Trams in Lisbon on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Lisbon tramway network ( pt, Rede de elétricos de Lisboa) is a system of

 The first line, put into operation on 15 August 1890, was long and ran from Praça Camões to Largo da Estrela. At the Estrela terminal, the company set up a small depot where the steam-operated powerhouse was also located. Rolling stock consisted of a tug and trailer. Since single-ended vehicles were used on the Estrela route, there was a turntable there and a turning loop (''raquette'') at Praça Camões. The service ran until 1913 when it was rendered economically unviable by competing electric trams. Its former route is now part of 28E's.
The first line, put into operation on 15 August 1890, was long and ran from Praça Camões to Largo da Estrela. At the Estrela terminal, the company set up a small depot where the steam-operated powerhouse was also located. Rolling stock consisted of a tug and trailer. Since single-ended vehicles were used on the Estrela route, there was a turntable there and a turning loop (''raquette'') at Praça Camões. The service ran until 1913 when it was rendered economically unviable by competing electric trams. Its former route is now part of 28E's.
 The second line ran from Rua da Palma on a long route to Largo da Graça, climbing in altitude. It was opened on 26 March 1893. The depot and powerhouse were at the Graça terminal. The Graça route was served by bidirectional vehicles. Service ended in 1913 but part of the route was revived in 1915 and continues to operate as an electric tram line (12E).
The second line ran from Rua da Palma on a long route to Largo da Graça, climbing in altitude. It was opened on 26 March 1893. The depot and powerhouse were at the Graça terminal. The Graça route was served by bidirectional vehicles. Service ended in 1913 but part of the route was revived in 1915 and continues to operate as an electric tram line (12E).
 On 30 August 1901, Lisbon's first electric tramway commenced operations. Within a year, all of the city's ''americano'' routes had been converted to electric traction, and by 1913 the cable trams were retired.
Until 1959, the network of lines continued to be developed, and in that year it reached its greatest extent. At that time, there were 27 tram lines in Lisbon, of which six operated as circle lines. As the circle lines operated in both clockwise and anticlockwise directions, each with its own route number, it is more correct to speak of a total of 24 tram routes, all of them running on
On 30 August 1901, Lisbon's first electric tramway commenced operations. Within a year, all of the city's ''americano'' routes had been converted to electric traction, and by 1913 the cable trams were retired.
Until 1959, the network of lines continued to be developed, and in that year it reached its greatest extent. At that time, there were 27 tram lines in Lisbon, of which six operated as circle lines. As the circle lines operated in both clockwise and anticlockwise directions, each with its own route number, it is more correct to speak of a total of 24 tram routes, all of them running on
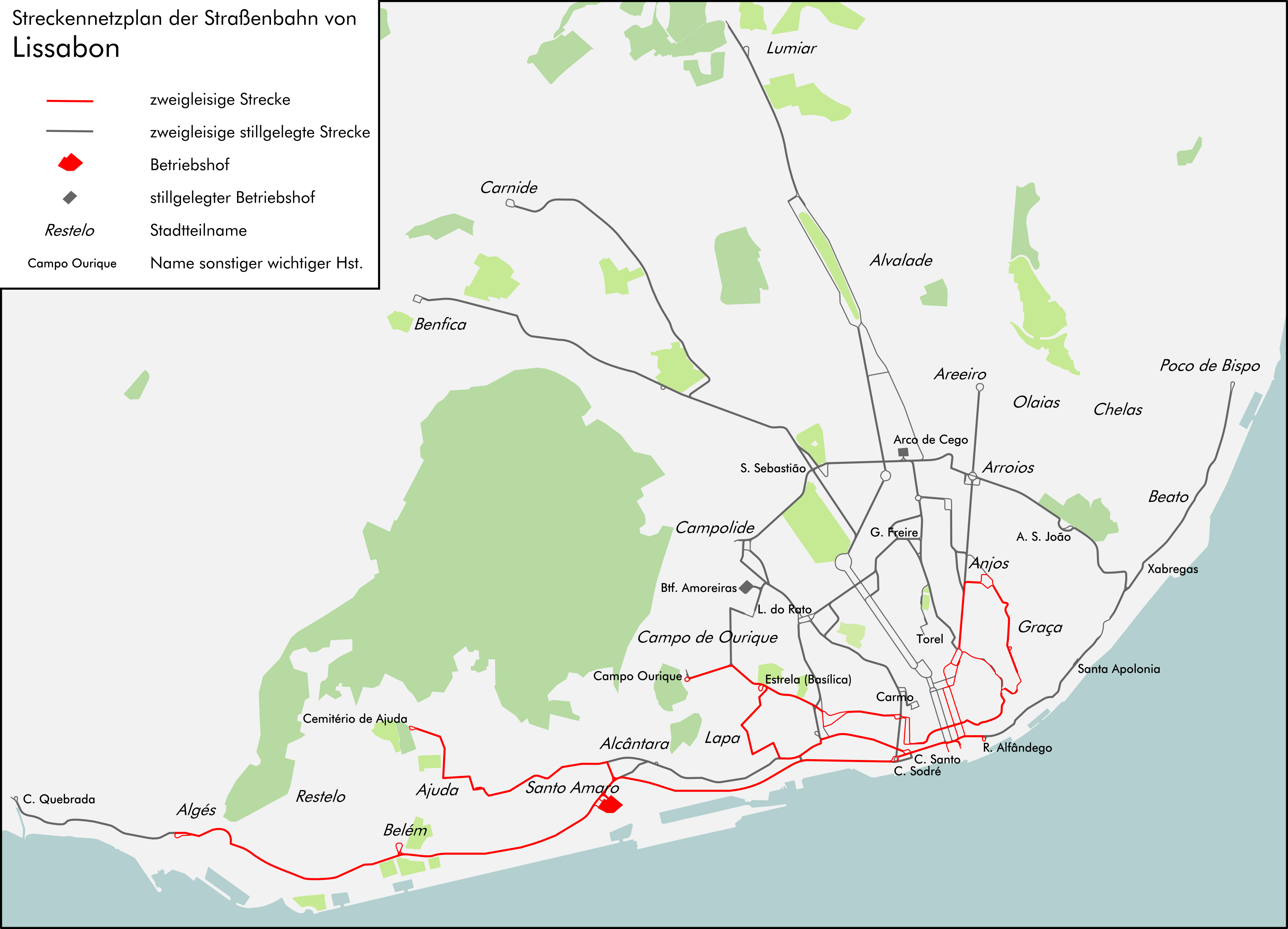
 The current lines are:
*12 -
The current lines are:
*12 -
Tram 28 in Lisbon
Tram 28 route on Google Map
''This article is based on a translation of the German language version as of March 2011.'' {{coord missing, Portugal
tram
A tram (called a streetcar or trolley in North America) is a rail vehicle that travels on tramway tracks on public urban streets; some include segments on segregated right-of-way. The tramlines or networks operated as public transport ...
s that serves Lisbon
Lisbon (; pt, Lisboa ) is the capital and largest city of Portugal, with an estimated population of 544,851 within its administrative limits in an area of 100.05 km2. Lisbon's urban area extends beyond the city's administrative limits w ...
, capital city
A capital city or capital is the municipality holding primary status in a country, state, province, department, or other subnational entity, usually as its seat of the government. A capital is typically a city that physically encompasses t ...
of Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic ( pt, República Portuguesa, links=yes ), is a country whose mainland is located on the Iberian Peninsula of Southwestern Europe, and whose territory also includes the Atlantic archipelagos of th ...
. In operation since 1873, it presently comprises six lines. The system has a length of 31 km, and 63 trams in operation (45 historic "Remodelados", 8 historic "Ligeiros" and 10 modern articulated trams). The depot is located in Santo Amaro, in Alcântara.
History

Origin
Lisbon's municipal government wished to develop urban transit and granted concessions to build and operate various systems that included funiculars and tramways. The first tramway in Lisbon entered service on 17 November 1873 as a horsecar line. The vehicles, called ''americanos'' after their point of origin, were initially deployed in the flat parts of the city where animals were capable of hauling their passenger loads.Cable trams
To surmount the steep slopes where draft animal conveyance was impossible, funiculars were envisioned in proposals made to the municipal government in 1882. The first of them started operating in 1884. This inaugurated the era of cable-driven transport, but the technology of electrical generation, transmission and power was developing concurrently and would eventually supersede it. Cable tram services (or cable cars) afforded an alternative to funiculars for the longer and curved routes required to follow Lisbon's streets. Individual vehicles grasp a steel cable that runs continuously in a channel below the roadway surface. The transport company that ran the funiculars applied for and received the concessions to operate cable trams and from 1890 initially proposed two routes based on plans by the Portuguese engineerRaoul Mesnier du Ponsard
Raoul Mesnier du Ponsard ( São Nicolau, Porto, 2 April 1848 — Inhambane, Mozambique 26 May 1914) was a Portuguese engineer of French parentage, known for building many elevators and funiculars in Portugal. He is particularly known for his eng ...
, who had already designed Lisbon's funiculars. In all, three lines operated in the city. Each had a gauge, corresponding to that of the extant ''americanos''. The rolling stock on the Estrela and Graça lines were built by Maschinenfabrik Esslingen; the São Sebastião cars apparently were designed by Maschinenfabrik Esslingen but built in Portugal.
Elevador da Estrela
 The first line, put into operation on 15 August 1890, was long and ran from Praça Camões to Largo da Estrela. At the Estrela terminal, the company set up a small depot where the steam-operated powerhouse was also located. Rolling stock consisted of a tug and trailer. Since single-ended vehicles were used on the Estrela route, there was a turntable there and a turning loop (''raquette'') at Praça Camões. The service ran until 1913 when it was rendered economically unviable by competing electric trams. Its former route is now part of 28E's.
The first line, put into operation on 15 August 1890, was long and ran from Praça Camões to Largo da Estrela. At the Estrela terminal, the company set up a small depot where the steam-operated powerhouse was also located. Rolling stock consisted of a tug and trailer. Since single-ended vehicles were used on the Estrela route, there was a turntable there and a turning loop (''raquette'') at Praça Camões. The service ran until 1913 when it was rendered economically unviable by competing electric trams. Its former route is now part of 28E's.
Elevador da Graça
 The second line ran from Rua da Palma on a long route to Largo da Graça, climbing in altitude. It was opened on 26 March 1893. The depot and powerhouse were at the Graça terminal. The Graça route was served by bidirectional vehicles. Service ended in 1913 but part of the route was revived in 1915 and continues to operate as an electric tram line (12E).
The second line ran from Rua da Palma on a long route to Largo da Graça, climbing in altitude. It was opened on 26 March 1893. The depot and powerhouse were at the Graça terminal. The Graça route was served by bidirectional vehicles. Service ended in 1913 but part of the route was revived in 1915 and continues to operate as an electric tram line (12E).
Elevador de São Sebastião
On 15 January 1899 a third cable tram line started operating under a different concession from the other two. It was the longest of the lines, extending for between São Sebastião and Rossio. The depot and powerhouse were in Palhavá (São Sebastião). It also ran for the shortest time of any of the lines, suffering bankruptcy in 1901.Electrification and modern era

 On 30 August 1901, Lisbon's first electric tramway commenced operations. Within a year, all of the city's ''americano'' routes had been converted to electric traction, and by 1913 the cable trams were retired.
Until 1959, the network of lines continued to be developed, and in that year it reached its greatest extent. At that time, there were 27 tram lines in Lisbon, of which six operated as circle lines. As the circle lines operated in both clockwise and anticlockwise directions, each with its own route number, it is more correct to speak of a total of 24 tram routes, all of them running on
On 30 August 1901, Lisbon's first electric tramway commenced operations. Within a year, all of the city's ''americano'' routes had been converted to electric traction, and by 1913 the cable trams were retired.
Until 1959, the network of lines continued to be developed, and in that year it reached its greatest extent. At that time, there were 27 tram lines in Lisbon, of which six operated as circle lines. As the circle lines operated in both clockwise and anticlockwise directions, each with its own route number, it is more correct to speak of a total of 24 tram routes, all of them running on narrow gauge
A narrow-gauge railway (narrow-gauge railroad in the US) is a railway with a track gauge narrower than standard . Most narrow-gauge railways are between and .
Since narrow-gauge railways are usually built with tighter curves, smaller structu ...
tram lines.
The slow decline of the network began with the construction of the Lisbon Metro
The Lisbon Metro ( pt, Metropolitano de Lisboa) is the rapid transit system in Lisbon, Portugal. Opened in December 1959, it was the first metro system in Portugal.
, the system's four lines total of route and serve 56 stations.
History
...
and the expansion of the bus system.
Current network
 The current lines are:
*12 -
The current lines are:
*12 - Praça da Figueira
The Praça da Figueira (, ''Square of the Fig Tree'') is a large square in the centre of Lisbon, in Portugal. It is part of the Lisbon Baixa, the area of the city reurbanised after the 1755 Lisbon earthquake.
In the 16th century the square did ...
→ Miradouro de Santa Luzia ''circular route (clockwise only)''
*15 - Praça da Figueira ↔ Belém
Belém (; Portuguese for Bethlehem; initially called Nossa Senhora de Belém do Grão-Pará, in English Our Lady of Bethlehem of Great Pará) often called Belém of Pará, is a Brazilian city, capital and largest city of the state of Pará in ...
↔ Algés
*18 - Cais do Sodré railway station
The Cais do Sodré Railway Station () is an intermodal railway station in the civil parish of Misericórdia, in the municipality of Lisbon, serving as the terminus of the suburban route to the resort town Cascais.
History
In 1925, the c ...
↔ Cemitério da Ajuda
Ajuda () is a ''freguesia'' (civil parish) and district of Lisbon, the capital of Portugal. Ajuda is located in western Lisbon, northeast of Belém and west of Alcântara. The population in 2011 was 15,617.Campolide
Campolide () is a ''freguesia'' (civil parish) and district of Lisbon, the capital of Portugal. Located in central Lisbon, Campolide is west of Avenidas Novas, north of Campo de Ourique, east of Benfica, and south of São Domingos de Benfica. ...
*25 - Praça da Figueira ↔ Campo de Ourique
Campo de Ourique () is a ''freguesia'' (civil parish) and district of Lisbon, the capital of Portugal. Located in the historic center of Lisbon, Campo de Ourique is east of Alcântara, north of Estrela, west of Santo António, and south of Camp ...
(Prazeres)
*28 - Praça Martim Moniz
Praça Martim Moniz is a square in Lisbon, Portugal. It is named after Martim Moniz.
There are stops on the Lisbon Metro
The Lisbon Metro ( pt, Metropolitano de Lisboa) is the rapid transit system in Lisbon, Portugal. Opened in December 195 ...
↔ Graça ↔ Estrela ↔ Campo de Ourique (Prazeres)
The six remaining lines operate in the southern city centre and west of the city only. Aside from the obvious tourist attraction, those lines are still important because sections of the city's topography
Topography is the study of the forms and features of land surfaces. The topography of an area may refer to the land forms and features themselves, or a description or depiction in maps.
Topography is a field of geoscience and planetary sc ...
can only be crossed by small trams. Tram 15 also connects the entire western riverfront of the city to the centre and allows a better link for passengers with the bus system towards an area that still is not served by the metro.
Although reports prepared by both the École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne
École may refer to:
* an elementary school in the French educational stages normally followed by secondary education establishments (collège and lycée)
* École (river), a tributary of the Seine flowing in région Île-de-France
* École, Savoi ...
and the Verkehrsbetriebe Zürich
Verkehrsbetriebe Zürich (VBZ) is a public transport operator in the Swiss city of Zürich, and is wholly owned by the city. Previously known as the Städtische Strassenbahn Zürich (StStZ), the organisation was founded in 1896 and adopted its c ...
concluded that the network should be retained and even extended, the process of decline continued until 1997, with the closing of the Alto de São João branch and the Arco Cego depot. By that time, many trams were destroyed or sold to other companies. In the following twenty years, there was only one change to the system, the shortening of Line 18 to Cais do Sodré.
Expansion
In an apparent reversal of policy, the mayor (president of the city council) of Lisbon,Fernando Medina
Fernando Medina Maciel Almeida Correia (born 10 March 1973) is a Portuguese economist and politician Socialist Party (PS) who has been serving as Minister of Finance in the government of Prime Minister António Costa since 2022. He previously serv ...
, announced in December 2016 that tram 24 would be restored to service in 2017 between Cais do Sodré and Campolide
Campolide () is a ''freguesia'' (civil parish) and district of Lisbon, the capital of Portugal. Located in central Lisbon, Campolide is west of Avenidas Novas, north of Campo de Ourique, east of Benfica, and south of São Domingos de Benfica. ...
, saying that it was a mistake to reduce the city's network of electric trams and that work would be undertaken to reconstruct it.
Carris originally said this was not a priority, but its 2018 ''Activity and Budget Plan'' provides for the purchase in 2020-2021 of:
* 10 more ''remodelados'' to augment the current historical fleet and reopen line 24 between Cais do Sodré and Campolide, at a cost of €8 million;
* 20 more articulated trams to extend line 15 eastwards to Santa Apolónia station
Santa Claus, also known as Father Christmas, Saint Nicholas, Saint Nick, Kris Kringle, or simply Santa, is a legendary figure originating in Western Christian culture who is said to bring children gifts during the late evening and overnigh ...
and the Parque das Nações
The Parque das Nações (; en, Park of the Nations), colloquially known as Expo (as the site of the 1998 Lisbon World Exposition), is a ''freguesia'' (civil parish) of Lisbon, the capital of Portugal. Located in eastern Lisbon, Parque das Naçõ ...
, at a cost of €50 million.
On 24 April 2018, Line 24 was reopened, albeit initially between Camões and Campolide only. Track connections to the rebuilt loop at Cais do Sodré and some other track issues between Camões and Cais do Sodré will need to be attended to before operation to Cais do Sodré is possible.
In July 2021 agreement was reached for two further extensions:
* a 12.1 km U-shaped surface metro connecting the terminus of the yellow line at Odivelas to the Hospital Beatriz Ângelo in one direction and Loures in the other;
* an additional 24 km of line on route 15, extending it to Linda-a-Velha in the west and to Sacavém in the north-east.''Tramways and Urban Transit, September 2021, p. 387''
Rolling stock
The tram fleet has fallen in size from 57 in 2012 to 48 in 2016. Vehicles used are: *'Articulado' trams made bySiemens
Siemens AG ( ) is a German multinational conglomerate corporation and the largest industrial manufacturing company in Europe headquartered in Munich with branch offices abroad.
The principal divisions of the corporation are ''Industry'', ''E ...
(Siemens/ CAF nos 501-506 and Siemens/Sorefame
Sorefame (an abbreviation of ''Sociedades Reunidas de Fabricações Metálicas'') was a Portuguese manufacturer of railway rolling stock and industrial equipment, such as dam gates equipment. The company was established in 1943.
In the 1990s the ...
nos 507–510). These articulated vehicles were introduced in 1995 and run only on route 15.
*'Remodelado' trams (nos 541–585) used on all routes.
*Tourist trams used on some routes.
See also
* Ascensor da Bica *Ascensor da Glória
The Glória Funicular ( pt, Ascensor da Glória), sometimes known as the ''Elevador da Glória'' (''Glória Elevator, Lift''), is a funicular railway line in the Freguesia (Portugal), civil parish of Santo António (Lisbon), Santo António, in th ...
* Ascensor do Lavra
* Carris
Carris (''Companhia Carris de Ferro de Lisboa'') (Lisbon Tramways Company) is a public transportation company in Lisbon, Portugal. Carris operates Lisbon's buses, trams, and funiculars. It does not operate the Lisbon Metro. Carris was founded Se ...
* List of town tramway systems in Portugal
References
Notes
Books
* *Website
* *External links
Tram 28 in Lisbon
Tram 28 route on Google Map
''This article is based on a translation of the German language version as of March 2011.'' {{coord missing, Portugal
Lisbon
Lisbon (; pt, Lisboa ) is the capital and largest city of Portugal, with an estimated population of 544,851 within its administrative limits in an area of 100.05 km2. Lisbon's urban area extends beyond the city's administrative limits w ...
Transport in Lisbon
Lisbon
Lisbon (; pt, Lisboa ) is the capital and largest city of Portugal, with an estimated population of 544,851 within its administrative limits in an area of 100.05 km2. Lisbon's urban area extends beyond the city's administrative limits w ...
900 mm gauge railways in Portugal
600 V DC railway electrification
1873 establishments in Portugal