Upper Paleolithic on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
ROAD database
(CC BY-SA 4.0 ROCEEH)" width="400", height="300">
 The Upper Paleolithic (or Upper Palaeolithic) is the third and last subdivision of the
The Upper Paleolithic (or Upper Palaeolithic) is the third and last subdivision of the
''Science Daily'', July 1998 The Neanderthals continued to use Mousterian stone tool technology and possibly Châtelperronian technology. These
"The Caribou/Wild Reindeer as a Human Resource"
''American Antiquity'', Vol. 37, No. 3 (July 1972), pp. 339–368. Technological advances included significant developments in flint tool manufacturing, with industries based on fine
 The climate of the period in Europe saw dramatic changes, and included the
The climate of the period in Europe saw dramatic changes, and included the  The Last Glacial Maximum was followed by the
The Last Glacial Maximum was followed by the
 * First human inhabitants in
* First human inhabitants in  * Examples of cave art in Spain are dated from around 40,000 BP, making them the oldest examples of cave art yet discovered in Europe (see: Caves of Nerja). Scientists theorise that the paintings may have been made by
* Examples of cave art in Spain are dated from around 40,000 BP, making them the oldest examples of cave art yet discovered in Europe (see: Caves of Nerja). Scientists theorise that the paintings may have been made by
Charles T. Keally.

 * Spotted human hands are painted at Pech Merle cave,
* Spotted human hands are painted at Pech Merle cave,
 * Older Dryas stadial, Allerød interstadial.
* Paleo-Indians searched for big game near what is now the Hovenweep National Monument.
* Bison, on the ceiling of a cave at Altamira, Spain, is painted. Discovered in 1879. Accepted as authentic in 1902.
*
* Older Dryas stadial, Allerød interstadial.
* Paleo-Indians searched for big game near what is now the Hovenweep National Monument.
* Bison, on the ceiling of a cave at Altamira, Spain, is painted. Discovered in 1879. Accepted as authentic in 1902.
*
The Upper Paleolithic Revolution
.
– Libor Balák at the Czech Academy of Sciences, the Institute of Archaeology in Brno, The Center for Paleolithic and Paleoethnological Research. {{Authority control Pleistocene Quaternary geochronology Historical eras
(CC BY-SA 4.0 ROCEEH)" width="400", height="300">
 The Upper Paleolithic (or Upper Palaeolithic) is the third and last subdivision of the
The Upper Paleolithic (or Upper Palaeolithic) is the third and last subdivision of the Paleolithic
The Paleolithic or Palaeolithic ( years ago) ( ), also called the Old Stone Age (), is a period in human prehistory that is distinguished by the original development of stone tools, and which represents almost the entire period of human prehist ...
or Old Stone Age
The Stone Age was a broad prehistory, prehistoric period during which Rock (geology), stone was widely used to make stone tools with an edge, a point, or a percussion surface. The period lasted for roughly 3.4 million years and ended b ...
. Very broadly, it dates to between 50,000 and 12,000 years ago (the beginning of the Holocene
The Holocene () is the current geologic time scale, geological epoch, beginning approximately 11,700 years ago. It follows the Last Glacial Period, which concluded with the Holocene glacial retreat. The Holocene and the preceding Pleistocene to ...
), according to some theories coinciding with the appearance of behavioral modernity in early modern humans. It is followed by the Mesolithic
The Mesolithic (Ancient Greek language, Greek: μέσος, ''mesos'' 'middle' + λίθος, ''lithos'' 'stone') or Middle Stone Age is the Old World archaeological period between the Upper Paleolithic and the Neolithic. The term Epipaleolithic i ...
.
Anatomically modern humans (i.e. ''Homo sapiens'') are believed to have emerged in Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent after Asia. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 20% of Earth's land area and 6% of its total surfac ...
around 300,000 years ago. It has been argued by some that their ways of life changed relatively little from that of archaic humans
''Homo'' () is a genus of great ape (family Hominidae) that emerged from the genus ''Australopithecus'' and encompasses only a single extant species, ''Homo sapiens'' (modern humans), along with a number of extinct species (collectively calle ...
of the Middle Paleolithic, until about 50,000 years ago, when there was a marked increase in the diversity of artefacts found associated with modern human remains. This period coincides with the most common date assigned to expansion of modern humans from Africa throughout Asia and Eurasia, which may have contributed to the extinction of the Neanderthals.
The Upper Paleolithic has the earliest known evidence of organized settlements, in the form of campsites, some with storage pits. Artistic work blossomed, with cave painting, petroglyph
A petroglyph is an image created by removing part of a rock surface by incising, picking, carving, or abrading, as a form of rock art. Outside North America, scholars often use terms such as "carving", "engraving", or other descriptions ...
s, carvings and engravings on bone or ivory. The first evidence of human fishing is also found from a 125,000 years old artefacts in Buya, Eritrea, and in other places such as Blombos cave in South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the Southern Africa, southernmost country in Africa. Its Provinces of South Africa, nine provinces are bounded to the south by of coastline that stretches along the Atlantic O ...
. More complex social groupings emerged, supported by more varied and reliable food sources and specialized tool
A tool is an Physical object, object that can extend an individual's ability to modify features of the surrounding environment or help them accomplish a particular task. Although many Tool use by animals, animals use simple tools, only human bei ...
types. This probably contributed to increasing group identification or ethnicity
An ethnicity or ethnic group is a group of people with shared attributes, which they Collective consciousness, collectively believe to have, and long-term endogamy. Ethnicities share attributes like language, culture, common sets of ancestry, ...
.
The peopling of Australia most likely took place before c. 60 ka. Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east ...
was peopled after c. 45 ka.
Anatomically modern humans are known to have expanded northward into Siberia
Siberia ( ; , ) is an extensive geographical region comprising all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has formed a part of the sovereign territory of Russia and its predecessor states ...
as far as the 58th parallel by about 45 ka ( Ust'-Ishim man).
The Upper Paleolithic is divided by the Last Glacial Maximum
The Last Glacial Maximum (LGM), also referred to as the Last Glacial Coldest Period, was the most recent time during the Last Glacial Period where ice sheets were at their greatest extent between 26,000 and 20,000 years ago.
Ice sheets covered m ...
(LGM), from about 25 to 15 ka. The peopling of the Americas occurred during this time, with East and Central Asia populations reaching the Bering land bridge after about 35 ka, and expanding into the Americas by about 15 ka.
In Western Eurasia, the Paleolithic eases into the so-called Epipaleolithic or Mesolithic
The Mesolithic (Ancient Greek language, Greek: μέσος, ''mesos'' 'middle' + λίθος, ''lithos'' 'stone') or Middle Stone Age is the Old World archaeological period between the Upper Paleolithic and the Neolithic. The term Epipaleolithic i ...
from the end of the LGM, beginning 15 ka. The Holocene glacial retreat begins 11.7 ka ( 10th millennium BC), falling well into the Old World Epipaleolithic, and marking the beginning of the earliest forms of farming
Agriculture encompasses crop and livestock production, aquaculture, and forestry for food and non-food products. Agriculture was a key factor in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created ...
in the Fertile Crescent
The Fertile Crescent () is a crescent-shaped region in the Middle East, spanning modern-day Iraq, Israel, Jordan, Lebanon, Palestine, and Syria, together with northern Kuwait, south-eastern Turkey, and western Iran. Some authors also include ...
.
Lifestyle and technology
Both ''Homo erectus
''Homo erectus'' ( ) is an extinction, extinct species of Homo, archaic human from the Pleistocene, spanning nearly 2 million years. It is the first human species to evolve a humanlike body plan and human gait, gait, to early expansions of h ...
'' and Neanderthals
Neanderthals ( ; ''Homo neanderthalensis'' or sometimes ''H. sapiens neanderthalensis'') are an extinction, extinct group of archaic humans who inhabited Europe and Western and Central Asia during the Middle Pleistocene, Middle to Late Plei ...
used the same crude stone tools. Archaeologist Richard G. Klein, who has worked extensively on ancient stone tools, describes the stone tool kit of archaic hominids as impossible to categorize. He argues that almost everywhere, whether Asia
Asia ( , ) is the largest continent in the world by both land area and population. It covers an area of more than 44 million square kilometres, about 30% of Earth's total land area and 8% of Earth's total surface area. The continent, which ...
, Africa or Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east ...
, before 50,000 years ago all the stone tools are much alike and unsophisticated.
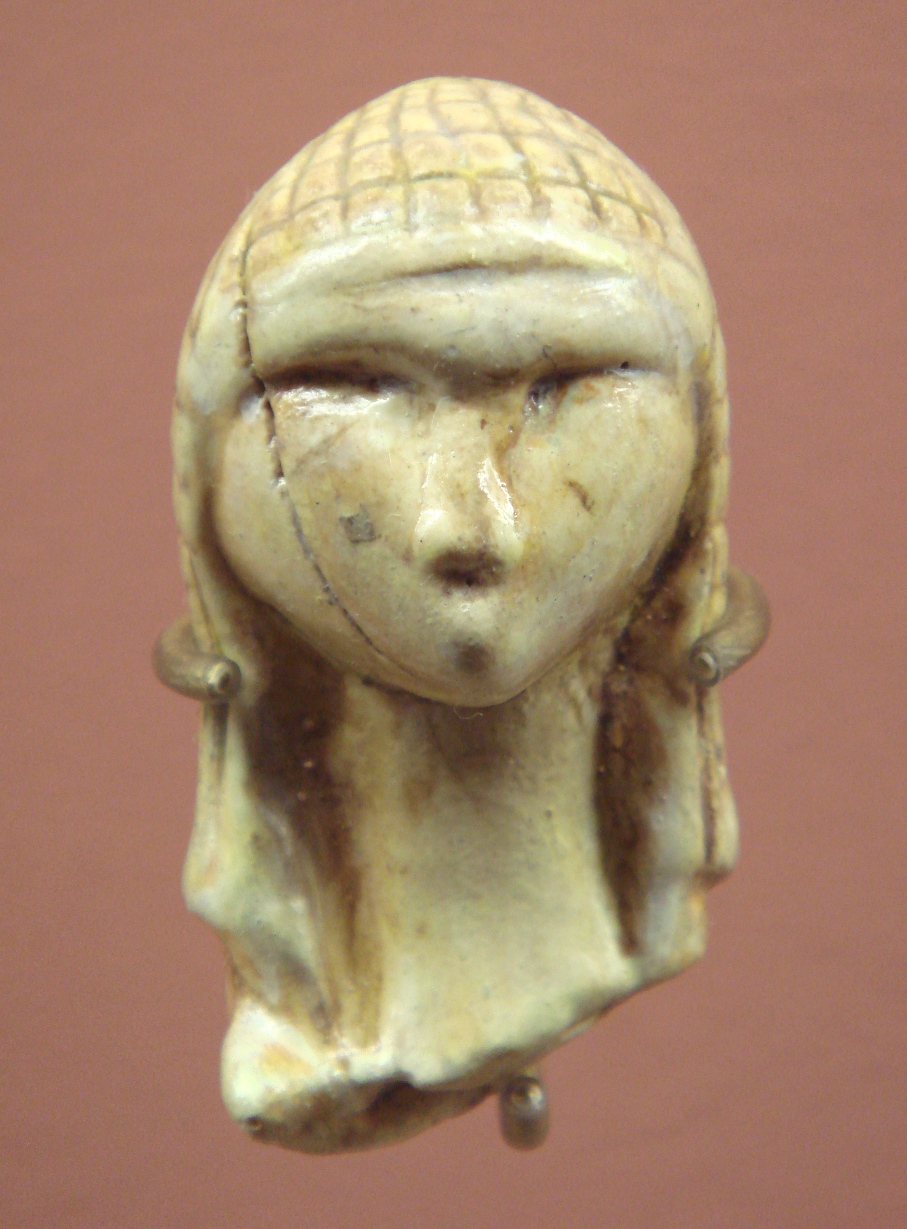
Firstly among the artefacts of Africa, archeologists found they could differentiate and classify those of less than 50,000 years into many different categories, such as projectile points, engraving tools, knife blades, and drilling and piercing tools. These new stone-tool types have been described as being distinctly differentiated from each other; each tool had a specific purpose. The early modern humans who expanded into Europe, commonly referred to as the Cro-Magnons, left many sophisticated stone tools, carved and engraved pieces on bone, ivory and antler
Antlers are extensions of an animal's skull found in members of the Cervidae (deer) Family (biology), family. Antlers are a single structure composed of bone, cartilage, fibrous tissue, skin, nerves, and blood vessels. They are generally fo ...
, cave paintings and Venus figurines
A Venus figurine is any Upper Palaeolithic statue portraying a woman, usually carved in the round.Fagan, Brian M., Beck, Charlotte, "Venus Figurines", beliefs '' The Oxford Companion to Archaeology'', 1996, Oxford University Press, pp. 740– ...
.Modern' Behavior Began 40,000 Years Ago In Africa"''Science Daily'', July 1998 The Neanderthals continued to use Mousterian stone tool technology and possibly Châtelperronian technology. These
tools
A tool is an object that can extend an individual's ability to modify features of the surrounding environment or help them accomplish a particular task. Although many animals use simple tools, only human beings, whose use of stone tools dates ...
disappeared from the archeological record at around the same time the Neanderthals themselves disappeared from the fossil record, about 40,000 cal BP.
Settlements were often located in narrow valley bottoms, possibly associated with hunting of passing herd
A herd is a social group of certain animals of the same species, either wild or domestic. The form of collective animal behavior associated with this is called '' herding''. These animals are known as gregarious animals.
The term ''herd'' ...
s of animals. Some of them may have been occupied year round, though more commonly they appear to have been used seasonally; people moved between the sites to exploit different food sources at different times of the year. Hunting was important, and caribou/wild reindeer "may well be the species of single greatest importance in the entire anthropological literature on hunting"."In North America and Eurasia the species has long been an important resource—in many areas ''the'' most important resource—for peoples' inhabiting the northern boreal forest
Taiga or tayga ( ; , ), also known as boreal forest or snow forest, is a biome characterized by pinophyta, coniferous forests consisting mostly of pines, spruces, and larches. The taiga, or boreal forest, is the world's largest land biome. I ...
and tundra
In physical geography, a tundra () is a type of biome where tree growth is hindered by frigid temperatures and short growing seasons. There are three regions and associated types of tundra: #Arctic, Arctic, Alpine tundra, Alpine, and #Antarctic ...
regions. Known human dependence on caribou/wild reindeer has a long history, beginning in the Middle Pleistocene
The Chibanian, more widely known as the Middle Pleistocene (its previous informal name), is an Age (geology), age in the international geologic timescale or a Stage (stratigraphy), stage in chronostratigraphy, being a division of the Pleistocen ...
(Banfield 1961:170; Kurtén 1968:170) and continuing to the present. ... The caribou/wild reindeer is thus an animal that has been a major resource for humans throughout a tremendous geographic area and across a time span of tens of thousands of years." Ernest S. Burch, Jr"The Caribou/Wild Reindeer as a Human Resource"
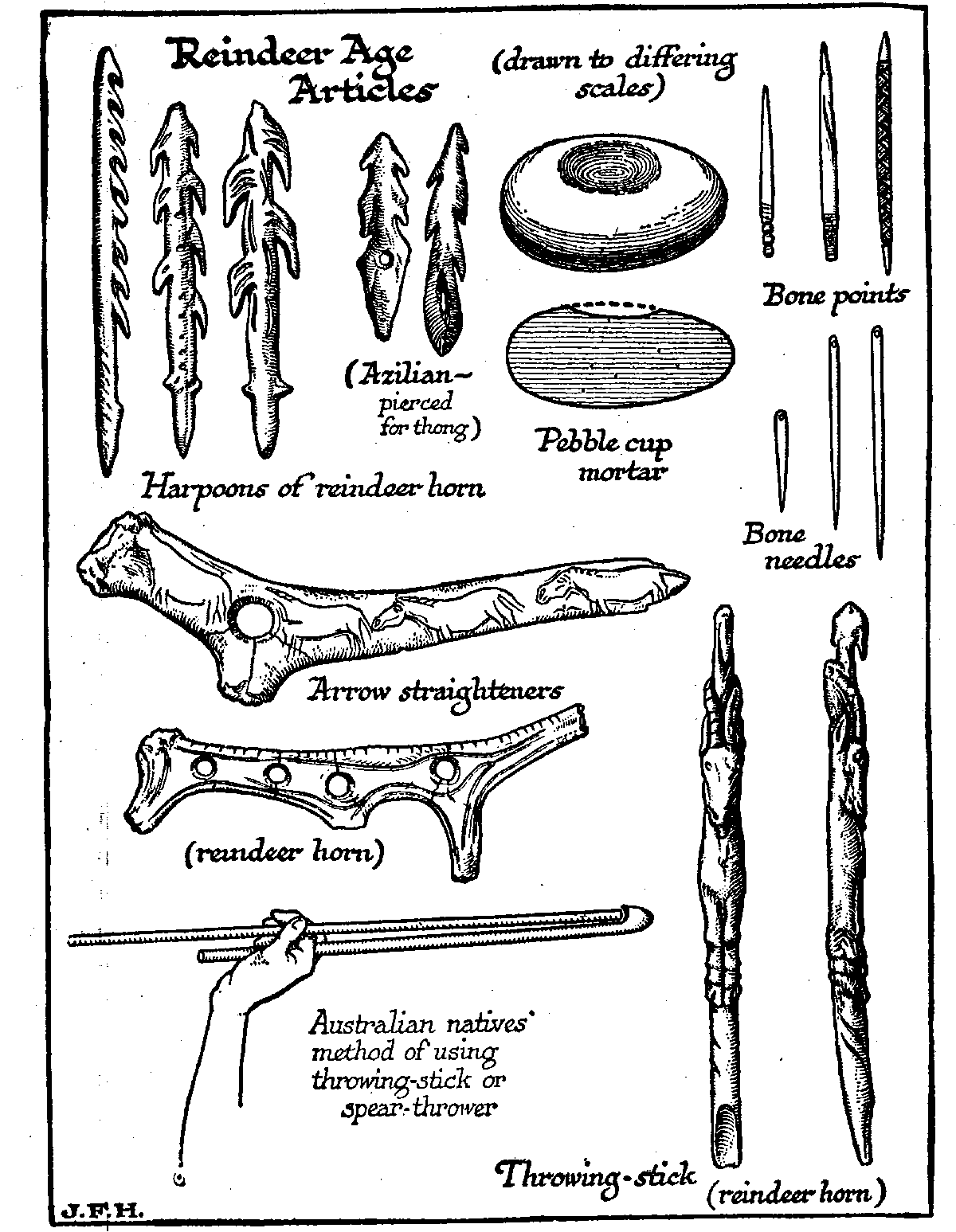
''American Antiquity'', Vol. 37, No. 3 (July 1972), pp. 339–368. Technological advances included significant developments in flint tool manufacturing, with industries based on fine
blade
A blade is the Sharpness (cutting), sharp, cutting portion of a tool, weapon, or machine, specifically designed to puncture, chop, slice, or scrape surfaces or materials. Blades are typically made from materials that are harder than those they a ...
s rather than simpler and shorter flakes. Burins and racloirs were used to work bone, antler and hides. Advanced darts and harpoons also appear in this period, along with the fish hook, the oil lamp
An oil lamp is a lamp used to produce light continuously for a period of time using an oil-based fuel source. The use of oil lamps began thousands of years ago and continues to this day, although their use is less common in modern times. The ...
, rope
A rope is a group of yarns, Plying, plies, fibres, or strands that are plying, twisted or braided together into a larger and stronger form. Ropes have high tensile strength and can be used for dragging and lifting. Rope is thicker and stronger ...
, and the eyed needle. Fishing of pelagic
The pelagic zone consists of the water column of the open ocean and can be further divided into regions by depth. The word ''pelagic'' is derived . The pelagic zone can be thought of as an imaginary cylinder or water column between the sur ...
fish species and navigating the open ocean is evidenced by sites from Timor
Timor (, , ) is an island at the southern end of Maritime Southeast Asia, in the north of the Timor Sea. The island is Indonesia–Timor-Leste border, divided between the sovereign states of Timor-Leste in the eastern part and Indonesia in the ...
and Buka (Solomon Islands
Solomon Islands, also known simply as the Solomons,John Prados, ''Islands of Destiny'', Dutton Caliber, 2012, p,20 and passim is an island country consisting of six major islands and over 1000 smaller islands in Melanesia, part of Oceania, t ...
).
The changes in human behavior have been attributed to changes in climate, encompassing a number of global temperature
Temperature is a physical quantity that quantitatively expresses the attribute of hotness or coldness. Temperature is measurement, measured with a thermometer. It reflects the average kinetic energy of the vibrating and colliding atoms making ...
drops. These led to a worsening of the already bitter cold of the last glacial period (popularly but incorrectly called the last ice age
An ice age is a long period of reduction in the temperature of Earth's surface and atmosphere, resulting in the presence or expansion of continental and polar ice sheets and alpine glaciers. Earth's climate alternates between ice ages, and g ...
). Such changes may have reduced the supply of usable timber
Lumber is wood that has been processed into uniform and useful sizes (dimensional lumber), including beams and planks or boards. Lumber is mainly used for construction framing, as well as finishing (floors, wall panels, window frames). ...
and forced people to look at other materials. In addition, flint becomes brittle at low temperatures and may not have functioned as a tool.
Notational signs
Some notational signs, used next to images of animals, may have appeared as early as the Upper Palaeolithic in Europe circa 35,000 BCE, and may be the earliest proto-writing: several symbols were used in combination as a way to convey seasonal behavioural information about hunted animals. Lines (, ) and dots (•) were apparently used interchangeably to denote lunar months, while the (Y) sign apparently signified "To give birth". These characters were seemingly combined to convey the breeding period of hunted animals.Changes in climate and geography
 The climate of the period in Europe saw dramatic changes, and included the
The climate of the period in Europe saw dramatic changes, and included the Last Glacial Maximum
The Last Glacial Maximum (LGM), also referred to as the Last Glacial Coldest Period, was the most recent time during the Last Glacial Period where ice sheets were at their greatest extent between 26,000 and 20,000 years ago.
Ice sheets covered m ...
, the coldest phase of the last glacial period, which lasted from about 26.5 to 19 kya, being coldest at the end, before relatively rapid warming (all dates vary somewhat for different areas, and in different studies). During the Maximum, most of Northern Europe was covered by an ice-sheet, forcing human populations into the areas known as Last Glacial Maximum refugia, including modern Italy and the Balkans
The Balkans ( , ), corresponding partially with the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throug ...
, parts of the Iberian Peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula ( ), also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in south-western Europe. Mostly separated from the rest of the European landmass by the Pyrenees, it includes the territories of peninsular Spain and Continental Portugal, comprisin ...
and areas around the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal sea, marginal Mediterranean sea (oceanography), mediterranean sea lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bound ...
.
This period saw cultures such as the Solutrean in France and Spain. Human life may have continued on top of the ice sheet, but we know next to nothing about it, and very little about the human life that preceded the European glaciers. In the early part of the period, up to about 30 kya, the Mousterian Pluvial made northern Africa, including the Sahara
The Sahara (, ) is a desert spanning across North Africa. With an area of , it is the largest hot desert in the world and the list of deserts by area, third-largest desert overall, smaller only than the deserts of Antarctica and the northern Ar ...
, well-watered and with lower temperatures than today; after the end of the Pluvial the Sahara became arid.
 The Last Glacial Maximum was followed by the
The Last Glacial Maximum was followed by the Allerød oscillation Allerød may refer to:
* Allerød Municipality, a municipality in Denmark
** Lillerød, also called ''Allerød'', seat of the municipality
** Allerød station, a railway station in the Danish town
* Allerød oscillation, a climatic period at the en ...
, a warm and moist global interstadial
Stadials and interstadials are phases dividing the Quaternary period, or the last 2.6 million years. Stadials are periods of colder climate, and interstadials are periods of warmer climate.
Each Quaternary climate phase has been assigned with a ...
that occurred around 13.5 to 13.8 kya. Then there was a very rapid onset, perhaps within as little as a decade, of the cold and dry Younger Dryas
The Younger Dryas (YD, Greenland Stadial GS-1) was a period in Earth's geologic history that occurred circa 12,900 to 11,700 years Before Present (BP). It is primarily known for the sudden or "abrupt" cooling in the Northern Hemisphere, when the ...
climate period, giving sub-arctic conditions to much of northern Europe.
The Preboreal rise in temperatures also began sharply around 10.3 kya, and by its end around 9.0 kya had brought temperatures nearly to present day levels, although the climate was wetter.
This period saw the Upper Paleolithic give way to the start of the following Mesolithic
The Mesolithic (Ancient Greek language, Greek: μέσος, ''mesos'' 'middle' + λίθος, ''lithos'' 'stone') or Middle Stone Age is the Old World archaeological period between the Upper Paleolithic and the Neolithic. The term Epipaleolithic i ...
cultural period.
As the glaciers receded sea levels rose; the English Channel
The English Channel, also known as the Channel, is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that separates Southern England from northern France. It links to the southern part of the North Sea by the Strait of Dover at its northeastern end. It is the busi ...
, Irish Sea
The Irish Sea is a body of water that separates the islands of Ireland and Great Britain. It is linked to the Celtic Sea in the south by St George's Channel and to the Inner Seas off the West Coast of Scotland in the north by the North Ch ...
and North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Denmark, Norway, Germany, the Netherlands, Belgium, and France. A sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the Norwegian Se ...
were land at this time, and the Black Sea a fresh-water lake. In particular the Atlantic coastline was initially far out to sea in modern terms in most areas, though the Mediterranean coastline has retreated far less, except in the north of the Adriatic and the Aegean. The rise in sea levels continued until at least 7.5 kya ( 5500 BC), so evidence of human activity along Europe's coasts in the Upper Paleolithic is mostly lost, though some traces have been recovered by fishing boats and marine archaeology, especially from Doggerland, the lost area beneath the North Sea.
Timeline
50,000–40,000 BP
50,000 BP
* Numerous Aboriginal stone tools were found in gravel sediments in Castlereagh, Sydney, Australia. At first when these results were new they were controversial; more recently dating of the same strata has revised and corroborated these dates. * Start of the Mousterian Pluvial in North Africa. * Occupants of the Fa-Hien Lena cave,Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka, officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka, also known historically as Ceylon, is an island country in South Asia. It lies in the Indian Ocean, southwest of the Bay of Bengal, separated from the Indian subcontinent, ...
had developed bow and arrow
The bow and arrow is a ranged weapon system consisting of an elasticity (physics), elastic launching device (bow) and long-shafted projectiles (arrows). Humans used bows and arrows for hunting and aggression long before recorded history, and the ...
technology 48,000 BP (though the earliest known bow and arrow technology dates to about 65,000 BP from Sibudu Cave
Sibudu Cave is a rock shelter in a sandstone cliff in northern KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. It is an important Middle Stone Age site occupied, with some gaps, from years ago to years ago.
Evidence of some of the earliest examples of modern h ...
, South Africa).48,000 BP
The first direct evidence forNeanderthals
Neanderthals ( ; ''Homo neanderthalensis'' or sometimes ''H. sapiens neanderthalensis'') are an extinction, extinct group of archaic humans who inhabited Europe and Western and Central Asia during the Middle Pleistocene, Middle to Late Plei ...
hunting cave lions. This is based on a cave lion skeleton found in Seigsdorf, Germany which has hunting lesions.
45,000–43,000 BP
* Earliest evidence of modern humans found in Europe, in Southern Italy. These are indirectly dated. * Earliest mathematical artifact, the notched Lebombo bone, a possible tally stick or lunar calendar, dated to 44,000–43,000 BP in Eswatini (Swaziland), southern Africa. * Oldest-known mining in archaeological record, the Ngwenya Mine in Swaziland, at about 43,000 years ago, where humans minedhematite
Hematite (), also spelled as haematite, is a common iron oxide compound with the formula, Fe2O3 and is widely found in rocks and soils. Hematite crystals belong to the rhombohedral lattice system which is designated the alpha polymorph of . ...
to make the red pigment ochre
Ochre ( ; , ), iron ochre, or ocher in American English, is a natural clay earth pigment, a mixture of ferric oxide and varying amounts of clay and sand. It ranges in colour from yellow to deep orange or brown. It is also the name of the colou ...
.
* Earliest directly dated figurative cave art of mankind at Leang Bulu' Sipong in Sulawesi
Sulawesi ( ), also known as Celebes ( ), is an island in Indonesia. One of the four Greater Sunda Islands, and the List of islands by area, world's 11th-largest island, it is situated east of Borneo, west of the Maluku Islands, and south of Min ...
, Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania, between the Indian Ocean, Indian and Pacific Ocean, Pacific oceans. Comprising over List of islands of Indonesia, 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, ...
.
43,000–41,000 BP
* Microlithic artefacts have been excavated from Kana,West Bengal
West Bengal (; Bengali language, Bengali: , , abbr. WB) is a States and union territories of India, state in the East India, eastern portion of India. It is situated along the Bay of Bengal, along with a population of over 91 million inhabi ...
, India.
* Ornaments and skeletal remains of modern humans, at Ksar Akil in Lebanon
Lebanon, officially the Republic of Lebanon, is a country in the Levant region of West Asia. Situated at the crossroads of the Mediterranean Basin and the Arabian Peninsula, it is bordered by Syria to the north and east, Israel to the south ...
. These are directly dated.
* Denisova hominins live in the Altai Mountains
The Altai Mountains (), also spelled Altay Mountains, are a mountain range in Central Asia, Central and East Asia, where Russia, China, Mongolia, and Kazakhstan converge, and where the rivers Irtysh and Ob River, Ob have their headwaters. The ...
(Russia, China, Mongolia, and Kazakhstan).
40,000–30,000 BP
40,000–35,000 BP
 * First human inhabitants in
* First human inhabitants in Perth
Perth () is the list of Australian capital cities, capital city of Western Australia. It is the list of cities in Australia by population, fourth-most-populous city in Australia, with a population of over 2.3 million within Greater Perth . The ...
, Australia, as evidenced by archaeological findings on the Upper Swan River.
* During this time period, Melbourne
Melbourne ( , ; Boonwurrung language, Boonwurrung/ or ) is the List of Australian capital cities, capital and List of cities in Australia by population, most populous city of the States and territories of Australia, Australian state of Victori ...
, Australia was occupied by hunter-gatherer
A hunter-gatherer or forager is a human living in a community, or according to an ancestrally derived Lifestyle, lifestyle, in which most or all food is obtained by foraging, that is, by gathering food from local naturally occurring sources, esp ...
s.Isabel Ellender and Peter Christiansen, ''People of the Merri Merri. The Wurundjeri in Colonial Days'', Merri Creek Management Committee, 2001
* Early cultural centre in the Swabian Alps, oldest depiction of a human being (Venus of Hohle Fels
The Venus of Hohle Fels (also known as the Venus of Schelklingen; in German variously ') is an Upper Paleolithic Venus figurine made of mammoth ivory that was unearthed in 2008 in Hohle Fels, a cave near Schelklingen, Germany, part of the Ca ...
), beginning of the Aurignacian
The Aurignacian () is an archaeological industry of the Upper Paleolithic associated with Cro-Magnon, Early European modern humans (EEMH) lasting from 43,000 to 26,000 years ago. The Upper Paleolithic developed in Europe some time after the L ...
.
* figure created in Hohlenstein-Stadel, one of the earliest figurative art. It is now in Ulmer Museum, Ulm, Germany.
* The first flutes
The flute is a member of a family of musical instruments in the woodwind group. Like all woodwinds, flutes are aerophones, producing sound with a vibrating column of air. Flutes produce sound when the player's air flows across an opening. In th ...
appear in Germany.
* Notational signs in caves, apparently conveying calendar
A calendar is a system of organizing days. This is done by giving names to periods of time, typically days, weeks, months and years. A calendar date, date is the designation of a single and specific day within such a system. A calendar is ...
ic meaning about the behaviour of animal species drawn next to them, are the first known (proto-)writing
Writing is the act of creating a persistent representation of language. A writing system includes a particular set of symbols called a ''script'', as well as the rules by which they encode a particular spoken language. Every written language ...
in history .
* Most of the giant vertebrates and megafauna in Australia became extinct.
* Fishing of pelagic fish species at Jerimalai shelter, Timor. * Examples of cave art in Spain are dated from around 40,000 BP, making them the oldest examples of cave art yet discovered in Europe (see: Caves of Nerja). Scientists theorise that the paintings may have been made by
* Examples of cave art in Spain are dated from around 40,000 BP, making them the oldest examples of cave art yet discovered in Europe (see: Caves of Nerja). Scientists theorise that the paintings may have been made by Neanderthals
Neanderthals ( ; ''Homo neanderthalensis'' or sometimes ''H. sapiens neanderthalensis'') are an extinction, extinct group of archaic humans who inhabited Europe and Western and Central Asia during the Middle Pleistocene, Middle to Late Plei ...
, rather than by modern humans.
* Wall painting with horses, rhinoceroses and aurochs is made at Chauvet Cave, Vallon-Pont-d'Arc, Ardéche gorge, France. Discovered in December 1994.
*Evidence for continued Neanderthal presence in the Iberian Peninsula at 37,000 years ago was published in 2017.
* Archaeological
Archaeology or archeology is the study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of Artifact (archaeology), artifacts, architecture, biofact (archaeology), biofacts or ecofacts, ...
studies support human presence in the Chek Lap Kok area (now Hong Kong International Airport) from 35,000 to 39,000 years ago.
* Zar, Yataghyeri, Damjili and Taghlar caves in Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan, officially the Republic of Azerbaijan, is a Boundaries between the continents, transcontinental and landlocked country at the boundary of West Asia and Eastern Europe. It is a part of the South Caucasus region and is bounded by ...
.
* First evidence of people inhabiting Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea ...
."Prehistoric Archaeological Periods in Japan"Charles T. Keally.
35,000-30,000 BP
* Kostenki XVII, a layer of the Kostenki (Kostyonki) site, on the middle Don River, was occupied by the early upper paleolithic Spitsyn culture. * The Red Lady of Paviland (really a young man) lived around 33,600 years ago.30,000 BP
* First ground stone tools appear in Japan. * End of the Mousterian Pluvial in North Africa. * The area ofSydney
Sydney is the capital city of the States and territories of Australia, state of New South Wales and the List of cities in Australia by population, most populous city in Australia. Located on Australia's east coast, the metropolis surrounds Syd ...
was occupied by Aboriginal Australians
Aboriginal Australians are the various indigenous peoples of the Mainland Australia, Australian mainland and many of its islands, excluding the ethnically distinct people of the Torres Strait Islands.
Humans first migrated to Australia (co ...
(specifically, the Eora and Dharug people) during this time period, as evidenced by radiocarbon dating
Radiocarbon dating (also referred to as carbon dating or carbon-14 dating) is a method for Chronological dating, determining the age of an object containing organic material by using the properties of carbon-14, radiocarbon, a radioactive Isotop ...
.
*
* In an archaeological dig in Parramatta
Parramatta (; ) is a suburb (Australia), suburb and major commercial centre in Greater Western Sydney. Parramatta is located approximately west of the Sydney central business district, Sydney CBD, on the banks of the Parramatta River. It is co ...
, Western Sydney, it was found that the Aboriginals used charcoal, stone tools and possible ancient campfires.
* First human settlement in Alice Springs, Northern Territory
The Northern Territory (abbreviated as NT; known formally as the Northern Territory of Australia and informally as the Territory) is an states and territories of Australia, Australian internal territory in the central and central-northern regi ...
, Australia.
* Kilu Cave at Buka in the Solomons is evidence for the first human settlement of an oceanic island and for navigating the open ocean.

30,000–20,000 BP
29,000–25,000 BP
* Eruption of the Ciomad volcano, the last volcanic eruption in the Carpathians. * Venus of Dolní Věstonice (Czech Republic). It is the oldest known ceramic in the world. *Venus of Willendorf
The Venus of Willendorf is an Venus figurine estimated to have been made years ago. It was recovered on 7 August 1908 from an archaeological dig conducted by Josef Szombathy, Hugo Obermaier, and Josef Bayer at a Paleolithic site near Willendorf ...
, Austria, created. It is now at the Natural History Museum, Vienna.
* Human settlement in Beijing
Beijing, Chinese postal romanization, previously romanized as Peking, is the capital city of China. With more than 22 million residents, it is the world's List of national capitals by population, most populous national capital city as well as ...
, China dates from about 27,000 to 10,000 years ago.
* Paintings of spotted horses, Pech Merle cave, Dordogne
Dordogne ( , or ; ; ) is a large rural departments of France, department in south west France, with its Prefectures in France, prefecture in Périgueux. Located in the Nouvelle-Aquitaine region roughly half-way between the Loire Valley and ...
, date to c.25,000 years ago
24,000 BP
* Start of the second Mousterian Pluvial in North Africa.23,000 BP
* Venus of Petřkovice is created at Petřkovice inOstrava
Ostrava (; ; ) is a city in the north-east of the Czech Republic and the capital of the Moravian-Silesian Region. It has about 283,000 inhabitants. It lies from the border with Poland, at the confluences of four rivers: Oder, Opava (river), Opa ...
, Czech Republic. It is now in Archeological Institute, Brno
Brno ( , ; ) is a Statutory city (Czech Republic), city in the South Moravian Region of the Czech Republic. Located at the confluence of the Svitava (river), Svitava and Svratka (river), Svratka rivers, Brno has about 403,000 inhabitants, making ...
.
22,000 BP
*Last Glacial Maximum
The Last Glacial Maximum (LGM), also referred to as the Last Glacial Coldest Period, was the most recent time during the Last Glacial Period where ice sheets were at their greatest extent between 26,000 and 20,000 years ago.
Ice sheets covered m ...
: Venus of Brassempouy, Grotte du Pape, Brassempouy, Landes, France, created. It is now at Musée des Antiquités Nationales, Saint-Germain-en-Laye
Saint-Germain-en-Laye () is a Communes of France, commune in the Yvelines Departments of France, department in the Île-de-France in north-central France. It is located in the western suburbs of Paris, from the Kilometre Zero, centre of Paris. ...
.
21,000 BP
*Artifacts suggests early human activity occurred at some point inCanberra
Canberra ( ; ) is the capital city of Australia. Founded following the Federation of Australia, federation of the colonies of Australia as the seat of government for the new nation, it is Australia's list of cities in Australia, largest in ...
, Australia. Archaeological evidence of settlement in the region includes inhabited rock shelter
A rock shelter (also rockhouse, crepuscular cave, bluff shelter, or abri) is a shallow cave-like opening at the base of a bluff or cliff. In contrast to solutional caves (karst), which are often many miles long or wide, rock shelters are alm ...
s, rock art, burial places, camps and quarry sites, and stone tools and arrangements.
* End of the second Mousterian Pluvial in North Africa.
20,000–10,000 BP
*Last Glacial Maximum
The Last Glacial Maximum (LGM), also referred to as the Last Glacial Coldest Period, was the most recent time during the Last Glacial Period where ice sheets were at their greatest extent between 26,000 and 20,000 years ago.
Ice sheets covered m ...
. Mean sea level
Mean sea level (MSL, often shortened to sea level) is an mean, average surface level of one or more among Earth's coastal Body of water, bodies of water from which heights such as elevation may be measured. The global MSL is a type of vertical ...
s are believed to be ''lower than present'', with the direct implication that many coastal and lower riverine valley archaeological sites of interest are today under water.
18,000 BP
* Ibex-headedspear-thrower
A spear-thrower, spear-throwing lever, or ''atlatl'' (pronounced or ; Classical Nahuatl, Nahuatl ''ahtlatl'' ) is a tool that uses leverage to achieve greater velocity in Dart (missile), dart or javelin-throwing, and includes a Plain bearing, b ...
, from Mas-d'Azil cave, now at the Musée de la Préhistoire in the village of Le Mas-d'Azil
Le Mas-d'Azil (; ) is a Communes of France, commune in the Ariège (department), Ariège Departments of France, department in southwestern France, containing a cave that is the typesite for the prehistoric Azilian culture. The ''Mas d'Azil cav ...
.
* Mammoth
A mammoth is any species of the extinct elephantid genus ''Mammuthus.'' They lived from the late Miocene epoch (from around 6.2 million years ago) into the Holocene until about 4,000 years ago, with mammoth species at various times inhabi ...
-bone village in Mezhyrich, Ukraine
Ukraine is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the List of European countries by area, second-largest country in Europe after Russia, which Russia–Ukraine border, borders it to the east and northeast. Ukraine also borders Belarus to the nor ...
17,000 BP
 * Spotted human hands are painted at Pech Merle cave,
* Spotted human hands are painted at Pech Merle cave, Dordogne
Dordogne ( , or ; ; ) is a large rural departments of France, department in south west France, with its Prefectures in France, prefecture in Périgueux. Located in the Nouvelle-Aquitaine region roughly half-way between the Loire Valley and ...
, France. Discovered in December 1994.
* Oldest Dryas stadial.
* Hall of Bulls at Lascaux
Lascaux ( , ; , "Lascaux Cave") is a network of caves near the village of Montignac, Dordogne, Montignac, in the Departments of France, department of Dordogne in southwestern France. Over 600 Parietal art, parietal cave painting, wall paintin ...
in France is painted. Discovered in 1940. Closed to the public in 1963.
* Bird-Headed man with bison and Rhinoceros, Lascaux
Lascaux ( , ; , "Lascaux Cave") is a network of caves near the village of Montignac, Dordogne, Montignac, in the Departments of France, department of Dordogne in southwestern France. Over 600 Parietal art, parietal cave painting, wall paintin ...
, is painted.
* Lamp with ibex design, from La Mouthe cave, Dordogne
Dordogne ( , or ; ; ) is a large rural departments of France, department in south west France, with its Prefectures in France, prefecture in Périgueux. Located in the Nouvelle-Aquitaine region roughly half-way between the Loire Valley and ...
, France, is made. It is now at Musée des Antiquités Nationales, Saint-Germain-en-Laye
Saint-Germain-en-Laye () is a Communes of France, commune in the Yvelines Departments of France, department in the Île-de-France in north-central France. It is located in the western suburbs of Paris, from the Kilometre Zero, centre of Paris. ...
.
* Paintings in Cosquer Cave are made, where the cave mouth is now under water at Cap Margiou, France.
15,000 BP
* Bølling interstadial. * Bison, Le Tuc d'Audoubert, Ariège, France. * Paleo-Indians move across North America, then southward through Central America. * Pregnant woman and deer (?), from Laugerie-Basse, France was made. It is now at Musée des Antiquités Nationales, St.-Germain-en-Laye. 14,000 BP * Older Dryas stadial, Allerød interstadial.
* Paleo-Indians searched for big game near what is now the Hovenweep National Monument.
* Bison, on the ceiling of a cave at Altamira, Spain, is painted. Discovered in 1879. Accepted as authentic in 1902.
*
* Older Dryas stadial, Allerød interstadial.
* Paleo-Indians searched for big game near what is now the Hovenweep National Monument.
* Bison, on the ceiling of a cave at Altamira, Spain, is painted. Discovered in 1879. Accepted as authentic in 1902.
* Younger Dryas
The Younger Dryas (YD, Greenland Stadial GS-1) was a period in Earth's geologic history that occurred circa 12,900 to 11,700 years Before Present (BP). It is primarily known for the sudden or "abrupt" cooling in the Northern Hemisphere, when the ...
stadial.
* Beginning of the Holocene extinction
The Holocene extinction, also referred to as the Anthropocene extinction or the sixth mass extinction, is an ongoing extinction event caused exclusively by human activities during the Holocene epoch. This extinction event spans numerous families ...
.
12,000 BP
* Wooden buildings in South America (Chile
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in western South America. It is the southernmost country in the world and the closest to Antarctica, stretching along a narrow strip of land between the Andes, Andes Mountains and the Paci ...
).
* First pottery
Pottery is the process and the products of forming vessels and other objects with clay and other raw materials, which are fired at high temperatures to give them a hard and durable form. The place where such wares are made by a ''potter'' is al ...
vessels in Japan.
11,000 BP
* First evidence of human settlement inArgentina
Argentina, officially the Argentine Republic, is a country in the southern half of South America. It covers an area of , making it the List of South American countries by area, second-largest country in South America after Brazil, the fourt ...
.
* The Arlington Springs Man dies on the island of Santa Rosa, off the coast of California, United States.
* Human remains deposited in caves which are now located off the coast of Yucatán, Mexico.
* Creswellian culture settlement on Hengistbury Head, England, dates from around this year.
10,000 BP
*Evidence of a massacre near Lake Turkana,Kenya
Kenya, officially the Republic of Kenya, is a country located in East Africa. With an estimated population of more than 52.4 million as of mid-2024, Kenya is the 27th-most-populous country in the world and the 7th most populous in Africa. ...
indicates upper paleolithic warfare.
Cultures
The Upper Paleolithic in the Franco-Cantabrian region: *The Châtelperronian culture was located around central and south western France, and northern Spain. It appears to be derived from the Mousterian culture, and represents the period of overlap betweenNeanderthal
Neanderthals ( ; ''Homo neanderthalensis'' or sometimes ''H. sapiens neanderthalensis'') are an extinction, extinct group of archaic humans who inhabited Europe and Western and Central Asia during the Middle Pleistocene, Middle to Late Plei ...
s and ''Homo sapiens
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') or modern humans are the most common and widespread species of primate, and the last surviving species of the genus ''Homo''. They are Hominidae, great apes characterized by their Prehistory of nakedness and clothing ...
''. This culture lasted from approximately 45,000 BP to 40,000 BP.
*The Aurignacian
The Aurignacian () is an archaeological industry of the Upper Paleolithic associated with Cro-Magnon, Early European modern humans (EEMH) lasting from 43,000 to 26,000 years ago. The Upper Paleolithic developed in Europe some time after the L ...
culture was located in Europe and south west Asia, and flourished between 43,000 and 26,000 BP. It may have been contemporary with the Périgordian (a contested grouping of the earlier Châtelperronian and later Gravettian cultures).
*The Gravettian culture was located across Europe. Gravettian sites generally date between 33,000 and 20,000 BP.
*The Solutrean culture was located in eastern France, Spain, and England. Solutrean artifacts have been dated c. 22,000 to 17,000 BP.
*The Magdalenian culture left evidence from Portugal to Poland during the period from 17,000 to 12,000 BP.
*Central and east Europe:
**33,000 BP, Gravettian culture in southern Ukraine
**30,000 BP, Szeletian culture
**22,000 BP, Pavlovian, Aurignacian
The Aurignacian () is an archaeological industry of the Upper Paleolithic associated with Cro-Magnon, Early European modern humans (EEMH) lasting from 43,000 to 26,000 years ago. The Upper Paleolithic developed in Europe some time after the L ...
cultures
**13,000 BP, Ahrensburg culture (Western Germany, Netherlands, England)
**12,000 BP, Epigravettian
*North and west Africa, and Sahara:
**32,000 BP, Aterian culture (Algeria, Libya)
**12,000 BP, Ibero-Maurusian (a.k.a. Oranian, Ouchtatian), and Sebilian cultures
**10,000 BP, Capsian culture (Tunisia, Algeria)
*Central, south, and east Africa:
**50,000 BP, Fauresmith culture
**30,000 BP, Stillbayan culture
**12,000 BP, Lupembian culture
**11,000 BP, Magosian culture (Zambia, Tanzania)
**9,000 BP, Wiltonian culture
*West Asia (including Middle East):
**50,000 BP, Jabroudian culture (Levant)
**40,000 BP, Amoudian culture
**30,000 BP, Emireh culture
**20,000 BP, Aurignacian
The Aurignacian () is an archaeological industry of the Upper Paleolithic associated with Cro-Magnon, Early European modern humans (EEMH) lasting from 43,000 to 26,000 years ago. The Upper Paleolithic developed in Europe some time after the L ...
culture
**12,000 BP, Kebarian, Athlitian cultures
*South, central and northern Asia:
**30,000 BP, Angara culture
**11,000 BP, Khandivili culture
*East and southeast Asia:
**30,000 BP, Sen-Doki culture
**16,000 BP, Jōmon period
In Japanese history, the is the time between , during which Japan was inhabited by the Jōmon people, a diverse hunter-gatherer and early agriculturalist population united by a common culture, which reached a considerable degree of sedentism an ...
starts in Ancient Japan
**12,000 BP, pre-Jōmon ceramic culture (Japan)
**10,000 BP, Hoabinhian culture (Northern Vietnam)
**9,000 BP, Jōmon culture (Japan)
*Oceania:
**40,000 BP, Whadjuk and Noongar
The Noongar (, also spelt Noongah, Nyungar , Nyoongar, Nyoongah, Nyungah, Nyugah, and Yunga ) are Aboriginal Australian people who live in the South West, Western Australia, south-west corner of Western Australia, from Geraldton, Western Aus ...
culture (Perth, Australia)
**35,000 BP, Wurundjeri, Boonwurrung and Wathaurong culture (Melbourne, Australia)
**30,000 BP, Eora and Darug culture (Sydney, Australia)
**30,000 BP, Arrernte culture ( Alice Springs, Central Australia
Central Australia, also sometimes referred to as the Red Centre, is an inexactly defined region associated with the geographic centre of Australia. In its narrowest sense it describes a region that is limited to the town of Alice Springs and ...
)
See also
*Last Glacial Maximum
The Last Glacial Maximum (LGM), also referred to as the Last Glacial Coldest Period, was the most recent time during the Last Glacial Period where ice sheets were at their greatest extent between 26,000 and 20,000 years ago.
Ice sheets covered m ...
* Mesolithic
The Mesolithic (Ancient Greek language, Greek: μέσος, ''mesos'' 'middle' + λίθος, ''lithos'' 'stone') or Middle Stone Age is the Old World archaeological period between the Upper Paleolithic and the Neolithic. The term Epipaleolithic i ...
* Neolithic
The Neolithic or New Stone Age (from Ancient Greek, Greek 'new' and 'stone') is an archaeological period, the final division of the Stone Age in Mesopotamia, Asia, Europe and Africa (c. 10,000 BCE to c. 2,000 BCE). It saw the Neolithic Revo ...
* Neolithic Europe
* Behavioral modernity
* Cro-Magnon 1
* Aurignacian
The Aurignacian () is an archaeological industry of the Upper Paleolithic associated with Cro-Magnon, Early European modern humans (EEMH) lasting from 43,000 to 26,000 years ago. The Upper Paleolithic developed in Europe some time after the L ...
* Epigravettian
* Sungir
* Cultural universal
* Quaternary extinction event
* Early human migrations
* Dean R. Snow – A leading archeologist who has conducted extensive Paleolithic research.
References
* Gilman, Antonio (1996). "Explaining the Upper Palaeolithic Revolution". Pp. 220–239 (Chap. 8) in ''Contemporary Archaeology in Theory: A Reader''. Cambridge, MA: Blackwell.External links
The Upper Paleolithic Revolution
.
– Libor Balák at the Czech Academy of Sciences, the Institute of Archaeology in Brno, The Center for Paleolithic and Paleoethnological Research. {{Authority control Pleistocene Quaternary geochronology Historical eras