VRAM on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
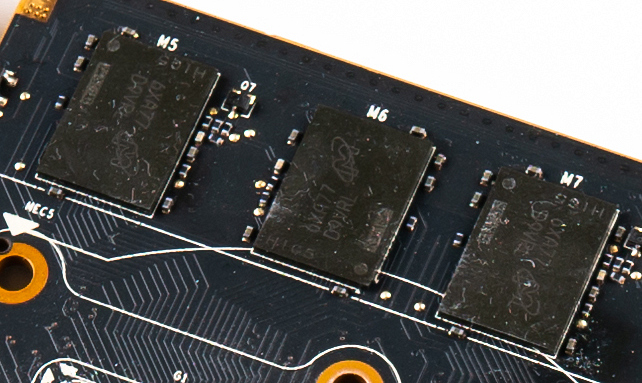 Video random-access memory (VRAM) is dedicated
Video random-access memory (VRAM) is dedicated
 Video random-access memory (VRAM) is dedicated
Video random-access memory (VRAM) is dedicated computer memory
Computer memory stores information, such as data and programs, for immediate use in the computer. The term ''memory'' is often synonymous with the terms ''RAM,'' ''main memory,'' or ''primary storage.'' Archaic synonyms for main memory include ...
used to store the pixel
In digital imaging, a pixel (abbreviated px), pel, or picture element is the smallest addressable element in a Raster graphics, raster image, or the smallest addressable element in a dot matrix display device. In most digital display devices, p ...
s and other graphics data as a framebuffer to be rendered on a computer monitor. It often uses a different technology than other computer memory, in order to be read quickly for display on a screen.
Relation to GPUs
Many modern GPUs rely on VRAM. In contrast, a GPU that does ''not'' use VRAM, and relies instead on system RAM, is said to have a unified memory architecture, or shared graphics memory. System RAM and VRAM have been segregated due to the bandwidth requirements of GPUs, and to achieve lower latency, since VRAM is physically closer to the GPU die. Modern VRAM is typically found in a BGA package soldered onto a graphics card. The VRAM is cooled along with the GPU by the GPU heatsink.Technologies
* Dual-ported video RAM, used in the 1990s and at the time often called "VRAM" * SGRAM * GDDR SDRAM * High Bandwidth Memory (HBM)See also
*Graphics processing unit
A graphics processing unit (GPU) is a specialized electronic circuit designed for digital image processing and to accelerate computer graphics, being present either as a discrete video card or embedded on motherboards, mobile phones, personal ...
* Tiled rendering, a method to reduce VRAM bandwidth requirements
References
{{reflist Types of RAM