Vindhya Range on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Vindhya Range (also known as Vindhyachal) () is a complex, discontinuous chain of mountain
 Earlier, the term "Vindhyas" was used in a wider sense and included a number of hill ranges between the
Earlier, the term "Vindhyas" was used in a wider sense and included a number of hill ranges between the
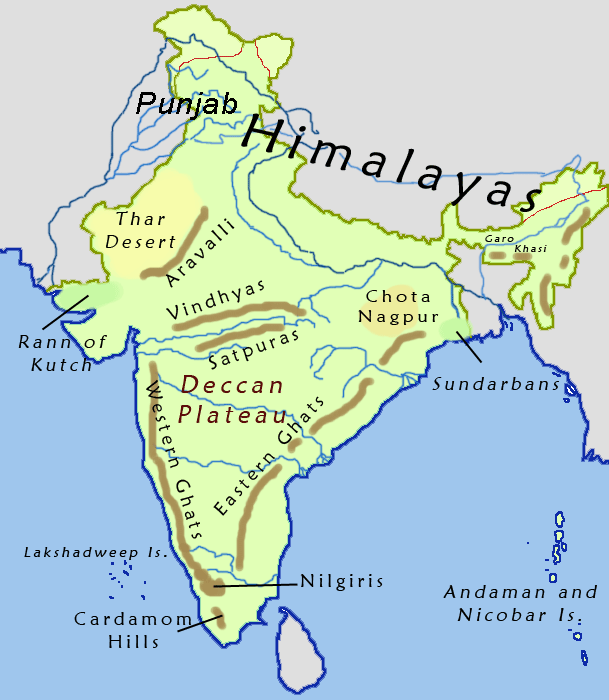 Today, the definition of the Vindhyas is primarily restricted to the Central Indian escarpments, hills and highlands located to the north of the Narmada River. Some of these are actually distinct hill systems.
The western end of the Vindhya range is located in the state of
Today, the definition of the Vindhyas is primarily restricted to the Central Indian escarpments, hills and highlands located to the north of the Narmada River. Some of these are actually distinct hill systems.
The western end of the Vindhya range is located in the state of
 The Vindhyas are regarded as the traditional geographical boundary between northern and southern India, and have a distinguished status in both mythology and geography of India. In the ancient Indian texts, the Vindhyas are seen as the demarcating line between the territories of the Indo-Aryans and that of the others. The most ancient Hindu texts consider it as the southern boundary of Aryavarta. The
The Vindhyas are regarded as the traditional geographical boundary between northern and southern India, and have a distinguished status in both mythology and geography of India. In the ancient Indian texts, the Vindhyas are seen as the demarcating line between the territories of the Indo-Aryans and that of the others. The most ancient Hindu texts consider it as the southern boundary of Aryavarta. The
ridge
A ridge or a mountain ridge is a geographical feature consisting of a chain of mountains or hills that form a continuous elevated crest for an extended distance. The sides of the ridge slope away from the narrow top on either side. The line ...
s, hill ranges, highlands and plateau escarpment
An escarpment is a steep slope or long cliff that forms as a result of faulting or erosion and separates two relatively level areas having different elevations.
The terms ''scarp'' and ''scarp face'' are often used interchangeably with ''esca ...
s in west-central India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area, the List of countries and dependencies by population, second-most populous ...
.
Technically, the Vindhyas do not form a single mountain range in the geological sense. The exact extent of the Vindhyas is loosely defined, and historically, the term covered a number of distinct hill systems in central India, including the one that is now known as the Satpura Range. Today, the term principally refers to the escarpment and its hilly extensions that runs north of and roughly parallel to the Narmada River in Madhya Pradesh
Madhya Pradesh (, ; meaning 'central province') is a state in central India. Its capital is Bhopal, and the largest city is Indore, with Jabalpur, Ujjain, Gwalior, Sagar, and Rewa being the other major cities. Madhya Pradesh is the second ...
. Depending on the definition, the range extends up to Gujarat
Gujarat (, ) is a state along the western coast of India. Its coastline of about is the longest in the country, most of which lies on the Kathiawar peninsula. Gujarat is the fifth-largest Indian state by area, covering some ; and the ninth ...
in the west, Uttar Pradesh
Uttar Pradesh (; , 'Northern Province') is a state in northern India. With over 200 million inhabitants, it is the most populated state in India as well as the most populous country subdivision in the world. It was established in 195 ...
and Bihar
Bihar (; ) is a state in eastern India. It is the 2nd largest state by population in 2019, 12th largest by area of , and 14th largest by GDP in 2021. Bihar borders Uttar Pradesh to its west, Nepal to the north, the northern part of West ...
in the north, and Chhattisgarh
Chhattisgarh (, ) is a landlocked state in Central India. It is the ninth largest state by area, and with a population of roughly 30 million, the seventeenth most populous. It borders seven states – Uttar Pradesh to the north, Madhya Prad ...
in the east.
The Vindhyas have a great significance in Indian mythology and history. Several ancient texts mention the Vindhyas as the southern boundary of the '' Āryāvarta'', the territory of the ancient Indo-Aryan peoples
Indo-Aryan peoples are a diverse collection of Indo-European peoples speaking Indo-Aryan languages in the Indian subcontinent. Historically, Aryan were the Indo-European pastoralists who migrated from Central Asia into South Asia and int ...
. Although today Indo-Aryan languages
The Indo-Aryan languages (or sometimes Indic languages) are a branch of the Indo-Iranian languages in the Indo-European language family. As of the early 21st century, they have more than 800 million speakers, primarily concentrated in India, P ...
are spoken south of the Vindhyas, the range continues to be considered as the traditional boundary between north and south India. The former Vindhya Pradesh was named after the Vindhya Range.
Etymology and names
According to the author of a commentary on '' Amarakosha'', the word Vindhya derives from theSanskrit
Sanskrit (; attributively , ; nominally , , ) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in South Asia after its predecessor languages had Trans-cultural diffusion ...
word ''vaindh'' (to obstruct). A mythological story (see below
Below may refer to:
*Earth
* Ground (disambiguation)
*Soil
*Floor
* Bottom (disambiguation)
*Less than
*Temperatures below freezing
*Hell or underworld
People with the surname
*Ernst von Below (1863–1955), German World War I general
*Fred Below ...
) states that the Vindhyas once obstructed the path of the sun, resulting in this name. Ramayana from Valmiki states that the great mountain Vindhya that was growing incessantly and obstructing the path of the Sun stopped growing any more in obedience to Agastya's words. According to another theory, the name "Vindhya" means "hunter" in Sanskrit, and may refer to the tribal hunter-gatherer
A traditional hunter-gatherer or forager is a human living an ancestrally derived lifestyle in which most or all food is obtained by foraging, that is, by gathering food from local sources, especially edible wild plants but also insects, fung ...
s inhabiting the region.
The Vindhya range is also known as "Vindhyachala" or "Vindhyachal"; the suffix ''achala'' (Sanskrit) or ''achal'' (Hindi) refers to a mountain. In the Mahabharata
The ''Mahābhārata'' ( ; sa, महाभारतम्, ', ) is one of the two major Sanskrit epics of ancient India in Hinduism, the other being the '' Rāmāyaṇa''. It narrates the struggle between two groups of cousins in the K ...
, the range is also referred to as ''Vindhyapadaparvata''. The Greek geographer Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; grc-gre, Πτολεμαῖος, ; la, Claudius Ptolemaeus; AD) was a mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist, who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were of importanc ...
called the range Vindius or Ouindion, describing it as the source of Namados ( Narmada) and Nanagouna (Tapti
The Tapti River (or Tapi) is a river in central India located to the south of the Narmada river that flows westwards before draining into the Arabian Sea. The river has a length of around and flows through the states of Maharashtra, Gujara ...
) rivers. The "Daksinaparvata" ("Southern Mountain") mentioned in the Kaushitaki Upanishad
The ''Kaushitaki Upanishad'' ( sa, कौषीतकि उपनिषद्, ) is an ancient Sanskrit text contained inside the Rigveda. It is associated with the ''Kaushitaki'' shakha, but a Sāmānya Upanishad, meaning that it is "common" ...
is also identified with the Vindhyas.
Extent
The Vindhyas do not form a single range in the proper geological sense: the hills collectively known as the Vindhyas do not lie along ananticlinal Anticlinal may refer to:
*Anticline, in structural geology, an anticline is a fold that is convex up and has its oldest beds at its core.
*Anticlinal, in stereochemistry, a torsion angle between 90° to 150°, and –90° to –150°; see Alkane_st ...
or synclinal ridge. The Vindhya range is actually a group of discontinuous chain of mountain ridge
A ridge or a mountain ridge is a geographical feature consisting of a chain of mountains or hills that form a continuous elevated crest for an extended distance. The sides of the ridge slope away from the narrow top on either side. The line ...
s, hill ranges, highlands and plateau escarpment
An escarpment is a steep slope or long cliff that forms as a result of faulting or erosion and separates two relatively level areas having different elevations.
The terms ''scarp'' and ''scarp face'' are often used interchangeably with ''esca ...
s. The term "Vindhyas" is defined by convention, and therefore, the exact definition of the Vindhya range has varied at different times in history.
Historical definitions
 Earlier, the term "Vindhyas" was used in a wider sense and included a number of hill ranges between the
Earlier, the term "Vindhyas" was used in a wider sense and included a number of hill ranges between the Indo-Gangetic plain
The Indo-Gangetic Plain, also known as the North Indian River Plain, is a fertile plain encompassing northern regions of the Indian subcontinent, including most of northern and eastern India, around half of Pakistan, virtually all of Bangla ...
and the Deccan Plateau
The large Deccan Plateau in southern India is located between the Western Ghats and the Eastern Ghats, and is loosely defined as the peninsular region between these ranges that is south of the Narmada river. To the north, it is bounded by th ...
. According to the various definitions mentioned in the older texts, the Vindhyas extend up to Godavari
The Godavari ( IAST: ''Godāvarī'' �od̪aːʋəɾiː is India's second longest river after the Ganga river and drains into the third largest basin in India, covering about 10% of India's total geographical area. Its source is in Trimbakesh ...
in the south and Ganges
The Ganges ( ) (in India: Ganga ( ); in Bangladesh: Padma ( )). "The Ganges Basin, known in India as the Ganga and in Bangladesh as the Padma, is an international river to which India, Bangladesh, Nepal and China are the riparian states." is ...
in the north.
In certain Puranas
Purana (; sa, , '; literally meaning "ancient, old"Merriam-Webster's Encyclopedia of Literature (1995 Edition), Article on Puranas, , page 915) is a vast genre of Indian literature about a wide range of topics, particularly about legends an ...
, the term Vindhya specifically covers the mountain range located between the Narmada and the Tapti
The Tapti River (or Tapi) is a river in central India located to the south of the Narmada river that flows westwards before draining into the Arabian Sea. The river has a length of around and flows through the states of Maharashtra, Gujara ...
rivers; that is, the one which is now known as the Satpura Range. The Varaha Purana uses the name "Vindhya-pada" ("foot of the Vindhyas") for the Satpura range.
Several ancient Indian texts and inscriptions (e.g. the ''Nasik Prasasti'' of Gautamiputra Satakarni
Gautamiputra Satakarni (Brahmi: 𑀕𑁄𑀢𑀫𑀺𑀧𑀼𑀢 𑀲𑀸𑀢𑀓𑀡𑀺, ''Gotamiputa Sātakaṇi'', IAST: ) was a ruler of the Satavahana Empire in present-day Deccan region of India. He was mentioned as the important an ...
) mention three mountain ranges in Central India: Vindhya (or "Vindhya proper"), Rksa (also Rksavat or Riksha) and Pariyatra (or Paripatra). The three ranges are included in the seven ''Kula Parvatas'' ("clan mountains") of Bharatavarsha i.e. India. The exact identification of these three ranges is difficult due to contrasting descriptions in the various texts. For example, the Kurma
Kurma ( sa, कूर्म; , 'Turtle', 'Tortoise'), is the second avatar of the Hindu preserver deity, Vishnu. Originating in Vedic literature such as the Yajurveda as being synonymous with the Saptarishi called Kashyapa, Kurma is mo ...
, Matsya and Brahmanda Puranas mention Vindhya as the source of Tapti; while Vishnu
Vishnu ( ; , ), also known as Narayana and Hari, is one of the principal deities of Hinduism. He is the supreme being within Vaishnavism, one of the major traditions within contemporary Hinduism.
Vishnu is known as "The Preserver" withi ...
and Brahma
Brahma ( sa, ब्रह्मा, Brahmā) is a Hindu god, referred to as "the Creator" within the Trimurti, the trinity of supreme divinity that includes Vishnu, and Shiva.Jan Gonda (1969)The Hindu Trinity Anthropos, Bd 63/64, H 1/2, pp ...
Puranas mention the Rksa as its source. Some texts use the term Vindhyas to describe all the hills in Central India.
In one passage, Valmiki
Valmiki (; Sanskrit: वाल्मीकि, ) is celebrated as the harbinger-poet in Sanskrit literature. The epic ''Ramayana'', dated variously from the 5th century BCE to first century BCE, is attributed to him, based on the attributio ...
's Ramayana
The ''Rāmāyana'' (; sa, रामायणम्, ) is a Sanskrit epic composed over a period of nearly a millennium, with scholars' estimates for the earliest stage of the text ranging from the 8th to 4th centuries BCE, and later stages ...
describes Vindhya as being situated to the south of Kishkindha (Ramayana IV-46. 17), which is identified with a part of the present-day Karnataka
Karnataka (; ISO 15919, ISO: , , also known as Karunāḍu) is a States and union territories of India, state in the southwestern region of India. It was Unification of Karnataka, formed on 1 November 1956, with the passage of the States Reor ...
. It further implies that the sea was located just to the south of the Vindhyas, and Lanka
Lanka (, ) is the name given in Hindu epics to the island fortress capital of the legendary asura king Ravana in the epics of the ''Ramayana'' and the ''Mahabharata''. The fortress was situated on a plateau between three mountain peaks known ...
was located across this sea. Many scholars have attempted to explain this anomaly in different ways. According to one theory, the term "Vindhyas" covered a number of mountains to the south of the Indo-Aryan territories at the time Ramayana was written. Others, such as Frederick Eden Pargiter, believe that there was another mountain in South India, with the same name. Madhav Vinayak Kibe
Sardar Madhavrao Vinayak Kibe (Devanagari: माधव विनायक किबे; 1877–?) was a scholar from Indore State, India. He was from the Karhade Brahmin Kibe family founded by Vithalrao Mahadeo Kibe, known as Tantya Jog, the Pr ...
placed the location of Lanka in Central India.
The Barabar Cave inscription of Maukhari Anantavarman mentions the Nagarjuni hill of Bihar as a part of the Vindhyas.
Present-day definition
 Today, the definition of the Vindhyas is primarily restricted to the Central Indian escarpments, hills and highlands located to the north of the Narmada River. Some of these are actually distinct hill systems.
The western end of the Vindhya range is located in the state of
Today, the definition of the Vindhyas is primarily restricted to the Central Indian escarpments, hills and highlands located to the north of the Narmada River. Some of these are actually distinct hill systems.
The western end of the Vindhya range is located in the state of Gujarat
Gujarat (, ) is a state along the western coast of India. Its coastline of about is the longest in the country, most of which lies on the Kathiawar peninsula. Gujarat is the fifth-largest Indian state by area, covering some ; and the ninth ...
, near the state's border with Rajasthan
Rajasthan (; lit. 'Land of Kings') is a state in northern India. It covers or 10.4 per cent of India's total geographical area. It is the largest Indian state by area and the seventh largest by population. It is on India's northwestern ...
and Madhya Pradesh
Madhya Pradesh (, ; meaning 'central province') is a state in central India. Its capital is Bhopal, and the largest city is Indore, with Jabalpur, Ujjain, Gwalior, Sagar, and Rewa being the other major cities. Madhya Pradesh is the second ...
, at the eastern side of the Kathiawar
Kathiawar () is a peninsula, near the far north of India's west coast, of about bordering the Arabian Sea. It is bounded by the Gulf of Kutch in the northwest and by the Gulf of Khambhat (Gulf of Cambay) in the east. In the northeast, i ...
peninsula. A series of hills connects the Vindhya extension to the Aravalli Range
The Aravalli Range (also spelled ''Aravali'') is a mountain range in Northern- Western India, running approximately in a south-west direction, starting near Delhi, passing through southern Haryana, Rajasthan, and ending in Ahmedabad Gujarat. ...
near Champaner
Champaner is a historical city in the state of Gujarat, in western India. It is located in Panchmahal district, 47 kilometres from the city of Vadodara. The city was briefly the capital of the Sultanate of Gujarat.
History
Champaner is named ...
. The Vindhya range rises in height east of Chhota Udaipur
Chhota Udaipur is a town and a municipality in Chhota Udaipur district in the state of Gujarat, India. It is the headquarters of Chhota Udaipur district.
History
Chhota Udaipur was originally ruled by Bhil king , The last Bhil king of Chho ...
.
The principal Vindhya range forms the southern escarpment of the Central Indian upland. It runs roughly parallel to the Naramada river in the east-west direction, forming the southern wall of the Malwa
Malwa is a historical region of west-central India occupying a plateau of volcanic origin. Geologically, the Malwa Plateau generally refers to the volcanic upland north of the Vindhya Range. Politically and administratively, it is also sy ...
plateau in Madhya Pradesh.
The eastern portion of the Vindhyas comprises multiple chains, as the range divides into branches east of Malwa. A southern chain of Vindhyas runs between the upper reaches of the Son
A son is a male offspring; a boy or a man in relation to his parents. The female counterpart is a daughter. From a biological perspective, a son constitutes a first degree relative.
Social issues
In pre-industrial societies and some curren ...
and Narmada rivers to meet the Satpura Range in the Maikal Hills near Amarkantak
Amarkantak (NLK ''Amarakaṇṭaka'') is a pilgrim town and a Nagar Panchayat in Anuppur, Madhya Pradesh, India. The Amarkantak region is a unique natural heritage area and is the meeting point of the Vindhya and the Satpura Ranges, with the M ...
. A northern chain of the Vindhyas continues eastwards as Bhander Plateau
The Bhander Plateau is a plateau in the state of Madhya Pradesh in India. It has an area of . It links the Deccan Plateau to the south with the Indo-Gangetic Plains and the Chota Nagpur Plateau to the north and east respectively. The plateau is pa ...
and Kaimur Range, which runs north of the Son River
Son River ( hi, सोन नदी, also spelt Sone River) is a perennial river located in central India. It originates near Amarkantak Hill in Gaurela-Pendra-Marwahi district of Chhattisgarh and finally merges with the Ganges River near Pa ...
. This extended range runs through what was once Vindhya Pradesh, reaching up to the Kaimur district of Bihar. The branch of the Vindhya range spanning across Bundelkhand
Bundelkhand (, ) is a geographical and cultural region and a proposed state and also a mountain range in central & North India. The hilly region is now divided between the states of Uttar Pradesh and Madhya Pradesh, with the larger portion l ...
is known as the Panna range. Another northern extension (known as the Vindhyachal hills) runs up to Uttar Pradesh
Uttar Pradesh (; , 'Northern Province') is a state in northern India. With over 200 million inhabitants, it is the most populated state in India as well as the most populous country subdivision in the world. It was established in 195 ...
, stopping before the shores of Ganga
The Ganges ( ) (in India: Ganga ( ); in Bangladesh: Padma ( )). "The Ganges Basin, known in India as the Ganga and in Bangladesh as the Padma, is an international river to which India, Bangladesh, Nepal and China are the riparian states." is ...
at multiple places, including Vindhyachal and Chunar ( Mirzapur District), near Varanasi
Varanasi (; ; also Banaras or Benares (; ), and Kashi.) is a city on the Ganges river in northern India that has a central place in the traditions of pilgrimage, death, and mourning in the Hindu world.
*
*
*
* The city has a syncretic t ...
.
The Vindhyan tableland is a plateau that lies to the north of the central part of the range. The Rewa- Panna plateaus are also collectively known as the Vindhya plateau.
Elevation
Different sources vary on the average elevation of the Vindhyas, depending on their definition of the range. M. C. Chaturvedi mentions the average elevation as . Pradeep Sharma states that the "general elevation" of the Vindhyas is , with the range rarely going over during its extent. The highest point of the Vindhyas is the Sad-bhawna Shikhar ("Goodwill Peak"), which lies above the sea level. Also known as the Kalumar peak or Kalumbe peak, it lies nearSingrampur
Singrampur is a historical place where final battle fought between Rani Durgawati and Mughal king Akbar's Senapati Asaf Khan. The town in named after ''Sangram'' which in Hindi means war.
Singrampur comes under district Damoh, Madhya Pradesh ...
in the Damoh district, in the area known as Bhanrer or Panna hills. Historical texts include Amarkantak
Amarkantak (NLK ''Amarakaṇṭaka'') is a pilgrim town and a Nagar Panchayat in Anuppur, Madhya Pradesh, India. The Amarkantak region is a unique natural heritage area and is the meeting point of the Vindhya and the Satpura Ranges, with the M ...
(+) in the Vindhyas, but today, it is considered a part of the Maikal Range, which is considered as an extension of the Satpuras.
Cultural significance
 The Vindhyas are regarded as the traditional geographical boundary between northern and southern India, and have a distinguished status in both mythology and geography of India. In the ancient Indian texts, the Vindhyas are seen as the demarcating line between the territories of the Indo-Aryans and that of the others. The most ancient Hindu texts consider it as the southern boundary of Aryavarta. The
The Vindhyas are regarded as the traditional geographical boundary between northern and southern India, and have a distinguished status in both mythology and geography of India. In the ancient Indian texts, the Vindhyas are seen as the demarcating line between the territories of the Indo-Aryans and that of the others. The most ancient Hindu texts consider it as the southern boundary of Aryavarta. The Mahabharata
The ''Mahābhārata'' ( ; sa, महाभारतम्, ', ) is one of the two major Sanskrit epics of ancient India in Hinduism, the other being the '' Rāmāyaṇa''. It narrates the struggle between two groups of cousins in the K ...
mentions that the Nishadas and other Mleccha tribes reside in the forests of the Vindhyas. Although the Indo-Aryan languages (such as Marathi and Konkani) spread to the south of Vindhyas later, the Vindhyas continued to be seen as the traditional boundary between the northern and the southern Indian nations.
Vindhyas appear prominently in the Indian mythological tales. Although the Vindhyas are not very high, historically, they were considered highly inaccessible and dangerous due to dense vegetation and the hostile tribes residing there. In the older Sanskrit texts, such as the Ramayana
The ''Rāmāyana'' (; sa, रामायणम्, ) is a Sanskrit epic composed over a period of nearly a millennium, with scholars' estimates for the earliest stage of the text ranging from the 8th to 4th centuries BCE, and later stages ...
, they are described as the unknown territory infested with cannibals and demon
A demon is a malevolent supernatural entity. Historically, belief in demons, or stories about demons, occurs in religion, occultism, literature, fiction, mythology, and folklore; as well as in Media (communication), media such as comics, video ...
s. The later texts describe the Vindhya range as the residence of fierce form of Shakti
In Hinduism, especially Shaktism (a theological tradition of Hinduism), Shakti (Devanagari: शक्ति, IAST: Śakti; lit. "Energy, ability, strength, effort, power, capability") is the primordial cosmic energy, female in aspect, and r ...
(goddess Kali
Kali (; sa, काली, ), also referred to as Mahakali, Bhadrakali, and Kalika ( sa, कालिका), is a Hindu goddess who is considered to be the goddess of ultimate power, time, destruction and change in Shaktism. In this tra ...
or Durga
Durga ( sa, दुर्गा, ) is a major Hindu goddess, worshipped as a principal aspect of the mother goddess Mahadevi. She is associated with protection, strength, motherhood, destruction, and wars.
Durga's legend centres around c ...
), who has lived there since slaying the demons. She is described as Vindhyavasini
Yogamaya (), also venerated as Vindhyavasini, Mahamaya, and Ekanamsha, is a Hindu goddess.
In Vaishnava tradition, she is accorded the epithet Narayani, and serves as the personification of Vishnu's powers of illusion. The deity is regarded ...
("Vindhya dweller"), and a temple dedicated to her is located in the Vindhyachal town of Uttar Pradesh. The Mahabharata
The ''Mahābhārata'' ( ; sa, महाभारतम्, ', ) is one of the two major Sanskrit epics of ancient India in Hinduism, the other being the '' Rāmāyaṇa''. It narrates the struggle between two groups of cousins in the K ...
mentions the Vindhyas as the "eternal abode" of Kali.
According to one legend, the Vindhya mountain once competed with the Mount Meru, growing so high that it obstructed the sun. The sage Agastya
Agastya ( kn, ಅಗಸ್ತ್ಯ, ta, அகத்தியர், sa, अगस्त्य, te, అగస్త్యుడు, ml, അഗസ്ത്യൻ, hi, अगस्त्य) was a revered Indian sage of Hinduism. In the I ...
then asked Vindhya to lower itself, in order to facilitate his passage across to the south. In reverence for Agastya, the Vindhya lowered its height and promised not to grow until Agastya returned to the north. Agastya settled in the south, and the Vindhya mountain, true to its word, never grew further.
The Kishkindha Kanda of Valmiki's Ramayana mentions that Maya built a mansion in the Vindhyas. In ''Dashakumaracharita
''Dashakumaracharita'' (''The narrative of ten young men'', IAST: ''Daśa-kumāra-Carita'', Devanagari: दशकुमारचरित) is a prose romance in Sanskrit, attributed to Dandin (दण्डी), believed to have flourished in the ...
'', the King Rajahamsa of Magadha and his ministers create a new colony in the Vindhya forest, after being forced out of their kingdom following a war defeat.
The Vindhyas are one of the only two mountain ranges mentioned in the national anthem of India
"" (Sanskrit: जन गण मन) is the national anthem of the Republic of India. It was originally composed as '' Bharoto Bhagyo Bidhata'' in Bengali by polymath Rabindranath Tagore. The first stanza of the song ''Bharoto Bhagyo Bidhata ...
, the other being the Himalayas.
Rivers
Several tributaries of the Ganga-Yamuna system originate from the Vindhyas. These include Chambal, Betwa, Dhasan, Ken, Tamsa, Kali Sindh and Parbati. The northern slopes of the Vindhyas are drained by these rivers. Narmada andSon
A son is a male offspring; a boy or a man in relation to his parents. The female counterpart is a daughter. From a biological perspective, a son constitutes a first degree relative.
Social issues
In pre-industrial societies and some curren ...
rivers drain the southern slopes of the Vindhyas. Both these rivers rise in the Maikal hills, which are now defined as an extension of the Satpuras, although several older texts use the term Vindhyas to cover them (see Historical definitions above).
Geology and palaeontology
The "Vindhyan Supergroup" is one of the largest and thickestsedimentary
Sedimentary rocks are types of rock that are formed by the accumulation or deposition of mineral or organic particles at Earth's surface, followed by cementation. Sedimentation is the collective name for processes that cause these particles ...
successions in the world.
The earliest known multicellular
A multicellular organism is an organism that consists of more than one cell, in contrast to unicellular organism.
All species of animals, land plants and most fungi are multicellular, as are many algae, whereas a few organisms are partially ...
fossil
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved ...
s of eukaryote
Eukaryotes () are organisms whose cells have a nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, and many unicellular organisms, are Eukaryotes. They belong to the group of organisms Eukaryota or Eukarya, which is one of the three domains of life. Bacter ...
s ( filamentous algae) have been discovered from Vindhya basin dating back to 1.6 to 1.7 billion years ago. Shelled creatures are documented to have first evolved at the start of the Cambrian 'explosion of life', about 550 million years ago.
See also
*Geology of India
The geology of India is diverse. Different regions of India contain rocks belonging to different geologic periods, dating as far back as the Eoarchean Era. Some of the rocks are very deformed and altered. Other deposits include recently d ...
* Geology of the Himalayas
The geology of the Himalayas is a record of the most dramatic and visible creations of the immense mountain range formed by plate tectonic forces and sculpted by weathering and erosion. The Himalayas, which stretch over 2400 km between th ...
References
{{Authority control Mountain ranges of India Ancient Indian mountains Geography of Malwa Landforms of Madhya Pradesh Geography of Ujjain Mountains in Buddhism