Virgo Cluster on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Virgo Cluster is a
(with frames) It contains a mixture of elliptical, lenticular, and spiral galaxies which are generally gas-poor, The three subgroups are in the process of merging to form a larger single cluster, and are surrounded by other smaller
The three subgroups are in the process of merging to form a larger single cluster, and are surrounded by other smaller
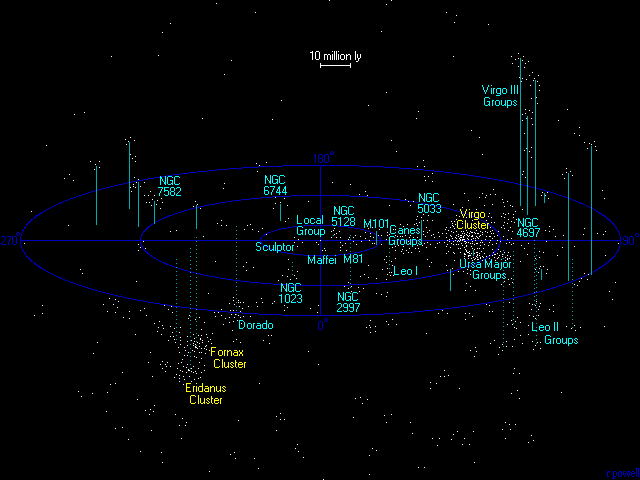 Below is a table of bright or notable objects in the cluster and their subcluster. In some cases a galaxy may be considered to be in a different subcluster by other researchers (sources:)
:Column 1: The name of the galaxy.
:Column 2: The right ascension for epoch 2000.
:Column 3: The declination for epoch 2000.
:Column 4: The blue apparent magnitude of the galaxy.
:Column 5: The galaxy type: E=Elliptical, S0=Lenticular, Sa,Sb,Sc,Sd=Spiral, SBa,SBb,SBc,SBd=Barred spiral, Sm,SBm,Irr=Irregular.
:Column 6: The angular diameter of the galaxy (arcminutes).
:Column 7: The diameter of the galaxy (thousands of light years).
:Column 8: The recessional velocity (km/s) of the galaxy relative to the
Below is a table of bright or notable objects in the cluster and their subcluster. In some cases a galaxy may be considered to be in a different subcluster by other researchers (sources:)
:Column 1: The name of the galaxy.
:Column 2: The right ascension for epoch 2000.
:Column 3: The declination for epoch 2000.
:Column 4: The blue apparent magnitude of the galaxy.
:Column 5: The galaxy type: E=Elliptical, S0=Lenticular, Sa,Sb,Sc,Sd=Spiral, SBa,SBb,SBc,SBd=Barred spiral, Sm,SBm,Irr=Irregular.
:Column 6: The angular diameter of the galaxy (arcminutes).
:Column 7: The diameter of the galaxy (thousands of light years).
:Column 8: The recessional velocity (km/s) of the galaxy relative to the
The Virgo Cluster at An Atlas of the Universe
map (and table) of the 160 largest galaxies
on Virgo cluster.
SEDS Messier pages
Partial Virgo cluster centered on M87 (Dark Atmospheres)
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Virgo Cluster Virgo Supercluster Virgo (constellation) Coma Berenices
cluster of galaxies
A galaxy cluster, or a cluster of galaxies, is a structure that consists of anywhere from hundreds to thousands of galaxy, galaxies that are bound together by gravity, with typical masses ranging from 1014 to 1015 solar masses. Clusters consist o ...
whose center is 53.8 ± 0.3 Mly (16.5 ± 0.1 Mpc) away in the Virgo constellation. Comprising approximately 1,300 (and possibly up to 2,000) member galaxies, the cluster forms the heart of the larger Virgo Supercluster
The Local Supercluster (LSC or LS), or Virgo Supercluster is a formerly defined supercluster containing the Virgo Cluster and Local Group, which itself contains the Milky Way and Andromeda galaxies, as well as others. At least 100 galaxy group ...
, of which the Local Group (containing the Milky Way galaxy
The Milky Way or Milky Way Galaxy is the galaxy that includes the Solar System, with the name describing the galaxy's appearance from Earth: a hazy band of light seen in the night sky formed from stars in other arms of the galaxy, which are ...
) is a member. The Local Group actually experiences the mass of the Virgo Supercluster as the Virgocentric flow. It is estimated that the Virgo Cluster's mass is 1.2 out to 8 degrees of the cluster's center or a radius of about 2.2 Mpc.
Many of the brighter galaxies in this cluster, including the giant elliptical galaxy
An elliptical galaxy is a type of galaxy with an approximately ellipsoidal shape and a smooth, nearly featureless image. They are one of the three main galaxy morphological classification, classes of galaxy described by Edwin Hubble in his Hub ...
Messier 87
Messier 87 (also known as Virgo A or NGC 4486, generally abbreviated to M87) is a Type-cD galaxy, supergiant elliptical galaxy, elliptical galaxy in the constellation Virgo (constellation), Virgo that contains several trillion s ...
, were discovered in the late 1770s and early 1780s and subsequently included in Charles Messier
Charles Messier (; 26 June 1730 – 12 April 1817) was a French astronomer. He published an astronomical catalogue consisting of 110 nebulae and star clusters, which came to be known as the ''Messier objects'', referred to with th ...
's catalogue of non-cometary fuzzy objects. Described by Messier as nebula
A nebula (; or nebulas) is a distinct luminescent part of interstellar medium, which can consist of ionized, neutral, or molecular hydrogen and also cosmic dust. Nebulae are often star-forming regions, such as in the Pillars of Creation in ...
e without stars, their true nature was not recognized until the 1920s.
The cluster extends across approximately 8 degrees centered in the constellation Virgo. Some of its most prominent members can be seen with binoculars and small telescopes, while a 6-inch telescope will reveal about 160 of the cluster's galaxies on a clear night. Its brightest member is the elliptical galaxy
An elliptical galaxy is a type of galaxy with an approximately ellipsoidal shape and a smooth, nearly featureless image. They are one of the three main galaxy morphological classification, classes of galaxy described by Edwin Hubble in his Hub ...
Messier 49.
Characteristics
The cluster is a fairlyheterogeneous
Homogeneity and heterogeneity are concepts relating to the uniformity of a substance, process or image. A homogeneous feature is uniform in composition or character (i.e., color, shape, size, weight, height, distribution, texture, language, i ...
mixture of spiral
In mathematics, a spiral is a curve which emanates from a point, moving further away as it revolves around the point. It is a subtype of whorled patterns, a broad group that also includes concentric objects.
Two-dimensional
A two-dimension ...
and elliptical galaxies. , it is believed that the spiral galaxies of the cluster are distributed in an oblong prolate filament, approximately four times as long as it is wide, stretching along the line of sight from the Milky Way
The Milky Way or Milky Way Galaxy is the galaxy that includes the Solar System, with the name describing the #Appearance, galaxy's appearance from Earth: a hazy band of light seen in the night sky formed from stars in other arms of the galax ...
. The elliptical galaxies are more centrally concentrated than the spiral galaxies.
The cluster is an aggregate of at least three separate subclumps: Virgo A, centered on M87, a second centered on the galaxy M86, and Virgo B, centered on M49, with some authors including a Virgo C subcluster, centered on the galaxy M60 as well as a Low Velocity Cloud (LVC) subclump, centered on the large spiral galaxy NGC 4216. The giant elliptical galaxy
An elliptical galaxy is a type of galaxy with an approximately ellipsoidal shape and a smooth, nearly featureless image. They are one of the three main galaxy morphological classification, classes of galaxy described by Edwin Hubble in his Hub ...
M87 contains a supermassive black hole
A supermassive black hole (SMBH or sometimes SBH) is the largest type of black hole, with its mass being on the order of hundreds of thousands, or millions to billions, of times the mass of the Sun (). Black holes are a class of astronomical ...
, whose event horizon
In astrophysics, an event horizon is a boundary beyond which events cannot affect an outside observer. Wolfgang Rindler coined the term in the 1950s.
In 1784, John Michell proposed that gravity can be strong enough in the vicinity of massive c ...
was observed by the Event Horizon Telescope
The Event Horizon Telescope (EHT) is a Astronomical interferometer, telescope array consisting of a global network of radio telescopes. The EHT project combines data from several very-long-baseline interferometry (VLBI) stations around Earth, wh ...
Collaboration in 2019.
Virgo A is the dominant subclump; its mass of approximately 1014 is approximately ten times larger than the other two subclumps.The Virgo Super Cluster: home of M87(with frames) It contains a mixture of elliptical, lenticular, and spiral galaxies which are generally gas-poor,
 The three subgroups are in the process of merging to form a larger single cluster, and are surrounded by other smaller
The three subgroups are in the process of merging to form a larger single cluster, and are surrounded by other smaller galaxy cloud
Galaxy groups and clusters are the largest Observable universe, known Gravitational binding energy, gravitationally bound objects to have arisen thus far in the process of cosmic structure formation. They form the densest part of the Observable u ...
s, mostly composed of spiral galaxies, known as N Cloud, S Cloud, and Virgo E that are in the process of infalling to merge with them, plus other farther isolated galaxies and galaxy groups (like the galaxy cloud Coma I) that are also attracted by the gravity of Virgo to merge with it in the future. This strongly suggests the Virgo cluster is a dynamically young cluster that is still forming.
Nearby aggregations known as M Cloud, W Cloud, and W' Cloud seem to be background systems independent of the main cluster.
The large mass of the cluster is indicated by the high peculiar velocities of many of its galaxies, sometimes as high as 1,600 km/ s with respect to the cluster's center.
The Virgo cluster lies within the Virgo Supercluster
The Local Supercluster (LSC or LS), or Virgo Supercluster is a formerly defined supercluster containing the Virgo Cluster and Local Group, which itself contains the Milky Way and Andromeda galaxies, as well as others. At least 100 galaxy group ...
, and its gravitational effect slows down the nearby galaxies. The large mass of the cluster has the effect of slowing down the recession of the Local Group from the cluster by approximately ten percent.
Molecular gasses in Virgo Cluster has been swept away by a huge cosmic broom that is preventing nearby galaxies from birthing new stars. The actual cause of it has been a long standing mystery in astrophysics
Astrophysics is a science that employs the methods and principles of physics and chemistry in the study of astronomical objects and phenomena. As one of the founders of the discipline, James Keeler, said, astrophysics "seeks to ascertain the ...
. According to scientists, it occurs because of the extreme environment of the Virgo Cluster.
Intracluster medium
As with many other rich galaxy clusters, Virgo's intracluster medium is filled with a hot, rarefied plasma at temperatures of 30 millionkelvin
The kelvin (symbol: K) is the base unit for temperature in the International System of Units (SI). The Kelvin scale is an absolute temperature scale that starts at the lowest possible temperature (absolute zero), taken to be 0 K. By de ...
s that emits X-Rays
An X-ray (also known in many languages as Röntgen radiation) is a form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength shorter than those of ultraviolet rays and longer than those of gamma rays. Roughly, X-rays have a wavelength ran ...
. Within the intracluster medium (ICM) are found a large number of intergalactic stars (up to 10% of the stars in the cluster), including some planetary nebula
A planetary nebula is a type of emission nebula consisting of an expanding, glowing shell of ionized gas ejected from red giant stars late in their lives.
The term "planetary nebula" is a misnomer because they are unrelated to planets. The ...
e. It is theorized that these were expelled from their home galaxies by interactions with other galaxies. The ICM also contains some globular cluster
A globular cluster is a spheroidal conglomeration of stars that is bound together by gravity, with a higher concentration of stars towards its center. It can contain anywhere from tens of thousands to many millions of member stars, all orbiting ...
s, possibly stripped off dwarf galaxies, and even at least one star formation
Star formation is the process by which dense regions within molecular clouds in interstellar space—sometimes referred to as "stellar nurseries" or "star-forming regions"—Jeans instability, collapse and form stars. As a branch of astronomy, sta ...
region
In geography, regions, otherwise referred to as areas, zones, lands or territories, are portions of the Earth's surface that are broadly divided by physical characteristics (physical geography), human impact characteristics (human geography), and ...
.
Galaxies
 Below is a table of bright or notable objects in the cluster and their subcluster. In some cases a galaxy may be considered to be in a different subcluster by other researchers (sources:)
:Column 1: The name of the galaxy.
:Column 2: The right ascension for epoch 2000.
:Column 3: The declination for epoch 2000.
:Column 4: The blue apparent magnitude of the galaxy.
:Column 5: The galaxy type: E=Elliptical, S0=Lenticular, Sa,Sb,Sc,Sd=Spiral, SBa,SBb,SBc,SBd=Barred spiral, Sm,SBm,Irr=Irregular.
:Column 6: The angular diameter of the galaxy (arcminutes).
:Column 7: The diameter of the galaxy (thousands of light years).
:Column 8: The recessional velocity (km/s) of the galaxy relative to the
Below is a table of bright or notable objects in the cluster and their subcluster. In some cases a galaxy may be considered to be in a different subcluster by other researchers (sources:)
:Column 1: The name of the galaxy.
:Column 2: The right ascension for epoch 2000.
:Column 3: The declination for epoch 2000.
:Column 4: The blue apparent magnitude of the galaxy.
:Column 5: The galaxy type: E=Elliptical, S0=Lenticular, Sa,Sb,Sc,Sd=Spiral, SBa,SBb,SBc,SBd=Barred spiral, Sm,SBm,Irr=Irregular.
:Column 6: The angular diameter of the galaxy (arcminutes).
:Column 7: The diameter of the galaxy (thousands of light years).
:Column 8: The recessional velocity (km/s) of the galaxy relative to the cosmic microwave background
The cosmic microwave background (CMB, CMBR), or relic radiation, is microwave radiation that fills all space in the observable universe. With a standard optical telescope, the background space between stars and galaxies is almost completely dar ...
.
:Column 9: Subcluster where the galaxy is located.
Fainter galaxies within the cluster are usually known by their numbers in the Virgo Cluster Catalog, particularly members of the numerous dwarf galaxy population.
See also
* Virgo III Groups * Coma Cluster – another large, nearby cluster of galaxies * Eridanus Cluster *Fornax Cluster
The Fornax Cluster is a cluster of galaxies lying at a distance of 19 megaparsecs (62 million light-years). It has an estimated mass of solar masses, making it the second richest galaxy cluster within 100 million light-years, after the consider ...
– a smaller nearby cluster of galaxies
* Norma Cluster
* List of galaxy clusters
* Virgocentric flow
Notes
References
External links
The Virgo Cluster at An Atlas of the Universe
map (and table) of the 160 largest galaxies
on Virgo cluster.
SEDS Messier pages
Partial Virgo cluster centered on M87 (Dark Atmospheres)
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Virgo Cluster Virgo Supercluster Virgo (constellation) Coma Berenices