Volatility (physics) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In
In

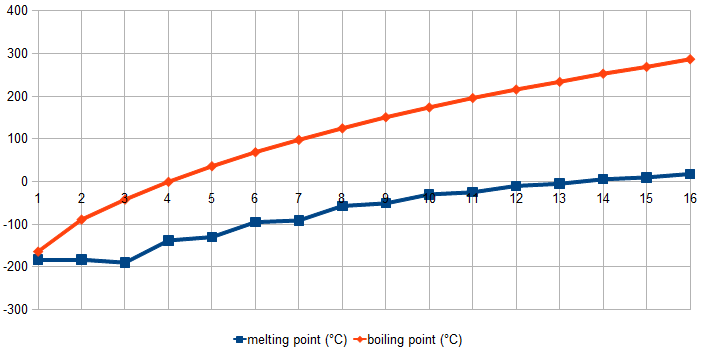 An important factor influencing a substance's volatility is the strength of the interactions between its molecules. Attractive forces between molecules are what holds materials together, and materials with stronger
An important factor influencing a substance's volatility is the strength of the interactions between its molecules. Attractive forces between molecules are what holds materials together, and materials with stronger
 Knowledge of volatility is often useful in the separation of components from a mixture. When a mixture of condensed substances contains multiple substances with different levels of volatility, its temperature and pressure can be manipulated such that the more volatile components change to a vapor while the less volatile substances remain in the liquid or solid phase. The newly formed vapor can then be discarded or condensed into a separate container. When the vapors are collected, this process is known as
Knowledge of volatility is often useful in the separation of components from a mixture. When a mixture of condensed substances contains multiple substances with different levels of volatility, its temperature and pressure can be manipulated such that the more volatile components change to a vapor while the less volatile substances remain in the liquid or solid phase. The newly formed vapor can then be discarded or condensed into a separate container. When the vapors are collected, this process is known as
Volatility from ilpi.com
* Definition of volatile from Wiktionary {{States of matter Physical chemistry Chemical properties Thermodynamic properties Engineering thermodynamics Gases
 In
In chemistry
Chemistry is the scientific study of the properties and behavior of matter. It is a natural science that covers the elements that make up matter to the compounds made of atoms, molecules and ions: their composition, structure, proper ...
, volatility is a material quality which describes how readily a substance vaporizes
Vaporization (or vaporisation) of an element or compound is a phase transition from the liquid phase to vapor. There are two types of vaporization: evaporation and boiling. Evaporation is a surface phenomenon, whereas boiling is a bulk phenomenon ...
. At a given temperature
Temperature is a physical quantity that expresses quantitatively the perceptions of hotness and coldness. Temperature is measured with a thermometer.
Thermometers are calibrated in various temperature scales that historically have relied o ...
and pressure
Pressure (symbol: ''p'' or ''P'') is the force applied perpendicular to the surface of an object per unit area over which that force is distributed. Gauge pressure (also spelled ''gage'' pressure)The preferred spelling varies by country a ...
, a substance with high volatility is more likely to exist as a vapour, while a substance with low volatility is more likely to be a liquid
A liquid is a nearly incompressible fluid that conforms to the shape of its container but retains a (nearly) constant volume independent of pressure. As such, it is one of the four fundamental states of matter (the others being solid, gas, ...
or solid
Solid is one of the four fundamental states of matter (the others being liquid, gas, and plasma). The molecules in a solid are closely packed together and contain the least amount of kinetic energy. A solid is characterized by structur ...
. Volatility can also describe the tendency of a vapor to condense into a liquid or solid; less volatile substances will more readily condense from a vapor than highly volatile ones. Differences in volatility can be observed by comparing how fast substances within a group evaporate (or sublimate in the case of solids) when exposed to the atmosphere. A highly volatile substance such as rubbing alcohol (isopropyl alcohol
Isopropyl alcohol (IUPAC name propan-2-ol and also called isopropanol or 2-propanol) is a colorless, flammable organic compound with a pungent alcoholic odor. As an isopropyl group linked to a hydroxyl group ( chemical formula ) it is the s ...
) will quickly evaporate, while a substance with low volatility such as vegetable oil
Vegetable oils, or vegetable fats, are oils extracted from seeds or from other parts of fruits. Like animal fats, vegetable fats are ''mixtures'' of triglycerides. Soybean oil, grape seed oil, and cocoa butter are examples of seed oils, or f ...
will remain condensed. In general, solids are much less volatile than liquids, but there are some exceptions. Solids that sublimate (change directly from solid to vapor) such as dry ice (solid carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide ( chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is t ...
) or iodine
Iodine is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol I and atomic number 53. The heaviest of the stable halogens, it exists as a semi-lustrous, non-metallic solid at standard conditions that melts to form a deep violet liquid at , ...
can vaporize at a similar rate as some liquids under standard conditions.
Description
Volatility itself has no defined numerical value, but it is often described using vapor pressures or boiling points (for liquids). High vapor pressures indicate a high volatility, while high boiling points indicate low volatility. Vapor pressures and boiling points are often presented in tables and charts that can be used to compare chemicals of interest. Volatility data is typically found through experimentation over a range of temperatures and pressures.Vapor pressure
Vapor pressure
Vapor pressure (or vapour pressure in English-speaking countries other than the US; see spelling differences) or equilibrium vapor pressure is defined as the pressure exerted by a vapor in thermodynamic equilibrium with its condensed pha ...
is a measurement of how readily a condensed phase forms a vapor at a given temperature. A substance enclosed in a sealed vessel initially at vacuum (no air inside) will quickly fill any empty space with vapor. After the system reaches equilibrium and no more vapor is formed, this vapor pressure can be measured. Increasing the temperature increases the amount of vapor that is formed and thus the vapor pressure. In a mixture, each substance contributes to the overall vapor pressure of the mixture, with more volatile compounds making a larger contribution.
Boiling point
Boiling point
The boiling point of a substance is the temperature at which the vapor pressure of a liquid equals the pressure surrounding the liquid and the liquid changes into a vapor.
The boiling point of a liquid varies depending upon the surrounding env ...
is the temperature at which the vapor pressure of a liquid is equal to the surrounding pressure, causing the liquid to rapidly evaporate, or boil. It is closely related to vapor pressure, but is dependent on pressure. The normal boiling point is the boiling point at atmospheric pressure, but it can also be reported at higher and lower pressures.
Contributing factors
Intermolecular forces
 An important factor influencing a substance's volatility is the strength of the interactions between its molecules. Attractive forces between molecules are what holds materials together, and materials with stronger
An important factor influencing a substance's volatility is the strength of the interactions between its molecules. Attractive forces between molecules are what holds materials together, and materials with stronger intermolecular forces
An intermolecular force (IMF) (or secondary force) is the force that mediates interaction between molecules, including the electromagnetic forces of attraction
or repulsion which act between atoms and other types of neighbouring particles, e.g. a ...
, such as most solids, are typically not very volatile. Ethanol
Ethanol (abbr. EtOH; also called ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol, drinking alcohol, or simply alcohol) is an organic compound. It is an alcohol with the chemical formula . Its formula can be also written as or (an ethyl group linked to a ...
and dimethyl ether
Dimethyl ether (DME; also known as methoxymethane) is the organic compound with the formula CH3OCH3,
(sometimes ambiguously simplified to C2H6O as it is an isomer of ethanol). The simplest ether, it is a colorless gas that is a useful precursor ...
, two chemicals with the same formula (C2H6O), have different volatilities due to the different interactions that occur between their molecules in the liquid phase: ethanol molecules are capable of hydrogen bonding
In chemistry, a hydrogen bond (or H-bond) is a primarily electrostatic force of attraction between a hydrogen (H) atom which is covalently bound to a more electronegative "donor" atom or group (Dn), and another electronegative atom bearing a l ...
while dimethyl ether molecules are not. The result in an overall stronger attractive force between the ethanol molecules, making it the less volatile substance of the two.
Molecular weight
In general, volatility tends to decrease with increasingmolecular mass
The molecular mass (''m'') is the mass of a given molecule: it is measured in daltons (Da or u). Different molecules of the same compound may have different molecular masses because they contain different isotopes of an element. The related quant ...
because larger molecules can participate in more intermolecular bonding, although other factors such as structure and polarity play a significant role. The effect of molecular mass can be partially isolated by comparing chemicals of similar structure (i.e. esters, alkanes, etc.). For instance, linear alkanes
In organic chemistry, an alkane, or paraffin (a historical trivial name that also has other meanings), is an acyclic saturated hydrocarbon. In other words, an alkane consists of hydrogen and carbon atoms arranged in a tree structure in ...
exhibit decreasing volatility as the number of carbons in the chain increases.
Applications
Distillation
distillation
Distillation, or classical distillation, is the process of separating the components or substances from a liquid mixture by using selective boiling and condensation, usually inside an apparatus known as a still. Dry distillation is the he ...
.
The process of petroleum refinement utilizes a technique known as fractional distillation
Fractional distillation is the separation of a mixture into its component parts, or fractions. Chemical compounds are separated by heating them to a temperature at which one or more fractions of the mixture will vaporize. It uses distillation ...
, which allows several chemicals of varying volatility to be separated in a single step. Crude oil
Petroleum, also known as crude oil, or simply oil, is a naturally occurring yellowish-black liquid mixture of mainly hydrocarbons, and is found in geological formations. The name ''petroleum'' covers both naturally occurring unprocessed crude ...
entering a refinery is composed of many useful chemicals that need to be separated. The crude oil flows into a distillation tower and is heated up, which allows the more volatile components such as butane
Butane () or ''n''-butane is an alkane with the formula C4H10. Butane is a gas at room temperature and atmospheric pressure. Butane is a highly flammable, colorless, easily liquefied gas that quickly vaporizes at room temperature. The name but ...
and kerosene
Kerosene, paraffin, or lamp oil is a combustible hydrocarbon liquid which is derived from petroleum. It is widely used as a fuel in aviation as well as households. Its name derives from el, κηρός (''keros'') meaning " wax", and was re ...
to vaporize. These vapors move up the tower and eventually come in contact with cold surfaces, which causes them to condense and be collected. The most volatile chemical condense at the top of the column while the least volatile chemicals to vaporize condense in the lowest portion. On the right is a picture illustrating the design of a distillation tower
A fractionating column or fractional column is an essential item used in the distillation of liquid mixtures to separate the mixture into its component parts, or fractions, based on the differences in volatilities. Fractionating columns are used in ...
.
The difference in volatility between water and ethanol has traditionally been used in the refinement of drinking alcohol
Alcohol, sometimes referred to by the chemical name ''ethanol'', is a depressant drug that is the active ingredient in drinks such as beer, wine, and distilled spirits (hard liquor). It is one of the oldest and most commonly consumed recreat ...
. In order to increase the concentration of ethanol
Ethanol (abbr. EtOH; also called ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol, drinking alcohol, or simply alcohol) is an organic compound. It is an alcohol with the chemical formula . Its formula can be also written as or (an ethyl group linked to a ...
in the product, alcohol makers would heat the initial alcohol mixture to a temperature where most of the ethanol vaporizes while most of the water remains liquid. The ethanol vapor is then collected and condensed in a separate container, resulting in a much more concentrated product.
Perfume
Volatility is an important consideration when craftingperfume
Perfume (, ; french: parfum) is a mixture of fragrant essential oils or aroma compounds (fragrances), fixatives and solvents, usually in liquid form, used to give the human body, animals, food, objects, and living-spaces an agreeable scent ...
s. Humans detect odor
An odor (American English) or odour (Commonwealth English; see spelling differences) is caused by one or more volatilized chemical compounds that are generally found in low concentrations that humans and animals can perceive via their sense ...
s when aromatic vapors come in contact with receptors in the nose. Ingredients that vaporize quickly after being applied will produce fragrant vapors for a short time before the oils evaporate. Slow-evaporating ingredients can stay on the skin for weeks or even months, but may not produce enough vapors to produce a strong aroma. To prevent these problems, perfume designers carefully consider the volatility of essential oils and other ingredients in their perfumes. Appropriate evaporation rates are achieved by modifying the amount of highly volatile and non-volatile ingredients used.
See also
*Clausius–Clapeyron relation
The Clausius–Clapeyron relation, named after Rudolf Clausius and Benoît Paul Émile Clapeyron, specifies the temperature dependence of pressure, most importantly vapor pressure, at a discontinuous phase transition between two phases of matter ...
* Distillation
Distillation, or classical distillation, is the process of separating the components or substances from a liquid mixture by using selective boiling and condensation, usually inside an apparatus known as a still. Dry distillation is the he ...
* Fractional distillation
Fractional distillation is the separation of a mixture into its component parts, or fractions. Chemical compounds are separated by heating them to a temperature at which one or more fractions of the mixture will vaporize. It uses distillation ...
* Partial pressure
In a mixture of gases, each constituent gas has a partial pressure which is the notional pressure of that constituent gas as if it alone occupied the entire volume of the original mixture at the same temperature. The total pressure of an ideal g ...
* Raoult's law
* Relative volatility Relative volatility is a measure comparing the vapor pressures of the components in a liquid mixture of chemicals. This quantity is widely used in designing large industrial distillation processes. In effect, it indicates the ease or difficulty of u ...
* Vapor–liquid equilibrium
In thermodynamics and chemical engineering, the vapor–liquid equilibrium (VLE) describes the distribution of a chemical species between the vapor phase and a liquid phase.
The concentration of a vapor in contact with its liquid, especially a ...
* Volatile organic compound
Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) are organic compounds that have a high vapour pressure at room temperature. High vapor pressure correlates with a low boiling point, which relates to the number of the sample's molecules in the surrounding air, a ...
References
External links
Volatility from ilpi.com
* Definition of volatile from Wiktionary {{States of matter Physical chemistry Chemical properties Thermodynamic properties Engineering thermodynamics Gases