Ventricular Tachycardia on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Ventricular tachycardia (V-tach or VT) is a fast heart rate arising from the lower chambers of the heart. Although a few seconds of VT may not result in permanent problems, longer periods are dangerous; and multiple episodes over a short period of time are referred to as an electrical storm. Short periods may occur without symptoms, or present with
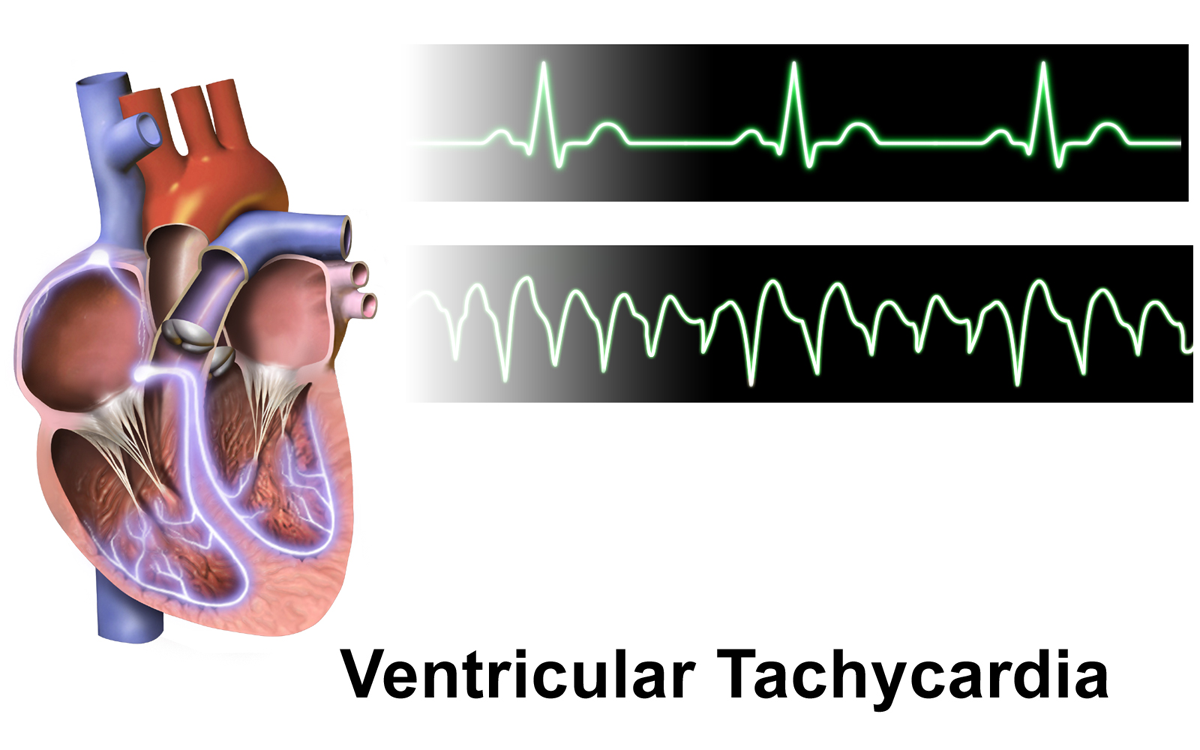 Ventricular tachycardia can be classified based on its ''morphology'':
* Monomorphic ventricular tachycardia means that the appearance of all the beats match each other in each lead of a surface electrocardiogram (ECG).
** Scar-related monomorphic ventricular tachycardia is the most common type and a frequent cause of death in patients having survived a heart attack, especially if they have weak heart muscle.
** Right ventricular outflow tract (RVOT) tachycardia is a type of monomorphic ventricular tachycardia originating in the right ventricular outflow tract. RVOT morphology refers to the characteristic pattern of this type of tachycardia on an ECG.
** The source of the re-entry circuit can be identified by evaluating the morphology of the QRS complex in the V1 lead of a surface ECG. If the R wave is dominant (consistent with a right bundle branch block morphology), this indicates the origin of the VT is the left ventricle. Conversely, if the S wave is dominant (consistent with a
Ventricular tachycardia can be classified based on its ''morphology'':
* Monomorphic ventricular tachycardia means that the appearance of all the beats match each other in each lead of a surface electrocardiogram (ECG).
** Scar-related monomorphic ventricular tachycardia is the most common type and a frequent cause of death in patients having survived a heart attack, especially if they have weak heart muscle.
** Right ventricular outflow tract (RVOT) tachycardia is a type of monomorphic ventricular tachycardia originating in the right ventricular outflow tract. RVOT morphology refers to the characteristic pattern of this type of tachycardia on an ECG.
** The source of the re-entry circuit can be identified by evaluating the morphology of the QRS complex in the V1 lead of a surface ECG. If the R wave is dominant (consistent with a right bundle branch block morphology), this indicates the origin of the VT is the left ventricle. Conversely, if the S wave is dominant (consistent with a
lightheadedness
Lightheadedness is a common and typically unpleasant sensation of dizziness or a feeling that one may faint. The sensation of lightheadedness can be short-lived, prolonged, or, rarely, recurring. In addition to dizziness, the individual may feel ...
, palpitations, or chest pain. Ventricular tachycardia may result in ventricular fibrillation (VF) and turn into cardiac arrest. This conversion of the VT into VF is called the degeneration of the VT. It is found initially in about 7% of people in cardiac arrest.
Ventricular tachycardia can occur due to coronary heart disease
Coronary artery disease (CAD), also called coronary heart disease (CHD), ischemic heart disease (IHD), myocardial ischemia, or simply heart disease, involves the reduction of blood flow to the heart muscle due to build-up of atherosclerotic pl ...
, aortic stenosis
Aortic stenosis (AS or AoS) is the narrowing of the exit of the left ventricle of the heart (where the aorta begins), such that problems result. It may occur at the aortic valve as well as above and below this level. It typically gets worse ov ...
, cardiomyopathy, electrolyte problems
Electrolyte imbalance, or water-electrolyte imbalance, is an abnormality in the concentration of electrolytes in the body. Electrolytes play a vital role in maintaining homeostasis in the body. They help to regulate heart and neurological function, ...
, or a heart attack. Diagnosis is by an electrocardiogram (ECG) showing a rate of greater than 120 beats per minute and at least three wide QRS complex
The QRS complex is the combination of three of the graphical deflections seen on a typical electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG). It is usually the central and most visually obvious part of the tracing. It corresponds to the depolarization of the ri ...
es in a row. It is classified as non-sustained versus sustained based on whether it lasts less than or more than 30 seconds. The term ventricular arrhythmia refers to the group of abnormal cardiac rhythms originating from the ventricle, which includes ventricular tachycardia, ventricular fibrillation, and torsades de pointes
''Torsades de pointes, torsade de pointes'' or ''torsades des pointes'' (TdP) (, , translated as "twisting of peaks") is a specific type of abnormal heart rhythm that can lead to sudden cardiac death. It is a polymorphic ventricular tachycardia t ...
.
In those who have normal blood pressure and strong pulse
In medicine, a pulse represents the tactile arterial palpation of the cardiac cycle (heartbeat) by trained fingertips. The pulse may be palpated in any place that allows an artery to be compressed near the surface of the body, such as at the n ...
, the antiarrhythmic
Antiarrhythmic agents, also known as cardiac dysrhythmia medications, are a group of pharmaceuticals that are used to suppress abnormally fast rhythms (Tachycardia, tachycardias), such as atrial fibrillation, supraventricular tachycardia and vent ...
medication procainamide
Procainamide (PCA) is a medication of the antiarrhythmic class used for the treatment of cardiac arrhythmias. It is classified by the Vaughan Williams classification system as class Ia; thus it is a sodium channel blocker of cardiomyocytes. In add ...
may be used. Otherwise, immediate cardioversion is recommended, preferably with a biphasic DC shock of 200 joules. In those in cardiac arrest due to ventricular tachycardia, cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) and defibrillation is recommended. Biphasic defibrillation may be better than monophasic. While waiting for a defibrillator, a precordial thump
Precordial thump is a medical procedure used in the treatment of ventricular fibrillation or pulseless ventricular tachycardia under certain conditions. The procedure has a very low success rate, but may be used in those with witnessed, monitored ...
may be attempted (However reserved to those who have the prior experience of doing so) in those on a heart monitor who are seen going into an unstable ventricular tachycardia. In those with cardiac arrest due to ventricular tachycardia, survival is about 45%. An implantable cardiac defibrillator or medications such as calcium channel blockers or amiodarone
Amiodarone is an antiarrhythmic medication used to treat and prevent a number of types of cardiac dysrhythmias. This includes ventricular tachycardia (VT), ventricular fibrillation (VF), and wide complex tachycardia, as well as atrial fibril ...
may be used to prevent recurrence.
Signs and symptoms
While a few seconds may not result in problems, longer periods are dangerous. Short periods may occur without symptoms or present with lightheadedness, palpitations, or chest pain. Ventricular tachycardia may turn into ventricular fibrillation and can result in cardiac arrest.Cause
Ventricular tachycardia can occur due tocoronary heart disease
Coronary artery disease (CAD), also called coronary heart disease (CHD), ischemic heart disease (IHD), myocardial ischemia, or simply heart disease, involves the reduction of blood flow to the heart muscle due to build-up of atherosclerotic pl ...
, aortic stenosis
Aortic stenosis (AS or AoS) is the narrowing of the exit of the left ventricle of the heart (where the aorta begins), such that problems result. It may occur at the aortic valve as well as above and below this level. It typically gets worse ov ...
, cardiomyopathy, electrolyte problems
Electrolyte imbalance, or water-electrolyte imbalance, is an abnormality in the concentration of electrolytes in the body. Electrolytes play a vital role in maintaining homeostasis in the body. They help to regulate heart and neurological function, ...
(e.g., low blood levels of magnesium or potassium), inherited channelopathies
Channelopathies are a group of diseases caused by the dysfunction of ion channel subunits or their interacting proteins. These diseases can be inherited or acquired by other disorders, drugs, or toxins. Mutations in genes encoding ion channels, wh ...
(e.g., long-QT syndrome
Long QT syndrome (LQTS) is a condition affecting repolarization (relaxing) of the heart after a heartbeat, giving rise to an abnormally lengthy QT interval. It results in an increased risk of an irregular heartbeat which can result in fainting, ...
), catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia
Catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia (CPVT) is an inherited genetic disorder that predisposes those affected to potentially life-threatening abnormal heart rhythms or arrhythmias. The arrhythmias seen in CPVT typically occur du ...
, arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia
Arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy (ACM), arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia (ARVD), or arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy (ARVC), most commonly is an inherited heart disease.
ACM is caused by genetic defects of the parts of hea ...
, alcohol withdrawal syndrome (typically following atrial fibrillation), or a myocardial infarction
A myocardial infarction (MI), commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when blood flow decreases or stops to the coronary artery of the heart, causing damage to the heart muscle. The most common symptom is chest pain or discomfort which may ...
.
Pathophysiology
The morphology of the tachycardia depends on its cause and the origin of the re-entry electrical circuit in the heart. In monomorphic ventricular tachycardia, the shape of each heart beat on the ECG looks the same because the impulse is either being generated from increasedautomaticity
Automaticity is the ability to do things without occupying the mind with the low-level details required, allowing it to become an automatic response pattern or habit. It is usually the result of learning, repetition, and practice. Examples of tas ...
of a single point in either the left or the right ventricle, or due to a reentry
Atmospheric entry is the movement of an object from outer space into and through the gases of an atmosphere of a planet, dwarf planet, or natural satellite. There are two main types of atmospheric entry: ''uncontrolled entry'', such as the ...
circuit within the ventricle. The most common cause of monomorphic ventricular tachycardia is scarring of the heart muscle from a previous myocardial infarction
A myocardial infarction (MI), commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when blood flow decreases or stops to the coronary artery of the heart, causing damage to the heart muscle. The most common symptom is chest pain or discomfort which may ...
(heart attack). This scar cannot conduct electrical activity, so there is a potential circuit ''around'' the scar that results in the tachycardia. This is similar to the re-entrant circuits that are the cause of atrial flutter
Atrial flutter (AFL) is a common abnormal heart rhythm that starts in the atrial chambers of the heart. When it first occurs, it is usually associated with a fast heart rate and is classified as a type of supraventricular tachycardia. Atrial f ...
and the re-entrant forms of supraventricular tachycardia. Other rarer congenital causes of monomorphic VT include right ventricular dysplasia, and right and left ventricular outflow tract VT.
Polymorphic ventricular tachycardia, on the other hand, is most commonly caused by abnormalities of ventricular muscle repolarization. The predisposition to this problem usually manifests on the ECG as a prolongation of the QT interval. QT prolongation may be congenital or acquired. Congenital problems include long QT syndrome and catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia
Catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia (CPVT) is an inherited genetic disorder that predisposes those affected to potentially life-threatening abnormal heart rhythms or arrhythmias. The arrhythmias seen in CPVT typically occur du ...
. Acquired problems are usually related to drug toxicity or electrolyte abnormalities, but can occur as a result of myocardial ischemia. Class III anti-arrhythmic drugs such as sotalol and amiodarone
Amiodarone is an antiarrhythmic medication used to treat and prevent a number of types of cardiac dysrhythmias. This includes ventricular tachycardia (VT), ventricular fibrillation (VF), and wide complex tachycardia, as well as atrial fibril ...
prolong the QT interval and may in some circumstances be pro-arrhythmic. Other relatively common drugs including some antibiotics and antihistamines may also be a danger, in particular in combination with one another. Problems with blood levels of potassium, magnesium and calcium may also contribute. High-dose magnesium is often used as an antidote in cardiac arrest protocols.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of ventricular tachycardia is made based on the rhythm seen on either a 12-lead ECG or a telemetry rhythm strip. It may be very difficult to differentiate between ventricular tachycardia and a wide-complex supraventricular tachycardia in some cases. In particular, supraventricular tachycardias with aberrant conduction from a pre-existingbundle branch block
A bundle branch block is a defect in one the bundle branches in the electrical conduction system of the heart.
Anatomy and physiology
The heart's electrical activity begins in the sinoatrial node (the heart's natural pacemaker), which is situat ...
are commonly misdiagnosed as ventricular tachycardia. Other rarer phenomena include Ashman beats and antidromic atrioventricular re-entry tachycardias.
Various diagnostic criteria have been developed to determine whether a wide complex tachycardia is ventricular tachycardia or a more benign rhythm. In addition to these diagnostic criteria, if the individual has a history of a myocardial infarction
A myocardial infarction (MI), commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when blood flow decreases or stops to the coronary artery of the heart, causing damage to the heart muscle. The most common symptom is chest pain or discomfort which may ...
, congestive heart failure, or recent angina, the wide complex tachycardia is much more likely to be ventricular tachycardia.
The proper diagnosis is important, as the misdiagnosis of supraventricular tachycardia when ventricular tachycardia is present is associated with worse prognosis. This is particularly true if calcium channel blockers, such as verapamil, are used to attempt to terminate a presumed supraventricular tachycardia. Therefore, it is wisest to assume that all wide complex tachycardia is VT until proven otherwise.
ECG features of Ventricular Tachycardia in addition to the increased Heart rate are:
# A wide QRS Complex (because the ectopics for the generation of the cardiac impulse originates in the Ventricular Myocyte and propagated via the intermyocyte conduction, which is a delayed conduction)
# A Josephson's sign where there is the notch in the downsloping of the S wave near its nadir (considered very specific for the VT).
# Capture beats (normal QRS complex in between when the Heart pick up the sinus rhythm from the impulses generated by the SA node), fusion beats (due to the fusion of the Abnormal and the Normal QRS complexes) which has a unique morphology.
# Positive or negative concordance.
# Extreme Axis deviation or NORTH WEST axis (axis between -90 to +180 degrees)
Classification
 Ventricular tachycardia can be classified based on its ''morphology'':
* Monomorphic ventricular tachycardia means that the appearance of all the beats match each other in each lead of a surface electrocardiogram (ECG).
** Scar-related monomorphic ventricular tachycardia is the most common type and a frequent cause of death in patients having survived a heart attack, especially if they have weak heart muscle.
** Right ventricular outflow tract (RVOT) tachycardia is a type of monomorphic ventricular tachycardia originating in the right ventricular outflow tract. RVOT morphology refers to the characteristic pattern of this type of tachycardia on an ECG.
** The source of the re-entry circuit can be identified by evaluating the morphology of the QRS complex in the V1 lead of a surface ECG. If the R wave is dominant (consistent with a right bundle branch block morphology), this indicates the origin of the VT is the left ventricle. Conversely, if the S wave is dominant (consistent with a
Ventricular tachycardia can be classified based on its ''morphology'':
* Monomorphic ventricular tachycardia means that the appearance of all the beats match each other in each lead of a surface electrocardiogram (ECG).
** Scar-related monomorphic ventricular tachycardia is the most common type and a frequent cause of death in patients having survived a heart attack, especially if they have weak heart muscle.
** Right ventricular outflow tract (RVOT) tachycardia is a type of monomorphic ventricular tachycardia originating in the right ventricular outflow tract. RVOT morphology refers to the characteristic pattern of this type of tachycardia on an ECG.
** The source of the re-entry circuit can be identified by evaluating the morphology of the QRS complex in the V1 lead of a surface ECG. If the R wave is dominant (consistent with a right bundle branch block morphology), this indicates the origin of the VT is the left ventricle. Conversely, if the S wave is dominant (consistent with a left bundle branch block
Left bundle branch block (LBBB) is a conduction abnormality in the heart that can be seen on an electrocardiogram (ECG). In this condition, activation of the left ventricle of the heart is delayed, which causes the left ventricle to contract late ...
morphology, this is consistent with VT originating from the right ventricle or interventricular septum.
* Polymorphic ventricular tachycardia, on the other hand, has beat-to-beat variations in morphology. This may appear as a cyclical progressive change in cardiac axis, previously referred to by its French name ''torsades de pointes
''Torsades de pointes, torsade de pointes'' or ''torsades des pointes'' (TdP) (, , translated as "twisting of peaks") is a specific type of abnormal heart rhythm that can lead to sudden cardiac death. It is a polymorphic ventricular tachycardia t ...
'' ("twisting of the spikes"). However, at the current time, the term ''torsades de pointes'' is reserved for polymorphic VT occurring in the context of a prolonged resting QT interval.
Another way to classify ventricular tachycardias is the ''duration of the episodes'': Three or more beats in a row on an ECG that originate from the ventricle at a rate of more than 120 beats per minute constitute a ventricular tachycardia.
* If the fast rhythm self-terminates within 30 seconds, it is considered a non-sustained ventricular tachycardia.
* If the rhythm lasts more than 30 seconds, it is known as a sustained ventricular tachycardia (even if it terminates on its own after 30 seconds).
A third way to classify ventricular tachycardia is on the basis of its ''symptoms'': Pulseless VT is associated with no effective cardiac output, hence, no effective pulse, and is a cause of cardiac arrest (see also: pulseless electrical activity
Pulseless electrical activity (PEA) refers to cardiac arrest in which the electrocardiogram shows a heart rhythm that should produce a pulse, but does not. Pulseless electrical activity is found initially in about 55% of people in cardiac arrest.
...
EA. In this circumstance, it is best treated the same way as ventricular fibrillation (VF), and is recognized as one of the shockable rhythm
Defibrillation is a treatment for life-threatening cardiac arrhythmias, specifically ventricular fibrillation (V-Fib) and non-perfusing ventricular tachycardia (V-Tach). A defibrillator delivers a dose of electric current (often called a ''coun ...
s on the cardiac arrest protocol. Some VT is associated with reasonable cardiac output and may even be asymptomatic. The heart usually tolerates this rhythm poorly in the medium to long term, and patients may certainly deteriorate to pulseless VT or to VF.
Occasionally in ventricular tachycardia, supraventricular impulses are conducted to the ventricles, generating QRS complexes with normal or aberrant supraventricular morphology (ventricular capture). Or, those impulses can be merged with complexes that are originated in the ventricle and produce a summation pattern (fusion complexes).
Less common is ventricular tachycardia that occurs in individuals with structurally normal hearts. This is known as ''idiopathic ventricular tachycardia'' and in the monomorphic form coincides with little or no increased risk of sudden cardiac death. In general, ''idiopathic ventricular tachycardia'' occurs in younger individuals diagnosed with VT. While the causes of idiopathic VT are not known, in general it is presumed to be congenital, and can be brought on by any number of diverse factors.
Treatment
Therapy may be directed either at terminating an episode of the abnormal heart rhythm or at reducing the risk of another VT episode. The treatment for stable VT is tailored to the specific person, with regard to how well the individual tolerates episodes of ventricular tachycardia, how frequently episodes occur, their comorbidities, and their wishes. Individuals with pulseless VT or unstable VT are hemodynamically compromised and require immediate electric cardioversion to shock them out of the VT rhythm.Cardioversion
If a person still has a pulse, it is usually possible to terminate the episode using electric cardioversion. This should be synchronized to the heartbeat if the waveform is monomorphic if possible, in order to avoid degeneration of the rhythm to ventricular fibrillation. An initial energy of 100J is recommended. If the waveform is polymorphic, then higher energies and an unsynchronized shock should be provided (also known as defibrillation).Defibrillation
A person with pulseless VT is treated the same as ventricular fibrillation with high-energy (360J with a monophasic defibrillator, or 200J with a biphasic defibrillator) unsynchronised cardioversion ( defibrillation). They will be unconscious. The shock may be delivered to the outside of the chest using the two pads of an external defibrillator, or internally to the heart by an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD) if one has previously been inserted. An ICD may also be set to attempt to overdrive pace the ventricle. Pacing the ventricle at a rate faster than the underlying tachycardia can sometimes be effective in terminating the rhythm. If this fails after a short trial, the ICD will usually stop pacing, charge up and deliver a defibrillation grade shock.Medication
For those who are stable with amonomorphic waveform
The QRS complex is the combination of three of the graphical deflections seen on a typical electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG). It is usually the central and most visually obvious part of the tracing. It corresponds to the depolarization of the ri ...
the medications procainamide
Procainamide (PCA) is a medication of the antiarrhythmic class used for the treatment of cardiac arrhythmias. It is classified by the Vaughan Williams classification system as class Ia; thus it is a sodium channel blocker of cardiomyocytes. In add ...
or sotalol may be used and are better than lidocaine. Evidence does not show that amiodarone
Amiodarone is an antiarrhythmic medication used to treat and prevent a number of types of cardiac dysrhythmias. This includes ventricular tachycardia (VT), ventricular fibrillation (VF), and wide complex tachycardia, as well as atrial fibril ...
is better than procainamide.
As a low magnesium level in the blood is a common cause of VT, magnesium sulfate can be given for torsades de pointes or if a low blood magnesium level is found/suspected.
Long-term anti-arrhythmic therapy may be indicated to prevent recurrence of VT. Beta-blockers and a number of class III anti-arrhythmics are commonly used, such as the beta-blockers carvedilol, metoprolol, and bisoprolol, and the Potassium-Channel-Blockers amiodarone, dronedarone, bretylium, sotalol, ibutilide, and dofetilide. Angiotensin-converting-enzyme (ACE) inhibitors and aldosterone antagonists are also sometimes used in this setting.
Invasive treatment
An ICD (implantable cardioverter defibrillator ) is more effective than drug therapy for prevention of sudden cardiac death due to VT and VF, but does not prevent these rhythm from happening.Catheter ablation
Catheter ablation is a procedure used to remove or terminate a faulty electrical pathway from sections of the heart of those who are prone to developing cardiac arrhythmias such as atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter and Wolff-Parkinson-White syn ...
is a potentially definitive treatment option for those with recurrent VT. Remote magnetic navigation is one effective method to do the procedure.
In the past, ablation was often not considered until pharmacological options had been exhausted, often after the patient had developed substantial morbidity from recurrent episodes of VT and ICD shocks. Antiarrhythmic medications can reduce the frequency of ICD therapies, but have efficacy varies and side effects can be significant. Advances in technology and understanding of VT substrates now allow ablation of multiple and unstable VTs with acceptable safety and efficacy, even in patients with advanced heart disease.
References
External links
{{Authority control Cardiac arrhythmia Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate Wikipedia emergency medicine articles ready to translate