Vimy Ridge on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Battle of Vimy Ridge was part of the Battle of Arras, in the
 Vimy Ridge is an
Vimy Ridge is an
 On their return from the lectures, the Canadian Corps staff officers produced a tactical analysis of the Verdun battles and delivered a series of corps and divisional-level lectures to promote the primacy of artillery and stress the importance of harassing fire and company and platoon flexibility. The report of
On their return from the lectures, the Canadian Corps staff officers produced a tactical analysis of the Verdun battles and delivered a series of corps and divisional-level lectures to promote the primacy of artillery and stress the importance of harassing fire and company and platoon flexibility. The report of
 The experience of the
The experience of the
 The eight field artillery brigades of the Canadian Corps divisional artillery and two heavy artillery groups, were reinforced with British artillery units. Four heavy artillery groups, nine field artillery brigades, three divisional artillery groups and the artillery complement of the 5th Division was attached to the Canadian Corps. Ten heavy artillery groups of the flanking I and XVII Corps were assigned tasks in support of the Canadian Corps. The artillery batteries of
The eight field artillery brigades of the Canadian Corps divisional artillery and two heavy artillery groups, were reinforced with British artillery units. Four heavy artillery groups, nine field artillery brigades, three divisional artillery groups and the artillery complement of the 5th Division was attached to the Canadian Corps. Ten heavy artillery groups of the flanking I and XVII Corps were assigned tasks in support of the Canadian Corps. The artillery batteries of
 In February 1917, the British General Staff released a training pamphlet titled ''SS 143 Instructions for the Training of Platoons for Offensive Action'', espousing the return to the pre-war emphasis on
In February 1917, the British General Staff released a training pamphlet titled ''SS 143 Instructions for the Training of Platoons for Offensive Action'', espousing the return to the pre-war emphasis on
 Operations along the Vimy Ridge were accompanied by extensive underground excavations. The Arras–Vimy sector was conducive to tunnelling owing to the soft, porous yet extremely stable nature of the
Operations along the Vimy Ridge were accompanied by extensive underground excavations. The Arras–Vimy sector was conducive to tunnelling owing to the soft, porous yet extremely stable nature of the
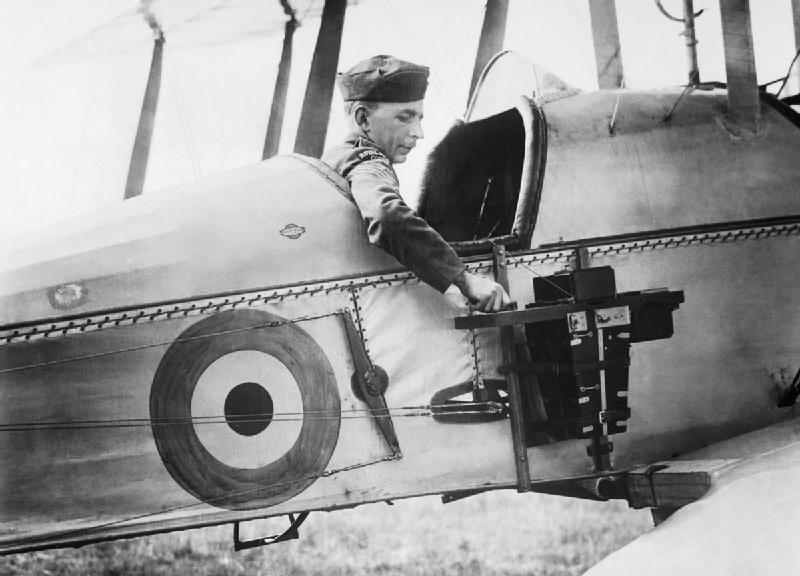 The RFC launched a determined effort to gain air superiority over the battlefield in support of the spring offensive. The Canadians considered activities such as artillery-observation and photography of opposing trench systems, troop movements and gun emplacements essential to continue their offensive. The Royal Flying Corps deployed 25 squadrons totalling 365 aircraft along the Arras sector, outnumbering the ''
The RFC launched a determined effort to gain air superiority over the battlefield in support of the spring offensive. The Canadians considered activities such as artillery-observation and photography of opposing trench systems, troop movements and gun emplacements essential to continue their offensive. The Royal Flying Corps deployed 25 squadrons totalling 365 aircraft along the Arras sector, outnumbering the ''
 German 6th Army commander General
German 6th Army commander General
 Foreign intelligence gathering by the Germans, big Allied trench raids and troop concentrations seen west of Arras, made it clear to the Germans that a spring offensive in the area was being prepared. In February 1917, a German-born Canadian soldier deserted and helped confirm many of the suspicions held by the Germans, providing them with a great deal of useful information. By March 1917, the 6th Army knew that an offensive was imminent and would include operations aimed at capturing Vimy Ridge. General of Infantry Ernst August Marx von Bachmeister, commanding the German 79th Reserve Division, reported in late March that he believed the Canadian Corps was moving into an
Foreign intelligence gathering by the Germans, big Allied trench raids and troop concentrations seen west of Arras, made it clear to the Germans that a spring offensive in the area was being prepared. In February 1917, a German-born Canadian soldier deserted and helped confirm many of the suspicions held by the Germans, providing them with a great deal of useful information. By March 1917, the 6th Army knew that an offensive was imminent and would include operations aimed at capturing Vimy Ridge. General of Infantry Ernst August Marx von Bachmeister, commanding the German 79th Reserve Division, reported in late March that he believed the Canadian Corps was moving into an
 The attack was to begin at 5:30 am on
The attack was to begin at 5:30 am on  A mine explosion that killed many German troops of Reserve Infantry Regiment 262 manning the front line, preceded the advance of the 3rd Canadian Division. The remaining German troops could do no more than man temporary lines of resistance until later manning a full defence at the German third line. As a result, the southern section of the 3rd Canadian Division was able to reach the Red Line at the western edge of the Bois de la Folie at around 7:30 am. At 9:00 am the division learned of its exposed left flank, as the 4th Canadian Division had not yet captured Hill 145. The 3rd Canadian Division was thus called upon to establish a divisional defensive flank to its north. Although the German commanders were able to maintain open lines of communication and issue orders, even with swift staff work the tempo of the assault was such that German decision cycle was unable to react decisively.
The only portion of the Canadian assault that did not go as planned was the advance of the 4th Canadian Division, collapsing almost immediately after exiting their trenches. The commanding officer of one of the assaulting battalions requested that the artillery leave a portion of German trench undamaged. Machine gun nests in the undamaged sections of the German line pinned down, wounded, or killed much of the 4th Canadian Division's right flank. The progress on the left flank was eventually impeded by harassing fire from the Pimple that was made worse when the creeping barrage got too far ahead of the advancing troops. In view of the German defence, the 4th Canadian Division did not attempt a further frontal assault throughout the afternoon.
A mine explosion that killed many German troops of Reserve Infantry Regiment 262 manning the front line, preceded the advance of the 3rd Canadian Division. The remaining German troops could do no more than man temporary lines of resistance until later manning a full defence at the German third line. As a result, the southern section of the 3rd Canadian Division was able to reach the Red Line at the western edge of the Bois de la Folie at around 7:30 am. At 9:00 am the division learned of its exposed left flank, as the 4th Canadian Division had not yet captured Hill 145. The 3rd Canadian Division was thus called upon to establish a divisional defensive flank to its north. Although the German commanders were able to maintain open lines of communication and issue orders, even with swift staff work the tempo of the assault was such that German decision cycle was unable to react decisively.
The only portion of the Canadian assault that did not go as planned was the advance of the 4th Canadian Division, collapsing almost immediately after exiting their trenches. The commanding officer of one of the assaulting battalions requested that the artillery leave a portion of German trench undamaged. Machine gun nests in the undamaged sections of the German line pinned down, wounded, or killed much of the 4th Canadian Division's right flank. The progress on the left flank was eventually impeded by harassing fire from the Pimple that was made worse when the creeping barrage got too far ahead of the advancing troops. In view of the German defence, the 4th Canadian Division did not attempt a further frontal assault throughout the afternoon.
 Reserve units from the 4th Canadian Division came forward and once again attacked the German positions on the top of the ridge. Persistent attacks eventually forced the German troops holding the southwestern portion of Hill 145 to withdraw, but only after they had run out of ammunition, mortar rounds, and grenades. Towards midday, the 79th Reserve Division was ordered to recapture the portions of its third line lost during the progression of the Canadian attack. However, it was not until 6:00 pm that the force was able to organize and counterattack, clearing the Canadian Corps troops out of the ruined village of Vimy, but not recapturing the third line south of the village. By night time, the German forces holding the top of the ridge believed they had overcome the immediate crisis for the time being. Additional German reinforcements began arriving and by late evening portions of the 111th Infantry Division occupied the third line near
Reserve units from the 4th Canadian Division came forward and once again attacked the German positions on the top of the ridge. Persistent attacks eventually forced the German troops holding the southwestern portion of Hill 145 to withdraw, but only after they had run out of ammunition, mortar rounds, and grenades. Towards midday, the 79th Reserve Division was ordered to recapture the portions of its third line lost during the progression of the Canadian attack. However, it was not until 6:00 pm that the force was able to organize and counterattack, clearing the Canadian Corps troops out of the ruined village of Vimy, but not recapturing the third line south of the village. By night time, the German forces holding the top of the ridge believed they had overcome the immediate crisis for the time being. Additional German reinforcements began arriving and by late evening portions of the 111th Infantry Division occupied the third line near
 The British moved three fresh
The British moved three fresh
 By nightfall on 12 April 1917, the Canadian Corps was in firm control of the ridge, having suffered 10,602 casualties; 3,598 men had been killed and 7,004 wounded. The 6th Army casualties were not known at first in the disorganisation after the defeat. Later sources state around 20,000 casualties, German historians credit the high number of German casualties to Canadian and British artillery. Approximately 4,000 men were taken
By nightfall on 12 April 1917, the Canadian Corps was in firm control of the ridge, having suffered 10,602 casualties; 3,598 men had been killed and 7,004 wounded. The 6th Army casualties were not known at first in the disorganisation after the defeat. Later sources state around 20,000 casualties, German historians credit the high number of German casualties to Canadian and British artillery. Approximately 4,000 men were taken  Following the defeat, the chief of the
Following the defeat, the chief of the  The Germans did not see the capture of Vimy Ridge by the Canadian Corps as a loss. Contemporary German sources viewed the action, at worst, as a draw, given that no breakthrough occurred following the attack. The Germans did not attempt to recapture the ridge, even during the Spring Offensive, and it remained under British control until the end of the war. The loss of Vimy Ridge forced the Germans to reassess their defensive strategy in the area. Instead of mounting a counterattack, they pursued a
The Germans did not see the capture of Vimy Ridge by the Canadian Corps as a loss. Contemporary German sources viewed the action, at worst, as a draw, given that no breakthrough occurred following the attack. The Germans did not attempt to recapture the ridge, even during the Spring Offensive, and it remained under British control until the end of the war. The loss of Vimy Ridge forced the Germans to reassess their defensive strategy in the area. Instead of mounting a counterattack, they pursued a
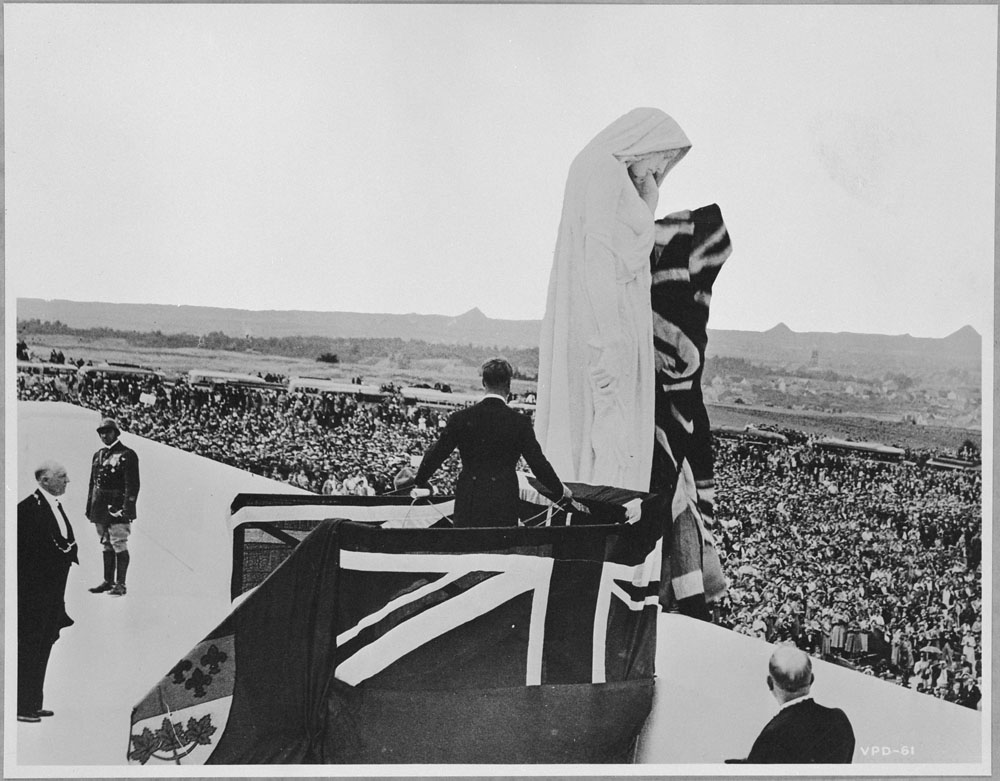 The Canadian National Vimy Memorial is its largest and principal overseas war memorial. Located on the highest point of the Vimy Ridge, the memorial is dedicated to the commemoration of the Battle of Vimy Ridge and Canadian Expeditionary Force members killed during the First World War and those killed in France during the First World War with no known grave. France granted Canada perpetual use of a section of land at Vimy Ridge in 1922 for a battlefield park and memorial. A portion of the former battlefield is preserved as part of the memorial park that surrounds the monument. The grounds of the site are still honeycombed with wartime tunnels, trenches, craters and unexploded munitions and are largely closed for public safety. A section of preserved trenches and a portion of a tunnel have been made accessible to visitors.
The memorial was designed by Toronto architect and sculptor
The Canadian National Vimy Memorial is its largest and principal overseas war memorial. Located on the highest point of the Vimy Ridge, the memorial is dedicated to the commemoration of the Battle of Vimy Ridge and Canadian Expeditionary Force members killed during the First World War and those killed in France during the First World War with no known grave. France granted Canada perpetual use of a section of land at Vimy Ridge in 1922 for a battlefield park and memorial. A portion of the former battlefield is preserved as part of the memorial park that surrounds the monument. The grounds of the site are still honeycombed with wartime tunnels, trenches, craters and unexploded munitions and are largely closed for public safety. A section of preserved trenches and a portion of a tunnel have been made accessible to visitors.
The memorial was designed by Toronto architect and sculptor  The Canadian Prime Minister
The Canadian Prime Minister
The Battle of Vimy Ridge Battle info, video footage and photos
The Vimy Foundation
Canadian War MuseumThe Battle of Vimy Ridge
Heritage MinutesVimy Ridge
at Historica Canada
The Underground War: Military Mining Operations in Support of the Attack on Vimy Ridge, 9 April 1917
Veterans Affairs CanadaVimy Ridge 100th anniversary
Vimy Ridge played by the Band of H.M. Royal Marines
{{DEFAULTSORT:Vimy Ridge, Battle of 1917 in France Battles of the Western Front (World War I) Battles of World War I involving Canada Battles of World War I involving Germany Battles of World War I involving the United Kingdom
Pas-de-Calais
Pas-de-Calais (, "strait of Calais"; pcd, Pas-Calés; also nl, Nauw van Kales) is a department in northern France named after the French designation of the Strait of Dover, which it borders. It has the most communes of all the departments of ...
department of France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
, during the First World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
. The main combatants were the four divisions of the Canadian Corps
The Canadian Corps was a World War I corps formed from the Canadian Expeditionary Force in September 1915 after the arrival of the 2nd Canadian Division in France. The corps was expanded by the addition of the 3rd Canadian Division in December ...
in the First Army, against three divisions of the German 6th Army. The battle took place from 9 to 12 April 1917 at the beginning of the Battle of Arras, the first attack of the Nivelle Offensive
The Nivelle offensive (16 April – 9 May 1917) was a Franco-British operation on the Western Front in the First World War which was named after General Robert Nivelle, the commander-in-chief of the French metropolitan armies, who led the offensi ...
, which was intended to attract German reserves from the French, before the French attempt at a decisive offensive on the Aisne and the Chemin des Dames
In France, the Chemin des Dames (; literally, the "ladies' path") is part of the route départementale (local road) D18 and runs east and west in the Aisne department, between in the west, the Route Nationale 2 (Laon to Soissons), and in the eas ...
ridge further south, several days later.
The Canadian Corps were to capture the German-held high ground of Vimy Ridge, an escarpment
An escarpment is a steep slope or long cliff that forms as a result of faulting or erosion and separates two relatively level areas having different elevations.
The terms ''scarp'' and ''scarp face'' are often used interchangeably with ''esca ...
on the northern flank of the Arras front. This would protect the First Army and the Third Army farther south from German enfilade
Enfilade and defilade are concepts in military tactics used to describe a military formation's exposure to enemy fire. A formation or position is "in enfilade" if weapon fire can be directed along its longest axis. A unit or position is "in de ...
fire. Supported by a creeping barrage
In military usage, a barrage is massed sustained artillery fire ( shelling) aimed at a series of points along a line. In addition to attacking any enemy in the kill zone, a barrage intends to suppress enemy movements and deny access across th ...
, the Canadian Corps captured most of the ridge during the first day. The village of Thélus
Thélus is a commune in the Pas-de-Calais department in the Hauts-de-France region of France. It is located southeast of the Canadian National Vimy Memorial dedicated to the Battle of Vimy Ridge and the missing First World War Canadian soldiers ...
fell during the second day, as did the crest of the ridge, once the Canadian Corps overran a salient against considerable German resistance. The final objective, a fortified knoll outside the village of Givenchy-en-Gohelle
Givenchy-en-Gohelle (; pcd, Givinchy-in-Gohelle) is a commune in the Pas-de-Calais department in the Hauts-de-France region of France. It is located north of the Canadian National Vimy Memorial dedicated to the Battle of Vimy Ridge and the miss ...
, fell to the Canadians on 12 April. The 6th Army then retreated to the Oppy– Méricourt line.
Historians attribute the success of the Canadian Corps to technical and tactical innovation, meticulous planning, powerful artillery support and extensive training, as well as the inability of the 6th Army to properly apply the new German defensive doctrine. The battle was the first occasion when the four divisions of the Canadian Expeditionary Force
The Canadian Expeditionary Force (CEF) was the expeditionary field force of Canada during the First World War. It was formed following Britain’s declaration of war on Germany on 15 August 1914, with an initial strength of one infantry divisi ...
fought together and it was made a symbol of Canadian national achievement and sacrifice. A portion of the former battleground serves as a memorial park and site of the Canadian National Vimy Memorial
The Canadian National Vimy Memorial is a war memorial site in France dedicated to the memory of Canadian Expeditionary Force members killed during the First World War. It also serves as the place of commemoration for Canadian soldiers of the Fir ...
.
Background
Vimy Ridge 1914–1916
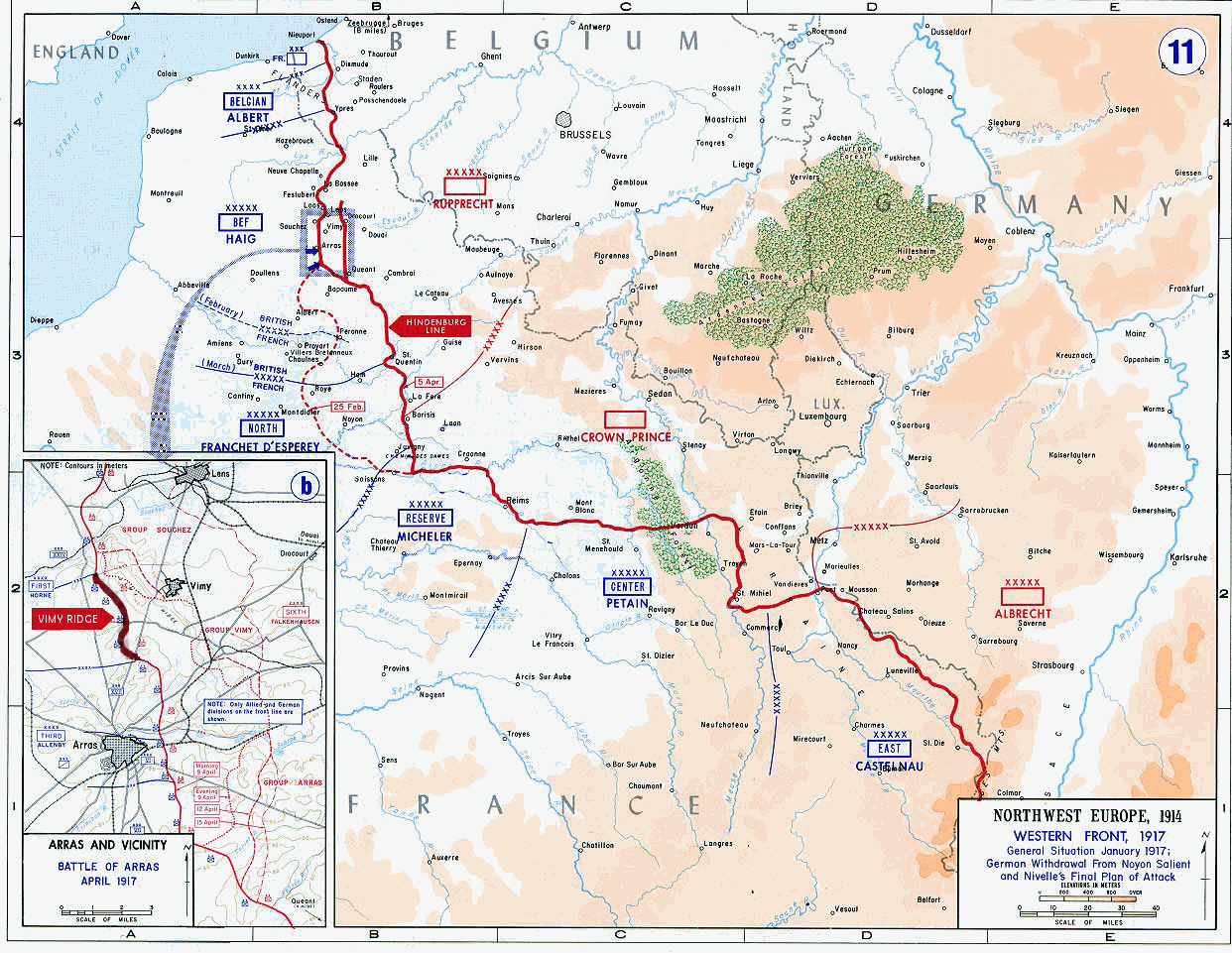
 Vimy Ridge is an
Vimy Ridge is an escarpment
An escarpment is a steep slope or long cliff that forms as a result of faulting or erosion and separates two relatively level areas having different elevations.
The terms ''scarp'' and ''scarp face'' are often used interchangeably with ''esca ...
northeast of Arras
Arras ( , ; pcd, Aro; historical nl, Atrecht ) is the prefecture of the Pas-de-Calais department, which forms part of the region of Hauts-de-France; before the reorganization of 2014 it was in Nord-Pas-de-Calais. The historic centre of ...
on the western edge of the Douai Plain. The ridge rises gradually on its western side and drops more quickly on the eastern side. At approximately in length and culminating at an elevation of or above the Douai Plains, the ridge provides a natural unobstructed view for tens of kilometres in all directions. The ridge fell under German control in October 1914 during the Race to the Sea
The Race to the Sea (; , ) took place from about 1914 during the First World War, after the Battle of the Frontiers () and the German advance into France. The invasion had been stopped at the First Battle of the Marne and was followed by the ...
as the Franco-British and German forces continually attempted to outflank each other through northeastern France. The French Tenth Army attempted to dislodge the Germans from the region during the Second Battle of Artois in May 1915 by attacking their positions at Vimy Ridge and Notre Dame de Lorette
Notre Dame de Lorette (), also known as Ablain St.-Nazaire French Military Cemetery, is the world's largest French military cemetery.Third Battle of Artois
The Third Battle of Artois (25 September – 4 November 1915, also the Loos–Artois Offensive), was fought by the French Tenth Army against the German 6th Army on the Western Front of the First World War. The battle included the Battle of Lo ...
in September 1915 but only captured the village of Souchez
Souchez () is a commune in the Pas-de-Calais department in the Hauts-de-France region of France. It is located northwest of the Canadian National Vimy Memorial dedicated to the Battle of Vimy Ridge and the missing First World War Canadian soldie ...
at the western base of the ridge. The Vimy sector calmed following the offensive with both sides taking a largely live and let live approach. The French suffered approximately 150,000 casualties in their attempts to gain control of Vimy Ridge and surrounding territory.
1916–1917
The French Tenth Army was relieved in February 1916 by British XVII Corps (Lieutenant-General
Lieutenant general (Lt Gen, LTG and similar) is a three-star military rank (NATO code OF-8) used in many countries. The rank traces its origins to the Middle Ages, where the title of lieutenant general was held by the second-in-command on the ...
Sir Julian Byng) and transferred to join in the Battle of Verdun
The Battle of Verdun (french: Bataille de Verdun ; german: Schlacht um Verdun ) was fought from 21 February to 18 December 1916 on the Western Front in France. The battle was the longest of the First World War and took place on the hills north ...
. The British soon discovered that German tunnelling companies had taken advantage of the relative calm on the surface to build an extensive network of tunnels and deep mines from which they would attack French positions by setting off explosive charges underneath their trenches. The Royal Engineers
The Corps of Royal Engineers, usually called the Royal Engineers (RE), and commonly known as the ''Sappers'', is a corps of the British Army. It provides military engineering and other technical support to the British Armed Forces and is head ...
sent specialist tunnelling companies to the ridge to combat the German mining operations and German artillery and trench mortar fire intensified in early May 1916. On 21 May 1916, after shelling the British forward trenches and divisional artillery positions from eighty hidden batteries on the reverse slope of the ridge, the German infantry began , an attack on the British lines along a front, to eject them from positions along the ridge. The Germans captured several British-controlled tunnels and mine craters before halting their advance and digging in. Small counter-attacks by battalions of the 140th and 141st Brigades took place on 22 May but were ineffective. The Canadian Corps relieved IV Corps along the western slopes of Vimy Ridge in October 1916.
Prelude
Strategic planning
On 28 May 1916, Byng took command of the Canadian Corps from Lieutenant-General SirEdwin Alderson
Lieutenant General Sir Edwin Alfred Hervey Alderson, KCB (8 April 1859 – 14 December 1927) was a senior British Army officer who served in several campaigns of the late nineteenth and early twentieth centuries. From 1915 to 1916 during the F ...
. Formal discussions for a spring offensive near Arras
Arras ( , ; pcd, Aro; historical nl, Atrecht ) is the prefecture of the Pas-de-Calais department, which forms part of the region of Hauts-de-France; before the reorganization of 2014 it was in Nord-Pas-de-Calais. The historic centre of ...
began, following a conference of corps commanders held at the First Army Headquarters on 21 November 1916. In March 1917, the First Army headquarters formally presented Byng with orders outlining Vimy Ridge as the Canadian Corps objective for the Arras Offensive. A formal assault plan, adopted in early March 1917, drew heavily on the briefings of staff officers sent to learn from the experiences of the French Army during the Battle of Verdun. For the first time the four Canadian divisions would fight together. The nature and size of the attack needed more resources than the Canadian Corps possessed; the British 5th Division In military terms, 5th Division may refer to:
Infantry divisions
*5th Division (Australia)
* 5th Division (People's Republic of China)
* 5th Division (Colombia)
* Finnish 5th Division (Continuation War)
*5th Light Cavalry Division (France)
* 5th M ...
, artillery, engineer and labour units were attached to the corps, bringing the nominal strength of the Canadian Corps to about 170,000 men, of whom 97,184 were Canadian.
Tactical plan
In January 1917, three Canadian Corps officers accompanied other British and Dominion officers attending a series of lectures hosted by the French Army regarding their experiences during theBattle of Verdun
The Battle of Verdun (french: Bataille de Verdun ; german: Schlacht um Verdun ) was fought from 21 February to 18 December 1916 on the Western Front in France. The battle was the longest of the First World War and took place on the hills north ...
. The French counter offensive devised by General Robert Nivelle
Robert Georges Nivelle (15 October 1856 – 22 March 1924) was a French artillery general officer who served in the Boxer Rebellion and the First World War. In May 1916, he succeeded Philippe Pétain as commander of the French Second Army in t ...
had been one of a number of Allied successes of 1916. Following extensive rehearsal, eight French divisions had assaulted German positions in two waves along a front. Supported by extremely strong artillery, the French had recovered lost ground and inflicted heavy casualties on five German divisions.
 On their return from the lectures, the Canadian Corps staff officers produced a tactical analysis of the Verdun battles and delivered a series of corps and divisional-level lectures to promote the primacy of artillery and stress the importance of harassing fire and company and platoon flexibility. The report of
On their return from the lectures, the Canadian Corps staff officers produced a tactical analysis of the Verdun battles and delivered a series of corps and divisional-level lectures to promote the primacy of artillery and stress the importance of harassing fire and company and platoon flexibility. The report of 1st Canadian Division
The 1st Canadian Division (French: ''1re Division du Canada'' ) is a joint operational command and control formation based at CFB Kingston, and falls under Canadian Joint Operations Command. It is a high-readiness unit, able to move on very short ...
commander Arthur Currie
General Sir Arthur William Currie, (5 December 187530 November 1933) was a senior officer of the Canadian Army who fought during World War I. He had the unique distinction of starting his military career on the very bottom rung as a pre-wa ...
highlighted the lessons he believed the Canadian Corps could learn from the experiences of the French. The final plan for the assault on Vimy Ridge drew heavily on the experience and tactical analysis of the officers who attended the Verdun lectures. British First Army commander General
A general officer is an officer of high rank in the armies, and in some nations' air forces, space forces, and marines or naval infantry.
In some usages the term "general officer" refers to a rank above colonel."general, adj. and n.". O ...
Henry Horne approved the plan on 5 March 1917.
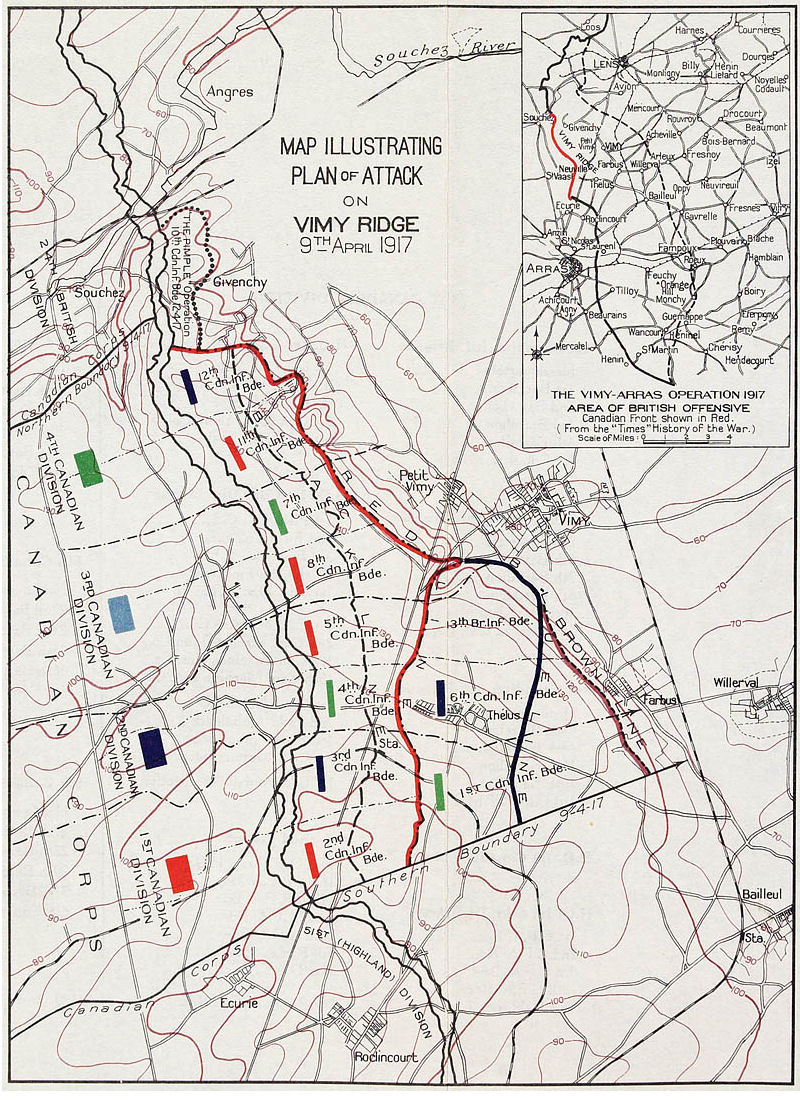
The plan divided the Canadian Corps advance into four coloured objective lines. The attack would be made on a front of , with its centre opposite the village of Vimy
Vimy ( or ; ; Dutch: ''Wimi'') is a commune in the Pas-de-Calais department in the Hauts-de-France region of France. Located east of Vimy is the Canadian National Vimy Memorial dedicated to the Battle of Vimy Ridge and the Canadian soldiers wh ...
, to the east of the ridge. The first objective, represented by the Black Line, was to seize the German forward defensive line. The final objective of the northern flank was the Red Line: taking the highest point on the ridge, the fortified knoll known as the Pimple, la Folie Farm, the ''Zwischen-Stellung'' (Intermediate Position) and the hamlet of Les Tilleuls. The southern two divisions were to achieve two additional objectives, the Blue Line encompassing the village of Thélus and the woods outside the village of Vimy and the Brown Line, which aimed at capturing the Zwölfer-Graben (Twelve Trench) and the German second line. The infantry would proceed close behind a creeping barrage
In military usage, a barrage is massed sustained artillery fire ( shelling) aimed at a series of points along a line. In addition to attacking any enemy in the kill zone, a barrage intends to suppress enemy movements and deny access across th ...
by field guns, advancing in timed increments. The medium and heavy howitzer
A howitzer () is a long- ranged weapon, falling between a cannon (also known as an artillery gun in the United States), which fires shells at flat trajectories, and a mortar, which fires at high angles of ascent and descent. Howitzers, like ot ...
s would establish a series of standing barrages further ahead of the infantry against defensive positions.
The plan called for units to leapfrog over one another, as the advance progressed, to maintain momentum during the attack. The initial wave would capture and consolidate the Black Line and then push forward to the Red Line. The barrage would pause, to enable reserve units to move up and then move forward with the units pushing beyond the Red Line to the Blue Line. Once the corps secured the Blue Line, advancing units would once again leapfrog established ones and capture the Brown Line. Conducted properly, the plan would leave the German forces little time to exit their deep dugouts and defend their positions against the infantry. If the corps maintained its schedule, the troops would advance as much as and have the majority of the ridge under control by 1:00 pm of the first day.
German defences
 The experience of the
The experience of the Battle of the Somme
The Battle of the Somme (French: Bataille de la Somme), also known as the Somme offensive, was a battle of the First World War fought by the armies of the British Empire and French Third Republic against the German Empire. It took place be ...
led the German command to conclude that the policy of rigidly defending a trench position line was no longer effective against the firepower that the Entente armies had accumulated. Ludendorff published a new defensive doctrine in December 1916, in which deeper defences were to be built, within which the garrison would have room to manoeuvre, rather than rigidly holding successive lines of trenches. Along Vimy Ridge, the German forces spent two years constructing fortifications designed for rigid defence. Little reconstruction based upon the new defence-in-depth
Defence in depth (also known as deep defence or elastic defence) is a military strategy that seeks to delay rather than prevent the advance of an attacker, buying time and causing additional casualties by yielding space. Rather than defeating ...
doctrine had been accomplished by April 1917 because the terrain made it impractical.
The topography
Topography is the study of the forms and features of land surfaces. The topography of an area may refer to the land forms and features themselves, or a description or depiction in maps.
Topography is a field of geoscience and planetary sc ...
of the Vimy battlefield made defence-in-depth difficult to realize. The ridge was wide at its narrowest point, with a steep drop on the eastern side, all but eliminating the possibility of counterattacks if the ridge was captured. The Germans were apprehensive about the inherent weakness of the Vimy Ridge defences. The German defensive scheme was to maintain a front line defence of sufficient strength to defend against an initial assault and move operational reserves forward, before the enemy could consolidate their gains or overrun remaining German positions. As a result, the German defence at Vimy Ridge relied largely on machine guns, which acted as force multipliers for the defending infantry.
Three line divisions, comprising seven infantry regiments were responsible for the immediate defence of the ridge. The paper strength of each division was approximately 15,000 men but their actual strength was significantly fewer. In 1917, a full-strength German rifle company consisted of 264 men; at Vimy Ridge, each rifle company contained approximately 150 men. Each German regiment held a zone approximately wide as far back as the rear area. When the Canadian Corps attacked, each German company faced two or more battalions of approximately 1,000 men each. Reserve divisions were kept about back instead of assembling close behind the second line according to the defence-in-depth theory.
Artillery
 The eight field artillery brigades of the Canadian Corps divisional artillery and two heavy artillery groups, were reinforced with British artillery units. Four heavy artillery groups, nine field artillery brigades, three divisional artillery groups and the artillery complement of the 5th Division was attached to the Canadian Corps. Ten heavy artillery groups of the flanking I and XVII Corps were assigned tasks in support of the Canadian Corps. The artillery batteries of
The eight field artillery brigades of the Canadian Corps divisional artillery and two heavy artillery groups, were reinforced with British artillery units. Four heavy artillery groups, nine field artillery brigades, three divisional artillery groups and the artillery complement of the 5th Division was attached to the Canadian Corps. Ten heavy artillery groups of the flanking I and XVII Corps were assigned tasks in support of the Canadian Corps. The artillery batteries of I Corps I Corps, 1st Corps, or First Corps may refer to:
France
* 1st Army Corps (France)
* I Cavalry Corps (Grande Armée), a cavalry unit of the Imperial French Army during the Napoleonic Wars
* I Corps (Grande Armée), a unit of the Imperial French Ar ...
were particularly important because they enfiladed German gun positions behind Vimy Ridge. The British provided twenty-four brigade artillery groups consisting of four hundred and eighty 18 pounder field guns, one hundred thirty-eight 4.5 inch howitzers, ninety-six 2 inch trench mortars, twenty-four 9.45 inch mortars, supported by 245 siege guns and heavy mortars. This firepower gave a density of one heavy gun for every and one field gun for every of the corps frontage, representing a considerable average increase, including three times the heavy guns, over the distribution of artillery at the Battle of the Somme in 1916.
On 8 February, the First Army issued a 3,000-word artillery plan devised by Horne and his principal artillery commander, Major General H.F. Mercer. Brigadier-General
Brigadier general or Brigade general is a military rank used in many countries. It is the lowest ranking general officer in some countries. The rank is usually above a colonel, and below a major general or divisional general. When appointed t ...
Edward Morrison developed and subsequently issued a 35-page multi-phased fire support plan called ''Canadian Corps Artillery Instruction No. 1 for the Capture of Vimy Ridge'' to support the efforts of the infantry. For its operations, the Canadian Corps received three times the artillery normally assigned to a corps for regular operations. To manage the logistics associated with the increased artillery, Royal Artillery staff officer Major Alan Brooke
Field Marshal Alan Francis Brooke, 1st Viscount Alanbrooke, (23 July 1883 – 17 June 1963), was a senior officer of the British Army. He was Chief of the Imperial General Staff (CIGS), the professional head of the British Army, during the Sec ...
developed coordinated communication and transport plans to work in conjunction with the complex barrage plans.
A 1.6 million shell allotment allowed the artillery along the Canadian Corps front to maintain a high sustained rate of fire. Improvements in the quality of the shells compared to those used earlier in the war ensured fewer dud
A dud is an ammunition round or explosive that fails to fire or detonate, respectively, on time or on command. Poorly designed devices (for example, improvised explosive devices (IEDs)), and small devices, have higher chances of being duds.
Du ...
s. The introduction of the instantaneous No. 106 fuze greatly improved the effectiveness of the artillery since this fuse burst reliably with the slightest of contact, unlike older timed fuses, making it especially effective at cutting barbed wire before the advance. To maintain communications during the battle, particularly with the artillery, field units laid over of telegraph and field telephone
Field telephones are telephones used for military communications. They can draw power from their own battery, from a telephone exchange (via a central battery known as CB), or from an external power source. Some need no battery, being sound-powere ...
cabling, normally at a depth of . In addition, the corps conducted coordinated counter-battery
Counter-battery fire (sometimes called counter-fire) is a battlefield tactic employed to defeat the enemy's indirect fire elements ( multiple rocket launchers, artillery and mortars), including their target acquisition, as well as their command ...
initiatives before the battle. The First Army Field Survey Company printed barrage maps for all batteries, produced artillery boards and provided counter-battery support with their flash spotting groups and sound ranging
In land warfare, artillery sound ranging is a method of determining the coordinates of a hostile battery using data derived from the sound of its guns (or mortar or rockets) firing. The same methods can also be used to direct artillery fire at a ...
sections. Utilizing flash spotting, sound ranging and aerial reconnaissance from No. 16 Squadron and Balloon Companies of the Royal Flying Corps
"Through Adversity to the Stars"
, colors =
, colours_label =
, march =
, mascot =
, anniversaries =
, decorations ...
(RFC) in the week before the battle, the counter battery artillery under command of Lieutenant-Colonel
Lieutenant colonel ( , ) is a rank of commissioned officers in the armies, most marine forces and some air forces of the world, above a major and below a colonel. Several police forces in the United States use the rank of lieutenant colo ...
Andrew McNaughton
Andrew is the English form of a given name common in many countries. In the 1990s, it was among the top ten most popular names given to boys in English-speaking countries. "Andrew" is frequently shortened to "Andy" or "Drew". The word is derived ...
fired 125,900 shells, harassing an estimated 83% of the German gun positions.
Training
 In February 1917, the British General Staff released a training pamphlet titled ''SS 143 Instructions for the Training of Platoons for Offensive Action'', espousing the return to the pre-war emphasis on
In February 1917, the British General Staff released a training pamphlet titled ''SS 143 Instructions for the Training of Platoons for Offensive Action'', espousing the return to the pre-war emphasis on fire and movement
Fire and movement, or fire and maneuver, is the basic modern military low-level unit tactic used to maneuver on the battlefield in the presence of the enemy, especially when under fire. It involves heavy use of all available cover, and highly-c ...
tactics and the use of the platoon
A platoon is a military unit typically composed of two or more squads, sections, or patrols. Platoon organization varies depending on the country and the branch, but a platoon can be composed of 50 people, although specific platoons may rang ...
as the basic tactical unit. The pamphlet noted the importance of specialist hand grenade, rifle grenade, rifle and Lewis gun sections in suppressing enemy strong points with an appropriate level of fire to permit other military units to advance. Coupled with the observations and suggestions made by Currie in the report he submitted in January 1917 following the Verdun lectures, the Canadian Corps instilled the tactical change with vigour. The corps implemented the tactical doctrine for small units by assigning objectives down to the platoon level. Assaulting infantry battalions used hills behind the lines as full-scale models of the battlefield. Taped lines demarcated German trench lines while officers on horseback carried flags to represent the advancing front of the artillery barrage.
Recognizing that the men in leadership positions were likely to be wounded or killed, soldiers learned the jobs of those beside and above them. At the British First Army headquarters, a large plasticine
Plasticine is a putty-like modelling material made from calcium salts, petroleum jelly and aliphatic acids. Though originally a brand name for the British version of the product, it is now applied generically in English as a product category ...
model of the Vimy sector was constructed and used to show commissioned and senior non-commissioned officers the topographical features of the battlefield and details of the German trench system. Upwards of 40,000 topographical trench map
A Trench map shows trenches dug for use in war. This article refers mainly to those produced by the British during the Great War, 1914–1918 although other participants made or used them..
For much of the Great War, trench warfare was almost s ...
s were printed and distributed to ensure that even platoon sergeants and section commanders possessed a wider awareness of the battlefield. The new measures gave each platoon a clearer picture of how it fitted into the greater battle plan and in so doing, reduced the command and control
Command and control (abbr. C2) is a "set of organizational and technical attributes and processes ...
problems that plagued First World War combat.
hat
A hat is a head covering which is worn for various reasons, including protection against weather conditions, ceremonial reasons such as university graduation, religious reasons, safety, or as a fashion accessory. Hats which incorporate mecha ...
employs human, physical, and information resources to solve problems and accomplish missions" to achieve the goals of an organization o ...Underground operations
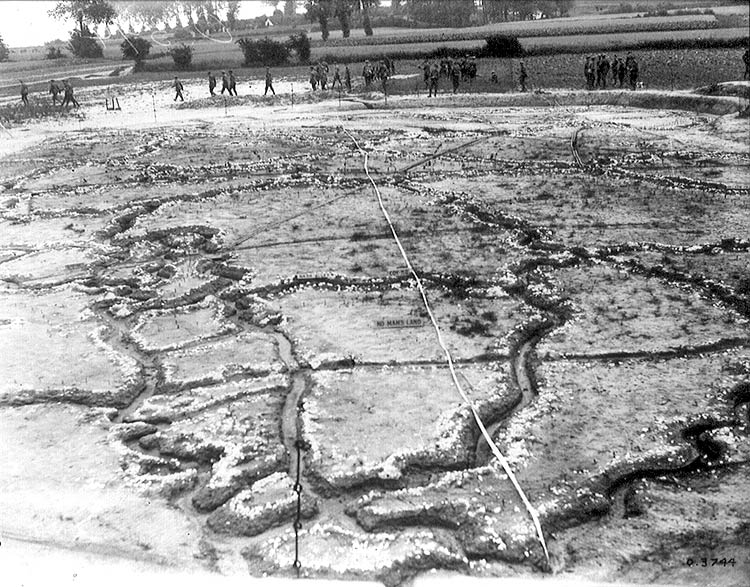
 Operations along the Vimy Ridge were accompanied by extensive underground excavations. The Arras–Vimy sector was conducive to tunnelling owing to the soft, porous yet extremely stable nature of the
Operations along the Vimy Ridge were accompanied by extensive underground excavations. The Arras–Vimy sector was conducive to tunnelling owing to the soft, porous yet extremely stable nature of the chalk
Chalk is a soft, white, porous, sedimentary carbonate rock. It is a form of limestone composed of the mineral calcite and originally formed deep under the sea by the compression of microscopic plankton that had settled to the sea floor. C ...
underground. Underground warfare had been conducted on the Vimy sector since 1915. Bavarian engineers had blown twenty mines in the sector by March 1915. By early 1916, German miners had gained an advantage over their French counterparts. British tunnelling companies of the Royal Engineers
Royal Engineer tunnelling companies were specialist units of the Corps of Royal Engineers within the British Army, formed to dig attacking tunnels under enemy lines during the First World War.
The stalemate situation in the early part of the wa ...
took over progressively from the French between February and May 1916.
On their arrival, the British began offensive mining against German miners, first stopping the German underground advance and then developing a defensive strategy that prevented the Germans from gaining a tactical advantage by mining. From spring 1916, the British had deployed five tunnelling companies along the Vimy Ridge and during the first two months of their tenure of the area, 70 mines were fired, mostly by the Germans. Between October 1915 and April 1917 an estimated 150 French, British and German charges were fired in this sector of the Western Front. In May 1916, Operation Schleswig-Holstein, a German infantry attack, forced the British back , to stop British mining by capturing the shaft entrances. In the second half of 1916, the British constructed strong defensive underground positions and from August 1916, the Royal Engineers developed a mining scheme for a big infantry attack on the Vimy Ridge proposed for autumn 1916, although this was postponed. After September 1916, when the Royal Engineers had completed their network of defensive galleries along most of the front line, offensive mining largely ceased although activities continued until 1917. The British gallery network beneath Vimy Ridge eventually grew to a length of .
The Canadian Corps was posted to the northern part of Vimy Ridge in October 1916 and preparations for an attack were revived in February 1917. British tunnelling companies created extensive underground networks and fortifications. Twelve subways, up to long were excavated at a depth of and used to connect reserve lines to front lines, permitting soldiers to advance to the front quickly, securely and unseen. Often incorporated into subways were light rail lines, hospitals, command posts, water reservoirs, ammunition stores, mortar and machine gun posts and communication centres. The Germans dug a number of similar tunnels on the Vimy front, to provide covered routes to the front line and protection for headquarters, resting personnel, equipment, and ammunition. The Germans also conducted counter-mining against the British tunnellers and destroyed a number of British attempts to plant mines under or near their lines.
Prior to the Battle of Vimy Ridge, the British tunnelling companies also secretly laid 13 mines under German positions to destroy surface fortifications before the assault. To protect some advancing troops from German machine gun fire, as they crossed no man's land during the attack, eight smaller ''Wombat'' charges were laid at the end of the subways to allow troops to move more quickly and safely enter the German trench system by creating an elongated trench-depth crater that spanned the length of no man's land. At the same time, 19 crater groups existed along this section of the Western Front, each with several large craters. To assess the consequences of infantry having to advance across cratered ground after a mining attack, officers from the Canadian Corps visited La Boisselle and Fricourt
Fricourt () is a commune in the Somme department in Hauts-de-France in northern France.
Geography
Fricourt is situated on the D147 and D64 junction, some northeast of Amiens.
History
Fricourt is about a kilometre from Mametz. It was close to ...
where the mines had been blown on the First day of the Somme
The first day on the Somme, 1 July 1916, was the beginning of the Battle of Albert the name given by the British to the first two weeks of the 141 days of the Battle of the Somme () in the First World War. Nine corps of the French Sixth A ...
. Their reports and the experience of the Canadians at The Actions of St Eloi Craters in April 1916, where mines had so altered and damaged the landscape as to render occupation of the mine craters by the infantry all but impossible, led to the decision to remove offensive mining from the central sector allocated to the Canadian Corps at Vimy Ridge. Further British mines in the area were vetoed following the blowing by the Germans on 23 March 1917 of nine craters along no man's land
No man's land is waste or unowned land or an uninhabited or desolate area that may be under dispute between parties who leave it unoccupied out of fear or uncertainty. The term was originally used to define a contested territory or a dump ...
as it was probable that the Germans were aiming to restrict an Allied attack to predictable points. The three mines already laid by 172nd Tunnelling Company
The 172nd Tunnelling Company was one of the Tunnelling companies of the Royal Engineers, tunnelling companies of the Royal Engineers created by the British Army during World War I. The tunnelling units were occupied in offensive and defensive minin ...
were also dropped from the British plans. The mines were left in place after the assault and were only removed in the 1990s. Another mine, prepared by 176th Tunnelling Company
The 176th Tunnelling Company was one of the tunnelling companies of the Royal Engineers created by the British Army during World War I. The tunnelling units were occupied in offensive and defensive mining involving the placing and maintaining of ...
against the German strongpoint known as the Pimple, was not completed in time for the attack. The gallery had been pushed silently through the clay, avoiding the sandy and chalky layers of the Vimy Ridge but by 9 April 1917 was still short of its target. In the end, two mines were blown before the attack, while three mines and two ''Wombat'' charges were fired to support the attack, including those forming a northern flank.
Trench raiding
Trench raiding involved making small-scale surprise attacks on enemy positions, often in the middle of the night for reasons of stealth. All belligerents employed trench raiding as a tactic to harass their enemy and gainintelligence
Intelligence has been defined in many ways: the capacity for abstraction, logic, understanding, self-awareness, learning, emotional knowledge, reasoning, planning, creativity, critical thinking, and problem-solving. More generally, it can ...
. In the Canadian Corps trench raiding developed into a training and leadership-building mechanism. The size of a raid would normally be anything from a few men to an entire company, or more, depending on the size of the mission. The four months before the April attack saw the Canadian Corps execute no fewer than 55 separate trench raids. Competition between units even developed with units competing for the honour of the greatest number of prisoners captured or most destruction wrought. The policy of aggressive trench raiding was not without its cost. A large-scale trench raid on 13 February 1917, involving 900 men from the 4th Canadian Division
The 4th Canadian Division is a formation of the Canadian Army. The division was first created as a formation of the Canadian Corps during the First World War. During the Second World War the division was reactivated as the 4th Canadian Infant ...
, resulted in 150 casualties. An even more ambitious trench raid, using chlorine gas, on 1 March 1917, once again by the 4th Canadian Division, failed and resulted in 637 casualties including two battalion commanders and a number of company commanders killed. This experience did not lessen the extent to which the Canadian Corps employed trench raiding with raids being conducted nightly between 20 March and the opening of the offensive on 9 April, resulting in approximately 1,400 additional Canadian casualties. The Germans operated an active patrolling policy and although not as large and ambitious as those of the Canadian Corps, they also engaged in trench raiding. As an example, a German trench raid launched by 79 men against the 3rd Canadian Division on 15 March 1917 was successful in capturing prisoners and causing damage.
Air operations
 The RFC launched a determined effort to gain air superiority over the battlefield in support of the spring offensive. The Canadians considered activities such as artillery-observation and photography of opposing trench systems, troop movements and gun emplacements essential to continue their offensive. The Royal Flying Corps deployed 25 squadrons totalling 365 aircraft along the Arras sector, outnumbering the ''
The RFC launched a determined effort to gain air superiority over the battlefield in support of the spring offensive. The Canadians considered activities such as artillery-observation and photography of opposing trench systems, troop movements and gun emplacements essential to continue their offensive. The Royal Flying Corps deployed 25 squadrons totalling 365 aircraft along the Arras sector, outnumbering the ''Luftstreitkräfte
The ''Deutsche Luftstreitkräfte'' (, German Air Force)—known before October 1916 as (Flyer Troops)—was the air arm of the Imperial German Army. In English-language sources it is usually referred to as the Imperial German Air Service, alth ...
'' (Imperial German Air Service) by 2-to-1. Byng was given use of No. 2 Squadron, No. 8 (Naval) Squadron, No. 25 Squadron, No. 40 Squadron and No. 43 Squadron, with No. 16 Squadron permanently attached to the Canadian Corps and employed exclusively for reconnaissance and artillery-observation.
Aerial reconnaissance was often a hazardous task because of the necessity of flying at slow speeds and at low altitude. The task was made more dangerous with the arrival of German air reinforcements, including the highly experienced and well equipped Jasta 11
Royal Prussian Jagdstaffel 11 ("No 11 Fighter Squadron"; commonly abbreviated to Jasta 11) was founded on 28 September 1916 from elements of 4 Armee's “Kampfeinsitzer” or KEKs) 1, 2 and 3 and mobilized on 11 October as part of the Germ ...
(Manfred von Richthofen
Manfred Albrecht Freiherr von Richthofen (; 2 May 1892 – 21 April 1918), known in English as Baron von Richthofen or the Red Baron, was a fighter pilot with the German Air Force during World War I. He is considered the ace-of-aces of ...
) which led to a sharp increase in RFC losses. Although significantly outnumbering the Germans, the RFC lost 131 aircraft during the first week of April (Bloody April
Bloody April was the (largely successful) British air support operation during the Battle of Arras in April 1917, during which particularly heavy casualties were suffered by the Royal Flying Corps at the hands of the German ''Luftstreitkräfte' ...
). Despite the losses suffered by the RFC, the ''Luftstreitkräfte'' failed to prevent the British from carrying out its priority, air support of the army during the Battle of Arras with up-to-date aerial photographs and other reconnaissance information.
Battle
Belligerents
 German 6th Army commander General
German 6th Army commander General Ludwig von Falkenhausen
Ludwig Alexander Friedrich August Philipp Freiherr von Falkenhausen (13 September 1844 – 4 May 1936) was a German officer most notable for his activities during World War I.
Before World War I
Falkenhausen was born in Guben. His parents were ...
was responsible for the Cambrai–Lille sector and commanded 20 divisions, plus reserves. Vimy Ridge itself was principally defended by the ad hoc formation based under I Bavarian Reserve Corps commander General der Infanterie General of the Infantry is a military rank of a General officer in the infantry and refers to:
* General of the Infantry (Austria)
* General of the Infantry (Bulgaria)
* General of the Infantry (Germany) ('), a rank of a general in the German Imp ...
Karl von Fasbender
Karl Ritter von Fasbender (3 December 1852 – 13 May 1933) was a Bavarian General der Infanterie who served as a corps commander throughout World War I and briefly commanded an army at the end of the war.
Military service
Although he was a nat ...
. However, a division of , under VIII Reserve Corps General of the Infantry Georg Karl Wichura, was involved in the frontline defence along the northernmost portion of the ridge.
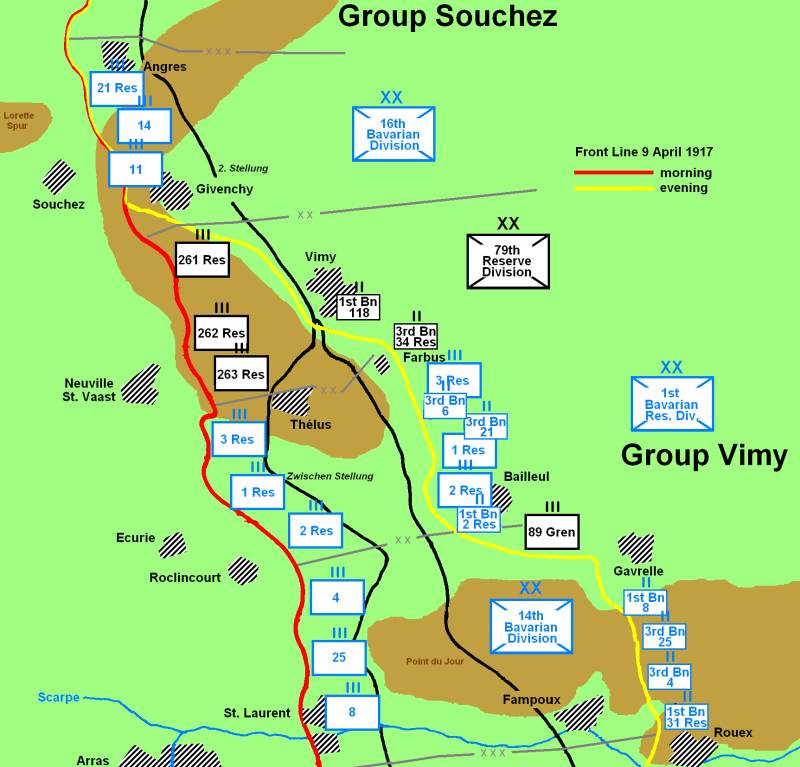
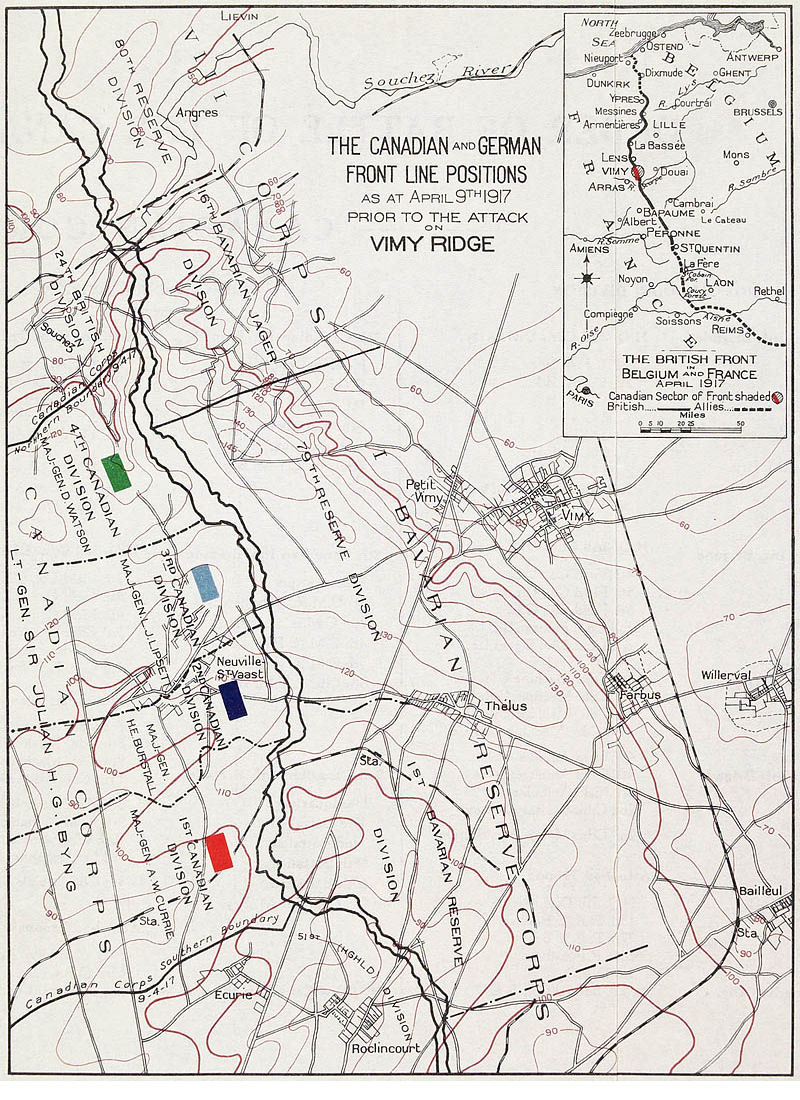
Three divisions were ultimately responsible for manning the frontline defences opposite the Canadian Corps. The 16th Bavarian Division was located opposite the village of Souchez and responsible for the defence of the northernmost section of the ridge. The division had been created in January 1917 by amalgamating existing Bavarian formations and had so far only opposed the Canadian Corps. The 79th Reserve Division was responsible for the defence of the vast central section, including the highest point of the ridge, Hill 145. The 79th Reserve Division had fought for two years on the Eastern Front before being transferred to the Vimy sector at the end of February 1917. The 1st Bavarian Reserve Division
The 1st Bavarian Reserve Division (''1. Bayerische Reserve-Division'') was a unit of the Royal Bavarian Army, part of the German Army, in World War I. The division was formed on mobilization of the German Army in August 1914 as part of I Royal Bav ...
had been in the Arras area since October 1914 and held the villages of Thélus, Bailleul and the southern slope of the ridge.
Byng commanded four attacking divisions, one division in reserve and numerous support units. He was supported to the north by the 24th Division, I Corps, which advanced north of the Souchez river and by the XVII Corps to the south. The 4th Canadian Division was responsible for the northern portion of the advance that included the capture of the highest point of the ridge, followed by the elaborately fortified Pimple just west of the village of Givenchy-en-Gohelle
Givenchy-en-Gohelle (; pcd, Givinchy-in-Gohelle) is a commune in the Pas-de-Calais department in the Hauts-de-France region of France. It is located north of the Canadian National Vimy Memorial dedicated to the Battle of Vimy Ridge and the miss ...
. The 3rd Canadian Division
The 3rd Canadian Division is a formation of the Canadian Army responsible for the command and mobilization of all army units in the provinces of Manitoba, Saskatchewan, Alberta and British Columbia, as well as all units extending westwards from t ...
was responsible for the narrow central section of the ridge, including the capture of La Folie Farm. The 2nd Canadian Division
The 2nd Canadian Division (2 Cdn Div; french: 2e Division du Canada) is a formation of the Canadian Army in the province of Quebec, Canada. The present command was created 2013 when Land Force Quebec Area was re-designated. The main unit housed ...
, which later included a brigade from the 5th Division, was directly south of 3rd Canadian Division and entrusted with the capture of the village of Thélus. The 1st Canadian Division was responsible for the broad southern sector of the corps advance and expected to cover the longest distance. Byng planned for a healthy reserve for contingencies that included the relief of forward troops, help in consolidating positions and aiding the 4th Canadian Division with the capture of the Pimple. As a result, the 9th Canadian Brigade and the British 15th and 95th Brigades were kept in corps reserve.
Preliminary attack
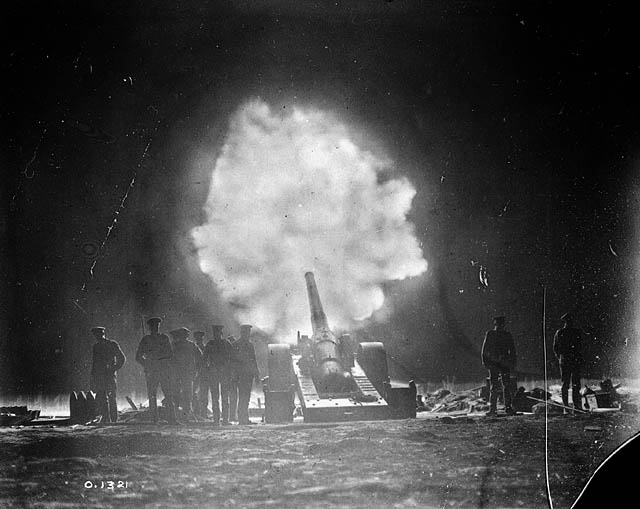
 Foreign intelligence gathering by the Germans, big Allied trench raids and troop concentrations seen west of Arras, made it clear to the Germans that a spring offensive in the area was being prepared. In February 1917, a German-born Canadian soldier deserted and helped confirm many of the suspicions held by the Germans, providing them with a great deal of useful information. By March 1917, the 6th Army knew that an offensive was imminent and would include operations aimed at capturing Vimy Ridge. General of Infantry Ernst August Marx von Bachmeister, commanding the German 79th Reserve Division, reported in late March that he believed the Canadian Corps was moving into an
Foreign intelligence gathering by the Germans, big Allied trench raids and troop concentrations seen west of Arras, made it clear to the Germans that a spring offensive in the area was being prepared. In February 1917, a German-born Canadian soldier deserted and helped confirm many of the suspicions held by the Germans, providing them with a great deal of useful information. By March 1917, the 6th Army knew that an offensive was imminent and would include operations aimed at capturing Vimy Ridge. General of Infantry Ernst August Marx von Bachmeister, commanding the German 79th Reserve Division, reported in late March that he believed the Canadian Corps was moving into an echelon formation
An echelon formation () is a (usually military) formation in which its units are arranged diagonally. Each unit is stationed behind and to the right (a "right echelon"), or behind and to the left ("left echelon"), of the unit ahead. The name of ...
and were preparing for a big attack. The Germans quickly planned Operation Munich (''Unternehmen München''), a spoiling attack to capture the northern section of the Zouave Valley, along the northernmost portion of the Canadian front. Munich was not undertaken because the extent of Canadian Corps artillery fire made it impracticable.
The preliminary phase of the Canadian Corps artillery bombardment began on 20 March 1917, with a systematic two-week bombardment of German batteries, trenches and strong points. The Canadian Corps gunners paid particular attention to eliminating German barbed wire, a task made easier with the introduction of the No. 106 instantaneous fuse. Only half of the artillery fired at once and the intensity of the barrage was varied to confuse the Germans about Canadian intentions. Phase two lasted the week beginning 2 April 1917 and employed all of the guns supporting the Canadian Corps, massing the equivalent of a heavy gun for every and a field gun for every . The German soldiers came to refer to the week before the attack as "the week of suffering". In the German account, their trenches and defensive works were almost completely demolished. The health and morale of the German troops suffered from the stress of remaining at the ready for eleven straight days under extremely heavy artillery bombardment. Compounding German difficulties was the inability of ration parties to bring food supplies to the front lines. On 3 April, General von Falkenhausen ordered his reserve divisions to prepare to relieve front line divisions over the course of a long drawn-out defensive battle in a manner similar to the Battle of the Somme and the divisions were kept from the battlefield to avoid being shelled.
Main assault
9 April
 The attack was to begin at 5:30 am on
The attack was to begin at 5:30 am on Easter Monday
Easter Monday refers to the day after Easter Sunday in either the Eastern or Western Christian traditions. It is a public holiday in some countries. It is the second day of Eastertide. In Western Christianity, it marks the second day of the ...
, 9 April 1917. The attack was originally planned for the morning of 8 April (Easter Sunday) but it was postponed for 24 hours at the request of the French. During the late hours of 8 April and early morning of 9 April the men of the leading and supporting wave of the attack were moved into their forward assembly positions. The weather was cold and later changed to sleet and snow. Although physically discomforting for everyone, the northwesterly storm provided some advantage to the assaulting troops by blowing snow in the faces of the defending troops. Light Canadian and British artillery bombardments continued throughout the night but stopped in the few minutes before the attack, as the artillery recalibrated their guns in preparation for the synchronized barrage. At 5:30 am, every artillery piece at the disposal of the Canadian Corps began firing. Thirty seconds later, engineers detonated the mine charges laid under no man's land and the German trench line, destroying a number of German strong points and creating secure communication trenches directly across no man's land.
Field guns laid down a barrage that mostly advanced at a rate of in three minutes while medium and heavy howitzers established a series of standing barrages further ahead against known defensive systems. During the early fighting, the German divisional artilleries, despite many losses, were able to maintain their defensive firing. As the Canadian assault advanced, it overran many of the German guns because large numbers of their draught horses had been killed in the initial gas attack. The 1st, 2nd and 3rd Canadian Divisions reported reaching and capturing their first objective, the Black Line, by 6:25 am. The 4th Canadian Division encountered a great deal of trouble during its advance and was unable to complete its first objective until some hours later. After a planned pause when the 1st, 2nd and 3rd Canadian Divisions consolidated their positions, the advance resumed. Shortly after 7:00 am, the 1st Canadian Division captured the left half of its second objective, the Red Line and moved the 1st Canadian Brigade forward to mount an attack on the remainder. The 2nd Canadian Division reported reaching the Red Line and capturing the village of Les Tilleuls at approximately the same time.
 A mine explosion that killed many German troops of Reserve Infantry Regiment 262 manning the front line, preceded the advance of the 3rd Canadian Division. The remaining German troops could do no more than man temporary lines of resistance until later manning a full defence at the German third line. As a result, the southern section of the 3rd Canadian Division was able to reach the Red Line at the western edge of the Bois de la Folie at around 7:30 am. At 9:00 am the division learned of its exposed left flank, as the 4th Canadian Division had not yet captured Hill 145. The 3rd Canadian Division was thus called upon to establish a divisional defensive flank to its north. Although the German commanders were able to maintain open lines of communication and issue orders, even with swift staff work the tempo of the assault was such that German decision cycle was unable to react decisively.
The only portion of the Canadian assault that did not go as planned was the advance of the 4th Canadian Division, collapsing almost immediately after exiting their trenches. The commanding officer of one of the assaulting battalions requested that the artillery leave a portion of German trench undamaged. Machine gun nests in the undamaged sections of the German line pinned down, wounded, or killed much of the 4th Canadian Division's right flank. The progress on the left flank was eventually impeded by harassing fire from the Pimple that was made worse when the creeping barrage got too far ahead of the advancing troops. In view of the German defence, the 4th Canadian Division did not attempt a further frontal assault throughout the afternoon.
A mine explosion that killed many German troops of Reserve Infantry Regiment 262 manning the front line, preceded the advance of the 3rd Canadian Division. The remaining German troops could do no more than man temporary lines of resistance until later manning a full defence at the German third line. As a result, the southern section of the 3rd Canadian Division was able to reach the Red Line at the western edge of the Bois de la Folie at around 7:30 am. At 9:00 am the division learned of its exposed left flank, as the 4th Canadian Division had not yet captured Hill 145. The 3rd Canadian Division was thus called upon to establish a divisional defensive flank to its north. Although the German commanders were able to maintain open lines of communication and issue orders, even with swift staff work the tempo of the assault was such that German decision cycle was unable to react decisively.
The only portion of the Canadian assault that did not go as planned was the advance of the 4th Canadian Division, collapsing almost immediately after exiting their trenches. The commanding officer of one of the assaulting battalions requested that the artillery leave a portion of German trench undamaged. Machine gun nests in the undamaged sections of the German line pinned down, wounded, or killed much of the 4th Canadian Division's right flank. The progress on the left flank was eventually impeded by harassing fire from the Pimple that was made worse when the creeping barrage got too far ahead of the advancing troops. In view of the German defence, the 4th Canadian Division did not attempt a further frontal assault throughout the afternoon.
 Reserve units from the 4th Canadian Division came forward and once again attacked the German positions on the top of the ridge. Persistent attacks eventually forced the German troops holding the southwestern portion of Hill 145 to withdraw, but only after they had run out of ammunition, mortar rounds, and grenades. Towards midday, the 79th Reserve Division was ordered to recapture the portions of its third line lost during the progression of the Canadian attack. However, it was not until 6:00 pm that the force was able to organize and counterattack, clearing the Canadian Corps troops out of the ruined village of Vimy, but not recapturing the third line south of the village. By night time, the German forces holding the top of the ridge believed they had overcome the immediate crisis for the time being. Additional German reinforcements began arriving and by late evening portions of the 111th Infantry Division occupied the third line near
Reserve units from the 4th Canadian Division came forward and once again attacked the German positions on the top of the ridge. Persistent attacks eventually forced the German troops holding the southwestern portion of Hill 145 to withdraw, but only after they had run out of ammunition, mortar rounds, and grenades. Towards midday, the 79th Reserve Division was ordered to recapture the portions of its third line lost during the progression of the Canadian attack. However, it was not until 6:00 pm that the force was able to organize and counterattack, clearing the Canadian Corps troops out of the ruined village of Vimy, but not recapturing the third line south of the village. By night time, the German forces holding the top of the ridge believed they had overcome the immediate crisis for the time being. Additional German reinforcements began arriving and by late evening portions of the 111th Infantry Division occupied the third line near Acheville
Acheville is a commune in the Pas-de-Calais department in northern France.
Geography
Acheville is situated some 4 miles (7 km) southeast of Lens, on the D33.
Population
See also
Communes of the Pas-de-Calais department
The following ...
and Arleux
Arleux () is a commune in the Nord department in northern France.
Geography
The river Sensée joins the Canal du Nord at Arleux.
Population
Heraldry
See also
*Communes of the Nord department
The following is a list of the 648 communes of ...
, with the remainder of the division arriving the following day.
10 April
 The British moved three fresh
The British moved three fresh brigade
A brigade is a major tactical military formation that typically comprises three to six battalions plus supporting elements. It is roughly equivalent to an enlarged or reinforced regiment. Two or more brigades may constitute a division.
...
s up to the Red Line by 9:30 am on 10 April to support the advance of the 1st and 2nd Canadian Division, whereupon they were to leapfrog existing units occupying the Red line and advance to the Blue Line. Fresh units including two sections of tanks and the 13th British Brigade were called up from reserve to support the advance of the 2nd Canadian Division. By approximately 11:00 am, the Blue Line, including Hill 135 and the village of Thélus, had been captured. To permit the troops time to consolidate the Blue Line, the advance halted and the barrage remained stationary for 90 minutes while machine guns were brought forward. Shortly before 1:00 pm, the advance recommenced with both the 1st and 2nd Canadian Divisions reporting their final objective. The tank-supported advance via Farbus
Farbus is a commune in the Pas-de-Calais department in the Hauts-de-France region of France. It is located 7 kilometres from the Canadian National Vimy Memorial dedicated to the Battle of Vimy Ridge (part of the Battle of Arras) and the missing ...
and directed at the rear of the 79th Reserve Division, was eventually halted by concentrated German fire short of the village. The Canadian 1st and 2nd Divisions were nonetheless able to secure the Brown Line by approximately 2:00 pm.
The 4th Canadian Division had made an attempt to capture the northern half of Hill 145 at around 3:15 pm, briefly capturing the peak before a German counterattack retook the position. The Germans occupying the small salient on the ridge soon found themselves being attacked along their flanks by continuously reinforced Canadian Corps troops. When it became obvious that the position was completely outflanked and there was no prospect of reinforcement, the German troops pulled back. The German forces were evacuated off the ridge with German artillery batteries moved west of the Vimy–Bailleul railway embankment or to the Oppy–Méricourt line. By nightfall of 10 April, the only Canadian objective not yet achieved was the capture of the Pimple.
12 April
The 4th Canadian Division faced difficulties at the start of the battle that forced it to delay its assault on the Pimple until 12 April. The Pimple was initially defended by the 16th Bavarian Infantry Division but the Canadian Corps' preliminary artillery bombardment leading up to the assault on 9 April caused heavy casualties amongst its ranks. On 11 April, the 4th Guards Infantry Division first reinforced and then relieved affected 16th Bavarian Infantry Division units. The night before the attack, artillery harassed German positions while a gas section of Royal Engineers, employingLivens Projector
The Livens Projector was a simple mortar-like weapon that could throw large drums filled with flammable or toxic chemicals.
In the First World War, the Livens Projector became the standard means of delivering gas attacks by the British Army an ...
s, fired more than 40 drums of gas directly into the village of Givenchy-en-Gohelle to cause confusion. The defending German troops managed to drive back the initial Canadian assaults at around 4:00 am using small arms fire. The 10th Canadian Brigade attacked once again at 5:00 am, this time supported by a significant amount of artillery and the 24th Division of I Corps to the north. The German defensive artillery fire was late and too light to cause the assaulting troops great difficulty, allowing the Canadian Corps to exploit wide gaps and break into the German positions. The 10th Canadian Brigade, assisted by snow and a westerly wind, fought hastily entrained German troops to capture the entire Pimple by 6:00 pm.
Aftermath
 By nightfall on 12 April 1917, the Canadian Corps was in firm control of the ridge, having suffered 10,602 casualties; 3,598 men had been killed and 7,004 wounded. The 6th Army casualties were not known at first in the disorganisation after the defeat. Later sources state around 20,000 casualties, German historians credit the high number of German casualties to Canadian and British artillery. Approximately 4,000 men were taken
By nightfall on 12 April 1917, the Canadian Corps was in firm control of the ridge, having suffered 10,602 casualties; 3,598 men had been killed and 7,004 wounded. The 6th Army casualties were not known at first in the disorganisation after the defeat. Later sources state around 20,000 casualties, German historians credit the high number of German casualties to Canadian and British artillery. Approximately 4,000 men were taken prisoner
A prisoner (also known as an inmate or detainee) is a person who is deprived of liberty against their will. This can be by confinement, captivity, or forcible restraint. The term applies particularly to serving a prison sentence in a prison. ...
. The German Historical Service estimated that the 6th Army suffered 79,418 casualties during April and May 1917, 22,792 were classified as missing. Crown Prince Rupprecht estimated 85,000 casualties for the 6th Army, with 3,404 men taken prisoner at Vimy Ridge. Losses of the 79th Reserve Division from 1 to 11 April were 3,473 and in the 1st Bavarian Reserve Division 3,133. Casualties from the bombardment amongst reinforcements and divisions are additional.
 Following the defeat, the chief of the
Following the defeat, the chief of the German General Staff
The German General Staff, originally the Prussian General Staff and officially the Great General Staff (german: Großer Generalstab), was a full-time body at the head of the Prussian Army and later, the German Army, responsible for the continuou ...
, Field Marshal
Field marshal (or field-marshal, abbreviated as FM) is the most senior military rank, ordinarily senior to the general officer ranks. Usually, it is the highest rank in an army and as such few persons are appointed to it. It is considered as ...
Paul von Hindenburg
Paul Ludwig Hans Anton von Beneckendorff und von Hindenburg (; abbreviated ; 2 October 1847 – 2 August 1934) was a German field marshal and statesman who led the Imperial German Army during World War I and later became President of Germany fr ...
, ordered (OHL, Supreme Army Command) to conduct a court of enquiry into the defensive collapse of the Arras sector. The court concluded that the 6th Army headquarters had disregarded reports from commanders in the front line noting a possible imminent attack and reserve units were too distant to counter-attack before the Canadians could consolidate. The court concluded that 6th Army commander General Ludwig von Falkenhausen failed to apply an elastic defence
Defence in depth (also known as deep defence or elastic defence) is a military strategy that seeks to delay rather than prevent the advance of an attacker, buying time and causing additional casualties by yielding space. Rather than defeating ...
according to German defensive doctrine. Instead, the defensive system comprised strong points and lines of resistance, which the Allied had artillery isolated and destroyed. Hindenburg removed Falkenhausen from his command and transferred him to Belgium, where he served the remainder of the war as governor-general.
 The Germans did not see the capture of Vimy Ridge by the Canadian Corps as a loss. Contemporary German sources viewed the action, at worst, as a draw, given that no breakthrough occurred following the attack. The Germans did not attempt to recapture the ridge, even during the Spring Offensive, and it remained under British control until the end of the war. The loss of Vimy Ridge forced the Germans to reassess their defensive strategy in the area. Instead of mounting a counterattack, they pursued a
The Germans did not see the capture of Vimy Ridge by the Canadian Corps as a loss. Contemporary German sources viewed the action, at worst, as a draw, given that no breakthrough occurred following the attack. The Germans did not attempt to recapture the ridge, even during the Spring Offensive, and it remained under British control until the end of the war. The loss of Vimy Ridge forced the Germans to reassess their defensive strategy in the area. Instead of mounting a counterattack, they pursued a scorched earth
A scorched-earth policy is a military strategy that aims to destroy anything that might be useful to the enemy. Any assets that could be used by the enemy may be targeted, which usually includes obvious weapons, transport vehicles, commun ...
policy and retreated to the Oppy–Méricourt line. The failure of the French Nivelle Offensive
The Nivelle offensive (16 April – 9 May 1917) was a Franco-British operation on the Western Front in the First World War which was named after General Robert Nivelle, the commander-in-chief of the French metropolitan armies, who led the offensi ...
in the week after the Arras Offensive placed pressure on Field Marshal
Field marshal (or field-marshal, abbreviated as FM) is the most senior military rank, ordinarily senior to the general officer ranks. Usually, it is the highest rank in an army and as such few persons are appointed to it. It is considered as ...
Douglas Haig to keep the Germans occupied in the Arras sector to minimize French losses. The Canadian Corps participated in several of these actions including the Battle of Arleux
The Battle of Arras (also known as the Second Battle of Arras) was a British offensive on the Western Front during the First World War. From 9 April to 16 May 1917, British troops attacked German defences near the French city of Arras on the W ...
and the Third Battle of the Scarpe in late April and early May 1917. After the end of the war, Byng was raised to the peerage
A peerage is a legal system historically comprising various hereditary titles (and sometimes non-hereditary titles) in a number of countries, and composed of assorted noble ranks.
Peerages include:
Australia
* Australian peers
Belgium
* Be ...
as Baron Byng of Vimy, of Thorpe-le-Soken in the County of Essex, on 7 October 1919. The next month, he retired from the military.
Awards
Victoria Cross
Four members of the Canadian Corps received theVictoria Cross
The Victoria Cross (VC) is the highest and most prestigious award of the British honours system. It is awarded for valour "in the presence of the enemy" to members of the British Armed Forces and may be awarded posthumously. It was previousl ...
, highest military award of the British honours system
In the United Kingdom and the British Overseas Territories, personal bravery, achievement, or service are rewarded with honours. The honours system consists of three types of award:
*Honours are used to recognise merit in terms of achievement a ...
for their actions during the battle:
* Private
Private or privates may refer to:
Music
* " In Private", by Dusty Springfield from the 1990 album ''Reputation''
* Private (band), a Denmark-based band
* "Private" (Ryōko Hirosue song), from the 1999 album ''Private'', written and also recorde ...
William Johnstone Milne
William Johnstone Milne VC (21 December 1892 – 9 April 1917) was a First World War Canadian soldier. Milne was a posthumous recipient of the Victoria Cross, the highest and most prestigious award for gallantry in the face of the enemy tha ...
, 16th (Canadian Scottish) Battalion
* Lance-Sergeant
Lance sergeant (LSgt or L/Sgt) is an appointment in the armies of the Commonwealth and formerly also a rank in the United States Army.
Commonwealth
Lance-sergeant in the armies of the Commonwealth was an appointment given to a corporal so they c ...
Ellis Wellwood Sifton
Ellis Wellwood Sifton (12 October 1891 – 9 April 1917) was a Canadian soldier. Sifton was a recipient of the Victoria Cross, the highest and most prestigious award for gallantry in the face of the enemy that can be awarded to British and ...
, 18th (Western Ontario) Battalion
* Private John George Pattison
John George Pattison (8 September 1875 – 3 June 1917) was a Canadian soldier. Pattison was a recipient of the Victoria Cross, the highest and most prestigious award for valour in the face of the enemy that can be awarded to British and Co ...
, 50th (Calgary) Battalion
* Captain Thain Wendell MacDowell
Thain Wendell MacDowell, VC, DSO (September 16, 1890 – March 28, 1960), was a Canadian soldier. MacDowell was a recipient of the Victoria Cross, the highest and most prestigious award for gallantry in the face of the enemy that can be award ...
, 38th (Ottawa) Battalion
Pour le Mérite
At least two OrdersPour le Mérite
The ' (; , ) is an order of merit (german: Verdienstorden) established in 1740 by King Frederick II of Prussia. The was awarded as both a military and civil honour and ranked, along with the Order of the Black Eagle, the Order of the Red Eag ...
, the Kingdom of Prussia
The Kingdom of Prussia (german: Königreich Preußen, ) was a German kingdom that constituted the state of Prussia between 1701 and 1918.Marriott, J. A. R., and Charles Grant Robertson. ''The Evolution of Prussia, the Making of an Empire''. ...
's highest military order, were awarded to German commanders for their actions during the battle:
* Oberstleutnant
() is a senior field officer rank in several German-speaking and Scandinavian countries, equivalent to Lieutenant colonel. It is currently used by both the ground and air forces of Austria, Germany, Switzerland, Denmark, and Norway. The Swedi ...
Wilhelm von Goerne, commander of the 261st Prussian Reserve Infantry Regiment, of the German 79th Reserve Division.
* General of the Infantry Georg Karl Wichura commander of the VIII Reserve Corps and .
Commemoration
Influence on Canada
The Battle of Vimy Ridge has considerable significance for Canada. Although the battle is not generally considered the greatest achievement of the Canadian Corps in strategic importance or results obtained, it was the first instance in which all four Canadian divisions, made up of troops drawn from all parts of the country, fought together. The image of national unity and achievement is what, according to one of many recent patriotic narratives, initially gave the battle importance for Canada. According to Pierce, "The historical reality of the battle has been reworked and reinterpreted in a conscious attempt to give purpose and meaning to an event that came to symbolize Canada's coming of age as a nation". That Canadian national identity and nationhood were born out of the battle is an opinion that in the late twentieth century became widely held in military and general histories of Canada. McKay and Swift contend that the theory that Vimy Ridge is a source of Canada's rise as a nation is highly contested and developed in the latter part of the twentieth century after most of those who experienced the Great War had died but in 1919 Hopkins had attributed to F.A. MacKenzie the recognition "...that Dominions sharing the common burden shall share the common direction of the Empire's war policy" and related Lloyd George's commitment that the Dominions would not again be engaged in wars without consultation.Vimy Memorial
 The Canadian National Vimy Memorial is its largest and principal overseas war memorial. Located on the highest point of the Vimy Ridge, the memorial is dedicated to the commemoration of the Battle of Vimy Ridge and Canadian Expeditionary Force members killed during the First World War and those killed in France during the First World War with no known grave. France granted Canada perpetual use of a section of land at Vimy Ridge in 1922 for a battlefield park and memorial. A portion of the former battlefield is preserved as part of the memorial park that surrounds the monument. The grounds of the site are still honeycombed with wartime tunnels, trenches, craters and unexploded munitions and are largely closed for public safety. A section of preserved trenches and a portion of a tunnel have been made accessible to visitors.
The memorial was designed by Toronto architect and sculptor
The Canadian National Vimy Memorial is its largest and principal overseas war memorial. Located on the highest point of the Vimy Ridge, the memorial is dedicated to the commemoration of the Battle of Vimy Ridge and Canadian Expeditionary Force members killed during the First World War and those killed in France during the First World War with no known grave. France granted Canada perpetual use of a section of land at Vimy Ridge in 1922 for a battlefield park and memorial. A portion of the former battlefield is preserved as part of the memorial park that surrounds the monument. The grounds of the site are still honeycombed with wartime tunnels, trenches, craters and unexploded munitions and are largely closed for public safety. A section of preserved trenches and a portion of a tunnel have been made accessible to visitors.
The memorial was designed by Toronto architect and sculptor Walter Seymour Allward
Walter Seymour Allward, (18 November 1874 – 24 April 1955) was a Canadian monumental sculptor best known for the Canadian National Vimy Memorial. Featuring expressive classical figures within modern compositions, Allward's monuments evoke them ...
, who described it as a "sermon against the futility of war". The memorial took eleven years and cost $1.5 million ($ million in present terms) to build. The unveiling was conducted on 26 July 1936, by King Edward VIII
Edward VIII (Edward Albert Christian George Andrew Patrick David; 23 June 1894 – 28 May 1972), later known as the Duke of Windsor, was King of the United Kingdom and the Dominions of the British Empire and Emperor of India from 20 January 19 ...
accompanied by President Albert Lebrun
Albert François Lebrun (; 29 August 1871 – 6 March 1950) was a French politician, President of France from 1932 to 1940. He was the last president of the Third Republic. He was a member of the centre-right Democratic Republican Alliance (A ...
of France and a crowd of over 50,000 people, including at least 6,200 Canadian veterans and their families.
 The Canadian Prime Minister
The Canadian Prime Minister Mackenzie King
William Lyon Mackenzie King (December 17, 1874 – July 22, 1950) was a Canadian statesman and politician who served as the tenth prime minister of Canada for three non-consecutive terms from 1921 to 1926, 1926 to 1930, and 1935 to 1948. A L ...
was absent, it being well understood that he was reluctant to meet veterans and felt it more appropriate for a war veteran in Cabinet to act as minister in attendance. Edward VIII thanked France, in both English and French, for its generosity and assured those assembled that Canada would never forget its war missing and dead. A restoration project began in 2004, which included general cleaning and the recarving of many inscribed names. Queen
Queen or QUEEN may refer to:
Monarchy
* Queen regnant, a female monarch of a Kingdom
** List of queens regnant
* Queen consort, the wife of a reigning king
* Queen dowager, the widow of a king
* Queen mother, a queen dowager who is the mother ...
Elizabeth II
Elizabeth II (Elizabeth Alexandra Mary; 21 April 1926 – 8 September 2022) was Queen of the United Kingdom and other Commonwealth realms from 6 February 1952 until her death in 2022. She was queen regnant of 32 sovereign states durin ...
rededicated the restored monument on 9 April 2007, during a ceremony commemorating the 90th anniversary of the battle. Veterans Affairs Canada
Veterans Affairs Canada (VAC; french: Anciens Combattants Canada) is the department within the Government of Canada with responsibility for pensions, benefits and services for war veterans, retired and still-serving members of the Canadian Arme ...
maintains the memorial site. The commemoration at the memorial on 9 April 2017 for the 100th anniversary of the Battle of Vimy Ridge was attended by dignitaries including Canadian Prime Minister Justin Trudeau
Justin Pierre James Trudeau ( , ; born December 25, 1971) is a Canadian politician who is the 23rd and current prime minister of Canada. He has served as the prime minister of Canada since 2015 and as the leader of the Liberal Party since ...
, Governor General David Johnston
David Lloyd Johnston (born June 28, 1941) is a Canadian academic, author, and statesman who served from 2010 to 2017 as Governor General of Canada, the 28th since Canadian Confederation. He is the commissioner of the Leaders' Debates Commis ...
, Charles, Prince of Wales
Charles III (Charles Philip Arthur George; born 14 November 1948) is King of the United Kingdom and the 14 other Commonwealth realms. He was the longest-serving heir apparent and Prince of Wales and, at age 73, became the oldest person to a ...
, Prince William, Duke of Cambridge
William, Prince of Wales, (William Arthur Philip Louis; born 21 June 1982) is the heir apparent to the British throne. He is the elder son of King Charles III and his first wife Diana, Princess of Wales.
Born in London, William was educ ...
, Prince Harry
Prince Harry, Duke of Sussex, (Henry Charles Albert David; born 15 September 1984) is a member of the British royal family. He is the younger son of Charles III and his first wife Diana, Princess of Wales. He is fifth in the line of succ ...
and President of France François Hollande
François Gérard Georges Nicolas Hollande (; born 12 August 1954) is a French politician who served as President of France from 2012 to 2017. He previously was First Secretary of the Socialist Party (France), First Secretary of the Socialist P ...
.
See also
* *Notes
Citations
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *Further reading
* * * * *External links
The Battle of Vimy Ridge Battle info, video footage and photos
The Vimy Foundation
Canadian War MuseumThe Battle of Vimy Ridge
Heritage MinutesVimy Ridge
at Historica Canada
The Underground War: Military Mining Operations in Support of the Attack on Vimy Ridge, 9 April 1917
Veterans Affairs CanadaVimy Ridge 100th anniversary
Vimy Ridge played by the Band of H.M. Royal Marines
{{DEFAULTSORT:Vimy Ridge, Battle of 1917 in France Battles of the Western Front (World War I) Battles of World War I involving Canada Battles of World War I involving Germany Battles of World War I involving the United Kingdom
Battle of Vimy Ridge
The Battle of Vimy Ridge was part of the Battle of Arras, in the Pas-de-Calais department of France, during the First World War. The main combatants were the four divisions of the Canadian Corps in the First Army, against three divisions ...
Conflicts in 1917
April 1917 events
Tunnel warfare in World War I
World War I in the Pas-de-Calais