Turkish Armed Forces on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Turkish Armed Forces (TAF; tr, Türk Silahlı Kuvvetleri, TSK) are the military forces of the Republic of Turkey. Turkish Armed Forces consist of the General Staff, the

 Turkey participated in the
Turkey participated in the
, Council of the european union, updated Council Decision 2011/70/CFSP of 31 January 2011 which has involved frequent forays into neighbouring


 The General Staff of the Turkish Armed Forces is the general staff of the Turkish Armed Forces. Chief of the General Staff reports to Minister of National Defence. General staff is responsible for:
* Preparing the Armed Forces and its personnel for military operations.
* Gathering military intelligence
* Organization and training of the Armed Forces
* Management of the logistic services
The Chief of the General Staff is also, Commander-in-Chief of the Armed Forces in the name of the President, in wartime.
Also, the General Staff is in command of the Special Forces, which is not aligned to any force command within the TAF. The Special Forces get their orders directly from the General Staff of the Turkish Armed Forces.
The General Staff of the Turkish Armed Forces is the general staff of the Turkish Armed Forces. Chief of the General Staff reports to Minister of National Defence. General staff is responsible for:
* Preparing the Armed Forces and its personnel for military operations.
* Gathering military intelligence
* Organization and training of the Armed Forces
* Management of the logistic services
The Chief of the General Staff is also, Commander-in-Chief of the Armed Forces in the name of the President, in wartime.
Also, the General Staff is in command of the Special Forces, which is not aligned to any force command within the TAF. The Special Forces get their orders directly from the General Staff of the Turkish Armed Forces.
 The
The
p. 88.
GNA gorvernment's army won the Turkish War of Independence in 1922.
p. 99.
The ''Su Altı Taarruz'' (S.A.T. – Underwater Attack) is dedicated to missions including the acquisition of military intelligence, amphibious assault, counter-terrorism and VIP protection; while the ''Su Altı Savunma'' (S.A.S. – Underwater Defense) is dedicated to coastal defense operations (such as clearing mines or unexploded torpedoes) and disabling enemy vessels or weapons with underwater operations; as well as counter-terrorism and VIP protection missions.
 The Turkish Air Force is the aerial warfare service branch of the Turkish Armed Forces. It is primarily responsible for the protection and sovereignty of Turkish airspace but also provides air-power to the other Military branch, service branches. Turkey is one of five NATO member states which are part of the
The Turkish Air Force is the aerial warfare service branch of the Turkish Armed Forces. It is primarily responsible for the protection and sovereignty of Turkish airspace but also provides air-power to the other Military branch, service branches. Turkey is one of five NATO member states which are part of the
 * – 24 troops in Pasha Liman Base, with 2 frigates. An Albanian-Turkish military cooperation agreement was signed in 1992 that encompassed rebuilding Albania's Pasha Liman Base by Turkey alongside granted access for Turkish use.
* – Buildings and structures in Gizil Sherg military town, and one terminal building located in the airfield in Hacı Zeynalabdin settlement. An observation base was also built by Turkey in the Nagorno-Karabakh region after the 44-day 2020 Nagorno-Karabakh war. The base was established in Aghdam under the name "Ceasefire Observation Center", and officially started to operate in January 2021 with 60 Turkish and Russian soldiers stationed at the base.
* – Under EUROFOR Operation Althea 242 troops, previously under Implementation Force and Stabilisation Force in Bosnia and Herzegovina.
* – Turkey has signed agreement with Iraq which includes allowing the Turkish army to pursue elements of the Kurdistan Workers' Party (PKK) in northern Iraq, with the permission of, and in coordination with the Federal Government of Iraq. It also includes opening two liaison offices between Baghdad and Ankara to exchange intelligence and security information between the two countries. As of 2020, Turkey has a military base with 2,000 personnel in Bashiqa and Bamarni Air Base garrisoned with around 60 tanks, Armoured personnel carriers and one commando battalion. Turkey has more than 40+ military and intelligence bases scattered all around
* – 24 troops in Pasha Liman Base, with 2 frigates. An Albanian-Turkish military cooperation agreement was signed in 1992 that encompassed rebuilding Albania's Pasha Liman Base by Turkey alongside granted access for Turkish use.
* – Buildings and structures in Gizil Sherg military town, and one terminal building located in the airfield in Hacı Zeynalabdin settlement. An observation base was also built by Turkey in the Nagorno-Karabakh region after the 44-day 2020 Nagorno-Karabakh war. The base was established in Aghdam under the name "Ceasefire Observation Center", and officially started to operate in January 2021 with 60 Turkish and Russian soldiers stationed at the base.
* – Under EUROFOR Operation Althea 242 troops, previously under Implementation Force and Stabilisation Force in Bosnia and Herzegovina.
* – Turkey has signed agreement with Iraq which includes allowing the Turkish army to pursue elements of the Kurdistan Workers' Party (PKK) in northern Iraq, with the permission of, and in coordination with the Federal Government of Iraq. It also includes opening two liaison offices between Baghdad and Ankara to exchange intelligence and security information between the two countries. As of 2020, Turkey has a military base with 2,000 personnel in Bashiqa and Bamarni Air Base garrisoned with around 60 tanks, Armoured personnel carriers and one commando battalion. Turkey has more than 40+ military and intelligence bases scattered all around
Turkish Armed Forces
(English)
Bosphorus Naval News
(turkishnavy.net) {{North Atlantic Treaty Organization Military of Turkey,
Land Forces
Land, also known as dry land, ground, or earth, is the solid terrestrial surface of the planet Earth that is not submerged by the ocean or other bodies of water. It makes up 29% of Earth's surface and includes the continents and various islan ...
, the Naval Forces and the Air Forces
An air force – in the broadest sense – is the national military branch that primarily conducts aerial warfare. More specifically, it is the branch of a nation's armed services that is responsible for aerial warfare as distinct from an ar ...
. The current Chief of the General Staff is General Yaşar Güler. The Chief of the General Staff is the Commander of the Armed Forces. In wartime, the Chief of the General Staff acts as the Commander-in-Chief on behalf of the President, who represents the Supreme Military Command of the TAF on behalf of the Grand National Assembly of Turkey
The Grand National Assembly of Turkey ( tr, ), usually referred to simply as the TBMM or Parliament ( tr, or ''Parlamento''), is the unicameral Turkish legislature. It is the sole body given the legislative prerogatives by the Turkish Const ...
. Coordinating the military relations of the TAF with other NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two No ...
member states and friendly states is the responsibility of the General Staff.
The history of the Turkish Armed Forces began with its formation after the collapse of the Ottoman Empire. The Turkish military perceived itself as the guardian of Kemalism, the official state ideology, especially of its emphasis on secularism. After becoming a member of NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two No ...
in 1952, Turkey initiated a comprehensive modernization program for its armed forces. The Turkish Army sent 14,936 troops to fight in the Korean War
, date = {{Ubl, 25 June 1950 – 27 July 1953 (''de facto'')({{Age in years, months, weeks and days, month1=6, day1=25, year1=1950, month2=7, day2=27, year2=1953), 25 June 1950 – present (''de jure'')({{Age in years, months, weeks a ...
alongside South Korea and NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two No ...
. Towards the end of the 1980s, a second restructuring process was initiated. The Turkish Armed Forces participate in an EU Battlegroup
An EU Battlegroup (EU BG) is a military unit adhering to the Common Security and Defence Policy (CSDP) of the European Union (EU). Often based on contributions from a coalition of member states, each of the eighteen Battlegroups consists of a ba ...
under the control of the European Council, the Italian-Romanian-Turkish Battlegroup. The TAF also contributes operational staff to the Eurocorps
Eurocorps, located in the French city of Strasbourg (Bas-Rhin), is a multinational corps headquarters. Founded by France and Germany in 1992, it is today composed of personnel from six framework nations and five associated nations. The framework ...
multinational army corps initiative of the EU and NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two No ...
.
The Turkish Armed Forces is the second largest standing military force in NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two No ...
, after the U.S. Armed Forces, and the thirteenth in the world, with an estimated strength of 775,000 military and paramilitary personnel in 2022.
Turkey is one of five NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two No ...
member states which are part of the nuclear sharing
Nuclear sharing is a concept in NATO's policy of nuclear deterrence, which allows member countries without nuclear weapons of their own to participate in the planning for the use of nuclear weapons by NATO. In particular, it provides for the ar ...
policy of the alliance, together with Belgium, Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
, Italy, and the Netherlands
)
, anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands
, established_title = Before independence
, established_date = Spanish Netherl ...
. A total of 50 U.S. B61 nuclear bomb
The B61 nuclear bomb is the primary thermonuclear gravity bomb in the United States Enduring Stockpile following the end of the Cold War. It is a low to intermediate-yield strategic and tactical nuclear weapon featuring a two-stage radiation im ...
s are hosted at the Incirlik Air Base
Incirlik Air Base ( tr, İncirlik Hava Üssü) is a Turkish air base of slightly more than 3320 ac (1335 ha), located in the İncirlik quarter of the city of Adana, Turkey. The base is within an urban area of 1.7 million people, east of ...
, the most of the five countries.
History
War of Independence
After the end ofWorld War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
, following the occupation of Anatolia by Entente Powers, many Ottoman military personnel escaped from Rumelia to Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The ...
in order to join the new Turkish National Movement (TNM). During the War of Independence, on 3 May 1920, Birinci Ferik Mustafa Fevzi Pasha (Çakmak) was appointed the Minister of National Defence, and Mirliva İsmet Pasha (İnönü) was appointed the Minister of the Chief of General Staff of the government of the Grand National Assembly
The Government of the Grand National Assembly ( tr, Büyük Millet Meclisi Hükûmeti), self-identified as the State of Turkey () or Turkey (), commonly known as the Ankara Government (),Kemal Kirişci, Gareth M. Winrow: ''The Kurdish Question and ...
(GNA).Harp Akademileri Komutanlığı, ''Harp Akademilerinin 120 Yılı'', İstanbul, 1968, p. 26, 46. But on 3 August 1921, the GNA fired İsmet Pasha from the post of Minister of National Defence because of his failure at the Battle of Afyonkarahisar–Eskişehir and on 5 August, just before the Battle of Sakarya, appointed the chairman of the GNA Mustafa Kemal Pasha
Mustafa ( ar, مصطفى
, Muṣṭafā) is one of the names of Prophet Muhammad, and the name means "chosen, selected, appointed, preferred", used as an Arabic given name and surname. Mustafa is a common name in the Muslim world.
Given name Mou ...
(Atatürk) as commander-in-chief of the Army of the GNA. The TNM won the War of Independence after İzmir
İzmir ( , ; ), also spelled Izmir, is a metropolitan city in the western extremity of Anatolia, capital of the province of the same name. It is the third most populous city in Turkey, after Istanbul and Ankara and the second largest urban aggl ...
was retrieved in 1922 as a result of Greco-Turkish Wars (1919–1922).

First Kurdish rebellions
There were several rebellionssoutheastern Turkey
The Southeastern Anatolia Region ( tr, Güneydoğu Anadolu Bölgesi) is a geographical region of Turkey. The most populous city in the region is Gaziantep. Other examples of big cities are Şanlıurfa, Diyarbakır, Mardin and Adıyaman.
It is b ...
in the 1920s and 1930s, the most important of which were the 1925 Sheikh Said rebellion and the 1937 Dersim rebellion. All were suppressed by the TAF, sometimes involving large-scale mobilisations of up to 50,000 troops.
World War II
Turkey remained neutral until the final stages ofWorld War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
. In the initial stage of World War II, Turkey signed a treaty of mutual assistance with Great Britain and France. But after the fall of France, the Turkish government tried to maintain an equal distance with both the Allies and the Axis
An axis (plural ''axes'') is an imaginary line around which an object rotates or is symmetrical. Axis may also refer to:
Mathematics
* Axis of rotation: see rotation around a fixed axis
* Axis (mathematics), a designator for a Cartesian-coordinat ...
. Following Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
's occupation of the Balkans
The Balkans ( ), also known as the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throughout the who ...
, upon which the Axis-controlled territory in Thrace
Thrace (; el, Θράκη, Thráki; bg, Тракия, Trakiya; tr, Trakya) or Thrake is a geographical and historical region in Southeast Europe, now split among Bulgaria, Greece, and Turkey, which is bounded by the Balkan Mountains to ...
and the eastern islands of the Aegean Sea
The Aegean Sea ; tr, Ege Denizi (Greek: Αιγαίο Πέλαγος: "Egéo Pélagos", Turkish: "Ege Denizi" or "Adalar Denizi") is an elongated embayment of the Mediterranean Sea between Europe and Asia. It is located between the Balkans ...
bordered Turkey, the Turkish government signed a Treaty of Friendship and Non-Aggression with Germany on 18 June 1941.
After the German invasion of the Soviet Union
Operation Barbarossa (german: link=no, Unternehmen Barbarossa; ) was the invasion of the Soviet Union by Nazi Germany and many of its Axis allies, starting on Sunday, 22 June 1941, during the Second World War. The operation, code-named afte ...
, the Turkish government sent a military delegation of observers under Lieutenant General Ali Fuat Erden to Germany and the Eastern Front. Following the German retreat from the Caucasus
The Caucasus () or Caucasia (), is a region between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, mainly comprising Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia (country), Georgia, and parts of Southern Russia. The Caucasus Mountains, including the Greater Caucasus range ...
, the Turkish government then moved closer to the Allies and Winston Churchill secretly met with İsmet İnönü at the Adana Conference in Yenice Train Station in southern Turkey on 30 January 1943, with the intent of persuading Turkey to join the war on the side of the Allies. A few days before the start of Operation Zitadelle in July 1943, the Turkish government sent a military delegation under General Cemil Cahit Toydemir to Russia and observed the exercises of the 503rd Heavy Panzer Battalion and its equipment. But after the failure of Operation Zitadelle, the Turkish government participated in the Second Cairo Conference
The Second Cairo Conference of December 4–6, 1943, held in Cairo, Egypt, addressed Turkey's possible contribution to the Allies in World War II.
in December 1943, where Franklin D. Roosevelt
Franklin Delano Roosevelt (; ; January 30, 1882April 12, 1945), often referred to by his initials FDR, was an American politician and attorney who served as the 32nd president of the United States from 1933 until his death in 1945. As the ...
, Churchill and İnönü reached an agreement on issues regarding Turkey's possible contribution to the Allies. On 23 February 1945, Turkey joined the Allies by declaring war against Germany and Japan, after it was announced at the Yalta Conference that only the states which were formally at war with Germany and Japan by 1 March 1945 would be admitted to the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmoniz ...
.
Korean War
 Turkey participated in the
Turkey participated in the Korean War
, date = {{Ubl, 25 June 1950 – 27 July 1953 (''de facto'')({{Age in years, months, weeks and days, month1=6, day1=25, year1=1950, month2=7, day2=27, year2=1953), 25 June 1950 – present (''de jure'')({{Age in years, months, weeks a ...
as a member state of the United Nations and sent the Turkish Brigade, which suffered 731 losses in combat, to South Korea. On 18 February 1952, Turkey became a member of NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two No ...
. The South Korean government donated a war memorial for the Turkish soldiers who fought and died in Korea. The Korean pagoda is in Ankara and it was donated in 1973 for the 50th anniversary of the Turkish Republic.
Invasion in Cyprus
On 20 July 1974, the TAF launched an amphibious and airborne assault operation onCyprus
Cyprus ; tr, Kıbrıs (), officially the Republic of Cyprus,, , lit: Republic of Cyprus is an island country located south of the Anatolian Peninsula in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Its continental position is disputed; while it is ge ...
, in response to the 1974 Cypriot coup d'état
The 1974 Cypriot coup d'état was a military coup d'état sponsored by the Greek Army in Cyprus, the Cypriot National Guard and the Greek military junta. On 15 July 1974 the coup plotters removed the sitting President of Cyprus, Archbishop Maka ...
which had been staged by EOKA-B
EOKA-B () was a Greek Cypriot paramilitary organisation formed in 1971 by General Georgios Grivas ("Digenis"). It followed an ultra right-wing nationalistic ideology and had the ultimate goal of achieving the ''enosis'' (union) of Cyprus with ...
and the Cypriot National Guard
, name2 = National Guard General Staff
, image = Emblem of the Cypriot National Guard.svg
, image_size = 100px
, caption = Emblem of the National Guard of Cyprus
, image2 = Flag of the ...
against president Makarios III with the intention of annexing the island to Greece; but the military intervention ended up with Turkey occupying a considerable area on the northern part of Cyprus and helping to establish a local government of Turkish Cypriots
Turkish Cypriots or Cypriot Turks ( tr, Kıbrıs Türkleri or ''Kıbrıslı Türkler''; el, Τουρκοκύπριοι, Tourkokýprioi) are ethnic Turks originating from Cyprus. Following the Ottoman conquest of the island in 1571, about 30,0 ...
there, which has thus far been recognized only by Turkey. The intervention came after more than a decade of intercommunal violence (1963–1974) between the island's Greek Cypriots
Greek Cypriots or Cypriot Greeks ( el, Ελληνοκύπριοι, Ellinokýprioi, tr, Kıbrıs Rumları) are the ethnic Greek population of Cyprus, forming the island's largest ethnolinguistic community. According to the 2011 census, 659,115 ...
and Turkish Cypriots
Turkish Cypriots or Cypriot Turks ( tr, Kıbrıs Türkleri or ''Kıbrıslı Türkler''; el, Τουρκοκύπριοι, Tourkokýprioi) are ethnic Turks originating from Cyprus. Following the Ottoman conquest of the island in 1571, about 30,0 ...
, resulting from the constitutional breakdown of 1963. Turkey invoked its role as a guarantor under the Treaty of Guarantee in justification for the military intervention. Turkish forces landed on the island in two waves, invading and occupying 37% of the island's territory in the northeast for the Turkish Cypriots, who had been isolated in small enclaves across the island prior to the military intervention.
In the aftermath, the Turkish Cypriots declared a separate political entity in the form of the Turkish Federated State of Cyprus
The Turkish Federated State of Cyprus ( tr, ) was a state on the region of Northern Cyprus declared in 1975 and existing until 1983, that was not recognised by the international community. It was succeeded by the Turkish Republic of Northern C ...
in 1975; and in 1983 made a unilateral declaration of independence as the Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus
Northern Cyprus ( tr, Kuzey Kıbrıs), officially the Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus (TRNC; tr, Kuzey Kıbrıs Türk Cumhuriyeti, ''KKTC''), is a ''de facto'' state that comprises the northeastern portion of the island of Cyprus. Reco ...
, which is recognized only by Turkey to this day. The United Nations continues to recognize the sovereignty of the Republic of Cyprus
Cyprus ; tr, Kıbrıs (), officially the Republic of Cyprus,, , lit: Republic of Cyprus is an island country located south of the Anatolian Peninsula in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Its continental position is disputed; while it is ge ...
according to the terms of its independence in 1960. The conflict continues to overshadow Turkish relations with Greece and with the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been de ...
. In 2004, during the referendum
A referendum (plural: referendums or less commonly referenda) is a direct vote by the electorate on a proposal, law, or political issue. This is in contrast to an issue being voted on by a representative. This may result in the adoption of a ...
for the Annan Plan for Cyprus (a United Nations proposal to resolve the Cyprus dispute) 76% of the Greek Cypriots
Greek Cypriots or Cypriot Greeks ( el, Ελληνοκύπριοι, Ellinokýprioi, tr, Kıbrıs Rumları) are the ethnic Greek population of Cyprus, forming the island's largest ethnolinguistic community. According to the 2011 census, 659,115 ...
rejected the proposal, while 65% of the Turkish Cypriots
Turkish Cypriots or Cypriot Turks ( tr, Kıbrıs Türkleri or ''Kıbrıslı Türkler''; el, Τουρκοκύπριοι, Tourkokýprioi) are ethnic Turks originating from Cyprus. Following the Ottoman conquest of the island in 1571, about 30,0 ...
accepted it.
Kurdish–Turkish conflict
The TAF are in a protracted campaign against thePKK
The Kurdistan Workers' Party or PKK is a Kurdish militant political organization and armed guerrilla movement, which historically operated throughout Kurdistan, but is now primarily based in the mountainous Kurdish-majority regions of sout ...
(recognized as a terrorist organization by the United States, the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been de ...
and NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two No ...
)European Union List of Terrorist Organisations, Council of the european union, updated Council Decision 2011/70/CFSP of 31 January 2011 which has involved frequent forays into neighbouring
Iraq
Iraq,; ku, عێراق, translit=Êraq officially the Republic of Iraq, '; ku, کۆماری عێراق, translit=Komarî Êraq is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Turkey to the north, Iran to the east, the Persian Gulf and K ...
and Syria. Abdullah Öcalan, the leader of the PKK was arrested in 1999 in Nairobi and taken to Turkey. In 2015, the PKK cancelled their 2013 ceasefire after tension due to various events.
War in Bosnia and Kosovo
Turkey contributed troops in several NATO-led peace forces in Bosnia andKosovo
Kosovo ( sq, Kosova or ; sr-Cyrl, Косово ), officially the Republic of Kosovo ( sq, Republika e Kosovës, links=no; sr, Република Косово, Republika Kosovo, links=no), is a partially recognised state in Southeast Euro ...
. Currently there are 402 Turkish troops in Kosovo Force.
War in Afghanistan
After the 2003 Istanbul Bombings were linked to Al-Qaeda, Turkey deployed troops toAfghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan,; prs, امارت اسلامی افغانستان is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is bordere ...
to fight Taliban forces and Al-Qaeda operatives, with the hopes of dismantling both groups. Turkey's responsibilities include providing security in Kabul (it formerly lead Regional Command Capital), as well as in Wardak Province, where it leads PRT Maidan Shahr. Turkey was once the third largest contingent within the International Security Assistance Force
' ps, کمک او همکاري '
, allies = Afghanistan
, opponents = Taliban Al-Qaeda
, commander1 =
, commander1_label = Commander
, commander2 =
, commander2_label =
, commander3 =
, command ...
. Turkey's troops are not engaged in combat operations and Ankara has long resisted pressure from Washington to offer more combat troops. According to the Washington Post
''The Washington Post'' (also known as the ''Post'' and, informally, ''WaPo'') is an American daily newspaper published in Washington, D.C. It is the most widely circulated newspaper within the Washington metropolitan area and has a large na ...
, in December 2009, after US President Barack Obama
Barack Hussein Obama II ( ; born August 4, 1961) is an American politician who served as the 44th president of the United States from 2009 to 2017. A member of the Democratic Party, Obama was the first African-American president of the ...
announced he would deploy 30,000 more U.S. soldiers, and that Washington wants others to follow suit, Turkish Prime Minister Recep Tayyip Erdoğan reacted with the message that Turkey would not contribute additional troops to Afghanistan. "Turkey has already done what it can do by boosting its contingent of soldiers there to 1,750 from around 700 without being asked", said Erdoğan, who stressed that Turkey would continue its training of Afghan security forces.
Turkey withdrew their troops from Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan,; prs, امارت اسلامی افغانستان is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is bordere ...
after the fall of Kabul (2021).
Humanitarian relief
The TAF have performed "Disaster Relief Operations," as in the 1999 İzmit earthquake in the Marmara Region of Turkey. Apart from contributing to NATO, the Turkish Navy also contributes to the Black Sea Naval Co-operation Task Group, which was created in early 2001 by Turkey,Bulgaria
Bulgaria (; bg, България, Bǎlgariya), officially the Republic of Bulgaria,, ) is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern flank of the Balkans, and is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Macedo ...
, Georgia, Romania, Russia and Ukraine for search and rescue and other humanitarian operations in the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, Rom ...
.

Today
According to theInternational Institute for Strategic Studies
The International Institute for Strategic Studies (IISS) is a British research institute or think tank in the area of international affairs. Since 1997, its headquarters have been Arundel House in London, England.
The 2017 Global Go To Think ...
(IISS), in 2020 the Turkish Armed Forces had an active strength of around 355,200 active personnel consisting of 260,200 armed forces, 45,000 naval forces, and 50,000 air forces. In addition, it was estimated that there were 378,700 reserve personnel and 156,800 paramilitary personnel (Turkish Gendarmerie
The Gendarmerie General Command ( tr, Jandarma Genel Komutanlığı) is the national Gendarmerie force of the Republic of Turkey. It is a service branch of the Turkish Ministry of Interior responsible for the maintenance of the public order in a ...
and Turkish Coast Guard
The Coast Guard Command ( tr, ) is the coast guard service of Turkey. The Turkish Coast Guard is under the command of the Ministry of the Interior. However, during wartime some of its elements can be subordinated to Turkish Naval Forces by the ...
), giving a combined active and reserve strength of around 890,500 personnel. IISS 2020, pp. 164–168 In 2020, the defence budget amounted to 76.3 billion liras. The Law on the Court of Accounts was supposed to initiate external ex-post audits of armed forces' expenditure and pave the way for audits of extra budgetary resources earmarked for the defence sector, including the Defence Industry Support Fund. However, the Ministry of Defense has not provided the necessary information, so the armed forces expenditure is not being properly checked.
In 1998, Turkey announced a programme of modernisation worth US$160 billion over a twenty-year period in various projects including tanks, fighter jet
Fighter aircraft are fixed-wing military aircraft designed primarily for air-to-air combat. In military conflict, the role of fighter aircraft is to establish air superiority of the battlespace. Domination of the airspace above a battlefield ...
s, helicopter
A helicopter is a type of rotorcraft in which lift and thrust are supplied by horizontally spinning rotors. This allows the helicopter to take off and land vertically, to hover, and to fly forward, backward and laterally. These attributes ...
s, submarines, warships and assault rifles. Turkey is a Level 3 contributor to the Joint Strike Fighter
Joint Strike Fighter (JSF) is a development and acquisition program intended to replace a wide range of existing fighter, strike, and ground attack aircraft for the United States, the United Kingdom, Italy, Canada, Australia, the Netherlands ...
(JSF) programme. The final goal of Turkey is to produce new-generation indigenous military equipment and to become increasingly self-sufficient in terms of military technologies.
HAVELSAN of Turkey and Boeing
The Boeing Company () is an American multinational corporation that designs, manufactures, and sells airplanes, rotorcraft, rockets, satellites, telecommunications equipment, and missiles worldwide. The company also provides leasing and p ...
of the United States are in the process of developing a next-generation, high-altitude ballistic missile defence shield. Turkey has chosen the Chinese defense firm CPMIEC to co-produce a $4 billion long-range air and missile system.

General staff
 The General Staff of the Turkish Armed Forces is the general staff of the Turkish Armed Forces. Chief of the General Staff reports to Minister of National Defence. General staff is responsible for:
* Preparing the Armed Forces and its personnel for military operations.
* Gathering military intelligence
* Organization and training of the Armed Forces
* Management of the logistic services
The Chief of the General Staff is also, Commander-in-Chief of the Armed Forces in the name of the President, in wartime.
Also, the General Staff is in command of the Special Forces, which is not aligned to any force command within the TAF. The Special Forces get their orders directly from the General Staff of the Turkish Armed Forces.
The General Staff of the Turkish Armed Forces is the general staff of the Turkish Armed Forces. Chief of the General Staff reports to Minister of National Defence. General staff is responsible for:
* Preparing the Armed Forces and its personnel for military operations.
* Gathering military intelligence
* Organization and training of the Armed Forces
* Management of the logistic services
The Chief of the General Staff is also, Commander-in-Chief of the Armed Forces in the name of the President, in wartime.
Also, the General Staff is in command of the Special Forces, which is not aligned to any force command within the TAF. The Special Forces get their orders directly from the General Staff of the Turkish Armed Forces.
Land Forces
 The
The Turkish Land Forces
The Turkish Land Forces ( tr, Türk Kara Kuvvetleri), or Turkish Army (Turkish: ), is the main branch of the Turkish Armed Forces responsible for land-based military operations. The army was formed on November 8, 1920, after the collapse of the ...
, or Turkish Army, can trace its origins in the remnants of Ottoman forces during the fall of the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
at the end of World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
. When Mustafa Kemal Atatürk and his colleagues formed the Grand National Assembly (GNA) in Ankara on 23 April 1920, the XV Corps under the command of Kâzım Karabekir
Musa Kâzım Karabekir (also spelled Kiazim Karabekir in English; 1882 – 26 January 1948) was a Turkish general and politician. He was the commander of the Eastern Army of the Ottoman Empire at the end of World War I and served as Speaker of ...
was the only corps which had any combat value. On 8 November 1920, the GNA decided to establish a standing army (''Düzenli ordu'') instead of irregular troops (the ''Kuva-yi Milliye
The Kuva-yi Milliye ( ota, قواى مليه; 'National Forces' or 'Nationalist Forces') were irregular Turkish militia forces active in the early period of the Turkish War of Independence. These irregular forces emerged after the occupation of ...
'', ''Kuva-yi Seyyare'', etc.).Suat İlhan, ''Atatürk ve Askerlik: Düşünce ve Uygulamaları'', Atatürk Araştırma Merkezi, 1990p. 88.
GNA gorvernment's army won the Turkish War of Independence in 1922.
Naval Forces
The Turkish Naval Forces, or Turkish Navy, constitutes the naval warfare service branch of the Turkish Armed Forces. The Turkish Navy maintains several Marines and Special Operations units. The ''Amphibious Marines Brigade'' (Amfibi Deniz Piyade Tugayı) based in Foça nearİzmir
İzmir ( , ; ), also spelled Izmir, is a metropolitan city in the western extremity of Anatolia, capital of the province of the same name. It is the third most populous city in Turkey, after Istanbul and Ankara and the second largest urban aggl ...
consists of 4,500 men, three amphibious battalions, an Main Battle Tank, MBT battalion, an artillery battalion, a support battalion and other company-sized units.Ray Bonds, David Miller, ''Illustrated Directory of Special Forces'', Zenith Imprint, 2003p. 99.
The ''Su Altı Taarruz'' (S.A.T. – Underwater Attack) is dedicated to missions including the acquisition of military intelligence, amphibious assault, counter-terrorism and VIP protection; while the ''Su Altı Savunma'' (S.A.S. – Underwater Defense) is dedicated to coastal defense operations (such as clearing mines or unexploded torpedoes) and disabling enemy vessels or weapons with underwater operations; as well as counter-terrorism and VIP protection missions.
Air Force
 The Turkish Air Force is the aerial warfare service branch of the Turkish Armed Forces. It is primarily responsible for the protection and sovereignty of Turkish airspace but also provides air-power to the other Military branch, service branches. Turkey is one of five NATO member states which are part of the
The Turkish Air Force is the aerial warfare service branch of the Turkish Armed Forces. It is primarily responsible for the protection and sovereignty of Turkish airspace but also provides air-power to the other Military branch, service branches. Turkey is one of five NATO member states which are part of the nuclear sharing
Nuclear sharing is a concept in NATO's policy of nuclear deterrence, which allows member countries without nuclear weapons of their own to participate in the planning for the use of nuclear weapons by NATO. In particular, it provides for the ar ...
policy of the alliance, together with Belgium, Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
, Italy, and the Netherlands
)
, anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands
, established_title = Before independence
, established_date = Spanish Netherl ...
. A total of 90 B61 nuclear bomb
The B61 nuclear bomb is the primary thermonuclear gravity bomb in the United States Enduring Stockpile following the end of the Cold War. It is a low to intermediate-yield strategic and tactical nuclear weapon featuring a two-stage radiation im ...
s are hosted at the Incirlik Air Base
Incirlik Air Base ( tr, İncirlik Hava Üssü) is a Turkish air base of slightly more than 3320 ac (1335 ha), located in the İncirlik quarter of the city of Adana, Turkey. The base is within an urban area of 1.7 million people, east of ...
, 40 of which are allocated for use by the Turkish Air Force in case of a nuclear conflict, but their use requires the approval of NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two No ...
.
The Air Force took part in the Operation Deliberate Force of 1995 and 1999 NATO bombing of the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, Operation Allied Force of 1999, and later participated in the United Nations peacekeeping mission in Bosnia-Herzegovina, employing two squadrons (one in the Ghedi fighter wing, and after 2000 one in the Aviano fighter wing.) They returned to Turkey in 2001. In 2006, 4 Turkish F-16 fighter jets were deployed for NATO's Baltic Air Policing operation.
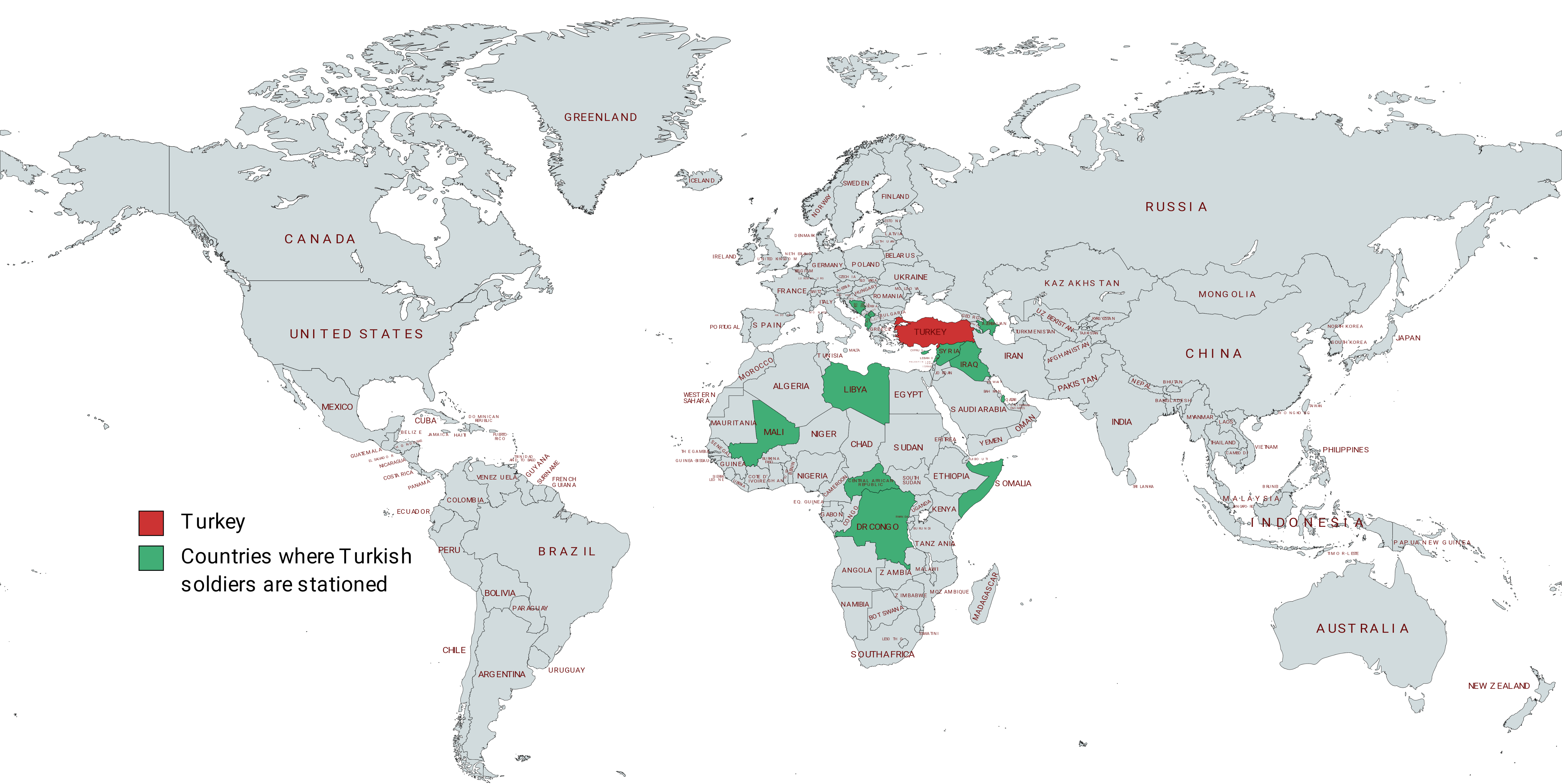
Military bases and soldiers stationed abroad
As of February 2021, Turkey has at least over 60,000+ military personnel stationed outside its territory. The only military base stationed permanently abroad, regardless of the organizations that are members of Turkey, which has been temporarily holding troops several times abroad due to its responsibilities arising from many international political members, particularlyNATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two No ...
membership, is the Cyprus Turkish Peace Force Command. The military bases of the Turkish Armed Forces in Qatar, Syria, Somalia and Bashiqa, among an unknown amount of other bases internationally, are currently active. It was announced in 2017 that Turkey would start working on establishing a research base in Antarctica.
According to a study conducted in England, Turkey has the largest deployment of international troops after the United States, with an estimated strength of at least 60,000+ military personnel stationed outside of the borders of Turkey. This means that 1 in 6 of the active military troops of Turkey (which is estimated to be 355,200 in 2020) are deployed outside of the borders of the country.
The Republic of Turkey currently has a military presence in 14 countries spanning 3 continents;
 * – 24 troops in Pasha Liman Base, with 2 frigates. An Albanian-Turkish military cooperation agreement was signed in 1992 that encompassed rebuilding Albania's Pasha Liman Base by Turkey alongside granted access for Turkish use.
* – Buildings and structures in Gizil Sherg military town, and one terminal building located in the airfield in Hacı Zeynalabdin settlement. An observation base was also built by Turkey in the Nagorno-Karabakh region after the 44-day 2020 Nagorno-Karabakh war. The base was established in Aghdam under the name "Ceasefire Observation Center", and officially started to operate in January 2021 with 60 Turkish and Russian soldiers stationed at the base.
* – Under EUROFOR Operation Althea 242 troops, previously under Implementation Force and Stabilisation Force in Bosnia and Herzegovina.
* – Turkey has signed agreement with Iraq which includes allowing the Turkish army to pursue elements of the Kurdistan Workers' Party (PKK) in northern Iraq, with the permission of, and in coordination with the Federal Government of Iraq. It also includes opening two liaison offices between Baghdad and Ankara to exchange intelligence and security information between the two countries. As of 2020, Turkey has a military base with 2,000 personnel in Bashiqa and Bamarni Air Base garrisoned with around 60 tanks, Armoured personnel carriers and one commando battalion. Turkey has more than 40+ military and intelligence bases scattered all around
* – 24 troops in Pasha Liman Base, with 2 frigates. An Albanian-Turkish military cooperation agreement was signed in 1992 that encompassed rebuilding Albania's Pasha Liman Base by Turkey alongside granted access for Turkish use.
* – Buildings and structures in Gizil Sherg military town, and one terminal building located in the airfield in Hacı Zeynalabdin settlement. An observation base was also built by Turkey in the Nagorno-Karabakh region after the 44-day 2020 Nagorno-Karabakh war. The base was established in Aghdam under the name "Ceasefire Observation Center", and officially started to operate in January 2021 with 60 Turkish and Russian soldiers stationed at the base.
* – Under EUROFOR Operation Althea 242 troops, previously under Implementation Force and Stabilisation Force in Bosnia and Herzegovina.
* – Turkey has signed agreement with Iraq which includes allowing the Turkish army to pursue elements of the Kurdistan Workers' Party (PKK) in northern Iraq, with the permission of, and in coordination with the Federal Government of Iraq. It also includes opening two liaison offices between Baghdad and Ankara to exchange intelligence and security information between the two countries. As of 2020, Turkey has a military base with 2,000 personnel in Bashiqa and Bamarni Air Base garrisoned with around 60 tanks, Armoured personnel carriers and one commando battalion. Turkey has more than 40+ military and intelligence bases scattered all around Iraq
Iraq,; ku, عێراق, translit=Êraq officially the Republic of Iraq, '; ku, کۆماری عێراق, translit=Komarî Êraq is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Turkey to the north, Iran to the east, the Persian Gulf and K ...
, the most out of any country. There are plans to build a new base in the Metina area of Duhok governorate in Kurdistan Region, Iraqi Kurdistan Region as of April 2021. In total, Turkey has stationed around 5,000 to 10,000 soldiers in Iraq
Iraq,; ku, عێراق, translit=Êraq officially the Republic of Iraq, '; ku, کۆماری عێراق, translit=Komarî Êraq is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Turkey to the north, Iran to the east, the Persian Gulf and K ...
.
* – 152 units for MONUSCO mission.
* – An estimated 321 troops serve in the Kosovo Security Battalion command. They are stationed at Sultan Murat base in the city of Prizren for UNMIK mission and Kosovo Force, KFOR NATO peacekeeping, peacekeeping force's.
* – 100 Personnel for UNIFIL mission and Maritime Task Force (MTF) participant units.
* – Airbases at Al-Watiya Air Base, al-Watiya, Mitiga and Misrata, in addition to Zwara. The amount of Turkish soldiers stationed in Libya is unknown.
* – A total of 35,000 to 40,000 armed forces of the Republic of Turkey are currently in active duty Cyprus Turkish Peace Force Command.
* – A military base in Doha with 5,000 personnel.
* – Camp TURKSOM with 2,000 personnel.
* – Bases in Al-Bab, Al-Rai, Syria, Al-Rai, Akhtarin, Afrin, Syria, Afrin, Jindires, Rajo, Syria, Rajo and Jarablus with at least 5,000 personnel in Operation Euphrates Shield, Euphrates Shield and Operation Olive Branch, Olive Branch regions. New bases were followed at south of Afrin Canton, Afrin canton in Atme and Darat Izza There are 114 Turkish bases in Syria as of January 2022. After operation Peace Spring, approximately 6,400 personnel are working around the Peace Spring region between Ras al-Ayn and Tell Abyad. 19 observation points are settled around Idlib Governorate, Idlib and Aleppo Governorate, Aleppo Province. Altogether, there are an estimated 10,500 Turkish soldiers and 250 tanks stationed in Syria. These numbers are constantly subject to modifications.
* – 50 Turkish soldiers are stationed in the CAR as part of the UN Multidimensional Integrated Stabilization Mission (MINUSCA).
* – 50 Turkish soldiers are serving in Mali as part of the UN Multidimensional Integrated Stabilization Mission (MINUSMA).
* – Suakin was allocated to Turkey for 99 years after an agreement with Sudan in December 2017. Many claim that Turkey is planning to militarize the port city due to its geostrategic significance in the Red Sea, which has strained Turkey's and Sudan's relationship with Egypt severely. There has, however, been no development regarding a military base within the city as of July 2022.
Role of the military in Turkish politics
After the Republic of Turkey was founded in 1923, Mustafa Kemal Atatürk prohibited the political activities of officers in active service with the Military Penal Code numbered 1632 and dated 22 May 1930 ('':tr:s:Askeri Ceza Kanunu, Askeri Ceza Kanunu''). However, after the coup d'état, coups d'état 1960 Turkish coup d'état, in 1960, the '':tr:Millî Birlik Komitesi, Millî Birlik Komitesi'' (National Unity Committee) established the Inner Service Act of the Turkish Armed Forces ('':tr:Türk Silahlı Kuvvetleri İç Hizmet Kanunu, Türk Silahlı Kuvvetleri İç Hizmet Kanunu'') on 4 January 1961 to legitimize their military interventions in politics. In subsequent coups d'état and coup d'état attempts, they showed reasons to justify their political activities especially with the article 35 and 85 of this act. The Turkish military perceived itself as the guardian of Kemalist ideology, the official state ideology, especially of the Secularism in Turkey, secular aspects of Kemalism. The TAF still maintains an important degree of influence over the decision-making process regarding issues related to Turkish national security, albeit decreased in the past decades, via the National Security Council (Turkey), National Security Council. The military had a record of intervening in politics, removing elected governments four times in the past. Indeed, it assumed power for several periods in the latter half of the 20th century. It executed three coup d'état, coups d'état: in 1960 (1960 Turkish coup d'état, 27 May coup), in 1971 (1971 Turkish coup d'état, 12 March coup), and in 1980 (1980 Turkish coup d'état, 12 September coup). Following the 1960 coup d'état, the military executed the first democratically elected prime minister in Turkey, Adnan Menderes, in 1961. Most recently, it maneuvered the removal of an Islamism, Islamist prime minister, Necmettin Erbakan, in 1997 (known as the 1997 military memorandum (Turkey), 28 February memorandum). Contrary to outsider expectations, the Turkish populace was not uniformly averse to coups; many welcomed the ejection of governments they perceived as unconstitutional. On 27 April 2007, in advance of the 4 November 2007 presidential election, and in reaction to the politics of Abdullah Gül, who has a past record of involvement in Islamist political movements and banned Islamist parties such as the Refah Partisi, Welfare Party, the army issued a statement of its interests. It said that the army is a party to "arguments" regarding secularism; that Islamism ran counter to the secular nature of Turkey, and to the legacy of Mustafa Kemal Atatürk. The Army's statement ended with a clear warning that the TAF stood ready to intervene if the secular nature of the Turkish Constitution is compromised, stating that "the Turkish Armed Forces maintain their sound determination to carry out their duties stemming from laws to protect the unchangeable characteristics of the Republic of Turkey. Their loyalty to this determination is absolute." Over a hundred people, including several generals, have been detained or questioned since July 2008 with respect to the so-called organisation Ergenekon (organization), Ergenekon, an alleged clandestine, Ultranationalism, ultra-nationalist organization with ties to members of the country's military and Law enforcement in Turkey, security forces. The group is accused of terrorism in Turkey. These accusing claims are reported, even while the trials are going on, mostly in the counter-secular and Islamist media organs. On 22 February 2010 more than 40 officers were arrested and then formally charged with attempting to overthrow the government with respect to the so-called "Sledgehammer" plot. They include four admirals, a general and two colonels, some of them retired, including former commanders of the Turkish navy and air force (three days later, the former commanders of the navy and air force were released). Partially as a result, theWashington Post
''The Washington Post'' (also known as the ''Post'' and, informally, ''WaPo'') is an American daily newspaper published in Washington, D.C. It is the most widely circulated newspaper within the Washington metropolitan area and has a large na ...
reported in April 2010 that the military's power had decreased.
On the eve of the Supreme Military Council of August 2011, the Chief of the General Staff, along with the Army, Navy, and Air Force commanders, requested their retirement, in protest of the mass arrests which they perceived as a deliberate and planned attack against the Kemalist and secular-minded officers of the Turkish Armed Forces by the Islamists in Turkey, who began to control key positions in the Turkish government, judiciary and police. The swift replacement of the force commanders in the Supreme Military Council meeting affirmed the government's control over the appointment of top-level commanders. However, promotions continue to be determined by the General Staff with limited civilian control. The European Commission, in its 2011 regular yearly report on Turkey's progress towards Accession of Turkey to the European Union, EU accession, stated that "further reforms on the composition and powers of the Supreme Military Council, particularly on the legal basis of promotions, still need to materialise." The service branch commanders continue to report to the Prime Minister instead of the Defence Minister.
In July 2016, a few rogue factions of the Turkish Armed Forces 2016 Turkish coup d'état attempt, attempted to take over the government, but Erdogan supporters and other loyal military units stopped the coup attempt. Many people died and hundreds were injured. The parliament house and some other buildings in Ankara and Istanbul were damaged. Thousands of military personnel have been arrested and the structure of the armed forces has been overhauled.
Medals and awards
* Turkish Armed Forces Medal of Honor * Turkish Armed Forces Medal of Distinguished Service * Turkish Armed Forces Medal of Distinguished Courage and Self-Sacrifice * Turkish Armed Forces Medal of Bravery and Valour * Turkish Armed Forces State Medal of HonorSee also
* Conscription in Turkey * List of Chiefs of the Turkish General Staff * Military equipment of Turkey * 2016 Turkish coup d'état attempt * Gendarmerie General Command, Gendarmerie General Command (Turkey) * Coast Guard Command (Turkey) * Village guard system * Defense industry of Turkey * List of countries by military expenditures * List of countries by number of military and paramilitary personnelNotes
References
Bibliography
* * * *Gareth Jenkins, 'Power and unaccountability in the Turkish security forces,' Conflict, Security, and Development, Volume 1, Issue 1.External links
Turkish Armed Forces
(English)
Bosphorus Naval News
(turkishnavy.net) {{North Atlantic Treaty Organization Military of Turkey,