
Vayakhel, Wayyaqhel, VaYakhel, Va-Yakhel, Vayak'hel, Vayak'heil, or Vayaqhel (—
Hebrew
Hebrew (; ''ʿÎbrit'') is a Northwest Semitic languages, Northwest Semitic language within the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family. A regional dialect of the Canaanite languages, it was natively spoken by the Israelites and ...
for "and he assembled," the
first word in the parashah) is the 22nd
weekly Torah portion
The weekly Torah portion refers to a lectionary custom in Judaism in which a portion of the Torah (or Pentateuch) is read during Jewish prayer services on Monday, Thursday, and Saturday. The full name, ''Parashat HaShavua'' (), is popularly abbre ...
(, ''parashah'') in the
weekly Torah portion
The weekly Torah portion refers to a lectionary custom in Judaism in which a portion of the Torah (or Pentateuch) is read during Jewish prayer services on Monday, Thursday, and Saturday. The full name, ''Parashat HaShavua'' (), is popularly abbre ...
and the 10th of the
Book of Exodus
The Book of Exodus (from ; ''Šəmōṯ'', 'Names'; ) is the second book of the Bible. It is the first part of the narrative of the Exodus, the origin myth of the Israelites, in which they leave slavery in Biblical Egypt through the strength of ...
. The parashah tells of the making of the
Tabernacle
According to the Hebrew Bible, the tabernacle (), also known as the Tent of the Congregation (, also Tent of Meeting), was the portable earthly dwelling of God used by the Israelites from the Exodus until the conquest of Canaan. Moses was instru ...
and its sacred vessels. It constitutes Exodus 35:1–38:20. The parashah is made up of 6181 Hebrew letters, 1,558 Hebrew words, 122
verses, and 211 lines in a Torah scroll (, ''
Sefer Torah
file:SeferTorah.jpg, A Sephardic Torah scroll rolled to the first paragraph of the Shema
file:Köln-Tora-und-Innenansicht-Synagoge-Glockengasse-040.JPG, An Ashkenazi Torah scroll rolled to the Decalogue
file:Keneseth Eliyahoo Synagogue, Inte ...
'').
Rabbinic Jews read it on the 22nd
Shabbat
Shabbat (, , or ; , , ) or the Sabbath (), also called Shabbos (, ) by Ashkenazi Hebrew, Ashkenazim, is Judaism's day of rest on the seventh day of the seven-day week, week—i.e., Friday prayer, Friday–Saturday. On this day, religious Jews ...
after
Simchat Torah
Simchat Torah (; Ashkenazi: ), also spelled Simhat Torah, is a Jewish holiday that celebrates and marks the conclusion of the annual cycle of public Torah readings, and the beginning of a new cycle. Simchat Torah is a component of the Hebrew Bible ...
, generally in March or rarely in late February. The
lunisolar
A lunisolar calendar is a calendar in many cultures, that combines monthly lunar cycles with the solar year. As with all calendars which divide the year into months, there is an additional requirement that the year have a whole number of months ...
Hebrew calendar
The Hebrew calendar (), also called the Jewish calendar, is a lunisolar calendar used today for Jewish religious observance and as an official calendar of Israel. It determines the dates of Jewish holidays and other rituals, such as '' yahrze ...
contains up to 55
week
A week is a unit of time equal to seven days. It is the standard time period used for short cycles of days in most parts of the world. The days are often used to indicate common work days and rest days, as well as days of worship. Weeks are ofte ...
s, the exact number varying between 50 in common years and 54 or 55 in leap years. In leap years (for example, 2024 and 2027), Parashat Vayakhel is read separately. In common years (for example, 2023 and 2026), Parashat Vayakhel is usually combined with the next parashah,
Pekudei
Pekudei, Pekude, Pekudey, P'kude, or P'qude (—Hebrew language, Hebrew for "amounts of," the second word, and the Incipit, first distinctive word, in the parashah) is the 23rd weekly Torah portion (, ''parashah'') in the annual Judaism, Jewish cy ...
, to help achieve the number of weekly readings needed (although in some non-leap years, such as 2025, they are not combined).
Readings
In traditional Sabbath Torah reading, the parashah is divided into seven readings, or , ''
aliyot''.


First reading—Exodus 35:1–20
In the first reading (, ''aliyah''),
Moses
In Abrahamic religions, Moses was the Hebrews, Hebrew prophet who led the Israelites out of slavery in the The Exodus, Exodus from ancient Egypt, Egypt. He is considered the most important Prophets in Judaism, prophet in Judaism and Samaritani ...
convoked the
Israelite
Israelites were a Hebrew language, Hebrew-speaking ethnoreligious group, consisting of tribes that lived in Canaan during the Iron Age.
Modern scholarship describes the Israelites as emerging from indigenous Canaanites, Canaanite populations ...
s to build the Tabernacle. Moses started by reminding them of
God's commandment to keep the Sabbath of complete rest. Then Moses told them to collect gifts of materials from those whose heart so moved them—gifts of
gold
Gold is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol Au (from Latin ) and atomic number 79. In its pure form, it is a brightness, bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile metal. Chemically, gold is a transition metal ...
,
silver
Silver is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ag () and atomic number 47. A soft, whitish-gray, lustrous transition metal, it exhibits the highest electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and reflectivity of any metal. ...
,
copper
Copper is a chemical element; it has symbol Cu (from Latin ) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish-orang ...
, colored
yarn
Yarn is a long continuous length of interlocked fibres, used in sewing, crocheting, knitting, weaving, embroidery, ropemaking, and the production of textiles. '' Thread'' is a type of yarn intended for sewing by hand or machine. Modern ...
s, fine
linen
Linen () is a textile made from the fibers of the flax plant.
Linen is very strong and absorbent, and it dries faster than cotton. Because of these properties, linen is comfortable to wear in hot weather and is valued for use in garments. Lin ...
,
goats
The goat or domestic goat (''Capra hircus'') is a species of goat-antelope that is mostly kept as livestock. It was domesticated from the wild goat (''C. aegagrus'') of Southwest Asia and Eastern Europe. The goat is a member of the famil ...
hair, tanned ram skins,
acacia
''Acacia'', commonly known as wattles or acacias, is a genus of about of shrubs and trees in the subfamily Mimosoideae of the pea family Fabaceae. Initially, it comprised a group of plant species native to Africa, South America, and Austral ...
wood,
olive oil
Olive oil is a vegetable oil obtained by pressing whole olives (the fruit of ''Olea europaea'', a traditional Tree fruit, tree crop of the Mediterranean Basin) and extracting the oil.
It is commonly used in cooking for frying foods, as a cond ...
,
spice
In the culinary arts, a spice is any seed, fruit, root, Bark (botany), bark, or other plant substance in a form primarily used for flavoring or coloring food. Spices are distinguished from herbs, which are the leaves, flowers, or stems of pl ...
s,
lapis lazuli
Lapis lazuli (; ), or lapis for short, is a deep-blue metamorphic rock used as a semi-precious stone that has been prized since antiquity for its intense color. Originating from the Persian word for the gem, ''lāžward'', lapis lazuli is ...
, and other stones. Moses invited all who were skilled to make the Tabernacle, its furnishings, and the
priests' vestments.
Second reading—Exodus 35:21–29
In the second reading (, ''aliyah''), the Israelites brought the gifts that Moses requested.
Third reading—Exodus 35:30–36:7
In the third reading (, ''aliyah''), Moses announced that God had singled out
Bezalel
In Exodus 31:1-6 and chapters 36 to 39, Bezalel, Bezaleel, or Betzalel (, ''Bəṣalʼēl''), was the chief artisan of the Tabernacle and was in charge of building the Ark of the Covenant, assisted by Oholiab. The section in chapter 31 descr ...
and
Oholiab to endow them with the skills needed to construct the Tabernacle. And Moses called on them and all skilled persons to undertake the task. The Israelites brought more than was needed, so Moses proclaimed an end to the collection.
Fourth reading—Exodus 36:8–19
In the fourth reading (, ''aliyah''), the skilled workers fashioned the Tabernacle's curtains, loop, clasps, and coverings.
Fifth reading—Exodus 36:20–37:16
In the long fifth reading (, ''aliyah''), they made the Tabernacle's standing, gold clad, polished boards each with 2 tenons, and their 2 silver sockets, bars of acacia-wood overlaid with gold, rings of gold, veil of the covering, 4 pillars of acacia-wood overlaid with gold, screen for the door held by 5 gold clad pillars, and sockets of brass. Bezalel made the ark, cover, and 7 golden oil lamps pushed over against the golden lampstand which partially covers the table.
Sixth reading—Exodus 37:17–29
In the sixth reading (, ''aliyah''), Bezalel made the
temple menorah
The Temple menorah (; , Tiberian Hebrew ) is a seven-branched candelabrum that is described in the Hebrew Bible and later ancient sources as having been used in the Tabernacle and the Temple in Jerusalem.
Since ancient times, it has served as a ...
and
incense altar.
Seventh reading—Exodus 38:1–20
In the seventh reading (, ''aliyah''), Bezalel made the altar for
sacrifice
Sacrifice is an act or offering made to a deity. A sacrifice can serve as propitiation, or a sacrifice can be an offering of praise and thanksgiving.
Evidence of ritual animal sacrifice has been seen at least since ancient Hebrews and Gree ...
s, laver, and enclosure for the Tabernacle.
Readings according to the triennial cycle
Jews who read the Torah according to the
triennial cycle
The Triennial cycle of Torah reading may refer to either
* The historical practice in ancient Israel by which the entire Torah was read in serial fashion over a three-year period, or
* The practice adopted by many Reform, Conservative, Reconstruct ...
of Torah reading may read the parashah according to a different schedule.

In ancient parallels
The parashah has parallels in these ancient sources:
Exodus chapter 35
Noting that
Sargon of Akkad
Sargon of Akkad (; ; died 2279 BC), also known as Sargon the Great, was the first ruler of the Akkadian Empire, known for his conquests of the Sumerian city-states in the 24th to 23rd centuries BC.The date of the reign of Sargon is highly unc ...
was the first to use a seven-day week, Professor
Gregory S. Aldrete of the
University of Wisconsin–Green Bay
The University of Wisconsin–Green Bay (UW–Green Bay, UWGB, or Green Bay) is a public university in Green Bay, Wisconsin, United States. Founded in 1965, it is part of the University of Wisconsin System. As of fall 2024, student enrollment h ...
speculated that the Israelites may have adopted the idea from the
Akkadian Empire
The Akkadian Empire () was the first known empire, succeeding the long-lived city-states of Sumer. Centered on the city of Akkad (city), Akkad ( or ) and its surrounding region, the empire united Akkadian language, Akkadian and Sumerian languag ...
.
Inner-biblical interpretation
The parashah has parallels or is discussed in these Biblical sources:
Exodus chapters 25–39
This is the pattern of instruction and construction of the Tabernacle and its furnishings:

Exodus chapter 35
Exodus 35:1 opens, "And Moses assembled" (, ''wayyaqhēl Moše''), in an echo of Exodus 32:1, which says, "the people assembled" (, ''vayyiqāhēl hāʿām'').

The Sabbath
Exodus 35:1–3 refers to the Sabbath. Exodus 35:3 prohibits kindling fire on Shabbat. Numbers 15:32–33 reports that when the Israelites came upon a man gathering
wood
Wood is a structural tissue/material found as xylem in the stems and roots of trees and other woody plants. It is an organic materiala natural composite of cellulosic fibers that are strong in tension and embedded in a matrix of lignin t ...
on Shabbat, apparently with the intent to fuel a fire, they brought him before Moses,
Aaron
According to the Old Testament of the Bible, Aaron ( or ) was an Israelite prophet, a high priest, and the elder brother of Moses. Information about Aaron comes exclusively from religious texts, such as the Hebrew Bible, the New Testament ...
, and the community and placed him in custody, "because it had not been declared what should be done to him." Clearing up any uncertainty about whether the man had violated the law and what punishment should be given, God told Moses that the whole community was to
pelt him with stones outside the camp, which they did.
Commentators note that the Hebrew Bible repeats the commandment to observe the Sabbath 12 times.
Genesis 2:1–3 reports that on the seventh day of Creation, God finished God’s work, rested, blessed, and hallowed the seventh day.
Observance of the Sabbath is one of the
Ten Commandments
The Ten Commandments (), or the Decalogue (from Latin , from Ancient Greek , ), are religious and ethical directives, structured as a covenant document, that, according to the Hebrew Bible, were given by YHWH to Moses. The text of the Ten ...
. Exodus 20:8–11 commands that one remember the Sabbath day, keep it holy, and not do any manner of work or cause anyone under one’s control to work, for in six days God made heaven and earth and rested on the seventh day, blessed the Sabbath, and hallowed it. Deuteronomy 5:12–15 commands that one observe the Sabbath day, keep it holy, and not do any manner of work or cause anyone under one’s control to work — so that one’s subordinates might also rest — and remember that the Israelites were servants in the land of Egypt, and God brought them out with a mighty hand and by an outstretched arm.
In the incident of the
manna
Manna (, ; ), sometimes or archaically spelled Mahna or Mana, is described in the Bible and the Quran as an edible substance that God in Abrahamic religions, God bestowed upon the Israelites while they were wandering the desert during the 40-year ...
(, ''man'') in Exodus 16:22–30, Moses told the Israelites that the Sabbath is a solemn rest day; prior to the Sabbath one should cook what one would cook, and lay up food for the Sabbath. And God told Moses to let no one go out of one’s place on the seventh day.
In Exodus 31:12–17, just before giving Moses the second
Tablets of Stone
According to the Hebrew Bible, the Tablets of the Law (also Tablets of Stone, Stone Tablets, or Tablets of Testimony; Biblical Hebrew: לוּחֹת הַבְּרִית ''lūḥōṯ habbǝrīṯ'' "tablets of the covenant", לֻחֹת הָאֶבֶ ...
, God commanded that the Israelites keep and observe the Sabbath throughout their generations, as a sign between God and the children of Israel forever, for in six days God made heaven and earth, and on the seventh day God rested.
In Exodus 35:1–3, just before issuing the instructions for the
Tabernacle
According to the Hebrew Bible, the tabernacle (), also known as the Tent of the Congregation (, also Tent of Meeting), was the portable earthly dwelling of God used by the Israelites from the Exodus until the conquest of Canaan. Moses was instru ...
, Moses again told the Israelites that no one should work on the Sabbath, specifying that one must not kindle fire on the Sabbath.
In Leviticus 23:1–3, God told Moses to repeat the Sabbath commandment to the people, calling the Sabbath a holy convocation.
The
prophet
In religion, a prophet or prophetess is an individual who is regarded as being in contact with a divinity, divine being and is said to speak on behalf of that being, serving as an intermediary with humanity by delivering messages or teachings ...
Isaiah
Isaiah ( or ; , ''Yəšaʿyāhū'', "Yahweh is salvation"; also known as Isaias or Esaias from ) was the 8th-century BC Israelite prophet after whom the Book of Isaiah is named.
The text of the Book of Isaiah refers to Isaiah as "the prophet" ...
taught in
Isaiah
Isaiah ( or ; , ''Yəšaʿyāhū'', "Yahweh is salvation"; also known as Isaias or Esaias from ) was the 8th-century BC Israelite prophet after whom the Book of Isaiah is named.
The text of the Book of Isaiah refers to Isaiah as "the prophet" ...
1:12–13 that iniquity is inconsistent with the Sabbath. In Isaiah 58:13–14, the prophet taught that if people turn away from pursuing or speaking of business on the Sabbath and call the Sabbath a delight, then God will make them ride upon the high places of the earth and will feed them with the heritage of Jacob. And in Isaiah 66:23, the prophet taught that in times to come, from one Sabbath to another, all people will come to worship God.
The prophet
Jeremiah
Jeremiah ( – ), also called Jeremias, was one of the major prophets of the Hebrew Bible. According to Jewish tradition, Jeremiah authored the Book of Jeremiah, book that bears his name, the Books of Kings, and the Book of Lamentations, with t ...
taught in
Jeremiah
Jeremiah ( – ), also called Jeremias, was one of the major prophets of the Hebrew Bible. According to Jewish tradition, Jeremiah authored the Book of Jeremiah, book that bears his name, the Books of Kings, and the Book of Lamentations, with t ...
17:19–27 that the fate of
Jerusalem
Jerusalem is a city in the Southern Levant, on a plateau in the Judaean Mountains between the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean and the Dead Sea. It is one of the List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, oldest cities in the world, and ...
depended on whether the people abstained from work on the Sabbath, refraining from carrying burdens outside their houses and through the city gates.
The prophet
Ezekiel
Ezekiel, also spelled Ezechiel (; ; ), was an Israelite priest. The Book of Ezekiel, relating his visions and acts, is named after him.
The Abrahamic religions acknowledge Ezekiel as a prophet. According to the narrative, Ezekiel prophesied ...
told in
Ezekiel
Ezekiel, also spelled Ezechiel (; ; ), was an Israelite priest. The Book of Ezekiel, relating his visions and acts, is named after him.
The Abrahamic religions acknowledge Ezekiel as a prophet. According to the narrative, Ezekiel prophesied ...
20:10–22 how God gave the Israelites God’s Sabbaths, to be a sign between God and them, but the Israelites rebelled against God by profaning the Sabbaths, provoking God to pour out God’s fury upon them, but God stayed God’s hand.
In
Nehemiah
Nehemiah (; ''Nəḥemyā'', "Yahweh, Yah comforts") is the central figure of the Book of Nehemiah, which describes his work in rebuilding Jerusalem during the Second Temple period as the governor of Yehud Medinata, Persian Judea under Artaxer ...
13:15–22,
Nehemiah
Nehemiah (; ''Nəḥemyā'', "Yahweh, Yah comforts") is the central figure of the Book of Nehemiah, which describes his work in rebuilding Jerusalem during the Second Temple period as the governor of Yehud Medinata, Persian Judea under Artaxer ...
told how he saw some treading winepresses on the Sabbath, and others bringing all manner of burdens into Jerusalem on the Sabbath day, so when it began to be dark before the Sabbath, he commanded that the city gates be shut and not opened till after the Sabbath and directed the Levites to keep the gates to sanctify the Sabbath.
Exodus chapter 38
2 Chronicles
The Book of Chronicles ( , "words of the days") is a book in the Hebrew Bible, found as two books (1–2 Chronicles) in the Christian Old Testament. Chronicles is the final book of the Hebrew Bible, concluding the third section of the Jewish Tan ...
1:5–6 reports that the bronze altar, which Exodus 38:1–2 reports Bezalel made, still stood before the Tabernacle in
Solomon
Solomon (), also called Jedidiah, was the fourth monarch of the Kingdom of Israel (united monarchy), Kingdom of Israel and Judah, according to the Hebrew Bible. The successor of his father David, he is described as having been the penultimate ...
's time, and Solomon sacrificed a thousand burnt offerings on it.
Exodus 38:8 reports that Bezalel made the bronze laver and its base from "the mirrors of the serving women who did service at the door of the tent of meeting."
1 Samuel 2:22 reports that the
Shophet
In several ancient Semitic-speaking cultures and associated historical regions, the shopheṭ or shofeṭ (plural shophetim or shofetim; , , , the last loaned into Latin as sūfes; see also ) was a community leader of significant civic stature, o ...
Eli's sons "lay with the women who did service at the door of the tent of meeting."

In early nonrabbinic interpretation
The parashah has parallels or is discussed in these early nonrabbinic sources:
Exodus chapter 35
1 Maccabees
1 Maccabees, also known as the First Book of Maccabees, First Maccabees, and abbreviated as 1 Macc., is a deuterocanonical book which details the history of the Maccabean Revolt against the Seleucid Empire as well as the founding and earliest hi ...
tells a story related to the Sabbath. Verses 2:27–38 told how in the 2nd century BCE, many followers of the pious Jewish priest
Mattathias
Mattathias ben Johanan (, ''Mattīṯyāhū haKōhēn ben Yōḥānān''; died 166–165 BCE) was a Kohen (Jewish priest) who helped spark the Maccabean Revolt against the Hellenistic Seleucid Empire. Mattathias's story is related in the deuter ...
rebelled against the
Seleucid emperor Antiochus IV Epiphanes
Antiochus IV Epiphanes ( 215 BC–November/December 164 BC) was king of the Seleucid Empire from 175 BC until his death in 164 BC. Notable events during Antiochus' reign include his near-conquest of Ptolemaic Egypt, his persecution of the Jews of ...
. Antiochus; soldiers attacked a group of them on the Sabbath, and when the Pietists failed to defend themselves to honor the Sabbath (commanded in, among other places, Exodus 35:1–3), a thousand died. Veses 2:39–41 reported that when Mattathias and his friends heard, they reasoned that if they did not fight on the Sabbath, they would soon be destroyed. They decided that they would fight anyone who attacked them on the Sabbath.
Josephus
Flavius Josephus (; , ; ), born Yosef ben Mattityahu (), was a Roman–Jewish historian and military leader. Best known for writing '' The Jewish War'', he was born in Jerusalem—then part of the Roman province of Judea—to a father of pr ...
wrote that when the Israelites brought together the materials with great diligence, Moses set architects over the works by the command of God. And these were the very same people that the people themselves would have chosen, had the election been allowed to them: Bezalel, the son of Uri, of the
tribe of Judah
According to the Hebrew Bible, the tribe of Judah (, ''Shevet Yehudah'') was one of the twelve Tribes of Israel, named after Judah (son of Jacob), Judah, the son of Jacob. Judah was one of the tribes to take its place in Canaan, occupying it ...
, the grandson of
Miriam
Miriam (, lit. ‘rebellion’) is described in the Hebrew Bible as the daughter of Amram and Jochebed, and the older sister of Moses and Aaron. She was a prophetess and first appears in the Book of Exodus.
The Torah refers to her as "Miria ...
, the sister of Moses; and Oholiab, file son of
Ahisamach, of the
tribe of Dan
The Tribe of Dan (, "Judge") was one of the twelve tribes of Israel, according to the Torah. According to the Hebrew Bible, the tribe initially settled in the hill lands bordering Tribe of Ephraim, Ephraim and Tribe of Benjamin, Benjamin on the ...
.
Classical rabbinic interpretation
The parashah is discussed in these
rabbi
A rabbi (; ) is a spiritual leader or religious teacher in Judaism. One becomes a rabbi by being ordained by another rabbi—known as ''semikha''—following a course of study of Jewish history and texts such as the Talmud. The basic form of t ...
nic sources from the era of the
Mishnah
The Mishnah or the Mishna (; , from the verb ''šānā'', "to study and review", also "secondary") is the first written collection of the Jewish oral traditions that are known as the Oral Torah. Having been collected in the 3rd century CE, it is ...
and the
Talmud
The Talmud (; ) is the central text of Rabbinic Judaism and the primary source of Jewish religious law (''halakha'') and Jewish theology. Until the advent of Haskalah#Effects, modernity, in nearly all Jewish communities, the Talmud was the cen ...
:
Exodus chapter 35
The ''
Seder Olam Rabbah
''Seder Olam Rabbah'' (, "The Great Order of the World") is a 2nd-century CE Hebrew language chronology detailing the dates of biblical events from creation to Alexander the Great's conquest of Persia. It adds no stories beyond what is in the bi ...
'' taught that Moses descended from
Mount Sinai
Mount Sinai, also known as Jabal Musa (), is a mountain on the Sinai Peninsula of Egypt. It is one of several locations claimed to be the Mount Sinai (Bible), biblical Mount Sinai, the place where, according to the sacred scriptures of the thre ...
on the 10th of
Tishrei
Tishrei () or Tishri (; ''tīšrē'' or ''tīšrī''; from Akkadian ''tašrītu'' "beginning", from ''šurrû'' "to begin") is the first month of the civil year (which starts on 1 Tishrei) and the seventh month of the ecclesiastical year (wh ...
—
Yom Kippur
Yom Kippur ( ; , ) is the holiest day of the year in Judaism. It occurs annually on the 10th of Tishrei, corresponding to a date in late September or early October.
For traditional Jewish people, it is primarily centered on atonement and ...
—and announced that God had shown the Israelites God's pleasure, as Exodus 34:9 says, "You will forgive our crimes and sins and let us inherit," and after that, all the Israelites presented themselves in the assembly that Moses called in Exodus 35:1, and Moses commanded them to build the Tabernacle.
The ''
Mekhilta of Rabbi Ishmael
The Mekhilta of Rabbi Ishmael ( IPA , "a collection of rules of interpretation") is midrash halakha to the Book of Exodus. The Aramaic title ''Mekhilta'' corresponds to the Mishnaic Hebrew term ' "measure," "rule", and is used to denote a compi ...
'' taught that Exodus 35:1–3 sets forth laws of Sabbath observance here because in Exodus 25:8 God directed, "And let them make Me a sanctuary," and one might have understood that they could build the sanctuary both on weekdays and the Sabbath. The ''Mekhilta'' taught that God's direction in Exodus 25:8 to "make Me a sanctuary" applied on all days other than the Sabbath. The ''Mekhilta'' posited that one might argue that since the
Temple
A temple (from the Latin ) is a place of worship, a building used for spiritual rituals and activities such as prayer and sacrifice. By convention, the specially built places of worship of some religions are commonly called "temples" in Engli ...
service occurs even on the Sabbath, then perhaps the preparation for the service, without which the priests could not perform the service, could occur even on the Sabbath. One might conclude that if the horn of the altar broke off or a knife became defective, one might repair them on the Sabbath. Exodus 35:1–3 teaches, however, that even such work must be done only on weekdays, and not on the Sabbath.
Judah haNasi
Judah ha-Nasi (, ''Yəhūḏā hanNāsīʾ''; Yehudah HaNasi or Judah the Prince or Judah the President) or Judah I, known simply as Rebbi or Rabbi, was a second-century rabbi (a tannaim, tanna of the fifth generation) and chief redactor and e ...
taught that the words "These are the words" in Exodus 35:1 referred to the
39 Melakhot
The 39 ''Melakhot'' (, '' lamed-tet avot melakhah'', "39 categories of work") are thirty-nine categories of activity which Jewish law identifies as prohibited by biblical law on Shabbat. These activities are also prohibited on the Jewish holidays l ...
that God taught Moses at Mount Sinai. Similarly,
Hanina bar Hama
Hanina bar Hama (died c. 250) () was a Jewish Talmudist, halakhist and aggadist frequently quoted in the Babylonian and the Jerusalem Talmud, and in the Midrashim.
He is generally cited by the name R. Hanina, but sometimes with his patronymi ...
said that the labors forbidden on the Sabbath in Exodus 35:2 correspond to the 39 labors necessary to construct the Tabernacle.
Tractate
Shabbat
Shabbat (, , or ; , , ) or the Sabbath (), also called Shabbos (, ) by Ashkenazi Hebrew, Ashkenazim, is Judaism's day of rest on the seventh day of the seven-day week, week—i.e., Friday prayer, Friday–Saturday. On this day, religious Jews ...
in the Mishnah,
Tosefta
The Tosefta ( "supplement, addition") is a compilation of Jewish Oral Law from the late second century, the period of the Mishnah and the Jewish sages known as the '' Tannaim''.
Background
Jewish teachings of the Tannaitic period were cha ...
,
Jerusalem Talmud
The Jerusalem Talmud (, often for short) or Palestinian Talmud, also known as the Talmud of the Land of Israel, is a collection of rabbinic notes on the second-century Jewish oral tradition known as the Mishnah. Naming this version of the Talm ...
, and Babylonian Talmud interpreted the laws of the Sabbath in Exodus 16:23 and 29; 20:8–11; 23:12; 31:13–17; 35:2–3; Leviticus 19:3; 23:3; Numbers 15:32–36; and
Deuteronomy
Deuteronomy (; ) is the fifth book of the Torah (in Judaism), where it is called () which makes it the fifth book of the Hebrew Bible and Christian Old Testament.
Chapters 1–30 of the book consist of three sermons or speeches delivered to ...
5:12.
The Mishnah taught that every act that violates the law of the Sabbath also violates the law of a festival, except that one may prepare food on a festival but not on the Sabbath.
A
Midrash
''Midrash'' (;["midrash"]
. ''Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary''. ; or ''midrashot' ...
asked to which commandment Deuteronomy 11:22 refers when it says, "FIf, then, you faithfully keep all this Instruction that I command you, loving your God
יהוה
The TetragrammatonPronounced ; ; also known as the Tetragram. is the four-letter Hebrew-language theonym (transliterated as YHWH or YHVH), the name of God in the Hebrew Bible. The four Hebrew letters, written and read from right to left, ar ...
, walking in all God’s ways, and holding fast to
od...]". Rabbi Levi said that "this Instruction" refers to the recitation of the
Shema
''Shema Yisrael'' (''Shema Israel'' or ''Sh'ma Yisrael''; , “Hear, O Israel”) is a Jewish prayer (known as the Shema) that serves as a centerpiece of the morning and evening Jewish prayer services. Its first verse encapsulates the monothe ...
(Deuteronomy 6:4–9), but the rabbis said that it refers to the Sabbath, which is equal to all the precepts of the Torah.
The ''
Alphabet of Rabbi Akiva'' taught that when God was giving Israel the Torah, God told them that if they accepted the Torah and observed God's commandments, then God would give them for eternity a most precious thing that God possessed — the
World To Come
The world to come, age to come, heaven on Earth, and the Kingdom of God are eschatology, eschatological phrases reflecting the belief that the World (theology), current world or Dispensation (period), current age is flawed or cursed and will be r ...
. When Israel asked to see in this world an example of the World To Come, God replied that the Sabbath is an example of the World To Come.
Reading the words "One who profanes it shall be put to death" in Exodus 31:14 (in which the verb for death is doubled),
Samuel of Nehardea
Samuel of Nehardea or Samuel bar Abba, often simply called Samuel (Hebrew: שמואל) and occasionally Mar Samuel, was a Jewish Amora of the first generation; son of Abba bar Abba and head of the Yeshiva at Nehardea, Babylonia. He was a teach ...
deduced that the Torah decreed many deaths for desecrating the Sabbath. The Gemara posited that perhaps Exodus 31:14 refers to willful desecration. The Gemara answered that Exodus 31:14 is not needed to teach that willful transgression of the Sabbath is a capital crime, for Exodus 35:2 says, "whoever does any work on it shall be put to death." The Gemara concluded that Exodus 31:14 thus must apply to an unwitting offender, and in that context, the words "shall be put to death" mean that the inadvertent Sabbath violator will "die" monetarily because of the violator's need to bring costly sacrifices.
A
baraita
''Baraita'' ( "external" or "outside"; pl. ''bārayāṯā'' or in Hebrew ''baraitot''; also baraitha, beraita; Ashkenazi pronunciation: berayse) designates a tradition in the Oral Torah of Rabbinical Judaism that is not incorporated in the Mi ...
read the words "You shall kindle no fire throughout your settlements on the sabbath day" in Exodus 35:3 to teach that only on the Sabbath is kindling fire prohibited, and one may kindle fire on a
festival day, including for purposes other than food preparation.

Rav Huna
Rav Huna (Hebrew: רב הונא) was a Jewish Talmudist and Exilarch who lived in Babylonia, known as an amora of the second generation and head of the Academy of Sura; he was born about 216 CE (212 CE according to Gratz) and died in 296–297 ...
and
Rav Ḥisda reconciled the prohibition of kindling fire on the Sabbath in Exodus 35:3 with the priests' sacrificial duties. The Mishnah taught that the priests could lower the
Passover sacrifice
The Passover sacrifice (), also known as the Paschal lamb or the Passover lamb, is the sacrifice that the Torah mandates the Israelites to ritually slaughter on the evening of Nisan 14, before Passover of Nisan 15, and eat lamb on the first night ...
into the oven just before nightfall (and leave it to roast on the Sabbath), and the priests could light the fire with chips in the pile in the Temple chamber of the hearth (just before nightfall). Interpreting this Mishnah, Rav Huna cited the prohibition of Exodus 35:3: "You shall kindle no fire throughout your habitations." Rav Huna argued that since Exodus 35:3 says only "throughout your habitations," the priests could kindle the pile in the Temple chamber of the hearth (even on the Sabbath). Rav Ḥisda demurred from Rav Huna's argument, as it would allow kindling even on the Sabbath. Rather, Rav Ḥisda taught that Exodus 35:3 permits only the burning of the limbs and the fat (of animals sacrificed on Friday before nightfall). Rav Ḥisda explained that this burning was allowed because the priests were very particular (in their observance of the Sabbath and would not stoke the fire after nightfall).
The Gemara told that
Rav Joseph's wife used to kindle the Sabbath lights late (just before nightfall). Rav Joseph told her that it was taught in a Baraita that the words of Exodus 13:22, "the pillar of cloud by day, and the pillar of fire by night, departed not," teach that the pillar of cloud overlapped the pillar of fire, and the pillar of fire overlapped the pillar of cloud. So she thought of lighting the Sabbath lights very early. But an elder told her that one may kindle when one chooses, provided that one does not light too early (as it would not evidently honor the Sabbath) or too late (later than just before nightfall).
A Baraita taught that a disciple in the name of
Rabbi Ishmael
Rabbi Yishmael ben Elisha Nachmani (Hebrew: רבי ישמעאל בן אלישע), often known as Rabbi Yishmael and sometimes given the title "Ba'al HaBaraita" (Hebrew: בעל הברייתא, “Master of the Outside Teaching”), was a rabbi of ...
noted that the words "in all your dwellings" (, ''b'chol moshvoteichem'') appear both in the phrase, "You shall kindle no fire throughout your habitations upon the Sabbath day," in Exodus 35:3 and in the phrase, "these things shall be for a statute of judgment unto you throughout your generations in all your dwellings," in Numbers 35:29. The Baraita reasoned from this similar usage that just as the law prohibits kindling fire at home, so the law also prohibits kindling fire in the furtherance of criminal justice. And thus, since some executions require kindling a fire, the Baraita taught that the law prohibits executions on the Sabbath.
Rabbi Hama bar Hanina interpreted the words "the plaited (, ''serad'') garments for ministering in the holy place" in Exodus 35:19 to teach that but for the priestly garments described in Exodus 28 (and the atonement achieved by the garments or the priests who wore them), no remnant (, ''sarid'') of the Jews would have survived.

Rabbi Levi read Exodus 26:28, regarding "the middle bar in the midst of the boards, which shall pass through from end to end," calculated that the beam must have been 32 cubits in length, and asked where the Israelites would find such a beam in the desert. Rabbi Levi deduced that the Israelites had stored up the cedar to construct the Tabernacle since the days of
Jacob
Jacob, later known as Israel, is a Hebrew patriarch of the Abrahamic religions. He first appears in the Torah, where he is described in the Book of Genesis as a son of Isaac and Rebecca. Accordingly, alongside his older fraternal twin brother E ...
. Thus Exodus 35:24 reports, "And every man, with whom ''was found'' acacia-wood," not "with whom ''would be found'' acacia-wood." Rabbi Levi taught that the Israelites cut the trees down in
Magdala
Magdala (; ; ) was an ancient Jews, Jewish city on the shore of the Sea of Galilee, north of Tiberias. In the Babylonian Talmud it is known as Magdala Nunayya (), and which some historical geographers think may refer to Tarichaea (). It is belie ...
of the Dyers near
Tiberias
Tiberias ( ; , ; ) is a city on the western shore of the Sea of Galilee in northern Israel. A major Jewish center during Late Antiquity, it has been considered since the 16th century one of Judaism's Four Holy Cities, along with Jerusalem, Heb ...
and brought them with them to
Egypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northe ...
, and no knot or crack was found in them.
The Rabbis taught in a Baraita that the Tabernacle's lower curtains were made of blue wool, purple wool, crimson wool, and fine linen, while the upper curtains that made the tent spread were made of goats' hair. And they taught that the upper curtains required greater skill than the lower, for Exodus 35:25 says of the lower ones, "And all the women that were wise-hearted did spin with their hands," while Exodus 35:26 says of the upper ones, "And all the women whose heart stirred them up in wisdom spun the goats." It was taught in Rabbi Nehemiah's name that the hair was washed on the goats and spun while still on the goats.
 Rabbi Isaac Nappaha
Rabbi Isaac Nappaha deduced from Exodus 35:30 that we must not appoint a leader over a community without first consulting the community. In Exodus 35:30, Moses said to the Israelites: "See, the Lord has called by name Bezalel, the son of Uri." Rabbi Isaac read Exodus 35:30 to indicate that God asked Moses whether Moses considered Bezalel suitable. Moses replied that if God thought Bezalel suitable, then surely Moses would have to, as well. God told Moses nonetheless to go and consult the Israelites. Moses asked the Israelites whether they considered Bezalel suitable. And they replied that if God and Moses considered him suitable, surely they had to, as well.
Johanan bar Nappaha
:''See Johanan (name) for more rabbis by this name''.
Johanan bar Nappaha ( Yoḥanan bar Nafḥa or Napaḥa), also known simply as Rabbi Yochanan or Johanan bar Nafcha (180–279 CE), was a leading rabbi and second-generation '' Amora'' duri ...
taught that God proclaims three things for God's Self: famine, plenty, and a good leader.
2 Kings
The Book of Kings (, '' Sēfer Məlāḵīm'') is a book in the Hebrew Bible, found as two books (1–2 Kings) in the Old Testament of the Christian Bible. It concludes the Deuteronomistic history, a history of ancient Israel also including ...
8:1 shows that God proclaims famine, when it says: "The Lord has called for a famine." Ezekiel 36:29 shows that God proclaims plenty, when it says: "I will call for the corn and will increase it." And Exodus 31:1–2 shows that God proclaims a good leader, when it says: "And the Lord spoke to Moses, saying, ‘See I have called by name Bezalel, the son of Uri.'"
Samuel ben Nahman
Samuel ben Nahman (), or Samuel arNahmani (), was a rabbi and amora mentioned throughout the Talmud and Midrashic literature who lived in the Land of Israel from the beginning of the 3rd century CE until the start of the 4th century CE.
Biograp ...
said in the name of Johanan that Bezalel (, whose name can be read , ''betzel El'', "in the shadow of God") was so called because of his wisdom.
When God told Moses (in Exodus 31:7) to tell Bezalel to make a tabernacle, an ark, and vessels, Moses reversed the order and told Bezalel to make an ark, vessels, and a tabernacle. Bezalel replied to Moses that as a rule, one first builds a house and then brings vessels into it, but Moses directed to make an ark, vessels, and a tabernacle. Bezalel asked where he would put the vessels. And Bezalel asked whether God had told Moses to make a tabernacle, an ark, and vessels. Moses replied that perhaps Bezalel had been in the shadow of God (, ''betzel El'') and had thus come to know this.
[Babylonian Talmud Berakhot 55a]
The ''
Tanḥuma bar Abba'' taught in the name of Rav Huna that even the things that Bezalel did not hear from Moses he conceived of on his own exactly as they were told to Moses from Sinai. Rabbi Tanḥuma said in the name of Rav Huna that one can deduce this from the words of Exodus 38:22, "And Bezalel the son of Uri, the son of Hur, of the tribe of Judah, made all that the Lord commanded Moses." For Exodus 38:22 does not say, "that ''Moses'' commanded ''him''," but, "that ''the Lord'' commanded ''Moses''."
And the
Agadat Shir ha-Shirim taught that Bezalel and Oholiab went up Mount Sinai, where the heavenly Sanctuary was shown to them.
A
midrash
''Midrash'' (;["midrash"]
. ''Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary''. ; or ''midrashot' ...
interpreted Exodus 35:30 in light of
Ecclesiastes
Ecclesiastes ( ) is one of the Ketuvim ('Writings') of the Hebrew Bible and part of the Wisdom literature of the Christian Old Testament. The title commonly used in English is a Latin transliteration of the Greek translation of the Hebrew word ...
7:1, "A good name is better than precious oil." The midrash taught that name of Bezalel was better than precious oil, as Exodus 35:30 proclaims his fame when it says, "See, the Lord has called by name Bezalel." (God proclaimed the name of Bezalel as the Divine architect, while Moses proclaimed the priest as such by anointing with oil.)
Reading the words, "see, the Lord has called by name Bezalel," in Exodus 35:30, a midrash explained that Israel sinned with fire in making the
Golden Calf
According to the Torah, the Bible, and the Quran, the golden calf () was a cult image made by the Israelites when Moses went up to Mount Sinai (bible), Mount Sinai. In Hebrew, the incident is known as "the sin of the calf" (). It is first mentio ...
, as Exodus 32:24 says, "And I cast it into the fire, and there came out this calf." And then Bezalel came and healed the wound (and the construction of the Tabernacle made atonement for the sins of the people in making the Golden Calf). The midrash likened it to the words of
Isaiah
Isaiah ( or ; , ''Yəšaʿyāhū'', "Yahweh is salvation"; also known as Isaias or Esaias from ) was the 8th-century BC Israelite prophet after whom the Book of Isaiah is named.
The text of the Book of Isaiah refers to Isaiah as "the prophet" ...
54:16, "Behold, I have created the smith who blows the fire of coals." The midrash taught that Bezalel was the smith whom God had created to address the fire. And the midrash likened it to the case of a doctor's disciple who applied a plaster to a wound and healed it. When people began to praise him, his teacher, the doctor, said that they should praise the doctor, for he taught the disciple. Similarly, when everybody said that Bezalel had constructed the Tabernacle through his knowledge and understanding, God said that it was God who created him and taught him, as Isaiah 54:16 says, "Behold, I have created the smith." Thus, Moses said in Exodus 35:30, "see, the Lord has called by name Bezalel."
Exodus 35:30 identifies Bezalel's grandfather as Hur, whom either
Abba Arikha
Rav Abba bar Aybo (; 175–247 CE), commonly known as Abba Arikha () or simply as Rav (), was a Jewish amora of the 3rd century. He was born and lived in Kafri, Asoristan, in the Sasanian Empire.
In Sura, Arikha established the systematic st ...
or Samuel deduced was the son of Miriam and
Caleb
Caleb ( ; , Tiberian vocalization: , Modern Israeli Hebrew: ) is a figure who appears in the Hebrew Bible as a representative of the Tribe of Judah during the Israelites' journey to the Promised Land.
Following the Israelite conquest of Ca ...
. A midrash explained that Exodus 35:30 mentions Hur because when the Israelites were about to serve the
Golden Calf
According to the Torah, the Bible, and the Quran, the golden calf () was a cult image made by the Israelites when Moses went up to Mount Sinai (bible), Mount Sinai. In Hebrew, the incident is known as "the sin of the calf" (). It is first mentio ...
, Hur risked his life on God's behalf to prevent them from doing so, and they killed him. Whereupon God assured Hur that God would repay him for his sacrifice.
The midrash likened it to the case of a king whose legions rebelled against him, and his field marshal fought against the rebels, questioning how they could dare rebel against the king. In the end, the rebels killed the field marshal. The king reasoned that if the field marshal had given the king money, the king would have had to repay him. So even more so the king had an obligation to repay the field marshal when he gave his life on the king's behalf. The king rewarded the field marshal by ordaining that all his male offspring would become generals and officers.
Similarly, when Israel made the Golden Calf, Hur gave his life for the glory of God. Thus God assured Hur that God would give all Hur's descendants a great name in the world. And thus Exodus 35:30 says, "see, the Lord has called by name Bezalel, the son of Uri, the son of Hur."
Judah bar Ezekiel
Judah bar Ezekiel (220–299 CE) () often known as Rav Yehudah, was a Babylonian amora of the 2nd generation.
Biography
Judah was the most prominent disciple of Rav, in whose house he often stayed, and whose son Hiyya b. Rav was his pupil. Af ...
taught in the name of Abba Arikha that Exodus 35:31 indicated that God endowed Bezalel with the same attribute that God used in creating the universe. Judah said in the name of Abba Arikha that Bezalel knew how to combine the letters by which God created the heavens and earth. For Exodus 35:31 says (about Bezalel), "And He has filled him with the spirit of God, in wisdom and in understanding, and in knowledge," and
Proverbs
A proverb (from ) or an adage is a simple, traditional saying that expresses a perceived truth based on common sense or experience. Proverbs are often metaphorical and are an example of formulaic language. A proverbial phrase or a proverbial ...
3:19 says (about creation), "The Lord by wisdom founded the earth; by understanding He established the heavens," and Proverbs 3:20 says, "By His knowledge the depths were broken up."
[
A midrash taught that God considers studying the sanctuary’s structure as equivalent to rebuilding it.
]
Exodus chapter 36
Doing the math implied by Exodus 36:4, Exodus 38:22, Joshua
Joshua ( ), also known as Yehoshua ( ''Yəhōšuaʿ'', Tiberian Hebrew, Tiberian: ''Yŏhōšuaʿ,'' Literal translation, lit. 'Yahweh is salvation'), Jehoshua, or Josue, functioned as Moses' assistant in the books of Book of Exodus, Exodus and ...
14:7, and 1 Chronicles 2:19–20, the Gemara deduced that in earlier generations, a boy of eight could father children. Exodus 38:22 reports that "Bezalel, son of Uri, son of Hur, of the tribe of Judah, made all that the Lord had commanded Moses," when they built the Tabernacle. And 1 Chronicles 2:19–20 reports that Caleb fathered the Hur who fathered Uri who fathered Bezalel. Exodus 36:4 reports that "wise men . . . wrought all the work of the Sanctuary," so Bezalel must have been at least 13 years old to have been a man when he worked on the Tabernacle. A Baraita taught that Moses made the Tabernacle in the first year after the Exodus, and in the second, he erected it and sent out the spies, so the Gemara deduced that Bezalel must have been at least 14 years old when Moses sent out the spies, the year after Bezalel worked on the Tabernacle. And Joshua 14:7 reports that Caleb said that he was 40 years old when Moses sent him to spy out the land. Thus, the Gemara deduced that Caleb was only 26 years older than his great-grandson Bezalel. Deducting two years for the three pregnancies needed to create the three intervening generations, the Gemara concluded that each of Caleb, Hur, and Uri must have conceived his son at the age of eight.
Exodus chapter 37
A midrash taught that the righteous learn from God's example in creating the world that in beginning any work they should start with light. Thus when God told Moses to build the Tabernacle, Bezalel pondered with what thing he should begin. He concluded that he had better start with the Ark (in which the Israelites would deposit the Torah, the light of the world). And thus Exodus 37:1 commences the report of the construction of the Tabernacle's furnishings, "And Bezalel made the Ark."
Similarly, a midrash taught that when God told Moses to make the Tabernacle, he came to Bezalel and conveyed the command, and Bezalel asked what the purpose of the Tabernacle was. Moses replied that it was so that God might make God's Shechinah
Shekhinah () is the English transliteration of a Hebrew word meaning "dwelling" or "settling" and denotes the presence of God in a place. This concept is found in Judaism from Talmudic literature.
The word "Shekhinah" is found in the Bible onl ...
to dwell there and teach the Torah to Israel. Bezalel then asked where the Israelites would keep the Torah. Moses replied that when they had made the Tabernacle, they would then make the Ark. Then Bezalel said that since it would not be fitting for the Torah to be without a home, they should first make the Ark and then the Tabernacle. On that account, Exodus 37:1 associates Bezalel's name with the Ark, saying, "And Bezalel made the Ark."
Reading the words, "Bezalel made the Ark of acacia-wood," in Exodus 37:1, a midrash taught that God heals with the very thing with which God wounds. Thus, Israel sinned in Shittim (so called because of its many acacia trees), as Numbers 25:1 says, "And Israel abode in Shittim, and the people began to commit harlotry with the daughters of Moab" (and also worshipped the Baal of Peor). But it was also through Shittim wood, or acacia-wood, that God healed the Israelites, for as Exodus 37:1 reports, "Bezalel made the Ark of acacia-wood."
A Baraita taught that Josiah
Josiah () or Yoshiyahu was the 16th king of Judah (–609 BCE). According to the Hebrew Bible, he instituted major religious reforms by removing official worship of gods other than Yahweh. Until the 1990s, the biblical description of Josiah’s ...
hid away the Ark referred to in Exodus 37:1–5, the anointing oil referred to in Exodus 30:22–33, the jar of manna
Manna (, ; ), sometimes or archaically spelled Mahna or Mana, is described in the Bible and the Quran as an edible substance that God in Abrahamic religions, God bestowed upon the Israelites while they were wandering the desert during the 40-year ...
referred to in Exodus 16:33, Aaron's rod with its almond
The almond (''Prunus amygdalus'', Synonym (taxonomy)#Botany, syn. ''Prunus dulcis'') is a species of tree from the genus ''Prunus''. Along with the peach, it is classified in the subgenus ''Amygdalus'', distinguished from the other subgenera ...
s and blossoms referred to in Numbers 17:23, and the coffer that the Philistines
Philistines (; LXX: ; ) were ancient people who lived on the south coast of Canaan during the Iron Age in a confederation of city-states generally referred to as Philistia.
There is compelling evidence to suggest that the Philistines origi ...
sent the Israelites as a gift along with the Ark and concerning which the priests said in 1 Samuel 6:8, "And put the jewels of gold, which you returned Him for a guilt offering, in a coffer by the side thereof f the Ark and send it away that it may go." Having observed that Deuteronomy 28:36 predicted, "The Lord will bring you and your king . . . to a nation that you have not known," Josiah ordered the Ark hidden away, as 2 Chronicles 35:3 reports, "And he osiahsaid to the Levite
Levites ( ; ) or Levi are Jewish males who claim patrilineal descent from the Tribe of Levi. The Tribe of Levi descended from Levi, the third son of Jacob and Leah. The surname ''Halevi'', which consists of the Hebrew definite article "" ''Ha-' ...
s who taught all Israel, that were holy to the Lord, ‘Put the Holy Ark into the house that Solomon the son of David
David (; , "beloved one") was a king of ancient Israel and Judah and the third king of the United Monarchy, according to the Hebrew Bible and Old Testament.
The Tel Dan stele, an Aramaic-inscribed stone erected by a king of Aram-Dam ...
, King of Israel, built; there shall no more be a burden upon your shoulders; now serve the Lord your God and his people Israel.’" Rabbi Eleazar deduced that Josiah hid the anointing oil and the other objects at the same time as the Ark from the common use of the expressions "there" in Exodus 16:33 with regard to the manna and "there" in Exodus 30:6 with regard to the Ark, "to be kept" in Exodus 16:33 with regard to the manna and "to be kept" in Numbers 17:25 with regard to Aaron's rod, and "generations" in Exodus 16:33 with regard to the manna and "generations" in Exodus 30:31 with regard to the anointing oil.
Exodus chapter 38
A midrash explained the mirrors of the women who "performed tasks" (, ''ha-tzovot'') at the entrance of the Tent of Meeting in Exodus 38:8. The midrash told that when the Israelites were suffering hard labor in Egypt, Pharaoh decreed that they should not sleep at home or have sexual relations with their wives. Rabbi Shimon ben Halafta told that the Israelite women would go down to draw water from the river, whereupon God caused them to draw up small fish in their pitchers. The Israelite women would sell some of the fish, cook some of them, buy wine with the proceeds, and go out to the work fields to feed their husbands. After they had eaten, the Israelite women took their mirrors and looked into them together with their husbands. The wives would say that they were better looking than the husbands. The husbands would say that they were better looking. And in this way, they aroused their sexual desire and became fruitful and multiplied, as Exodus 1:7 reports, "And the children of Israel were fruitful and swarmed and multiplied and became exceedingly mighty." It was through the use of these mirrors that the Israelites were able to continue to have children even under the demands of harsh labor. When God told Moses to make the Tabernacle, all of the men came to contribute. Some brought silver, some brought gold or brass, onyx, and other gems to be set. They readily brought everything. The women brought the mirrors and presented them to Moses. When Moses saw the mirrors, he was furious with the women, saying that whoever brought the mirrors should be punished, asking what possible use they could have in the Tabernacle. God told Moses not to look down on them, for it was those mirrors that raised up all of the hosts of children born in Egypt. God thus directed Moses to take them and make from them the washbasin and its base for the priests.
In medieval Jewish interpretation
The parashah is discussed in these medieval
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of World history (field), global history. It began with the fall of the West ...
Jewish sources:

Exodus chapter 35
In the Zohar
The ''Zohar'' (, ''Zōhar'', lit. "Splendor" or "Radiance") is a foundational work of Kabbalistic literature. It is a group of books including commentary on the mystical aspects of the Torah and scriptural interpretations as well as material o ...
, Rabbi Jose expounded on Exodus 35:10: "And let every wise-hearted man among you come and make all that the Lord has commanded." Rabbi Jose taught that when God told Moses in Deuteronomy 1:13, "Get you wise men and men of discernment," Moses searched all of Israel but did not find men of discernment, and so in Deuteronomy 1:15, Moses said, "So I took the heads of your tribes, wise men, and full of knowledge," without mentioning men of discernment. Rabbi Jose deduced that the man of discernment (''navan'') is of a higher degree than the wise man (''hacham''), for even a pupil who gives new ideas to a teacher is called "wise." A wise man knows for himself as much as is required, but the man of discernment apprehends the whole, knowing both his own point of view and that of others. Exodus 35:10 uses the term "wise-hearted" because the heart was seen to be the seat of wisdom. Rabbi Jose taught that the man of discernment apprehends the lower world and the upper world, his own being and the being of others.
In modern interpretation
The parashah is discussed in these modern sources:
Exodus chapters 35–39
 Noting that Exodus 35–39 repeats material from Exodus 25–31,
Noting that Exodus 35–39 repeats material from Exodus 25–31, Julius Popper
Julius Popper (December 15, 1857 – June 5, 1893), known in Spanish as Julio Popper (), was a Romanian Jew and later Argentinian colonial engineer and explorer. He was known as a modern "conquistador" of Tierra del Fuego in southern South Amer ...
argued that Exodus 35–39 was a later addition, and the Dutch
Dutch or Nederlands commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
** Dutch people as an ethnic group ()
** Dutch nationality law, history and regulations of Dutch citizenship ()
** Dutch language ()
* In specific terms, i ...
Protestant
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that emphasizes Justification (theology), justification of sinners Sola fide, through faith alone, the teaching that Salvation in Christianity, salvation comes by unmerited Grace in Christianity, divin ...
theologian
Theology is the study of religious belief from a religious perspective, with a focus on the nature of divinity. It is taught as an academic discipline, typically in universities and seminaries. It occupies itself with the unique content of ...
Abraham Kuenen
Abraham Kuenen (16 September 1828 – 10 December 1891) was a Dutch Protestant theologian.
Kuenen was born in Haarlem, the son of an apothecary. On his father's death it became necessary for him to leave school and take a humble place in the busi ...
and the German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany, the country of the Germans and German things
**Germania (Roman era)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizenship in Germany, see also Ge ...
biblical scholar
Biblical studies is the academic application of a set of diverse disciplines to the study of the Bible, with ''Bible'' referring to the books of the canonical Hebrew Bible in mainstream Jewish usage and the Christian Bible including the can ...
Julius Wellhausen
Julius Wellhausen (17 May 1844 – 7 January 1918) was a German biblical scholar and orientalist. In the course of his career, his research interest moved from Old Testament research through Islamic studies to New Testament scholarship. Wellhau ...
agreed. But the mid-20th-century Italian
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, a Romance ethnic group related to or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance languag ...
- Israeli scholar Umberto Cassuto
Umberto Cassuto, also known as Moshe David Cassuto (16 September 1883 – 19 December 1951), was an Italian historian, a rabbi, and a scholar of the Hebrew Bible and Ugaritic literature, in the University of Florence, then at the University ...
, formerly of the Hebrew University of Jerusalem
The Hebrew University of Jerusalem (HUJI; ) is an Israeli public university, public research university based in Jerusalem. Co-founded by Albert Einstein and Chaim Weizmann in July 1918, the public university officially opened on 1 April 1925. ...
, argued that this conjecture was ignorant of ancient Eastern literary style. Cassuto noted that the theme of the founding and building of a shrine was a set literary type in early Eastern writings, and such passages often first recorded the divine utterance describing the plan for the sanctuary and then gave an account of the construction that repeated the description given in the divine communication. Cassuto cited the Ugaritic
Ugaritic () is an extinct Northwest Semitic languages, Northwest Semitic language known through the Ugaritic texts discovered by French archaeology, archaeologists in 1928 at Ugarit, including several major literary texts, notably the Baal cycl ...
epic of King Keret, which tells that in a dream, the king received from the god El instructions for the offering of sacrifices, the mustering of an army, the organizing of a military campaign to the land of King Pabel, and the request that Pabel's daughter or granddaughter be given him as a wife. After the instructions, the epic repeats the instructions, varying only the verb forms to the past tense, adding or deleting a conjunction, substituting a synonym, or varying the sequence of words—exactly as Exodus 35–39 does. Cassuto concluded that Exodus 35–39 was thus not a later addition, but required where it is by the literary style. Professor James Kugel
James L. Kugel (Hebrew: Yaakov Kaduri, יעקב כדורי; born August 22, 1945) is professor emeritus in the Bible department at Bar Ilan University in Israel and the Harry M. Starr Professor Emeritus of Classical and Modern Hebrew Literature at ...
of Bar Ilan University
Bar-Ilan University (BIU, , ''Universitat Bar-Ilan'') is a public research university in the Tel Aviv District city of Ramat Gan, Israel. Established in 1955, Bar Ilan is Israel's second-largest academic university institution. It has 20,000 ...
wrote that the detailed account must have held a fascination for ancient Israelites who viewed the Tabernacle as highly significant, as the structure that allowed God to reside in the midst of humankind for the first time since the Garden of Eden
In Abrahamic religions, the Garden of Eden (; ; ) or Garden of God ( and ), also called the Terrestrial Paradise, is the biblical paradise described in Genesis 2–3 and Ezekiel 28 and 31..
The location of Eden is described in the Book of Ge ...
. And Gunther Plaut
Wolf Gunther Plaut, (November 1, 1912 – February 8, 2012) was an American Reform rabbi and writer who was based in Canada. Plaut was the rabbi of Holy Blossom Temple in Toronto for several decades and since 1978 was its senior scholar.
...
cautioned not to approach Exodus 35–39 with modern stylistic prejudices, arguing that a person of the ancient Near East—who was primarily a listener, not a reader—found repetition a welcome way of supporting familiarity with the text, giving assurance that the tradition had been faithfully transmitted.

Exodus chapter 35
Plaut noted that this important chapter in Israel's wilderness story—the order to construct the Tabernacle—begins in Exodus 35:1 with the words "Moses then convoked" (, ''vayakheil Mosheh''), heralding the conclusion of the cycle of apostasy and reconciliation that started in Exodus 32:1 with a word with the same spelling and root, "the people gathered themselves" (, ''vayikheil ha-am''). In Exodus 32:1, the people assembled to rebel against God's desires in the incident of the Golden Calf, but in Exodus 35:1, with an assembling (, ''vayakheil'') that God approved, God demonstrated God's forgiving grace.[W. Gunther Plaut. ''The Torah: A Modern Commentary: Revised Edition''. Revised edition edited by David E.S. Stern, page 611.]
Plaut noted that the command to observe the Sabbath in Exodus 35:2–3 preceded the account of the Tabernacle's construction just as it had been commanded at the end of the original instructions in Exodus 31:12–17, so the Sabbath was the bridge that connected the building of the Tabernacle with its deeper purpose.[ Nahum Sarna wrote that the injunction to observe the Sabbath in Exodus 35:2–3 practically repeats Exodus 31:15 verbatim, with an addition not to kindle fire on the Sabbath. The wording of this prohibition led the Rabbis of the Talmud to understand that fire may not be kindled on the Sabbath itself but may be lit before the Sabbath if not refueled on the Sabbath. The Karaites rejected this interpretation and spent the day without lights (although some later adherents did accept the Rabbinic practice). Sarna wrote that it was probably to demonstrate opposition to the early Karaite view that the Rabbis mandated lighting candles on Friday nights, and to that end, the ]Geonim
''Geonim'' (; ; also Romanization of Hebrew, transliterated Gaonim, singular Gaon) were the presidents of the two great Talmudic Academies in Babylonia, Babylonian Talmudic Academies of Sura Academy , Sura and Pumbedita Academy , Pumbedita, in t ...
(the post-Talmudic heads of the Babylonian academies) instituted the recital of a blessing over them.
Plaut argued that Exodus 35:3 includes the words "throughout your settlements" to make clear that the injunction not to kindle fire on the Sabbath applied not only to the primary prohibition during the building of the Tabernacle, but also in general. Thus Numbers 15:32, reporting a man gathering sticks on the Sabbath, recorded a violation of Exodus 35:3.
In 1950, the Committee on Jewish Law and Standards
The Committee on Jewish Law and Standards is the central authority on halakha (Jewish law and tradition) within Conservative Judaism; it is one of the most active and widely known committees on the Conservative movement's Rabbinical Assembly. Wit ...
of Conservative Judaism
Conservative Judaism, also known as Masorti Judaism, is a Jewish religious movements, Jewish religious movement that regards the authority of Jewish law and tradition as emanating primarily from the assent of the people through the generations ...
ruled: “Refraining from the use of a motor vehicle is an important aid in the maintenance of the Sabbath spirit of repose. Such restraint aids, moreover, in keeping the members of the family together on the Sabbath. However where a family resides beyond reasonable walking distance from the synagogue, the use of a motor vehicle for the purpose of synagogue attendance shall in no wise be construed as a violation of the Sabbath but, on the contrary, such attendance shall be deemed an expression of loyalty to our faith. . . . the spirit of a living and developing Halachah responsive to the changing needs of our people, we declare it to be permitted to use electric lights on the Sabbath for the purpose of enhancing the enjoyment of the Sabbath, or reducing personal discomfort in the performance of a mitzvah.” In 2023, the Committee on Jewish Law and Standards reexamined the issue of driving on Shabbat and concluded that using an electric car for Shabbat purposes is not a violation of Shabbat, although the Committee encouraged walking or riding a bicycle, when possible.
Professor Carol Meyers
Carol Lyons Meyers (born 1942) is an American feminist biblical scholar. She is the Mary Grace Wilson Professor Emerita of Religious Studies at Duke University. Meyers' field of research is focused on biblical studies, archaeology in the Middle Ea ...
of Duke University
Duke University is a Private university, private research university in Durham, North Carolina, United States. Founded by Methodists and Quakers in the present-day city of Trinity, North Carolina, Trinity in 1838, the school moved to Durham in 1 ...
noted that both women and men provided the materials to which Exodus 25:1–9 and Exodus 35:4–29 refer, as Exodus 35:22 and 29 make clear, including fabrics made and donated by women craftspersons (as indicated in Exodus 35:25–26).
Jeffrey Tigay, Professor Emeritus at the University of Pennsylvania
The University of Pennsylvania (Penn or UPenn) is a Private university, private Ivy League research university in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, United States. One of nine colonial colleges, it was chartered in 1755 through the efforts of f ...
, argued that the word , ''avodah'', in Exodus 35:21, translated as "service" in the New Jewish Publication Society translation (as well as in Exodus 27:19; 30:16; 35:24; 36:1, 3, 5; and 39:40) is better rendered "labor" (referring to construction), as the materials contributed were for the construction of the Tabernacle, not for the worship that would be conducted there afterwards.
Exodus chapter 37
Exodus 37:24 speaks of "a talent of pure gold." This table translates units of weight used in the Bible into their modern equivalents:

Commandments
According to Maimonides
Moses ben Maimon (1138–1204), commonly known as Maimonides (, ) and also referred to by the Hebrew acronym Rambam (), was a Sephardic rabbi and Jewish philosophy, philosopher who became one of the most prolific and influential Torah schola ...
and Sefer ha-Chinuch
''Sefer ha-Chinuch'' (, "Book of Education") is a rabbinic text which systematically discusses the 613 commandments of the Torah. It was written in 13th-century Spain by an anonymous "Levite of Barcelona".
Content
The work's enumeration of th ...
, there is one negative commandment
Commandment may refer to:
* The Ten Commandments
* One of the 613 mitzvot of Judaism
* The Great Commandment
* The New Commandment
* Commandment (album), ''Commandment'' (album), a 2007 album by Six Feet Under
* Commandments (film), ''Commandments' ...
in the parashah:
*The court must not inflict punishment on the Sabbath.
Liturgy
Following the Kabbalat Shabbat prayer service and prior to the Friday evening (''Ma'ariv
''Maariv'' or ''Maʿariv'' (, ), also known as ''Arvit'', or ''Arbit'' (, ), is a Jewish prayer service held in the evening or at night. It consists primarily of the evening '' Shema'' and ''Amidah''.
The service will often begin with two ...
'') service, Jews traditionally read rabbinic sources on the observance of the Sabbath, starting wit
Mishnah Shabbat 2:5Mishnah Shabbat 2:5
in turn, interprets the laws of kindling lights in Exodus 35:3.
Haftarah
Parashat Vayakhel
When Parashat Vayakhel is read alone, the haftarah
The ''haftara'' or (in Ashkenazi Jews, Ashkenazic pronunciation) ''haftorah'' (alt. ''haftarah, haphtara'', ) "parting," "taking leave" (plural form: ''haftarot'' or ''haftoros''), is a series of selections from the books of ''Nevi'im'' ("Pr ...
is:
*for Ashkenazi Jews
Ashkenazi Jews ( ; also known as Ashkenazic Jews or Ashkenazim) form a distinct subgroup of the Jewish diaspora, that emerged in the Holy Roman Empire around the end of the first millennium CE. They traditionally speak Yiddish, a language ...
: 1 Kings 7:40–50
*for Sephardi Jews
Sephardic Jews, also known as Sephardi Jews or Sephardim, and rarely as Iberian Peninsular Jews, are a Jewish diaspora population associated with the historic Jewish communities of the Iberian Peninsula (Spain and Portugal) and their descendant ...
: 1 Kings 7:13–26
Ashkenazi—1 Kings 7:40–50
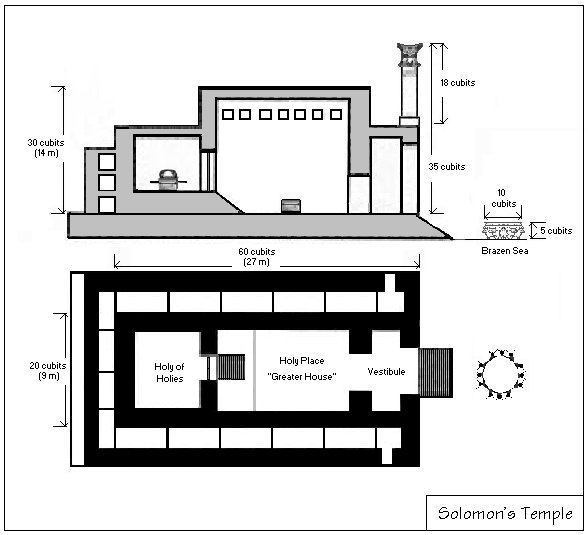
Both the parashah and the haftarah in 1 Kings 7 report the leader's erection of the holy place, Moses' building of the Tabernacle in the parashah, and Solomon's building of the Temple in Jerusalem
The Temple in Jerusalem, or alternatively the Holy Temple (; , ), refers to the two religious structures that served as the central places of worship for Israelites and Jews on the modern-day Temple Mount in the Old City of Jerusalem. Accord ...
in the haftarah. Both the parashah and the haftarah note particular metals for the holy space.
Sephardi—1 Kings 7:13–26
Both the parashah and the haftarah note the skill (''chokhmah''), ability (''tevunah''), and knowledge (''da‘at''), of the artisan (Bezalel in the parashah, Hiram in the haftarah) in every craft (''kol mela'khah'').
Shabbat Shekalim
When Parashat Vayakhel coincides with the special Sabbath Shabbat Shekalim, (as it does in 2019), the haftarah is 2 Kings 12:1–17.
Parashat Vayakhel–Pekudei
When Parashat Vayakhel is combined with Parashat Pekudei, the haftarah is:
*for Ashkenazi Jews: 1 Kings 7:51–8:21
*for Sephardi Jews: 1 Kings 7:40–50

Shabbat HaChodesh
When the parashah coincides with Shabbat HaChodesh ("Sabbath fthe month," the special Sabbath preceding the Hebrew month of Nissan
is a Japanese multinational Automotive industry, automobile manufacturer headquartered in Yokohama, Kanagawa, Japan. The company sells its vehicles under the ''Nissan'' and ''Infiniti'' brands, and formerly the ''Datsun'' brand, with in-house ...
(as it did in 2013 and 2017), the haftarah is:
*for Ashkenazi Jews: Ezekiel 45:16–46:18
*for Sephardi Jews: Ezekiel 45:18–46:15
On Shabbat HaChodesh, Jews read Exodus 12:1–20, in which God commands that "This month issanshall be the beginning of months; it shall be the first month of the year," and in which God issued the commandments of Passover. Similarly, the haftarah in Ezekiel 45:21–25 discusses Passover. In both the special reading and the haftarah, God instructs the Israelites to apply blood to doorposts.
Shabbat Parah
When the parashah coincides with Shabbat Parah (one of the special Sabbaths prior to Passover—as it did in 2025), the haftarah is:
*for Ashkenazi Jews: Ezekiel 36:16–38
*for Sephardi Jews: Ezekiel 36:16–36
On Shabbat Parah, the Sabbath of the red heifer
The red heifer () was a reddish brown Cattle, cow sacrificed by Temple priests as a ritual purification, purification ritual in biblical times.
Ritual in the Torah
The red heifer offering is described in Book of Numbers, Numbers 19. The Tora ...
, Jews read Numbers 19:1–22, which describes the rites of purification using the red heifer (''parah adumah''). Similarly, the haftarah in Ezekiel 36 also describes purification. In both the special reading and the haftarah in Ezekiel 36, sprinkled water cleansed the Israelites.[; .]
Notes
Further reading
The parashah has parallels or is discussed in these sources:
Ancient
*The Ba‘lu Myth. Ugarit
Ugarit (; , ''ủgrt'' /ʾUgarītu/) was an ancient port city in northern Syria about 10 kilometers north of modern Latakia. At its height it ruled an area roughly equivalent to the modern Latakia Governorate. It was discovered by accident in 19 ...
, 2nd millennium BCE. In ''The Context of Scripture, Volume I: Canonical Compositions from the Biblical World'', pages 260–61. Edited by William W. Hallo. Pilgrim Press, 1997. (building of a palace for Ba'al
Baal (), or Baʻal, was a title and honorific meaning 'owner' or 'lord' in the Northwest Semitic languages spoken in the Levant during antiquity. From its use among people, it came to be applied to gods. Scholars previously associated the t ...
).
Biblical
*Isaiah 56:6–7 (keeping the Sabbath); 66:23 (universally observed Sabbath).
*Psalms
The Book of Psalms ( , ; ; ; ; , in Islam also called Zabur, ), also known as the Psalter, is the first book of the third section of the Tanakh (Hebrew Bible) called ('Writings'), and a book of the Old Testament.
The book is an anthology of B ...
26:6 (washing, altar); 51:16–19 (sacrifices); 80:2 (cherubim); 84:2–3, 11 (Tabernacle, courts); 92:14 (courts); 96:6 (God's sanctuary); 100:4 (court of the Tabernacle); 134:2 (God's sanctuary); 141:2 (incense); 150:1 (God's sanctuary).

Early nonrabbinic
*Philo
Philo of Alexandria (; ; ; ), also called , was a Hellenistic Jewish philosopher who lived in Alexandria, in the Roman province of Egypt.
The only event in Philo's life that can be decisively dated is his representation of the Alexandrian J ...
''Allegorical Interpretation''
3:33:101
17:97–98. Alexandria
Alexandria ( ; ) is the List of cities and towns in Egypt#Largest cities, second largest city in Egypt and the List of coastal settlements of the Mediterranean Sea, largest city on the Mediterranean coast. It lies at the western edge of the Nile ...
, Egypt, early 1st century CE. In, e.g., ''The Works of Philo: Complete and Unabridged, New Updated Edition''. Translated by Charles Duke Yonge
Charles Duke Yonge (30 November 1812 – 30 November 1891) was an English historian, classicist and cricketer. He wrote numerous works of modern history, and translated several classical works. His younger brother was George Edward Yonge.
Bi ...
, pages 61, 262. Peabody, Massachusetts: Hendrickson Publishers, 1993.
*Josephus
Flavius Josephus (; , ; ), born Yosef ben Mattityahu (), was a Roman–Jewish historian and military leader. Best known for writing '' The Jewish War'', he was born in Jerusalem—then part of the Roman province of Judea—to a father of pr ...
, ''Antiquities of the Jews
''Antiquities of the Jews'' (; , ''Ioudaikē archaiologia'') is a 20-volume historiographical work, written in Greek, by the Roman-Jewish historian Josephus in the 13th year of the reign of the Roman emperor Domitian, which was 94 CE. It cont ...
'
3:6:1
Circa 93–94. In, e.g., ''The Works of Josephus: Complete and Unabridged, New Updated Edition''. Translated by William Whiston
William Whiston (9 December 166722 August 1752) was an English theologian, historian, natural philosopher, and mathematician, a leading figure in the popularisation of the ideas of Isaac Newton. He is now probably best known for helping to inst ...
, pages 85–95. Peabody, Massachusetts: Hendrickson Publishers, 1987.
Classical rabbinic
*Seder Olam Rabbah
''Seder Olam Rabbah'' (, "The Great Order of the World") is a 2nd-century CE Hebrew language chronology detailing the dates of biblical events from creation to Alexander the Great's conquest of Persia. It adds no stories beyond what is in the bi ...
, chapter 6. 2nd century CE. In, e.g., ''Seder Olam: The Rabbinic View of Biblical Chronology''. Translated and with commentary by Heinrich W. Guggenheimer, pages 73–78. Lanham, Maryland
Lanham is an unincorporated community and census-designated place in Prince George's County, Maryland. As of the 2020 United States census, it has a population of 11,282. The New Carrollton station (the terminus of the Washington Metro's O ...
: Jason Aronson
Jason Aronson was an American publisher of books in the field of psychotherapy. Topics dealt with in these books include child therapy, family therapy, couple therapy, object relations therapy, play therapy, depression, eating disorders, per ...
, 1998.
*Mishnah
The Mishnah or the Mishna (; , from the verb ''šānā'', "to study and review", also "secondary") is the first written collection of the Jewish oral traditions that are known as the Oral Torah. Having been collected in the 3rd century CE, it is ...
: Shabbat 1:1–24:5
Beitzah 5:2Megillah 1:5
Land of Israel, circa 200 CE. In, e.g., ''The Mishnah: A New Translation''. Translated by Jacob Neusner
Jacob Neusner (July 28, 1932 – October 8, 2016) was an American academic scholar of Judaism. He was named as one of the most published authors in history, having written or edited more than 900 books.
Neusner's application of form criticism� ...
, pages 179–208, 298, 317. New Haven: Yale University Press, 1988.
*Tosefta
The Tosefta ( "supplement, addition") is a compilation of Jewish Oral Law from the late second century, the period of the Mishnah and the Jewish sages known as the '' Tannaim''.
Background
Jewish teachings of the Tannaitic period were cha ...
Shabbat 1:1–17:29. Land of Israel, circa 250 CE. In, e.g., The Tosefta: Translated from the Hebrew, with a New Introduction. Translated by Jacob Neusner, volume 1, pages 357–427. Peabody, Massachusetts: Hendrickson Publishers, 2002.
* Mekhilta According to Rabbi Ishmael 82:1. Land of Israel, late 4th century. In, e.g., ''Mekhilta According to Rabbi Ishmael''. Translated by Jacob Neusner
Jacob Neusner (July 28, 1932 – October 8, 2016) was an American academic scholar of Judaism. He was named as one of the most published authors in history, having written or edited more than 900 books.
Neusner's application of form criticism� ...
, volume 2, pages 258–62. Atlanta: Scholars Press, 1988.
*Jerusalem Talmud
The Jerusalem Talmud (, often for short) or Palestinian Talmud, also known as the Talmud of the Land of Israel, is a collection of rabbinic notes on the second-century Jewish oral tradition known as the Mishnah. Naming this version of the Talm ...
: Terumot 31b
Shabbat 1a–113b
Shekalim 2a, 48b; Beitzah 47a; Nazir 21a, 25b–26a; Sotah 16b; Sanhedrin 27b; Shevuot 1b. Tiberias
Tiberias ( ; , ; ) is a city on the western shore of the Sea of Galilee in northern Israel. A major Jewish center during Late Antiquity, it has been considered since the 16th century one of Judaism's Four Holy Cities, along with Jerusalem, Heb ...
, Land of Israel, circa 400 CE. In, e.g., ''Talmud Yerushalmi''. Edited by Chaim Malinowitz, Yisroel Simcha Schorr, and Mordechai Marcus, volumes 7, 13–15, 20, 23, 34–36, 44, 46. Brooklyn: Mesorah Publications, 2010–2020. And in, e.g., ''The Jerusalem Talmud: A Translation and Commentary''. Edited by Jacob Neusner and translated by Jacob Neusner, Tzvee Zahavy, B. Barry Levy, and Edward Goldman. Peabody, Massachusetts: Hendrickson Publishers, 2009.
*Genesis Rabbah
Genesis Rabbah (, also known as Bereshit Rabbah and abbreviated as GenR) is a religious text from Judaism's classical period, probably written between 300 and 500 CE with some later additions. It is an expository midrash comprising a collection of ...
94:4. Land of Israel, 5th century. In, e.g., ''Midrash Rabbah: Genesis''. Translated by Harry Freedman and Maurice Simon, volume 2, page 871. London: Soncino Press, 1939.
*Midrash Tanhuma
Midrash Tanhuma (), also known as Yelammedenu, is the name given to a homiletic midrash on the entire Torah, and it is known in several different versions or collections. Tanhuma bar Abba is not the author of the text but instead is a figure to w ...
Vayakhel. 5th–10th centuries. In, e.g., ''The Metsudah Midrash Tanchuma: Shemos II.'' Translated and annotated by Avrohom Davis; edited by Yaakov Y.H. Pupko, volume 4 (Shemos volume 2), pages 339–89. Monsey, New York
Monsey (, ) is a hamlet and census-designated place in the town of Ramapo, Rockland County, New York, United States, north of Airmont, east of Viola, south of New Hempstead, and west of Spring Valley. The village of Kaser is surrounded by ...
: Eastern Book Press, 2004.
*Babylonian Talmud
The Talmud (; ) is the central text of Rabbinic Judaism and the primary source of Jewish religious law (''halakha'') and Jewish theology. Until the advent of Haskalah#Effects, modernity, in nearly all Jewish communities, the Talmud was the cen ...
Babylonian Berakhot 55aShabbat 20a49b70a74b96bEruvin 2bYoma 66b72b75aBeitzah 4b36bRosh Hashanah 34aMegillah 7bChagigah 10a–bKiddushin 37aMakkot 21bShevuot 26bZevachim 59bBekhorot 41a
Babylonia, 6th century. In, e.g., ''Talmud Bavli''. Edited by Yisroel Simcha Schorr, Chaim Malinowitz, and Mordechai Marcus, 72 volumes. Brooklyn: Mesorah Pubs., 2006.

Medieval
*Bede
Bede (; ; 672/326 May 735), also known as Saint Bede, Bede of Jarrow, the Venerable Bede, and Bede the Venerable (), was an English monk, author and scholar. He was one of the most known writers during the Early Middle Ages, and his most f ...
. ''Of the Tabernacle and Its Vessels, and of the Priestly Vestments''. Monkwearmouth
Monkwearmouth is an area of Sunderland, Tyne and Wear in England. Monkwearmouth is located at the north side of the mouth of the River Wear. It was one of the three original settlements on the banks of the River Wear along with Bishopwearmouth ...
, England
England is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is located on the island of Great Britain, of which it covers about 62%, and List of islands of England, more than 100 smaller adjacent islands. It ...
, 720s. In ''Bede: On the Tabernacle''. Translated with notes and introduction by Arthur G. Holder. Liverpool: Liverpool University Press, 1994.
*Exodus Rabbah
Exodus Rabbah () is the midrash to Exodus.
Contents
Exodus Rabbah is almost purely aggadic in character.
It contains 52 sections. It consists of two sections with different styles, dubbed "Exodus Rabbah I" (sections 1–14, covering Exodus cha ...
48:1–50:5. 10th century. In, e.g., ''Midrash Rabbah: Exodus''. Translated by S. M. Lehrman, volume 3, pages 546–61. London: Soncino Press, 1939.
*Solomon ibn Gabirol
Solomon ibn Gabirol or Solomon ben Judah (, ; , ) was an 11th-century Jews, Jewish poet and Jewish philosopher, philosopher in the Neoplatonism, Neo-Platonic tradition in Al-Andalus. He published over a hundred poems, as well as works of biblical ...
. ''A Crown for the King''
9:105–06
Spain, 11th century. Translated by David R. Slavitt, pages 14–15. New York: Oxford University Press, 1998.
 *
*Rashi
Shlomo Yitzchaki (; ; ; 13 July 1105) was a French rabbi who authored comprehensive commentaries on the Talmud and Hebrew Bible. He is commonly known by the List of rabbis known by acronyms, Rabbinic acronym Rashi ().
Born in Troyes, Rashi stud ...
. ''Commentary''
Exodus 35–38
Troyes
Troyes () is a Communes of France, commune and the capital of the Departments of France, department of Aube in the Grand Est region of north-central France. It is located on the Seine river about south-east of Paris. Troyes is situated within ...
, France, late 11th century. In, e.g., Rashi. ''The Torah: With Rashi's Commentary Translated, Annotated, and Elucidated''. Translated and annotated by Yisrael Isser Zvi Herczeg, volume 2, pages 487–505. Brooklyn: Mesorah Publications, 1994.
*Rashbam
Samuel ben Meir (Troyes, c. 1085 – c. 1158), after his death known as the "Rashbam", a Hebrew acronym for RAbbi SHmuel Ben Meir, was a leading French Tosafist and grandson of Shlomo Yitzhaki, "Rashi".
Biography
He was born in the vicinity of ...
. ''Commentary on the Torah''. Troyes, early 12th century. In, e.g., ''Rashbam's Commentary on Exodus: An Annotated Translation''. Edited and translated by Martin I. Lockshin, pages 425–29. Atlanta: Scholars Press, 1997.
 *
*Abraham ibn Ezra
Abraham ben Meir Ibn Ezra (, often abbreviated as ; ''Ibrāhim al-Mājid ibn Ezra''; also known as Abenezra or simply ibn Ezra, 1089 / 1092 – 27 January 1164 / 23 January 1167)''Jewish Encyclopedia''online; '' Chambers Biographical Dictionar ...
. ''Commentary on the Torah''. France, 1153. In, e.g., ''Ibn Ezra's Commentary on the Pentateuch: Exodus (Shemot)''. Translated and annotated by H. Norman Strickman and Arthur M. Silver, volume 2, pages 730–46. New York: Menorah Publishing Company, 1996.
*Maimonides
Moses ben Maimon (1138–1204), commonly known as Maimonides (, ) and also referred to by the Hebrew acronym Rambam (), was a Sephardic rabbi and Jewish philosophy, philosopher who became one of the most prolific and influential Torah schola ...
. ''The Guide for the Perplexed
''The Guide for the Perplexed'' (; ; ) is a work of Jewish theology by Maimonides. It seeks to reconcile Aristotelianism with Rabbinical Jewish theology by finding rational explanations for many events in the text.
It was written in Judeo-Arabic ...
''. Cairo
Cairo ( ; , ) is the Capital city, capital and largest city of Egypt and the Cairo Governorate, being home to more than 10 million people. It is also part of the List of urban agglomerations in Africa, largest urban agglomeration in Africa, L ...
, Egypt, 1190. In, e.g., Moses Maimonides. ''The Guide for the Perplexed''. Translated by Michael Friedländer
Michael Friedländer (29 April 1833 – 10 December 1910) was an Orientalist and principal of Jews' College, London. He is best known for his English translation of Maimonides' '' Guide to the Perplexed'', which was the most popular such trans ...
, pages 29–31, 393, 397. New York: Dover Publications, 1956.
 *
*Hezekiah ben Manoah Hezekiah ben Manoah, or Hezekiah bar Manoah, was a French rabbi and Bible commentator of the 13th century. He is generally known by the title of his commentary, Chizkuni ().
In memory of his father, who lost his right hand through his steadfastness ...
. ''Hizkuni''. France, circa 1240. In, e.g., Chizkiyahu ben Manoach. ''Chizkuni: Torah Commentary''. Translated and annotated by Eliyahu Munk, volume 3, pages 645–50. Jerusalem: Ktav Publishers, 2013.
*Naḥmanides
Moses ben Nachman ( ''Mōše ben-Nāḥmān'', "Moses son of Nachman"; 1194–1270), commonly known as Nachmanides (; ''Nakhmanídēs''), and also referred to by the acronym Ramban (; ) and by the contemporary nickname Bonastruc ça Porta (; l ...
. ''Commentary on the Torah''. Jerusalem, circa 1270. In, e.g., ''Ramban (Naḥmanides): Commentary on the Torah.'' Translated by Charles B. Chavel, volume 2, pages 595–608. New York: Shilo Publishing House, 1973.
*Zohar
The ''Zohar'' (, ''Zōhar'', lit. "Splendor" or "Radiance") is a foundational work of Kabbalistic literature. It is a group of books including commentary on the mystical aspects of the Torah and scriptural interpretations as well as material o ...
2:194b–220a. Spain, late 13th century.
*Bahya ben Asher
Bahya ben Asher ibn Halawa (, 1255–1340) was a rabbi and scholar of Judaism, best known as a commentator on the Hebrew Bible.
He is one of two scholars now referred to as Rabbeinu Behaye, the other being philosopher Bahya ibn Paquda.
Biograp ...
. ''Commentary on the Torah''. Spain, early 14th century. In, e.g., ''Midrash Rabbeinu Bachya: Torah Commentary by Rabbi Bachya ben Asher''. Translated and annotated by Eliyahu Munk, volume 4, pages 1418–38. Jerusalem: Lambda Publishers, 2003.
*Jacob ben Asher
Jacob ben Asher (c. 1270–1340), also known as Ba'al ha-Turim as well as Yaakov ben haRosh, was an influential Medieval rabbinic authority. He is often referred to as the Ba'al ha-Turim ("Author of the ''Turim''"), after his main work, the ''A ...
(Baal Ha-Turim). ''Commentary on the Torah''. Early 14th century. In, e.g., ''Baal Haturim Chumash: Shemos/Exodus''. Translated by Eliyahu Touger; edited and annotated by Avie Gold, volume 2, pages 929–57. Brooklyn: Mesorah Publications, 2000.
* Isaac ben Moses Arama. ''Akedat Yizhak (The Binding of Isaac)''. Late 15th century. In, e.g., Yitzchak Arama. ''Akeydat Yitzchak: Commentary of Rabbi Yitzchak Arama on the Torah''. Translated and condensed by Eliyahu Munk, volume 1, pages 519–35. New York, Lambda Publishers, 2001.
Modern
* Isaac Abravanel. ''Commentary on the Torah''. Italy, between 1492–1509. In, e.g., ''Abarbanel: Selected Commentaries on the Torah: Volume 2: Shemos/Exodus''. Translated and annotated by Israel Lazar, pages 404–20. Brooklyn: CreateSpace, 2015.
* Abraham Saba. ''Ẓeror ha-Mor (Bundle of Myrrh)''. Fez, Morocco, circa 1500. In, e.g., ''Tzror Hamor: Torah Commentary by Rabbi Avraham Sabba''. Translated and annotated by Eliyahu Munk, volume 3, pages 1221–28. Jerusalem, Lambda Publishers, 2008.
*Obadiah ben Jacob Sforno
Ovadia ben Jacob Sforno (Obadja Sforno, Hebrew: עובדיה ספורנו) was an Italian rabbi, Biblical commentator, philosopher and physician. A member of the Sforno family, he was born in Cesena about 1475 and died in Bologna in 1549.
Bi ...
. ''Commentary on the Torah''. Venice, 1567. In, e.g., ''Sforno: Commentary on the Torah''. Translation and explanatory notes by Raphael Pelcovitz, pages 474–85. Brooklyn: Mesorah Publications, 1997.
* Moshe Alshich. ''Commentary on the Torah''. Safed
Safed (), also known as Tzfat (), is a city in the Northern District (Israel), Northern District of Israel. Located at an elevation of up to , Safed is the highest city in the Galilee and in Israel.
Safed has been identified with (), a fortif ...
, circa 1593. In, e.g., Moshe Alshich. ''Midrash of Rabbi Moshe Alshich on the Torah''. Translated and annotated by Eliyahu Munk, volume 2, pages 607–14. New York, Lambda Publishers, 2000.
*Shlomo Ephraim Luntschitz
Shlomo Ephraim ben Aaron Luntschitz (1550 – 21 February 1619) was a rabbi and Torah commentator, best known for his Torah commentary .Although most write this as ''Keli Yakar'', "the second word should be ''Yekar''" (יְקָר), as the voweliza ...
. ''Kli Yakar''. Lublin
Lublin is List of cities and towns in Poland, the ninth-largest city in Poland and the second-largest city of historical Lesser Poland. It is the capital and the centre of Lublin Voivodeship with a population of 336,339 (December 2021). Lublin i ...
, 1602. In, e.g., ''Kli Yakar: Shemos''. Translated by Elihu Levine, volume 2, pages 345–71. Southfield, Michigan
Southfield is a city in Oakland County, Michigan, Oakland County in the U.S. state of Michigan. An inner-ring suburb of Detroit, Southfield borders Detroit to the north, roughly northwest of downtown Downtown Detroit, Detroit. As of the 2020 Uni ...
: Targum Press/Feldheim Publishers, 2007.
*Avraham Yehoshua Heschel. ''Commentaries on the Torah''. Cracow, Poland, mid 17th century. Compiled as ''Chanukat HaTorah''. Edited by Chanoch Henoch Erzohn. Piotrkow, Poland, 1900. In Avraham Yehoshua Heschel. ''Chanukas HaTorah: Mystical Insights of Rav Avraham Yehoshua Heschel on Chumash''. Translated by Avraham Peretz Friedman, pages 199–202. Southfield, Michigan
Southfield is a city in Oakland County, Michigan, Oakland County in the U.S. state of Michigan. An inner-ring suburb of Detroit, Southfield borders Detroit to the north, roughly northwest of downtown Downtown Detroit, Detroit. As of the 2020 Uni ...
: Targum Press/Feldheim Publishers
Feldheim Publishers (or Feldheim) is an American Orthodox Jewish publisher of Torah books and literature. Its extensive catalog of titles includes books on Jewish law, Torah, Talmud, Jewish lifestyle, Shabbat and Jewish holidays, Jewish history, ...
, 2004.
*Thomas Hobbes
Thomas Hobbes ( ; 5 April 1588 – 4 December 1679) was an English philosopher, best known for his 1651 book ''Leviathan (Hobbes book), Leviathan'', in which he expounds an influential formulation of social contract theory. He is considered t ...
. ''Leviathan
Leviathan ( ; ; ) is a sea serpent demon noted in theology and mythology. It is referenced in several books of the Hebrew Bible, including Psalms, the Book of Job, the Book of Isaiah, and the pseudepigraphical Book of Enoch. Leviathan is of ...
'', 3:34. England, 1651. Reprint edited by C. B. Macpherson, page 431. Harmondsworth, England: Penguin Classics, 1982.
*Edward Taylor
Edward Taylor (1642 – June 29, 1729) was a colonial American poet, pastor and physician of English origin. His work remained unpublished for some 200 years but since then has established him as one of the foremost writers of his time. His p ...
. "18. Meditation. Heb. 13.10. Wee Have an Altar." In ''Preliminary Meditations: First Series''. Cambridge, Massachusetts: Early 18th century. In Harold Bloom
Harold Bloom (July 11, 1930 – October 14, 2019) was an American literary critic and the Sterling Professor of humanities at Yale University. In 2017, Bloom was called "probably the most famous literary critic in the English-speaking world". Af ...
. ''American Religious Poems'', pages 21–22. New York: Library of America, 2006.
*Chaim ibn Attar
Chaim ibn Attar or Ḥayyim ben Moshe ibn Attar (, ; – 7 July 1743) also known as the Or ha-Ḥayyim after his popular commentary on the Torah, was a Talmudist and Kabbalist. He is arguably considered to be one of the most prominent Rabbis o ...
. ''Ohr ha-Chaim''. Venice, 1742. In Chayim ben Attar. ''Or Hachayim: Commentary on the Torah''. Translated by Eliyahu Munk, volume 2, pages 894–909. Brooklyn: Lambda Publishers, 1999.
*Yitzchak Magriso. ''Me'am Lo'ez
''Me'am Lo'ez'' (), initiated by Rabbi Yaakov Culi in 1730, is a widely studied commentary on the Tanakh written in Judaeo-Spanish. It is perhaps the best known publication in that language.
History
''Me'Am Lo'ez'' marked one of the first ma ...
''. Constantinople
Constantinople (#Names of Constantinople, see other names) was a historical city located on the Bosporus that served as the capital of the Roman Empire, Roman, Byzantine Empire, Byzantine, Latin Empire, Latin, and Ottoman Empire, Ottoman empire ...
, 1746. In Yitzchak Magriso. ''The Torah Anthology: Me'am Lo'ez''. Translated by Aryeh Kaplan
Aryeh Moshe Eliyahu Kaplan (; October 23, 1934 – January 28, 1983) was an American Orthodox Judaism, Orthodox rabbi, author, and translator best known for his The Living Torah and Nach, Living Torah edition of the Torah and extensive Kabbalah, ...
, volume 10, pages 175–248. Jerusalem: Moznaim Publishing, 1991.
* Naḥman of Breslov. ''Teachings''. Bratslav
Bratslav (, ; ) is a rural settlement in Ukraine, located in Tulchyn Raion of Vinnytsia Oblast, by the Southern Bug river. It is a medieval European city and a regional center of the Eastern Podolia region (see Bracław Voivodeship) founded ...
, Ukraine
Ukraine is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the List of European countries by area, second-largest country in Europe after Russia, which Russia–Ukraine border, borders it to the east and northeast. Ukraine also borders Belarus to the nor ...
, before 1811. In ''Rebbe Nachman's Torah: Breslov Insights into the Weekly Torah Reading: Exodus-Leviticus''. Compiled by Chaim Kramer; edited by Y. Hall, pages 282–91. Jerusalem: Breslov Research Institute, 2011.
*Samson Raphael Hirsch
Samson Raphael Hirsch (; June 20, 1808 – December 31, 1888) was a German Orthodox rabbi best known as the intellectual founder of the '' Torah im Derech Eretz'' school of contemporary Orthodox Judaism. Occasionally termed ''neo-Orthodoxy'', hi ...
. ''The Pentateuch: Exodus''. Translated by Isaac Levy, volume 2, pages 664–94. Gateshead
Gateshead () is a town in the Gateshead Metropolitan Borough of Tyne and Wear, England. It is on the River Tyne's southern bank. The town's attractions include the twenty metre tall Angel of the North sculpture on the town's southern outskirts, ...
: Judaica Press, 2nd edition 1999. Originally published as ''Der Pentateuch uebersetzt und erklaert''. Frankfurt
Frankfurt am Main () is the most populous city in the States of Germany, German state of Hesse. Its 773,068 inhabitants as of 2022 make it the List of cities in Germany by population, fifth-most populous city in Germany. Located in the forela ...
, 1867–1878.
 *
*Samuel David Luzzatto
Samuel David Luzzatto (, ; 22 August 1800 – 30 September 1865), also known by the Hebrew acronym Shadal (), was an Italian-Austrian Jewish scholar, poet, and a member of the Wissenschaft des Judentums movement.
Early life
Luzzatto was born ...
(Shadal). ''Commentary on the Torah.'' Padua
Padua ( ) is a city and ''comune'' (municipality) in Veneto, northern Italy, and the capital of the province of Padua. The city lies on the banks of the river Bacchiglione, west of Venice and southeast of Vicenza, and has a population of 20 ...
, 1871. In, e.g., Samuel David Luzzatto. ''Torah Commentary''. Translated and annotated by Eliyahu Munk, volume 3, pages 894–95. New York: Lambda Publishers, 2012.
*Samson Raphael Hirsch. ''The Jewish Sabbath''. Frankfurt
Frankfurt am Main () is the most populous city in the States of Germany, German state of Hesse. Its 773,068 inhabitants as of 2022 make it the List of cities in Germany by population, fifth-most populous city in Germany. Located in the forela ...
, before 1889. Translated by Ben Josephussoro. 1911. Reprinted Lexington, Kentucky
Lexington is a Consolidated city-county, consolidated city coterminous with and the county seat of Fayette County, Kentucky, United States. As of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census the city's population was 322,570, making it the List of ...
: CreateSpace Independent Publishing Platform, 2014.
* Yehudah Aryeh Leib Alter. ''Sefat Emet''. Góra Kalwaria
Góra Kalwaria (; "Calvary Mountain", , ''Ger'') is a town on the Vistula River in the Masovian Voivodeship, in east-central Poland. It is situated approximately southeast of Warsaw and has a population of around 12,109 (as of 2019). The town has ...
(Ger), Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It extends from the Baltic Sea in the north to the Sudetes and Carpathian Mountains in the south, bordered by Lithuania and Russia to the northeast, Belarus and Ukrai ...
, before 1906. Excerpted in ''The Language of Truth: The Torah Commentary of Sefat Emet''. Translated and interpreted by Arthur Green
Arthur Green (, born March 21, 1941) is an American scholar of Jewish mysticism and Neo-Hasidic theologian. He was a founding dean of the non-denominational rabbinical program at Hebrew College in Boston. He describes himself as an American Jew ...
, pages 135–38. Philadelphia: Jewish Publication Society, 1998. Reprinted 2012.
*Alexander Alan Steinbach. ''Sabbath Queen: Fifty-four Bible Talks to the Young Based on Each Portion of the Pentateuch'', pages 68–70. New York: Behrman's Jewish Book House, 1936.
*Benno Jacob
Benno Jacob (7 September 1862 – 24 January 1945) was a liberal rabbi and Bible scholar.
Biography
Jacob studied in the Rabbinical Seminary and University of his native Breslau (now Wrocław, Poland). He served as a rabbi between the years 1 ...
. ''The Second Book of the Bible: Exodus''. London, 1940. Translated by Walter Jacob
Walter Jacob (March 13, 1930 – October 20, 2024) was an American Reform rabbi. He was rabbi at the Rodef Shalom Congregation in Pittsburgh from 1955 to 1997. He served as chairman of organizations such as the Central Conference of American R ...
, pages 1007–31. Hoboken, New Jersey: KTAV Publishing House, 1992.
*''The Sabbath Anthology.'' Edited by Abraham E. Millgram. Philadelphia: The Jewish Publication Society, 1944; reprinted 2018. (Exodus 35:1–3).
*Morris Adler, Jacob B. Agus, and Theodore Friedman. “Responsum on the Sabbath.” ''Proceedings of the Rabbinical Assembly'', volume 14 (1950), pages 112–88. New York: Rabbinical Assembly
The Rabbinical Assembly (RA) is the international association of Conservative rabbis. The RA was founded in 1901 to shape the ideology, programs, and practices of the Conservative movement. It publishes prayerbooks and books of Jewish interest, an ...
of America, 1951. In ''Proceedings of the Committee on Jewish Law and Standards of the Conservative Movement 1927–1970'', volume 3 (Responsa), pages 1109–34. Jerusalem: The Rabbinical Assembly and The Institute of Applied Hallakhah, 1997.
*Umberto Cassuto
Umberto Cassuto, also known as Moshe David Cassuto (16 September 1883 – 19 December 1951), was an Italian historian, a rabbi, and a scholar of the Hebrew Bible and Ugaritic literature, in the University of Florence, then at the University ...
. ''A Commentary on the Book of Exodus''. Jerusalem, 1951. Translated by Israel Abrahams, pages 452–68. Jerusalem: The Magnes Press, The Hebrew University
The Hebrew University of Jerusalem (HUJI; ) is an Israeli public research university based in Jerusalem. Co-founded by Albert Einstein and Chaim Weizmann in July 1918, the public university officially opened on 1 April 1925. It is the second-ol ...
, 1967.
 *
*Abraham Joshua Heschel
Abraham Joshua Heschel (January 11, 1907 – December 23, 1972) was a Polish-American rabbi and one of the leading Jewish theologians and Jewish philosophers of the 20th century. Heschel, a professor of Jewish mysticism at the Jewish Theolo ...
. ''The Sabbath''. New York: Farrar, Straus and Giroux
Farrar, Straus and Giroux (FSG) is an American book publishing company, founded in 1946 by Roger Williams Straus Jr. and John C. Farrar. FSG is known for publishing literary books, and its authors have won numerous awards, including Pulitzer P ...
, 1951. Reprinted 2005.
*Morris Adler. ''The World of the Talmud'', pages 28–29. B'nai B'rith Hillel Foundations, 1958. Reprinted Kessinger Publishing, 2007.
*Gerhard von Rad
Gerhard von Rad (21 October 1901 – 31 October 1971) was a German academic, Old Testament scholar, Lutheran theologian, exegete, and professor at the University of Heidelberg.
Early life, education, career
Gerhard von Rad was born in Nu ...
. "The Tent and the Ark." In ''The Problem of the Hexateuch and Other Essays'', pages 103–24. New York: McGraw-Hill Book Company, 1966. LCCN 66-11432.
* Elie Munk. ''The Call of the Torah: An Anthology of Interpretation and Commentary on the Five Books of Moses''. Translated by E.S. Mazer, volume 2, pages 505–29. Brooklyn: Mesorah Publications, 1995. Originally published as ''La Voix de la Thora''. Paris
Paris () is the Capital city, capital and List of communes in France with over 20,000 inhabitants, largest city of France. With an estimated population of 2,048,472 residents in January 2025 in an area of more than , Paris is the List of ci ...
: Fondation Samuel et Odette Levy, 1981.
*Victor (Avigdor) Hurowitz
"The Priestly Account of Building the Tabernacle."
''Journal of the American Oriental Society'', volume 105 (number 1) (January–March 1985): pages 21–30.
* Pinchas H. Peli. ''Torah Today: A Renewed Encounter with Scripture'', pages 95–98. Washington, D.C.: B'nai B'rith Books, 1987.
*Craig R. Koester. ''Dwelling of God: The Tabernacle in the Old Testament, Intertestamental Jewish Literature, and the New Testament''. Washington: Catholic Biblical Association of America, 1989.
*Harvey J. Fields
Harvey J. Fields (1935–2014) was an American Reform Judaism, Reform rabbi. He served as the rabbi of Holy Blossom Temple in Toronto, the largest synagogue in Canada, from 1978 to 1982. He then served as the rabbi of Wilshire Boulevard Temple, th ...
. ''A Torah Commentary for Our Times: Volume II: Exodus and Leviticus'', pages 86–94. New York: UAHC Press, 1991.
*Nahum M. Sarna
Nahum Mattathias Sarna (Hebrew: נחום סרנא; March 27, 1923 – June 23, 2005) was a modern biblical scholar who is best known for the study of Genesis and Exodus represented in his ''Understanding Genesis'' (1966) and in his contribution ...
. ''The JPS Torah Commentary: Exodus: The Traditional Hebrew Text with the New JPS Translation'', pages 222–31. Philadelphia: Jewish Publication Society, 1991.
* Neḥama Leibowitz. ''New Studies in Shemot (Exodus)'', volume 2, pages 644–88. Jerusalem: Haomanim Press, 1993. Reprinted as ''New Studies in the Weekly Parasha''. Lambda Publishers, 2010.
*Walter Brueggemann
Walter Albert Brueggemann (March 11, 1933 – June 5, 2025) was an American Christian scholar and theologian who is widely considered an influential Old Testament scholar. His work often focused on the Hebrew prophetic tradition and the sociop ...
. "The Book of Exodus." In '' The New Interpreter's Bible''. Edited by Leander E. Keck, volume 1, pages 957–74. Nashville: Abingdon Press, 1994.
*Judith S. Antonelli. "Women's Wisdom." In ''In the Image of God: A Feminist Commentary on the Torah'', pages 221–30. Northvale, New Jersey
Northvale is a Borough (New Jersey), borough in Bergen County, New Jersey, Bergen County, in the U.S. state of New Jersey. As of the 2020 United States census, the borough's population was 4,761, an increase of 121 (+2.6%) from the 2010 United S ...
: Jason Aronson
Jason Aronson was an American publisher of books in the field of psychotherapy. Topics dealt with in these books include child therapy, family therapy, couple therapy, object relations therapy, play therapy, depression, eating disorders, per ...
, 1995.
*Ellen Frankel
Ellen Frankel (born 1951) was the editor-in-chief of the Jewish Publication Society (JPS) from 1991 until 2009, and its CEO for ten years. She retired in 2009 to pursue her own writing and scholarly projects, as JPS's first editor emerita.
Biogra ...
. ''The Five Books of Miriam: A Woman’s Commentary on the Torah'', pages 142–45. New York: G. P. Putnam's Sons, 1996.
* W. Gunther Plaut. ''The Haftarah Commentary'', pages 217–21. New York: UAHC Press, 1996.
*Robert Goodman. "Shabbat." In ''Teaching Jewish Holidays: History, Values, and Activities'', pages 1–19. Denver
Denver ( ) is a List of municipalities in Colorado#Consolidated city and county, consolidated city and county, the List of capitals in the United States, capital and List of municipalities in Colorado, most populous city of the U.S. state of ...
: A.R.E. Publishing, 1997.
*Sorel Goldberg Loeb and Barbara Binder Kadden. ''Teaching Torah: A Treasury of Insights and Activities'', pages 148–54. Denver: A.R.E. Publishing, 1997.
*''Exodus to Deuteronomy: A Feminist Companion to the Bible (Second Series)''. Edited by Athalya Brenner, pages 34, 38–39. Sheffield: Sheffield Academic Press, 2000.
*Edward L. Greenstein
“Recovering ‘The Women Who Served at the Entrance.’”
In Gershon Galil
Gershon Galil () is Professor of Biblical Studies and Ancient History and former chair of the Department of Jewish History at the University of Haifa, Mount Carmel, Haifa, Israel.
Gershon Galil earned his doctorate from the Hebrew University in ...
and Moshe Weinfeld, editors. ''Studies in Historical Geography and Biblical Historiography: Presented to Zecharia Kallai'', pages 165–73. Leiden: Brill, 2000.
 *
*Carol Meyers
Carol Lyons Meyers (born 1942) is an American feminist biblical scholar. She is the Mary Grace Wilson Professor Emerita of Religious Studies at Duke University. Meyers' field of research is focused on biblical studies, archaeology in the Middle Ea ...
. “Women at the Entrance to the Tent of Meeting.” In ''Women in Scripture: A Dictionary of Named and Unnamed Women in the Hebrew Bible, the Apocryphal/Deuterocanonical Books and New Testament''. Boston: Houghton Mifflin, 2000.
*Nancy H. Wiener. "Of Women and Mirrors." In ''The Women's Torah Commentary: New Insights from Women Rabbis on the 54 Weekly Torah Portions''. Edited by Elyse Goldstein, pages 172–78. Woodstock, Vermont
Woodstock is the shire town (county seat) of Windsor County, Vermont, United States. As of the 2020 census, the town population was 3,005. It includes the villages of Woodstock, South Woodstock, Taftsville, and West Woodstock.
History
Cha ...
: Jewish Lights Publishing, 2000.
*Martin R. Hauge. ''The Descent from the Mountain: Narrative Patterns in Exodus 19–40''. Sheffield
Sheffield is a city in South Yorkshire, England, situated south of Leeds and east of Manchester. The city is the administrative centre of the City of Sheffield. It is historically part of the West Riding of Yorkshire and some of its so ...
: Journal for the Study of the Old Testament Press, 2001.
*Avivah Gottlieb Zornberg. ''The Particulars of Rapture: Reflections on Exodus'', pages 461–98. New York: Doubleday, 2001.
*Lainie Blum Cogan and Judy Weiss. ''Teaching Haftarah: Background, Insights, and Strategies'', pages 138–51. Denver: A.R.E. Publishing, 2002.
* Michael Fishbane. ''The JPS Bible Commentary: Haftarot'', pages 135–46. Philadelphia: Jewish Publication Society, 2002.
*Alan Lew. ''This Is Real and You Are Completely Unprepared: The Days of Awe as a Journey of Transformation'', pages 53–55. Boston: Little, Brown and Co., 2003.
*Martha Lynn Wade. ''Consistency of Translation Techniques in the Tabernacle Accounts of Exodus in the Old Greek''. Society of Biblical Literature, 2003.
*Robert Alter
Robert Bernard Alter (born 1935) is an American professor emeritus of Hebrew language, Hebrew and comparative literature at the University of California, Berkeley, where he has taught since 1967. He has published two dozen books, including an aw ...
. ''The Five Books of Moses: A Translation with Commentary'', pages 514–25. New York: W.W. Norton & Co., 2004.
*Jeffrey H. Tigay. "Exodus." In ''The Jewish Study Bible''. Edited by Adele Berlin
Adele Berlin (born May 23, 1943 in Philadelphia) is an American biblical scholar and Hebraist. Before her retirement, she was Robert H. Smith Professor of Biblical Studies at the University of Maryland.
Berlin is best known for 1994 work ''Poet ...
and Marc Zvi Brettler, pages 191–97. New York: Oxford University Press, 2004.
*''Professors on the Parashah: Studies on the Weekly Torah Reading'' Edited by Leib Moscovitz, pages 150–54. Jerusalem: Urim Publications, 2005.
*W. Gunther Plaut. ''The Torah: A Modern Commentary: Revised Edition''. Revised edition edited by David E.S. Stern, pages 611–26. New York: Union for Reform Judaism
The Union for Reform Judaism (URJ), formerly known as the Union of American Hebrew Congregations (UAHC) until 2003, founded in 1873 by Rabbi Isaac Mayer Wise, is the congregational arm of Reform Judaism in North America. The other two arms establ ...
, 2006.
*William H.C. Propp. ''Exodus 19–40'', volume 2A, pages 624–722. New York: Anchor Bible
The Anchor Bible Series, which consists of a commentary series, a Bible dictionary, and a reference library, is a scholarly and commercial co-venture which was begun in 1956, with the publication of individual volumes in the commentary series. O ...
, 2006.
 *Suzanne A. Brody. "Successful Campaign." In ''Dancing in the White Spaces: The Yearly Torah Cycle and More Poems'', page 84. Shelbyville, Kentucky: Wasteland Press, 2007.
* James L. Kugel. ''How To Read the Bible: A Guide to Scripture, Then and Now'', pages 289, 291, 486. New York: Free Press, 2007.
*Kenton L. Sparks
*Suzanne A. Brody. "Successful Campaign." In ''Dancing in the White Spaces: The Yearly Torah Cycle and More Poems'', page 84. Shelbyville, Kentucky: Wasteland Press, 2007.
* James L. Kugel. ''How To Read the Bible: A Guide to Scripture, Then and Now'', pages 289, 291, 486. New York: Free Press, 2007.
*Kenton L. Sparks
“‘Enūma Elish’ and Priestly Mimesis: Elite Emulation in Nascent Judaism.”
''Journal of Biblical Literature
The ''Journal of Biblical Literature'' (''JBL'') is one of three academic journal
An academic journal (or scholarly journal or scientific journal) is a periodical publication in which Scholarly method, scholarship relating to a particular academ ...
'', volume 126 (2007): 637–42. (“Priestly Mimesis in the Tabernacle Narrative (Exodus 25–40)”).
*Shmuel Goldin. ''Unlocking the Torah Text: An In-Depth Journey into the Weekly Parsha: Shmot'', pages 299–326. Jerusalem: Gefen Publishing House
Gefen Publishing House () is an English language publishing firm located in Jerusalem, which also has a department in New York City. History
Gefen was founded in 1981 by Murray and Hana Greenfield. Its CEO is Ilan Greenfield, son of the founder ...
, 2008.
*''The Torah: A Women's Commentary''. Edited by Tamara Cohn Eskenazi
Tamara Cohn Eskenazi is The Effie Wise Ochs Professor of Biblical Literature and History at the Reform Jewish seminary Hebrew Union College-Jewish Institute of Religion in Los Angeles.
She was the first woman hired by the Hebrew Union College-Jew ...
and Andrea L. Weiss, pages 521–44. New York: URJ Press, 2008.
*Thomas B. Dozeman. ''Commentary on Exodus'', pages 756–59. Grand Rapids, Michigan: William B. Eerdmans Publishing Company, 2009.
*Jill Hammer. "Listening to Heart-Wisdom: Parashat Vayakhel (Exodus 35:1–38:20)." In ''Torah Queeries: Weekly Commentaries on the Hebrew Bible''. Edited by Gregg Drinkwater, Joshua Lesser, and David Shneer; foreword by Judith Plaskow, pages 113–16. New York: New York University Press
New York University Press (or NYU Press) is a university press that is part of New York University
New York University (NYU) is a private university, private research university in New York City, New York, United States. Chartered in 1831 ...
, 2009.
* Reuven Hammer. ''Entering Torah: Prefaces to the Weekly Torah Portion'', pages 131–34. New York: Gefen Publishing House, 2009.
*Rebecca G.S. Idestrom
"Echoes of the Book of Exodus in Ezekiel."
''Journal for the Study of the Old Testament
The ''Journal for the Study of the Old Testament'' (JSOT) is a peer-reviewed academic journal covering the field of Biblical studies. The editors-in-chief are David Shepherd (Trinity College Dublin) and Lena-Sofia Tiemeyer ( Örebro School of Theol ...
'', volume 33 (number 4) (June 2009): pages 489–510. (Motifs from Exodus found in Ezekiel, including the call narrative, divine encounters, captivity, signs, plagues, judgment, redemption, tabernacle/temple, are considered.).
* John H. Walton. "The Seven Days of Genesis 1 Relate to the Cosmic Temple Inauguration." In ''The Lost World of Genesis One: Ancient Cosmology and the Origins Debate'', pages 87–92. Downers Grove, Illinois: IVP Academic, 2009.
*Bruce Wells. "Exodus." In ''Zondervan Illustrated Bible Backgrounds Commentary''. Edited by John H. Walton, volume 1, pages 264–65. Grand Rapids, Michigan
Grand Rapids is the largest city and county seat of Kent County, Michigan, United States. With a population of 198,917 at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census and estimated at 200,117 in 2024, Grand Rapids is the List of municipalities ...
: Zondervan
Zondervan is an international Christian media and publishing company located in Grand Rapids, Michigan, United States. Zondervan is a founding member of the Evangelical Christian Publishers Association (ECPA). It is a part of HarperCollins, Ha ...
, 2009.
 *
*Jonathan Sacks
Jonathan Henry Sacks, Baron Sacks (8 March 19487 November 2020) was an English Orthodox rabbi, philosopher, theologian, and author. Sacks served as the Chief Rabbi of the United Hebrew Congregations of the Commonwealth from 1991 to 2013. As ...
. ''Covenant & Conversation: A Weekly Reading of the Jewish Bible: Exodus: The Book of Redemption'', pages 277–301. Jerusalem: Maggid Books, 2010.
*Joe Lieberman
Joseph Isadore Lieberman (; February 24, 1942 – March 27, 2024) was an American politician and lawyer who served as a United States senator from Connecticut from 1989 to 2013. Originally a member of the Democratic Party (United States), Dem ...
and David Klinghoffer. ''The Gift of Rest: Rediscovering the Beauty of the Sabbath''. New York: Howard Books, 2011.
*James W. Watts
"Aaron and the Golden Calf in the Rhetoric of the Pentateuch."
''Journal of Biblical Literature'', volume 130 (number 3) (fall 2011): pages 417–30.
*William G. Dever
William Gwinn Dever (born November 27, 1933, Louisville, Kentucky) is an American archaeologist, Biblical scholar, historian, semiticist, and theologian. He is an active Biblical scholar, scholar of the Old Testament, and historian, specialized ...
. ''The Lives of Ordinary People in Ancient Israel: When Archaeology and the Bible Intersect'', page 245. Grand Rapids, Michigan: William B. Eerdmans Publishing Company, 2012.
 * Shmuel Herzfeld. "Inspirational Snapshots from Eretz Yisrael." In ''Fifty-Four Pick Up: Fifteen-Minute Inspirational Torah Lessons'', pages 128–34. Jerusalem:
* Shmuel Herzfeld. "Inspirational Snapshots from Eretz Yisrael." In ''Fifty-Four Pick Up: Fifteen-Minute Inspirational Torah Lessons'', pages 128–34. Jerusalem: Gefen Publishing House
Gefen Publishing House () is an English language publishing firm located in Jerusalem, which also has a department in New York City. History
Gefen was founded in 1981 by Murray and Hana Greenfield. Its CEO is Ilan Greenfield, son of the founder ...
, 2012.
* Daniel S. Nevins
"The Use of Electrical and Electronic Devices on Shabbat."
New York: Rabbinical Assembly, 2012.
*''Torah MiEtzion: New Readings in Tanach: Shemot''. Edited by Ezra Bick and Yaakov Beasley, pages 480–530. Jerusalem: Maggid Books, 2012.
*Michael B. Hundley. ''Gods in Dwellings: Temples and Divine Presence in the Ancient Near East''. Atlanta
Atlanta ( ) is the List of capitals in the United States, capital and List of municipalities in Georgia (U.S. state), most populous city in the U.S. state of Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia. It is the county seat, seat of Fulton County, Georg ...
: Society of Biblical Literature
The Society of Biblical Literature (SBL), founded in 1880 as the Society of Biblical Literature and Exegesis, is an American-based learned society dedicated to the academic study of the Bible and related ancient literature. Its current stated mis ...
, 2013.
*Amiel Ungar
"Tel Aviv and the Sabbath."
''The Jerusalem Report
''The Jerusalem Report'' is a fortnightly print and online news magazine that covers political, military, economic, religious and cultural issues in Israel, the Middle East, and the Jewish world.
Founded as an independent weekly publication in 1 ...
'', volume 24 (number 8) (July 29, 2013): page 37.
*Amanda Terkel
"Glenn Grothman, Wisconsin GOP Senator, Fights for a Seven-Day Workweek."
''The Huffington Post
''HuffPost'' (''The Huffington Post'' until 2017, itself often abbreviated as ''HPo'') is an American progressive news website, with localized and international editions. The site offers news, satire, blogs, and original content, and covers p ...
''. (January 3, 2014, updated January 23, 2014). (A Congressional candidate said, "Right now in Wisconsin, you're not supposed to work seven days in a row, which is a little ridiculous because all sorts of people want to work seven days a week.").
*Jonathan Sacks. ''Lessons in Leadership: A Weekly Reading of the Jewish Bible'', pages 111–14. New Milford, Connecticut: Maggid Books, 2015.
*Raanan Eichler
"The Poles of the Ark: On the Ins and Outs of a Textual Contradiction."
''Journal of Biblical Literature'', volume 135, number 4 (Winter 2016): pages 733–4.
*Jonathan Sacks. ''Essays on Ethics: A Weekly Reading of the Jewish Bible'', pages 137–43. New Milford, Connecticut: Maggid Books, 2016.
 * Shai Held. ''The Heart of Torah, Volume 1: Essays on the Weekly Torah Portion: Genesis and Exodus'', pages 213–20. Philadelphia: Jewish Publication Society, 2017.
*Steven Levy and Sarah Levy. ''The JPS Rashi Discussion Torah Commentary'', pages 68–70. Philadelphia: Jewish Publication Society, 2017.
* Leon R. Kass. ''Founding God's Nation: Reading Exodus'', pages 574–98. New Haven: Yale University Press, 2021.
* Abigail Pogrebin and
* Shai Held. ''The Heart of Torah, Volume 1: Essays on the Weekly Torah Portion: Genesis and Exodus'', pages 213–20. Philadelphia: Jewish Publication Society, 2017.
*Steven Levy and Sarah Levy. ''The JPS Rashi Discussion Torah Commentary'', pages 68–70. Philadelphia: Jewish Publication Society, 2017.
* Leon R. Kass. ''Founding God's Nation: Reading Exodus'', pages 574–98. New Haven: Yale University Press, 2021.
* Abigail Pogrebin and Dov Linzer
Rabbi Dov Linzer (Hebrew: דב נתן לינזר; born September 16, 1966) is the President and Rabbinic Head ( Rosh HaYeshiva) of the Modern Orthodox Yeshivat Chovevei Torah Rabbinical School in Riverdale, New York. He is a teacher, lecture ...
. ''It Takes Two to Torah: An Orthodox Rabbi and Reform Journalist Discuss and Debate Their Way Through the Five Books of Moses'', pages 131–36. Bedford, New York: Fig Tree Books, 2024.
External links

Texts
Masoretic text and 1917 JPS translation
Commentaries
Academy for Jewish Religion, CaliforniaAish.comAmerican Jewish University - Ziegler School of Rabbinic StudiesChabad.orgHadarJewish Theological SeminaryMyJewishLearning.comPardes from JerusalemReconstructing Judaism
Sephardic InstituteUnion for Reform JudaismUnited Synagogue of Conservative Judaism
Yeshiva University
{{Book of Exodus navbox
Weekly Torah readings in Adar
Weekly Torah readings from Exodus
 Vayakhel, Wayyaqhel, VaYakhel, Va-Yakhel, Vayak'hel, Vayak'heil, or Vayaqhel (—
Vayakhel, Wayyaqhel, VaYakhel, Va-Yakhel, Vayak'hel, Vayak'heil, or Vayaqhel (—





 Rabbi Levi read Exodus 26:28, regarding "the middle bar in the midst of the boards, which shall pass through from end to end," calculated that the beam must have been 32 cubits in length, and asked where the Israelites would find such a beam in the desert. Rabbi Levi deduced that the Israelites had stored up the cedar to construct the Tabernacle since the days of
Rabbi Levi read Exodus 26:28, regarding "the middle bar in the midst of the boards, which shall pass through from end to end," calculated that the beam must have been 32 cubits in length, and asked where the Israelites would find such a beam in the desert. Rabbi Levi deduced that the Israelites had stored up the cedar to construct the Tabernacle since the days of  Rabbi Isaac Nappaha deduced from Exodus 35:30 that we must not appoint a leader over a community without first consulting the community. In Exodus 35:30, Moses said to the Israelites: "See, the Lord has called by name Bezalel, the son of Uri." Rabbi Isaac read Exodus 35:30 to indicate that God asked Moses whether Moses considered Bezalel suitable. Moses replied that if God thought Bezalel suitable, then surely Moses would have to, as well. God told Moses nonetheless to go and consult the Israelites. Moses asked the Israelites whether they considered Bezalel suitable. And they replied that if God and Moses considered him suitable, surely they had to, as well.
Rabbi Isaac Nappaha deduced from Exodus 35:30 that we must not appoint a leader over a community without first consulting the community. In Exodus 35:30, Moses said to the Israelites: "See, the Lord has called by name Bezalel, the son of Uri." Rabbi Isaac read Exodus 35:30 to indicate that God asked Moses whether Moses considered Bezalel suitable. Moses replied that if God thought Bezalel suitable, then surely Moses would have to, as well. God told Moses nonetheless to go and consult the Israelites. Moses asked the Israelites whether they considered Bezalel suitable. And they replied that if God and Moses considered him suitable, surely they had to, as well.

 Noting that Exodus 35–39 repeats material from Exodus 25–31,
Noting that Exodus 35–39 repeats material from Exodus 25–31, 





 *
* *
* *
* *
* *
* *
* *Suzanne A. Brody. "Successful Campaign." In ''Dancing in the White Spaces: The Yearly Torah Cycle and More Poems'', page 84. Shelbyville, Kentucky: Wasteland Press, 2007.
* James L. Kugel. ''How To Read the Bible: A Guide to Scripture, Then and Now'', pages 289, 291, 486. New York: Free Press, 2007.
*Kenton L. Sparks
*Suzanne A. Brody. "Successful Campaign." In ''Dancing in the White Spaces: The Yearly Torah Cycle and More Poems'', page 84. Shelbyville, Kentucky: Wasteland Press, 2007.
* James L. Kugel. ''How To Read the Bible: A Guide to Scripture, Then and Now'', pages 289, 291, 486. New York: Free Press, 2007.
*Kenton L. Sparks *
* * Shmuel Herzfeld. "Inspirational Snapshots from Eretz Yisrael." In ''Fifty-Four Pick Up: Fifteen-Minute Inspirational Torah Lessons'', pages 128–34. Jerusalem:
* Shmuel Herzfeld. "Inspirational Snapshots from Eretz Yisrael." In ''Fifty-Four Pick Up: Fifteen-Minute Inspirational Torah Lessons'', pages 128–34. Jerusalem:  * Shai Held. ''The Heart of Torah, Volume 1: Essays on the Weekly Torah Portion: Genesis and Exodus'', pages 213–20. Philadelphia: Jewish Publication Society, 2017.
*Steven Levy and Sarah Levy. ''The JPS Rashi Discussion Torah Commentary'', pages 68–70. Philadelphia: Jewish Publication Society, 2017.
* Leon R. Kass. ''Founding God's Nation: Reading Exodus'', pages 574–98. New Haven: Yale University Press, 2021.
* Abigail Pogrebin and
* Shai Held. ''The Heart of Torah, Volume 1: Essays on the Weekly Torah Portion: Genesis and Exodus'', pages 213–20. Philadelphia: Jewish Publication Society, 2017.
*Steven Levy and Sarah Levy. ''The JPS Rashi Discussion Torah Commentary'', pages 68–70. Philadelphia: Jewish Publication Society, 2017.
* Leon R. Kass. ''Founding God's Nation: Reading Exodus'', pages 574–98. New Haven: Yale University Press, 2021.
* Abigail Pogrebin and 