traditional fishing boat on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Traditionally, many different kinds of boats have been used as fishing boats to catch fish in the sea, or on a lake or river. Even today, many traditional fishing boats are still in use. According to the United Nations
Traditionally, many different kinds of boats have been used as fishing boats to catch fish in the sea, or on a lake or river. Even today, many traditional fishing boats are still in use. According to the United Nations
 Early
Early
File:Gambian fishing boats.jpg, These fishing boats in
Artisan fishing is small-scale
 A
A

 Boats, rafts and even small floating islands have been made from reeds. Reed rafts can be distinguished from reed boats, since the rafts are not made watertight.
The earliest known boat made with reeds (and tar) is a 7000-year-old sea going boat found in Kuwait.
The
Boats, rafts and even small floating islands have been made from reeds. Reed rafts can be distinguished from reed boats, since the rafts are not made watertight.
The earliest known boat made with reeds (and tar) is a 7000-year-old sea going boat found in Kuwait.
The
Lake Titicaca
Retrieved 12 July 2007. Each floating island supports between three and ten houses, also built of reeds. The Uros also build their boats from bundled dried reeds. These days some Uros boats, used for fishing and hunting seabirds, have motors. Reed boats were constructed in
 Coracles are light boats shaped like a bowl, typically with a frame of woven grass or reeds, or strong saplings covered with animal hides. The
Coracles are light boats shaped like a bowl, typically with a frame of woven grass or reeds, or strong saplings covered with animal hides. The
File:Coracles River Teifi.jpg, Welsh coracle fishermen use a net to catch
In North America, American Indians and frontiersmen made coracles, called bull boats, by covering a
File:VIetnamese one-man fishing boat.jpg, Vietnamese one-man fishing coracle
File:Vietnamese coracle fishing boat.jpg, Off to work
File:Coracle fishing boats in Vietnam 02.jpg, Waiting for the tow at Mui Ne Beach
File:Vietnamese fishing coracles 02.jpg, Being towed to the fishing ground.
In
File:0057-Ancient-British-Canoes-q75-500x225.jpg, Ancient British dugout canoe
File:Great Andamanese - boats 1875.jpg,
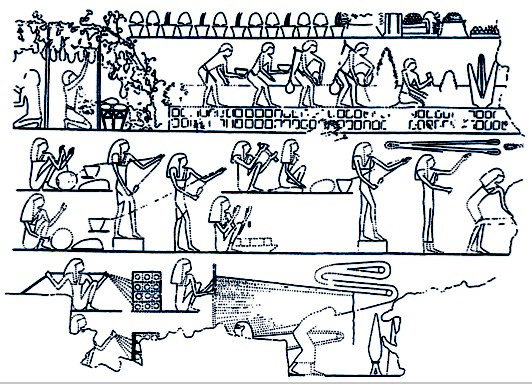 The availability of reliable and durable ropes and lines has had many consequences for the development and utility of traditional fishing boats. They can be used to lash planks and frames together, as stay lines for masts, as anchor lines to secure the boat, and as
The availability of reliable and durable ropes and lines has had many consequences for the development and utility of traditional fishing boats. They can be used to lash planks and frames together, as stay lines for masts, as anchor lines to secure the boat, and as
 Before engines became available, boats could be propelled manually or by the wind. Boats could be propelled by the wind by attaching
Before engines became available, boats could be propelled manually or by the wind. Boats could be propelled by the wind by attaching
Image:Jangada-Tibau.jpg,
They used woven
File:African fishing boats.jpg, Fishing boats at
 A further development was the use of timber frames, to which the planks could be lashed, stitched or nailed. With the use of frames, it is possible to develop carvel-style and clinker-style planking (in the USA the term ''lapstrake'' is used instead of ''clinker'').
A further development was the use of timber frames, to which the planks could be lashed, stitched or nailed. With the use of frames, it is possible to develop carvel-style and clinker-style planking (in the USA the term ''lapstrake'' is used instead of ''clinker'').
''The Oxford Illustrated History of the Vikings''
Page 183. Oxford University Press. Carvel construction dates back even earlier. A
File:Maltese fishing boats 02.jpg, Carvel built
 Boats in
Boats in 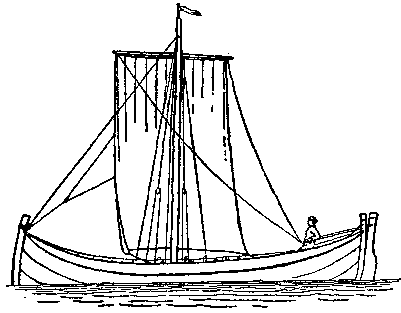 By 1000 AD the
By 1000 AD the  In the 15th century, the Dutch developed a type of sea-going
In the 15th century, the Dutch developed a type of sea-going  During the 17th century, the British developed the dogger, an early type of sailing trawler or
During the 17th century, the British developed the dogger, an early type of sailing trawler or  Dory, Dories are small, shallow-draft (hull), draft boats, usually about five to seven metres (15 to 22 feet) long. They are lightweight versatile boats with high sides, a flat bottom and sharp bows, and are easy to build because of their simple lines. The dory first appeared in New England fishing towns sometime after the early 18th century.Chapelle, page 85 The Banks dory, Banks dories appeared in the 1830s. They were designed to be carried on mother ships and used for fishing cod at the Grand Banks. Adapted almost directly from the low freeboard, French river bateau, with their straight sides and removable thwarts, bank dories could be nested inside each other and stored on the decks of fishing schooners, such as the ''Gazela, Gazela Primeiro'', for their trip to the Grand Banks fishing grounds.
Dory, Dories are small, shallow-draft (hull), draft boats, usually about five to seven metres (15 to 22 feet) long. They are lightweight versatile boats with high sides, a flat bottom and sharp bows, and are easy to build because of their simple lines. The dory first appeared in New England fishing towns sometime after the early 18th century.Chapelle, page 85 The Banks dory, Banks dories appeared in the 1830s. They were designed to be carried on mother ships and used for fishing cod at the Grand Banks. Adapted almost directly from the low freeboard, French river bateau, with their straight sides and removable thwarts, bank dories could be nested inside each other and stored on the decks of fishing schooners, such as the ''Gazela, Gazela Primeiro'', for their trip to the Grand Banks fishing grounds.
 In the 19th century, a more effective design for sailing Fishing trawler, trawlers was developed at the English fishing port, Brixham. These elegant wooden sailing boats spread across the world, influencing fishing fleets everywhere. Their distinctive sails inspired the song Red Sails in the Sunset (song), Red Sails in the Sunset, written aboard a Brixham sailing trawler called the ''Torbay Lass''. In the 1890s there were about 300 trawling vessels there, each usually owned by the skipper of the boat. Several of these old sailing trawlers have been preserved.
In the 19th century, a more effective design for sailing Fishing trawler, trawlers was developed at the English fishing port, Brixham. These elegant wooden sailing boats spread across the world, influencing fishing fleets everywhere. Their distinctive sails inspired the song Red Sails in the Sunset (song), Red Sails in the Sunset, written aboard a Brixham sailing trawler called the ''Torbay Lass''. In the 1890s there were about 300 trawling vessels there, each usually owned by the skipper of the boat. Several of these old sailing trawlers have been preserved.Pilgrim's restoration under full sail
BBC. Retrieved 2 March 2009.
 Throughout history, local conditions have led to the development of a wide range of types of fishing boats. The Nobby (boat)#Lancashire nobby, Lancashire nobby was used down the north west coast of England as a shrimp trawler from 1840 until World War II. The bawley and the Smack (ship), smack were used in the Thames Estuary and off East Anglia, while trawlers and drifters were used on the east coast. Herring fishing started in the Moray Firth in 1819. The Nobby (boat)#Manx nobby, Manx nobby was used as a herring drifter around the Isle of Man, and the fifie were used as herring Drifter (fishing boat), drifters along the east coast of Scotland from the 1850s until well into the 20th century.
Throughout history, local conditions have led to the development of a wide range of types of fishing boats. The Nobby (boat)#Lancashire nobby, Lancashire nobby was used down the north west coast of England as a shrimp trawler from 1840 until World War II. The bawley and the Smack (ship), smack were used in the Thames Estuary and off East Anglia, while trawlers and drifters were used on the east coast. Herring fishing started in the Moray Firth in 1819. The Nobby (boat)#Manx nobby, Manx nobby was used as a herring drifter around the Isle of Man, and the fifie were used as herring Drifter (fishing boat), drifters along the east coast of Scotland from the 1850s until well into the 20th century.
''Bucking the trades''
Bloomsbury Press. * FAO: CWP Handbook of Fishery Statistical Standards
Section L: Fishery Fleet
* FAO (2007
State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture, Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, Rome. * Forman, Shepard (1970) ''The raft fishermen: Tradition & change in the Brazilian peasant economy'', Indiana University Press for International Affairs Center. * Gardner, John (1987) ''The Dory Book.'' Mystic Seaport Museum, Mystic Connecticut. * Johnstone, Paul (1889
''The Sea-Craft of Prehistory''
Routledge. * McGrail, Sean (2004)
''Boats of the World: From the Stone Age to Medieval Times''
USA: Oxford University Press. . * (1997)
''The First Modern Economy. Success, Failure, and Perseverance of the Dutch Economy, 1500-1815''
Cambridge University Press,
''Bark Canoes and Skin Boats of North America''
Skyhorse Publishing. * Gerr, Dave (1995
''The Nature of Boats: Insights and Esoterica for the Nautically Obsessed''
McGraw-Hill Professional. * Smylie, Michael (1999) ''Traditional Fishing Boats of Britain & Ireland: Design, History and Evolution.'' Adlard Coles Nautical. * Smylie, Mike (2013
''Traditional Fishing Boats of Europe''
Amberley Publishing Limited. . * Traung, Jan-Olaf (1960
''Fishing Boats of the World 2''
Fishing News (Books) Ltd
Download PDF (99MB)
* Traung, Jan-Olaf (1967
''Fishing Boats of the World 3''
Kiefer Press.
Download PDF (56MB)
* Vigor, John (2004
''The Practical Encyclopedia of Boating: An A-Z Compendium of Seamanship, Boat Maintenance, Navigation, and Nautical Wisdom''
McGraw-Hill Professional. * Woodman, Richard (1998) ''The History of the Ship: The Comprehensive Story of Seafaring from the Earliest Times to the Present Day'', Lyons Press.
The Uros People at GlobalAmity.net
Video tour of Uros
floating fishing villages]
Uros Indian Culture - Home
Floating islands on Google Maps
Indigenous boats: Small craft outside the Western tradition
Indigenous sails
{{fisheries and fishing Reed boats Fishing vessels,

Food and Agriculture Organization
The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO)french: link=no, Organisation des Nations unies pour l'alimentation et l'agriculture; it, Organizzazione delle Nazioni Unite per l'Alimentazione e l'Agricoltura is an intern ...
(FAO), at the end of 2004, the world fishing fleet consisted of about 4 million vessels, of which 2.7 million were undecked (open) boats. While nearly all decked vessels were mechanised, only one-third of the undecked fishing boats were powered, usually with outboard engines. The remaining 1.8 million boats were traditional craft of various types, operated by sail and oars.
This article is about the boats used for fishing that are or were built from designs that existed before engines became available.
__TOC__
Overview
 Early
Early fishing vessel
A fishing vessel is a boat or ship used to catch fish in the sea, or on a lake or river. Many different kinds of vessels are used in commercial, artisanal and recreational fishing.
The total number of fishing vessels in the world in 2016 was e ...
s included raft
A raft is any flat structure for support or transportation over water. It is usually of basic design, characterized by the absence of a hull. Rafts are usually kept afloat by using any combination of buoyant materials such as wood, sealed barrel ...
s, dugout canoes
A dugout canoe or simply dugout is a boat made from a hollowed tree. Other names for this type of boat are logboat and monoxylon. ''Monoxylon'' (''μονόξυλον'') (pl: ''monoxyla'') is Greek – ''mono-'' (single) + '' ξύλον xylon'' (t ...
, reed boats
Reed boats and rafts, along with dugout canoes and other rafts, are among the oldest known types of boats. Often used as traditional fishing boats, they are still used in a few places around the world, though they have generally been replaced wit ...
, and boats constructed from a frame covered with hide or tree bark
Bark is the outermost layers of stems and roots of woody plants. Plants with bark include trees, woody vines, and shrubs. Bark refers to all the tissues outside the vascular cambium and is a nontechnical term. It overlays the wood and consist ...
, such as coracle
A coracle is a small, rounded, lightweight boat of the sort traditionally used in Wales, and also in parts of the West Country and in Ireland, particularly the River Boyne, and in Scotland, particularly the River Spey. The word is also used of s ...
s.McGrail 2004, page 431 The oldest boats found by archaeological excavation are dugout canoes dating back to the Neolithic Period
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several part ...
around 7,000-9,000 years ago. These canoes were often cut from coniferous tree
Conifers are a group of cone-bearing seed plants, a subset of gymnosperms. Scientifically, they make up the division Pinophyta (), also known as Coniferophyta () or Coniferae. The division contains a single extant class, Pinopsida. All extan ...
logs, using simple stone tool
A stone tool is, in the most general sense, any tool made either partially or entirely out of stone. Although stone tool-dependent societies and cultures still exist today, most stone tools are associated with prehistoric (particularly Stone Ag ...
s.
A 7000-year-old sea going boat made from reeds and tar has been found in Kuwait. These early vessels had limited capability; they could float and move on water, but were not suitable for use any great distance from the shoreline. They were used mainly for fishing
Fishing is the activity of trying to catch fish. Fish are often caught as wildlife from the natural environment, but may also be caught from fish stocking, stocked bodies of water such as fish pond, ponds, canals, park wetlands and reservoirs. ...
and hunting
Hunting is the human practice of seeking, pursuing, capturing, or killing wildlife or feral animals. The most common reasons for humans to hunt are to harvest food (i.e. meat) and useful animal products (fur/ hide, bone/tusks, horn/antler, e ...
.
The development of fishing boats took place in parallel with the development of boats built for trade and war. Early navigators began to use animal skins or woven fabrics for sail
A sail is a tensile structure—which is made from fabric or other membrane materials—that uses wind power to propel sailing craft, including sailing ships, sailboats, windsurfers, ice boats, and even sail-powered land vehicles. Sails ma ...
s. Affixed to a pole set upright in the boat, these sails gave early boats more range, allowing voyages of exploration
According to the FAO, at the end of 2004, the world fishing fleet included 1.8 million traditional craft of various types which were operated by sail and oars.FAO 2007 These figures for small fishing vessels are probably under reported. The FAO compiles these figures largely from national registers. These records often omit smaller boats where registration is not required or where fishing licences are granted by provincial or municipal authorities. Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Guinea. In ...
reportedly has about 700,000 current fishing boats, 25 percent of which are dugout canoe
A dugout canoe or simply dugout is a boat made from a hollowed tree. Other names for this type of boat are logboat and monoxylon. ''Monoxylon'' (''μονόξυλον'') (pl: ''monoxyla'') is Greek – ''mono-'' (single) + '' ξύλον xylon'' (t ...
s, and half of which are without motors. The Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
have reported a similar number of small fishing boats.
Traditional fishing boats are usually characteristic of the stretch of coast along which they operate. They evolve over time to meet the local conditions, such as the materials available locally for boat building, the type of sea conditions the boats will encounter, and the demands of the local fisheries
Fishery can mean either the enterprise of raising or harvesting fish and other aquatic life; or more commonly, the site where such enterprise takes place ( a.k.a. fishing ground). Commercial fisheries include wild fisheries and fish farms, bot ...
.
Gambia
The Gambia,, ff, Gammbi, ar, غامبيا officially the Republic of The Gambia, is a country in West Africa. It is the smallest country within mainland AfricaHoare, Ben. (2002) ''The Kingfisher A-Z Encyclopedia'', Kingfisher Publicatio ...
conform to a local design.
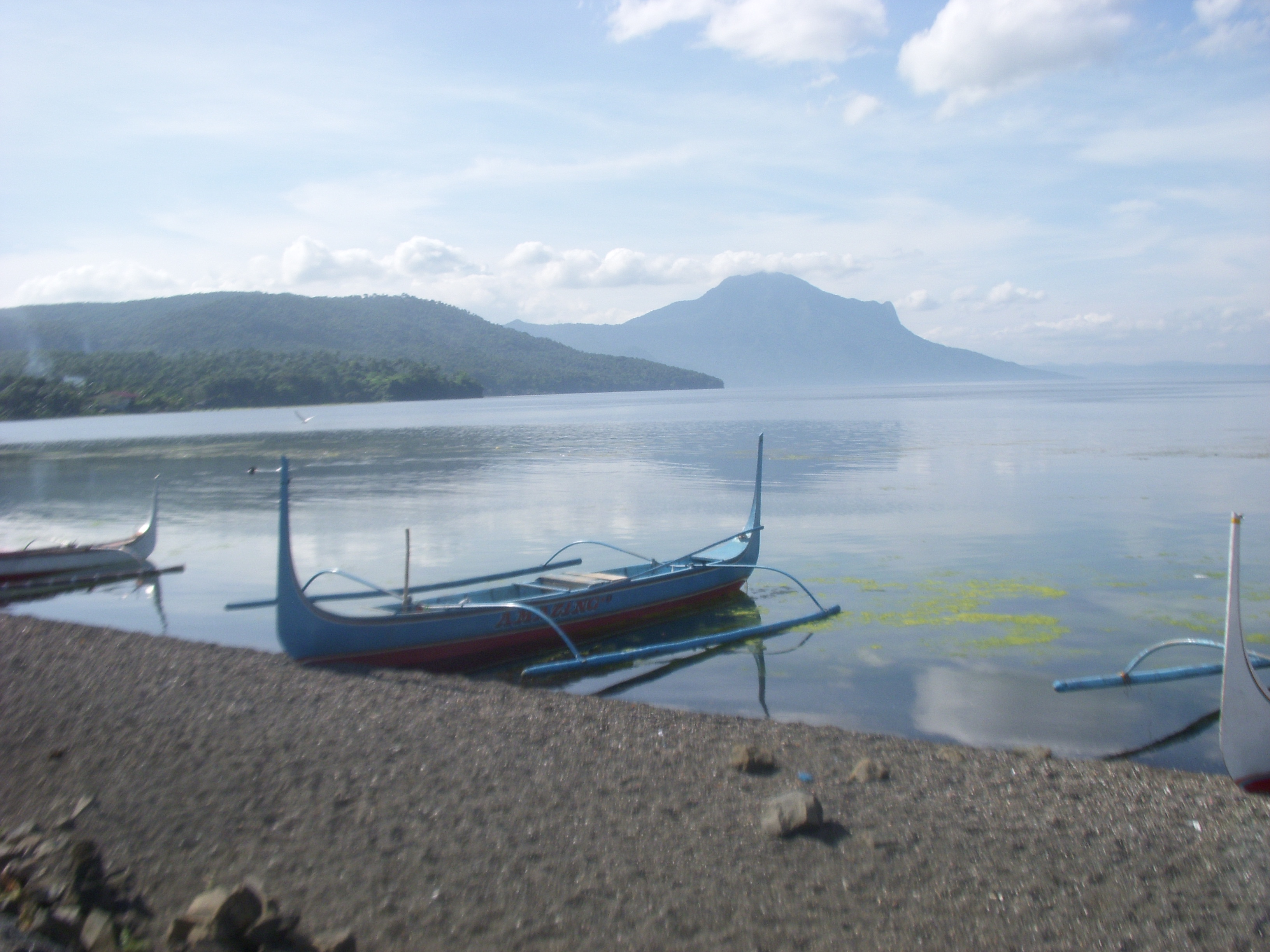
File:Vietnamese fishing boats.jpg, These fishing boats conform to a different local design in Vietnam
Vietnam or Viet Nam ( vi, Việt Nam, ), officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam,., group="n" is a country in Southeast Asia, at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of and population of 96 million, making it ...
File:Koh Tao Mae Haad longtails.jpg, Fishing boats in Thailand
Thailand ( ), historically known as Siam () and officially the Kingdom of Thailand, is a country in Southeast Asia, located at the centre of the Indochinese Peninsula, spanning , with a population of almost 70 million. The country is b ...
, at Surat Thani
Surat Thani ( th, สุราษฎร์ธานี, ) is a city in Amphoe Mueang Surat Thani, Surat Thani Province, southern Thailand. It lies south of Bangkok. It is the capital of Surat Thani Province. The city has a population of 1 ...
, follow this style
File:Thai fishing boats at the beach.jpg, Fishing boats in Thailand
Thailand ( ), historically known as Siam () and officially the Kingdom of Thailand, is a country in Southeast Asia, located at the centre of the Indochinese Peninsula, spanning , with a population of almost 70 million. The country is b ...
, at Bang Sen, follow another style
commercial
Commercial may refer to:
* a dose of advertising conveyed through media (such as - for example - radio or television)
** Radio advertisement
** Television advertisement
* (adjective for:) commerce, a system of voluntary exchange of products and s ...
or subsistence
A subsistence economy is an economy directed to basic subsistence (the provision of food, clothing, shelter) rather than to the market. Henceforth, "subsistence" is understood as supporting oneself at a minimum level. Often, the subsistence econo ...
fishing, particularly practices involving coastal or island ethnic groups using traditional fishing techniques
Fishing techniques are methods for catching fish. The term may also be applied to methods for catching other aquatic animals such as molluscs (shellfish, squid, octopus) and edible marine invertebrates.
Fishing techniques include Gathering seaf ...
and traditional boats. This may also include heritage groups involved in customary fishing practices. Artisan fishers usually use small traditional fishing boats that are open (undecked) and have sails; these boats use little to no mechanised or electronic gear. Large numbers of artisan fishing boats are still in use, particularly in developing countries with long productive marine coastlines.
Rafts
 A
A raft
A raft is any flat structure for support or transportation over water. It is usually of basic design, characterized by the absence of a hull. Rafts are usually kept afloat by using any combination of buoyant materials such as wood, sealed barrel ...
is a structure with a flat top that floats. It is the most basic boat design, characterised by the absence of a hull
Hull may refer to:
Structures
* Chassis, of an armored fighting vehicle
* Fuselage, of an aircraft
* Hull (botany), the outer covering of seeds
* Hull (watercraft), the body or frame of a ship
* Submarine hull
Mathematics
* Affine hull, in affi ...
. The classic raft is constructed by lashing several logs, placed side by side, to two or more additional logs placed transverse to the others. In many Asian countries, the rafts are similarly constructed using bamboo.
In shallow waters, rafts can be punted with a push pole. They can be used as stealthy platforms for fishing shallow waters around lakes. In sheltered coastal waters, anchored or drifting rafts can become effective fish aggregating device
A fish aggregating (or aggregation) device (FAD) is a man-made object used to attract ocean-going pelagic fish such as marlin, tuna and mahi-mahi (dolphin fish). They usually consist of buoys or floats tethered to the ocean floor with concrete bloc ...
s. Payaos were traditional bamboo rafts used in Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, also spelled South East Asia and South-East Asia, and also known as Southeastern Asia, South-eastern Asia or SEA, is the geographical United Nations geoscheme for Asia#South-eastern Asia, south-eastern region of Asia, consistin ...
as aggregating device. Fishermen on the top of the raft used handline
Handline fishing, or handlining, is a fishing technique where a single fishing line is held in the hands, rather than with a fishing rod like the usual angling. It is a type of angling, and is not to be confused with handfishing, which is catch ...
s to catch tuna
A tuna is a saltwater fish that belongs to the tribe Thunnini, a subgrouping of the Scombridae (mackerel) family. The Thunnini comprise 15 species across five genera, the sizes of which vary greatly, ranging from the bullet tuna (max length: ...
.
Pontoon boat
A pleasure boat with two lengthwise pontoons
A pontoon boat is a flattish boat that relies on floats to remain buoyant. These pontoons (also called ''tubes'') contain much reserve buoyancy and allow designers to create large deck plans fitted wi ...
s, and to some degree the punt, can be viewed as modern derivatives of rafts.
Reed boats

 Boats, rafts and even small floating islands have been made from reeds. Reed rafts can be distinguished from reed boats, since the rafts are not made watertight.
The earliest known boat made with reeds (and tar) is a 7000-year-old sea going boat found in Kuwait.
The
Boats, rafts and even small floating islands have been made from reeds. Reed rafts can be distinguished from reed boats, since the rafts are not made watertight.
The earliest known boat made with reeds (and tar) is a 7000-year-old sea going boat found in Kuwait.
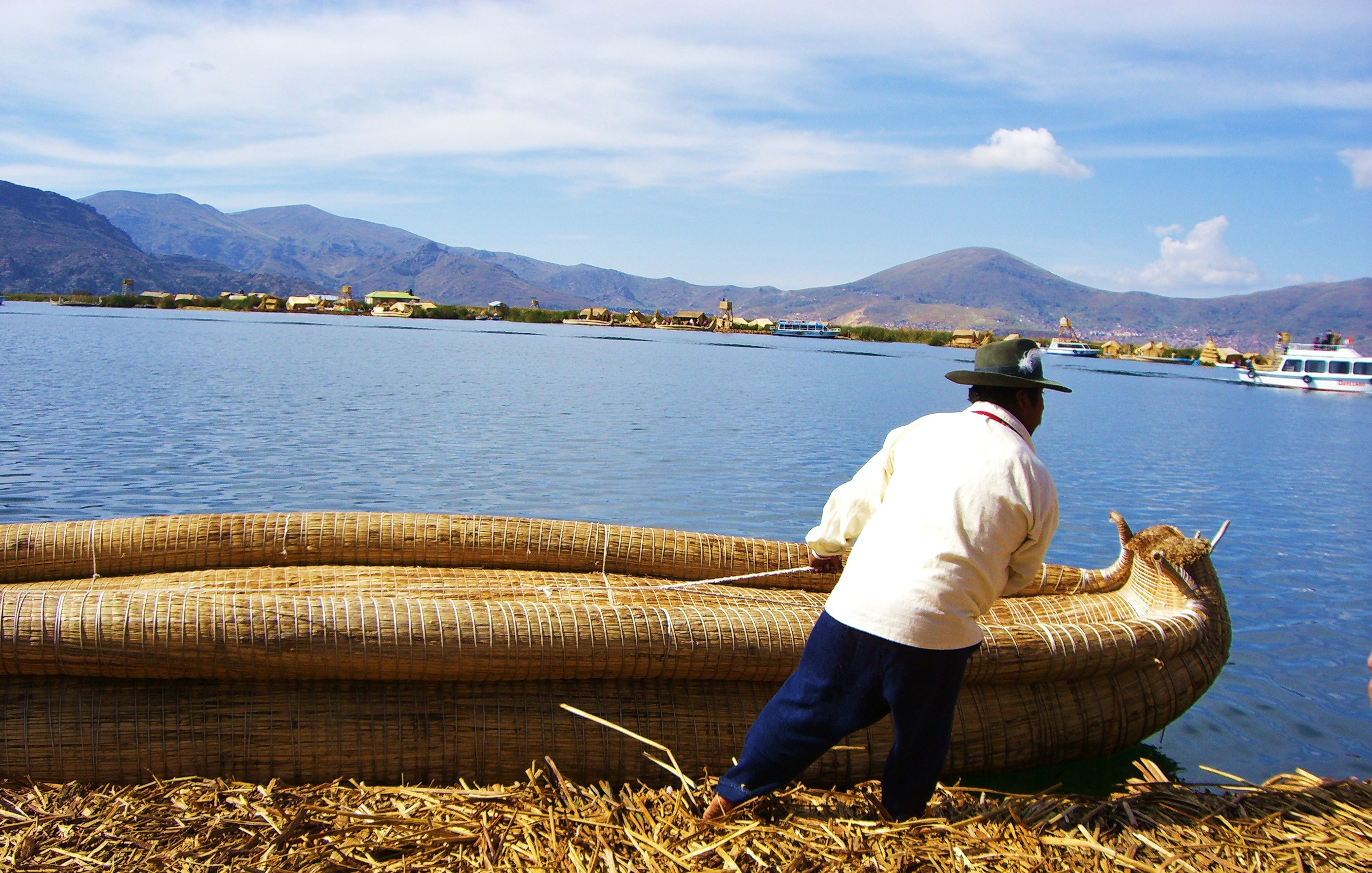
The Uros
The Uru or Uros ( ure, Qhas Qut suñi) are an indigenous people of Bolivia. They live on an approximate and still growing 120 self-fashioned floating islands in Lake Titicaca near Puno. They form three main groups: the Uru-Chipaya, Uru-Mura ...
are an indigenous people pre-dating the Incas
The Inca Empire (also known as the Incan Empire and the Inka Empire), called ''Tawantinsuyu'' by its subjects, (Quechua for the "Realm of the Four Parts", "four parts together" ) was the largest empire in pre-Columbian America. The admin ...
. They live, still today, on man-made floating islands scattered across Lake Titicaca
Lake Titicaca (; es, Lago Titicaca ; qu, Titiqaqa Qucha) is a large freshwater lake in the Andes mountains on the border of Bolivia and Peru. It is often called the highest navigable lake in the world. By volume of water and by surface area, i ...
. These islands are constructed from totora reeds.Encyclopædia Britannica
The (Latin for "British Encyclopædia") is a general knowledge English-language encyclopaedia. It is published by Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc.; the company has existed since the 18th century, although it has changed ownership various time ...
OnlineLake Titicaca
Retrieved 12 July 2007. Each floating island supports between three and ten houses, also built of reeds. The Uros also build their boats from bundled dried reeds. These days some Uros boats, used for fishing and hunting seabirds, have motors. Reed boats were constructed in
Easter Island
Easter Island ( rap, Rapa Nui; es, Isla de Pascua) is an island and special territory of Chile in the southeastern Pacific Ocean, at the southeasternmost point of the Polynesian Triangle in Oceania. The island is most famous for its nearly ...
with a markedly similar design to those used in Peru. Apart from Peru and Bolivia, reed boats are still used in Ethiopia
Ethiopia, , om, Itiyoophiyaa, so, Itoobiya, ti, ኢትዮጵያ, Ítiyop'iya, aa, Itiyoppiya officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country in the Horn of Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the no ...
and were used until recently in Corfu
Corfu (, ) or Kerkyra ( el, Κέρκυρα, Kérkyra, , ; ; la, Corcyra.) is a Greek islands, Greek island in the Ionian Sea, of the Ionian Islands, and, including its small satellite islands, forms the margin of the northwestern frontier of G ...
.
Coracles
 Coracles are light boats shaped like a bowl, typically with a frame of woven grass or reeds, or strong saplings covered with animal hides. The
Coracles are light boats shaped like a bowl, typically with a frame of woven grass or reeds, or strong saplings covered with animal hides. The keel
The keel is the bottom-most longitudinal structural element on a vessel. On some sailboats, it may have a hydrodynamic and counterbalancing purpose, as well. As the laying down of the keel is the initial step in the construction of a ship, in Br ...
-less, flat bottom evenly spreads the weight across the structure reducing the required depth of water often to only a few inches. Coracles have been used, and to a degree are still used, in India, Vietnam, Iraq, Tibet, North America and Britain.
Coracles in Iraq
Iraq,; ku, عێراق, translit=Êraq officially the Republic of Iraq, '; ku, کۆماری عێراق, translit=Komarî Êraq is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Turkey to the north, Iran to the east, the Persian Gulf and K ...
are called "''quffa
A kuphar (also transliterated kufa, kuffah, quffa, quffah, etc.) is a type of coracle or round boat traditionally used on the Tigris and Euphrates rivers in ancient and modern Mesopotamia. Its circular shape means that it does not sail well agains ...
''." Their history goes back to antiquity where they appear on Assyrian
Assyrian may refer to:
* Assyrian people, the indigenous ethnic group of Mesopotamia.
* Assyria, a major Mesopotamian kingdom and empire.
** Early Assyrian Period
** Old Assyrian Period
** Middle Assyrian Empire
** Neo-Assyrian Empire
* Assyrian ...
-era reliefs sculpted between 600 and 900 BC. These reliefs are now in the British Museum
The British Museum is a public museum dedicated to human history, art and culture located in the Bloomsbury area of London. Its permanent collection of eight million works is among the largest and most comprehensive in existence. It documen ...
. Herodotus
Herodotus ( ; grc, , }; BC) was an ancient Greek historian and geographer from the Greek city of Halicarnassus, part of the Persian Empire (now Bodrum, Turkey) and a later citizen of Thurii in modern Calabria ( Italy). He is known for ha ...
visited Babylon in the 5th century BC, and wrote a long description of the coracles he encountered there. Traditionally, ''quffa'' were framed with willow
Willows, also called sallows and osiers, from the genus ''Salix'', comprise around 400 speciesMabberley, D.J. 1997. The Plant Book, Cambridge University Press #2: Cambridge. of typically deciduous trees and shrubs, found primarily on moist so ...
or juniper
Junipers are coniferous trees and shrubs in the genus ''Juniperus'' () of the cypress family Cupressaceae. Depending on the taxonomy, between 50 and 67 species of junipers are widely distributed throughout the Northern Hemisphere, from the Arcti ...
and covered with hides or reeds. The outside was then coated with hot bitumen
Asphalt, also known as bitumen (, ), is a sticky, black, highly viscous liquid or semi-solid form of petroleum. It may be found in natural deposits or may be a refined product, and is classed as a pitch. Before the 20th century, the term a ...
for waterproofing, although the inside could also be coated for larger vessels. These coracles have been in continuous use on the Tigris
The Tigris () is the easternmost of the two great rivers that define Mesopotamia, the other being the Euphrates. The river flows south from the mountains of the Armenian Highlands through the Syrian and Arabian Deserts, and empties into the ...
and Euphrates
The Euphrates () is the longest and one of the most historically important rivers of Western Asia. Together with the Tigris, it is one of the two defining rivers of Mesopotamia ( ''the land between the rivers''). Originating in Turkey, the Euph ...
rivers, particularly around Baghdad
Baghdad (; ar, بَغْدَاد , ) is the capital of Iraq and the second-largest city in the Arab world after Cairo. It is located on the Tigris near the ruins of the ancient city of Babylon and the Sassanid Persian capital of Ctesiphon ...
, through the 1970s. Some of the Iraqi coracles are very large, with the largest reaching up to in diameter and being able to carry up to 5 tons.
Coracles are known to have been in use in Britain in 49 BC when Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (; ; 12 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC), was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in a civil war, and ...
encountered them. They are still used in Wales
Wales ( cy, Cymru ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by England to the east, the Irish Sea to the north and west, the Celtic Sea to the south west and the Bristol Channel to the south. It had a population in 2 ...
, where they were traditionally framed with split and interwoven willow
Willows, also called sallows and osiers, from the genus ''Salix'', comprise around 400 speciesMabberley, D.J. 1997. The Plant Book, Cambridge University Press #2: Cambridge. of typically deciduous trees and shrubs, found primarily on moist so ...
rods, tied with willow bark. The outer layer was an animal skin, such as horse
The horse (''Equus ferus caballus'') is a Domestication, domesticated, odd-toed ungulate, one-toed, ungulate, hoofed mammal. It belongs to the taxonomic family Equidae and is one of two Extant taxon, extant subspecies of wild horse, ''Equus fer ...
or bullock
Bullock may refer to:
Animals
* Bullock (in British English), a castrated male bovine animal of any age
* Bullock (in North America), a young bull (an uncastrated male bovine animal)
* Bullock (in Australia, India and New Zealand), an ox, an adu ...
hide, with a thin layer of tar
Tar is a dark brown or black viscous liquid of hydrocarbons and free carbon, obtained from a wide variety of organic materials through destructive distillation. Tar can be produced from coal, wood, petroleum, or peat. "a dark brown or black b ...
for waterproofing. Today tarred calico
Calico (; in British usage since 1505) is a heavy plain-woven textile made from unbleached, and often not fully processed, cotton. It may also contain unseparated husk parts. The fabric is far coarser than muslin, but less coarse and thick tha ...
or canvas
Canvas is an extremely durable plain-woven fabric used for making sails, tents, marquees, backpacks, shelters, as a support for oil painting and for other items for which sturdiness is required, as well as in such fashion objects as handbags, ...
, or simply fiberglass
Fiberglass (American English) or fibreglass (Commonwealth English) is a common type of fiber-reinforced plastic using glass fiber. The fibers may be randomly arranged, flattened into a sheet called a chopped strand mat, or woven into glass cloth ...
can be used. Different Welsh rivers have their own designs, tailored to the flow of the river. The Teifi coracle, for instance, is flat-bottomed, as it is designed to negotiate shallow rapids, common on the river in the summer, while the Carmarthen
Carmarthen (, RP: ; cy, Caerfyrddin , "Merlin's fort" or "Sea-town fort") is the county town of Carmarthenshire and a community in Wales, lying on the River Towy. north of its estuary in Carmarthen Bay. The population was 14,185 in 2011, d ...
coracle is rounder and deeper, because it is used in tidal waters on the Tywi
The River Towy ( cy, Afon Tywi, ) is one of the longest rivers flowing entirely within Wales. Its total length is . It is noted for its sea trout and salmon fishing.
Route
The Towy rises within of the source of the River Teifi on the lower slo ...
, where there are no rapids.
Coracles can be effective fishing vessels. When operated skilfully, they hardly disturb the water or the fish. Welsh coracle fishing is performed by two men, each seated in his coracle and with one hand holding the net while with the other he plies his paddle. When a fish is caught, each hauls up his end of the net until the two coracles touch and the fish are secured. Many coracles are so light and portable that they can easily be carried on the fisherman's shoulders.
salmon
Salmon () is the common name for several commercially important species of euryhaline ray-finned fish from the family Salmonidae, which are native to tributaries of the North Atlantic (genus ''Salmo'') and North Pacific (genus ''Oncorhynchus' ...
on the River Teifi
, name_etymology =
, image = File:Llyn Teifi - geograph.org.uk - 41773.jpg
, image_size =
, image_caption = Llyn Teifi, the source of the Teifi
, map =
, map_size =
, map_caption ...
, 1972
File:Mandan Bull Boats and Lodges- George Catlin.jpg, Painting of North American coracles ( bull boats), c.a. 1832
File:India-TamilNadu-Hogenakkal-falls-Coracle-Cafeteria.jpg, Indian coracle on the Kaveri river
The Kaveri (also known as Cauvery, the anglicized name) is one of the major Indian rivers flowing through the states of Karnataka and Tamil Nadu. The Kaveri river rises at Talakaveri in the Brahmagiri range in the Western Ghats, Kodagu dist ...
File:Bundesarchiv Bild 135-BB-082-12, Tibetexpedition, Floß bei Chagsam.jpg, Yak
The domestic yak (''Bos grunniens''), also known as the Tartary ox, grunting ox or hairy cattle, is a species of long-haired domesticated cattle found throughout the Himalayan region of the Indian subcontinent, the Tibetan Plateau, Kachin Sta ...
skin coracle in Tibet
Tibet (; ''Böd''; ) is a region in East Asia, covering much of the Tibetan Plateau and spanning about . It is the traditional homeland of the Tibetan people. Also resident on the plateau are some other ethnic groups such as Monpa, Taman ...
, 1938
willow
Willows, also called sallows and osiers, from the genus ''Salix'', comprise around 400 speciesMabberley, D.J. 1997. The Plant Book, Cambridge University Press #2: Cambridge. of typically deciduous trees and shrubs, found primarily on moist so ...
frame with buffalo hide. The buffalo hair was left on the hide because it inhibited the craft from spinning, and the tails were also left intact and used to tie bull boats together.
Indian coracles commonly operate on the rivers Kaveri
The Kaveri (also known as Cauvery, the anglicized name) is one of the major Indian rivers flowing through the states of Karnataka and Tamil Nadu. The Kaveri river rises at Talakaveri in the Brahmagiri range in the Western Ghats, Kodagu dis ...
and Tungabhadra in Southern India
South India, also known as Dakshina Bharata or Peninsular India, consists of the peninsular southern part of India. It encompasses the Indian states of Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Kerala, Tamil Nadu, and Telangana, as well as the union territo ...
. The smaller ones are about 6.2 feet (1.9 metres) in diameter, and are used primarily for fishing. Indian coracles have been used since prehistoric times.
In Tibet
Tibet (; ''Böd''; ) is a region in East Asia, covering much of the Tibetan Plateau and spanning about . It is the traditional homeland of the Tibetan people. Also resident on the plateau are some other ethnic groups such as Monpa, Taman ...
, coracles, used for fishing and ferrying people, are made by stretching yak hide over juniper
Junipers are coniferous trees and shrubs in the genus ''Juniperus'' () of the cypress family Cupressaceae. Depending on the taxonomy, between 50 and 67 species of junipers are widely distributed throughout the Northern Hemisphere, from the Arcti ...
frames, and fastened with leather thongs. They are shaped like the Iraq coracles. Yack butter is used for waterproofing. Again, different rivers have their own designs. Sometimes two coracles are strapped together for added stability.
Vietnam
Vietnam or Viet Nam ( vi, Việt Nam, ), officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam,., group="n" is a country in Southeast Asia, at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of and population of 96 million, making it ...
, elegant coracles constructed with bamboo, are still used from many beaches, such as at Nha Trang
Nha Trang ( or ; ) is a coastal city and capital of Khánh Hòa Province, on the South Central Coast of Vietnam. It is bounded on the north by Ninh Hoà town, on the south by Cam Ranh city and on the west by Diên Khánh District. The city has ...
, Phan Thiết
Phan Thiết () is the capital of Bình Thuận Province on the southeast coast in Vietnam. While most of the inhabitants live in the city center, others reside in the four urban coastal wards, extending from Suối Nước beach in the northea ...
and Mui Ne. The coracles are towed in a line behind a motor boat, like beads on a string, to their fishing ground. There the fisherman lay fishing nets
A fishing net is a Net (device), net used for fishing. Nets are devices made from fibers woven in a grid-like structure. Some fishing nets are also called fish traps, for example #Fyke nets, fyke nets. Fishing nets are usually meshes formed by ...
in the sea. Later, another tow returns the coracle fishermen to the beach with their catch.
Canoes
Acanoe
A canoe is a lightweight narrow water vessel, typically pointed at both ends and open on top, propelled by one or more seated or kneeling paddlers facing the direction of travel and using a single-bladed paddle.
In British English, the term ...
is a small narrow boat, usually pointed at both bow and stern and normally open on top, though they can be covered. A dugout is a canoe hollowed from a tree trunk. The oldest known canoe is the dugout Pesse canoe
The Pesse canoe is believed to be the world's oldest known boat and certainly the oldest known canoe. Carbon dating indicates that the boat was constructed during the early mesolithic period between 8040 BC and 7510 BC. It is now in the Drents M ...
found in the Netherlands. According to C14 dating
Radiocarbon dating (also referred to as carbon dating or carbon-14 dating) is a method for determining the age of an object containing organic material by using the properties of radiocarbon, a radioactive isotope of carbon.
The method was de ...
analysis it was constructed somewhere between 8200 and 7600 BC. This canoe is exhibited in the Drents Museum in Assen
Assen () is a municipality and a city in the northeastern Netherlands, and is the capital of the province of Drenthe. It received city rights in 1809. Assen is known for TT Circuit Assen, the motorcycle racing circuit, where on the last Sund ...
, Netherlands. Another dugout, almost as old, has been found at Noyen-sur-Seine. The oldest known canoe found in Africa is the Dufuna canoe
The Dufuna canoe is a dugout canoe discovered in 1987 by a Fulani cattle herdsman a few kilometers from the village of Dufuna in the Fune Local Government Area, not far from the Komadugu Gana River, in Yobe State, Nigeria. Radiocarbon dating of ...
, constructed about 6000 BC. It was discovered by Fulani
The Fula, Fulani, or Fulɓe people ( ff, Fulɓe, ; french: Peul, links=no; ha, Fulani or Hilani; pt, Fula, links=no; wo, Pël; bm, Fulaw) are one of the largest ethnic groups in the Sahel and West Africa, widely dispersed across the region. ...
herdsman in Nigeria
Nigeria ( ), , ig, Naìjíríyà, yo, Nàìjíríà, pcm, Naijá , ff, Naajeeriya, kcg, Naijeriya officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a country in West Africa. It is situated between the Sahel to the north and the Gulf of G ...
in 1987.
During the Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age (Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age ( Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostly ap ...
residents of Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the northwest coast of continental Europe. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the largest European island and the ninth-largest island in the world. It is ...
used dugouts for fishing and transport. Two ancient dugouts discovered in Newport, Shropshire
Newport is a constituent market town in Telford and Wrekin in Shropshire, England. It lies north of Telford, west of Stafford, and is near the Shropshire-Staffordshire border. The 2001 Census in the United Kingdom, census recorded 10,814 peop ...
are on display at Harper Adams University
Harper Adams University, founded in 1901 as Harper Adams College, is a public university located close to the village of Edgmond, near Newport, in Shropshire, England. Established in 1901, the college is a specialist provider of higher educa ...
in Newport. In 1964, a dugout was uncovered in Poole Harbour
Poole Harbour is a large natural harbour in Dorset, southern England, with the town of Poole on its shores. The harbour is a drowned valley (ria) formed at the end of the last ice age and is the estuary of several rivers, the largest being the ...
, Dorset
Dorset ( ; archaically: Dorsetshire , ) is a county in South West England on the English Channel coast. The ceremonial county comprises the unitary authority areas of Bournemouth, Christchurch and Poole and Dorset. Covering an area of , Do ...
. The Poole Logboat, dated to 300 BC, was large enough to accommodate 18 people and was constructed from a large oak tree
An oak is a tree or shrub in the genus ''Quercus'' (; Latin "oak tree") of the beech family, Fagaceae. There are approximately 500 extant species of oaks. The common name "oak" also appears in the names of species in related genera, notably ''L ...
.
Best known are the canoes of the Eastern North American Indians
The Indigenous peoples of the Americas are the inhabitants of the Americas before the arrival of the European settlers in the 15th century, and the ethnic groups who now identify themselves with those peoples.
Many Indigenous peoples of the Am ...
. These, often elegant canoes, were not dugouts, but were made of a wooden frame covered with bark of a birch tree, pitched to make it waterproof.
Typically canoes are propelled with paddle
A paddle is a handheld tool with an elongated handle and a flat, widened distal end (i.e. the ''blade''), used as a lever to apply force onto the bladed end. It most commonly describes a completely handheld tool used to propel a human-powered wa ...
s, often by two people. Paddlers face in the direction of travel, either seated on supports in the hull
Hull may refer to:
Structures
* Chassis, of an armored fighting vehicle
* Fuselage, of an aircraft
* Hull (botany), the outer covering of seeds
* Hull (watercraft), the body or frame of a ship
* Submarine hull
Mathematics
* Affine hull, in affi ...
, or kneeling directly upon the hull. Paddles can be single-bladed or double-bladed.
A pirogue
A pirogue ( or ), also called a piragua or piraga, is any of various small boats, particularly dugouts and native canoes. The word is French and is derived from Spanish , which comes from the Carib '. Description
The term 'pirogue' does ...
is a small, flat-bottomed boat of a design associated particularly with West Africa
West Africa or Western Africa is the westernmost region of Africa. The United Nations geoscheme for Africa#Western Africa, United Nations defines Western Africa as the 16 countries of Benin, Burkina Faso, Cape Verde, The Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, ...
n fishermen
A fisher or fisherman is someone who captures fish and other animals from a body of water, or gathers shellfish.
Worldwide, there are about 38 million commercial and subsistence fishers and fish farmers. Fishers may be professional or recreati ...
and the Cajun
The Cajuns (; French: ''les Cadjins'' or ''les Cadiens'' ), also known as Louisiana ''Acadians'' (French: ''les Acadiens''), are a Louisiana French ethnicity mainly found in the U.S. state of Louisiana.
While Cajuns are usually described as ...
s of the Louisiana
Louisiana , group=pronunciation (French: ''La Louisiane'') is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It is the 20th-smallest by area and the 25th most populous of the 50 U.S. states. Louisiana is border ...
marsh. These are usually dugouts, and are light and small enough to be easily taken onto land. The design allows the pirogue to move through the very shallow water of marshes and be easily turned over to drain any water that may get into the boat. The pirogue is usually propelled by paddles
A paddle is a handheld tool with an elongated handle and a flat, widened distal end (i.e. the ''blade''), used as a lever to apply force onto the bladed end. It most commonly describes a completely handheld tool used to propel a human-powered wa ...
with one blade. It can also be punted with a push pole in shallow water. Small sail
A sail is a tensile structure—which is made from fabric or other membrane materials—that uses wind power to propel sailing craft, including sailing ships, sailboats, windsurfers, ice boats, and even sail-powered land vehicles. Sails ma ...
s can also be used. Outboard motors are increasingly being used in many regions.
The log canoe
The log canoe is a type of sailboat developed in the Chesapeake Bay region. Based on the dugout, it was the principal traditional fishing boat of the bay until superseded by the bugeye and the skipjack. However, it is most famous as a racing ...
of Chesapeake Bay
The Chesapeake Bay ( ) is the largest estuary in the United States. The Bay is located in the Mid-Atlantic region and is primarily separated from the Atlantic Ocean by the Delmarva Peninsula (including the parts: the Eastern Shore of Maryland / E ...
is in the modern sense not a canoe at all, though it evolved through the enlargement of dugout canoes.
For stability in rougher waters, canoes can be fitted with outrigger
An outrigger is a projecting structure on a boat, with specific meaning depending on types of vessel. Outriggers may also refer to legs on a wheeled vehicle that are folded out when it needs stabilization, for example on a crane that lifts ...
s. One or two small logs are mounted parallel to the main hull by long poles. In the case of two outriggers, one is mounted to either side of the hull. These are called outrigger canoe
Outrigger boats are various watercraft featuring one or more lateral support floats known as outriggers, which are fastened to one or both sides of the main hull. They can range from small dugout canoes to large plank-built vessels. Outrigger ...
s.
Many of the fishing boats in Indonesia and the Philippines are double-outrigger craft, consisting of a narrow main hull with two attached outriggers, commonly known as ''jukung
A jukung or kano, also known as cadik is a small wooden Indonesian outrigger canoe. It is a traditional fishing boat, but newer uses include "Jukung Dives", using the boat as a vehicle for small groups of SCUBA divers.
The double outrigger jukun ...
'' in Indonesia and ''banca'' in the Philippines.
The jukung
A jukung or kano, also known as cadik is a small wooden Indonesian outrigger canoe. It is a traditional fishing boat, but newer uses include "Jukung Dives", using the boat as a vehicle for small groups of SCUBA divers.
The double outrigger jukun ...
is of Balinese origin, one of many genre of Pacific/Asian outrigger canoes. The considerable stability provided by the outriggers means that the jukung copes well with a lateen
A lateen (from French ''latine'', meaning "Latin") or latin-rig is a triangular sail set on a long yard mounted at an angle on the mast, and running in a fore-and-aft direction. The settee can be considered to be an associated type of the same ...
(triangular) sail. While the lateen sail presents some difficulties in tacking into the wind, requiring a jibe
A jibe (US) or gybe (Britain) is a sailing maneuver whereby a sailing vessel reaching downwind turns its stern through the wind, which then exerts its force from the opposite side of the vessel. Because the mainsail boom can swing acro ...
, the jukung is superb in its reaching ability and jybe-safe running. They are usually highly decorated and bear a marlin-like prow
The bow () is the forward part of the hull of a ship or boat, the point that is usually most forward when the vessel is underway. The aft end of the boat is the stern.
Prow may be used as a synonym for bow or it may mean the forward-most part ...
.
A traditional catamaran
A Formula 16 beachable catamaran
Powered catamaran passenger ferry at Salem, Massachusetts, United States
A catamaran () (informally, a "cat") is a multi-hulled watercraft featuring two parallel hulls of equal size. It is a geometry-sta ...
consists of two canoes, or vakas, joined by a frame, formed of aka
Aka, AKA or a.k.a. may refer to:
* "Also known as", used to introduce an alternative name
Languages
* Aka language (Sudan)
* Aka language, in the Central African Republic
* Hruso language, in India, also referred to as Aka
* a prefix in the n ...
s. Catamarans were used by the ancient Tamil Chola dynasty
The Chola dynasty was a Tamil thalassocratic empire of southern India and one of the longest-ruling dynasties in the history of the world. The earliest datable references to the Chola are from inscriptions dated to the 3rd century BCE d ...
as early as the 5th century AD for moving their invasion fleets. Since then, they have been widely used for fishing in South East Asia and Polynesia.
Kayak
A kayak is a small, narrow watercraft which is typically propelled by means of a double-bladed paddle. The word kayak originates from the Greenlandic word '' qajaq'' ().
The traditional kayak has a covered deck and one or more cockpits, each s ...
s are generally differentiated from canoes by the sitting position of the paddler and the number of blades on the paddle. In a kayak the paddler faces forward, legs in front, using a double bladed paddle. In a canoe the paddler faces forward and sits or kneels in the boat, using a single bladed paddle. In some parts of the world, such as the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and Nor ...
, kayaks are considered a subtype of canoe
A canoe is a lightweight narrow water vessel, typically pointed at both ends and open on top, propelled by one or more seated or kneeling paddlers facing the direction of travel and using a single-bladed paddle.
In British English, the term ...
. Continental European and British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
canoeing clubs and associations of the 19th Century used craft similar to kayaks, but referred to them as canoes.
Andamanese
The Andamanese are the indigenous peoples of the Andaman Islands, part of India's Andaman and Nicobar Islands union territory in the southeastern part of the Bay of Bengal in Southeast Asia. The Andamanese peoples are among the various groups ...
dugout canoes
A dugout canoe or simply dugout is a boat made from a hollowed tree. Other names for this type of boat are logboat and monoxylon. ''Monoxylon'' (''μονόξυλον'') (pl: ''monoxyla'') is Greek – ''mono-'' (single) + '' ξύλον xylon'' (t ...
, 1875
File:OjIBWE BIRCH BARK CANOE 1910 mINNESOTA.jpg, North American birch-bark canoe
File:Catamaran india.jpg, Split log fishing canoe in India
Ropes and lines
 The availability of reliable and durable ropes and lines has had many consequences for the development and utility of traditional fishing boats. They can be used to lash planks and frames together, as stay lines for masts, as anchor lines to secure the boat, and as
The availability of reliable and durable ropes and lines has had many consequences for the development and utility of traditional fishing boats. They can be used to lash planks and frames together, as stay lines for masts, as anchor lines to secure the boat, and as fishing line
A fishing line is a flexible, high-tensile cord used in angling to tether and pull in fish, in conjunction with at least one hook. Fishing lines are usually pulled by and stored in a reel, but can also be retrieved by hand, with a fixed attach ...
s for making fishing nets.
Rope
A rope is a group of yarns, plies, fibres, or strands that are twisted or braided together into a larger and stronger form. Ropes have tensile strength and so can be used for dragging and lifting. Rope is thicker and stronger than similarly ...
s and lines are made of fibre
Fiber or fibre (from la, fibra, links=no) is a natural or artificial substance that is significantly longer than it is wide. Fibers are often used in the manufacture of other materials. The strongest engineering materials often incorporate ...
lengths, twisted or braid
A braid (also referred to as a plait) is a complex structure or pattern formed by interlacing two or more strands of flexible material such as textile yarns, wire, or hair.
The simplest and most common version is a flat, solid, three-strande ...
ed together to provide tensile
In physics, tension is described as the pulling force transmitted axially by the means of a string, a rope, chain, or similar object, or by each end of a rod, truss member, or similar three-dimensional object; tension might also be described as t ...
strength. They are used for pulling, but not for pushing.
Fossil
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved in ...
ised fragments of "probably two-ply laid rope of about 7 mm diameter" have been found in one of the caves at Lascaux
Lascaux ( , ; french: Grotte de Lascaux , "Lascaux Cave") is a network of caves near the village of Montignac, in the department of Dordogne in southwestern France. Over 600 parietal wall paintings cover the interior walls and ceilings of t ...
, dated about 15,000 BC.J.C. Turner and P. van de Griend (ed.), ''The History and Science of Knots'' (Singapore: World Scientific, 1996), 14. Egyptian rope dates back to 4000 to 3500 BC and was generally made of water reed fibers. Other rope in antiquity was made from the fibers of date palm
''Phoenix dactylifera'', commonly known as date or date palm, is a flowering plant species in the palm family, Arecaceae, cultivated for its edible sweet fruit called dates. The species is widely cultivated across northern Africa, the Middle Eas ...
s, flax
Flax, also known as common flax or linseed, is a flowering plant, ''Linum usitatissimum'', in the family Linaceae. It is cultivated as a food and fiber crop in regions of the world with temperate climates. Textiles made from flax are known in ...
, grass
Poaceae () or Gramineae () is a large and nearly ubiquitous family of monocotyledonous flowering plants commonly known as grasses. It includes the cereal grasses, bamboos and the grasses of natural grassland and species cultivated in lawns and ...
, papyrus
Papyrus ( ) is a material similar to thick paper that was used in ancient times as a writing surface. It was made from the pith of the papyrus plant, ''Cyperus papyrus'', a wetland sedge. ''Papyrus'' (plural: ''papyri'') can also refer to a d ...
, leather
Leather is a strong, flexible and durable material obtained from the tanning, or chemical treatment, of animal skins and hides to prevent decay. The most common leathers come from cattle, sheep, goats, equine animals, buffalo, pigs and hogs ...
, or animal hair. Rope made of hemp
Hemp, or industrial hemp, is a botanical class of '' Cannabis sativa'' cultivars grown specifically for industrial or medicinal use. It can be used to make a wide range of products. Along with bamboo, hemp is among the fastest growing plants ...
fibres was in use in China from about 2800 BC.
Propulsion
 Before engines became available, boats could be propelled manually or by the wind. Boats could be propelled by the wind by attaching
Before engines became available, boats could be propelled manually or by the wind. Boats could be propelled by the wind by attaching sail
A sail is a tensile structure—which is made from fabric or other membrane materials—that uses wind power to propel sailing craft, including sailing ships, sailboats, windsurfers, ice boats, and even sail-powered land vehicles. Sails ma ...
s to masts set upright in the boat. Manual propulsion could be done in shallow water by punting with a push pole, and in deeper water by paddling
Paddling with regard to watercraft is the act of manually propelling a boat using a paddle. The paddle, which consists of one or two blades joined to a shaft, is also used to steer the vessel. The paddle is not connected to the boat (unlike in r ...
with a paddle
A paddle is a handheld tool with an elongated handle and a flat, widened distal end (i.e. the ''blade''), used as a lever to apply force onto the bladed end. It most commonly describes a completely handheld tool used to propel a human-powered wa ...
or rowing
Rowing is the act of propelling a human-powered watercraft using the sweeping motions of oars to displace water and generate reactional propulsion. Rowing is functionally similar to paddling, but rowing requires oars to be mechanically att ...
with oar
An oar is an implement used for water-borne propulsion. Oars have a flat blade at one end. Rowers grasp the oar at the other end.
The difference between oars and paddles is that oars are used exclusively for rowing. In rowing the oar is connec ...
s. The difference between paddling and rowing is that when rowing the oars have a mechanical connection with the boat, while when paddling the paddles are hand-held with no mechanical connection. Canoes were traditionally paddled, with the paddler facing the bow of the boat. Small boats that use oars are called rowboats
Rowing is the act of propelling a human-powered watercraft using the sweeping motions of oars to displace water and generate reactional propulsion. Rowing is functionally similar to paddling, but rowing requires oars to be mechanically atta ...
, and the rower typically faces the stern.
Around 4000 BC, Egyptians
Egyptians ( arz, المَصرِيُون, translit=al-Maṣriyyūn, ; arz, المَصرِيِين, translit=al-Maṣriyyīn, ; cop, ⲣⲉⲙⲛ̀ⲭⲏⲙⲓ, remenkhēmi) are an ethnic group native to the Nile Valley in Egypt. Egyptian identi ...
were building long narrow boats powered by many oarsmen. Over the next 1,000 years, they made a series of remarkable advances in boat design. They developed cotton-made sails to help their boats go faster with less work. Then they built boats large enough to cross the oceans. These boats had sails and oarsmen, and were used for war and trade. Some ancient vessels were propelled by either oars or sail, depending on the speed and direction of the wind (see trireme and bireme
A bireme (, ) is an ancient oared warship (galley) with two superimposed rows of oars on each side. Biremes were long vessels built for military purposes and could achieve relatively high speed. They were invented well before the 6th century BC an ...
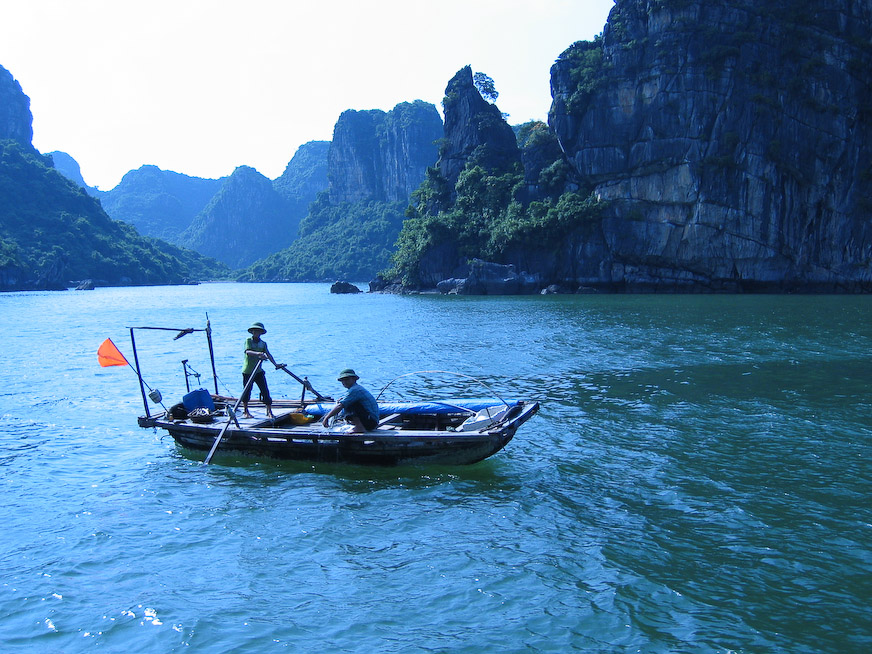
). The Chinese were using sails around 3000 BC, of a type that can still be seen on traditional fishing boats sailing off the coast of Vietnam in Ha Long Bay.
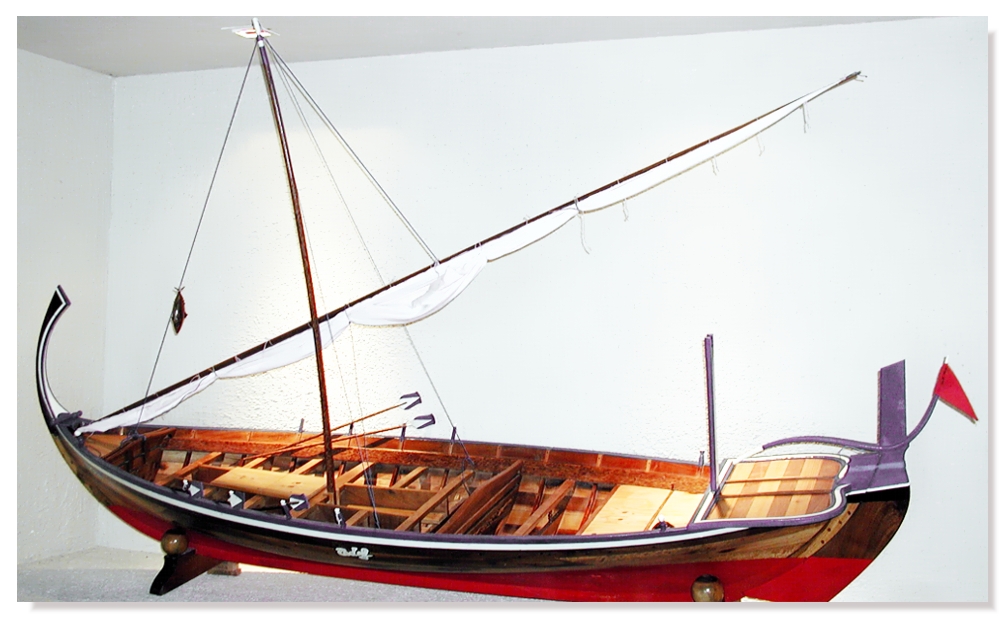
A jangada
A jangada is a traditional fishing boat (in fact a sailing raft) made of wood used in the northern region of Brazil.
The construction of the jangada incorporates some improvements in neolithic handcraft - better materials were found and the p ...
is an elegant planked fishing boat used in northern Brazil. It has been claimed the jangada dates back to ancient Greek times. It uses a triangular (lateen
A lateen (from French ''latine'', meaning "Latin") or latin-rig is a triangular sail set on a long yard mounted at an angle on the mast, and running in a fore-and-aft direction. The settee can be considered to be an associated type of the same ...
) sail, which allows it to sail against the wind.
A felucca
A felucca ( ar, فلوكة, falawaka, possibly originally from Greek , ) is a traditional wooden sailing boat used in the eastern Mediterranean—including around Malta and Tunisia—in Egypt and Sudan (particularly along the Nile and in protec ...
is a traditional wood-planked sailing boat used in protected waters of the Red Sea
The Red Sea ( ar, البحر الأحمر - بحر القلزم, translit=Modern: al-Baḥr al-ʾAḥmar, Medieval: Baḥr al-Qulzum; or ; Coptic: ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϩⲁϩ ''Phiom Enhah'' or ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϣⲁⲣⲓ ''Phiom ǹšari''; T ...
and eastern Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the ea ...
including Malta
Malta ( , , ), officially the Republic of Malta ( mt, Repubblika ta' Malta ), is an island country in the Mediterranean Sea. It consists of an archipelago, between Italy and Libya, and is often considered a part of Southern Europe. It lies ...
, and particularly along the Nile
The Nile, , Bohairic , lg, Kiira , Nobiin: Áman Dawū is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea. The Nile is the longest river in Africa and has historically been considered the longest ...
in Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning the North Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via a land bridg ...
. Its rig consists of one or two lateen
A lateen (from French ''latine'', meaning "Latin") or latin-rig is a triangular sail set on a long yard mounted at an angle on the mast, and running in a fore-and-aft direction. The settee can be considered to be an associated type of the same ...
sail
A sail is a tensile structure—which is made from fabric or other membrane materials—that uses wind power to propel sailing craft, including sailing ships, sailboats, windsurfers, ice boats, and even sail-powered land vehicles. Sails ma ...
s.
Lateen
A lateen (from French ''latine'', meaning "Latin") or latin-rig is a triangular sail set on a long yard mounted at an angle on the mast, and running in a fore-and-aft direction. The settee can be considered to be an associated type of the same ...
-rigged jangada
A jangada is a traditional fishing boat (in fact a sailing raft) made of wood used in the northern region of Brazil.
The construction of the jangada incorporates some improvements in neolithic handcraft - better materials were found and the p ...
on the coast off Mossoró
Mossoró () is the second most populous city in the state of Rio Grande do Norte, Brazil, and also the largest municipality of that state. It is equidistant (four hours' drive) from Natal (approximately 277 km or 172 miles), the state capi ...
, Brazil
Image:901 Felucca.JPG, Lateen
A lateen (from French ''latine'', meaning "Latin") or latin-rig is a triangular sail set on a long yard mounted at an angle on the mast, and running in a fore-and-aft direction. The settee can be considered to be an associated type of the same ...
-rigged felucca
A felucca ( ar, فلوكة, falawaka, possibly originally from Greek , ) is a traditional wooden sailing boat used in the eastern Mediterranean—including around Malta and Tunisia—in Egypt and Sudan (particularly along the Nile and in protec ...
s at Luxor
Luxor ( ar, الأقصر, al-ʾuqṣur, lit=the palaces) is a modern city in Upper (southern) Egypt which includes the site of the Ancient Egyptian city of ''Thebes''.
Luxor has frequently been characterized as the "world's greatest open-a ...
, Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning the North Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via a land bridg ...
Image:Madagascar - Traditional fishing pirogue.jpg, Traditional fishing lakana
''Lakana'', also known as ''la'kana'' or ''laka'', are traditional outrigger canoes of the Malagasy people of Madagascar. It is a single-outrigger canoe with a dugout main hull. It was traditionally rigged with the Austronesian crab claw sail, b ...
with distinctive Austronesian Crab-claw sail
The crab claw sail is a fore-and-aft triangular sail with spars along upper and lower edges. The crab claw sail was first developed by the Austronesian peoples some time around 1500 BC. It is used in many traditional Austronesian cultures in Isla ...
from Madagascar
Madagascar (; mg, Madagasikara, ), officially the Republic of Madagascar ( mg, Repoblikan'i Madagasikara, links=no, ; french: République de Madagascar), is an island country in the Indian Ocean, approximately off the coast of East Africa ...
File:Negombo 02.jpg, Square sail fishing boat from Negombo
Negombo (, ) is a major city in Sri Lanka, situated on the west coast and at the mouth of the Negombo Lagoon, in Western Province, from Colombo via Colombo - Katunayake Expressway.
Negombo is one of the major commercial hubs in the country and ...
, Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka (, ; si, ශ්රී ලංකා, Śrī Laṅkā, translit-std=ISO (); ta, இலங்கை, Ilaṅkai, translit-std=ISO ()), formerly known as Ceylon and officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka, is an ...
File:Vietnam junk.jpg, Small junk sailing in Halong Bay, Vietnam
Planking
Building boats from planks meant boats could be more precisely constructed along the line of large canoes than hollowing tree trunks allowed. It is possible that planked canoes were developed as early as 8,500 years ago in Southern California. By3000 BC
The 30th century BC was a century that lasted from the year 3000 BC to 2901 BC.
Events
* Before 3000 BC: An image of a deity (detail from a cong) recovered from Tomb 12 in Fanshan, Yuyao, Zhejiang, is made during the Neolithic period by the L ...
, the Egyptians knew how to assemble planks of wood
Wood is a porous and fibrous structural tissue found in the stems and roots of trees and other woody plants. It is an organic materiala natural composite of cellulose fibers that are strong in tension and embedded in a matrix of lignin th ...
into a ship hull.Ward, Cheryl. "World's Oldest Planked Boats," in ''Archaeology
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landscape ...
'' (Volume 54, Number 3, May/June 2001). Archaeological Institute of America
The Archaeological Institute of America (AIA) is North America's oldest society and largest organization devoted to the world of archaeology. AIA professionals have carried out archaeological fieldwork around the world and AIA has established re ...
They used woven
strap
A strap, sometimes also called strop, is an elongated flap or ribbon, usually of leather or other flexible materials.
Thin straps are used as part of clothing or baggage, or bedding such as a sleeping bag. See for example spaghetti strap, sho ...
s to lash planks together, and reeds or grass
Poaceae () or Gramineae () is a large and nearly ubiquitous family of monocotyledonous flowering plants commonly known as grasses. It includes the cereal grasses, bamboos and the grasses of natural grassland and species cultivated in lawns and ...
stuffed between the planks to seal the seams. An example of their skill is the Khufu ship
The Khufu ship is an intact full-size solar barque from ancient Egypt. It was sealed into a pit at the foot of the Great Pyramid of pharaoh Khufu around 2500 BC, during the Fourth Dynasty of the ancient Egyptian Old Kingdom. Like other buried ...
, a vessel in length entombed at the foot of the Great Pyramid of Giza
The Great Pyramid of Giza is the biggest Egyptian pyramids, Egyptian pyramid and the tomb of Fourth Dynasty of Egypt, Fourth Dynasty pharaoh Khufu. Built in the early 26th century BC during a period of around 27 years, the pyramid is the oldes ...
around 2500 BC and found intact in 1954.
Mbour
M'Bour or Mbour ( ar, مبور; Wolof: ''Mbuur''), is a city in the Thiès Region of Senegal. It lies on the Petite Côte, approximately eighty kilometers south of Dakar. It is home to a population of nearly 233,000 (2013 census).
The city's ma ...
, Senegal
Senegal,; Wolof: ''Senegaal''; Pulaar: 𞤅𞤫𞤲𞤫𞤺𞤢𞥄𞤤𞤭 (Senegaali); Arabic: السنغال ''As-Sinighal'') officially the Republic of Senegal,; Wolof: ''Réewum Senegaal''; Pulaar : 𞤈𞤫𞤲𞤣𞤢𞥄𞤲𞤣� ...
constructed along the lines of a large canoe using planks.
File:Yoff-Retour.jpg, Another Senegal
Senegal,; Wolof: ''Senegaal''; Pulaar: 𞤅𞤫𞤲𞤫𞤺𞤢𞥄𞤤𞤭 (Senegaali); Arabic: السنغال ''As-Sinighal'') officially the Republic of Senegal,; Wolof: ''Réewum Senegaal''; Pulaar : 𞤈𞤫𞤲𞤣𞤢𞥄𞤲𞤣� ...
planked fishing boat at Dakar
Dakar ( ; ; wo, Ndakaaru) (from daqaar ''tamarind''), is the capital and largest city of Senegal. The city of Dakar proper has a population of 1,030,594, whereas the population of the Dakar metropolitan area is estimated at 3.94 million in 20 ...
.
File:Uganda fishing boat.jpg, Planked fishing boat in Kasenyi, Uganda
}), is a landlocked country in East Africa. The country is bordered to the east by Kenya, to the north by South Sudan, to the west by the Democratic Republic of the Congo, to the south-west by Rwanda, and to the south by Tanzania. The souther ...
File:Fishing Boat BD1.JPG, Planked fishing boat on the beach of Narikel Zinzira, Bangladesh
Bangladesh (}, ), officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh, is a country in South Asia. It is the eighth-most populous country in the world, with a population exceeding 165 million people in an area of . Bangladesh is among the mos ...
Scandinavia
Scandinavia; Sámi languages: /. ( ) is a subregion in Northern Europe, with strong historical, cultural, and linguistic ties between its constituent peoples. In English usage, ''Scandinavia'' most commonly refers to Denmark, Norway, and Swed ...
ns were using clinker construction by at least 350 BC.Sawyer, Peter Hayes (2001''The Oxford Illustrated History of the Vikings''
Page 183. Oxford University Press. Carvel construction dates back even earlier. A
luzzu
A ''luzzu'' (, pl. ''luzzijiet'') is a traditional fishing boat from the Maltese islands. This type of boat developed in the early 20th century, although it is very similar to much older traditional Maltese boats such as the '' ferilla''. They ...
is a double-ended carvel-built fishing boat from the Maltese islands. Traditionally, they are brightly painted in shades of yellow, red, green and blue, and the bow is normally pointed with a pair of eyes. These eyes may be the modern survival of an ancient Phoenicia
Phoenicia () was an ancient thalassocratic civilization originating in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily located in modern Lebanon. The territory of the Phoenician city-states extended and shrank throughout their histo ...
n custom (also practiced by the ancient Greeks
Ancient Greece ( el, Ἑλλάς, Hellás) was a northeastern Mediterranean civilization, existing from the Greek Dark Ages of the 12th–9th centuries BC to the end of classical antiquity ( AD 600), that comprised a loose collection of cult ...
); they are sometimes (and probably inaccurately) referred to as the Eye of Horus
The Eye of Horus, ''wedjat'' eye or ''udjat'' eye is a concept and symbol in ancient Egyptian religion that represents well-being, healing, and protection. It derives from the mythical conflict between the god Horus with his rival Set, in wh ...
or of Osiris
Osiris (, from Egyptian ''wsjr'', cop, ⲟⲩⲥⲓⲣⲉ , ; Phoenician: 𐤀𐤎𐤓, romanized: ʾsr) is the god of fertility, agriculture, the afterlife, the dead, resurrection, life, and vegetation in ancient Egyptian religion. He was ...
. The luzzu has survived because it tends to be a sturdy and stable boat even in bad weather. Originally, the luzzu was equipped with sails although nowadays almost all are motorised, with onboard diesel engine
The diesel engine, named after Rudolf Diesel, is an internal combustion engine in which ignition of the fuel is caused by the elevated temperature of the air in the cylinder due to mechanical compression; thus, the diesel engine is a so-cal ...
s being the most common.
luzzu
A ''luzzu'' (, pl. ''luzzijiet'') is a traditional fishing boat from the Maltese islands. This type of boat developed in the early 20th century, although it is very similar to much older traditional Maltese boats such as the '' ferilla''. They ...
at Marsaxlokk
Marsaxlokk () is a small, traditional fishing village in the South Eastern Region of Malta. It has a harbour, and is a tourist attraction known for its views, fishermen and history. As at March 2014, the village had a population of 3,534. The ...
, Malta
Malta ( , , ), officially the Republic of Malta ( mt, Repubblika ta' Malta ), is an island country in the Mediterranean Sea. It consists of an archipelago, between Italy and Libya, and is often considered a part of Southern Europe. It lies ...
File:Trenails.jpg, Building a carvel boat at Quee Ngon, Vietnam
Vietnam or Viet Nam ( vi, Việt Nam, ), officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam,., group="n" is a country in Southeast Asia, at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of and population of 96 million, making it ...
File:Jantar.jpg, Clinker built fishing boats at Jantar Beach
File:Cambodian fishing boat.jpg, Decked fishing boat at Koh Rung Samleom, Cambodia
Cambodia (; also Kampuchea ; km, កម្ពុជា, UNGEGN: ), officially the Kingdom of Cambodia, is a country located in the southern portion of the Indochinese Peninsula in Southeast Asia, spanning an area of , bordered by Thailand ...
European boats
 Boats in
Boats in South East Asia
Southeast Asia, also spelled South East Asia and South-East Asia, and also known as Southeastern Asia, South-eastern Asia or SEA, is the geographical south-eastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of mainland ...
and Polynesia
Polynesia () "many" and νῆσος () "island"), to, Polinisia; mi, Porinihia; haw, Polenekia; fj, Polinisia; sm, Polenisia; rar, Porinetia; ty, Pōrīnetia; tvl, Polenisia; tkl, Polenihia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania, made up of ...
centred on canoes, outriggers and multihull boats. By contrast, boats in Europe centred on framed and keeled monohulls
right
A monohull is a type of boat having only one hull, unlike multihulled boats which can have two or more individual hulls connected to one another.
Fundamental concept
Among the earliest hulls were simple logs, but these were generally unstab ...
.
The Scandinavia
Scandinavia; Sámi languages: /. ( ) is a subregion in Northern Europe, with strong historical, cultural, and linguistic ties between its constituent peoples. In English usage, ''Scandinavia'' most commonly refers to Denmark, Norway, and Swed ...
ns were building innovative boats millennia ago, as shown by the many petroglyph
A petroglyph is an image created by removing part of a rock surface by incising, picking, carving, or abrading, as a form of rock art. Outside North America, scholars often use terms such as "carving", "engraving", or other description ...
images of Nordic Bronze Age
The Nordic Bronze Age (also Northern Bronze Age, or Scandinavian Bronze Age) is a period of Scandinavian prehistory from c. 2000/1750–500 BC.
The Nordic Bronze Age culture emerged about 1750 BC as a continuation of the Battle Axe culture (t ...
boats. The oldest archaeological find of a wooden Nordic boat is the Hjortspring boat
The Hjortspring boat ( da, Hjortspringbåden) is a vessel designed as a large canoe, from the Scandinavian Pre-Roman Iron Age. It was built circa 400–300 BC. The hull and remains were rediscovered and excavated in 1921–1922 from the bog of ''H ...
, built about 350 BC. This is the oldest known boat to use clinker planking, where the planks overlap one another. It was designed as a large canoe, 19 m long and crewed by 22–23 men using paddle
A paddle is a handheld tool with an elongated handle and a flat, widened distal end (i.e. the ''blade''), used as a lever to apply force onto the bladed end. It most commonly describes a completely handheld tool used to propel a human-powered wa ...
s. Scandinavians continued to develop better boats, incorporating iron
Iron () is a chemical element with symbol Fe (from la, ferrum) and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, right in fr ...
and other metal into the design, adding keel
The keel is the bottom-most longitudinal structural element on a vessel. On some sailboats, it may have a hydrodynamic and counterbalancing purpose, as well. As the laying down of the keel is the initial step in the construction of a ship, in Br ...
s, and developing oars
An oar is an implement used for water-borne propulsion. Oars have a flat blade at one end. Rowers grasp the oar at the other end.
The difference between oars and paddles is that oars are used exclusively for rowing. In rowing the oar is connec ...
for propulsion. Another Nordic shipfind is the Nydam boat
The Nydam Mose, also known as Nydam Bog, is an archaeological site located at Øster Sottrup, a town located in Sundeved, eight kilometres from Sønderborg, Denmark.
History
In the Iron Age, the site of the bog was a sacred place, where the wea ...
, found preserved in the Nydam Mose
The Nydam Mose, also known as Nydam Bog, is an archaeological site located at Øster Sottrup, a town located in Sundeved, eight kilometres from Sønderborg, Denmark.
History
In the Iron Age, the site of the bog was a sacred place, where the we ...
bog in Sundeved
Sundeved is a peninsula on the east coast of the Jutland peninsula in south Denmark. It lies between Åbenrå Fjord and Als Fjord to the north, Alssund to the east and Flensborg Fjord to the south. The westernmost part of the city of Sønderbor ...
, Denmark
)
, song = ( en, "King Christian stood by the lofty mast")
, song_type = National and royal anthem
, image_map = EU-Denmark.svg
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of Denmark
, established ...
. It has been dendro dated to 310-320 AD. Built of oak, it is also clinker-built, is 23 metres long and was rowed by thirty men.
 By 1000 AD the
By 1000 AD the Norsemen
The Norsemen (or Norse people) were a North Germanic ethnolinguistic group of the Early Middle Ages, during which they spoke the Old Norse language. The language belongs to the North Germanic branch of the Indo-European languages and is the pre ...
were pre-eminent on the oceans. They were skilled seamen and boat builders, with clinker-built boat designs that varied according to the type of boat. Trading boats, such as the knarr
A knarr is a type of Norse merchant ship used by the Vikings. The knarr ( non, knǫrr, plural ) was constructed using the same clinker-built method as longships, karves, and faerings.
History
''Knarr'' is the Old Norse term for a type of sh ...
s, were wide to allow large cargo storage. Raiding boats, such as the longship
Longships were a type of specialised Scandinavian warships that have a long history in Scandinavia, with their existence being archaeologically proven and documented from at least the fourth century BC. Originally invented and used by the Nors ...
, were long and narrow and very fast. The vessels they used for fishing were scaled down versions of their cargo boats. The Scandinavia
Scandinavia; Sámi languages: /. ( ) is a subregion in Northern Europe, with strong historical, cultural, and linguistic ties between its constituent peoples. In English usage, ''Scandinavia'' most commonly refers to Denmark, Norway, and Swed ...
n innovations influenced fishing boat design long after the Viking period came to an end. For example, yole
A yole is a clinker built boat that was used for fishing particularly in the north of Scotland. The best known of these is the Orkney Yole. They were rigged for sail or used as rowing boats. The yole is a Nordic design and closely related in shap ...
s from the Orkney Island of Stroma
The Island of Stroma or Isle of Stroma or Stroma, is an uninhabited island off the northern coast of the mainland of Scotland, just north of John o' Groats. It is the most southerly of the islands in the Pentland Firth between the Orkney isl ...
were built in the same way as the Norse boats, as were the Shetland
Shetland, also called the Shetland Islands and formerly Zetland, is a subarctic archipelago in Scotland lying between Orkney, the Faroe Islands and Norway. It is the northernmost region of the United Kingdom.
The islands lie about to the n ...
yoal
The yoal, often referred to as the ness yoal, is a clinker-built craft used traditionally in Shetland, Scotland. It is designed primarily for rowing, but also handles well under its traditional square sail when running before the wind or on a broad ...
s and the sgoths of the Outer Hebrides
The Outer Hebrides () or Western Isles ( gd, Na h-Eileanan Siar or or ("islands of the strangers"); sco, Waster Isles), sometimes known as the Long Isle/Long Island ( gd, An t-Eilean Fada, links=no), is an island chain off the west coas ...
..
 In the 15th century, the Dutch developed a type of sea-going
In the 15th century, the Dutch developed a type of sea-going herring
Herring are forage fish, mostly belonging to the family of Clupeidae.
Herring often move in large schools around fishing banks and near the coast, found particularly in shallow, temperate waters of the North Pacific and North Atlantic Oceans, ...
drifter that became a blueprint for subsequent European fishing boats. This was the herring buss
A herring buss ( nl, Haringbuis) was a type of seagoing fishing vessel, mostly used by Dutch and Flemish herring fishermen in the 15th through early 19th centuries.
The buss ship type has a long history. It was already known around the time of th ...
, used by Dutch herring fishermen until the early 19th centuries. The ship type buss
Buss is a surname. Notable people with the surname include:
* Benjamin Buss (born 1977), German guitarist better known as Matthew Greywolf
* David Buss (born 1953), American evolutionary psychologist
* Frances Buss, British pioneer of women's educ ...
has a long history. It was known around 1000 AD in Scandinavia as a ''bǘza'', a robust variant of the Viking longship. The first herring buss was probably built in Hoorn
Hoorn () is a city and municipality in the northwest of the Netherlands, in the province of North Holland. It is the largest town and the traditional capital of the region of West Friesland. Hoorn is located on the Markermeer, 20 kilometers ...
around 1415. The last one was built in Vlaardingen
Vlaardingen () is a city in South Holland in the Netherlands. It is located on the north bank of the Nieuwe Maas river at the confluence with the Oude Maas. The municipality administers an area of , of which is land, with residents in .
Geogr ...
in 1841. The ship was about 20 metres long and displaced between 60 and 100 tons. It was a massive round-bilge
The bilge of a ship or boat is the part of the hull that would rest on the ground if the vessel were unsupported by water. The "turn of the bilge" is the transition from the bottom of a hull to the sides of a hull.
Internally, the bilges (us ...
d keel
The keel is the bottom-most longitudinal structural element on a vessel. On some sailboats, it may have a hydrodynamic and counterbalancing purpose, as well. As the laying down of the keel is the initial step in the construction of a ship, in Br ...
ship with a bluff bow and stern
The stern is the back or aft-most part of a ship or boat, technically defined as the area built up over the sternpost, extending upwards from the counter rail to the taffrail. The stern lies opposite the bow, the foremost part of a ship. Ori ...
, the latter relatively high, and with a gallery. The busses used long drifting gill net
Gillnetting is a fishing method that uses gillnets: vertical panels of netting that hang from a line with regularly spaced floaters that hold the line on the surface of the water. The floats are sometimes called "corks" and the line with corks is ...
s to catch the herring. The nets would be retrieved at night and the crews of eighteen to thirty menDe Vries & Woude (1977), pages 244–245 would set to gibbing
Gibbing is the process of preparing salt herring (or soused herring), in which the gills and part of the gullet are removed from the fish, eliminating any bitter taste. The liver and pancreas are left in the fish during the salt-curing process ...
, salting and barrelling the catch on the broad deck. The ships sailed in fleets of 400 to 500 ships to the Dogger Bank
Dogger Bank (Dutch: ''Doggersbank'', German: ''Doggerbank'', Danish: ''Doggerbanke'') is a large sandbank in a shallow area of the North Sea about off the east coast of England.
During the last ice age the bank was part of a large landmass ...
fishing grounds and the Shetland
Shetland, also called the Shetland Islands and formerly Zetland, is a subarctic archipelago in Scotland lying between Orkney, the Faroe Islands and Norway. It is the northernmost region of the United Kingdom.
The islands lie about to the n ...
isles. They were usually escorted by naval vessels, because the English considered they were "poaching". The fleet would stay at sea for weeks at a time. The catch would sometimes be transferred to special ships (called ''ventjagers''), and taken home while the fleet would still be at sea (the picture shows a ''ventjager'' in the distance).
 During the 17th century, the British developed the dogger, an early type of sailing trawler or
During the 17th century, the British developed the dogger, an early type of sailing trawler or longliner
Longline fishing, or longlining, is a commercial fishing angling technique that uses a long ''main line'' with baited hooks attached at intervals via short branch lines called ''snoods'' or ''gangions''.North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Norway, Denmark, Germany, the Netherlands and Belgium. An epeiric sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the Norwegia ...
. The dogger takes its name from the Dutch word ''dogger'', meaning a fishing vessel which tows a trawl
Trawling is a method of fishing that involves pulling a fishing net through the water behind one or more boats. The net used for trawling is called a trawl. This principle requires netting bags which are towed through water to catch different speci ...
. Dutch trawling boats were common in the North Sea, and the word ''dogger'' was given to the area where they often fished, which became known as the Dogger Bank
Dogger Bank (Dutch: ''Doggersbank'', German: ''Doggerbank'', Danish: ''Doggerbanke'') is a large sandbank in a shallow area of the North Sea about off the east coast of England.
During the last ice age the bank was part of a large landmass ...
.Oxford Companion to Ships and the Sea, p. 256 Doggers were slow but sturdy, capable of fishing in the rough conditions of the North Sea.Fagan 2008 Like the herring buss, they were wide-beamed and bluff-bowed, but considerably smaller, about 15 metres long, a maximum beam of 4.5 m, a draught of 1.5 m, and displacing about 13 tonnes. They could carry a tonne of bait, three tonnes of salt, half a tonne each of food and firewood for the crew, and return with six tonnes of fish. Decked areas forward and aft probably provided accommodation, storage and a cooking area. An anchor would have allowed extended periods fishing in the same spot, in waters up to 18 m deep. The dogger would also have carried a small open boat for maintaining lines and rowing ashore.
During the same period, small boats were also undergoing development. The French bateau
A bateau or batteau is a shallow- draft, flat-bottomed boat which was used extensively across North America, especially in the colonial period and in the fur trade. It was traditionally pointed at both ends but came in a wide variety of sizes. T ...
type boat was a small flat bottom boat with straight sides used as early as 1671 on the Saint Lawrence River
The St. Lawrence River (french: Fleuve Saint-Laurent, ) is a large river in the middle latitudes of North America. Its headwaters begin flowing from Lake Ontario in a (roughly) northeasterly direction, into the Gulf of St. Lawrence, connecting t ...
.Gardner 1987, page 18 The common coastal boat of the time was the wherry
A wherry is a type of boat that was traditionally used for carrying cargo or passengers on rivers and canals in England, and is particularly associated with the River Thames and the River Cam. They were also used on the Broadland rivers of No ...
and the merging of the wherry design with the simplified flat bottom of the bateau resulted in the birth of the dory. Anecdotal evidence exists of much older precursors throughout Europe. England, France, Italy, and Belgium have small boats from medieval periods that could reasonably be construed as predecessors of the dory.Gardner 1987, page 15 In Ireland, the Gandelow was used to fish for salmon in the River Shannon, Shannon estuary from the 1600s onwards.
 Dory, Dories are small, shallow-draft (hull), draft boats, usually about five to seven metres (15 to 22 feet) long. They are lightweight versatile boats with high sides, a flat bottom and sharp bows, and are easy to build because of their simple lines. The dory first appeared in New England fishing towns sometime after the early 18th century.Chapelle, page 85 The Banks dory, Banks dories appeared in the 1830s. They were designed to be carried on mother ships and used for fishing cod at the Grand Banks. Adapted almost directly from the low freeboard, French river bateau, with their straight sides and removable thwarts, bank dories could be nested inside each other and stored on the decks of fishing schooners, such as the ''Gazela, Gazela Primeiro'', for their trip to the Grand Banks fishing grounds.
Dory, Dories are small, shallow-draft (hull), draft boats, usually about five to seven metres (15 to 22 feet) long. They are lightweight versatile boats with high sides, a flat bottom and sharp bows, and are easy to build because of their simple lines. The dory first appeared in New England fishing towns sometime after the early 18th century.Chapelle, page 85 The Banks dory, Banks dories appeared in the 1830s. They were designed to be carried on mother ships and used for fishing cod at the Grand Banks. Adapted almost directly from the low freeboard, French river bateau, with their straight sides and removable thwarts, bank dories could be nested inside each other and stored on the decks of fishing schooners, such as the ''Gazela, Gazela Primeiro'', for their trip to the Grand Banks fishing grounds.
 In the 19th century, a more effective design for sailing Fishing trawler, trawlers was developed at the English fishing port, Brixham. These elegant wooden sailing boats spread across the world, influencing fishing fleets everywhere. Their distinctive sails inspired the song Red Sails in the Sunset (song), Red Sails in the Sunset, written aboard a Brixham sailing trawler called the ''Torbay Lass''. In the 1890s there were about 300 trawling vessels there, each usually owned by the skipper of the boat. Several of these old sailing trawlers have been preserved.
In the 19th century, a more effective design for sailing Fishing trawler, trawlers was developed at the English fishing port, Brixham. These elegant wooden sailing boats spread across the world, influencing fishing fleets everywhere. Their distinctive sails inspired the song Red Sails in the Sunset (song), Red Sails in the Sunset, written aboard a Brixham sailing trawler called the ''Torbay Lass''. In the 1890s there were about 300 trawling vessels there, each usually owned by the skipper of the boat. Several of these old sailing trawlers have been preserved.BBC. Retrieved 2 March 2009.
 Throughout history, local conditions have led to the development of a wide range of types of fishing boats. The Nobby (boat)#Lancashire nobby, Lancashire nobby was used down the north west coast of England as a shrimp trawler from 1840 until World War II. The bawley and the Smack (ship), smack were used in the Thames Estuary and off East Anglia, while trawlers and drifters were used on the east coast. Herring fishing started in the Moray Firth in 1819. The Nobby (boat)#Manx nobby, Manx nobby was used as a herring drifter around the Isle of Man, and the fifie were used as herring Drifter (fishing boat), drifters along the east coast of Scotland from the 1850s until well into the 20th century.
Throughout history, local conditions have led to the development of a wide range of types of fishing boats. The Nobby (boat)#Lancashire nobby, Lancashire nobby was used down the north west coast of England as a shrimp trawler from 1840 until World War II. The bawley and the Smack (ship), smack were used in the Thames Estuary and off East Anglia, while trawlers and drifters were used on the east coast. Herring fishing started in the Moray Firth in 1819. The Nobby (boat)#Manx nobby, Manx nobby was used as a herring drifter around the Isle of Man, and the fifie were used as herring Drifter (fishing boat), drifters along the east coast of Scotland from the 1850s until well into the 20th century.
See also
* Boat * Fishing vessel * Maritime history of the United Kingdom * ShipNotes
References
* Chapelle, Howard L. (1951) ''American Small Sailing Craft'' WW Norton Company, New York, * Fagan, Brian (2008) ''The Great Warming.'' Chapter 10:''Bucking the trades''
Bloomsbury Press. * FAO: CWP Handbook of Fishery Statistical Standards
Section L: Fishery Fleet
* FAO (2007
State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture, Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, Rome. * Forman, Shepard (1970) ''The raft fishermen: Tradition & change in the Brazilian peasant economy'', Indiana University Press for International Affairs Center. * Gardner, John (1987) ''The Dory Book.'' Mystic Seaport Museum, Mystic Connecticut. * Johnstone, Paul (1889
''The Sea-Craft of Prehistory''
Routledge. * McGrail, Sean (2004)
''Boats of the World: From the Stone Age to Medieval Times''
USA: Oxford University Press. . * (1997)
''The First Modern Economy. Success, Failure, and Perseverance of the Dutch Economy, 1500-1815''
Cambridge University Press,
Reading
* Adney ET, Chappelle HI and McPhee J (2007''Bark Canoes and Skin Boats of North America''
Skyhorse Publishing. * Gerr, Dave (1995
''The Nature of Boats: Insights and Esoterica for the Nautically Obsessed''
McGraw-Hill Professional. * Smylie, Michael (1999) ''Traditional Fishing Boats of Britain & Ireland: Design, History and Evolution.'' Adlard Coles Nautical. * Smylie, Mike (2013
''Traditional Fishing Boats of Europe''
Amberley Publishing Limited. . * Traung, Jan-Olaf (1960
''Fishing Boats of the World 2''
Fishing News (Books) Ltd
Download PDF (99MB)
* Traung, Jan-Olaf (1967
''Fishing Boats of the World 3''
Kiefer Press.
Download PDF (56MB)
* Vigor, John (2004
''The Practical Encyclopedia of Boating: An A-Z Compendium of Seamanship, Boat Maintenance, Navigation, and Nautical Wisdom''
McGraw-Hill Professional. * Woodman, Richard (1998) ''The History of the Ship: The Comprehensive Story of Seafaring from the Earliest Times to the Present Day'', Lyons Press.
External links
The Uros People at GlobalAmity.net
Video tour of Uros
floating fishing villages]
Uros Indian Culture - Home
Floating islands on Google Maps
Indigenous boats: Small craft outside the Western tradition
Indigenous sails
{{fisheries and fishing Reed boats Fishing vessels,