Utians on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The Utians or Utii were
The Utians or Utii were
 The Utians or Utii were
The Utians or Utii were ancient
Ancient history is a time period from the beginning of writing and recorded human history through late antiquity. The span of recorded history is roughly 5,000 years, beginning with the development of Sumerian cuneiform script. Ancient h ...
western
Western may refer to:
Places
*Western, Nebraska, a village in the US
*Western, New York, a town in the US
*Western Creek, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western Junction, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western world, countries that id ...
Iranic
Iranian peoples, or Iranic peoples, are the collective ethnolinguistic groups who are identified chiefly by their native usage of any of the Iranian languages, which are a branch of the Indo-Iranian languages within the Indo-European langu ...
nomad
Nomads are communities without fixed habitation who regularly move to and from areas. Such groups include hunter-gatherers, pastoral nomads (owning livestock), tinkers and trader nomads. In the twentieth century, the population of nomadic pa ...
ic camel-driving people, known to us primarily through the writings of the ancient Greek
Ancient Greek (, ; ) includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the classical antiquity, ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Greek ...
historian Herodotus
Herodotus (; BC) was a Greek historian and geographer from the Greek city of Halicarnassus (now Bodrum, Turkey), under Persian control in the 5th century BC, and a later citizen of Thurii in modern Calabria, Italy. He wrote the '' Histori ...
. Herodotus describes them as "dressed in skin with the hair on".
There exists little independent record of these people, and it is somewhat unclear whom Herodotus was referring to. He describes them as forming part of the 14th province of the Persian empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire, also known as the Persian Empire or First Persian Empire (; , , ), was an Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great of the Achaemenid dynasty in 550 BC. Based in modern-day Iran, it was the larg ...
, sharing this province with other peoples named Sagartians, Sarangians, Thamanaeans, Mycians, and the unnamed inhabitants of the islands of the Erythraean Sea.
Herodotus also describes them as serving in the army of Xerxes I
Xerxes I ( – August 465 BC), commonly known as Xerxes the Great, was a List of monarchs of Persia, Persian ruler who served as the fourth King of Kings of the Achaemenid Empire, reigning from 486 BC until his assassination in 465 BC. He was ...
, under the command of Arsamenes
Arsamenes () was a prince of ancient Persia, the son of Darius the Great. We know very little about him today other than that he was, according to the historian Herodotus, the commander of the Utians (or "Utii") and Mycae people (or "Myci") in t ...
, son of Darius the Great
Darius I ( ; – 486 BCE), commonly known as Darius the Great, was the third King of Kings of the Achaemenid Empire, reigning from 522 BCE until his death in 486 BCE. He ruled the empire at its territorial peak, when it included much of West A ...
, during the Second Persian invasion of Greece
The second Persian invasion of Greece (480–479 BC) occurred during the Greco-Persian Wars, as King Xerxes I of Persia sought to conquer all of Greece. The invasion was a direct, if delayed, response to the defeat of the first Persian invasi ...
in 481 BCE.
On the Behistun Inscription
The Behistun Inscription (also Bisotun, Bisitun or Bisutun; , Old Persian: Bagastana, meaning "the place of god") is a multilingual Achaemenid royal inscriptions, Achaemenid royal inscription and large rock relief on a cliff at Mount Behistun i ...
of Darius the Great
Darius I ( ; – 486 BCE), commonly known as Darius the Great, was the third King of Kings of the Achaemenid Empire, reigning from 522 BCE until his death in 486 BCE. He ruled the empire at its territorial peak, when it included much of West A ...
, a land in Southern Persis called "Vautiya" or "Yautiya" is described. Some scholars have suggested that might be the same as the homeland of the people Herodotus called "Utians".
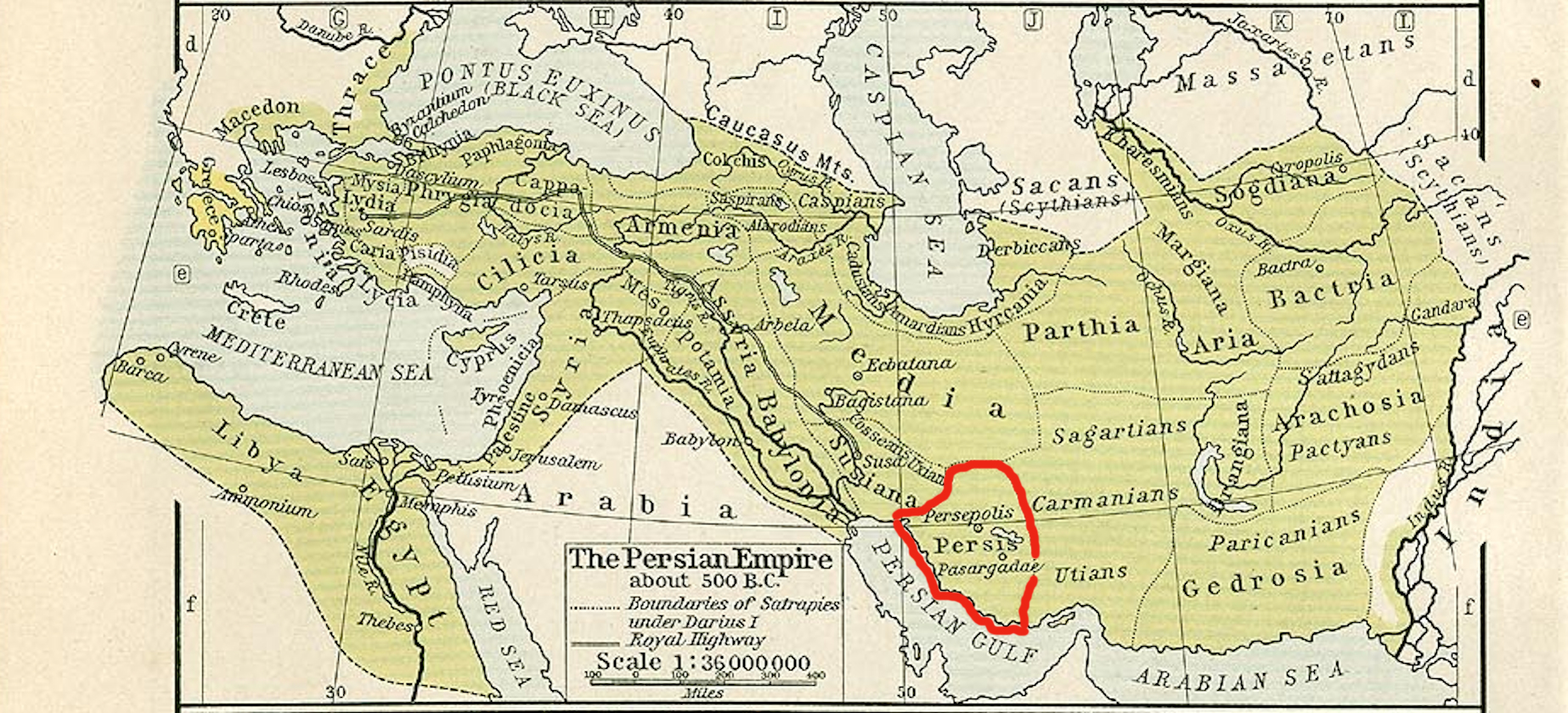
The Utians are generally believed to have ranged over southern Carmania near its border with Gedrosia
Gedrosia (; , ) is the Hellenization, Hellenized name of the part of coastal Balochistan that roughly corresponds to today's Makran. In books about Alexander the Great and his Diadochi, successors, the area referred to as Gedrosia runs from the I ...
. Other scholars, notably Josef Markwart, have proposed that Herodotus was confusing his references, and was actually talking about a group of Armenia
Armenia, officially the Republic of Armenia, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of West Asia. It is a part of the Caucasus region and is bordered by Turkey to the west, Georgia (country), Georgia to the north and Azerbaijan to ...
n people from Utik
Utik (), also known as Uti, was a historical province and principality within the Kingdom of Armenia. It was ceded to Caucasian Albania following the partition of Armenia between Sassanid Persia and the Eastern Roman Empire in 387 AD. Most o ...
, the Vitii, possibly the ancestors of the Udi people
Udis (endonym ''Udi'' or ''Uti'') are a native people of the Caucasus that live mainly in Russia and Azerbaijan, with smaller populations in Georgia (country), Georgia, Armenia, Kazakhstan, Ukraine, and other countries. Their total number is abou ...
. Still other scholars, such as Amélie Kuhrt, have proposed the Utians are identical to the Uxii.
References
{{reflist Historical Iranian peoples Iranian nomads Classical antiquity Tribes described primarily by Herodotus Near East in classical antiquity