Watertable control on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In


In addition, land drainage can help with
The soil's
or directly as PDF
/ref> is required to give the designer and manager of the drainage system a target to achieve in terms of maintenance of an optimum depth of the water table.
 The ''optimization'' of drainage design and the development of ''drainage criteria'' are discussed in the article on drainage research.
Figure 4 shows an example of the effect of drain depth on soil salinity and various irrigation/drainage parameters as simulated by the SaltMod program.
The ''optimization'' of drainage design and the development of ''drainage criteria'' are discussed in the article on drainage research.
Figure 4 shows an example of the effect of drain depth on soil salinity and various irrigation/drainage parameters as simulated by the SaltMod program.
By the end of the 19th century and early in the 20th century it was felt that the ditches were a hindrance for the farm operations and the ditches were replaced by buried lines of clay pipes (tiles), each tile about 30 cm long. Hence the term "
Since 1960, one started using long, flexible, corrugated
Thus, land drainage became a powerful industry. At the same time agriculture was steering towards maximum productivity, so that the installation of drainage systems came in full swing.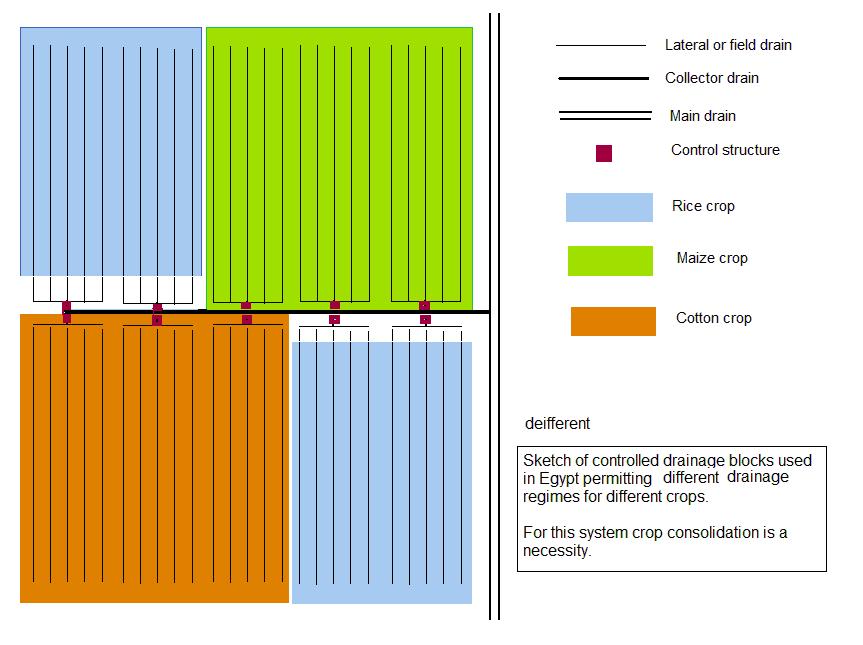
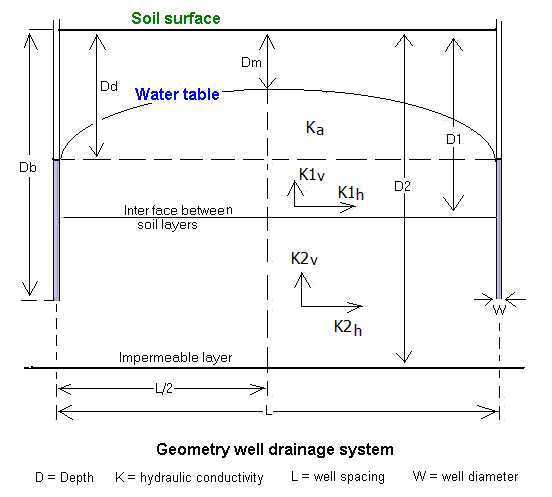 The design of subsurface drainage systems in terms layout, depth and spacing of the drains is often done using subsurface drainage equations with parameters like drain depth, depth of the water table, soil depth,
The design of subsurface drainage systems in terms layout, depth and spacing of the drains is often done using subsurface drainage equations with parameters like drain depth, depth of the water table, soil depth,
The computations can be done using computer models like EnDrain, which uses the hydraulic equivalent of Joule's law in electricity.
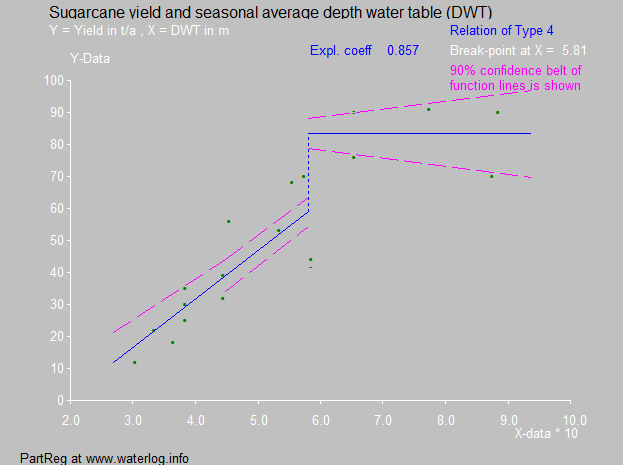 Most crops need a water table at a minimum depth. For some important food and fiber crops a classification was made because at shallower depths the crop suffers a yield decline.K.J.Lenselink et al. ''Crop tolerance to shallow water tables''. Online
Most crops need a water table at a minimum depth. For some important food and fiber crops a classification was made because at shallower depths the crop suffers a yield decline.K.J.Lenselink et al. ''Crop tolerance to shallow water tables''. Online
/ref> :(Where DWT = depth to water table)
American Wick Drain
Manufacturer of strip drain used in watertable management * Chapters of ILRI publication 16 on "Drainage Principles and Applications" can be viewed in: https://edepot.wur.nl/262058 * Website on Waterlogging and Land Drainage
* Various articles on Waterlogging and Land Drainage can be freely downloaded from
* For answers to frequently asked questions on Waterlogging and Land Drainage see
* Reports and case studies on Waterlogging and Land Drainage can be consulted at
* Software on Waterlogging and Land Drainage can be freely downloaded from
* A model of subsurface groundwater drainage for water table and soil salinity control ( SaltMod) can be freely downloaded from
* The combination of ''SaltMod'' with a polygonal model of groundwater flow ( SahysMod) can be freely downloaded from
{{Agricultural water management Drainage Aquifers Land management Land reclamation Water management Hydraulic engineering Water and the environment
geotechnical engineering
Geotechnical engineering, also known as geotechnics, is the branch of civil engineering concerned with the engineering behavior of earth materials. It uses the principles of soil mechanics and rock mechanics to solve its engineering problems. I ...
, watertable control is the practice of controlling the height of the water table
The water table is the upper surface of the phreatic zone or zone of saturation. The zone of saturation is where the pores and fractures of the ground are saturated with groundwater, which may be fresh, saline, or brackish, depending on the loc ...
by drainage
Drainage is the natural or artificial removal of a surface's water and sub-surface water from an area with excess water. The internal drainage of most agricultural soils can prevent severe waterlogging (anaerobic conditions that harm root gro ...
. Its main applications are in agricultural land
Agricultural land is typically land ''devoted to'' agriculture, the systematic and controlled use of other organism, forms of lifeparticularly the rearing of livestock and production of cropsto produce food for humans. It is generally synonymous ...
(to improve the crop yield
In agriculture, the yield is a measurement of the amount of a crop grown, or product such as wool, meat or milk produced, per unit area of land. The seed ratio is another way of calculating yields.
Innovations, such as the use of fertilizer, the ...
using agricultural drainage systems) and in cities to manage the extensive underground infrastructure
Infrastructure is the set of facilities and systems that serve a country, city, or other area, and encompasses the services and facilities necessary for its economy, households and firms to function. Infrastructure is composed of public and pri ...
that includes the foundations
Foundation(s) or The Foundation(s) may refer to: Common uses
* Foundation (cosmetics), a skin-coloured makeup cream applied to the face
* Foundation (engineering), the element of a structure which connects it to the ground, and transfers loads f ...
of large buildings, underground transit systems, and extensive utilities (water supply network
A water supply network or water supply system is a system of engineered hydrologic and hydraulic components that provide water supply. A water supply system typically includes the following:
# A drainage basin (see water purification – sour ...
s, sewerage
Sewerage (or sewage system) is the infrastructure that conveys sewage or surface runoff ( stormwater, meltwater, rainwater) using sewers. It encompasses components such as receiving drains, manholes, pumping stations, storm overflows, and scr ...
, storm drain
A storm drain, storm sewer (United Kingdom, U.S. and Canada), highway drain, surface water drain/sewer (United Kingdom), or stormwater drain (Australia and New Zealand) is infrastructure designed to drain excess rain and ground water from i ...
s, and underground electrical grid
An electrical grid (or electricity network) is an interconnected network for electricity delivery from producers to consumers. Electrical grids consist of power stations, electrical substations to step voltage up or down, electric power tran ...
s).
Description and definitions
Subsurface landdrainage
Drainage is the natural or artificial removal of a surface's water and sub-surface water from an area with excess water. The internal drainage of most agricultural soils can prevent severe waterlogging (anaerobic conditions that harm root gro ...
aims at controlling the water table
The water table is the upper surface of the phreatic zone or zone of saturation. The zone of saturation is where the pores and fractures of the ground are saturated with groundwater, which may be fresh, saline, or brackish, depending on the loc ...
of the groundwater
Groundwater is the water present beneath Earth's surface in rock and Pore space in soil, soil pore spaces and in the fractures of stratum, rock formations. About 30 percent of all readily available fresh water in the world is groundwater. A unit ...
in originally waterlogged land at a depth acceptable for the purpose for which the land is used. The depth of the water table with drainage is ''greater'' than without.

Purpose
In agricultural land drainage, the purpose of water table control is to establish a depth of the water table (Figure 1) that no longer interferes negatively with the necessary farm operations and crop yields (Figure 2, made with the SegReg model, see the page:segmented regression
Segmented regression, also known as piecewise regression or broken-stick regression, is a method in regression analysis in which the independent variable is partitioned into intervals and a separate line segment is fit to each interval. Segmented ...
).In addition, land drainage can help with
soil salinity control
Soil salinity control refers to controlling the process and progress of soil salinity to prevent soil degradation by salination and land reclamation, reclamation of already salty (saline) soils. Soil reclamation is also known as soil improvement ...
.The soil's
hydraulic conductivity
In science and engineering, hydraulic conductivity (, in SI units of meters per second), is a property of porous materials, soils and Rock (geology), rocks, that describes the ease with which a fluid (usually water) can move through the porosity, ...
plays an important role in drainage design.
The development of ''agricultural drainage criteria'' ''Agricultural Drainage Criteria'', Chapter 17 in: H.P.Ritzema (2006), Drainage Principles and Applications, Publication 16, International Institute for Land Reclamation and Improvement (ILRI), Wageningen, The Netherlands. . Download from or directly as PDF
/ref> is required to give the designer and manager of the drainage system a target to achieve in terms of maintenance of an optimum depth of the water table.
Optimization
Optimization of the depth of the water table is related to the benefits and costs of the drainage system (Figure 3). The shallower the permissible depth of the water table, the lower the cost of the drainage system to be installed to achieve this depth. However, the lowering of the originally too shallow depth by land drainage entails ''side effects''. These have also to be taken into account, including the costs of mitigation of negative side effects. The ''optimization'' of drainage design and the development of ''drainage criteria'' are discussed in the article on drainage research.
Figure 4 shows an example of the effect of drain depth on soil salinity and various irrigation/drainage parameters as simulated by the SaltMod program.
The ''optimization'' of drainage design and the development of ''drainage criteria'' are discussed in the article on drainage research.
Figure 4 shows an example of the effect of drain depth on soil salinity and various irrigation/drainage parameters as simulated by the SaltMod program.
History
Historically, agricultural landdrainage
Drainage is the natural or artificial removal of a surface's water and sub-surface water from an area with excess water. The internal drainage of most agricultural soils can prevent severe waterlogging (anaerobic conditions that harm root gro ...
started with the digging of relatively shallow open ditches that received both runoff from the land surface and outflow of groundwater
Groundwater is the water present beneath Earth's surface in rock and Pore space in soil, soil pore spaces and in the fractures of stratum, rock formations. About 30 percent of all readily available fresh water in the world is groundwater. A unit ...
. Hence the ditches had a surface as well as a subsurface drainage function.By the end of the 19th century and early in the 20th century it was felt that the ditches were a hindrance for the farm operations and the ditches were replaced by buried lines of clay pipes (tiles), each tile about 30 cm long. Hence the term "
tile drainage
Tile drainage is a form of agricultural drainage system that removes excess sub-surface water from fields to allow sufficient air space within the soil, proper cultivation, and access by heavy machinery to tend and harvest crops. While surface wa ...
". Since 1960, one started using long, flexible, corrugated
plastic
Plastics are a wide range of synthetic polymers, synthetic or Semisynthesis, semisynthetic materials composed primarily of Polymer, polymers. Their defining characteristic, Plasticity (physics), plasticity, allows them to be Injection moulding ...
( PVC or PE) pipes that could be installed efficiently in one go by trenching machines. The pipes could be pre-wrapped with an envelope material, like synthetic fibre
Synthetic fibers or synthetic fibres (in British English; see spelling differences) are fibers made by humans through chemical synthesis, as opposed to natural fibers that are directly derived from living organisms, such as plants like cotton or ...
and geotextile
Geotextiles are versatile permeable fabrics that, when used in conjunction with soil, can effectively perform multiple functions, including separation, filtration, reinforcement, protection, and drainage. Typically crafted from polypropylene or ...
, that would prevent the entry of soil particles into the drains. Thus, land drainage became a powerful industry. At the same time agriculture was steering towards maximum productivity, so that the installation of drainage systems came in full swing.

Environment
As a result of large scale developments, many modern drainage projects were ''over-designed'', while the negative environmental side effects were ignored. In circles with environmental concern, the profession of land drainage got a poor reputation, sometimes justly so, sometimes unjustified, notably when land drainage was confused with the more encompassing activity of wetland reclamation. Nowadays, in some countries, the hardliner trend is reversed. Further, ''checked'' or ''controlled'' drainage systems were introduced, as shown in Figure 5 and discussed on the page: Drainage system (agriculture).Drainage design
 The design of subsurface drainage systems in terms layout, depth and spacing of the drains is often done using subsurface drainage equations with parameters like drain depth, depth of the water table, soil depth,
The design of subsurface drainage systems in terms layout, depth and spacing of the drains is often done using subsurface drainage equations with parameters like drain depth, depth of the water table, soil depth, hydraulic conductivity
In science and engineering, hydraulic conductivity (, in SI units of meters per second), is a property of porous materials, soils and Rock (geology), rocks, that describes the ease with which a fluid (usually water) can move through the porosity, ...
of the soil and drain discharge. The drain discharge is found from an agricultural water balance.The computations can be done using computer models like EnDrain, which uses the hydraulic equivalent of Joule's law in electricity.
Drainage by wells
Subsurface drainage of groundwater can also be accomplished by pumped wells (''vertical'' drainage, in contrast to ''horizontal'' drainage). Drainage wells have been used extensively in the Salinity Control and Reclamation Program (SCARP) in the Indus valley ofPakistan
Pakistan, officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of over 241.5 million, having the Islam by country# ...
. Although the experiences were not overly successful, the feasibility of this technique in areas with deep and permeable aquifers is not to be discarded. The well spacings in these areas can be so wide (more than 1000m) that the installation of ''vertical'' drainage systems could be relatively cheap compared to ''horizontal'' subsurface drainage (drainage by pipes, ditches, trenches, at a spacing of 100m or less). For the design of a well field for control of the water table, the WellDrain model may be helpful.
Classification
A classification of drainage systems is found in the article Drainage system (agriculture).Effects on crop yield
 Most crops need a water table at a minimum depth. For some important food and fiber crops a classification was made because at shallower depths the crop suffers a yield decline.K.J.Lenselink et al. ''Crop tolerance to shallow water tables''. Online
Most crops need a water table at a minimum depth. For some important food and fiber crops a classification was made because at shallower depths the crop suffers a yield decline.K.J.Lenselink et al. ''Crop tolerance to shallow water tables''. Online/ref> :(Where DWT = depth to water table)
See also
* Dewatering * Subsurface dykeReferences
External links
American Wick Drain
Manufacturer of strip drain used in watertable management * Chapters of ILRI publication 16 on "Drainage Principles and Applications" can be viewed in: https://edepot.wur.nl/262058 * Website on Waterlogging and Land Drainage
* Various articles on Waterlogging and Land Drainage can be freely downloaded from
* For answers to frequently asked questions on Waterlogging and Land Drainage see
* Reports and case studies on Waterlogging and Land Drainage can be consulted at
* Software on Waterlogging and Land Drainage can be freely downloaded from
* A model of subsurface groundwater drainage for water table and soil salinity control ( SaltMod) can be freely downloaded from
* The combination of ''SaltMod'' with a polygonal model of groundwater flow ( SahysMod) can be freely downloaded from
{{Agricultural water management Drainage Aquifers Land management Land reclamation Water management Hydraulic engineering Water and the environment