Tsagantegia on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''Tsagantegia'' (; meaning Tsagan Teg) is a
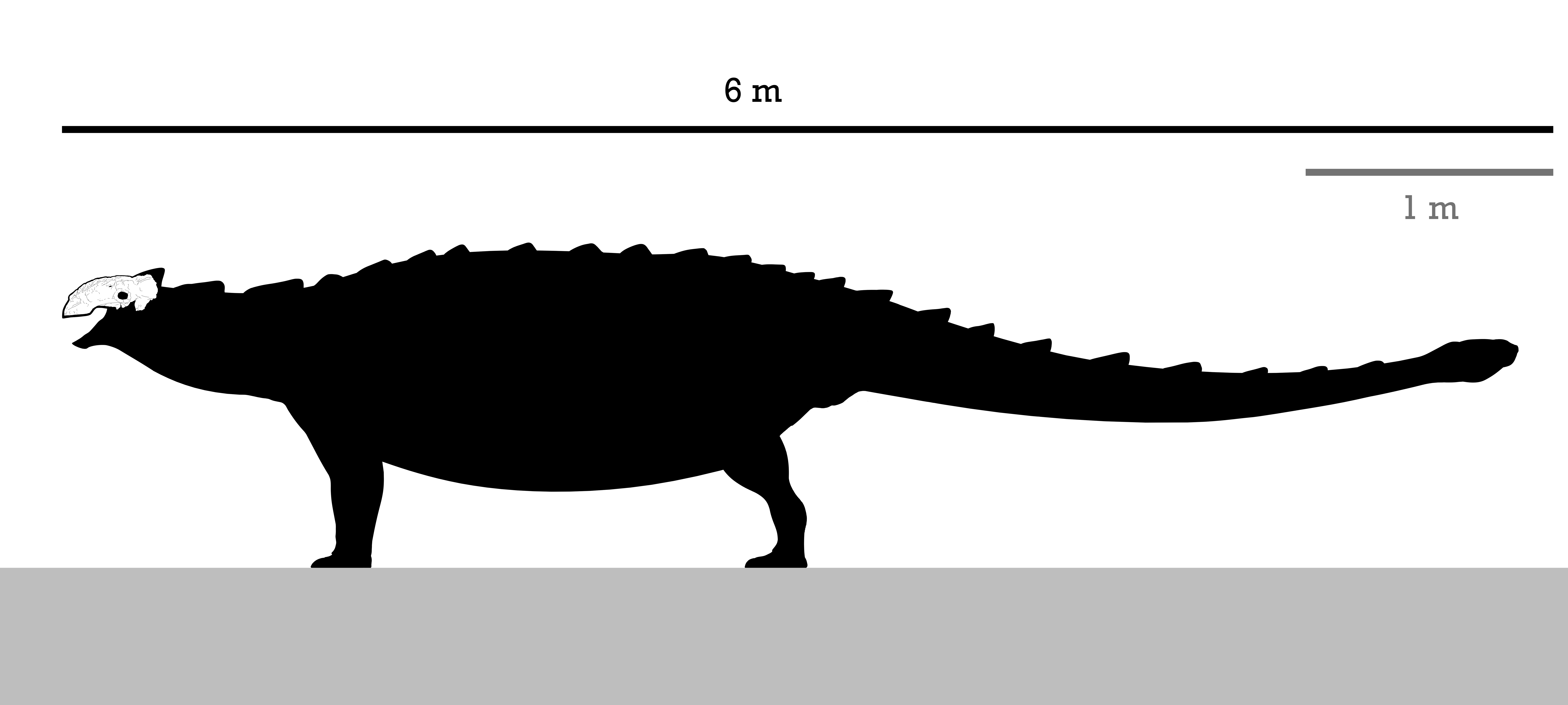 ''Tsagantegia'' was a medium to large-sized ankyosaur, with an estimated length of Genus List for Holtz 2012
''Tsagantegia'' was a medium to large-sized ankyosaur, with an estimated length of Genus List for Holtz 2012
/ref> and weighing about . The skull measures about in length, with a near width of , missing the lower jaws. Unlike other Asian ankylosaurs, in ''Tsagantegia'' the caputegulae (
 ''Tsagantegia'' was unearthed from the Tsagan Teg locality, which represents part of the Upper Bayan Shireh.
''Tsagantegia'' was unearthed from the Tsagan Teg locality, which represents part of the Upper Bayan Shireh. 

genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus com ...
of medium-sized ankylosaurid
Ankylosauridae () is a family of armored dinosaurs within Ankylosauria, and is the sister group to Nodosauridae. The oldest known Ankylosaurids date to around 122 million years ago and went extinct 66 million years ago during the Cretaceous–Pal ...
thyreophora
Thyreophora ("shield bearers", often known simply as "armored dinosaurs") is a group of armored ornithischian dinosaurs that lived from the Early Jurassic until the end of the Cretaceous.
Thyreophorans are characterized by the presence of body ...
n dinosaur
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic period, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago (mya), although the exact origin and timing of the evolution of dinosaurs is t ...
that lived in Asia
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either considered a continent in its own right or a subcontinent of Eurasia, which shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with Africa. Asia covers an area ...
during the Late Cretaceous
The Late Cretaceous (100.5–66 Ma) is the younger of two epochs into which the Cretaceous Period is divided in the geologic time scale. Rock strata from this epoch form the Upper Cretaceous Series. The Cretaceous is named after ''creta'', the ...
period. The genus is monotypic, including only the type species, ''T. longicranialis''. The specimen consists of a very partial individual, comprising the skull and lacking postcranial remains. Since it only preserves the skull, ''Tsagantegia'' is mainly characterized by its elongated snout and the flattened facial osteoderms, greatly differing from other ankylosaurs.
Discovery and naming
Theholotype
A holotype is a single physical example (or illustration) of an organism, known to have been used when the species (or lower-ranked taxon) was formally described. It is either the single such physical example (or illustration) or one of several ...
specimen, MPC 700/17, is a virtually complete skull
The skull is a bone protective cavity for the brain. The skull is composed of four types of bone i.e., cranial bones, facial bones, ear ossicles and hyoid bone. However two parts are more prominent: the cranium and the mandible. In humans, the ...
that was recovered from the locality Tsagan-Teg (or "White Mountain") of the Bayan Shireh Formation
The Bayan Shireh Formation (also known as Baynshiree/Baynshire, Baynshirenskaya Svita or Baysheen Shireh) is a geological formation in Mongolia, that dates to the Cretaceous period. It was first described and established by Vasiliev et al. 1959. ...
in the southeastern Gobi Desert
The Gobi Desert (Chinese: 戈壁 (沙漠), Mongolian: Говь (ᠭᠣᠪᠢ)) () is a large desert or brushland region in East Asia, and is the sixth largest desert in the world.
Geography
The Gobi measures from southwest to northeast an ...
, Mongolia
Mongolia; Mongolian script: , , ; lit. "Mongol Nation" or "State of Mongolia" () is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south. It covers an area of , with a population of just 3.3 million, ...
. It was formally described in 1993
File:1993 Events Collage.png, From left, clockwise: The Oslo I Accord is signed in an attempt to resolve the Israeli–Palestinian conflict; The Russian White House is shelled during the 1993 Russian constitutional crisis; Czechoslovakia is peace ...
by the Russian paleontologist Tatyana Alekseyevna Tumanova. The generic name, ''Tsagantegia'', is in reference to Tsagan Teg, the locality of its discovery, and the specific name Specific name may refer to:
* in Database management systems, a system-assigned name that is unique within a particular database
In taxonomy, either of these two meanings, each with its own set of rules:
* Specific name (botany), the two-part (bino ...
, ''longicranialis'', is derived from the Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
words and , in reference to its elongated skull.
Description
 ''Tsagantegia'' was a medium to large-sized ankyosaur, with an estimated length of Genus List for Holtz 2012
''Tsagantegia'' was a medium to large-sized ankyosaur, with an estimated length of Genus List for Holtz 2012/ref> and weighing about . The skull measures about in length, with a near width of , missing the lower jaws. Unlike other Asian ankylosaurs, in ''Tsagantegia'' the caputegulae (
cranial
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to unambiguously describe the anatomy of animals, including humans. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position pro ...
ornamentation) are not subdivided into a mosaic of polygons
In geometry, a polygon () is a plane figure that is described by a finite number of straight line segments connected to form a closed ''polygonal chain'' (or ''polygonal circuit''). The bounded plane region, the bounding circuit, or the two toge ...
but are amorphous and flattened; they show some degree of symmetry. The quadratojugal The quadratojugal is a skull bone present in many vertebrates, including some living reptiles and amphibians.
Anatomy and function
In animals with a quadratojugal bone, it is typically found connected to the jugal (cheek) bone from the front and ...
, squamosal The squamosal is a skull bone found in most reptiles, amphibians, and birds. In fishes, it is also called the pterotic bone.
In most tetrapods, the squamosal and quadratojugal The quadratojugal is a skull bone present in many vertebrates, including ...
and orbital horns are poorly preserved, in contrast with other ankylosaurs. The snout was long and flat with a pointed rostrum
Rostrum may refer to:
* Any kind of a platform for a speaker:
**dais
**pulpit
* Rostrum (anatomy), a beak, or anatomical structure resembling a beak, as in the mouthparts of many sucking insects
* Rostrum (ship), a form of bow on naval ships
* Ros ...
(beak); each maxilla
The maxilla (plural: ''maxillae'' ) in vertebrates is the upper fixed (not fixed in Neopterygii) bone of the jaw formed from the fusion of two maxillary bones. In humans, the upper jaw includes the hard palate in the front of the mouth. The t ...
preserves approximately 18 alveoli, no teeth were preserved. According to Arbour, ''Tsagantegia'' differs from ''Gobisaurus
''Gobisaurus'' is an extinct genus of herbivorous basal ankylosaurid ankylosaur from the Upper Cretaceous (and possibly also the Lower Cretaceous) of China (''Nei Mongol Zizhiqu''). The genus is monotypic, containing only the species ''Gobisaur ...
'' and ''Shamosaurus
''Shamosaurus'' is an extinct genus of herbivorous basal ankylosaurid ankylosaur from Early Cretaceous (Aptian to Albian stage) deposits of Höövör, Mongolia.
Discovery and naming
In 1977, a Soviet-Mongolian expedition discovered the skeleto ...
'' based on the more rounded, U-shaped premaxillary beak
The beak, bill, or rostrum is an external anatomical structure found mostly in birds, but also in turtles, non-avian dinosaurs and a few mammals. A beak is used for eating, preening, manipulating objects, killing prey, fighting, probing for food ...
and the flat ornamentation.
Classification
Although fragmentary, the phylogenetic position of ''Tsagantegia'' can be established. In 2012, Thompson et al. conducted an analysis of almost all known valid ankylosaurs and outgroup taxa at the time. They based their resulting phylogeny on characters representing cranial, post-cranial, and osteodermal anatomy, and details of synapomorphies for each recovered clade. ''Tsagantegia'' was found to be closely related to ''Pinacosaurus
''Pinacosaurus'' (meaning "Plank lizard") is a genus of ankylosaurid thyreophoran dinosaur that lived in Asia during the Late Cretaceous (Santonian-Campanian, roughly 75 million to 71 million years ago), mainly in Mongolia and China.
The first r ...
'' and ''Shamosaurus
''Shamosaurus'' is an extinct genus of herbivorous basal ankylosaurid ankylosaur from Early Cretaceous (Aptian to Albian stage) deposits of Höövör, Mongolia.
Discovery and naming
In 1977, a Soviet-Mongolian expedition discovered the skeleto ...
''. In the performed phylogenetic analysis by Arbour and Currie in 2015, below are the results for the analysis:
Paleoecology
 ''Tsagantegia'' was unearthed from the Tsagan Teg locality, which represents part of the Upper Bayan Shireh.
''Tsagantegia'' was unearthed from the Tsagan Teg locality, which represents part of the Upper Bayan Shireh. Calcite
Calcite is a Carbonate minerals, carbonate mineral and the most stable Polymorphism (materials science), polymorph of calcium carbonate (CaCO3). It is a very common mineral, particularly as a component of limestone. Calcite defines hardness 3 on ...
U–Pb analyses seem to confirm the age of the Bayan Shireh Formation from 92 million to 86 million years ago, Cenomanian
The Cenomanian is, in the ICS' geological timescale, the oldest or earliest age of the Late Cretaceous Epoch or the lowest stage of the Upper Cretaceous Series. An age is a unit of geochronology; it is a unit of time; the stage is a unit in the s ...
-Santonian
The Santonian is an age in the geologic timescale or a chronostratigraphic stage. It is a subdivision of the Late Cretaceous Epoch or Upper Cretaceous Series. It spans the time between 86.3 ± 0.7 mya (million years ago) and 83.6 ± 0.7 mya. The ...
ages. Based on comparisons between the snouts of ''Tsagantegia'' and the contemporary ''Talarurus
''Talarurus'' ( ; meaning "basket tail" or "wicker tail") is a genus of ankylosaurid dinosaur that lived in Asia during the Late Cretaceous period, about 96 million to 89 million years ago. The first remains of ''Talarurus'' were discovered in 19 ...
'', these taxa were divided by niche partitioning
In ecology, niche differentiation (also known as niche segregation, niche separation and niche partitioning) refers to the process by which competing species use the environment differently in a way that helps them to coexist. The competitive excl ...
. In a palatal view, the rostra
The rostra ( it, Rostri, links=no) was a large platform built in the city of Rome that stood during the republican and imperial periods. Speakers would stand on the rostra and face the north side of the comitium towards the senate house and deli ...
''Talarurus'' have a broad-like, rectangular shape, while ''Tsagantegia'' have a more shovel-like shaped rostra. These morphological differences indicate that ''Tsagantegia'' filled the niche of a browser herbivore
A herbivore is an animal anatomically and physiologically adapted to eating plant material, for example foliage or marine algae, for the main component of its diet. As a result of their plant diet, herbivorous animals typically have mouthpart ...
, while ''Talarurus'' was a grazer Grazer may refer to:
*grazer, an animal that grazes
*Grazer, a native or inhabitant of Graz
*GRAZER, the shoegaze band GRAZER
Astronomy
*Earth Grazer, Earth-grazing fireball that enters the Earth's atmosphere and leaves again
*Mercury grazer, ast ...
.

Caliche
Caliche () is a sedimentary rock, a hardened natural cement of calcium carbonate that binds other materials—such as gravel, sand, clay, and silt. It occurs worldwide, in aridisol and mollisol soil orders—generally in arid or semiarid regions, ...
-based boundary indicates a semi-arid environment and climate, but also, the presence of fluvial
In geography and geology, fluvial processes are associated with rivers and streams and the deposits and landforms created by them. When the stream or rivers are associated with glaciers, ice sheets, or ice caps, the term glaciofluvial or fluviog ...
and lacustrine
A lake is an area filled with water, localized in a basin, surrounded by land, and distinct from any river or other outlet that serves to feed or drain the lake. Lakes lie on land and are not part of the ocean, although, like the much larger ...
sediments
Sediment is a naturally occurring material that is broken down by processes of weathering and erosion, and is subsequently transported by the action of wind, water, or ice or by the force of gravity acting on the particles. For example, sand a ...
are indicators of large rivers
A river is a natural flowing watercourse, usually freshwater, flowing towards an ocean, sea, lake or another river. In some cases, a river flows into the ground and becomes dry at the end of its course without reaching another body of wate ...
and lakes
A lake is an area filled with water, localized in a basin, surrounded by land, and distinct from any river or other outlet that serves to feed or drain the lake. Lakes lie on land and are not part of the ocean, although, like the much larger ...
. As interpreted by Hicks et al. 1999, during the times of the Bayan Shireh Formation
The Bayan Shireh Formation (also known as Baynshiree/Baynshire, Baynshirenskaya Svita or Baysheen Shireh) is a geological formation in Mongolia, that dates to the Cretaceous period. It was first described and established by Vasiliev et al. 1959. ...
, large rivers drained the eastern part of the Gobi Desert
The Gobi Desert (Chinese: 戈壁 (沙漠), Mongolian: Говь (ᠭᠣᠪᠢ)) () is a large desert or brushland region in East Asia, and is the sixth largest desert in the world.
Geography
The Gobi measures from southwest to northeast an ...
. Additional to this, fossil
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved ...
fruits
In botany, a fruit is the seed-bearing structure in flowering plants that is formed from the ovary after flowering.
Fruits are the means by which flowering plants (also known as angiosperms) disseminate their seeds. Edible fruits in particula ...
remains have been recovered from the Bor Guvé and Khara Khutul localities (Upper and Lower Bayan Shireh, respectively), suggesting the presence of Angiosperm
Flowering plants are plants that bear flowers and fruits, and form the clade Angiospermae (), commonly called angiosperms. The term "angiosperm" is derived from the Greek words ('container, vessel') and ('seed'), and refers to those plants th ...
plants
Plants are predominantly Photosynthesis, photosynthetic eukaryotes of the Kingdom (biology), kingdom Plantae. Historically, the plant kingdom encompassed all living things that were not animals, and included algae and fungi; however, all curr ...
.
''Tsagantegia'' shared its habitat with numerous animals from other localities of the formation, compromising dinosaur and non-dinosaur genera; such as the theropods
Theropoda (; ), whose members are known as theropods, is a dinosaur clade that is characterized by hollow bones and three toes and claws on each limb. Theropods are generally classed as a group of saurischian dinosaurs. They were ancestrally c ...
''Achillobator
''Achillobator'' ( ; meaning "Achilles hero") is a genus of large dromaeosaurid dinosaurs that lived in Asia during the Late Cretaceous period about 96 million to 89 million years ago in what is now the Bayan Shireh Formation. The genus is curren ...
'', ''Alectrosaurus
''Alectrosaurus'' (; meaning "alone lizard") is a genus of tyrannosauroid theropod dinosaur that lived in Asia during the Late Cretaceous period, about some 96 million years ago in what is now the Iren Dabasu Formation.
It was a medium-sized, mo ...
'', ''Erlikosaurus
''Erlikosaurus'' (meaning "Erlik's lizard") is a genus of therizinosaurid that lived in Asia during the Late Cretaceous period. The fossils, a skull and some post-cranial fragments, were found in the Bayan Shireh Formation of Mongolia in 1972, da ...
'', ''Garudimimus
''Garudimimus'' (meaning "Garuda mimic") is a genus of ornithomimosaur that lived in Asia during the Late Cretaceous. The genus is known from a single specimen found in 1981 by a Soviet-Mongolian paleontological expedition in the Bayan Shireh Fo ...
'' and ''Segnosaurus
''Segnosaurus'' is a genus of therizinosaurid dinosaur that lived in what is now southeastern Mongolia during the Late Cretaceous, about 102–86 million years ago. Multiple incomplete but well-preserved specimens were discovered in the Go ...
''; the fellow ankylosaur
Ankylosauria is a group of herbivorous dinosaurs of the order Ornithischia. It includes the great majority of dinosaurs with armor in the form of bony osteoderms, similar to turtles. Ankylosaurs were bulky quadrupeds, with short, powerful limbs. ...
''Talarurus
''Talarurus'' ( ; meaning "basket tail" or "wicker tail") is a genus of ankylosaurid dinosaur that lived in Asia during the Late Cretaceous period, about 96 million to 89 million years ago. The first remains of ''Talarurus'' were discovered in 19 ...
''; Marginocephalia
Marginocephalia (/mär′jə-nō-sə-făl′ē-ən/ Latin: margin-head) is a clade of ornithischian dinosaurs that is characterized by a bony shelf or margin at the back of the skull. These fringes were likely used for display. There are two clade ...
ns: ''Amtocephale
''Amtocephale'' (meaning " Amtgai head") is a genus of pachycephalosaurid dinosaur from early Late Cretaceous (Turonian-Santonian stages) deposits of southern Gobi Desert, Mongolia.
''Amtocephale'' is known from the holotype MPC-D 100/120 ...
'' and ''Graciliceratops
''Graciliceratops'' (meaning "slender horn") is a genus of Ceratopsia#Phylogeny, neoceratopsian dinosaurs that lived in Asia during the Late Cretaceous period.
Discovery and naming
The holotype, ZPAL MgD-I/156, was discovered at the Bayan Shire ...
''; the hadrosauroid
Hadrosauroidea is a clade or superfamily of ornithischian dinosaurs that includes the "duck-billed" dinosaurs, or hadrosaurids, and all dinosaurs more closely related to them than to ''Iguanodon''. Their remains have been recovered in Asia, Eu ...
''Gobihadros
''Gobihadros'' is a genus of basal hadrosauroid dinosaur that lived in Asia during the Late Cretaceous period in what is now the Bayan Shireh Formation (Cenomanian-Santonian). It contains only the type species ''Gobihadros mongoliensis''. It has ...
'', and the large sauropod
Sauropoda (), whose members are known as sauropods (; from '' sauro-'' + '' -pod'', 'lizard-footed'), is a clade of saurischian ('lizard-hipped') dinosaurs. Sauropods had very long necks, long tails, small heads (relative to the rest of their bo ...
''Erketu
''Erketu'' (meaning "Erketü Tengri") is a genus of somphospondylan sauropod dinosaur that lived in Asia during the Late Cretaceous roughly between 96 million and 89 million years ago. Its fossils were found in Mongolia between 2002 and 2003 du ...
''. The turtle
Turtles are an order of reptiles known as Testudines, characterized by a special shell developed mainly from their ribs. Modern turtles are divided into two major groups, the Pleurodira (side necked turtles) and Cryptodira (hidden necked tu ...
'' Lindholmemys'', the crocodylomorph
Crocodylomorpha is a group of pseudosuchian archosaurs that includes the crocodilians and their extinct relatives. They were the only members of Pseudosuchia to survive the end-Triassic extinction.
During Mesozoic and early Cenozoic times, cro ...
''Paralligator
''Paralligator'' is an extinct genus of neosuchian crocodylomorph that lived during the Late Cretaceous (Cenomanian-Maastrichtian) period in what is now the Bayan Shireh and Nemegt formations of Mongolia, approximately 96 million to 70 million ...
'', unnamed azhdarchids
Azhdarchidae (from the Persian word , , a dragon-like creature in Persian mythology) is a family of pterosaurs known primarily from the Late Cretaceous Period, though an isolated vertebra apparently from an azhdarchid is known from the Early Cre ...
and the shark
Sharks are a group of elasmobranch fish characterized by a cartilaginous skeleton, five to seven gill slits on the sides of the head, and pectoral fins that are not fused to the head. Modern sharks are classified within the clade Selachimo ...
''Hybodus
''Hybodus'' (from el, ύβος , 'crooked' and el, ὀδούς 'tooth') is an extinct genus of hybodont, a group of shark-like elasmobranchs that lived from the Late Devonian to the end of the Cretaceous. Species closely related to the type sp ...
''.
See also
*Timeline of ankylosaur research
This timeline of ankylosaur research is a chronological listing of events in the history of paleontology focused on the ankylosaurs, quadrupedal herbivorous dinosaurs who were protected by a covering bony plates and spikes and sometimes by a club ...
* Cretaceous Mongolia
Cretaceous Mongolia is one of the strangest and best preserved of all Mesozoic ecosystems. The shifting sand of what was, even then, the Gobi Desert have ensured that fossils of the animals that lived there can be found in exactly the position in w ...
* Victoria Arbour
Victoria Megan Arbour is a Canadian evolutionary biologist and vertebrate palaeontologist at Royal BC Museum, where she is Curator of Palaeontology. An "expert on the armoured dinosaurs known as ankylosaurs", Arbour analyzes fossils and creates ...
References
{{Taxonbar, from=Q137444 Ankylosaurids Late Cretaceous dinosaurs of Asia Gobi Desert Fossil taxa described in 1993 Ornithischian genera