Urinary bladder on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The urinary bladder, or simply bladder, is a hollow organ in
 In humans, the bladder is a hollow muscular organ situated at the base of the
In humans, the bladder is a hollow muscular organ situated at the base of the
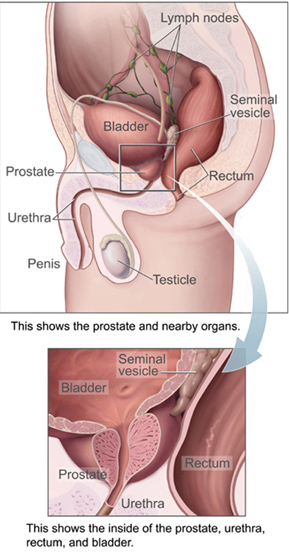 In men, the
In men, the
in:
File:Gray1141.png, Vertical section of bladder wall
File:Urinary bladder.JPG, Layers of the urinary bladder wall and cross-section of the detrusor muscle
File:2605 The Bladder.jpg, Anatomy of the male bladder, showing transitional epithelium and part of the wall in a histological cut-out
 Cystitis refers to infection or inflammation of the bladder. It commonly occurs as part of a urinary tract infection. In adults, it is more common in women than men, owing to a shorter
Cystitis refers to infection or inflammation of the bladder. It commonly occurs as part of a urinary tract infection. In adults, it is more common in women than men, owing to a shorter

 A number of investigations are used to examine the bladder. The investigations that are ordered will depend on the taking of a medical history and an examination. The examination may involve a
A number of investigations are used to examine the bladder. The investigations that are ordered will depend on the taking of a medical history and an examination. The examination may involve a
Bladder
() – An open-access journal on bladder biology and diseases. {{Use dmy dates, date=April 2017 Urinary bladder, Pelvis Organs (anatomy) Urinary system
human
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, cultu ...
s and other vertebrate
Vertebrates () comprise all animal taxa within the subphylum Vertebrata () ( chordates with backbones), including all mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish. Vertebrates represent the overwhelming majority of the phylum Chordata, with ...
s that stores urine
Urine is a liquid by-product of metabolism in humans and in many other animals. Urine flows from the kidneys through the ureters to the urinary bladder. Urination results in urine being excreted from the body through the urethra.
Cellul ...
from the kidney
The kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped organs found in vertebrates. They are located on the left and right in the retroperitoneal space, and in adult humans are about in length. They receive blood from the paired renal arteries; blo ...
s before disposal by urination. In humans the bladder is a distensible organ that sits on the pelvic floor. Urine enters the bladder via the ureters and exits via the urethra
The urethra (from Greek οὐρήθρα – ''ourḗthrā'') is a tube that connects the urinary bladder to the urinary meatus for the removal of urine from the body of both females and males. In human females and other primates, the urethra ...
. The typical adult human bladder will hold between 300 and (10.14 and ) before the urge to empty occurs, but can hold considerably more.
The Latin phrase for "urinary bladder" is ''vesica urinaria'', and the term ''vesical'' or prefix ''vesico -'' appear in connection with associated structures such as vesical veins. The modern Latin word for "bladder" – ''cystis'' – appears in associated terms such as cystitis (inflammation of the bladder).
Structure
pelvis
The pelvis (plural pelves or pelvises) is the lower part of the trunk, between the abdomen and the thighs (sometimes also called pelvic region), together with its embedded skeleton (sometimes also called bony pelvis, or pelvic skeleton).
The ...
. In gross anatomy
Gross anatomy is the study of anatomy at the visible or macroscopic level. The counterpart to gross anatomy is the field of histology, which studies microscopic anatomy. Gross anatomy of the human body or other animals seeks to understand the rela ...
, the bladder can be divided into a broad , a body, an apex, and a neck. The apex (also called the vertex) is directed forward toward the upper part of the pubic symphysis, and from there the median umbilical ligament continues upward on the back of the anterior abdominal wall to the umbilicus. The peritoneum
The peritoneum is the serous membrane forming the lining of the abdominal cavity or coelom in amniotes and some invertebrates, such as annelids. It covers most of the intra-abdominal (or coelomic) organs, and is composed of a layer of mes ...
is carried by it from the apex on to the abdominal wall to form the middle umbilical fold. The neck of the bladder is the area at the base of the trigone that surrounds the internal urethral orifice
The internal urethral orifice is the opening of the urinary bladder into the urethra. It is placed at the apex of the trigonum vesicae, in the most dependent part of the bladder, and is usually somewhat crescent-shaped; the mucous membrane immedi ...
that leads to the urethra. In males the neck of the urinary bladder is next to the prostate gland
The prostate is both an accessory gland of the male reproductive system and a muscle-driven mechanical switch between urination and ejaculation. It is found only in some mammals. It differs between species anatomically, chemically, and physi ...
.
The bladder has three openings. The two ureters enter the bladder at ureteric orifices, and the urethra
The urethra (from Greek οὐρήθρα – ''ourḗthrā'') is a tube that connects the urinary bladder to the urinary meatus for the removal of urine from the body of both females and males. In human females and other primates, the urethra ...
enters at the trigone of the bladder. These ureteric openings have mucosal flaps in front of them that act as valves in preventing the backflow of urine into the ureters, known as vesicoureteral reflux. Between the two ureteric openings is a raised area of tissue called the interureteric crest. This makes the upper boundary of the trigone. The trigone is an area of smooth muscle
Smooth muscle is an involuntary non- striated muscle, so-called because it has no sarcomeres and therefore no striations (''bands'' or ''stripes''). It is divided into two subgroups, single-unit and multiunit smooth muscle. Within single-unit ...
that forms the floor of the bladder above the urethra. It is an area of smooth tissue for the easy flow of urine into and from this part of the bladder - in contrast to the irregular surface formed by the rugae.
The walls of the bladder have a series of ridges, thick mucosal folds known as rugae
In anatomy, rugae are a series of ridges produced by folding of the wall of an organ. Most commonly rugae refers to the gastric rugae of the internal surface of the stomach.
Function
A purpose of the gastric rugae is to allow for expansion o ...
that allow for the expansion of the bladder. The detrusor muscle is the muscular layer of the wall made of smooth muscle
Smooth muscle is an involuntary non- striated muscle, so-called because it has no sarcomeres and therefore no striations (''bands'' or ''stripes''). It is divided into two subgroups, single-unit and multiunit smooth muscle. Within single-unit ...
fibers
Fiber or fibre (from la, fibra, links=no) is a natural or artificial substance that is significantly longer than it is wide. Fibers are often used in the manufacture of other materials. The strongest engineering materials often incorporate ...
arranged in spiral, longitudinal, and circular bundles. The detrusor muscle is able to change its length. It can also contract for a long time whilst voiding, and it stays relaxed whilst the bladder is filling. The wall of the urinary bladder is normally 3–5 mm thick. When well distended, the wall is normally less than 3 mm.
Nearby structures
 In men, the
In men, the prostate gland
The prostate is both an accessory gland of the male reproductive system and a muscle-driven mechanical switch between urination and ejaculation. It is found only in some mammals. It differs between species anatomically, chemically, and physi ...
lies outside the opening for the urethra. The middle lobe of the prostate causes an elevation in the mucous membrane behind the internal urethral orifice called the uvula of urinary bladder. The uvula can enlarge when the prostate becomes enlarged.
The bladder is located below the peritoneal cavity near the pelvic floor and behind the pubic symphysis. In men, it lies in front of the rectum, separated by the recto-vesical pouch, and is supported by fibres of the levator ani and of the prostate gland. In women, it lies in front of the uterus
The uterus (from Latin ''uterus'', plural ''uteri'') or womb () is the organ in the reproductive system of most female mammals, including humans that accommodates the embryonic and fetal development of one or more embryos until birth. The ...
, separated by the vesico-uterine pouch, and is supported by the elevator ani and the upper part of the vagina.Page 12in:
Blood and lymph supply
The bladder receives blood by the vesical arteries and drained into a network of vesical veins. The superior vesical artery supplies blood to the upper part of the bladder. The lower part of the bladder is supplied by the inferior vesical artery, both of which are branches of the internal iliac arteries. In females, the uterine andvaginal arteries
The vaginal artery is an artery in females that supplies blood to the vagina and the base of the bladder.
Structure
The vaginal artery is usually a branch of the internal iliac artery. Some sources say that the vaginal artery can arise from the ...
provide additional blood supply. Venous drainage begins in a network of small vessels on the lower surfaces of the bladder, which coalesce and travel with the lateral ligaments of the bladder into the internal iliac veins.
The lymph
Lymph (from Latin, , meaning "water") is the fluid that flows through the lymphatic system, a system composed of lymph vessels (channels) and intervening lymph nodes whose function, like the venous system, is to return fluid from the tissues ...
drained from the bladder begins in a series of networks throughout the mucosal, muscular and serosal layers. These then form three sets of vessels: one set near the trigone draining the bottom of the bladder; one set draining the top of the bladder; and another set draining the outer undersurface of the bladder. The majority of these vessels drain into the external iliac lymph nodes.
Nerve supply
The bladder receives both sensory and motor supply from sympathetic and theparasympathetic nervous system
The parasympathetic nervous system (PSNS) is one of the three divisions of the autonomic nervous system, the others being the sympathetic nervous system and the enteric nervous system. The enteric nervous system is sometimes considered part o ...
s. The motor supply from both sympathetic fibers, most of which arise from the superior
Superior may refer to:
*Superior (hierarchy), something which is higher in a hierarchical structure of any kind
Places
*Superior (proposed U.S. state), an unsuccessful proposal for the Upper Peninsula of Michigan to form a separate state
*Lake ...
and inferior hypogastric plexus
The inferior hypogastric plexus (pelvic plexus in some texts) is a network () of nerves that supplies the organs of the pelvic cavity. The inferior hypogastric plexus gives rise to the prostatic plexus in males and the uterovaginal plexus in femal ...
es and nerves, and from parasympathetic fibers, which come from the pelvic splanchnic nerves
Pelvic splanchnic nerves or nervi erigentes are splanchnic nerves that arise from sacral spinal nerves S2, S3, S4 to provide parasympathetic innervation to the organs of the pelvic cavity.
Structure
The pelvic splanchnic nerves arise from th ...
.
Sensation from the bladder, relating to distension or to irritation (such as by infection or a stone) is transmitted primarily through the parasympathetic nervous system. These travel via sacral nerves to S2-4. From here, sensation travels to the brain
A brain is an organ (biology), organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It is located in the head, usually close to the sensory organs for senses such as Visual perception, vision. I ...
via the dorsal columns
Dorsal (from Latin ''dorsum'' ‘back’) may refer to:
* Dorsal (anatomy), an anatomical term of location referring to the back or upper side of an organism or parts of an organism
* Dorsal, positioned on top of an aircraft's fuselage
* Dorsal co ...
in the spinal cord
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue, which extends from the medulla oblongata in the brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column (backbone). The backbone encloses the central canal of the sp ...
.
Microanatomy
When viewed under a microscope the bladder can be seen to have an inner lining (calledepithelium
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. It is a thin, continuous, protective layer of compactly packed cells with a little intercellul ...
), three layers of muscle fibres, and an outer adventitia.
The inner wall of the bladder is called urothelium
Transitional epithelium also known as urothelium is a type of stratified epithelium. Transitional epithelium is a type of tissue that changes shape in response to stretching (stretchable epithelium). The transitional epithelium usually appears ...
, a type of transitional epithelium
Transitional epithelium also known as urothelium is a type of stratified epithelium. Transitional epithelium is a type of tissue that changes shape in response to stretching (stretchable epithelium). The transitional epithelium usually appears ...
formed by three to six layers of cells; the cells may become more cuboidal or flatter depending on whether the bladder is empty or full. Additionally, these are lined with a mucous membrane consisting of a surface glycocalyx
The glycocalyx, also known as the pericellular matrix, is a glycoprotein and glycolipid covering that surrounds the cell membranes of bacteria, epithelial cells, and other cells. In 1970, Martinez-Palomo discovered the cell coating in animal c ...
that protects the cells beneath it from urine. The epithelium lies on a thin basement membrane
The basement membrane is a thin, pliable sheet-like type of extracellular matrix that provides cell and tissue support and acts as a platform for complex signalling. The basement membrane sits between epithelial tissues including mesothelium an ...
, and a lamina propria
The lamina propria is a thin layer of connective tissue that forms part of the moist linings known as mucous membranes or mucosae, which line various tubes in the body, such as the respiratory tract, the gastrointestinal tract, and the urogenit ...
. The mucosal lining also offers a urothelial barrier against the passing of infections.
These layers are surrounded by three layers of muscle fibres arranged as an inner layer of fibres orientated longitudinally, a middle layer of circular fibres, and an outermost layer of longitudinal fibres; these form the detrusor muscle, which can be seen with the naked eye.
The outside of the bladder is protected by a serous membrane called adventitia.
Development
In the developingembryo
An embryo is an initial stage of development of a multicellular organism. In organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization of the female egg cell by the male spe ...
, at the hind end lies a cloaca. This, over the fourth to the seventh week, divides into a urogenital sinus and the beginnings of the anal canal
The anal canal is the part that connects the rectum to the anus, located below the level of the pelvic diaphragm. It is located within the anal triangle of the perineum, between the right and left ischioanal fossa. As the final functional segme ...
, with a wall forming between these two inpouchings called the urorectal septum. The urogenital sinus divides into three parts, with the upper and largest part becoming the bladder; the middle part becoming the urethra
The urethra (from Greek οὐρήθρα – ''ourḗthrā'') is a tube that connects the urinary bladder to the urinary meatus for the removal of urine from the body of both females and males. In human females and other primates, the urethra ...
, and the lower part changes depending on the biological sex of the embryo.
The human urinary bladder derives from the urogenital sinus, and it is initially continuous with the allantois
The allantois (plural ''allantoides'' or ''allantoises'') is a hollow sac-like structure filled with clear fluid that forms part of a developing amniote's conceptus (which consists of all embryonic and extraembryonic tissues). It helps the embryo ...
. The upper and lower parts of the bladder develop separately and join together around the middle part of development. At this time the ureters move from the mesonephric ducts to the trigone. In males, the base of the bladder lies between the rectum and the pubic symphysis. It is superior to the prostate, and separated from the rectum
The rectum is the final straight portion of the large intestine in humans and some other mammals, and the gut in others. The adult human rectum is about long, and begins at the rectosigmoid junction (the end of the sigmoid colon) at the l ...
by the recto-vesical pouch. In females, the bladder sits inferior to the uterus and anterior to the vagina; thus its maximum capacity is lower than in males. It is separated from the uterus
The uterus (from Latin ''uterus'', plural ''uteri'') or womb () is the organ in the reproductive system of most female mammals, including humans that accommodates the embryonic and fetal development of one or more embryos until birth. The ...
by the vesico-uterine pouch. In infants
An infant or baby is the very young offspring of human beings. ''Infant'' (from the Latin word ''infans'', meaning 'unable to speak' or 'speechless') is a formal or specialised synonym for the common term ''baby''. The terms may also be used ...
and young children the urinary bladder is in the abdomen
The abdomen (colloquially called the belly, tummy, midriff, tucky or stomach) is the part of the body between the thorax (chest) and pelvis, in humans and in other vertebrates. The abdomen is the front part of the abdominal segment of the to ...
even when empty.
Function
Urine
Urine is a liquid by-product of metabolism in humans and in many other animals. Urine flows from the kidneys through the ureters to the urinary bladder. Urination results in urine being excreted from the body through the urethra.
Cellul ...
, excreted by the kidney
The kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped organs found in vertebrates. They are located on the left and right in the retroperitoneal space, and in adult humans are about in length. They receive blood from the paired renal arteries; blo ...
s, collects in the bladder because of drainage from two ureters, before disposal by urination (micturition). Urine leaves the bladder via the urethra
The urethra (from Greek οὐρήθρα – ''ourḗthrā'') is a tube that connects the urinary bladder to the urinary meatus for the removal of urine from the body of both females and males. In human females and other primates, the urethra ...
, a single muscular tube ending in an opening called the urinary meatus
The urinary meatus, (, ) also known as the external urethral orifice, is the opening of the urethra. It is the point where urine exits the urethra in both sexes and where semen exits the urethra in males. The meatus has varying degrees of sensit ...
, where it exits the body. Urination involves coordinated muscle changes involving a reflex based in the spine, with higher inputs from the brain. During urination, the detrusor muscle contracts, and the external urinary sphincter and muscles of the perineum relax, allowing urine to pass through the urethra
The urethra (from Greek οὐρήθρα – ''ourḗthrā'') is a tube that connects the urinary bladder to the urinary meatus for the removal of urine from the body of both females and males. In human females and other primates, the urethra ...
and out of the body.
The urge to pass urine stems from stretch receptors that activate when between 300 - 400 mL urine is held within the bladder. As urine accumulates, the rugae
In anatomy, rugae are a series of ridges produced by folding of the wall of an organ. Most commonly rugae refers to the gastric rugae of the internal surface of the stomach.
Function
A purpose of the gastric rugae is to allow for expansion o ...
flatten and the wall of the bladder thins as it stretches, allowing the bladder to store larger amounts of urine without a significant rise in internal pressure. Urination is controlled by the pontine micturition center in the brainstem
The brainstem (or brain stem) is the posterior stalk-like part of the brain that connects the cerebrum with the spinal cord. In the human brain the brainstem is composed of the midbrain, the pons, and the medulla oblongata. The midbrain is ...
.
Stretch receptors in the bladder signal the parasympathetic
The parasympathetic nervous system (PSNS) is one of the three divisions of the autonomic nervous system, the others being the sympathetic nervous system and the enteric nervous system. The enteric nervous system is sometimes considered part of ...
nervous system to stimulate the muscarinic receptor
Muscarinic acetylcholine receptors, or mAChRs, are acetylcholine receptors that form G protein-coupled receptor complexes in the cell membranes of certain neurons and other cells. They play several roles, including acting as the main end-rec ...
s in the detrusor to contract the muscle when the bladder is distended. This encourages the bladder to expel urine through the urethra. The main receptor activated is the M3 receptor
The muscarinic acetylcholine receptor, also known as cholinergic/acetylcholine receptor M3, or the muscarinic 3, is a muscarinic acetylcholine receptor encoded by the human gene CHRM3.
The M3 muscarinic receptors are located at many places in t ...
, although M2 receptors are also involved and whilst outnumbering the M3 receptors they are not so responsive.
The main relaxant pathway is via the adenylyl cyclase
Adenylate cyclase (EC 4.6.1.1, also commonly known as adenyl cyclase and adenylyl cyclase, abbreviated AC) is an enzyme with systematic name ATP diphosphate-lyase (cyclizing; 3′,5′-cyclic-AMP-forming). It catalyzes the following reaction:
:A ...
cAMP
Camp may refer to:
Outdoor accommodation and recreation
* Campsite or campground, a recreational outdoor sleeping and eating site
* a temporary settlement for nomads
* Camp, a term used in New England, Northern Ontario and New Brunswick to descri ...
pathway, activated via the β3 adrenergic receptors. The β2 adrenergic receptors are also present in the detrusor and even outnumber β3 receptors, but they do not have as important an effect in relaxing the detrusor smooth muscle.
Clinical significance
Inflammation and infection
 Cystitis refers to infection or inflammation of the bladder. It commonly occurs as part of a urinary tract infection. In adults, it is more common in women than men, owing to a shorter
Cystitis refers to infection or inflammation of the bladder. It commonly occurs as part of a urinary tract infection. In adults, it is more common in women than men, owing to a shorter urethra
The urethra (from Greek οὐρήθρα – ''ourḗthrā'') is a tube that connects the urinary bladder to the urinary meatus for the removal of urine from the body of both females and males. In human females and other primates, the urethra ...
. It is common in males during childhood, and in older men where an enlarged prostate may cause urinary retention. Other risk factors include other causes of blockage or narrowing, such as prostate cancer or the presence of vesico-ureteric reflux; the presence of outside structures in the urinary tract, such as urinary catheters; and neurologic problems that make passing urine difficult. Infections that involve the bladder can cause pain in the lower abdomen (above the pubic symphysis, so called "suprapubic" pain), particularly before and after passing urine, and a desire to pass urine frequently and with little warning ( urinary urgency). Infections are usually due to bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were am ...
, of which the most common is E coli
''Escherichia coli'' (),Wells, J. C. (2000) Longman Pronunciation Dictionary. Harlow ngland Pearson Education Ltd. also known as ''E. coli'' (), is a Gram-negative, facultative anaerobic, rod-shaped, coliform bacterium of the genus ''Esche ...
.
When a urinary tract infection or cystitis is suspected, a medical practitioner
A physician (American English), medical practitioner (Commonwealth English), medical doctor, or simply doctor, is a health professional who practices medicine, which is concerned with promoting, maintaining or restoring health through t ...
may request a urine sample. A dipstick placed in the urine may be used to see if the urine has white blood cells, or the presence of nitrates
Nitrate is a polyatomic ion with the chemical formula . Salts containing this ion are called nitrates. Nitrates are common components of fertilizers and explosives. Almost all inorganic nitrates are soluble in water. An example of an insolu ...
which may indicate an infection. The urine specimen may be also sent for microbial culture and sensitivity to assess if a particular bacteria grows in the urine, and identify its antibiotic sensitivities. Sometimes, additional investigations may be requested. These might include testing the function of the kidneys by assessing electrolytes and creatinine; investigating for blockages or narrowing of the renal tract with a ultrasound
Ultrasound is sound waves with frequencies higher than the upper audible limit of human hearing. Ultrasound is not different from "normal" (audible) sound in its physical properties, except that humans cannot hear it. This limit varies ...
, and testing for an enlarged prostate with a digital rectal examination
Digital rectal examination (DRE; la, palpatio per anum, PPA) is an internal examination of the rectum, performed by a healthcare provider. Prior to a 2018 report from the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force, the DRE was a common and "dreaded" c ...
.
Urinary tract infections or cystitis are treated with antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the treatment and prevention ...
s, many of which are consumed by mouth. Serious infections may require treatment with intravenous antibiotics.
Interstitial cystitis refers to a condition in which the bladder is infected due to a cause that is not bacteria.
Incontinence and retention
Frequent urination can be due to excessive urine production, small bladder capacity, irritability or incomplete emptying. Males with an enlarged prostate urinate more frequently. One definition of anoveractive bladder
Overactive bladder (OAB) is a condition where there is a frequent feeling of needing to urinate to a degree that it negatively affects a person's life. The frequent need to urinate may occur during the day, at night, or both. If there is loss ...
is when a person urinates more than eight times per day. An overactive bladder can often cause urinary incontinence. Though both urinary frequency and volumes have been shown to have a circadian rhythm, meaning day and night cycles, it is not entirely clear how these are disturbed in the overactive bladder. Urodynamic testing
Urodynamic testing or urodynamics is a study that assesses how the bladder and urethra are performing their job of storing and releasing urine. Urodynamic tests can help explain symptoms such as:
* incontinence
* frequent urination
* sudden, stro ...
can help to explain the symptoms. An underactive bladder
Underactive bladder syndrome (UAB) describes symptoms of difficulty with bladder emptying, such as hesitancy to start the stream, a poor or intermittent stream, or sensations of incomplete bladder emptying. The physical finding of detrusor activ ...
is the condition where there is a difficulty in passing urine and is the main symptom of a neurogenic bladder. Frequent urination at night may indicate the presence of bladder stones.
Disorders of or related to the bladder include:
* Bladder exstrophy
* Bladder sphincter dyssynergia, a condition in which the sufferer cannot coordinate relaxation of the urethra sphincter with the contraction of the bladder muscles
* Paruresis
* Trigonitis
* Underactive bladder
Underactive bladder syndrome (UAB) describes symptoms of difficulty with bladder emptying, such as hesitancy to start the stream, a poor or intermittent stream, or sensations of incomplete bladder emptying. The physical finding of detrusor activ ...
, a condition with its main symptom being urinary retention.
Disorders of bladder function may be dealt with surgically, by re-directing the flow of urine or by replacement with an artificial urinary bladder
The two main methods for replacing bladder function involve either redirecting urine flow or replacing the bladder ''in situ''. Replacement can be done with an artificial urinary bladder, an artificial organ.
Development
On January 30, 1999, scie ...
. The volume of the bladder may be increased by bladder augmentation. An obstruction of the bladder neck may be severe enough to warrant surgery.
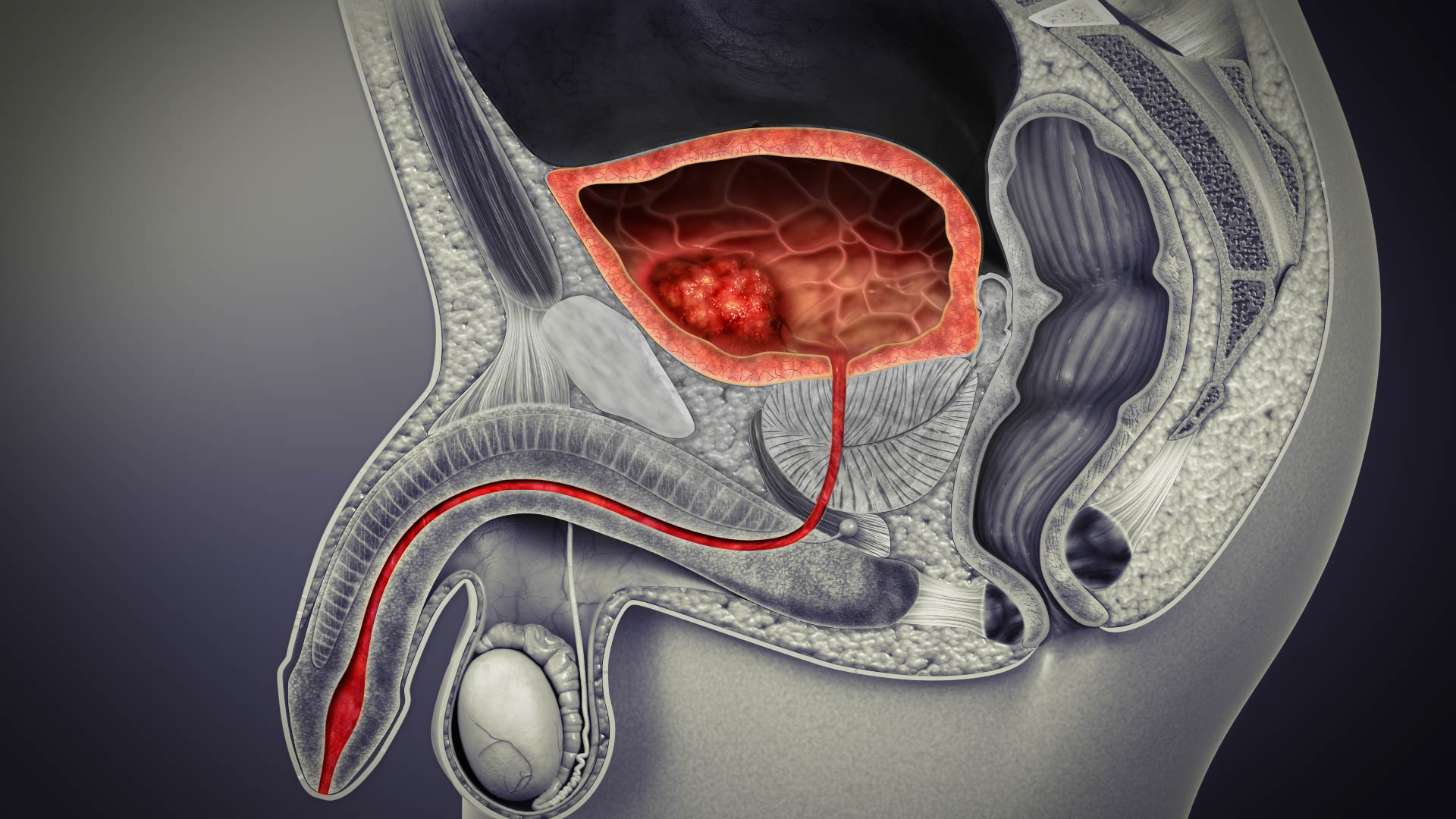
Cancer

Cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal b ...
of the bladder is known as bladder cancer
Bladder cancer is any of several types of cancer arising from the tissues of the urinary bladder. Symptoms include blood in the urine, pain with urination, and low back pain. It is caused when epithelial cells that line the bladder become ma ...
. It is usually due to cancer of the urothelium
Transitional epithelium also known as urothelium is a type of stratified epithelium. Transitional epithelium is a type of tissue that changes shape in response to stretching (stretchable epithelium). The transitional epithelium usually appears ...
, the cells that line the surface of the bladder. Bladder cancer is more common after the age of 40, and more common in men than women; other risk factors include smoking
Smoking is a practice in which a substance is burned and the resulting smoke is typically breathed in to be tasted and absorbed into the bloodstream. Most commonly, the substance used is the dried leaves of the tobacco plant, which have b ...
and exposure to dye
A dye is a colored substance that chemically bonds to the substrate to which it is being applied. This distinguishes dyes from pigments which do not chemically bind to the material they color. Dye is generally applied in an aqueous solution and ...
s such as aromatic amines and aldehydes. When cancer is present, the most common symptom in an affected person is blood in the urine; a physical medical examination
In a physical examination, medical examination, or clinical examination, a medical practitioner examines a patient for any possible medical signs or symptoms of a medical condition. It generally consists of a series of questions about the pat ...
may be otherwise normal, except in late disease. Bladder cancer is most often due to cancer of the cells lining the ureter, called transitional cell carcinoma, although it can more rarely occur as a squamous cell carcinoma if the type of cells lining the urethra have changed due to chronic inflammation, such as due to stones or schistosomiasis
Schistosomiasis, also known as snail fever, bilharzia, and Katayama fever, is a disease caused by parasitic flatworms called schistosomes. The urinary tract or the intestines may be infected. Symptoms include abdominal pain, diarrhea, blo ...
.
Investigations performed usually include collecting a sample of urine for an inspection for malignant cells under a microscope, called cytology, as well as medical imaging
Medical imaging is the technique and process of imaging the interior of a body for clinical analysis and medical intervention, as well as visual representation of the function of some organs or tissues (physiology). Medical imaging seeks to re ...
by a CT urogram or ultrasound
Ultrasound is sound waves with frequencies higher than the upper audible limit of human hearing. Ultrasound is not different from "normal" (audible) sound in its physical properties, except that humans cannot hear it. This limit varies ...
. If a concerning lesion is seen, a flexible camera may be inserted into the bladder, called cystoscopy, in order to view the lesion and take a biopsy
A biopsy is a medical test commonly performed by a surgeon, interventional radiologist, or an interventional cardiologist. The process involves extraction of sample cells or tissues for examination to determine the presence or extent of a dise ...
, and a CT scan will be performed of other body parts (a CT scan of the chest, abdomen and pelvis) to look for additional lesions.
Treatment depends on the cancer's stage. Cancer present only in the bladder may be removed surgically via cystoscopy; an injection of the chemotherapeutic
Chemotherapy (often abbreviated to chemo and sometimes CTX or CTx) is a type of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs (chemotherapeutic agents or alkylating agents) as part of a standardized chemotherapy regimen. Chemotherap ...
mitomycin C may be performed at the same time. Cancers that are high grade may be treated with an injection of the BCG vaccine into the bladder wall, and may require surgical removal if it does not resolve. Cancer that is invading through the bladder wall may be managed by complete surgical removal of the bladder (radical cystectomy
Cystectomy is a medical term for surgical removal of all or part of the urinary bladder. It may also be rarely used to refer to the removal of a cyst. The most common condition warranting removal of the urinary bladder is bladder cancer.
Two mai ...
), with the ureters diverted into a segment of part of ileum connected to a stoma bag on the skin. Prognosis can vary markedly depending on the cancer's stage and grade, with a better prognosis associated with tumours found only in the bladder, that are low grade, that don't invade through the bladder wall, and that is in visual appearance.
Investigation

 A number of investigations are used to examine the bladder. The investigations that are ordered will depend on the taking of a medical history and an examination. The examination may involve a
A number of investigations are used to examine the bladder. The investigations that are ordered will depend on the taking of a medical history and an examination. The examination may involve a medical practitioner
A physician (American English), medical practitioner (Commonwealth English), medical doctor, or simply doctor, is a health professional who practices medicine, which is concerned with promoting, maintaining or restoring health through t ...
feeling in the suprapubic area for tenderness or fullness that might indicate an inflamed or full bladder. Blood tests may be ordered that may indicate inflammation; for example a full blood count may demonstrate elevated white blood cells, or a C-reactive protein may be elevated in an infection.
Some forms of medical imaging
Medical imaging is the technique and process of imaging the interior of a body for clinical analysis and medical intervention, as well as visual representation of the function of some organs or tissues (physiology). Medical imaging seeks to re ...
exist to visualise the bladder. A bladder ultrasound may be conducted to view how much urine is within the bladder, indicating urinary retention. A urinary tract ultrasound, conducted by a more trained operator, may be conducted to view whether there are stones, tumours or sites of obstruction within the bladder and urinary tract. A Computed tomography of the abdomen and pelvis, CT scan may also be ordered.
A flexible internal camera, called a cystoscope, can be inserted to view the internal appearance of the bladder and take a biopsy
A biopsy is a medical test commonly performed by a surgeon, interventional radiologist, or an interventional cardiologist. The process involves extraction of sample cells or tissues for examination to determine the presence or extent of a dise ...
if required.
Urodynamic testing
Urodynamic testing or urodynamics is a study that assesses how the bladder and urethra are performing their job of storing and releasing urine. Urodynamic tests can help explain symptoms such as:
* incontinence
* frequent urination
* sudden, stro ...
can help to explain the symptoms.
Other animals
Mammals
All mammals have a urinary bladder. This structure begins as an embryonic cloaca. In the vast majority, this eventually becomes differentiated into a dorsal part connected to the intestine and a ventral part which becomes associated with the urinogenital passage and urinary bladder. The only mammals in which this does not take place are the platypus and the Echidna, spiny anteater both of which retain the cloaca into adulthood. The mammalian bladder is an organ that regularly stores a hyperosmotic concentration of urine. It therefore is relatively impermeable and has multiple epithelial layers. The urinary bladder of the cetaceans (whales and dolphins) is proportionally smaller than that of land-dwelling mammals.Reptiles
In all reptiles, the urinogenital ducts and the anus both empty into an organ called a cloaca. In some reptiles, a midventral wall in the cloaca may open into a urinary bladder, but not all. It is present in all turtles and tortoises as well as most lizards but is lacking in the monitor lizard, the legless lizards. It is absent in the snakes, alligators, and crocodiles. Many turtles, tortoises, and lizards have proportionally very large bladders. Charles Darwin noted that the Galapagos tortoise had a bladder which could store up to 20% of its body weight. Such adaptations are the result of environments such as remote islands and deserts where water is very scarce. Other desert-dwelling reptiles have large bladders that can store a long-term reservoir of water for up to several months and aid in osmoregulation. Turtles have two or more accessory urinary bladders, located lateral to the neck of the urinary bladder and dorsal to the pubis, occupying a significant portion of their body cavity. Their bladder is also usually bilobed with a left and right section. The right section is located under the liver, which prevents large stones from remaining in that side while the left section is more likely to have Bladder stone (animal), calculi.Amphibians
Most aquatic and semi-aquatic amphibians have a membranous skin which allows them to absorb water directly through it. Some semi-aquatic animals also have similarly permeable bladder membrane. As a result, they tend to have high rates of urine production to offset this high water intake, and have urine which is low in dissolved salts. The urinary bladder assists such animals to retain salts. Some aquatic amphibian such as ''Xenopus'' do not reabsorb water, to prevent excessive water influx. For land-dwelling amphibians, dehydration results in reduced urine output. The amphibian bladder is usually highly distensible and among some land-dwelling species of frogs and salamanders may account for between 20% and 50% of their total body weight.Fish
The gills of most teleost fish help to eliminate ammonia from the body, and fish live surrounded by water, but most still have a distinct bladder for storing waste fluid. The urinary bladder of teleosts is permeable to water, though this is less true for freshwater dwelling species than saltwater species. Most fish also have an organ called a swim-bladder which is unrelated to the urinary bladder except in its membranous nature. The loaches, pilchards, and herrings are among the few types of fish in which a urinary bladder is poorly developed. It is largest in those fish which lack an air bladder, and is situated in front of the oviducts and behind therectum
The rectum is the final straight portion of the large intestine in humans and some other mammals, and the gut in others. The adult human rectum is about long, and begins at the rectosigmoid junction (the end of the sigmoid colon) at the l ...
. The urinary bladders of fish and tetrapods are thought to be analogous while the former's swim-bladders and latter's lungs are considered homologous.
Birds
In nearly all bird species, there is no urinary bladder per se. Although all birds have kidneys, the ureters open directly into a cloaca which serves as a reservoir for urine, fecal matter, and eggs.Crustaceans
Unlike the urinary bladder of vertebrates, the urinary bladder of crustaceans both stores and modifies urine. The bladder consists of two sets of lateral and central lobes. The central lobes sit near the digestive organs and the lateral lobes extend along the front and sides of the crustacean's body cavity. The tissue of the bladder is thinepithelium
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. It is a thin, continuous, protective layer of compactly packed cells with a little intercellul ...
.
See also
* Alpha blocker * Cystitis glandularis * UPK1BReferences
;Books * *External links
* – "Mammal, bladder (LM, Medium)"Bladder
() – An open-access journal on bladder biology and diseases. {{Use dmy dates, date=April 2017 Urinary bladder, Pelvis Organs (anatomy) Urinary system