of a day – this factor derived from the division of the day first into 24 hours, then to 60 minutes and finally to 60 seconds ea ...
Persian invasions of Greece.
The Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
alliance, centred on Sparta and Athens, that had defeated the second Persian invasion had initially followed up this success by capturing the Persian garrisons of Sestos
Sestos ( el, Σηστός, la, Sestus) was an ancient city in Thrace. It was located at the Thracian Chersonese peninsula on the European coast of the Hellespont, opposite the ancient city of Abydos, and near the town of Eceabat in Turkey.
In ...
and Byzantium
Byzantium () or Byzantion ( grc, Βυζάντιον) was an ancient Greek city in classical antiquity that became known as Constantinople in late antiquity and Istanbul today. The Greek name ''Byzantion'' and its Latinization ''Byzantium' ...
, both in Thrace
Thrace (; el, Θράκη, Thráki; bg, Тракия, Trakiya; tr, Trakya) or Thrake is a geographical and historical region in Southeast Europe, now split among Bulgaria, Greece, and Turkey, which is bounded by the Balkan Mountains to ...
, in 479 and 478 BC respectively. After the capture of Byzantium, the Spartans elected not to continue the war effort, and a new alliance, commonly known as the Delian League, was formed, with Athens very much the dominant power. Over the next 30 years, Athens would gradually assume a more hegemonic position over the league, which gradually evolved into the Athenian Empire
The Delian League, founded in 478 BC, was an association of Greek city-states, numbering between 150 and 330, under the leadership of Athens, whose purpose was to continue fighting the Persian Empire after the Greek victory in the Battle of Plat ...
.
Throughout the 470s BC, the Delian League campaigned in Thrace and the Aegean to remove the remaining Persian garrisons from the region, primarily under the command of the Athenian politician Cimon
Cimon or Kimon ( grc-gre, Κίμων; – 450BC) was an Athenian ''strategos'' (general and admiral) and politician.
He was the son of Miltiades, also an Athenian ''strategos''. Cimon rose to prominence for his bravery fighting in the naval Batt ...
. In the early part of the next decade, Cimon began campaigning in Asia Minor
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The re ...
, seeking to strengthen the Greek position there. At the Battle of the Eurymedon
The Battle of the Eurymedon was a double battle, taking place both on water and land, between the Delian League of Athens and her Allies, and the Persian Empire of Xerxes I. It took place in either 469 or 466 BCE, in the vicinity of the mouth ...
in Pamphylia
Pamphylia (; grc, Παμφυλία, ''Pamphylía'') was a region in the south of Asia Minor, between Lycia and Cilicia, extending from the Mediterranean to Mount Taurus (all in modern-day Antalya province, Turkey). It was bounded on the north b ...
, the Athenians and allied fleet achieved a stunning double victory, destroying a Persian fleet and then landing the ships' marines to attack and rout the Persian army. After this battle, the Persians took an essentially passive role in the conflict, anxious not to risk battle where possible.
Towards the end of the 460s BC, the Athenians took the ambitious decision to support a revolt in the Egyptian satrapy of the Persian Empire. Although the Greek task force achieved initial success, they were unable to capture the Persian garrison in Memphis
Memphis most commonly refers to:
* Memphis, Egypt, a former capital of ancient Egypt
* Memphis, Tennessee, a major American city
Memphis may also refer to:
Places United States
* Memphis, Alabama
* Memphis, Florida
* Memphis, Indiana
* Memp ...
, despite a three year long siege. The Persians then counter-attacked, and the Athenian force was itself besieged for 18 months, before being wiped out. This disaster, coupled with ongoing warfare in Greece, dissuaded the Athenians from resuming conflict with Persia. In 451 BC, a truce was agreed in Greece, and Cimon was able to lead an expedition to Cyprus
Cyprus ; tr, Kıbrıs (), officially the Republic of Cyprus,, , lit: Republic of Cyprus is an island country located south of the Anatolian Peninsula in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Its continental position is disputed; while it is ...
. However, whilst besieging Kition
Kition ( Egyptian: ; Phoenician: , , or , ; Ancient Greek: , ; Latin: ) was a city-kingdom on the southern coast of Cyprus (in present-day Larnaca). According to the text on the plaque closest to the excavation pit of the Kathari site (as of ...
Cimon died, and the Athenian force decided to withdraw, winning another double victory at the Battle of Salamis-in-Cyprus in order to extricate themselves. This campaign marked the end of hostilities between the Delian League and Persia, and some ancient historians claim that a peace treaty, the Peace of Callias, was agreed to cement the final end of the Greco-Persian Wars.
Sources and chronology
 The military history of Greece between the end of the second Persian invasion of Greece and the
The military history of Greece between the end of the second Persian invasion of Greece and the Peloponnesian War
The Peloponnesian War (431–404 BC) was an ancient Greek war fought between Athens and Sparta and their respective allies for the hegemony of the Greek world. The war remained undecided for a long time until the decisive intervention of ...
(479–431 BC) is poorly attested by surviving ancient sources. This period, sometimes referred to as the ''pentekontaetia'' by ancient scholars, was a period of relative peace and prosperity within Greece.Finley, p. 16. The richest source for the period, and also the most contemporary with it, is Thucydides
Thucydides (; grc, , }; BC) was an Athenian historian and general. His '' History of the Peloponnesian War'' recounts the fifth-century BC war between Sparta and Athens until the year 411 BC. Thucydides has been dubbed the father of " scienti ...
's ''History of the Peloponnesian War
The ''History of the Peloponnesian War'' is a historical account of the Peloponnesian War (431–404 BC), which was fought between the Peloponnesian League (led by Sparta) and the Delian League (led by Athens). It was written by Thucydides, an ...
'', which is generally considered by modern historians to be a reliable primary account.Sealey, p. 264.Fine, p. 336.Finley, pp. 29–30. Thucydides only mentions this period in a digression on the growth of Athenian power in the run up to the Peloponnesian War, and the account is brief, probably selective and lacks any dates. Nevertheless, Thucydides's account can be, and is used by historians to draw up a skeleton chronology for the period, on to which details from archaeological records and other writers can be superimposed.
Much extra detail for the period is provided by Plutarch
Plutarch (; grc-gre, Πλούταρχος, ''Ploútarchos''; ; – after AD 119) was a Greek Middle Platonist philosopher, historian, biographer, essayist, and priest at the Temple of Apollo in Delphi. He is known primarily for hi ...
, in his biographies
A biography, or simply bio, is a detailed description of a person's life. It involves more than just the basic facts like education, work, relationships, and death; it portrays a person's experience of these life events. Unlike a profile or c ...
of Aristides
Aristides ( ; grc-gre, Ἀριστείδης, Aristeídēs, ; 530–468 BC) was an ancient Athenian statesman. Nicknamed "the Just" (δίκαιος, ''dikaios''), he flourished in the early quarter of Athens' Classical period and is remembe ...
and especially Cimon
Cimon or Kimon ( grc-gre, Κίμων; – 450BC) was an Athenian ''strategos'' (general and admiral) and politician.
He was the son of Miltiades, also an Athenian ''strategos''. Cimon rose to prominence for his bravery fighting in the naval Batt ...
. Plutarch was writing some 600 years after the events in question, and is therefore very much a secondary source, but he often explicitly names his sources, which allows some degree of verification of his statements. In his biographies, he explicitly draws on many ancient histories which have not survived, and thus often preserves details of the period which are omitted in Thucydides's brief account. The final major extant source for the period is the universal history (''Bibliotheca historica
''Bibliotheca historica'' ( grc, Βιβλιοθήκη Ἱστορική, ) is a work of universal history by Diodorus Siculus. It consisted of forty books, which were divided into three sections. The first six books are geographical in theme, ...
'') of the 1st century BC Sicilian, Diodorus Siculus
Diodorus Siculus, or Diodorus of Sicily ( grc-gre, Διόδωρος ; 1st century BC), was an ancient Greek historian. He is known for writing the monumental universal history '' Bibliotheca historica'', in forty books, fifteen of which ...
. Much of Diodorus's writing concerning this period seems to be derived from the much earlier Greek historian Ephorus, who also wrote a universal history. However, from what little is known of Ephorus, historians are generally disparaging towards his history; for this period he seems to have simply recycled Thucydides's research, but used it to draw completely different conclusions. Diodorus, who has often been dismissed by modern historians anyway, is therefore not a particularly good source for this period. Indeed, one of his translators, Oldfather, says of Diodorus's account of the Eurymedon campaign that "...the three preceding chapters reveal Diodorus in the worst light...".Oldfather, note to DiodoruXI, 62
/ref> There is also a reasonable body of archaeological evidence for the period, of which inscriptions detailing probable tribute lists of the Delian League are particularly important.
Chronology
Thucydides provides a succinct list of the main events occurring between the end of the second Persian invasion and the outbreak of the Peloponnesian War, but almost no chronological information.Sealey, p. 248. Various attempts have been made to reassemble the chronology, but there is no definitive answer. The assumption central to these attempts is that Thucydides is describing the events in the appropriate chronological order.Fine, p. 344. The one firmly accepted date is 465 BC for the beginning of the siege of Thasos. This is based on an anonymous ancient scholiast's annotations to one of the existing manuscripts ofAeschines
Aeschines (; Greek: , ''Aischínēs''; 389314 BC) was a Greek statesman and one of the ten Attic orators.
Biography
Although it is known he was born in Athens, the records regarding his parentage and early life are conflicting; but it seems ...
's works. The scholiast notes that the Athenians met disaster at 'Nine-Ways' in the archon
''Archon'' ( gr, ἄρχων, árchōn, plural: ἄρχοντες, ''árchontes'') is a Greek word that means "ruler", frequently used as the title of a specific public office. It is the masculine present participle of the verb stem αρχ-, mean ...
ship of Lysitheus (known to be 465/464 BC).Sealey, pp. 248–250. Thucydides mentions this attack on the 'Nine-Ways' in connection with the beginning of the siege of Thasos, and since Thucydides says that the siege ended in its third year, the siege of Thasos therefore dates to c. 465–463 BC.
Similarly, the anonymous scholiast provides a probable date for the siege of Eion
The Wars of the Delian League (477–449 BC) were a series of campaigns fought between the Delian League of Athens and her allies (and later subjects), and the Achaemenid Empire of Persia. These conflicts represent a continuation of the ...
. This annotation places the fall of Eion in the archonship of Phaidon (known to be 476/475 BC).Fine, p. 337. The siege may therefore have been between either 477–476 BC or 476–475 BC; both have found favour. The Battle of Eurymedon may be dated to 469 BC by Plutarch's anecdote about the Archon Apsephion (469/468 BC) choosing Cimon and his fellow generals as judges in a competition. The implication is that Cimon had recently achieved a great victory, and the most likely candidate is Eurymedon. However, since the Battle of Eurymedon seems to have occurred after the Athenian siege of Naxos (but before the siege of Thasos), the date of Eurymedon is clearly constrained by the date of Naxos. Whilst some accept a date of 469 or earlier for this Naxos,Kagan, p. 45. another school of thought places it as late as 467 BC.Fine, pp. 338–342. Since the Battle of Eurymedon seems to have occurred before Thasos, the alternative date for this battle would therefore be 466 BC.
The dating of Naxos is intimately connected with two other events in the Greek world which occurred at the same time. Thucydides claims that Pausanias Pausanias ( el, Παυσανίας) may refer to:
*Pausanias of Athens, lover of the poet Agathon and a character in Plato's ''Symposium''
*Pausanias the Regent, Spartan general and regent of the 5th century BC
* Pausanias of Sicily, physician of t ...
, having been stripped of his command after the siege of Byzantium, returned to Byzantium as a private citizen soon after and took command of the city until he was expelled by the Athenians. He then crossed the Bosporus
The Bosporus Strait (; grc, Βόσπορος ; tr, İstanbul Boğazı 'Istanbul strait', colloquially ''Boğaz'') or Bosphorus Strait is a natural strait and an internationally significant waterway located in Istanbul in northwestern Tu ...
and settled in Colonae
Kolonai ( grc, αἱ Κολωναί, hai Kolōnai; la, Colonae) was an ancient Greek city in the south-west of the Troad region of Anatolia. It has been located on a hill by the coast known as Beşiktepe ('cradle hill'), about equidistant betwe ...
in the Troad
The Troad ( or ; el, Τρωάδα, ''Troáda'') or Troas (; grc, Τρῳάς, ''Trōiás'' or , ''Trōïás'') is a historical region in northwestern Anatolia. It corresponds with the Biga Peninsula ( Turkish: ''Biga Yarımadası'') in the � ...
, until he was accused of collaborating with the Persians and was recalled by the Sparta
Sparta ( Doric Greek: Σπάρτα, ''Spártā''; Attic Greek: Σπάρτη, ''Spártē'') was a prominent city-state in Laconia, in ancient Greece. In antiquity, the city-state was known as Lacedaemon (, ), while the name Sparta referr ...
ns for trial (after which he starved himself to death). Thucydides again provides no chronology of these events.Fine, p. 339. Shortly afterwards, the Spartans accused the Athenian statesman Themistocles
Themistocles (; grc-gre, Θεμιστοκλῆς; c. 524–459 BC) was an Athenian politician and general. He was one of a new breed of non-aristocratic politicians who rose to prominence in the early years of the Athenian democracy. As ...
, then in exile in Argos, of complicity in Pausanias's treason. As a result, Themistocles fled from Argos, eventually to Asia Minor. Thucydides states that on his journey, Themistocles inadvertently ended up at Naxos
Naxos (; el, Νάξος, ) is a Greek island and the largest of the Cyclades. It was the centre of archaic Cycladic culture. The island is famous as a source of emery, a rock rich in corundum, which until modern times was one of the best ab ...
, at that time being besieged by Athenians.ThucydideI, 135–137
/ref> The three events, Pausanias's treason, Themistocles's flight and the siege of Naxos therefore occurred in close temporal sequence. These events certainly happened after 474 BC (the earliest possible date for Themistocles's
ostracism
Ostracism ( el, ὀστρακισμός, ''ostrakismos'') was an Athenian democratic procedure in which any citizen could be expelled from the city-state of Athens for ten years. While some instances clearly expressed popular anger at the ci ...
), and have generally been placed in around 470/469 BC.Fine, p. 341. However, there are several incongruities in the story of Themistocles if this date is accepted. A much later date for Pausanias's expulsion from Byzantium has been proposed, and if accepted, this pushes these three events into c. 467 BC, which resolves the problems regarding Themistocles, and also probably explains some incidental details mentioned in Plutarch's biography of Cimon. However, this modified timeline is not universally accepted by historians.
The Egyptian and Cyprian
Cyprian (; la, Thaschus Caecilius Cyprianus; 210 – 14 September 258 AD''The Liturgy of the Hours according to the Roman Rite: Vol. IV.'' New York: Catholic Book Publishing Company, 1975. p. 1406.) was a bishop of Carthage and an early Christ ...
campaigns are somewhat easier to date. Thucydides says that the Egyptian campaign lasted six years and that three years later, the Athenians and Spartans signed a five-year truce. This treaty is known to date to 451 BC, so the Egyptian campaign dates from c. 460–454 BC.Fine, p. 351. The Cyprian campaign, which directly followed the truce, thus dates to 451–450 BC.ThucydideI, 112
/ref>
Background
The Greco-Persian Wars had their roots in the conquest of the Greek cities of Asia Minor, and in particularIonia
Ionia () was an ancient region on the western coast of Anatolia, to the south of present-day Izmir. It consisted of the northernmost territories of the Ionian League of Greek settlements. Never a unified state, it was named after the Ionia ...
, by the Persian Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire (; peo, 𐎧𐏁𐏂, , ), also called the First Persian Empire, was an ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC. Based in Western Asia, it was contemporarily the largest emp ...
of Cyrus the Great
Cyrus II of Persia (; peo, 𐎤𐎢𐎽𐎢𐏁 ), commonly known as Cyrus the Great, was the founder of the Achaemenid Empire, the first Persian empire. Schmitt Achaemenid dynasty (i. The clan and dynasty) Under his rule, the empire embraced ...
shortly after 550 BC. The Persians found the Ionians difficult to rule, eventually settling for sponsoring a tyrant
A tyrant (), in the modern English usage of the word, is an absolute ruler who is unrestrained by law, or one who has usurped a legitimate ruler's sovereignty. Often portrayed as cruel, tyrants may defend their positions by resorting to ...
in each Ionian city.Holland, pp. 147–151. While Greek states had in the past often been ruled by tyrants, this was a form of government on the decline.Finepp. 269–277.
/ref> By 500 BC, Ionia appears to have been ripe for rebellion against these Persian place-men. The simmering tension finally broke into open revolt due to the actions of the tyrant of
Miletus
Miletus (; gr, Μῑ́λητος, Mī́lētos; Hittite transcription ''Millawanda'' or ''Milawata'' ( exonyms); la, Mīlētus; tr, Milet) was an ancient Greek city on the western coast of Anatolia, near the mouth of the Maeander River in ...
, Aristagoras. Attempting to save himself after a disastrous Persian-sponsored expedition in 499 BC, Aristagoras chose to declare Miletus a democracy.HerodotuV, 35
/ref> This triggered similar revolutions across Ionia, and indeed Doris and
Aeolis
Aeolis (; grc, Αἰολίς, Aiolís), or Aeolia (; grc, Αἰολία, Aiolía, link=no), was an area that comprised the west and northwestern region of Asia Minor (modern-day Turkey), mostly along the coast, and also several offshore islan ...
, beginning the Ionian Revolt
The Ionian Revolt, and associated revolts in Aeolis, Doris, Cyprus and Caria, were military rebellions by several Greek regions of Asia Minor against Persian rule, lasting from 499 BC to 493 BC. At the heart of the rebellion was the dissatisf ...
.Holland, pp. 155–157.
Eretria
Eretria (; el, Ερέτρια, , grc, Ἐρέτρια, , literally 'city of the rowers') is a town in Euboea, Greece, facing the coast of Attica across the narrow South Euboean Gulf. It was an important Greek polis in the 6th and 5th centur ...
allowed themselves to be drawn into this conflict by Aristagoras, and during their only campaigning season (498 BC) they contributed to the capture and burning of the Persian regional capital of Sardis
Sardis () or Sardes (; Lydian: 𐤳𐤱𐤠𐤭𐤣 ''Sfard''; el, Σάρδεις ''Sardeis''; peo, Sparda; hbo, ספרד ''Sfarad'') was an ancient city at the location of modern ''Sart'' (Sartmahmut before 19 October 2005), near Salihli, ...
.Holland, pp. 160–162. After this, the Ionian Revolt carried on (without further outside aid) for a further 5 years, until it was finally completely crushed by the Persians. However, in a decision of great historic significance, the Persian king Darius the Great
Darius I ( peo, 𐎭𐎠𐎼𐎹𐎺𐎢𐏁 ; grc-gre, Δαρεῖος ; – 486 BCE), commonly known as Darius the Great, was a Persian ruler who served as the third King of Kings of the Achaemenid Empire, reigning from 522 BCE until his d ...
decided that, despite successfully subduing the revolt, there remained the unfinished business of exacting punishment on Athens and Eretria for supporting the revolt.Holland, pp. 175–177. The Ionian Revolt had severely threatened the stability of Darius's empire, and the states of mainland Greece would continue to threaten that stability unless dealt with. Darius thus began to contemplate the complete conquest of Greece, beginning with the destruction of Athens and Eretria.
In the next two decades, there would be two Persian invasions of Greece, including some of the most famous battles in history. During the first invasion
''First Invasion'' is the debut EP by South Korean boy band Infinite (South Korean band), Infinite. It was released on June 9, 2010. They promoted the main single of the EP "Come Back Again" and followed with "She's Back (song), She's Back".
Tra ...
, Thrace, Macedon
Macedonia (; grc-gre, Μακεδονία), also called Macedon (), was an ancient kingdom on the periphery of Archaic and Classical Greece, and later the dominant state of Hellenistic Greece. The kingdom was founded and initially ruled ...
and the Aegean islands were added to the Persian Empire, and Eretria was duly destroyed.Holland, pp. 183–186. However, the invasion ended in 490 BC with the decisive Athenian victory at the Battle of Marathon
The Battle of Marathon took place in 490 BC during the first Persian invasion of Greece. It was fought between the citizens of Athens, aided by Plataea, and a Persian force commanded by Datis and Artaphernes. The battle was the culmination o ...
.Holland, pp. 187–194. Between the two invasions, Darius died, and responsibility for the war passed to his son Xerxes I
Xerxes I ( peo, 𐎧𐏁𐎹𐎠𐎼𐏁𐎠 ; grc-gre, Ξέρξης ; – August 465 BC), commonly known as Xerxes the Great, was the fourth King of Kings of the Achaemenid Empire, ruling from 486 to 465 BC. He was the son and successor of D ...
.Holland, pp. 202–203. Xerxes then led the second invasion personally in 480 BC, taking an enormous (although oft-exaggerated) army and navy to Greece.Holland, pp. 240–244. Those Greeks who chose to resist (the 'Allies') were defeated in the twin battles of Thermopylae
Thermopylae (; Ancient Greek and Katharevousa: (''Thermopylai'') , Demotic Greek (Greek): , (''Thermopyles'') ; "hot gates") is a place in Greece where a narrow coastal passage existed in antiquity. It derives its name from its hot sulphur ...
and Artemisium
Artemisium or Artemision (Greek: Ἀρτεμίσιον) is a cape in northern Euboea, Greece. The legendary hollow cast bronze statue of Zeus, or possibly Poseidon, known as the ''Artemision Bronze'', was found off this cape in a sunken ship,Wo ...
on land and at sea respectively.Holland, pp. 276–281. All of Greece except the Peloponnesus
The Peloponnese (), Peloponnesus (; el, Πελοπόννησος, Pelopónnēsos,(), or Morea is a peninsula and geographic region in southern Greece. It is connected to the central part of the country by the Isthmus of Corinth land bridge wh ...
thus fell into Persian hands, but then seeking to finally destroy the Allied navy, the Persians suffered a decisive defeat at the Battle of Salamis
The Battle of Salamis ( ) was a naval battle fought between an alliance of Greek city-states under Themistocles and the Persian Empire under King Xerxes in 480 BC. It resulted in a decisive victory for the outnumbered Greeks. The battle was ...
.Holland, pp. 320–326. The following year, 479 BC, the Allies assembled the largest Greek army yet seen and defeated the Persian invasion force at the Battle of Plataea
The Battle of Plataea was the final land battle during the second Persian invasion of Greece. It took place in 479 BC near the city of Plataea in Boeotia, and was fought between an alliance of the Greek city-states (including Sparta, Athens, ...
, ending the invasion and the threat to Greece.Holland, pp. 342–355.
According to tradition, on the same day as Plataea, the Allied fleet defeated the demoralised remnants of the Persian fleet in the Battle of Mycale
The Battle of Mycale ( grc, Μάχη τῆς Μυκάλης; ''Machē tēs Mykalēs'') was one of the two major battles (the other being the Battle of Plataea) that ended the second Persian invasion of Greece during the Greco-Persian Wars. It ...
.Holland, pp. 357–358. This action marks the end of the Persian invasion, and the beginning of the next phase in the Greco-Persian wars, the Greek counter-attack. After Mycale, the Greek cities of Asia Minor again revolted, with the Persians now powerless to stop them.ThucydideI, 89
/ref> The Allied fleet then sailed to the
Chersonesos
Chersonesus ( grc, Χερσόνησος, Khersónēsos; la, Chersonesus; modern Russian and Ukrainian: Херсоне́с, ''Khersones''; also rendered as ''Chersonese'', ''Chersonesos'', contracted in medieval Greek to Cherson Χερσών; ...
, still held by the Persians, and besieged and captured the town of Sestos
Sestos ( el, Σηστός, la, Sestus) was an ancient city in Thrace. It was located at the Thracian Chersonese peninsula on the European coast of the Hellespont, opposite the ancient city of Abydos, and near the town of Eceabat in Turkey.
In ...
.HerodotuIX, 114
/ref> The following year, 478 BC, the Allies sent a force to capture the city of
Byzantium
Byzantium () or Byzantion ( grc, Βυζάντιον) was an ancient Greek city in classical antiquity that became known as Constantinople in late antiquity and Istanbul today. The Greek name ''Byzantion'' and its Latinization ''Byzantium' ...
(modern day Istanbul
)
, postal_code_type = Postal code
, postal_code = 34000 to 34990
, area_code = +90 212 (European side) +90 216 (Asian side)
, registration_plate = 34
, blank_name_sec2 = GeoTLD
, blank_i ...
). The siege was successful, but the behaviour of the Spartan general Pausanias alienated many of the Allies, and resulted in Pausanias's recall.ThucydideI, 95
/ref> The siege of Byzantium was the last action of the Hellenic alliance which had defeated the Persian invasion.
Delian League
Leotychides
Leotychidas II ( grc-gre, Λεωτυχίδας; Doric: ; c. 545 – c. 469 BC) was king of Sparta between 491–476 BC, alongside Cleomenes I and later Leonidas I and Pleistarchus. He led Spartan forces during the Persian Wars from 490 BC to 478 ...
had proposed transplanting all the Greeks from Asia Minor to Europe as the only method of permanently freeing them from Persian dominion. Xanthippus
Xanthippus (; el, Ξάνθιππος, ; c. 525-475 BC) was a wealthy Athenian politician and general during the early part of the 5th century BC. His name means "Yellow Horse." He was the son of Ariphron and father of Pericles. A marriage to ...
, the Athenian commander at Mycale, had furiously rejected this; the Ionian cities were originally Athenian colonies, and the Athenians, if no one else, would protect the Ionians.Holland, p. 362. This marked the point at which the leadership of the Hellenic alliance effectively passed to the Athenians; with the Spartan withdrawal after Byzantium, the leadership of the Athenians became explicit.
The loose alliance of city states which had fought against Xerxes's invasion had been dominated by Sparta and the Peloponnesian league. With the withdrawal of these states, a congress was called on the holy island of Delos
The island of Delos (; el, Δήλος ; Attic: , Doric: ), near Mykonos, near the centre of the Cyclades archipelago, is one of the most important mythological, historical, and archaeological sites in Greece. The excavations in the island ar ...
to institute a new alliance to continue the fight against the Persians. This alliance, now including many of the Aegean islands, was formally constituted as the 'First Athenian Alliance', commonly known as the Delian League
The Delian League, founded in 478 BC, was an association of Greek city-states, numbering between 150 and 330, under the leadership of Athens, whose purpose was to continue fighting the Persian Empire after the Greek victory in the Battle of Pla ...
. According to Thucydides, the official aim of the League was to "avenge the wrongs they suffered by ravaging the territory of the king."ThucydideI, 96
/ref> In reality, this goal was divided into three main efforts - to prepare against any future invasion, to seek revenge against Persia, and to organize a means of dividing spoils of war. The members were given a choice of either offering armed forces or paying a tax to the joint treasury; most states chose the tax.Thucydide
I, 99
/ref> League members swore to have the same friends and enemies, and dropped ingots of iron into the sea to symbolize the permanence of their alliance. The ingots of iron were cast into the ocean because the oath the league members swore stipulated that their allegiance would not end, or be otherwise broken, until the iron floated to the surface. In other words, that they had made a pact perceived to be eternal. The Athenian politician
Aristides
Aristides ( ; grc-gre, Ἀριστείδης, Aristeídēs, ; 530–468 BC) was an ancient Athenian statesman. Nicknamed "the Just" (δίκαιος, ''dikaios''), he flourished in the early quarter of Athens' Classical period and is remembe ...
would spend the rest of his life occupied in the affairs of the alliance, dying (according to Plutarch) a few years later in Pontus
Pontus or Pontos may refer to:
* Short Latin name for the Pontus Euxinus, the Greek name for the Black Sea (aka the Euxine sea)
* Pontus (mythology), a sea god in Greek mythology
* Pontus (region), on the southern coast of the Black Sea, in modern ...
, whilst determining what the tax of new members was to be.
Non-Persian campaigns
Military expansion of the League
Thucydides provides just one example of the use of force to extend membership of the League, but since his account seems to be selective, there were presumably more; certainly, Plutarch provides details of one such instance.Karystos
Karystos ( el, Κάρυστος) or Carystus is a small coastal town on the Greek island of Euboea. It has about 5,000 inhabitants (12,000 in the municipality). It lies 129 km south of Chalkis. From Athens it is accessible by ferry via ...
, which had collaborated with the Persians during the second Persian invasion, was attacked by the League at some point in the 470s BC, and eventually agreed to become a member. Plutarch mentions the fate of Phaselis
Phaselis ( grc, Φασηλίς) or Faselis ( tr, Faselis) was a Greek and Roman city on the coast of ancient Lycia. Its ruins are located north of the modern town Tekirova in the Kemer district of Antalya Province in Turkey. It lies between ...
, which Cimon compelled to join the league during his Eurymedon campaign.
Internal rebellions
Naxos attempted to leave the League c. 470/467 BC but was attacked by the Athenians and forced to remain a member. A similar fate awaited theThasians
Thasos or Thassos ( el, Θάσος, ''Thásos'') is a Greek island in the North Aegean Sea. It is the northernmost major Greek island, and 12th largest by area.
The island has an area of and a population of about 13,000. It forms a separate re ...
after they tried to leave the League in 465 BC.ThucydideI, 100
/ref> Thucydides does not provide more examples, but from archaeological sources it is possible to deduce that there were further rebellions in the following years.Fine, p. 359. Thucydides leaves us under no illusions that the behaviour of the Athenians in crushing such rebellions led firstly to the hegemony of Athens over the league, and eventually to the transition from the Delian League to the
Athenian Empire
The Delian League, founded in 478 BC, was an association of Greek city-states, numbering between 150 and 330, under the leadership of Athens, whose purpose was to continue fighting the Persian Empire after the Greek victory in the Battle of Plat ...
.Kagan, p. 44.
Conflicts in Greece
During the period 479–461, the mainland Greek states were at least outwardly at peace with each other, even if divided into pro-Spartan and pro-Athenian factions. The Hellenic alliance still existed in name, and since Athens and Sparta were still allied, Greece achieved a modicum of stability.Kagan, p. 77. However, over this period, Sparta became increasingly suspicious and fearful of the growing power of Athens. It was this fear, according to Thucydides, which made the second, larger (and more famous) Peloponnesian War inevitable. Athens sent troops in 462 BC to aid Sparta with the Messenian Revolt (c. 465–461 BC), under the terms of the old Hellenic alliance.Thucydide
Athens sent troops in 462 BC to aid Sparta with the Messenian Revolt (c. 465–461 BC), under the terms of the old Hellenic alliance.ThucydideI, 102
/ref> The Spartans however, in the fear that Athens might interfere in the political situation between the Spartans and their
helots
The helots (; el, εἵλωτες, ''heílotes'') were a subjugated population that constituted a majority of the population of Laconia and Messenia – the territories ruled by Sparta. There has been controversy since antiquity as to their ...
, sent the Athenians home. This event directly led to the ostracism of Cimon (who had been leading the troops), the ascendancy of the radical democrats (led by Ephialtes
Ephialtes ( grc-gre, Ἐφιάλτης, ''Ephialtēs'') was an ancient Athenian politician and an early leader of the democratic movement there. In the late 460s BC, he oversaw reforms that diminished the power of the Areopagus, a traditional ba ...
and Pericles
Pericles (; grc-gre, Περικλῆς; c. 495 – 429 BC) was a Greek politician and general during the Golden Age of Athens. He was prominent and influential in Athenian politics, particularly between the Greco-Persian Wars and the Pelo ...
) over the previously dominant aristocratic faction (led by Cimon) in Athens, and the First Peloponnesian War
The First Peloponnesian War (460–445 BC) was fought between Sparta as the leaders of the Peloponnesian League and Sparta's other allies, most notably Thebes, Greece, Thebes, and the Delian League led by Athens with support from Ancient Argos, ...
between Athens and Sparta (and their respective allies).Kagan, pp. 73–74.
This conflict was really the Athenians' own struggle, and need not have involved the Delian allies. After all, the League members had signed up to fight against the Persians, not fellow Greeks.Fine, p. 358. Nevertheless, it does seem that at least at the Battle of Tanagra, a contingent of Ionians fought with the Athenians. The conflicts in Greece during these years are, however, not directly relevant to the history of the Delian League.
It can be seen, however, that the First Peloponnesian War may have hastened the transition of the Delian League from an Athenian-dominated alliance to an Athenian-ruled empire. During the early years of the war, Athens and her non-Delian allies scored a series of victories. However, the collapse of the simultaneous Delian League expedition in Egypt in 454 BC caused panic in Athens, and resulted in decreased military activity until 451 BC, when a five-year truce was concluded with Sparta.Sealey, pp. 271–273. During the panic, the treasury of the League was moved from Delos to the perceived safety of Athens in 454 BC. Although Athens had in practice had a hegemonic position over the rest of the league since the rebellion of Naxos (470/467 BC) was put down, the process by which the Delian league gradually transformed into the Athenian Empire accelerated after 461 BC.Kagan, p. 48. The transfer of the treasury to Athens is sometimes used as an arbitrary demarcation between the Delian League and the Athenian Empire. An alternative 'end-point' for the Delian League is the final end of hostilities with the Persians in 450 BC, after which, despite the fact that the stated aims of the League were fulfilled, the Athenians refused to allow member states to leave the alliance.Holland, pp. 366–367.Sealey, p. 282.
Campaigns against Persia
Thrace
Siege of Eion
 According to Thucydides, the League's opening campaign was against the city of
According to Thucydides, the League's opening campaign was against the city of Eion
Eion ( grc-gre, Ἠϊών, ''Ēiṓn''), ancient Chrysopolis, was an ancient Greek Eretrian colony in Thracian Macedonia specifically in the region of Edonis. It sat at the mouth of the Strymon River which flows into the Aegean from the interio ...
, at the mouth of the Strymon river.ThucydideI, 98
/ref> Since Thucydides does not provide a detailed chronology for his history of the league, the year in which this campaign took place is uncertain. The siege seems to have lasted from autumn of one year into the summer of the next, with historians supporting either 477–476 BC or 476–475 BC.Fine, p. 343. Eion seems to have been one of the Persian garrisons left in Thrace during and after the second Persian invasion, along with
Doriskos
Doriscus ( grc-gre, Δορίσκος and Δωρίσκος, ''Dorískos'') was a settlement in ancient Thrace (modern-day Greece), on the northern shores of Aegean Sea, in a plain west of the river Hebrus. It was notable for remaining in Persian h ...
.HerodotuVII, 107
/ref> The campaign against Eion should probably be seen as part of a general campaign aimed at removing the Persian presence from Thrace.Sealey, p. 250. Even though he does not directly cover this period, Herodotus alludes to several failed attempts, presumably Athenian, to dislodge the Persian governor of Doriskos,
Mascames
Mascames, also spelled Maskames (Old Persian: ''Maškāma'') was a Persian official and military commander, who flourished during the reign of Xerxes I (486–465). He was the son of Megadostes, and was appointed governor of Doriscus in 480 BC b ...
. Eion may have been worthy of particular mention by Thucydides because of its strategic importance; abundant supplies of timber were available in the region, and there were nearby silver mines. Furthermore, it was near the site of the future Athenian colony of Amphipolis, which was the site of several future disasters for the Athenians.
 The force which attacked Eion was under the command of Cimon. Plutarch says that Cimon first defeated the Persians in battle, whereupon they retreated to the city, and were besieged there.Plutarch, Cimon, 7 Cimon then expelled all Thracian collaborators from the region in order to starve the Persians into submission. Herodotus indicates that the Persian commander,
The force which attacked Eion was under the command of Cimon. Plutarch says that Cimon first defeated the Persians in battle, whereupon they retreated to the city, and were besieged there.Plutarch, Cimon, 7 Cimon then expelled all Thracian collaborators from the region in order to starve the Persians into submission. Herodotus indicates that the Persian commander, Boges
Boges was a Persian official and military commander, who functioned as governor (''hyparchos'') of Eion in Thrace (Achaemenid satrapy of Skudra) under the King of Kings Xerxes I (486–465 BC). According to Herodotus, following the Persian defea ...
, was offered terms upon which he might be allowed to evacuate the city and return to Asia. However, not wanting to be thought a coward by Xerxes, he resisted to the last. When the food in Eion ran out, Boges threw his treasure into the Strymon, killed his entire household and then immolated them, and himself, on a giant pyre. The Athenians thus captured the city and enslaved the remaining population.
After the fall of Eion, other coastal cities of the area surrendered to the Delian League, with the notable exception of Doriscus
Doriscus ( grc-gre, Δορίσκος and Δωρίσκος, ''Dorískos'') was a settlement in ancient Thrace (modern-day Greece), on the northern shores of Aegean Sea, in a plain west of the river Hebrus. It was notable for remaining in Persian h ...
, which was "never taken". The Achaemenids probably recalled the Governor of Doriscus Mascames
Mascames, also spelled Maskames (Old Persian: ''Maškāma'') was a Persian official and military commander, who flourished during the reign of Xerxes I (486–465). He was the son of Megadostes, and was appointed governor of Doriscus in 480 BC b ...
with his garrison around 465 BC, and finally abandoned this last Achaemenid stronghold in Europe.
Skyros
Following the action at Eion, and possibly in the same campaign, the Athenians, still under Cimon, attacked the island ofSkyros
Skyros ( el, Σκύρος, ), in some historical contexts Latinized Scyros ( grc, Σκῦρος, ), is an island in Greece, the southernmost of the Sporades, an archipelago in the Aegean Sea. Around the 2nd millennium BC and slightly later, the ...
. This was not an anti-Persian action, but a pragmatic assault on a native population that had lapsed into piracy.Plutarch, Cimon, 8 As a result of this action, the Athenians "liberated the Aegean", and they sent colonists to the island to prevent the island returning to piracy.
Chersonesos
Cimon returned a decade later to complete the expulsion of Persian forces from Europe. This action seems to have occurred concurrently with the siege of Thasos, and so is generally dated to 465 BC. Evidently, even at this point, some Persian forces were holding (or had re-taken) some part of theChersonesos
Chersonesus ( grc, Χερσόνησος, Khersónēsos; la, Chersonesus; modern Russian and Ukrainian: Херсоне́с, ''Khersones''; also rendered as ''Chersonese'', ''Chersonesos'', contracted in medieval Greek to Cherson Χερσών; ...
with the help of native Thracians.Plutarch, Cimon, 14 Cimon sailed to the Chersonesos with just 4 triremes, but managed to capture the 13 ships of the Persians, and then proceeded to drive them out of the peninsula. Cimon then turned the Chersonesos (of which his father, Miltiades the Younger, had been tyrant before the Greco-Persian Wars began) over to the Athenians for colonisation.
Asia Minor
 Once the Persian forces in Europe had largely been neutralised, the Athenians seem to have gone about starting to extend the League in Asia Minor.Plutarch, Cimon, 12Cawkwell, p. 133. The islands of Samos, Chios and Lesbos seem to have become members of the original Hellenic alliance after Mycale, and presumably were also therefore original members of the Delian League. However, it is unclear exactly when the other Ionian cities, or indeed the other Greek cities of Asia Minor, joined the league, though they certainly did at some point.Sealey, p. 247.
Cimon's Eurymedon campaign itself seems to have begun in response to the assembly of a large Persian fleet and army at
Once the Persian forces in Europe had largely been neutralised, the Athenians seem to have gone about starting to extend the League in Asia Minor.Plutarch, Cimon, 12Cawkwell, p. 133. The islands of Samos, Chios and Lesbos seem to have become members of the original Hellenic alliance after Mycale, and presumably were also therefore original members of the Delian League. However, it is unclear exactly when the other Ionian cities, or indeed the other Greek cities of Asia Minor, joined the league, though they certainly did at some point.Sealey, p. 247.
Cimon's Eurymedon campaign itself seems to have begun in response to the assembly of a large Persian fleet and army at Aspendos
Aspendos or Aspendus ( Pamphylian: ΕΣΤϜΕΔΥΣ; Attic: Ἄσπενδος) was an ancient Greco-Roman city in Antalya province of Turkey. The site is located 40 km east of the modern city of Antalya.
It was situated on the Eurymedon ...
, near the mouth of the Eurymedon River. It is usually argued that the Persians were the would-be aggressors, and that Cimon's campaign was launched in order to deal with this new threat.Powell, p. 19–20. Cawkwell suggests that the Persian build-up was the first concerted attempt to counter the activity of the Greeks since the failure of the second invasion. It is possible that internal strife with the Persian empire had contributed to the length of time it took to launch this campaign.Cawkwell, p. 132. Cawkwell suggests that the Persian forces gathered at Aspendos were aiming to move along the southern coast of Asia Minor, capturing each city, until eventually the Persian navy could begin operating in Ionia again.
Plutarch says that upon hearing that the Persian forces were gathering at Aspendos, Cimon sailed from Cnidus
Knidos or Cnidus (; grc-gre, Κνίδος, , , Knídos) was a Greek city in ancient Caria and part of the Dorian Hexapolis, in south-western Asia Minor, modern-day Turkey. It was situated on the Datça peninsula, which forms the southern sid ...
(in Caria
Caria (; from Greek: Καρία, ''Karia''; tr, Karya) was a region of western Anatolia extending along the coast from mid- Ionia (Mycale) south to Lycia and east to Phrygia. The Ionian and Dorian Greeks colonized the west of it and joine ...
) with 200 triremes. It is highly likely that Cimon had assembled this force because the Athenians had had some warning of a forthcoming Persian campaign to re-subjugate the Asiatic Greeks. According to Plutarch, Cimon sailed with these 200 triremes to the Greek city of Phaselis
Phaselis ( grc, Φασηλίς) or Faselis ( tr, Faselis) was a Greek and Roman city on the coast of ancient Lycia. Its ruins are located north of the modern town Tekirova in the Kemer district of Antalya Province in Turkey. It lies between ...
(in Lycia
Lycia ( Lycian: 𐊗𐊕𐊐𐊎𐊆𐊖 ''Trm̃mis''; el, Λυκία, ; tr, Likya) was a state or nationality that flourished in Anatolia from 15–14th centuries BC (as Lukka) to 546 BC. It bordered the Mediterranean Sea in what is ...
) but was refused admittance. He therefore began ravaging the lands of Phaselis, but with the mediation of the Chian contingent of his fleet, the people of Phaselis agreed to join the league. They were to contribute troops to the expedition, and to pay the Athenians ten talents. By capturing Phaselis, the furthest east Greek city in Asia Minor (and just to the west of the Eurymedon), he effectively blocked the Persian campaign before it had begun, denying them the first naval base they needed to control. Taking further initiative, Cimon then moved to directly attack the Persian fleet at Aspendos.
Battle of the Eurymedon
 Thucydides gives only the barest of details for this battle; the most reliable detailed account is given by Plutarch. According to Plutarch, the Persian fleet was anchored off the mouth of the Eurymedon, awaiting the arrival of 80 Phoenician ships from Cyprus. Several different estimates for the size of the Persian fleet are given. Thucydides says that there was a fleet of 200 Phoenician ships, and is generally considered the most reliable source.Cawkwell, p. 134. Plutarch gives numbers of 350 from Ephorus and 600 from Phanodemus.
Cimon, sailing from Phaselis, made to attack the Persians before the reinforcements arrived, whereupon the Persian fleet, eager to avoid fighting, retreated into the river itself. However, when Cimon continued to bear down on the Persians, they accepted battle. Regardless of their numbers, the Persian battle line was quickly breached, and the Persian ships then turned about, and made for the river bank. Grounding their ships, the crews sought sanctuary with the army waiting nearby. Despite the weariness of his troops after this first battle, Cimon landed the marines and proceeded to attack the Persian army. Initially the Persian line held the Athenian assault, but eventually, as at
Thucydides gives only the barest of details for this battle; the most reliable detailed account is given by Plutarch. According to Plutarch, the Persian fleet was anchored off the mouth of the Eurymedon, awaiting the arrival of 80 Phoenician ships from Cyprus. Several different estimates for the size of the Persian fleet are given. Thucydides says that there was a fleet of 200 Phoenician ships, and is generally considered the most reliable source.Cawkwell, p. 134. Plutarch gives numbers of 350 from Ephorus and 600 from Phanodemus.
Cimon, sailing from Phaselis, made to attack the Persians before the reinforcements arrived, whereupon the Persian fleet, eager to avoid fighting, retreated into the river itself. However, when Cimon continued to bear down on the Persians, they accepted battle. Regardless of their numbers, the Persian battle line was quickly breached, and the Persian ships then turned about, and made for the river bank. Grounding their ships, the crews sought sanctuary with the army waiting nearby. Despite the weariness of his troops after this first battle, Cimon landed the marines and proceeded to attack the Persian army. Initially the Persian line held the Athenian assault, but eventually, as at Battle of Mycale
The Battle of Mycale ( grc, Μάχη τῆς Μυκάλης; ''Machē tēs Mykalēs'') was one of the two major battles (the other being the Battle of Plataea) that ended the second Persian invasion of Greece during the Greco-Persian Wars. It ...
, the heavily armoured hoplites proved superior, and routed the Persian army.Plutarch, Cimon, 13 Thucydides says that 200 Phoenician ships were captured and destroyed. It is highly unlikely that this occurred during the apparently brief naval battle, so these were probably grounded ships captured after the battle and destroyed with fire, as has been the case at Mycale. According to Plutarch, Cimon then sailed with the Greek fleet as quickly as possible, to intercept the fleet of 80 Phoenician ships which the Persians had been expecting. Taking them by surprise, he captured or destroyed the entire fleet. However, Thucydides does not mention this subsidiary action, and some have cast doubt on whether it actually happened.
According to Plutarch, one tradition had it that the Persian king (who at the time would still have been Xerxes) had agreed a humiliating peace treaty in the aftermath of the Eurymedon (see below
Below may refer to:
*Earth
*Ground (disambiguation)
*Soil
*Floor
*Bottom (disambiguation)
*Less than
*Temperatures below freezing
*Hell or underworld
People with the surname
*Ernst von Below (1863–1955), German World War I general
*Fred Below ( ...
). However, as Plutarch admits, other authors denied that such a peace was made at this time, and the more logical date for any peace treaty would have been after the Cyprus campaign. The alternative suggested by Plutarch is that the Persian king ''acted'' as if he had made a humiliating peace with the Greeks, because he was so fearful of engaging in battle with them again. It is generally considered unlikely by modern historians that a peace treaty was made in the aftermath of Eurymedon. The Eurymedon was a highly significant victory for the Delian League, which probably ended once and for all the threat of another Persian invasion of Greece.Holland, p. 363. It also seems to have prevented any Persian attempt to reconquer the Asiatic Greeks until at least 451 BC. The accession of further cities of Asia Minor to the Delian league, particularly from Caria, probably followed Cimon's campaign there. The Greeks do not appear to have pressed their advantage home in a meaningful way.Fine, p. 345. If the later date of 466 BC for the Eurymedon campaign is accepted, this might be because the revolt in Thasos meant that resources were diverted away from Asia Minor to prevent the Thasians seceding from the League. The Persian fleet was effectively absent from the Aegean until 451 BC, and Greek ships were able to ply the coasts of Asia Minor with impunity.
Egypt
 The Egyptian campaign, as discussed above, is generally thought to have begun in 460 BC. Even this date is subject to some debate however, since at this time Athens was already at war with Sparta in the First Peloponnesian War. It has been questioned whether Athens would really commit to an Egyptian campaign under these circumstances, and therefore suggested that this campaign began ''before'' the war with Sparta, in 462 BC.Kagan, p. 82. However, this date is generally rejected, and it seems that the Egyptian campaign was, on the part of Athens, simply a piece of political opportunism.Fine, p. 352.
The Egyptian campaign, as discussed above, is generally thought to have begun in 460 BC. Even this date is subject to some debate however, since at this time Athens was already at war with Sparta in the First Peloponnesian War. It has been questioned whether Athens would really commit to an Egyptian campaign under these circumstances, and therefore suggested that this campaign began ''before'' the war with Sparta, in 462 BC.Kagan, p. 82. However, this date is generally rejected, and it seems that the Egyptian campaign was, on the part of Athens, simply a piece of political opportunism.Fine, p. 352.
 The
The Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning the North Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via a land bridg ...
ian satrapy of the Persian Empire was particularly prone to revolts, one of which had occurred as recently as 486 BC.Sealey, p. 269. In 461 or 460 BC, a new rebellion began under the command of Inaros, a Libyan king living on the border of Egypt. This rebellion quickly swept the country, which was soon largely in the hands of Inaros.ThucydideI, 104
/ref> Inaros now appealed to the Delian League for assistance in their fight against the Persians. There was a League fleet of 200 ships under Admiral
Charitimides
Charitimides ( grc, Χαριτιμίδης) (died 455 BCE) was an Athenian admiral of the 5th century BCE. At the time of the Wars of the Delian League, a continuing conflict between the Athenian-led Delian League of Greek city-states and the ...
already campaigning in Cyprus at this time, which the Athenians then diverted Egypt to support the revolt. Indeed, it is possible that the fleet had been dispatched to Cyprus in the first place because, with Persian attention focused on the Egyptian revolt, it seemed a favourable time to campaign in Cyprus. This would go some way towards explaining the apparently reckless decision of the Athenians to fight wars on two fronts.Kagan, p. 81 Thucydides seems to imply that the whole fleet was diverted to Egypt, although it has also been suggested that such a large fleet was unnecessary, and some portion of it remained of the coast of Asia Minor during this period. Ctesias
Ctesias (; grc-gre, Κτησίας; fl. fifth century BC), also known as Ctesias of Cnidus, was a Greek physician and historian from the town of Cnidus in Caria, then part of the Achaemenid Empire.
Historical events
Ctesias, who lived in the fi ...
suggests that the Athenians sent 40 ships, whereas Diodorus says 200, in apparent agreement with Thucydides.CtesiasPersica, 36
(from Photius's Epitome)Diodoru
XI, 74
/ref> Fine suggests a number of reasons that the Athenians may have been willing to engage themselves in Egypt, despite the ongoing war elsewhere; the opportunity to weaken Persia, the desire for a naval base in Egypt, the access to the
Nile
The Nile, , Bohairic , lg, Kiira , Nobiin: Áman Dawū is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea. The Nile is the longest river in Africa and has historically been considered the longest riv ...
's huge grain supply, and from the viewpoint of the Ionian allies, the chance to restore profitable trading links with Egypt.
At any rate, the Athenians arrived in Egypt, and sailed up the Nile to join up with Inaros's forces. Charitimides led his fleet against the Achaemenids in the Nile river
The Nile, , Bohairic , lg, Kiira , Nobiin: Áman Dawū is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea. The Nile is the longest river in Africa and has historically been considered the longest riv ...
, and defeated a fleet consisting of 50 Phoenician ships. It was the last great naval encounter between the Greeks and the Achaemenids. Of the 50 Phoenician ships, he managed to destroy 30 ships, and capture the remaining 20 that faced him in that battle.
The Persian king Artaxerxes I
Artaxerxes I (, peo, 𐎠𐎼𐎫𐎧𐏁𐏂𐎠 ; grc-gre, Ἀρταξέρξης) was the fifth King of Kings of the Achaemenid Empire, from 465 to December 424 BC. He was the third son of Xerxes I.
He may have been the " Artas ...
had in the meantime assembled a relief force to crush the revolt, under his uncle Achaemenes
Achaemenes ( peo, 𐏃𐎧𐎠𐎶𐎴𐎡𐏁 ; grc, Ἀχαιμένης ; la, Achaemenes) was the apical ancestor of the Achaemenid dynasty of rulers of Persia.
Other than his role as an apical ancestor, nothing is known of his life or a ...
. Diodorus and Ctesias give numbers for this force of 300,000 and 400,000 respectively, but these numbers are presumably over-inflated.
Battle of Papremis (460 BC)
According to Diodorus, the only detailed source for this campaign, the Persian relief force had pitched camp near the Nile. Although Herodotus does not cover this period in his history, he mentions as an aside that he "saw too the skulls of those Persians at Papremis who were killed with Darius' son Achaemenes by Inaros the Libyan". This provides some confirmation that this battle was factual, and provides a name for it, which Diodorus does not. Papremis (or Pampremis) seems to have been a city on the Nile delta, and a cult centre for the Egyptian equivalent ofAres
Ares (; grc, Ἄρης, ''Árēs'' ) is the Greek god of war and courage. He is one of the Twelve Olympians, and the son of Zeus and Hera. The Greeks were ambivalent towards him. He embodies the physical valor necessary for success in war ...
/Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and the second-smallest planet in the Solar System, only being larger than Mercury. In the English language, Mars is named for the Roman god of war. Mars is a terrestrial planet with a thin at ...
. Diodorus tells us that once the Athenians had arrived, they and the Egyptians accepted battle from the Persians. At first the Persians' superior numbers gave them the advantage, but eventually the Athenians broke through the Persian line, whereupon the Persian army routed and fled. Some portion of the Persian army found refuge in the citadel of Memphis
Memphis most commonly refers to:
* Memphis, Egypt, a former capital of ancient Egypt
* Memphis, Tennessee, a major American city
Memphis may also refer to:
Places United States
* Memphis, Alabama
* Memphis, Florida
* Memphis, Indiana
* Memp ...
(called the 'White Castle'), however, and could not be dislodged. Thucydides's rather compressed version of these events is: "and making themselves masters of the river and two-thirds of Memphis, addressed themselves to the attack of the remaining third, which is called White Castle".
Siege of Memphis (459–455 BCE)
 The Athenians and Egyptians thus settled down to besiege the White Castle. The siege evidently did not progress well, and probably lasted for at least four years, since Thucydides says that their whole expedition lasted 6 years,Thucydide
The Athenians and Egyptians thus settled down to besiege the White Castle. The siege evidently did not progress well, and probably lasted for at least four years, since Thucydides says that their whole expedition lasted 6 years,ThucydideI, 110
/ref> and of this time the final 18 months was occupied with the Siege of Prosoptis.Thucydide
I, 109
/ref> According to Thucydides, at first Artaxerxes sent Megabazus to try and bribe the Spartans into invading
Attica
Attica ( el, Αττική, Ancient Greek ''Attikḗ'' or , or ), or the Attic Peninsula, is a historical region that encompasses the city of Athens, the capital of Greece and its countryside. It is a peninsula projecting into the Aegean ...
, to draw off the Athenian forces from Egypt. When this failed, he instead assembled a large army under (confusingly) Megabyzus
Megabyzus ( grc, Μεγάβυζος, a folk-etymological alteration of Old Persian Bagabuxša, meaning "God saved") was an Achaemenid Persian general, son of Zopyrus, satrap of Babylonia, and grandson of Megabyzus I, one of the seven conspirato ...
, and dispatched it to Egypt. Diodorus has more or less the same story, with more detail; after the attempt at bribery failed, Artaxerxes put Megabyzus and Artabazus in charge of 300,000 men, with instructions to quell the revolt. They went first from Persia to Cilicia
Cilicia (); el, Κιλικία, ''Kilikía''; Middle Persian: ''klkyʾy'' (''Klikiyā''); Parthian: ''kylkyʾ'' (''Kilikiyā''); tr, Kilikya). is a geographical region in southern Anatolia in Turkey, extending inland from the northeastern co ...
and gathered a fleet of 300 triremes from the Cilicians, Phoenicia
Phoenicia () was an ancient thalassocratic civilization originating in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily located in modern Lebanon. The territory of the Phoenician city-states extended and shrank throughout their his ...
ns and Cypriots, and spent a year training their men. Then they finally headed to Egypt. Modern estimates, however, place the number of Persian troops at the considerably lower figure of 25,000 men given that it would have been highly impractical to deprive the already strained satrapies of any more man power than that. Thucydides does not mention Artabazus, who is reported by Herodotus to have taken part in the Second Persian invasion of Greece
The second Persian invasion of Greece (480–479 BC) occurred during the Greco-Persian Wars, as King Xerxes I of Persia sought to conquer all of Greece. The invasion was a direct, if delayed, response to the defeat of the first Persian invasio ...
; Diodorus may be mistaken about his presence in this campaign. It is clearly possible that the Persian forces did spend some prolonged time in training, since it took four years for them to respond to the Egyptian victory at Papremis. Although neither author gives many details, it is clear that when Megabyzus finally arrived in Egypt, he was able to quickly lift the siege of Memphis, defeating the Egyptians in battle, and driving the Athenians from Memphis.DiodoruXI, 77
/ref>
Siege of Prosopitis (455 BCE)
The Athenians now fell back to the island of Prosopitis in the Nile delta, where their ships were moored. There, Megabyzus laid siege to them for 18 months, until finally he was able to drain the river from around the island by digging canals, thus "joining the island to the mainland". In Thucydides's account the Persians then crossed over to the former island, and captured it. Only a few of the Athenian force, marching through Libya to Cyrene survived to return to Athens. In Diodorus's version, however, the draining of the river prompted the Egyptians (whom Thucydides does not mention) to defect and surrender to the Persians. The Persians, not wanting to sustain heavy casualties in attacking the Athenians, instead allowed them to depart freely to Cyrene, whence they returned to Athens. Since the defeat of the Egyptian expedition caused a genuine panic in Athens, including the relocation of the Delian treasury to Athens, Thucydides's version is probably more likely to be correct.Battle of Mendesium
As a final disastrous coda to the expedition, Thucydides mentions the fate of a squadron of fifty triremes sent to relieve the siege of Prosopitis. Unaware that the Athenians had finally succumbed, the fleet put in at the Mendesian mouth of the Nile, where it was promptly attacked from the land, and from the sea by the Phoenician navy. Most of the ships were destroyed, with only a handful managing to escape and return to Athens. Total Athenian casualties of the expedition totaled some 50,000 men and 250 ships.Cyprus
I, 94
/ref> Exactly what Thucydides means by this is unclear. Sealey suggests that this was essentially a raid to gather as much booty as possible from the Persian garrisons on Cyprus.Sealey, p. 242 There is no indication that the Allies made any attempt to actually take possession of the island, and shortly after they sailed to Byzantium. Certainly, the fact that the Delian League repeatedly campaigned in Cyprus suggests that the island was not garrisoned by the Allies in 478 BC, or that the garrisons were quickly expelled. The next time Cyprus is mentioned is in relation to c. 460 BC, when a League fleet was campaigning there, before being instructed to head to Egypt to support Inaros's rebellion, with the fateful consequences discussed above. The Egyptian disaster would eventually lead the Athenians to sign a five-year truce with Sparta in 451 BC. Thereby freed from fighting in Greece, the League was again able to dispatch a fleet to campaign in Cyprus in 451 BC, under the recently recalled Cimon.
Siege of Kition
Cimon sailed for Cyprus with a fleet of 200 ships provided by the Athenians and their allies. However, 60 of these ships were sent to Egypt at the request of Amyrtaeus, the so-called "King of the Marshes" (who still remained independent of, and opposed to Persian rule). The rest of the force besiegedKition
Kition ( Egyptian: ; Phoenician: , , or , ; Ancient Greek: , ; Latin: ) was a city-kingdom on the southern coast of Cyprus (in present-day Larnaca). According to the text on the plaque closest to the excavation pit of the Kathari site (as of ...
in Cyprus, but during the siege, Cimon died either of sickness or a wound.Plutarch, Cimon, 19 The Athenians lacked provisions, and apparently under the death-bed instructions of Cimon, the Athenians retreated towards Salamis-in-Cyprus.
Battles of Salamis-in-Cyprus
 Cimon's death was kept a secret from the Athenian army. 30 days after leaving Kition, the Athenians and their allies were attacked by a Persian force composed of Cilicians, Phoenicians, and Cyprians, whilst sailing off Salamis-in-Cyprus. Under the 'command' of the deceased Cimon, they defeated this force at sea, and also in a land battle. Having thus successfully extricated themselves, the Athenians sailed back to Greece, joined by the detachment which had been sent to Egypt.
These battles formed the end of the Greco-Persian Wars.
Cimon's death was kept a secret from the Athenian army. 30 days after leaving Kition, the Athenians and their allies were attacked by a Persian force composed of Cilicians, Phoenicians, and Cyprians, whilst sailing off Salamis-in-Cyprus. Under the 'command' of the deceased Cimon, they defeated this force at sea, and also in a land battle. Having thus successfully extricated themselves, the Athenians sailed back to Greece, joined by the detachment which had been sent to Egypt.
These battles formed the end of the Greco-Persian Wars.
Peace with Persia
After the Battles of Salamis-in-Cyprus, Thucydides makes no further mention of conflict with the Persians, simply saying that the Greeks returned home. Diodorus, on the other hand, claims that in the aftermath of Salamis, a full-blown peace treaty (the "Peace of Callias") was agreed with the Persians.DiodoruXII, 4
/ref> Diodorus was probably following the history of Ephorus at this point, who in turn was presumably influenced by his teacher
Isocrates
Isocrates (; grc, Ἰσοκράτης ; 436–338 BC) was an ancient Greek rhetorician, one of the ten Attic orators. Among the most influential Greek rhetoricians of his time, Isocrates made many contributions to rhetoric and education throu ...
— from whom we have the earliest reference to the supposed peace, in 380 BC.Fine, p. 360. Even during the 4th century BC the idea of the treaty was controversial, and two authors from that period, Callisthenes and Theopompus
Theopompus ( grc-gre, Θεόπομπος, ''Theópompos''; c. 380 BCc. 315 BC) was an ancient Greek historian and rhetorician.
Biography
Theopompus was born on the Aegean island of Chios. In early youth, he seems to have spent some time at Athen ...
appear to reject its existence.Sealey, p. 280.
It is possible that the Athenians had attempted to negotiate with the Persians previously. Plutarch suggests that in the aftermath of the victory at the Eurymedon, Artaxerxes had agreed a peace treaty with the Greeks, even naming Callias as the Athenian ambassador involved. However, as Plutarch admits, Callisthenes denied that such a peace was made at this point (c. 466 BC). Herodotus also mentions, in passing, an Athenian embassy headed by Callias, which was sent to Susa
Susa ( ; Middle elx, 𒀸𒋗𒊺𒂗, translit=Šušen; Middle and Neo- elx, 𒋢𒋢𒌦, translit=Šušun; Neo- Elamite and Achaemenid elx, 𒀸𒋗𒐼𒀭, translit=Šušán; Achaemenid elx, 𒀸𒋗𒐼, translit=Šušá; fa, شوش ...
to negotiate with Artaxerxes. This embassy included some Argive representatives and can probably be therefore dated to c. 461 BC (after forging of the alliance between Athens and Argos). This embassy may have been an attempt to reach some kind of peace agreement, and it has even been suggested that the failure of these hypothetical negotiations led to the Athenian decision to support the Egyptian revolt.Kagan, p. 84. The ancient sources therefore disagree as to whether there was an official peace or not, and if there was, when it was agreed.
Opinion amongst modern historians is also split; for instance, Fine accepts the concept of the Peace of Callias, whereas Sealey effectively rejects it.Sealey, p. 281. Holland accepts that some kind of accommodation was made between Athens and Persia, but no actual treaty.Holland, p. 366. Fine argues that Callisthenes's denial that a treaty was made after the Eurymedon does not preclude a peace being made at another point. Further, he suggests that Theopompus was actually referring to a treaty that had allegedly been negotiated with Persia in 423 BC. If these views are correct, it would remove one major obstacle to the acceptance of the treaty's existence. A further argument for the existence of the treaty is the sudden withdrawal of the Athenians from Cyprus in 450 BC, which makes most sense in the light of some kind of peace agreement.Fine, p. 363. On the other hand, if there was indeed some kind of accommodation, Thucydides's failure to mention it is odd. In his digression on the ''pentekontaetia'' his aim is to explain the growth of Athenian power, and such a treaty, and the fact that the Delian allies were not released from their obligations after it, would have marked a major step in the Athenian ascendancy. Conversely, it has been suggested that certain passages elsewhere in Thucydides's history are best interpreted as referring to a peace agreement. There is thus no clear consensus amongst modern historians as to the treaty's existence.
The ancient sources which give details of the treaty are reasonably consistent in their description of the terms:
* All Greek cities of Asia were to 'live by their own laws' ''or'' 'be autonomous' (depending on translation).
* Persian satraps (and presumably their armies) were not to travel west of the Halys (Isocrates
Isocrates (; grc, Ἰσοκράτης ; 436–338 BC) was an ancient Greek rhetorician, one of the ten Attic orators. Among the most influential Greek rhetoricians of his time, Isocrates made many contributions to rhetoric and education throu ...
) ''or'' closer than a day's journey
A day's journey in pre-modern literature, including the Bible, ancient geographers and ethnographers such as Herodotus, is a measurement of distance.
In the Bible, it is not as precisely defined as other Biblical measurements of distance; the dis ...
on horseback to the Aegean Sea ( Callisthenes) ''or'' closer than three days' journey on foot to the Aegean Sea ( Ephorus and Diodorus).
* No Persian warship was to sail west of Phaselis
Phaselis ( grc, Φασηλίς) or Faselis ( tr, Faselis) was a Greek and Roman city on the coast of ancient Lycia. Its ruins are located north of the modern town Tekirova in the Kemer district of Antalya Province in Turkey. It lies between ...
(on the southern coast of Asia Minor), nor west of the Cyanaean rocks (probably at the eastern end of the Bosporus
The Bosporus Strait (; grc, Βόσπορος ; tr, İstanbul Boğazı 'Istanbul strait', colloquially ''Boğaz'') or Bosphorus Strait is a natural strait and an internationally significant waterway located in Istanbul in northwestern Tu ...
, on the north coast).
* If the terms were observed by the king and his generals, then the Athenians were not to send troops to lands ruled by Persia.
Aftermath
As already noted, towards the end of the conflict with Persia, the process by which the Delian League became theAthenian Empire
The Delian League, founded in 478 BC, was an association of Greek city-states, numbering between 150 and 330, under the leadership of Athens, whose purpose was to continue fighting the Persian Empire after the Greek victory in the Battle of Plat ...
reached its conclusion. The allies of Athens were not released from their obligations to provide either money or ships, despite the cessation of hostilities. In Greece, the First Peloponnesian War
The First Peloponnesian War (460–445 BC) was fought between Sparta as the leaders of the Peloponnesian League and Sparta's other allies, most notably Thebes, Greece, Thebes, and the Delian League led by Athens with support from Ancient Argos, ...
between the power-blocs of Athens and Sparta, which had continued on and off since 460 BC, finally ended in 445 BC, with the agreement of a thirty-year truce. However, the growing enmity between Sparta and Athens would lead, just 14 years later, to the outbreak of the Second Peloponnesian War. This disastrous conflict, which dragged on for 27 years, would eventually result in the utter destruction of Athenian power, the dismemberment of the Athenian empire, and the establishment of a Spartan hegemony
The polis of Sparta was the greatest military land power of classical Greek antiquity. During the Classical period, Sparta governed, dominated or influenced the entire Peloponnese. Additionally, the defeat of the Athenians and the Delian League ...
over Greece. However, not just Athens suffered. The conflict would significantly weaken the whole of Greece.Dandamaev, p. 256.
Repeatedly defeated in battle by the Greeks, and plagued by internal rebellions which hindered their ability to fight the Greeks, after 450 BC Artaxerxes and his successors adopted a policy of divide-and-rule. Avoiding fighting the Greeks themselves, the Persians instead attempted to set Athens against Sparta, regularly bribing politicians to achieve their aims. In this way, they ensured that the Greeks remained distracted by internal conflicts, and were unable to turn their attentions to Persia. There was no open conflict between the Greeks and Persia until 396 BC, when the Spartan king Agesilaus briefly invaded Asia Minor; as Plutarch points out, the Greeks were far too busy overseeing the destruction of their own power to fight against the "barbarians".
If the wars of the Delian League shifted the balance of power between Greece and Persia in favour of the Greeks, then the subsequent half-century of internecine conflict in Greece did much to restore the balance of power to Persia. In 387 BC, Sparta, confronted by an alliance of Corinth
Corinth ( ; el, Κόρινθος, Kórinthos, ) is the successor to an ancient city, and is a former municipality in Corinthia, Peloponnese, which is located in south-central Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform, it has been part ...
, Thebes and Athens during the Corinthian War
The Corinthian War (395–387 BC) was a conflict in ancient Greece which pitted Sparta against a coalition of city-states comprising Thebes, Athens, Corinth and Argos, backed by the Achaemenid Empire. The war was caused by dissatisfaction with ...
, sought the aid of Persia to shore up her position. Under the so-called "King's Peace" which brought the war to an end, Artaxerxes II
Arses ( grc-gre, Ἄρσης; 445 – 359/8 BC), known by his regnal name Artaxerxes II ( peo, 𐎠𐎼𐎫𐎧𐏁𐏂 ; grc-gre, Ἀρταξέρξης), was King of Kings of the Achaemenid Empire from 405/4 BC to 358 BC. He was the son and suc ...
demanded and received the return of the cities of Asia Minor from the Spartans, in return for which the Persians threatened to make war on any Greek state which did not make peace. This humiliating treaty, which undid all the Greek gains of the previous century, sacrificed the Greeks of Asia Minor so that the Spartans could maintain their hegemony over Greece.Dandamaev, p. 294. It is in the aftermath of this treaty that Greek orators began to refer to the Peace of Callias (whether fictional or not), as a counterpoint to the shame of the King's Peace, and a glorious example of the "good old days" when the Greeks of the Aegean had been freed from Persian rule by the Delian League.
References
Bibliography
Primary sources
*Herodotus
Herodotus ( ; grc, , }; BC) was an ancient Greek historian and geographer from the Greek city of Halicarnassus, part of the Persian Empire (now Bodrum, Turkey) and a later citizen of Thurii in modern Calabria (Italy). He is known fo ...
''The Histories''
*
Thucydides
Thucydides (; grc, , }; BC) was an Athenian historian and general. His '' History of the Peloponnesian War'' recounts the fifth-century BC war between Sparta and Athens until the year 411 BC. Thucydides has been dubbed the father of " scienti ...
''History of the Peloponnesian War''
*
Xenophon
Xenophon of Athens (; grc, Ξενοφῶν ; – probably 355 or 354 BC) was a Greek military leader, philosopher, and historian, born in Athens. At the age of 30, Xenophon was elected commander of one of the biggest Greek mercenary armies o ...
, ''Hellenica
''Hellenica'' ( grc, Ἑλληνικά) simply means writings on Greek (Hellenic) subjects. Several histories of 4th-century Greece, written in the mould of Thucydides or straying from it, have borne the conventional Latin title ''Hellenica''. Th ...
''
*Diodorus Siculus''Biblioteca Historica''
*
Plutarch
Plutarch (; grc-gre, Πλούταρχος, ''Ploútarchos''; ; – after AD 119) was a Greek Middle Platonist philosopher, historian, biographer, essayist, and priest at the Temple of Apollo in Delphi. He is known primarily for hi ...
, ''Parallel Lives
Plutarch's ''Lives of the Noble Greeks and Romans'', commonly called ''Parallel Lives'' or ''Plutarch's Lives'', is a series of 48 biographies of famous men, arranged in pairs to illuminate their common moral virtues or failings, probably writt ...
'' — Aristides
Aristides ( ; grc-gre, Ἀριστείδης, Aristeídēs, ; 530–468 BC) was an ancient Athenian statesman. Nicknamed "the Just" (δίκαιος, ''dikaios''), he flourished in the early quarter of Athens' Classical period and is remembe ...
, Cimon
Cimon or Kimon ( grc-gre, Κίμων; – 450BC) was an Athenian ''strategos'' (general and admiral) and politician.
He was the son of Miltiades, also an Athenian ''strategos''. Cimon rose to prominence for his bravery fighting in the naval Batt ...
, Themistocles
Themistocles (; grc-gre, Θεμιστοκλῆς; c. 524–459 BC) was an Athenian politician and general. He was one of a new breed of non-aristocratic politicians who rose to prominence in the early years of the Athenian democracy. As ...
*Ctesias, Persica
' (from
Photius
Photios I ( el, Φώτιος, ''Phōtios''; c. 810/820 – 6 February 893), also spelled PhotiusFr. Justin Taylor, essay "Canon Law in the Age of the Fathers" (published in Jordan Hite, T.O.R., & Daniel J. Ward, O.S.B., "Readings, Cases, Materia ...
's Epitome)
Secondary sources
* * * * * * * * * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Wars Of The Delian LeagueDelian League
The Delian League, founded in 478 BC, was an association of Greek city-states, numbering between 150 and 330, under the leadership of Athens, whose purpose was to continue fighting the Persian Empire after the Greek victory in the Battle of Pla ...
Delian League
The Delian League, founded in 478 BC, was an association of Greek city-states, numbering between 150 and 330, under the leadership of Athens, whose purpose was to continue fighting the Persian Empire after the Greek victory in the Battle of Pla ...
Delian League
The Delian League, founded in 478 BC, was an association of Greek city-states, numbering between 150 and 330, under the leadership of Athens, whose purpose was to continue fighting the Persian Empire after the Greek victory in the Battle of Pla ...
Delian League
The Delian League, founded in 478 BC, was an association of Greek city-states, numbering between 150 and 330, under the leadership of Athens, whose purpose was to continue fighting the Persian Empire after the Greek victory in the Battle of Pla ...
Delian League
The Delian League, founded in 478 BC, was an association of Greek city-states, numbering between 150 and 330, under the leadership of Athens, whose purpose was to continue fighting the Persian Empire after the Greek victory in the Battle of Pla ...
Delian League
The Delian League, founded in 478 BC, was an association of Greek city-states, numbering between 150 and 330, under the leadership of Athens, whose purpose was to continue fighting the Persian Empire after the Greek victory in the Battle of Pla ...
Greco-Persian Wars
Delian League
The Delian League, founded in 478 BC, was an association of Greek city-states, numbering between 150 and 330, under the leadership of Athens, whose purpose was to continue fighting the Persian Empire after the Greek victory in the Battle of Pla ...