Weapon development on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A weapon, arm, or armament is any implement or device that is used to deter, threaten, inflict physical damage, harm, or kill. Weapons are used to increase the efficacy and efficiency of activities such as
A weapon, arm, or armament is any implement or device that is used to deter, threaten, inflict physical damage, harm, or kill. Weapons are used to increase the efficacy and efficiency of activities such as
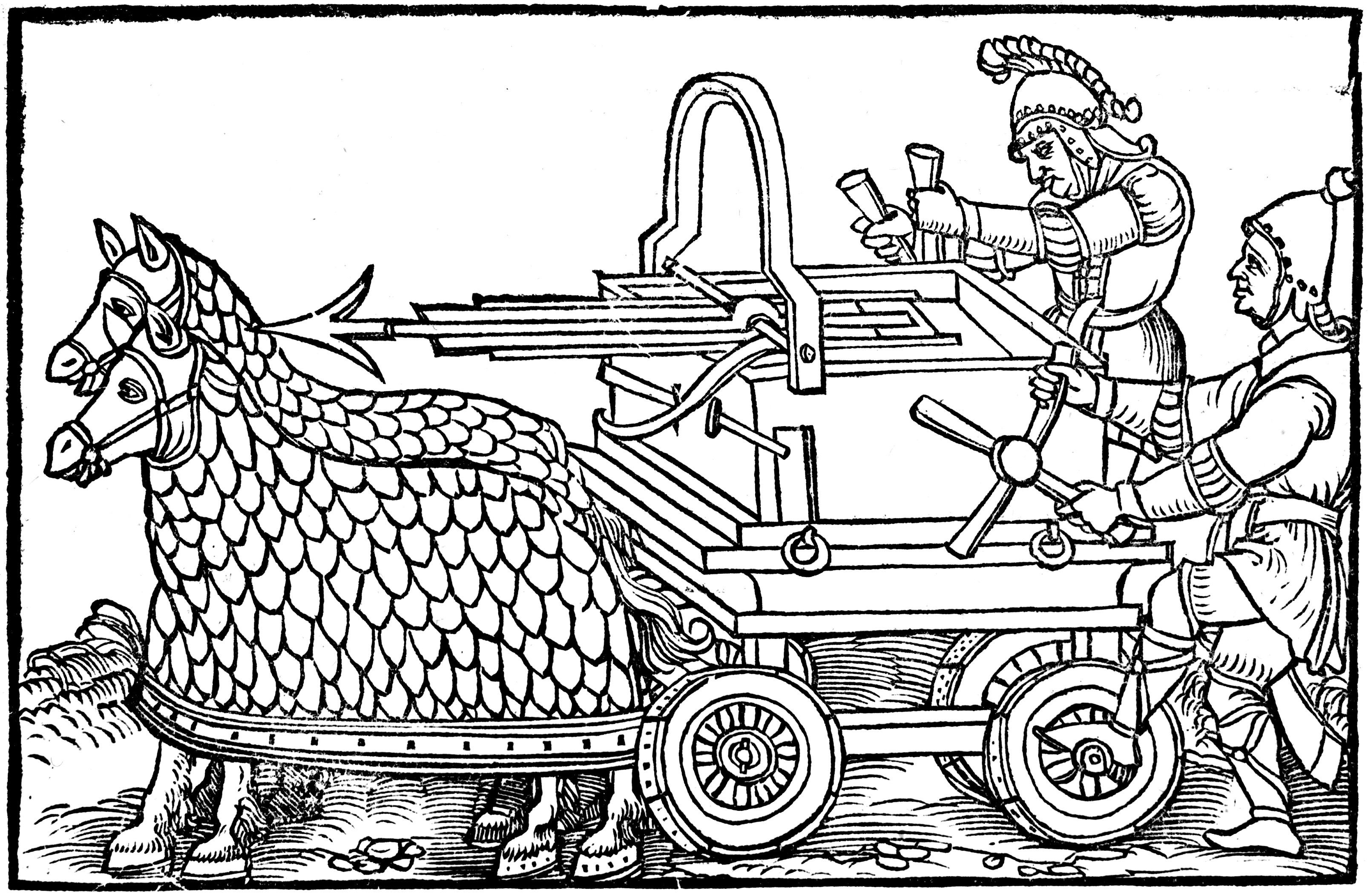 The earliest ancient weapons were evolutionary improvements of late
The earliest ancient weapons were evolutionary improvements of late
 European warfare during
European warfare during  In Eastern and
In Eastern and
 Since the mid-18th century North American French-Indian war through the beginning of the 20th century, human-powered weapons were reduced from the primary weaponry of the battlefield to yielding gunpowder-based weaponry. Sometimes referred to as the "Age of Rifles", this period was characterized by the development of firearms for infantry and cannons for support, as well as the beginnings of mechanized weapons such as the machine gun. Artillery pieces such as
Since the mid-18th century North American French-Indian war through the beginning of the 20th century, human-powered weapons were reduced from the primary weaponry of the battlefield to yielding gunpowder-based weaponry. Sometimes referred to as the "Age of Rifles", this period was characterized by the development of firearms for infantry and cannons for support, as well as the beginnings of mechanized weapons such as the machine gun. Artillery pieces such as
 An important feature of industrial age warfare was technological escalation – innovations were rapidly matched through replication or countered by another innovation.
An important feature of industrial age warfare was technological escalation – innovations were rapidly matched through replication or countered by another innovation.
 The arms industry is a global industry that involves the sale and manufacture of weaponry. It consists of a commerce, commercial Industry (economics), industry involved in the research and development, engineering, production, and servicing of military material, equipment, and facilities. Many industrialized countries have a domestic arms industry to supply their own military forces, and some also have a substantial trade in weapons for use by their citizens for self-defense, hunting, or sporting purposes.
Contracts to supply a given country's military are awarded by governments, making arms contracts of substantial political importance. The link between politics and the arms trade can result in the development of a "military–industrial complex", where the armed forces, commerce, and politics become closely linked.
According to research institute SIPRI, the volume of international transfers of major weapons in 2010–2014 was 16 percent higher than in 2005–2009, and the arms sales of the world's 100 largest private arms-producing and military services companies totaled $420 billion in 2018.
The arms industry is a global industry that involves the sale and manufacture of weaponry. It consists of a commerce, commercial Industry (economics), industry involved in the research and development, engineering, production, and servicing of military material, equipment, and facilities. Many industrialized countries have a domestic arms industry to supply their own military forces, and some also have a substantial trade in weapons for use by their citizens for self-defense, hunting, or sporting purposes.
Contracts to supply a given country's military are awarded by governments, making arms contracts of substantial political importance. The link between politics and the arms trade can result in the development of a "military–industrial complex", where the armed forces, commerce, and politics become closely linked.
According to research institute SIPRI, the volume of international transfers of major weapons in 2010–2014 was 16 percent higher than in 2005–2009, and the arms sales of the world's 100 largest private arms-producing and military services companies totaled $420 billion in 2018.
Weapon Specialist – Weapon Expert
''Bevic Huynh, New York, 2012.''. Retrieved July 26, 2012.
 A weapon, arm, or armament is any implement or device that is used to deter, threaten, inflict physical damage, harm, or kill. Weapons are used to increase the efficacy and efficiency of activities such as
A weapon, arm, or armament is any implement or device that is used to deter, threaten, inflict physical damage, harm, or kill. Weapons are used to increase the efficacy and efficiency of activities such as hunting
Hunting is the Human activity, human practice of seeking, pursuing, capturing, and killing wildlife or feral animals. The most common reasons for humans to hunt are to obtain the animal's body for meat and useful animal products (fur/hide (sk ...
, crime
In ordinary language, a crime is an unlawful act punishable by a State (polity), state or other authority. The term ''crime'' does not, in modern criminal law, have any simple and universally accepted definition,Farmer, Lindsay: "Crime, definiti ...
(e.g., murder
Murder is the unlawful killing of another human without justification (jurisprudence), justification or valid excuse (legal), excuse committed with the necessary Intention (criminal law), intention as defined by the law in a specific jurisd ...
), law enforcement
Law enforcement is the activity of some members of the government or other social institutions who act in an organized manner to enforce the law by investigating, deterring, rehabilitating, or punishing people who violate the rules and norms gove ...
, self-defense
Self-defense (self-defence primarily in Commonwealth English) is a countermeasure that involves defending the health and well-being of oneself from harm. The use of the right of self-defense as a legal justification for the use of Force (law), ...
, warfare, or suicide
Suicide is the act of intentionally causing one's own death.
Risk factors for suicide include mental disorders, physical disorders, and substance abuse. Some suicides are impulsive acts driven by stress (such as from financial or ac ...
. In a broader context, weapons may be construed to include anything used to gain a tactical, strategic, material, or mental advantage over an adversary or enemy target.
While ordinary objects such as rocks and bottle
A bottle is a narrow-necked container made of an impermeable material (such as glass, plastic or aluminium) in various shapes and sizes that stores and transports liquids. Its mouth, at the bottling line, can be sealed with an internal ...
s can be used as weapons, many objects are expressly designed for the purpose; these range from simple implements such as clubs
Club may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media
* Club (magazine), ''Club'' (magazine)
* Club, a ''Yie Ar Kung-Fu'' character
* Clubs (suit), a suit of playing cards
* Club music
* "Club", by Kelsea Ballerini from the album ''kelsea''
Brands a ...
and sword
A sword is an edged and bladed weapons, edged, bladed weapon intended for manual cutting or thrusting. Its blade, longer than a knife or dagger, is attached to a hilt and can be straight or curved. A thrusting sword tends to have a straighter ...
s to complicated modern firearm
A firearm is any type of gun that uses an explosive charge and is designed to be readily carried and operated by an individual. The term is legally defined further in different countries (see legal definitions).
The first firearms originate ...
s, tank
A tank is an armoured fighting vehicle intended as a primary offensive weapon in front-line ground combat. Tank designs are a balance of heavy firepower, strong armour, and battlefield mobility provided by tracks and a powerful engine; ...
s, missile
A missile is an airborne ranged weapon capable of self-propelled flight aided usually by a propellant, jet engine or rocket motor.
Historically, 'missile' referred to any projectile that is thrown, shot or propelled towards a target; this ...
s and biological weapons. Something that has been repurposed, converted, or enhanced to become a weapon of war is termed ''weaponized'', such as a weaponized virus or weaponized laser.
History
The use of weapons has been a major driver of cultural evolution andhuman history
Human history or world history is the record of humankind from prehistory to the present. Early modern human, Modern humans evolved in Africa around 300,000 years ago and initially lived as hunter-gatherers. They Early expansions of hominin ...
up to today since weapons are a type of tool that is used to dominate and subdue autonomous agents such as animals and, by doing so, allow for an expansion of the cultural niche, while simultaneously other weapon users (i.e., agents such as humans, groups, and cultures) are able to adapt to the weapons of enemies by learning, triggering a continuous process of competitive technological, skill, and cognitive improvement (arms race
An arms race occurs when two or more groups compete in military superiority. It consists of a competition between two or more State (polity), states to have superior armed forces, concerning production of weapons, the growth of a military, and ...
).
Prehistoric
The use of objects as weapons has been observed among chimpanzees, leading to speculation that earlyhominids
The Hominidae (), whose members are known as the great apes or hominids (), are a taxonomic family of primates that includes eight extant species in four genera: '' Pongo'' (the Bornean, Sumatran and Tapanuli orangutan); '' Gorilla'' (the ...
used weapons as early as five million years ago. However, this cannot be confirmed using physical evidence because wooden clubs, spears, and unshaped stones would have left an ambiguous record. The earliest unambiguous weapons to be found are the Schöningen spears
The Schöningen spears are a set of ten Palaeolithic wooden weapons that were excavated between 1994 and 1999 from the 'Schöningen site, Spear Horizon' in the Open-pit mining, open-cast lignite mine in Schöningen, Helmstedt (district), Helmstedt ...
, eight wooden throwing spears dating back more than 300,000 years. At the site of Nataruk in Turkana, Kenya, numerous human skeletons dating to 10,000 years ago may present evidence of traumatic injuries to the head, neck, ribs, knees, and hands, including obsidian
Obsidian ( ) is a naturally occurring volcanic glass formed when lava extrusive rock, extruded from a volcano cools rapidly with minimal crystal growth. It is an igneous rock. Produced from felsic lava, obsidian is rich in the lighter element ...
projectiles embedded in the bones that might have been caused by arrows and clubs during conflict between two hunter-gatherer groups. But the interpretation of warfare at Nataruk has been challenged due to conflicting evidence.
Ancient history
 The earliest ancient weapons were evolutionary improvements of late
The earliest ancient weapons were evolutionary improvements of late Neolithic
The Neolithic or New Stone Age (from Ancient Greek, Greek 'new' and 'stone') is an archaeological period, the final division of the Stone Age in Mesopotamia, Asia, Europe and Africa (c. 10,000 BCE to c. 2,000 BCE). It saw the Neolithic Revo ...
implements, but significant improvements in materials and crafting techniques led to a series of revolutions in military technology
Military technology is the application of technology for use in warfare. It comprises the kinds of technology that are distinctly military in nature and not civilian in application, usually because they lack useful or legal civilian application ...
.
The development of metal tools began with copper
Copper is a chemical element; it has symbol Cu (from Latin ) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish-orang ...
during the Copper Age (about 3,300 BC) and was followed by the Bronze Age
The Bronze Age () was a historical period characterised principally by the use of bronze tools and the development of complex urban societies, as well as the adoption of writing in some areas. The Bronze Age is the middle principal period of ...
, leading to the creation of the Bronze Age sword and similar weapons.
During the Bronze Age, the first defensive structures and fortification
A fortification (also called a fort, fortress, fastness, or stronghold) is a military construction designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from Lati ...
s appeared as well, indicating an increased need for security. Weapons designed to breach fortifications followed soon after, such as the battering ram, which was in use by 2500 BC.
The development of ironworking around 1300 BC in Greece had an important impact on the development of ancient weapons. It was not the introduction of early Iron Age swords, however, as they were not superior to their bronze predecessors, but rather the domestication of the horse
It is not entirely clear how, when or where the domestication of the horse took place. Although horses appeared in Paleolithic cave art as early as 30,000 BCE, these were wild horses and were probably hunted for meat. The clearest evidence o ...
and widespread use of spoked wheels by . This led to the creation of the light, horse-drawn chariot, whose improved mobility proved important during this era. Spoke-wheeled chariot usage peaked around 1300 BC and then declined, ceasing to be militarily relevant by the 4th century BC.
Cavalry
Historically, cavalry (from the French word ''cavalerie'', itself derived from ''cheval'' meaning "horse") are groups of soldiers or warriors who Horses in warfare, fight mounted on horseback. Until the 20th century, cavalry were the most mob ...
developed once horses were bred to support the weight of a human. The horse extended the range and increased the speed of attacks.
Alexander's conquest saw the increased use of spears and shields in the Middle East and Western Asia as a result Greek culture spread which saw many Greek and other European weapons be used in these regions and as a result many of these weapons were adapted to fit their new use in war
In addition to land-based weaponry, warship
A warship or combatant ship is a naval ship that is used for naval warfare. Usually they belong to the navy branch of the armed forces of a nation, though they have also been operated by individuals, cooperatives and corporations. As well as b ...
s, such as the trireme
A trireme ( ; ; cf. ) was an ancient navies and vessels, ancient vessel and a type of galley that was used by the ancient maritime civilizations of the Mediterranean Sea, especially the Phoenicians, ancient Greece, ancient Greeks and ancient R ...
, were in use by the 7th century BC.
During the first First Punic War
The First Punic War (264–241 BC) was the first of three wars fought between Rome and Carthage, the two main powers of the western Mediterranean in the early 3rd century BC. For 23 years, in the longest continuous conflict and grea ...
, the use of advanced warships contributed to a Roman victory over the Carthaginians.
Post-classical history
 European warfare during
European warfare during post-classical history
In Human history, world history, post-classical history refers to the period from about 500 CE to 1500 CE, roughly corresponding to the European Middle Ages. The period is characterized by the expansion of civilizations geographically an ...
was dominated by elite groups of knights supported by massed infantry
Infantry, or infantryman are a type of soldier who specialize in ground combat, typically fighting dismounted. Historically the term was used to describe foot soldiers, i.e. those who march and fight on foot. In modern usage, the term broadl ...
. They were involved in mobile combat and sieges, which involved various siege weapons and tactics. Knights on horseback developed tactics for charging with lances, providing an impact on the enemy formations, and then drawing more practical weapons (such as sword
A sword is an edged and bladed weapons, edged, bladed weapon intended for manual cutting or thrusting. Its blade, longer than a knife or dagger, is attached to a hilt and can be straight or curved. A thrusting sword tends to have a straighter ...
s) once they entered melee. By contrast, infantry, in the age before structured formations, relied on cheap, sturdy weapons such as spear
A spear is a polearm consisting of a shaft, usually of wood, with a pointed head. The head may be simply the sharpened end of the shaft itself, as is the case with Fire hardening, fire hardened spears, or it may be made of a more durable materia ...
s and billhooks in close combat and bows from a distance. As armies became more professional, their equipment was standardized, and infantry transitioned to pikes. Pikes are normally seven to eight feet in length and used in conjunction with smaller sidearms (short swords).
 In Eastern and
In Eastern and Middle Eastern
The Middle East (term originally coined in English language) is a geopolitical region encompassing the Arabian Peninsula, the Levant, Turkey, Egypt, Iran, and Iraq.
The term came into widespread usage by the United Kingdom and western Eur ...
warfare, similar tactics were developed independent of European influences.
The introduction of gunpowder
Gunpowder, also commonly known as black powder to distinguish it from modern smokeless powder, is the earliest known chemical explosive. It consists of a mixture of sulfur, charcoal (which is mostly carbon), and potassium nitrate, potassium ni ...
from Asia at the end of this period revolutionized warfare. Formations of musketeers, protected by pikemen, came to dominate open battles, and the cannon
A cannon is a large-caliber gun classified as a type of artillery, which usually launches a projectile using explosive chemical propellant. Gunpowder ("black powder") was the primary propellant before the invention of smokeless powder during th ...
replaced the trebuchet as the dominant siege weapon.
The Ottoman used the cannon to destroy much of the fortifications at Constantinople which would change warfare as gunpowder became more available and technology improved
Modern history
Early modern
The EuropeanRenaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) is a Periodization, period of history and a European cultural movement covering the 15th and 16th centuries. It marked the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and was characterized by an effort to revive and sur ...
marked the beginning of the implementation of firearms in western warfare. Guns and rockets were introduced to the battlefield.
Firearm
A firearm is any type of gun that uses an explosive charge and is designed to be readily carried and operated by an individual. The term is legally defined further in different countries (see legal definitions).
The first firearms originate ...
s are qualitatively different from earlier weapons because they release energy from combustible propellant
A propellant (or propellent) is a mass that is expelled or expanded in such a way as to create a thrust or another motive force in accordance with Newton's third law of motion, and "propel" a vehicle, projectile, or fluid payload. In vehicle ...
s, such as gunpowder
Gunpowder, also commonly known as black powder to distinguish it from modern smokeless powder, is the earliest known chemical explosive. It consists of a mixture of sulfur, charcoal (which is mostly carbon), and potassium nitrate, potassium ni ...
, rather than from a counterweight or spring. This energy is released very rapidly and can be replicated without much effort by the user. Therefore, even early firearms such as the arquebus were much more powerful than human-powered weapons. Firearms became increasingly important and effective during the 16th–19th centuries, with progressive improvements in ignition mechanisms followed by revolutionary changes in ammunition
Ammunition, also known as ammo, is the material fired, scattered, dropped, or detonated from any weapon or weapon system. The term includes both expendable weapons (e.g., bombs, missiles, grenades, land mines), and the component parts of oth ...
handling and propellant. During the American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861May 26, 1865; also known by Names of the American Civil War, other names) was a civil war in the United States between the Union (American Civil War), Union ("the North") and the Confederate States of A ...
, new applications of firearms, including the machine gun and ironclad warship, emerged that would still be recognizable and useful military weapons today, particularly in limited conflicts. In the 19th century, warship
A warship or combatant ship is a naval ship that is used for naval warfare. Usually they belong to the navy branch of the armed forces of a nation, though they have also been operated by individuals, cooperatives and corporations. As well as b ...
propulsion changed from sail
A sail is a tensile structure, which is made from fabric or other membrane materials, that uses wind power to propel sailing craft, including sailing ships, sailboats, windsurfers, ice boats, and even sail-powered land vehicles. Sails may b ...
power to fossil fuel
A fossil fuel is a flammable carbon compound- or hydrocarbon-containing material formed naturally in the Earth's crust from the buried remains of prehistoric organisms (animals, plants or microplanktons), a process that occurs within geolog ...
-powered steam engine
A steam engine is a heat engine that performs Work (physics), mechanical work using steam as its working fluid. The steam engine uses the force produced by steam pressure to push a piston back and forth inside a Cylinder (locomotive), cyl ...
s.
 Since the mid-18th century North American French-Indian war through the beginning of the 20th century, human-powered weapons were reduced from the primary weaponry of the battlefield to yielding gunpowder-based weaponry. Sometimes referred to as the "Age of Rifles", this period was characterized by the development of firearms for infantry and cannons for support, as well as the beginnings of mechanized weapons such as the machine gun. Artillery pieces such as
Since the mid-18th century North American French-Indian war through the beginning of the 20th century, human-powered weapons were reduced from the primary weaponry of the battlefield to yielding gunpowder-based weaponry. Sometimes referred to as the "Age of Rifles", this period was characterized by the development of firearms for infantry and cannons for support, as well as the beginnings of mechanized weapons such as the machine gun. Artillery pieces such as howitzer
The howitzer () is an artillery weapon that falls between a cannon (or field gun) and a mortar. It is capable of both low angle fire like a field gun and high angle fire like a mortar, given the distinction between low and high angle fire break ...
s were able to destroy masonry fortresses and other fortifications, and this single invention caused a revolution in military affairs, establishing tactics and doctrine that are still in use today.
World War I
 An important feature of industrial age warfare was technological escalation – innovations were rapidly matched through replication or countered by another innovation.
An important feature of industrial age warfare was technological escalation – innovations were rapidly matched through replication or countered by another innovation.
World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
marked the entry of fully industrialized warfare as well as weapons of mass destruction
A weapon of mass destruction (WMD) is a Biological agent, biological, chemical weapon, chemical, Radiological weapon, radiological, nuclear weapon, nuclear, or any other weapon that can kill or significantly harm many people or cause great dam ...
(''e.g.'', chemical
A chemical substance is a unique form of matter with constant chemical composition and characteristic properties. Chemical substances may take the form of a single element or chemical compounds. If two or more chemical substances can be combin ...
and biological weapons), and new weapons were developed quickly to meet wartime needs. The technological escalation during World War I was profound, including the wide introduction of aircraft
An aircraft ( aircraft) is a vehicle that is able to flight, fly by gaining support from the Atmosphere of Earth, air. It counters the force of gravity by using either Buoyancy, static lift or the Lift (force), dynamic lift of an airfoil, or, i ...
into warfare
War is an armed conflict between the armed forces of State (polity), states, or between governmental forces and armed groups that are organized under a certain command structure and have the capacity to sustain military operations, or betwe ...
and naval warfare with the introduction of aircraft carrier
An aircraft carrier is a warship that serves as a seagoing airbase, equipped with a full-length flight deck and hangar facilities for supporting, arming, deploying and recovering carrier-based aircraft, shipborne aircraft. Typically it is the ...
s. Above all, it promised the military commanders independence from horses and a resurgence in maneuver warfare
Maneuver warfare, or manoeuvre warfare, is a military strategy which emphasizes movement, initiative and surprise to achieve a position of advantage. Maneuver seeks to inflict losses indirectly by envelopment, encirclement and disruption, while ...
through the extensive use of motor vehicles. The changes that these military technologies underwent were evolutionary but defined their development for the rest of the century.
Interwar
This period of innovation in weapon design continued in the interwar period (between WWI and WWII) with the continuous evolution of weapon systems by all major industrial powers. The major armament firms were Schneider-Creusot (based in France),Škoda Works
The Škoda Works (, ) was one of the largest European industrial conglomerates of the 20th century. In 1859, Czech engineer Emil Škoda bought a foundry and machine factory in Plzeň, Bohemia, Austria-Hungary that had been established ten ye ...
(Czechoslovakia), and Vickers
Vickers was a British engineering company that existed from 1828 until 1999. It was formed in Sheffield as a steel foundry by Edward Vickers and his father-in-law, and soon became famous for casting church bells. The company went public in 18 ...
(Great Britain). The 1920s were committed to disarmament
Disarmament is the act of reducing, limiting, or abolishing Weapon, weapons. Disarmament generally refers to a country's military or specific type of weaponry. Disarmament is often taken to mean total elimination of weapons of mass destruction, ...
and the outlawing of war and poison gas, but rearmament picked up rapidly in the 1930s. The munitions makers responded nimbly to the rapidly shifting strategic and economic landscape. The main purchasers of munitions from the big three companies were Romania, Yugoslavia, Greece, and Turkeyand, to a lesser extent, Poland, Finland, the Baltic States, and the Soviet Union.
= Criminalizing poison gas
= Realistic critics understood that war could not really be outlawed, but its worst excesses might be banned. Poison gas became the focus of a worldwide crusade in the 1920s. Poison gas did not win battles, and the generals did not want it. The soldiers hated it far more intensely than bullets or explosive shells. By 1918, chemical shells made up 35 percent of French ammunition supplies, 25 percent of British, and 20 percent of American stock. The "Protocol for the Prohibition of the Use in War of Asphyxiating, Poisonous, or Other Gases and of Bacteriological Methods of Warfare", also known as the Geneva Protocol, was issued in 1925 and was accepted as policy by all major countries. In 1937, poison gas was manufactured in large quantities but not used except against nations that lacked modern weapons or gas masks.World War II and postwar
Many modern military weapons, particularly ground-based ones, are relatively minor improvements to weapon systems developed during World War II. World War II marked perhaps the most frantic period of weapon development in the history of humanity. Massive numbers of new designs and concepts were fielded, and all existing technologies were improved between 1939 and 1945. The most powerful weapon invented during this period was thenuclear bomb
A nuclear weapon is an explosive device that derives its destructive force from nuclear reactions, either fission (fission or atomic bomb) or a combination of fission and fusion reactions (thermonuclear weapon), producing a nuclear exp ...
; however, many other weapons influenced the world, such as jet aircraft
A jet aircraft (or simply jet) is an aircraft (nearly always a fixed-wing aircraft) propelled by one or more jet engines.
Whereas the engines in Propeller (aircraft), propeller-powered aircraft generally achieve their maximum efficiency at much ...
and radar
Radar is a system that uses radio waves to determine the distance ('' ranging''), direction ( azimuth and elevation angles), and radial velocity of objects relative to the site. It is a radiodetermination method used to detect and track ...
, but were overshadowed by the visibility of nuclear weapons and long-range rockets.
Nuclear weapons
Since the realization of mutual assured destruction (MAD), the nuclear option of all-out war is no longer considered a survivable scenario. During theCold War
The Cold War was a period of global Geopolitics, geopolitical rivalry between the United States (US) and the Soviet Union (USSR) and their respective allies, the capitalist Western Bloc and communist Eastern Bloc, which lasted from 1947 unt ...
in the years following World War II, both the United States and the Soviet Union engaged in a nuclear arms race
The nuclear arms race was an arms race competition for supremacy in nuclear warfare between the United States, the Soviet Union, and their respective allies during the Cold War. During this same period, in addition to the American and Soviet nuc ...
. Each country and their allies continually attempted to out-develop each other in the field of nuclear armaments. Once the joint technological capabilities reached the point of being able to ensure the destruction of the Earth by 100 fold, a new tactic had to be developed. With this realization, armaments development funding shifted back to primarily sponsoring the development of conventional arms technologies for support of limited wars rather than total war
Total war is a type of warfare that includes any and all (including civilian-associated) resources and infrastructure as legitimate military targets, mobilises all of the resources of society to fight the war, and gives priority to warfare ov ...
.
Types
By user
:''– what person or unit uses the weapon'' * Personal weapons (orsmall arms
A firearm is any type of gun that uses an explosive charge and is designed to be readily carried and operated by an individual. The term is legally defined further in different countries (see legal definitions).
The first firearms originate ...
) – designed to be used by a single person.
* Light weapons
A firearm is any type of gun that uses an explosive charge and is designed to be readily carried and operated by an individual. The term is legally defined further in different countries (see legal definitions).
The first firearms originated ...
– 'man-portable' weapons that may require a small team to operate.
* Heavy weapons – artillery
Artillery consists of ranged weapons that launch Ammunition, munitions far beyond the range and power of infantry firearms. Early artillery development focused on the ability to breach defensive walls and fortifications during sieges, and l ...
and similar weapons larger than light weapons (see SALW).
* Crew served weapons – larger than personal weapons, requiring two or more people to operate correctly.
* Fortification weapons – mounted in a permanent installation or used primarily within a fortification.
* Mountain weapons – for use by mountain forces or those operating in difficult terrain.
* Vehicle-mounted weapons – to be mounted on any type of combat vehicle.
* Railway weapon
A railway gun, also called a railroad gun, is a large artillery piece, often surplus naval artillery, mounted on, transported by, and fired from a specially designed railway wagon. Many countries have built railway guns, but the best-known a ...
s – designed to be mounted on railway cars, including armored trains.
* Aircraft weapons – carried on and used by some type of aircraft
An aircraft ( aircraft) is a vehicle that is able to flight, fly by gaining support from the Atmosphere of Earth, air. It counters the force of gravity by using either Buoyancy, static lift or the Lift (force), dynamic lift of an airfoil, or, i ...
, helicopter
A helicopter is a type of rotorcraft in which Lift (force), lift and thrust are supplied by horizontally spinning Helicopter rotor, rotors. This allows the helicopter to VTOL, take off and land vertically, to hover (helicopter), hover, and ...
, or other aerial vehicle.
* Naval weapons – mounted on ship
A ship is a large watercraft, vessel that travels the world's oceans and other Waterway, navigable waterways, carrying cargo or passengers, or in support of specialized missions, such as defense, research and fishing. Ships are generally disti ...
s and submarine
A submarine (often shortened to sub) is a watercraft capable of independent operation underwater. (It differs from a submersible, which has more limited underwater capability.) The term "submarine" is also sometimes used historically or infor ...
s.
* Space weapons – are designed to be used in or launched from space.
* Autonomous weapons – are capable of accomplishing a mission with limited or no human intervention.
By function
:''– the construction of the weapon and the principle of operation'' *Antimatter weapon
An antimatter weapon is a theoretically possible device using antimatter as a power source, a propellant, or an explosive for a weapon. Antimatter weapons are currently too costly and unreliable to be viable in warfare, as producing antimatter ...
s (theoretical) – would combine matter and antimatter
In modern physics, antimatter is defined as matter composed of the antiparticles (or "partners") of the corresponding subatomic particle, particles in "ordinary" matter, and can be thought of as matter with reversed charge and parity, or go ...
to cause a powerful explosion.
* Archery
Archery is the sport, practice, or skill of using a Bow and arrow, bow to shooting, shoot arrows.Paterson ''Encyclopaedia of Archery'' p. 17 The word comes from the Latin ''arcus'', meaning bow. Historically, archery has been used for hunting ...
weapons – operate by using a tensioned string and a bent solid to launch a projectile.
* Artillery
Artillery consists of ranged weapons that launch Ammunition, munitions far beyond the range and power of infantry firearms. Early artillery development focused on the ability to breach defensive walls and fortifications during sieges, and l ...
– firearms capable of launching heavy projectiles over long distances.
* Biological weapon
Biological agents, also known as biological weapons or bioweapons, are pathogens used as weapons. In addition to these living or replicating pathogens, toxins and Toxin#Biotoxins, biotoxins are also included among the bio-agents. More than 1,2 ...
s – spread biological agents, causing disease or infection.
* Blunt instruments – designed to break or fracture bones, produce concussion
A concussion, also known as a mild traumatic brain injury (mTBI), is a head injury that temporarily affects brain functioning. Symptoms may include headache, dizziness, difficulty with thinking and concentration, sleep disturbances, a brief ...
s, create organ ruptures, or crush injuries.
* Chemical weapons – poison people and cause reactions.
* Edged and bladed weapons – designed to pierce or cut through skin, muscle, or bone and cause internal or external bleeding.
* Energy weapons
Energy weapon may refer to:
* Directed-energy weapon, a real-life energy weapon used in the military and law enforcement
**Raygun
A raygun is a science-fiction directed-energy weapon usually with destructive effect.Jeff Prucher, '' Brave ...
– rely on concentrating forms of energy to attack, such as lasers or sonic attacks.
* Explosive weapons – use a physical explosion to create a blast, concussion, or spread shrapnel.
* Firearms
A firearm is any type of gun that uses an explosive charge and is designed to be readily carried and operated by an individual. The term is legally defined further in different countries (see legal definitions).
The first firearms originated ...
– use a chemical charge to launch projectiles.
* Improvised weapons – common objects reused as weapons, such as crowbars and kitchen knives.
* Incendiary weapons – cause damage by fire.
* Loitering munitions – designed to loiter over a battlefield, striking once a target is located.
* Magnetic weapons – use magnetic fields to propel projectiles or focus particle beams.
* Missile
A missile is an airborne ranged weapon capable of self-propelled flight aided usually by a propellant, jet engine or rocket motor.
Historically, 'missile' referred to any projectile that is thrown, shot or propelled towards a target; this ...
s – rockets that are guided to their target after launch. (Also a general term for projectile
A projectile is an object that is propelled by the application of an external force and then moves freely under the influence of gravity and air resistance. Although any objects in motion through space are projectiles, they are commonly found ...
weapons.)
* Non-lethal weapons – designed to subdue without killing.
* Nuclear weapon
A nuclear weapon is an explosive device that derives its destructive force from nuclear reactions, either fission (fission or atomic bomb) or a combination of fission and fusion reactions (thermonuclear weapon), producing a nuclear exp ...
s – use radioactive materials to create nuclear fission
Nuclear fission is a reaction in which the nucleus of an atom splits into two or more smaller nuclei. The fission process often produces gamma photons, and releases a very large amount of energy even by the energetic standards of radioactiv ...
or nuclear fusion
Nuclear fusion is a nuclear reaction, reaction in which two or more atomic nuclei combine to form a larger nuclei, nuclei/neutrons, neutron by-products. The difference in mass between the reactants and products is manifested as either the rele ...
detonations
* Rockets – self-propelled projectiles.
* Suicide weapons – exploit the willingness of their operators not surviving the attack.
By target
:''– the type of target the weapon is designed to attack'' * Anti-aircraft weapons – target missiles and aerial vehicles in flight. * Anti-fortification weapons – designed to target enemy installations. * Anti-personnel weapons – designed to attack people, either individually or in numbers. * Anti-radiation weapons – target sources of electronic radiation, particularly radar emitters. *Anti-satellite weapon
Anti-satellite weapons (ASAT) are space weapons designed to incapacitate or destroy satellites for Military strategy, strategic or Military tactics, tactical purposes. Although no ASAT system has been utilized in warfare, a few countries (China, ...
s – target orbiting satellites.
* :Anti-ship weapons, Anti-ship weapons – target ships and vessels on water.
* Anti-submarine weapons – target submarines and other underwater targets.
* Anti-tank weapons – designed to defeat armored targets.
* Area denial weapons – target territory, making it unsafe or unsuitable for enemy use or travel.
* Hunting weapons – weapons used to hunt game animals.
* :Infantry support weapons, Infantry support weapons – designed to attack various threats to infantry units.
* Siege engines – designed to break or circumvent heavy fortifications in siege warfare.
Manufacture of weapons
 The arms industry is a global industry that involves the sale and manufacture of weaponry. It consists of a commerce, commercial Industry (economics), industry involved in the research and development, engineering, production, and servicing of military material, equipment, and facilities. Many industrialized countries have a domestic arms industry to supply their own military forces, and some also have a substantial trade in weapons for use by their citizens for self-defense, hunting, or sporting purposes.
Contracts to supply a given country's military are awarded by governments, making arms contracts of substantial political importance. The link between politics and the arms trade can result in the development of a "military–industrial complex", where the armed forces, commerce, and politics become closely linked.
According to research institute SIPRI, the volume of international transfers of major weapons in 2010–2014 was 16 percent higher than in 2005–2009, and the arms sales of the world's 100 largest private arms-producing and military services companies totaled $420 billion in 2018.
The arms industry is a global industry that involves the sale and manufacture of weaponry. It consists of a commerce, commercial Industry (economics), industry involved in the research and development, engineering, production, and servicing of military material, equipment, and facilities. Many industrialized countries have a domestic arms industry to supply their own military forces, and some also have a substantial trade in weapons for use by their citizens for self-defense, hunting, or sporting purposes.
Contracts to supply a given country's military are awarded by governments, making arms contracts of substantial political importance. The link between politics and the arms trade can result in the development of a "military–industrial complex", where the armed forces, commerce, and politics become closely linked.
According to research institute SIPRI, the volume of international transfers of major weapons in 2010–2014 was 16 percent higher than in 2005–2009, and the arms sales of the world's 100 largest private arms-producing and military services companies totaled $420 billion in 2018.
Legislation
The production, possession, trade, and use of many weapons are controlled. This may be at a local government, local or central government level or by international treaty. Examples of such controls include: * The right of self-defense * Knife legislation * Air gun laws * Gun law * Arms trafficking laws * Arms control treaties * Space Preservation TreatyGun laws
All countries have laws and policies regulating aspects such as the manufacture, sale, transfer, possession, modification, and use of small arms by civilians. Countries that regulate access to firearms will typically restrict access to certain categories of firearms and then restrict the categories of persons who may be granted a license for access to such firearms. There may be separate licenses for hunting, sport shooting (a.k.a. target shooting), self-defense, collecting, and concealed carry, with different sets of requirements, permissions, and responsibilities.Arms control laws
International treaties and agreements place restrictions on the development, production, stockpiling, proliferation, and usage of weapons, fromsmall arms
A firearm is any type of gun that uses an explosive charge and is designed to be readily carried and operated by an individual. The term is legally defined further in different countries (see legal definitions).
The first firearms originate ...
and artillery, heavy weapons to weapons of mass destruction
A weapon of mass destruction (WMD) is a Biological agent, biological, chemical weapon, chemical, Radiological weapon, radiological, nuclear weapon, nuclear, or any other weapon that can kill or significantly harm many people or cause great dam ...
. Arms control is typically exercised through the use of diplomacy, which seeks to impose such limitations upon consenting participants, although it may also comprise efforts by a nation or group of nations to enforce limitations upon a non-consenting country.
Arms trafficking laws
Arms trafficking is the trafficking of contraband weapons andammunition
Ammunition, also known as ammo, is the material fired, scattered, dropped, or detonated from any weapon or weapon system. The term includes both expendable weapons (e.g., bombs, missiles, grenades, land mines), and the component parts of oth ...
. What constitutes legal trade in firearms varies widely, depending on local and national laws. In 2001, the United Nations had made a Protocol Against the Illicit Manufacturing of and Trafficking in Firearms, protocol against the manufacturing and trafficking of illicit arms. This protocol made governments dispose illegal arms, and to licence new firearms being produced, to ensure them being legitimate. It was signed by 122 parties.
Lifecycle problems
There are a number of issues around the potential ongoing risks from deployed weapons, the safe storage of weapons, and their eventual disposal when they are no longer effective or safe. * Ocean dumping of unused weapons such as bombs, ordnance, landmines, and chemical weapons has been common practice by many nations and has created hazards. * Unexploded ordnance (UXO) are bombs, land mines, naval mines, and similar devices that did not explode when they were employed and still pose a risk for many years or decades. * Demining or mine clearance from areas of past conflict is a difficult process, but every year, landmines kill 15,000 to 20,000 people and severely maim countless more. * Nuclear terrorism was a serious concern after the fall of the Soviet Union, with the prospect of "loose nukes" being available. While this risk may have receded, similar situations may arise in the future.In science fiction
Strange and exotic weapons are a recurring feature or theme in science fiction. In some cases, weapons first introduced in science fiction have now become a reality. Other science fiction weapons, such as force field (technology), force fields and stasis fields, remain purely fictional and are often beyond the realms of known physical possibility. At its most prosaic, science fiction features an endless variety of Sidearm (weapon), sidearms, mostly variations on real weapons such as guns andsword
A sword is an edged and bladed weapons, edged, bladed weapon intended for manual cutting or thrusting. Its blade, longer than a knife or dagger, is attached to a hilt and can be straight or curved. A thrusting sword tends to have a straighter ...
s. Among the best-known of these are the Weapons in Star Trek#Phaser, phaser used in the ''Star Trek'' television series, films, and novels, and the lightsaber and Blaster (Star Wars), blaster featured in the ''Star Wars'' movies, comics, novels, and TV series.
In addition to adding action and entertainment value, weaponry in science fiction sometimes becomes a theme when it touches on deeper concerns, often motivated by contemporary issues. One example is science fiction that deals with weapons of mass destruction
A weapon of mass destruction (WMD) is a Biological agent, biological, chemical weapon, chemical, Radiological weapon, radiological, nuclear weapon, nuclear, or any other weapon that can kill or significantly harm many people or cause great dam ...
like List of fictional doomsday devices, doomsday devices.
See also
* Arms industry * Improvised explosive device * List of martial arts weapons * List of practice weapons * Lists of weapons * Military technology * Offensive weapon * Riot control * Toy weapon * Weapon mountReferences
''Bevic Huynh, New York, 2012.''. Retrieved July 26, 2012.
External links
* * * {{Authority control Weapons, Military equipment Security War