Truso on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Truso was a
 Truso was situated in a central location upon the Eastern European trade routes, which led from
Truso was situated in a central location upon the Eastern European trade routes, which led from

 First attempts at finding the exact location of the town date back to the early sixteenth century. Based on Prussian archaeological finds from 1897 and excavations which began in the 1920s, archaeologists located Truso near Elbing (since 1945 Janów Pomorski near
First attempts at finding the exact location of the town date back to the early sixteenth century. Based on Prussian archaeological finds from 1897 and excavations which began in the 1920s, archaeologists located Truso near Elbing (since 1945 Janów Pomorski near
The Project Gutenberg Etext of Discovery of Muscovy
- The complete texts translated to modern English
{{Authority control Archaeological sites in Poland Former populated places in Eastern Europe Elbląg
Viking Age
The Viking Age () was the period during the Middle Ages when Norsemen known as Vikings undertook large-scale raiding, colonizing, conquest, and trading throughout Europe and reached North America. It followed the Migration Period and the Germ ...
port of trade (emporium) set up by the Scandinavians at the banks of the Nogat
The Nogat is a 62 km long delta branch of the Vistula River in northern Poland. Unlike the main river, it does not empty into Gdańsk Bay but rather into the Vistula Lagoon.
The Nogat has its origin near the village of Biała Góra as a ...
delta branch of the Vistula River
The Vistula (; pl, Wisła, ) is the longest river in Poland and the ninth-longest river in Europe, at in length. The drainage basin, reaching into three other nations, covers , of which is in Poland.
The Vistula rises at Barania Góra in ...
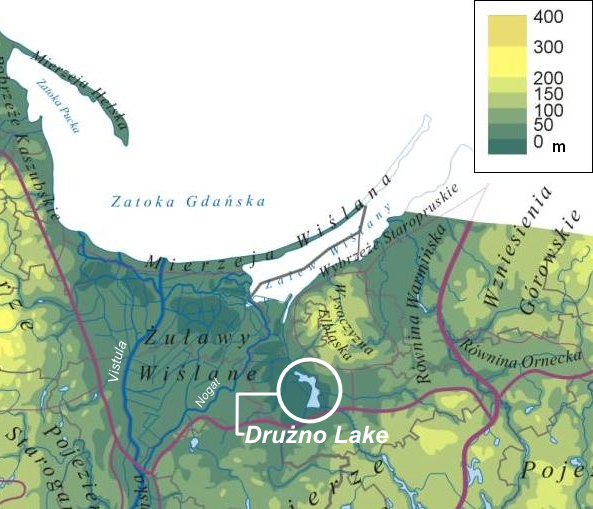
, close to a bay (the modern Drużno lake), where it emptied into the shallow and brackish
Brackish water, sometimes termed brack water, is water occurring in a natural environment that has more salinity than freshwater, but not as much as seawater. It may result from mixing seawater (salt water) and fresh water together, as in estua ...
Vistula Lagoon
The Vistula Lagoon ( pl, Zalew Wiślany; russian: Калининградский залив, transliterated: ''Kaliningradskiy Zaliv''; german: Frisches Haff; lt, Aistmarės) is a brackish water lagoon on the Baltic Sea roughly 56 miles (90 ...
. This sizeable lagoon is separated from the Gdańsk Bay
Gdańsk Bay or the Gulf of Gdańsk ( pl, Zatoka Gdańska; csb, Gduńskô Hôwinga; russian: Гданьская бухта, Gdan'skaja bukhta, and german: Danziger Bucht) is a southeastern bay of the Baltic Sea. It is named after the adjacent por ...
by the Vistula Spit
The Vistula Spit ( pl, Mierzeja Wiślana; russian: Балтийская коса; german: Frische Nehrung) is an aeolian sand spit, or peninsular stretch of land that separates Vistula Lagoon from Gdańsk Bay, in the Baltic Sea, with its tip sep ...
at the southern Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden and the North and Central European Plain.
The sea stretches from 53°N to 66°N latitude and from ...
coast. In the 9th century, the merchant Wulfstan of Hedeby
Wulfstan of Hedeby was a late ninth century traveller and trader. His travel accounts, as well as those of another trader, Ohthere of Hålogaland, were included in the '' Old English Orosius''. It is unclear if Wulfstan was English or indeed if ...
travelled to Truso in the service of the English King Alfred the Great
Alfred the Great (alt. Ælfred 848/849 – 26 October 899) was King of the West Saxons from 871 to 886, and King of the Anglo-Saxons from 886 until his death in 899. He was the youngest son of King Æthelwulf and his first wife Osburh, who bo ...
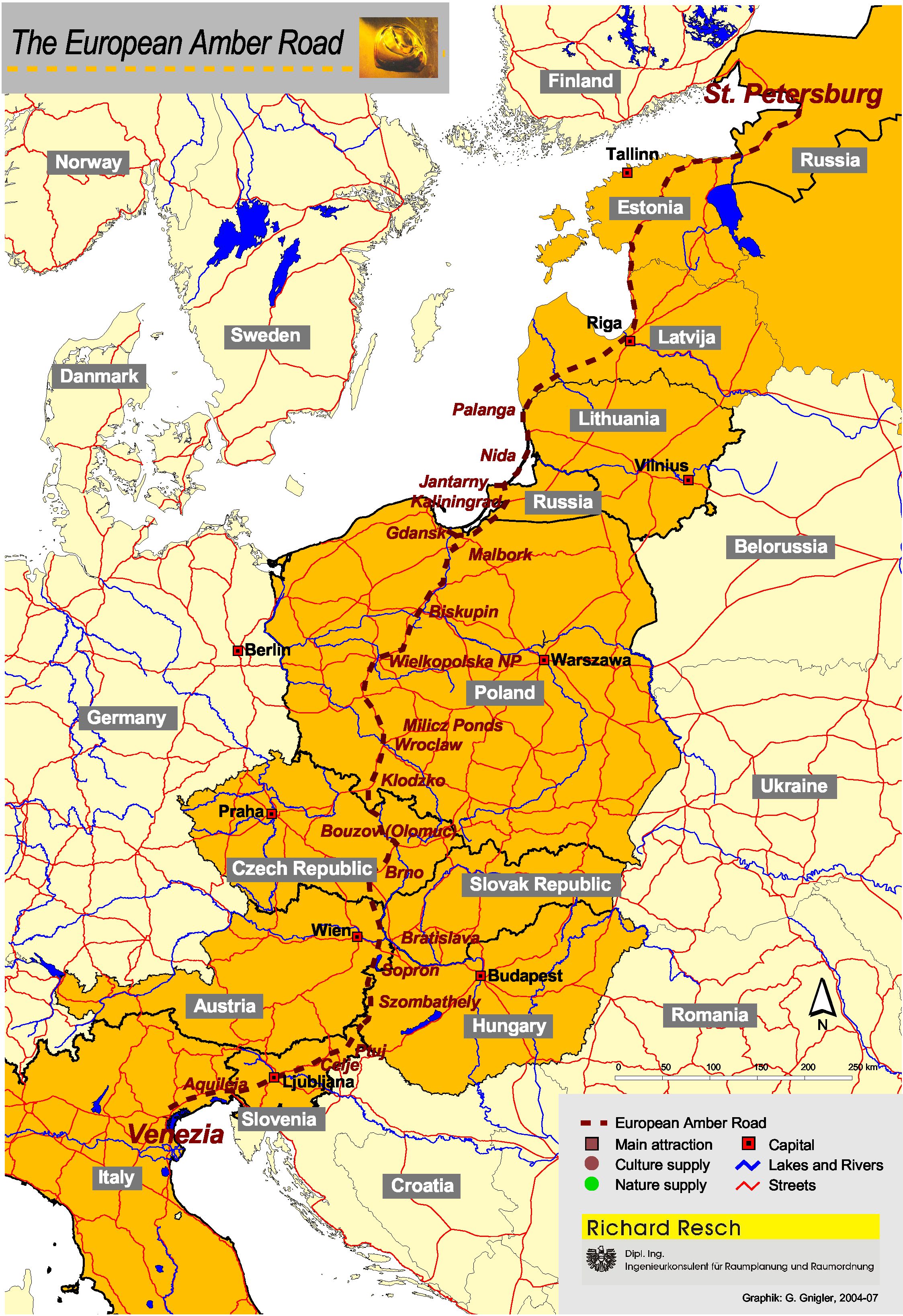
and wrote his account of the place at a prominent location of the Amber Road
The Amber Road was an ancient trade route for the transfer of amber from coastal areas of the North Sea and the Baltic Sea to the Mediterranean Sea. Prehistoric trade routes between Northern and Southern Europe were defined by the amber trade.
...
, which attracted merchants from central and southern Europe, who supplied the markets in the Mediterranean and the Middle East with the highly valued commodity.
The account of the voyage to the town of Truso in the land of the ''Pruzzens'' around the year 890 by Wulfstan of Hedeby
Wulfstan of Hedeby was a late ninth century traveller and trader. His travel accounts, as well as those of another trader, Ohthere of Hålogaland, were included in the '' Old English Orosius''. It is unclear if Wulfstan was English or indeed if ...
has been included in Alfred the Great
Alfred the Great (alt. Ælfred 848/849 – 26 October 899) was King of the West Saxons from 871 to 886, and King of the Anglo-Saxons from 886 until his death in 899. He was the youngest son of King Æthelwulf and his first wife Osburh, who bo ...
's translation of Orosius
Paulus Orosius (; born 375/385 – 420 AD), less often Paul Orosius in English, was a Roman priest, historian and theologian, and a student of Augustine of Hippo. It is possible that he was born in ''Bracara Augusta'' (now Braga, Portugal), t ...
' ''Histories''. Moreover, Wulfstan named Truso as being near ''Estmere'' (which is his rendition of the Old Prussian ''Aīstinmari'' and Lithuanian ''Aistmarės'' for Vistula Lagoon). In the words of Marija Gimbutas
Marija Gimbutas ( lt, Marija Gimbutienė, ; January 23, 1921 – February 2, 1994) was a Lithuanian archaeologist and anthropologist known for her research into the Neolithic and Bronze Age cultures of " Old Europe" and for her Kurgan hypothesis ...
, "the name of the town is the earliest known historically in the Baltic Sea area".
History
 Truso was situated in a central location upon the Eastern European trade routes, which led from
Truso was situated in a central location upon the Eastern European trade routes, which led from Birka
Birka (''Birca'' in medieval sources), on the island of Björkö (lit. "Birch Island") in present-day Sweden, was an important Viking Age trading center which handled goods from Scandinavia as well as many parts of the European continent and ...
in Sweden via Visby on the island of Gotland
Gotland (, ; ''Gutland'' in Gutnish), also historically spelled Gottland or Gothland (), is Sweden's largest island. It is also a province, county, municipality, and diocese. The province includes the islands of Fårö and Gotska Sandön to ...
towards the southern Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden and the North and Central European Plain.
The sea stretches from 53°N to 66°N latitude and from ...
shore, where in the 13th-century the Hanseatic city of Elbing was established. From there, trade continued further south along the Amber Road
The Amber Road was an ancient trade route for the transfer of amber from coastal areas of the North Sea and the Baltic Sea to the Mediterranean Sea. Prehistoric trade routes between Northern and Southern Europe were defined by the amber trade.
...
to Carnuntum
Carnuntum ( according to Ptolemy) was a Roman legionary fortress ( la, castra legionis) and headquarters of the Pannonian fleet from 50 AD. After the 1st century, it was capital of the Pannonia Superior province. It also became a large ...
in the Alps
The Alps () ; german: Alpen ; it, Alpi ; rm, Alps ; sl, Alpe . are the highest and most extensive mountain range system that lies entirely in Europe, stretching approximately across seven Alpine countries (from west to east): France, Sw ...
. These ancient roads led further south-west and south-east to the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, Rom ...
and eventually to North Africa and the Middle East. Gimbutas has observed thatFor Old Prussia, Truso played the same central role as Haithabu for north-western Germany or the Slavic Vineta forEast–western trade routes lead from Truso and Wiskiauten (a rival trading centre in Old Prussia, at the south-western corner of the Courish Lagoon), along the Baltic Sea toPomerania Pomerania ( pl, Pomorze; german: Pommern; Kashubian: ''Pòmòrskô''; sv, Pommern) is a historical region on the southern shore of the Baltic Sea in Central Europe, split between Poland and Germany. The western part of Pomerania belongs to ....
Jutland
Jutland ( da, Jylland ; german: Jütland ; ang, Ēota land ), known anciently as the Cimbric or Cimbrian Peninsula ( la, Cimbricus Chersonesus; da, den Kimbriske Halvø, links=no or ; german: Kimbrische Halbinsel, links=no), is a peninsula of ...
and from there up the Slien inlet to Haithabu (Hedeby), the large trading center in Jutland
Jutland ( da, Jylland ; german: Jütland ; ang, Ēota land ), known anciently as the Cimbric or Cimbrian Peninsula ( la, Cimbricus Chersonesus; da, den Kimbriske Halvø, links=no or ; german: Kimbrische Halbinsel, links=no), is a peninsula of ...
. This town, located close to the modern city of Schleswig
The Duchy of Schleswig ( da, Hertugdømmet Slesvig; german: Herzogtum Schleswig; nds, Hartogdom Sleswig; frr, Härtochduum Slaswik) was a duchy in Southern Jutland () covering the area between about 60 km (35 miles) north and 70 km ...
in Schleswig-Holstein
Schleswig-Holstein (; da, Slesvig-Holsten; nds, Sleswig-Holsteen; frr, Slaswik-Holstiinj) is the northernmost of the 16 states of Germany, comprising most of the historical duchy of Holstein and the southern part of the former Duchy of Sc ...
, was centrally located and could be reached from all four directions over land as well as from the North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Norway, Denmark, Germany, the Netherlands and Belgium. An epeiric sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the Norwegian ...
and the Baltic Sea.
Around the year 890, Wulfstan of Hedeby
Wulfstan of Hedeby was a late ninth century traveller and trader. His travel accounts, as well as those of another trader, Ohthere of Hålogaland, were included in the '' Old English Orosius''. It is unclear if Wulfstan was English or indeed if ...
embarked on his seven-day journey from Hedeby to Truso at the behest of king Alfred the Great
Alfred the Great (alt. Ælfred 848/849 – 26 October 899) was King of the West Saxons from 871 to 886, and King of the Anglo-Saxons from 886 until his death in 899. He was the youngest son of King Æthelwulf and his first wife Osburh, who bo ...
. He named the lands and the coasts he had passed as the ship was travelling under sail all the way. Weonodland was on his right and Langland, Laeland, Falster
Falster () is an island in south-eastern Denmark with an area of and 43,398 inhabitants as of 1 January 2010.
and Sconey on his left, all land that is subject to Denmark
)
, song = ( en, "King Christian stood by the lofty mast")
, song_type = National and royal anthem
, image_map = EU-Denmark.svg
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of Denmark
, establish ...
.
Wulfstan resumes: Then on our left we had the land of theThe most sought after commodities of Truso wereBurgundians The Burgundians ( la, Burgundes, Burgundiōnes, Burgundī; on, Burgundar; ang, Burgendas; grc-gre, Βούργουνδοι) were an early Germanic tribe or group of tribes. They appeared in the middle Rhine region, near the Roman Empire, and ..., who have a king to themselves. Then, after the land of the Burgundians, we had on our left the lands that have been called from the earliest timesBlekinge Blekinge (, old da, Bleking) is one of the traditional Swedish provinces (), situated in the southern coast of the geographic region of Götaland, in southern Sweden. It borders Småland, Scania and the Baltic Sea. It is the country's sec ...y, and Meore, and Eowland, andGotland Gotland (, ; ''Gutland'' in Gutnish), also historically spelled Gottland or Gothland (), is Sweden's largest island. It is also a province, county, municipality, and diocese. The province includes the islands of Fårö and Gotska Sandön to ..., all which territory is subject to the Sweons; and Weonodland (the land of theWends Wends ( ang, Winedas ; non, Vindar; german: Wenden , ; da, vendere; sv, vender; pl, Wendowie, cz, Wendové) is a historical name for Slavs living near Germanic settlement areas. It refers not to a homogeneous people, but to various people ...) was all the way on our right, as far as theVistula The Vistula (; pl, Wisła, ) is the longest river in Poland and the ninth-longest river in Europe, at in length. The drainage basin, reaching into three other nations, covers , of which is in Poland. The Vistula rises at Barania Góra in ...-estuary.
amber
Amber is fossilized tree resin that has been appreciated for its color and natural beauty since Neolithic times. Much valued from antiquity to the present as a gemstone, amber is made into a variety of decorative objects."Amber" (2004). In M ...
, animal furs and (pagan) slaves, while the industries of blacksmithing and amber working provided processed trading goods. The beginnings of the town has been dated back to approximately the end of the 7th century, while in the second half of the 10th century siltation
Siltation, is water pollution caused by particulate Terrestrial ecoregion, terrestrial Clastic rock, clastic material, with a particle size dominated by silt or clay. It refers both to the increased concentration of suspended sediments and to the ...
in the Nogat had begun to cut off the town from the Vistula lagoon and the Baltic Sea. The town's importance as trading port began to decline and was eventually eclipsed by the ascent of Gdańsk
Gdańsk ( , also ; ; csb, Gduńsk;Stefan Ramułt, ''Słownik języka pomorskiego, czyli kaszubskiego'', Kraków 1893, Gdańsk 2003, ISBN 83-87408-64-6. , Johann Georg Theodor Grässe, ''Orbis latinus oder Verzeichniss der lateinischen Benen ...
as the local trading center, that was situated right by the sea.
Historians still debate about the motive for this expedition. King Alfred obviously needed allies in his defense against the Danish and Norwegian Vikings
Vikings ; non, víkingr is the modern name given to seafaring people originally from Scandinavia (present-day Denmark, Norway and Sweden),
who from the late 8th to the late 11th centuries raided, pirated, traded and se ...
, who had already taken over most of England. However, that reason for the journey is rather unlikely, since Truso was at the time little more than a trading center and Alfred the Great
Alfred the Great (alt. Ælfred 848/849 – 26 October 899) was King of the West Saxons from 871 to 886, and King of the Anglo-Saxons from 886 until his death in 899. He was the youngest son of King Æthelwulf and his first wife Osburh, who bo ...
, the West Saxon ruler, already kept in close contact with the continental Saxons and the Franks.
Archaeology

 First attempts at finding the exact location of the town date back to the early sixteenth century. Based on Prussian archaeological finds from 1897 and excavations which began in the 1920s, archaeologists located Truso near Elbing (since 1945 Janów Pomorski near
First attempts at finding the exact location of the town date back to the early sixteenth century. Based on Prussian archaeological finds from 1897 and excavations which began in the 1920s, archaeologists located Truso near Elbing (since 1945 Janów Pomorski near Elbląg
Elbląg (; german: Elbing, Old Prussian: ''Elbings'') is a city in the Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship, Poland, located in the eastern edge of the Żuławy region with 117,390 inhabitants, as of December 2021. It is the capital of Elbląg Count ...
). Found artifacts, dating from the 7th to 12th century, were stored in the Elbing Museum, now the Elbląg Museum. In the 1980s, the Polish archaeologist Marek Jagodziński had resumed excavations and cleared a site of circa 20 hectare, in which a series of structures had burnt down around the year 1,000.
Trade must have been of great importance at the settlements, as the numerous merchant graves along the river testify. Artefacts unearthed at the site include scales, weights, silver horseshoe brooches, belt buckles, swords, coins, elaborate jewelry imported from Scandinavia, garment accessories and armament components. Scandinavian traders and craftmen lived and worked in central and port area, while peripheral area might be inhabitated also by Balts and Slavs. The Scandinavian influence on these settlements and artefacts is particularly obvious and confirms Viking expansion of settlement activity to Courland
Courland (; lv, Kurzeme; liv, Kurāmō; German and Scandinavian languages: ''Kurland''; la, Curonia/; russian: Курляндия; Estonian: ''Kuramaa''; lt, Kuršas; pl, Kurlandia) is one of the Historical Latvian Lands in western Latvia ...
and Livland. As early as the 8th century, the first incursions of North Germanic groups took place, which lead to the founding of the Grobin/Seeburg settlement near Liepája. Archbishop Rimbert of Bremen recorded the immigration of a group under the Svea king Olaf during the 9th century.
Author Gwyn Jones noted that at the circa 20 ha sized area "no true town has been found and excavated" and that the identification of the site in Elbląg with Truso is based on "finds of Norse weapons" and the presence of "a large Viking Age cemetery" nearby, According to Mateusz Bogucki "by now, there is no doubt that the settlement really is Wulfstan's Truso" The Elbląg Museum brochure: ''Truso- A Discovered Legend'', by Marek F. Jagodziński, describes a large number of buildings found during the recent excavations, with burnt remains of posts suggesting buildings of around and long houses of about . A thick layer of ash, debris and numerous arrowheads suggest that the city was destroyed by pirates or invaders.
Mateusz Bogucki of the Polish Academy of Sciences
The Polish Academy of Sciences ( pl, Polska Akademia Nauk, PAN) is a Polish state-sponsored institution of higher learning. Headquartered in Warsaw, it is responsible for spearheading the development of science across the country by a society o ...
at the Institute of Archaeology and Ethnology, states in his book ''Coin finds in the viking Age emporium at Janów Pomorski (Truso) and the Prussian phenomenon'' about ''...the end of Truso as a port of trade...a strong political power, probably of Piast origin...sent warriors to try to take control...and destroyed the town.''
References
External links
The Project Gutenberg Etext of Discovery of Muscovy
- The complete texts translated to modern English
{{Authority control Archaeological sites in Poland Former populated places in Eastern Europe Elbląg