Toledo, Ohio on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Toledo ( ) is a city in and the
''Ohio Archaeological and Historical Publications,'' Volume XII, 1903; hosted at American History and Genealogy Project, accessed 26 December 2015 The United States continued to work to extinguish land claims of Native Americans. In the Toledo was very slow to expand during its first two decades of settlement. The first lot was sold in the Port Lawrence section of the city in 1833. It held 1,205 persons in 1835, and five years later, it had gained just seven more persons. Settlers came and went quickly through Toledo and between 1833 and 1836, ownership of land had changed so many times that none of the original parties remained in the town. The canal and its Toledo sidecut entrance were completed in 1843. Soon after the canal was functional, the new canal boats had become too large to use the shallow waters at the terminus in Manhattan. More boats began using the Swan Creek sidecut than its official terminus, quickly putting the Manhattan warehouses out of business and triggering a rush to move business to Toledo. Most of Manhattan's residents moved out by 1844.
Toledo was very slow to expand during its first two decades of settlement. The first lot was sold in the Port Lawrence section of the city in 1833. It held 1,205 persons in 1835, and five years later, it had gained just seven more persons. Settlers came and went quickly through Toledo and between 1833 and 1836, ownership of land had changed so many times that none of the original parties remained in the town. The canal and its Toledo sidecut entrance were completed in 1843. Soon after the canal was functional, the new canal boats had become too large to use the shallow waters at the terminus in Manhattan. More boats began using the Swan Creek sidecut than its official terminus, quickly putting the Manhattan warehouses out of business and triggering a rush to move business to Toledo. Most of Manhattan's residents moved out by 1844.
 The 1850 census recorded Toledo as having 3,829 residents and Manhattan 541. The 1860 census shows Toledo with a population of 13,768 and Manhattan with 788. While the towns were only a mile apart, Toledo grew by 359% in 10 years. Manhattan's growth was on a small base and never competed, given the drawbacks of its lesser canal outlet. By the 1880s, Toledo expanded over the vacant streets of Manhattan and Tremainsville, a small town to the west.
In the last half of the 19th century, railroads slowly began to replace canals as the major form of transportation. They were faster and had greater capacity. Toledo soon became a hub for several railroad companies and a hotspot for industries such as furniture producers, carriage makers, breweries, and glass manufacturers. Large
The 1850 census recorded Toledo as having 3,829 residents and Manhattan 541. The 1860 census shows Toledo with a population of 13,768 and Manhattan with 788. While the towns were only a mile apart, Toledo grew by 359% in 10 years. Manhattan's growth was on a small base and never competed, given the drawbacks of its lesser canal outlet. By the 1880s, Toledo expanded over the vacant streets of Manhattan and Tremainsville, a small town to the west.
In the last half of the 19th century, railroads slowly began to replace canals as the major form of transportation. They were faster and had greater capacity. Toledo soon became a hub for several railroad companies and a hotspot for industries such as furniture producers, carriage makers, breweries, and glass manufacturers. Large 
 The postwar job boom and Great Migration brought thousands of
The postwar job boom and Great Migration brought thousands of

 The Old West End is a historic neighborhood of Victorian, Arts & Crafts, and other Edwardian-style houses. The historic district is listed on the
The Old West End is a historic neighborhood of Victorian, Arts & Crafts, and other Edwardian-style houses. The historic district is listed on the
 As of the 2010 census, the city proper had a population of 287,128. It is the principal city in the Toledo Metropolitan Statistical Area which had a population of 651,429 and was the sixth-largest metropolitan area in the state of Ohio, behind
As of the 2010 census, the city proper had a population of 287,128. It is the principal city in the Toledo Metropolitan Statistical Area which had a population of 651,429 and was the sixth-largest metropolitan area in the state of Ohio, behind

 Before the
Before the
 Toledo is home to a range of classical performing arts institutions, including The
Toledo is home to a range of classical performing arts institutions, including The

 * Auto Racing –
* Auto Racing –
 * The
* The
 Three major
Three major
Mercy Health - St. Vincent Medical Center, Toledo's first hospital and part of
Official website
Greater Toledo Convention and Visitors Bureau
Toledo, Ohio, 1876
from the
Toledo, Ohio
(via Britannica) {{Authority control Cities in Ohio Cities in Lucas County, Ohio County seats in Ohio Ohio populated places on Lake Erie Populated places established in 1833 1833 establishments in Ohio Inland port cities and towns in Ohio
county seat
A county seat is an administrative center, seat of government, or capital city of a county or civil parish. The term is in use in Canada, China, Hungary, Romania, Taiwan, and the United States. The equivalent term shire town is used in the US ...
of Lucas County, Ohio
Lucas County is a county located in the northwestern part of the U.S. state of Ohio. It is bordered to the east by Lake Erie, and to the southeast by the Maumee River, which runs to the lake. As of the 2020 census, the population was 431,279 ...
, United States. A major Midwestern United States
The Midwestern United States, also referred to as the Midwest or the American Midwest, is one of four census regions of the United States Census Bureau (also known as "Region 2"). It occupies the northern central part of the United States. I ...
port city, Toledo is the fourth-most populous city in the state of Ohio
Ohio () is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. Of the List of states and territories of the United States, fifty U.S. states, it is the List of U.S. states and territories by area, 34th-l ...
, after Columbus
Columbus is a Latinized version of the Italian surname "''Colombo''". It most commonly refers to:
* Christopher Columbus (1451-1506), the Italian explorer
* Columbus, Ohio, capital of the U.S. state of Ohio
Columbus may also refer to:
Places ...
, Cleveland
Cleveland ( ), officially the City of Cleveland, is a city in the United States, U.S. U.S. state, state of Ohio and the county seat of Cuyahoga County, Ohio, Cuyahoga County. Located in the northeastern part of the state, it is situated along ...
, and Cincinnati
Cincinnati ( ) is a city in the U.S. state of Ohio and the county seat of Hamilton County. Settled in 1788, the city is located at the northern side of the confluence of the Licking and Ohio rivers, the latter of which marks the state line w ...
, and according to the 2020 census, the 79th-largest city in the United States. With a population of 270,871, it is the principal city of the Toledo metropolitan area. It also serves as a major trade center for the Midwest
The Midwestern United States, also referred to as the Midwest or the American Midwest, is one of four Census Bureau Region, census regions of the United States Census Bureau (also known as "Region 2"). It occupies the northern central part of ...
; its port is the fifth-busiest in the Great Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes in the mid-east region of North America that connect to the Atlantic Ocean via the Saint Lawrence River. There are five lakes ...
and 54th-biggest in the United States. The city was founded in 1833 on the west bank of the Maumee River
The Maumee River (pronounced ) ( sjw, Hotaawathiipi; mia, Taawaawa siipiiwi) is a river running in the United States Midwest from northeastern Indiana into northwestern Ohio and Lake Erie. It is formed at the confluence of the St. Joseph and ...
, and originally incorporated as part of Monroe County Monroe County may refer to seventeen counties in the United States, all named for James Monroe:
*Monroe County, Alabama
* Monroe County, Arkansas
* Monroe County, Florida
*Monroe County, Georgia
* Monroe County, Illinois
* Monroe County, Indi ...
, Michigan Territory
The Territory of Michigan was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from June 30, 1805, until January 26, 1837, when the final extent of the territory was admitted to the Union as the State of Michigan. Detroit ...
. It was refounded in 1837, after the conclusion of the Toledo War
The Toledo War (1835–36), also known as the Michigan–Ohio War or the Ohio–Michigan War, was an almost bloodless boundary dispute between the U.S. state of Ohio and the adjoining territory of Michigan over what is now known as the Toledo ...
, when it was incorporated in Ohio.
After the 1845 completion of the Miami and Erie Canal
The Miami and Erie Canal was a canal that ran from Cincinnati to Toledo, Ohio, creating a water route between the Ohio River and Lake Erie. Construction on the canal began in 1825 and was completed in 1845 at a cost to the state government of $ ...
, Toledo grew quickly; it also benefited from its position on the railway line between New York City and Chicago
(''City in a Garden''); I Will
, image_map =
, map_caption = Interactive Map of Chicago
, coordinates =
, coordinates_footnotes =
, subdivision_type = List of sovereign states, Count ...
. The first of many glass manufacturers arrived in the 1880s, eventually earning Toledo its nickname: "The Glass City". It has since become a city with a distinctive and growing art community, auto assembly businesses, education, thriving healthcare, and well-supported local sports teams. Downtown Toledo has been subject to major revitalization efforts, allowing a bustling entertainment district.
History
The region was part of a larger area controlled by the historic tribes of the Wyandot and the people of theCouncil of Three Fires
The Council of Three Fires (in oj, label=Anishinaabe, Niswi-mishkodewinan, also known as the People of the Three Fires; the Three Fires Confederacy; or the United Nations of Chippewa, Ottawa, and Potawatomi Indians) is a long-standing Anishina ...
(Ojibwe
The Ojibwe, Ojibwa, Chippewa, or Saulteaux are an Anishinaabe people in what is currently southern Canada, the northern Midwestern United States, and Northern Plains.
According to the U.S. census, in the United States Ojibwe people are one of ...
, Potawatomi
The Potawatomi , also spelled Pottawatomi and Pottawatomie (among many variations), are a Native American people of the western Great Lakes region, upper Mississippi River and Great Plains. They traditionally speak the Potawatomi language, a m ...
, and Odawa
The Odawa (also Ottawa or Odaawaa ), said to mean "traders", are an Indigenous American ethnic group who primarily inhabit land in the Eastern Woodlands region, commonly known as the northeastern United States and southeastern Canada. They h ...
). The French established trading posts in the area by 1680 to take advantage of the lucrative fur trade
The fur trade is a worldwide industry dealing in the acquisition and sale of animal fur. Since the establishment of a world fur market in the early modern period, furs of boreal ecosystem, boreal, polar and cold temperate mammalian animals h ...
. The Odawa moved from Manitoulin Island
Manitoulin Island is an island in Lake Huron, located within the borders of the Canadian province of Ontario, in the bioregion known as Laurentia. With an area of , it is the largest lake island in the world, large enough that it has over 100 ...
and the Bruce Peninsula
The Bruce Peninsula is a peninsula in Ontario, Canada, that divides Georgian Bay of Lake Huron from the lake's main basin. The peninsula extends roughly northwestwards from the rest of Southwestern Ontario, pointing towards Manitoulin Island, ...
at the invitation of the French, who established a trading post at Fort Detroit
Fort Pontchartrain du Détroit or Fort Detroit (1701–1796) was a fort established on the north bank of the Detroit River by the French officer Antoine de la Mothe Cadillac and the Italian Alphonse de Tonty in 1701. In the 18th century, Fre ...
, about 60 miles to the north. They settled an area extending into northwest Ohio. By the early 18th century, the Odawa-occupied areas along most of the Maumee River to its mouth. They served as middlemen between the French and tribes further to the west and north. The Wyandot occupied central Ohio, and the Shawnee
The Shawnee are an Algonquian-speaking indigenous people of the Northeastern Woodlands. In the 17th century they lived in Pennsylvania, and in the 18th century they were in Pennsylvania, Ohio, Indiana and Illinois, with some bands in Kentucky a ...
and Lenape
The Lenape (, , or Lenape , del, Lënapeyok) also called the Leni Lenape, Lenni Lenape and Delaware people, are an indigenous peoples of the Northeastern Woodlands, who live in the United States and Canada. Their historical territory inclu ...
occupied the southern areas.
When the city of Toledo was preparing to pave its streets, it surveyed "two prehistoric semicircular earthworks
Earthworks may refer to:
Construction
*Earthworks (archaeology), human-made constructions that modify the land contour
*Earthworks (engineering), civil engineering works created by moving or processing quantities of soil
*Earthworks (military), mi ...
, presumably for stockade
A stockade is an enclosure of palisades and tall walls, made of logs placed side by side vertically, with the tops sharpened as a defensive wall.
Etymology
''Stockade'' is derived from the French word ''estocade''. The French word was derived f ...
s." One was at the intersection of Clayton and Oliver Streets on the south bank of Swan Creek; the other was at the intersection of Fassett and Fort Streets on the right bank of the Maumee River. Such earthworks were typical of mound-building peoples.
19th century
According to Charles E. Slocum, the American military builtFort Industry
A fortification is a military construction or building designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is also used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from Latin ''fortis'' ("strong") and ''face ...
at the mouth of Swan Creek about 1805, as a temporary stockade. No official reports support the 19th-century tradition of its earlier history there.Charles E. Slocum, "Forts Miami and Fort Industry"''Ohio Archaeological and Historical Publications,'' Volume XII, 1903; hosted at American History and Genealogy Project, accessed 26 December 2015 The United States continued to work to extinguish land claims of Native Americans. In the
Treaty of Detroit
The Treaty of Detroit was a treaty between the United States and the Ottawa, Chippewa, Wyandot and Potawatomi Native American nations. The treaty was signed in Detroit, Michigan on November 17, 1807, with William Hull, governor of the Mich ...
(1807), the above four tribes ceded a large land area to the United States of what became southeastern Michigan and northwestern Ohio, to the mouth of the Maumee River (where Toledo later developed). Reserves for the Odawa were set aside in northwestern Ohio for a limited time. The Native Americans signed the treaty at Detroit, Michigan
Detroit ( , ; , ) is the largest city in the U.S. state of Michigan. It is also the largest U.S. city on the United States–Canada border, and the seat of government of Wayne County. The City of Detroit had a population of 639,111 at ...
, on November 17, 1807, with William Hull
William Hull (June 24, 1753 – November 29, 1825) was an American soldier and politician. He fought in the American Revolutionary War and was appointed as Governor of Michigan Territory (1805–13), gaining large land cessions from several Am ...
, governor of the Michigan Territory and superintendent of Indian affairs, as the sole representative of the U.S.
More European-American settlers entered the area over the next few years, but many fled during the War of 1812
The War of 1812 (18 June 1812 – 17 February 1815) was fought by the United States of America and its indigenous allies against the United Kingdom and its allies in British North America, with limited participation by Spain in Florida. It be ...
, when British forces raided the area with their Indian allies. Resettlement began around 1818 after a Cincinnati syndicate purchased a tract at the mouth of Swan Creek and named it Port Lawrence, developing it as the modern downtown area of Toledo. Immediately to the north of that, another syndicate founded the town of Vistula, the historic north end. These two towns bordered each other across Cherry Street. This is why present-day streets on the street's northeast side run at a slightly different angle from those southwest of it.
In 1824, the Ohio state legislature authorized the construction of the Miami and Erie Canal
The Miami and Erie Canal was a canal that ran from Cincinnati to Toledo, Ohio, creating a water route between the Ohio River and Lake Erie. Construction on the canal began in 1825 and was completed in 1845 at a cost to the state government of $ ...
, and in 1833, its Wabash and Erie Canal
The Wabash and Erie Canal was a shipping canal that linked the Great Lakes to the Ohio River via an artificial waterway. The canal provided traders with access from the Great Lakes all the way to the Gulf of Mexico. Over 460 miles long, it was th ...
extension. The canal's purpose was to connect the city of Cincinnati to Lake Erie
Lake Erie ( "eerie") is the fourth largest lake by surface area of the five Great Lakes in North America and the eleventh-largest globally. It is the southernmost, shallowest, and smallest by volume of the Great Lakes and therefore also ha ...
for water transportation to eastern markets, including to New York City via the Erie Canal and Hudson River. At that time, no highways had been built in the state, and goods produced locally had great difficulty reaching the larger markets east of the Appalachian Mountains
The Appalachian Mountains, often called the Appalachians, (french: Appalaches), are a system of mountains in eastern to northeastern North America. The Appalachians first formed roughly 480 million years ago during the Ordovician Period. The ...
. During the canal's planning phase, many small towns along the northern shores of the Maumee River heavily competed to be the ending terminus of the canal, knowing it would give them a profitable status. The towns of Port Lawrence and Vistula merged in 1833 to better compete against the upriver towns of Waterville and Maumee.
The inhabitants of this joined settlement chose the name Toledo:
"but the reason for this choice is buried in a welter of legends. One recounts thatDespite Toledo's efforts, the canal built the final terminus in Manhattan, to the north of Toledo, because it was closer to Lake Erie. As a compromise, the state placed two sidecuts before the terminus, one in Toledo at Swan Creek and another in Maumee, about 10 miles to the southwest. Among the numerous treaties made between the Ottawa and the United States were two signed in this area: at Miami (Maumee) Bay in 1831 and umee, Ohio, upriver of Toledo, in 1833. These actions were among US purchases or exchanges of land to accomplishWashington Irving Washington Irving (April 3, 1783 – November 28, 1859) was an American short-story writer, essayist, biographer, historian, and diplomat of the early 19th century. He is best known for his short stories "Rip Van Winkle" (1819) and " The Legen ..., who was traveling in Spain at the time, suggested the name to his brother, a local resident; this explanation ignores the fact that Irving returned to the United States in 1832. Others award the honor to Two Stickney, son of the major who quaintly numbered his sons and named his daughters after States. The most popular version attributes the naming to Willard J. Daniels, a merchant, who reportedly suggested Toledo because it 'is easy to pronounce, is pleasant in sound, and there is no other city of that name on the American continent.'"
Indian Removal
Indian removal was the United States government policy of forced displacement of self-governing tribes of Native Americans from their ancestral homelands in the eastern United States to lands west of the Mississippi Riverspecifically, to a ...
of the Ottawa from areas wanted for European-American settlement. The last of the Odawa did not leave this area until 1839, when Ottokee, grandson of Pontiac Pontiac may refer to:
*Pontiac (automobile), a car brand
*Pontiac (Ottawa leader) ( – 1769), a Native American war chief
Places and jurisdictions Canada
*Pontiac, Quebec, a municipality
** Apostolic Vicariate of Pontiac, now the Roman Catholic D ...
, led his band from their village at the mouth of the Maumee River to Indian Territory
The Indian Territory and the Indian Territories are terms that generally described an evolving land area set aside by the United States Government for the relocation of Native Americans who held aboriginal title to their land as a sovereign ...
in Kansas.
An almost bloodless conflict between Ohio and the Michigan Territory, called the Toledo War (1835–1836), was "fought" over a narrow strip of land from the Indiana
Indiana () is a U.S. state in the Midwestern United States. It is the 38th-largest by area and the 17th-most populous of the 50 States. Its capital and largest city is Indianapolis. Indiana was admitted to the United States as the 19th ...
border to Lake Erie
Lake Erie ( "eerie") is the fourth largest lake by surface area of the five Great Lakes in North America and the eleventh-largest globally. It is the southernmost, shallowest, and smallest by volume of the Great Lakes and therefore also ha ...
, now containing the city and the suburbs of Sylvania and Oregon, Ohio. The strip, which varied between five and eight miles (13 km) in width, was claimed by both the state of Ohio and the Michigan Territory due to conflicting legislation concerning the location of the Ohio-Michigan state line. Militias from both states were sent to the border, but never engaged. The only casualty of the conflict was a Michigan deputy sheriff
A sheriff is a government official, with varying duties, existing in some countries with historical ties to England where the office originated. There is an analogous, although independently developed, office in Iceland that is commonly transla ...
—stabbed in the leg with a penknife by Two Stickney during the arrest of his elder brother, One Stickney—and the loss of two horses, two pigs, and a few chickens stolen from an Ohio farm by lost members of the Michigan militia. Major Benjamin Franklin Stickney, father of One and Two Stickney, had been instrumental in pushing Congress to rule in favor of Ohio gaining Toledo. In the end, the state of Ohio was awarded the land after the state of Michigan was given a larger portion of the Upper Peninsula
The Upper Peninsula of Michigan – also known as Upper Michigan or colloquially the U.P. – is the northern and more elevated of the two major landmasses that make up the U.S. state of Michigan; it is separated from the Lower Peninsula by ...
in exchange. Stickney Avenue in Toledo is named for Major Stickney.
 Toledo was very slow to expand during its first two decades of settlement. The first lot was sold in the Port Lawrence section of the city in 1833. It held 1,205 persons in 1835, and five years later, it had gained just seven more persons. Settlers came and went quickly through Toledo and between 1833 and 1836, ownership of land had changed so many times that none of the original parties remained in the town. The canal and its Toledo sidecut entrance were completed in 1843. Soon after the canal was functional, the new canal boats had become too large to use the shallow waters at the terminus in Manhattan. More boats began using the Swan Creek sidecut than its official terminus, quickly putting the Manhattan warehouses out of business and triggering a rush to move business to Toledo. Most of Manhattan's residents moved out by 1844.
Toledo was very slow to expand during its first two decades of settlement. The first lot was sold in the Port Lawrence section of the city in 1833. It held 1,205 persons in 1835, and five years later, it had gained just seven more persons. Settlers came and went quickly through Toledo and between 1833 and 1836, ownership of land had changed so many times that none of the original parties remained in the town. The canal and its Toledo sidecut entrance were completed in 1843. Soon after the canal was functional, the new canal boats had become too large to use the shallow waters at the terminus in Manhattan. More boats began using the Swan Creek sidecut than its official terminus, quickly putting the Manhattan warehouses out of business and triggering a rush to move business to Toledo. Most of Manhattan's residents moved out by 1844.
 The 1850 census recorded Toledo as having 3,829 residents and Manhattan 541. The 1860 census shows Toledo with a population of 13,768 and Manhattan with 788. While the towns were only a mile apart, Toledo grew by 359% in 10 years. Manhattan's growth was on a small base and never competed, given the drawbacks of its lesser canal outlet. By the 1880s, Toledo expanded over the vacant streets of Manhattan and Tremainsville, a small town to the west.
In the last half of the 19th century, railroads slowly began to replace canals as the major form of transportation. They were faster and had greater capacity. Toledo soon became a hub for several railroad companies and a hotspot for industries such as furniture producers, carriage makers, breweries, and glass manufacturers. Large
The 1850 census recorded Toledo as having 3,829 residents and Manhattan 541. The 1860 census shows Toledo with a population of 13,768 and Manhattan with 788. While the towns were only a mile apart, Toledo grew by 359% in 10 years. Manhattan's growth was on a small base and never competed, given the drawbacks of its lesser canal outlet. By the 1880s, Toledo expanded over the vacant streets of Manhattan and Tremainsville, a small town to the west.
In the last half of the 19th century, railroads slowly began to replace canals as the major form of transportation. They were faster and had greater capacity. Toledo soon became a hub for several railroad companies and a hotspot for industries such as furniture producers, carriage makers, breweries, and glass manufacturers. Large immigrant
Immigration is the international movement of people to a destination country of which they are not natives or where they do not possess citizenship in order to settle as permanent residents or naturalized citizens. Commuters, tourists, ...
populations came to the area.

20th century
In the 1920s, Toledo had one of the highest rates of industrial growth in the United States. Toledo continued to expand in population and industry, but because of its dependence on manufacturing, the city was hit hard by theGreat Depression
The Great Depression (19291939) was an economic shock that impacted most countries across the world. It was a period of economic depression that became evident after a major fall in stock prices in the United States. The economic contagio ...
. Many large-scale Works Progress Administration
The Works Progress Administration (WPA; renamed in 1939 as the Work Projects Administration) was an American New Deal agency that employed millions of jobseekers (mostly men who were not formally educated) to carry out public works projects, i ...
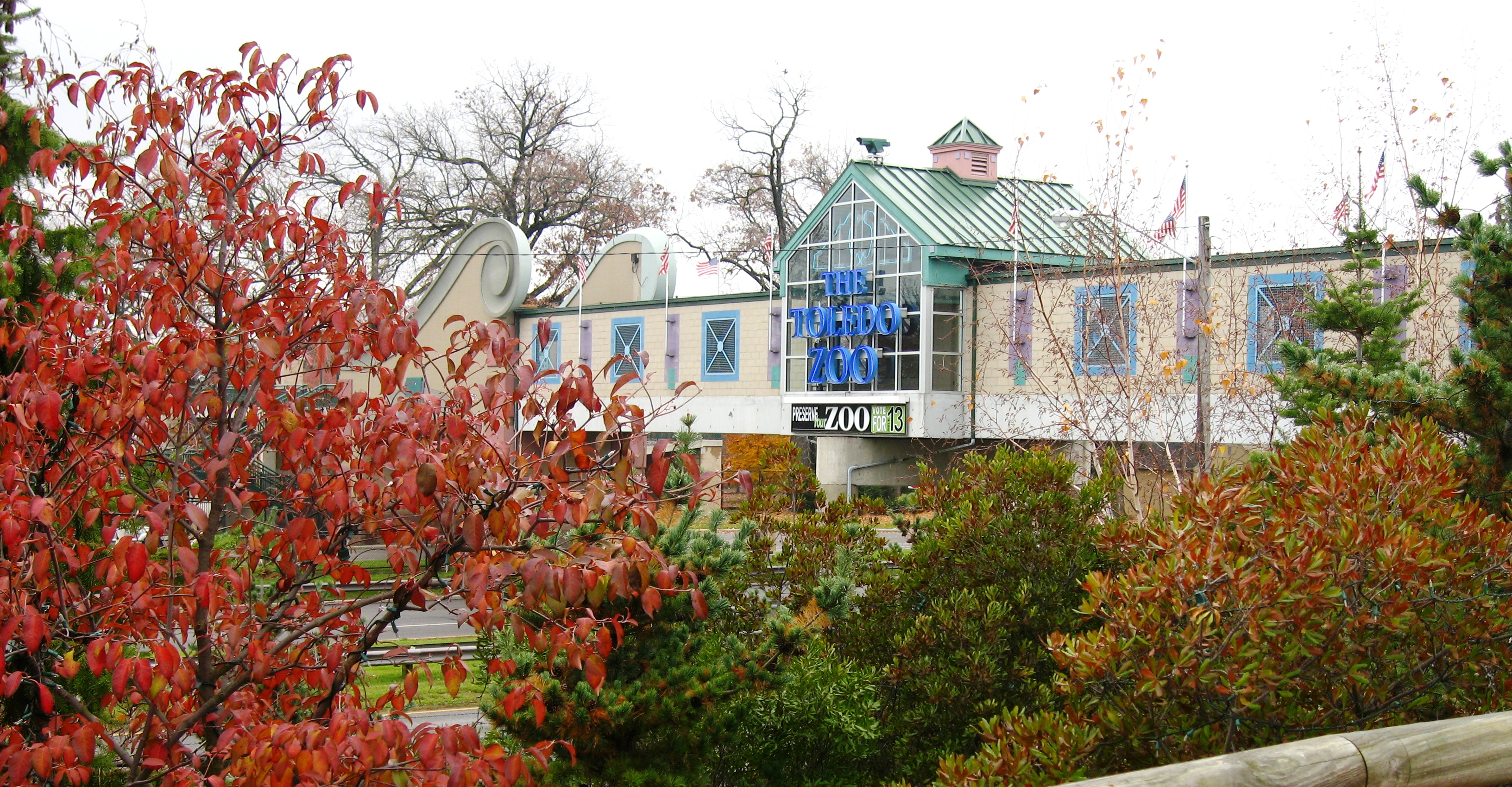
projects were constructed to re-employ citizens in the 1930s. Some of these include the amphitheater and aquarium at the Toledo Zoo
The Toledo Zoo & Aquarium, located in Toledo, Ohio, is a member of the World Association of Zoos and Aquariums (WAZA), and is accredited by the Association of Zoos and Aquariums (AZA), through the year 2022. The Toledo Zoo & Aquarium houses over ...
and a major expansion to the Toledo Museum of Art
The Toledo Museum of Art is an internationally known art museum located in the Old West End neighborhood of Toledo, Ohio. It houses a collection of more than 30,000 objects. With 45 galleries, it covers 280,000 square feet and is currently in th ...
.
 The postwar job boom and Great Migration brought thousands of
The postwar job boom and Great Migration brought thousands of African Americans
African Americans (also referred to as Black Americans and Afro-Americans) are an ethnic group consisting of Americans with partial or total ancestry from sub-Saharan Africa. The term "African American" generally denotes descendants of ens ...
to Toledo to work in industrial jobs, where they had previously been denied. Due to redlining
In the United States, redlining is a discriminatory practice in which services ( financial and otherwise) are withheld from potential customers who reside in neighborhoods classified as "hazardous" to investment; these neighborhoods have sign ...
, many of them settled along Dorr Street, which, during the 1950s and 60s was lined with flourishing black-owned businesses and homes. Desegregation
Desegregation is the process of ending the separation of two groups, usually referring to races. Desegregation is typically measured by the index of dissimilarity, allowing researchers to determine whether desegregation efforts are having impact o ...
, a failed urban renewal
Urban renewal (also called urban regeneration in the United Kingdom and urban redevelopment in the United States) is a program of land redevelopment often used to address urban decay in cities. Urban renewal involves the clearing out of blighte ...
project, and the construction of I-75
Interstate 75 (I-75) is a major north–south Interstate Highway in the Great Lakes and Southeastern regions of the United States. As with most Interstates that end in 5, it is a major cross-country, north–south route, traveling from St ...
displaced those residents and left behind a struggling community with minimal resources, even as it also drew more established, middle-class people, white and black, out of center cities for newer housing. The city rebounded, but the slump of American manufacturing in the second half of the 20th century during industrial restructuring cost many jobs.
By the 1980s, Toledo had a depressed economy. The destruction of many buildings downtown, along with several failed business ventures in housing in the core, led to a reverse city-suburb wealth problem common in small cities with land to spare.
21st century
In 2018, Cleveland-Cliffs, Inc. invested $700 million into an East Toledo location as the site of a new hot-briquetted iron plant, designed to modernize the steel industry. The plant was slated to create over 1200 jobs and be completed in 2020. Several initiatives have been taken by Toledo's citizens to improve the cityscape by urban gardening and revitalizing their communities. Local artists, supported by organizations like the Arts Commission of Greater Toledo and theOhio Arts Council
The Ohio Arts Council (OAC) is an agency serving the U.S. state of Ohio.
History
Established in 1965, its mission is to "foster and encourage the development of the arts and assist the preservation of Ohio's cultural heritage." Each year it awar ...
, have contributed an array of murals and beautification works to replace long standing blight. Many downtown historical buildings such as the Oliver House and Standart Lofts have been renovated into restaurants, condominiums, offices and art galleries.
Toledo Water Crisis
Harmful blooms of cyanobacteria, or blue-green algae, were so bad in the 1960s that Lake Erie was mocked as a dead zone. However through clean water rules the lake was revived. Recently though these blooms have returned and have been negatively affecting Lake Erie since the late 1990s now. Heightened levels of blue-green algae can affect both human and ecosystem health by causing fish to die, the water to be discolored and foul smelling, and oxygen deficient dead zones may even start to form. Sometimes the blooms are so thick that they slow boats. These large blooms are caused by agricultural runoff flowing into the lake. Agricultural runoff dumps phosphorus into the western basin of Lake Erie and acts as a fertilizer for the blue-green algae, and the warmer weather seen in July through October in Northern Ohio helps speed up the growing process. Because of Toledo’s closeness to the lake, Toledo citizens are affected each year by these algae blooms. Lake Erie provides drinking water to many cities along its coast, with Toledo being no exception, and in the summer of 2014 the water flowing into Toledo was thick with algae. On the evening of August 1, 2014 and the morning of August 2nd, 2014 the city of Toledo issued an urgent warning to all citizens in the city and surrounding areas not to drink or use their tap water, this left more than half a million people suddenly without water. Not only was the water unsafe to ingest, but citizens were urged not to even wash their hands or dishes with the water. A bloom of the toxic blue-green algae had formed directly over Toledo’s water intake pipe, which was situated a few miles off shore in Lake Erie. Because of the algae bloom forming just above the pipe, the water being pumped into Toledo showed levels of harmful bacteria that made the water unsafe to interact with. Because of the urgency of the warnings, it left citizens no time to prepare. The price of bottled water skyrocketed on August 2. With no end date in sight, bottled water flew off the shelves on the day the warning was issued, and in many places it sold out entirely. Some Toledo citizens had to drive for hours just to find safe, clean water, something that many older (14.5% of the population) or low income (24.5% of the population) citizens were unable to do at the time. Churches and other organizations tried to set up water distribution sites, but it was challenging due to the lack of resources. On the second full day of the crisis, August 3, 2014, churches, schools, and other buildings being used as refuge had run out of water. There was no way for the city to plan for a crisis of this scale, so it took the community by surprise. Later that night, around 4 pm, the National Guard was brought in to deliver over 10,000 gallons of water to citizens. This relieved many people, as bottled water was either sold out in stores or too expensive for the average citizen due to citizens panic buying and stores price gouging. The warning against using water lasted nearly three days, finally ending late on August 4. Fear of tap water still lingered, though. This event was later dubbed the “Toledo Water Crisis” and is still talked about today, especially during the months that see heightened algal blooms. Algal blooms can cause water bills to increase in this area $100 per year for a family of five. The effects of these blooms go beyond higher water bills as heightened blooms can even shut down parts of the economy such as tourism and fishing industries, and cause property values to drop, costing the local economy to lose tens of millions of dollars. Beyond the economy, the increase in toxic blooms exacts a psychological toll on residents, especially those living near the polluted waterways. Many citizens still find it difficult to trust the local government, and even the tap water, because of the 2014 crisis. Blue-green algae blooms continue to harm Lake Erie even years after the Toledo Water Crisis, but government officials and scientists are both working to find ways to decrease their impact on the environment and the economy.Geography
Toledo is located at (41.665682, −83.575337). The city has a total area of , of which is covered by water. The city straddles the Maumee River at its mouth at the southern end of Maumee Bay, the westernmost inlet of Lake Erie. The city is located north of what had been theGreat Black Swamp
The Great Black Swamp (also known simply as the Black Swamp) was a glacially fed wetland in northwest Ohio, sections of lower Michigan, and extreme northeast Indiana, United States, that existed from the end of the Wisconsin glaciation until t ...
, giving rise to another nickname, Frog Town. Toledo sits within the borders of a sandy oak savanna called the Oak Openings Region, an important ecological site that once comprised more than .
Toledo is within by road from seven metropolitan areas that have a population of more than two million people: Detroit
Detroit ( , ; , ) is the largest city in the U.S. state of Michigan. It is also the largest U.S. city on the United States–Canada border, and the seat of government of Wayne County. The City of Detroit had a population of 639,111 at t ...
, Cleveland
Cleveland ( ), officially the City of Cleveland, is a city in the United States, U.S. U.S. state, state of Ohio and the county seat of Cuyahoga County, Ohio, Cuyahoga County. Located in the northeastern part of the state, it is situated along ...
, Columbus
Columbus is a Latinized version of the Italian surname "''Colombo''". It most commonly refers to:
* Christopher Columbus (1451-1506), the Italian explorer
* Columbus, Ohio, capital of the U.S. state of Ohio
Columbus may also refer to:
Places ...
, Cincinnati
Cincinnati ( ) is a city in the U.S. state of Ohio and the county seat of Hamilton County. Settled in 1788, the city is located at the northern side of the confluence of the Licking and Ohio rivers, the latter of which marks the state line w ...
, Pittsburgh
Pittsburgh ( ) is a city in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, United States, and the county seat of Allegheny County, Pennsylvania, Allegheny County. It is the most populous city in both Allegheny County and Wester ...
, Indianapolis
Indianapolis (), colloquially known as Indy, is the state capital and most populous city of the U.S. state of Indiana and the seat of Marion County. According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the consolidated population of Indianapolis and Marion ...
, and Chicago
(''City in a Garden''); I Will
, image_map =
, map_caption = Interactive Map of Chicago
, coordinates =
, coordinates_footnotes =
, subdivision_type = List of sovereign states, Count ...
. In addition, it is within 300 miles of Toronto, Ontario
Toronto ( ; or ) is the capital city of the Canadian province of Ontario. With a recorded population of 2,794,356 in 2021, it is the most populous city in Canada and the fourth most populous city in North America. The city is the ancho ...
.
Climate
Toledo, as with much of theGreat Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes in the mid-east region of North America that connect to the Atlantic Ocean via the Saint Lawrence River. There are five lakes ...
region, has a humid continental climate
A humid continental climate is a climatic region defined by Russo-German climatologist Wladimir Köppen in 1900, typified by four distinct seasons and large seasonal temperature differences, with warm to hot (and often humid) summers and freez ...
( Köppen ''Dfa''), characterized by four distinct seasons. Lake Erie moderates the climate somewhat, especially in late spring and fall, when air and water temperature differences are maximal. However, this effect is lessened in the winter because Lake Erie (unlike the other Great Lakes) usually freezes over, coupled with prevailing winds that are often westerly, and in the summer, prevailing winds south and west over the lake bring heat and humidity to the city.
Summers are very warm and humid, with July averaging and temperatures of or more seen on 18.8 days. Winters are cold and somewhat snowy, with a January mean temperature of , and lows at or below on 5.6 nights. The spring months tend to be the wettest time of year, although precipitation is common year-round. November and December can get very cloudy, but January and February usually clear up after the lake freezes. July is the sunniest month overall. About of snow falls per year, much less than the Snow Belt cities, because of the prevailing wind direction. Temperature extremes have ranged from on January 21, 1984, to on July 14, 1936.
Cityscape

Neighborhoods and suburbs
National Register of Historic Places
The National Register of Historic Places (NRHP) is the United States federal government's official list of districts, sites, buildings, structures and objects deemed worthy of preservation for their historical significance or "great artistic ...
.
*Beverly
*Birmingham
*Darby (Eastern to South-Old South End)
*DeVeaux
*Crossgates
*Five Points
*Downtown
''Downtown'' is a term primarily used in North America by English speakers to refer to a city's sometimes commercial, cultural and often the historical, political and geographic heart. It is often synonymous with its central business district ...
*East Toledo
*Franklin Park
*Garfield
*Glendale-Heatherdowns (Byrne-Heatherdowns Village)
* Harvard Terrace
* Library Village
*Nasby
*North Towne
* Old Orchard
* Old West End
*Old South End
*Old Town
*ONE Village (includes the Polish International Village, Vistula, & North River)
*ONYX (includes historic Kuschwantz and Lenk's Hill neighborhoods)
*Ottawa
Ottawa (, ; Canadian French: ) is the capital city of Canada. It is located at the confluence of the Ottawa River and the Rideau River in the southern portion of the province of Ontario. Ottawa borders Gatineau, Quebec, and forms the c ...
* Point Place
*Reynolds Corners
*Roosevelt
*Scott Park
*Secor Gardens (includes the University of Toledo)
*Southwyck
*Wernert's Corner
*Trilby
*University Hills
*Uptown
* Warehouse District
*Warren Sherman
*Westgate
* Westmoreland
According to the US Census Bureau
The United States Census Bureau (USCB), officially the Bureau of the Census, is a principal agency of the U.S. Federal Statistical System, responsible for producing data about the American people and economy. The Census Bureau is part of th ...
, the Toledo Metropolitan Area covers four Ohio counties and one Michigan county, which combines with other micropolitan areas and counties for a combined statistical area. Some of what are now considered its suburbs in Ohio include: Bowling Green
A bowling green is a finely laid, close-mown and rolled stretch of turf for playing the game of bowls.
Before 1830, when Edwin Beard Budding of Thrupp, near Stroud, UK, invented the lawnmower, lawns were often kept cropped by grazing sheep ...
, Holland
Holland is a geographical regionG. Geerts & H. Heestermans, 1981, ''Groot Woordenboek der Nederlandse Taal. Deel I'', Van Dale Lexicografie, Utrecht, p 1105 and former Provinces of the Netherlands, province on the western coast of the Netherland ...
, Lake Township, Maumee, Millbury, Monclova Township, Northwood, Oregon
Oregon () is a U.S. state, state in the Pacific Northwest region of the Western United States. The Columbia River delineates much of Oregon's northern boundary with Washington (state), Washington, while the Snake River delineates much of it ...
, Ottawa Hills
Ottawa Hills is a village in Lucas County, Ohio, United States. The population was 4,517 at the 2010 census. The village was developed on both sides of the Ottawa River (Ohio) and serves as a bedroom community and suburb of Toledo. The Ottawa H ...
, Perrysburg, Rossford
Rossford is a city in Wood County, Ohio, United States, located along the Maumee River in the Toledo metropolitan area. The population was 6,293 at the 2010 census. The town includes the intersection of Interstate 75 and the Ohio Turnpike. Ross ...
, Springfield Township, Sylvania, Walbridge, Waterville, Whitehouse Whitehouse may refer to:
People
* Charles S. Whitehouse (1921-2001), American diplomat
* Cornelius Whitehouse (1796–1883), English engineer and inventor
* E. Sheldon Whitehouse (1883-1965), American diplomat
* Elliott Whitehouse (born 1993), ...
, and Washington Township. Bedford Township, Michigan including the communities of Lambertville, Michigan, Temperance, Michigan
Temperance is an unincorporated community and census-designated place (CDP) in Monroe County in the U.S. state of Michigan. The population was 9,188 at the 2020 census. The CDP is located within Bedford Township.
The community was established a ...
, and Erie Township, Michigan are Toledo's Michigan suburbs, just above the city over the state line in Monroe County.
Demographics
 As of the 2010 census, the city proper had a population of 287,128. It is the principal city in the Toledo Metropolitan Statistical Area which had a population of 651,429 and was the sixth-largest metropolitan area in the state of Ohio, behind
As of the 2010 census, the city proper had a population of 287,128. It is the principal city in the Toledo Metropolitan Statistical Area which had a population of 651,429 and was the sixth-largest metropolitan area in the state of Ohio, behind Cleveland
Cleveland ( ), officially the City of Cleveland, is a city in the United States, U.S. U.S. state, state of Ohio and the county seat of Cuyahoga County, Ohio, Cuyahoga County. Located in the northeastern part of the state, it is situated along ...
, Columbus
Columbus is a Latinized version of the Italian surname "''Colombo''". It most commonly refers to:
* Christopher Columbus (1451-1506), the Italian explorer
* Columbus, Ohio, capital of the U.S. state of Ohio
Columbus may also refer to:
Places ...
, Cincinnati
Cincinnati ( ) is a city in the U.S. state of Ohio and the county seat of Hamilton County. Settled in 1788, the city is located at the northern side of the confluence of the Licking and Ohio rivers, the latter of which marks the state line w ...
, Dayton
Dayton () is the sixth-largest city in the U.S. state of Ohio and the county seat of Montgomery County. A small part of the city extends into Greene County. The 2020 U.S. census estimate put the city population at 137,644, while Greater Da ...
, and Akron
Akron () is the fifth-largest city in the U.S. state of Ohio and is the county seat of Summit County. It is located on the western edge of the Glaciated Allegheny Plateau, about south of downtown Cleveland. As of the 2020 Census, the city ...
. The larger Toledo-Fremont Combined Statistical Area
Combined statistical area (CSA) is a United States Office of Management and Budget (OMB) term for a combination of adjacent metropolitan statistical area, metropolitan (MSA) and micropolitan statistical areas (µSA) across the 50 US states and ...
had a population of 712,373. According to the Toledo Metropolitan Council of Governments, the Toledo/Northwest Ohio region of 10 counties has over 1 million residents.
The U.S. Census Bureau estimated Toledo's population as 297,806 in 2006 and 295,029 in 2007. In response to an appeal by the City of Toledo, the Census Bureau's July 2007 estimate was revised to 316,851, slightly more than in 2000, which would have been the city's first population gain in 40 years. However, the 2010 census figures released in March 2011 showed the population as of April 1, 2010, at 287,208, indicating a 25% loss of population since its zenith in 1970.
2020 census
As of the 2020 census there were 270,871 people, 116,257 households, and an average of 2.27 persons per household residing in Toledo. The population per square mile was 3,365.4. The racial makeup of Toledo was 60.6% White, 28.1% African American, 0.3% Native American, Alaska Native or Native Hawaiian, and 1.3% were Asian. 6.7% of the population belonged to two or more races. Hispanic or Latino citizens make up 8.8% of the population. People who identified as White, not Hispanic or Latino, made up 57.3% of the population, down from 61.4% in 2010. Out of 270,871 people, 23.3% were under the age of 18, and 14.5% were 65 years old and over. 51.1% of the population were female. 14.1% of the population under 65 years of age were living with a disability, and 8.3% of those under 65 years of age didn’t have health insurance. Out of the 116,257 households, 83.7% had been living in the same house for one year or longer. 6.4% of households in Toledo spoke a language other than English at home. The total number of housing units was unavailable, however 51.9% of housing units were either owned or co-owned by its inhabitants. The median household income (in 2021 dollars) in Toledo was $41,671, with the per capita income in the past 12 months coming to $23,795. 24.5% of the population was living in poverty, compared to the National average at this time of 11.6% of the U.S. population. For education, 87.1% of people 25 years or older were a high school graduate or higher, with 19.6% of this demographic having a Bachelor’s Degree or higher.2010 census
As of thecensus
A census is the procedure of systematically acquiring, recording and calculating information about the members of a given population. This term is used mostly in connection with national population and housing censuses; other common censuses inc ...
of 2010, there were 287,208 people, 119,730 households, and 68,364 families residing in the city. The population density
Population density (in agriculture: standing stock or plant density) is a measurement of population per unit land area. It is mostly applied to humans, but sometimes to other living organisms too. It is a key geographical term.Matt RosenberPopu ...
was . There were 138,039 housing units at an average density of . The racial makeup of the city was 64.8% White
White is the lightest color and is achromatic (having no hue). It is the color of objects such as snow, chalk, and milk, and is the opposite of black. White objects fully reflect and scatter all the visible wavelengths of light. White ...
, 27.2% African American
African Americans (also referred to as Black Americans and Afro-Americans) are an ethnic group consisting of Americans with partial or total ancestry from sub-Saharan Africa. The term "African American" generally denotes descendants of ens ...
, 0.4% Native American, 1.1% Asian, 2.6% from other races, and 3.9% from two or more races. Hispanic
The term ''Hispanic'' ( es, hispano) refers to people, cultures, or countries related to Spain, the Spanish language, or Hispanidad.
The term commonly applies to countries with a cultural and historical link to Spain and to viceroyalties for ...
or Latino of any race were 7.4% of the population (The majority are Mexican American at 5.1%.) Non-Hispanic Whites
Non-Hispanic whites or Non-Latino whites are Americans who are classified as "white", and are not of Hispanic (also known as "Latino") heritage. The United States Census Bureau defines ''white'' to include European Americans, Middle Eastern Ame ...
were 61.4% of the population in 2010, down from 84% in 1970.
There were 119,730 households, of which 30.4% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 31.6% were married couples
Marriage, also called matrimony or wedlock, is a culturally and often legally recognized union between people called spouses. It establishes rights and obligations between them, as well as between them and their children, and between ...
living together, 19.9% had a female householder with no husband present, 5.7% had a male householder with no wife present, and 42.9% were non-families. 34.8% of all households were made up of individuals, and 10.7% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.33 and the average family size was 3.01. There was a total of 139,871 housing units in the city, of which 10,946 (9.8%) were vacant.
The median age in the city was 34.2 years. 24% of residents were under the age of 18; 12.8% were between the ages of 18 and 24; 26.3% were from 25 to 44; 24.8% were from 45 to 64; and 12.1% were 65 years of age or older. The gender makeup of the city was 48.4% male and 51.6% female.
2000 census
As of thecensus
A census is the procedure of systematically acquiring, recording and calculating information about the members of a given population. This term is used mostly in connection with national population and housing censuses; other common censuses inc ...
of 2000, there were 313,619 people, and 77,355 families residing in the city. The population density was 3,890.2 people per square mile (1,502.0/km2). There were 139,871 housing units at an average density of 1,734.9 per square mile (669.9/km2). The racial makeup of the city was 70.2% White
White is the lightest color and is achromatic (having no hue). It is the color of objects such as snow, chalk, and milk, and is the opposite of black. White objects fully reflect and scatter all the visible wavelengths of light. White ...
, 23.5% African American
African Americans (also referred to as Black Americans and Afro-Americans) are an ethnic group consisting of Americans with partial or total ancestry from sub-Saharan Africa. The term "African American" generally denotes descendants of ens ...
, 0.3% Native American,1.0% Asian, 0.0% Pacific Islander
Pacific Islanders, Pasifika, Pasefika, or rarely Pacificers are the peoples of the Pacific Islands. As an ethnic/ racial term, it is used to describe the original peoples—inhabitants and diasporas—of any of the three major subregions of O ...
, 2.3% from other races, and 2.6% from two or more races. Hispanic
The term ''Hispanic'' ( es, hispano) refers to people, cultures, or countries related to Spain, the Spanish language, or Hispanidad.
The term commonly applies to countries with a cultural and historical link to Spain and to viceroyalties for ...
or Latino of any race were 5.5% of the population in 2000. The most common ancestries cited were German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
(23.4%), Irish (10.8%), Polish (10.1%), English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ...
(6.0%), American
American(s) may refer to:
* American, something of, from, or related to the United States of America, commonly known as the "United States" or "America"
** Americans, citizens and nationals of the United States of America
** American ancestry, pe ...
(3.9%), Italian (3.0%), Hungarian, (2.0%), Dutch
Dutch commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
* Dutch people ()
* Dutch language ()
Dutch may also refer to:
Places
* Dutch, West Virginia, a community in the United States
* Pennsylvania Dutch Country
People E ...
(1.4%), and Arab
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
(1.2%).
In 2000 there were 128,925 households in Toledo, out of which 29.8% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 38.2% were married couples living together, 17.2% had a female householder with no husband present, and 40.0% were non-families. 32.8% of all households were made up of individuals, and 11.0% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.38 and the average family size was 3.04.
In the city the population was spread out, with 26.2% under the age of 18, 11.0% from 18 to 24, 29.8% from 25 to 44, 19.8% from 45 to 64, and 13.1% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 33 years. For every 100 females, there were 97.9 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 97.7 males.
The median income for a household in the city was $32,546, and the median income for a family was $41,175. Males had a median income of $35,407 versus $25,023 for females. The per capita income for the city was $17,388. About 14.2% of families and 17.9% of the population were below the poverty line, including 25.9% of those under age 18 and 10.4% of those age 65 or over.
Crime
In 2018, the city was ranked 43rd of the Top 100 Most Dangerous Cities in America. In the second decade of the 21st century, the city had a gradual peak in violent crime. In 2010, there was a combined total of 3,272 burglaries, 511 robberies, 753 aggravated assaults, 25 homicides, as well as 574 motor vehicle thefts out of what was then a decreasing population of 287,208. In 2011, there were 1,562 aggravated assaults, 30 homicides, 1,152 robberies, 8,366 burglaries, and 1,465 cases of motor vehicle theft. In 2012, there were a combined total of 39 murders, 2,015 aggravated assaults, 6,739 burglaries, and 1,334 cases of motor vehicle theft. In 2013 it had a drop in the crime rate. According to a state government task force, Toledo has been identified as the fourth-largest recruitment site for human trafficking in the US. The year 2020 brought the highest number of homicides in 39 years, according to the Toledo Police Department's 50-year trend chart. Beginning with the pandemic in 2020, homicides jumped to a record 61. There were a record of 70 homicides in Toledo in 2021. Toledo was one of 12 major U.S. cities to have broken annual homicide records in 2021 alongside: Indianapolis, Philadelphia, Baton Rouge, Rochester, Portland, St. Paul, Austin, Albuquerque, Tucson, Louisville, and Columbus.Economy
industrial revolution
The Industrial Revolution was the transition to new manufacturing processes in Great Britain, continental Europe, and the United States, that occurred during the period from around 1760 to about 1820–1840. This transition included going f ...
, Toledo was important as a port city on the Great Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes in the mid-east region of North America that connect to the Atlantic Ocean via the Saint Lawrence River. There are five lakes ...
. With the advent of the automobile, the city became best known for industrial manufacturing. Both General Motors
The General Motors Company (GM) is an American Multinational corporation, multinational Automotive industry, automotive manufacturing company headquartered in Detroit, Michigan, United States. It is the largest automaker in the United States and ...
and Chrysler
Stellantis North America (officially FCA US and formerly Chrysler ()) is one of the " Big Three" automobile manufacturers in the United States, headquartered in Auburn Hills, Michigan. It is the American subsidiary of the multinational automotiv ...
had factories in metropolitan Toledo, and automobile manufacturing has been important at least since Kirk
Kirk is a Scottish and former Northern English word meaning "church". It is often used specifically of the Church of Scotland. Many place names and personal names are also derived from it.
Basic meaning and etymology
As a common noun, ''kirk' ...
started manufacturing automobiles, which began operations early in the 20th century. The largest employer in Toledo was Jeep
Jeep is an American automobile marque, now owned by multi-national corporation Stellantis. Jeep has been part of Chrysler since 1987, when Chrysler acquired the Jeep brand, along with remaining assets, from its previous owner American Motors ...
for much of the 20th century. Since the late 20th century, industrial restructuring reduced the number of these well-paying jobs.
The University of Toledo
The University of Toledo (UToledo or UT) is a public research university in Toledo, Ohio. It is the northernmost campus of the University System of Ohio. The university also operates a Health Science campus, which includes the University of ...
is influential in the city, contributing to the prominence of healthcare as the city's biggest employer. The metro area contains four Fortune 500
The ''Fortune'' 500 is an annual list compiled and published by ''Fortune (magazine), Fortune'' magazine that ranks 500 of the largest United States Joint-stock company#Closely held corporations and publicly traded corporations, corporations by ...
companies: Dana Holding Corporation
Dana Incorporated is an American supplier of axles, driveshafts, transmissions, and electrodynamic, thermal, sealing, and digital equipment for conventional, hybrid, and electric-powered vehicles. The company's products and services are aimed ...
, Owens Corning
Owens Corning is an American company that develops and produces insulation, roofing, and fiberglass composites and related materials and products. It is the world's largest manufacturer of fiberglass composites. It was formed in 1935 as a partn ...
, The Andersons, and Owens Illinois
O-I Glass, Inc. is an American company that specializes in container glass products. It is one of the world's leading manufacturers of packaging products, holding the position of largest manufacturer of glass containers in North America, Sout ...
. ProMedica
ProMedica is a non-profit health care system with locations in northwest Ohio and southeast Michigan. The system includes a health education and research center, the health maintenance organization Paramount Health Care, nursing homes, a loc ...
is a Fortune 1000
The Fortune 1000 are the 1,000 largest American companies ranked by revenues, as compiled by the American business magazine '' Fortune''. It only includes companies which are incorporated or authorized to do business in the United States, and fo ...
company headquartered in Toledo. One SeaGate is the location of Fifth Third Bank's Northwest Ohio headquarters.
Glass industry
Toledo is known as the Glass City because of its long history of glass manufacturing, includingwindow
A window is an opening in a wall, door, roof, or vehicle that allows the exchange of light and may also allow the passage of sound and sometimes air. Modern windows are usually glazed or covered in some other transparent or translucent mat ...
s, bottle
A bottle is a narrow-necked container made of an impermeable material (such as glass, plastic or aluminium) in various shapes and sizes that stores and transports liquids. Its mouth, at the bottling line, can be sealed with an internal s ...
s, windshield
The windshield (North American English) or windscreen (Commonwealth English) of an aircraft, car, bus, motorbike, truck, train, boat or streetcar is the front window, which provides visibility while protecting occupants from the elements. ...
s, construction materials
This is a list of building materials. Many types of building materials are used in the construction industry to create buildings and structures.
These categories of materials and products are used by architects and construction project managers ...
, and glass art
Glass art refers to individual works of art that are substantially or wholly made of glass. It ranges in size from monumental works and installation pieces to wall hangings and windows, to works of art made in studios and factories, including gla ...
, of which the Toledo Museum of Art
The Toledo Museum of Art is an internationally known art museum located in the Old West End neighborhood of Toledo, Ohio. It houses a collection of more than 30,000 objects. With 45 galleries, it covers 280,000 square feet and is currently in th ...
has a large collection. Several large glass companies have their origins here. Owens-Illinois
O-I Glass, Inc. is an American company that specializes in container glass products. It is one of the world's leading manufacturers of packaging products, holding the position of largest manufacturer of glass containers in North America, South A ...
, Owens Corning
Owens Corning is an American company that develops and produces insulation, roofing, and fiberglass composites and related materials and products. It is the world's largest manufacturer of fiberglass composites. It was formed in 1935 as a partn ...
, Libbey Incorporated, Pilkington
Pilkington is a Japanese-owned glass-manufacturing company which is based in Lathom, Lancashire, United Kingdom. In the UK it includes several legal entities and is a subsidiary of Japanese company NSG Group.
Prior to its acquisition by NSG ...
North America (formerly Libbey-Owens-Ford), and Therma-Tru have long been a staple of Toledo's economy. Other offshoots and spinoffs of these companies also continue to play important roles in Toledo's economy. Fiberglass giant Johns Manville
Johns Manville is an American company based in Denver, Colorado, that manufactures insulation, roofing materials and engineered products. For much of the 20th century, the then-titled Johns-Manville Corporation was the global leader in the ...
's two plants in the metro area were originally built by a subsidiary of Libbey-Owens-Ford.
Automotive industry
Several Fortune 500 automotive-related companies had their headquarters in Toledo, including Electric AutoLite, Sheller-Globe Corporation, Champion Spark Plug, Questor, andDana Holding Corporation
Dana Incorporated is an American supplier of axles, driveshafts, transmissions, and electrodynamic, thermal, sealing, and digital equipment for conventional, hybrid, and electric-powered vehicles. The company's products and services are aimed ...
. Only the latter still operates as an independent entity.
Faurecia Exhaust Systems, a $2 billion subsidiary of France's Faurecia
Faurecia SE is a French global automotive supplier headquartered in Nanterre, in the western suburbs of Paris. In 2018 it was the 9th largest international automotive parts manufacturer in the world and #1 for vehicle interiors and emission contr ...
SA, is in Toledo.
Toledo is the Jeep headquarters and has two production facilities dubbed the Toledo Complex, one in the city and one in suburban Perrysburg. During World War II, the city's industries produced important products for the military, particularly the Willys Jeep
The Willys MB and the Ford GPW, both formally called the U.S. Army Truck, -ton, 4×4, Command Reconnaissance, commonly known as the Willys Jeep, Jeep, or jeep, and sometimes referred to by its supply catalogue designation G503,According to i ...
. Willys-Overland
Willys (pronounced , "Willis" )
was a brand name used by Willys–Overland Motors, an American automobile company, founded by John North Willys. It was best known for its design and production of World War II era and later military jeeps (MBs) ...
was a major automaker headquartered in Toledo until 1953.
Industrial restructuring and loss of jobs caused the city to adopt new strategies to retain its industrial companies. It offered tax incentives to DaimlerChrysler
The Mercedes-Benz Group AG (previously named Daimler-Benz, DaimlerChrysler and Daimler) is a German multinational automotive corporation headquartered in Stuttgart, Baden-Württemberg, Germany. It is one of the world's leading car manufacture ...
to expand its Jeep plant. In 2001, a taxpayer lawsuit was filed against Toledo that challenged the constitutionality of that action. In 2006, the city won the case by a unanimous ruling by the U.S. Supreme Court in '' DaimlerChrysler Corp. v. Cuno''.
General Motors also has operated a transmission plant in Toledo since 1916. It manufactures and assembles GM's six-speed and eight-speed rear-wheel-drive and six-speed front-wheel-drive transmissions that are used in a variety of GM vehicles.
Green industry
Belying itsRust Belt
The Rust Belt is a region of the United States that experienced industrial decline starting in the 1950s. The U.S. manufacturing sector as a percentage of the U.S. GDP peaked in 1953 and has been in decline since, impacting certain regions an ...
history, the city saw growth in "green jobs" related to solar energy in the 2000s. The University of Toledo
The University of Toledo (UToledo or UT) is a public research university in Toledo, Ohio. It is the northernmost campus of the University System of Ohio. The university also operates a Health Science campus, which includes the University of ...
and Bowling Green State University
Bowling Green State University (BGSU) is a public research university in Bowling Green, Ohio. The main academic and residential campus is south of Toledo, Ohio. The university has nationally recognized programs and research facilities in the ...
received Ohio grants for solar energy research. Xunlight and First Solar opened plants in Toledo and the surrounding area.
In May 2019 Balance Farms began operation of an 8,168 square foot indoor aquaponics
Aquaponics is a food production system that couples aquaculture (raising aquatic animals such as fish, crayfish, snails or prawns in tanks) with hydroponics (cultivating plants in water) whereby the nutrient-rich aquaculture water is fed to hydr ...
farm in downtown Toledo.
Arts and culture
Fine and performing arts
 Toledo is home to a range of classical performing arts institutions, including The
Toledo is home to a range of classical performing arts institutions, including The Toledo Opera
The Toledo Opera is an American opera company in Toledo, Ohio, performing in the Valentine Theatre in downtown Toledo. The company's season consists of three fully-realized operas, plus additional community programming for the Northwest Ohio re ...
, The Toledo Symphony Orchestra, the Toledo Jazz Orchestra and the Toledo Ballet. The city is also home to several theaters and performing arts institutions, including the Stranahan Theater, the historic Valentine Theatre, the Toledo Repertoire Theatre, the Collingwood Arts Center and the Ohio Theatre
Ohio () is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States. Of the fifty U.S. states, it is the 34th-largest by area, and with a population of nearly 11.8 million, is the seventh-most populous and tenth-most densely populated. The ...
.
The Toledo Museum of Art
The Toledo Museum of Art is an internationally known art museum located in the Old West End neighborhood of Toledo, Ohio. It houses a collection of more than 30,000 objects. With 45 galleries, it covers 280,000 square feet and is currently in th ...
is located in a Greek Revival
The Greek Revival was an architectural movement which began in the middle of the 18th century but which particularly flourished in the late 18th and early 19th centuries, predominantly in northern Europe and the United States and Canada, but a ...
building in the city's Old West End neighborhood. The Peristyle is the concert hall in Greek Revival style in its East Wing; it is the home of the Toledo Symphony Orchestra, and hosts many international orchestras as well. The Museum's Center for Visual Arts addition was designed by Frank Gehry
Frank Owen Gehry, , FAIA (; ; born ) is a Canadian-born American architect and designer. A number of his buildings, including his private residence in Santa Monica, California, have become world-renowned attractions.
His works are considered ...
and opened in the 21st century. In addition, the museum's new Glass Pavilion across Monroe Street opened in August 2006. Toledo was the first city in Ohio to adopt a One Percent for Art program and, as such, boasts many examples of public, outdoor art. A number of walking tours have been set up to explore these works, which include large sculptures, environmental structures, and murals by more than 40 artists, such as Alice Adams, Pierre Clerk
Pierre Clerk (born 1928) is a contemporary artist who works primarily in painting and sculpture.
Life
Clerk was born to Canadian parents in Atlanta, Georgia. He lived in Canada between 1932 and 1952. He studied fine arts at McGill University, Loy ...
, Dale Eldred
Dale Eldred (November 9, 1933 in Minneapolis, Minnesota – July 26, 1993 in Kansas City, Missouri) was an internationally acclaimed sculptor renowned for large-scale sculptures that emphasized both natural and generated light.
Biography
The ...
, Penelope Jencks, Hans Van De Bovenkamp, Jerry Peart, and Athena Tacha Athena Tacha ( el, Αθηνά Τάχα; born in Larissa, Greece, 1936-), is a multimedia visual artist. She is best known for her work in the fields of environmental public sculpture and conceptual art. She also worked in a wide array of materials ...
.
Music
Toledo has a rich history of music, dating back to their early to mid-20th century glory days as a jazz haven. During this time, Toledo produced or nurtured such jazz legends asArt Tatum
Arthur Tatum Jr. (, October 13, 1909 – November 5, 1956) was an American jazz pianist who is widely regarded as one of the greatest in his field. From early in his career, Tatum's technical ability was regarded by fellow musicians as extraord ...
, Jon Hendricks
John Carl Hendricks (September 16, 1921 – November 22, 2017), known professionally as Jon Hendricks, was an American jazz lyricist and singer. He is one of the originators of vocalese, which adds lyrics to existing instrumental songs and re ...
, trombonist Jimmy Harrison, pianist Claude Black, guitarist Arv Garrison, pianist Johnny O'Neal, and many, many others. Later jazz greats from Toledo include Stanley Cowell, Larry Fuller, Bern Nix
Bern Nix (September 21, 1947 – May 31, 2017) was an American jazz guitarist. He recorded and performed with Ornette Coleman from 1975 to 1987, notably with guitarist Charlie Ellerbee in Coleman's Prime Time group on their key recordings, inclu ...
and Jean Holden
Jean Holden (born February 2, 1940 in Masonville, Arkansas) is an American contemporary jazz singer and vocal coach
A vocal coach, also known as a voice coach (though this term often applies to those working with speech and communication ra ...
.
Other well-known singers and musicians with Toledo roots include Teresa Brewer, Tom Scholz, Anita Baker
Anita Denise Baker (born January 26, 1958) is an American singer-songwriter. She is one of the most popular singers of soulful ballads, especially renowned for her work during the height of the quiet storm period in the 1980s. Starting her career ...
, Shirley Murdock
Shirley Murdock (born May 22, 1957) is an American R&B singer-songwriter, who is best known for her 1986 R&B hit single "As We Lay" and for her vocals on Zapp and Roger's hit single " Computer Love". Her lead vocal special guest appearance wi ...
, American Idol
''American Idol'' is an American singing competition television series created by Simon Fuller, produced by Fremantle North America and 19 Entertainment, and distributed by Fremantle North America. It aired on Fox from June 11, 2002, to ...
runner-up Crystal Bowersox
Crystal Lynn Bowersox (born August 4, 1985) is an American singer, songwriter and actress who was the runner-up on the ninth season of ''American Idol''. She was the first female finalist in three years.
Bowersox's debut album, ''Farmer's Daug ...
, The Rance Allen Group, Lyfe Jennings and Weezer
Weezer is an American rock band formed in Los Angeles, California, in 1992. Since 2001, the band has consisted of Rivers Cuomo (vocals, guitar, keyboards), Patrick Wilson (drums, backing vocals), Scott Shriner (bass guitar, keyboards, backing ...
bassist Scott Shriner
Scott Gardner Shriner (born July 11, 1965) is an American musician best known as a member of the rock band Weezer, with whom he has recorded twelve studio albums. Joining the band in 2001, Shriner is the band's longest serving bass guitarist.
Prio ...
.
In popular culture
TheKenny Rogers
Kenneth Ray Rogers (August 21, 1938 – March 20, 2020) was an American singer, songwriter, and actor. He was inducted into the Country Music Hall of Fame in 2013. Rogers was particularly popular with country audiences but also charted mo ...
1977 hit song " Lucille" was written by Hal Bynum
Harold L. Bynum (September 29, 1934 – June 2, 2022) was an American songwriter associated with the Outlaw country movement in the 1970s. Bynum wrote more than 200 songs for popular country artists, including Kenny Rogers (" Lucille"), Patty ...
and inspired by his trip to Toledo in 1975.
Toledo is mentioned in the song " Our Song" by Yes
Yes or YES may refer to:
* An affirmative particle in the English language; see yes and no
Education
* YES Prep Public Schools, Houston, Texas, US
* YES (Your Extraordinary Saturday), a learning program from the Minnesota Institute for Talent ...
from their 1983 album ''90125
''90125'' is the eleventh studio album by the English progressive rock band Yes, released on 11 November 1983 by Atco Records. After Yes disbanded in 1981, following the ''Drama'' (1980) tour, bassist Chris Squire and drummer Alan White forme ...
''. According to Yes drummer Alan White, Toledo was especially memorable for a sweltering-hot 1977 show the group did at Toledo Sports Arena
Toledo Sports Arena was a 5,230-seat multi-purpose arena at 1 Main Street, Toledo, Ohio. It was built in 1947 and demolished in 2007.
As a concert venue, it seated 6,500, for theater concerts and stage shows, 4,400 and for boxing and wrestling, ...
.
The season 1 episode of the Warner Bros
Warner Bros. Entertainment Inc. (commonly known as Warner Bros. or abbreviated as WB) is an American Film studio, film and entertainment studio headquartered at the Warner Bros. Studios, Burbank, Warner Bros. Studios complex in Burbank, Califo ...
television series ''Supernatural
Supernatural refers to phenomena or entities that are beyond the laws of nature. The term is derived from Medieval Latin , from Latin (above, beyond, or outside of) + (nature) Though the corollary term "nature", has had multiple meanings si ...
'' titled "Bloody Mary" was set in Toledo.
The popular phrase "Holy Toledo," is thought to originally be a reference to the city's array of grand church designs from Gothic
Gothic or Gothics may refer to:
People and languages
*Goths or Gothic people, the ethnonym of a group of East Germanic tribes
**Gothic language, an extinct East Germanic language spoken by the Goths
**Crimean Gothic, the Gothic language spoken b ...
, Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history marking the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and covering the 15th and 16th centuries, characterized by an effort to revive and surpass ide ...
and Spanish Mission. There are many other theories as well.
Toledo is the setting for the 2010 television comedy ''Melissa & Joey
''Melissa & Joey'' is an American television sitcom starring Melissa Joan Hart and Joey Lawrence that aired for four seasons between 2010 and 2015 on ABC Family (now Freeform). The series follows local politician Mel Burke (Hart) and Joe Longo ...
'', with the first-named character being a city councilwoman.
John Denver
Henry John Deutschendorf Jr. (December 31, 1943 – October 12, 1997), known professionally as John Denver, was an American singer-songwriter, guitarist, actor, activist, and humanitarian whose greatest commercial success was as a solo singe ...
recorded "Saturday Night In Toledo, Ohio," composed by Randy Sparks. He wrote it in 1967 after arriving in Toledo with his group and finding no nightlife at 10 p.m. After Denver performed the song on ''The Tonight Show
''The Tonight Show'' is an American late-night talk show that has aired on NBC since 1954. The show has been hosted by six comedians: Steve Allen (1954–1957), Jack Paar (1957–1962), Johnny Carson (1962–1992), Jay Leno (1992–2009 and 201 ...
'', Toledo residents objected. In response, the City Fathers recorded a song entitled "We're Strong For Toledo". Ultimately the controversy was such that John Denver cancelled a concert in Toledo shortly thereafter. But when he returned for a 1980 concert, he set a one-show attendance record at the venue, Centennial Hall, and sang the song to the approval of the crowd.
Sports

 * Auto Racing –
* Auto Racing – Toledo Speedway
Toledo Speedway is a half-mile paved oval racetrack located in Toledo, Ohio, United States. It is owned jointly by Roy Mott and ARCA President Ron Drager. It is operated by ARCA and run as the sister track to Flat Rock Speedway in Flat Rock ...
is a local auto racetrack that features, among other events, stock car racing and concerts. The Automobile Racing Club of America
The Automobile Racing Club of America (ARCA) is an auto racing sanctioning body in the United States, founded in 1953 by John Marcum. The current president of ARCA is Ron Drager, who took over the position in 1996 following the death of Bob Log ...
(ARCA) has its headquarters in Toledo.
* Baseball – The Toledo Mud Hens
The Toledo Mud Hens are a Minor League Baseball team of the International League and the Triple-A affiliate of the Detroit Tigers. They are located in Toledo, Ohio, and play their home games at Fifth Third Field. A Mud Hens team has played in ...
are one of Minor League Baseball's oldest teams, having first played in 1896. They play at Fifth Third Field which was completed in 2002. They have won one American Association American Association may refer to:
Baseball
* American Association (1882–1891), a major league active from 1882 to 1891
* American Association (1902–1997), a minor league active from 1902 to 1962 and 1969 to 1997
* American Association of Profe ...
title and three International League
The International League (IL) is a Minor League Baseball league that operates in the United States. Along with the Pacific Coast League, it is one of two leagues playing at the Triple-A level, which is one grade below Major League Baseball ( ...
titles. The Mud Hens are the Triple-A affiliate of the MLB Detroit Tigers
The Detroit Tigers are an American professional baseball team based in Detroit. The Tigers compete in Major League Baseball (MLB) as a member of the American League (AL) Central division. One of the AL's eight charter franchises, the club was f ...
.
* Boxing - Jack Dempsey
William Harrison "Jack" Dempsey (June 24, 1895 – May 31, 1983), nicknamed Kid Blackie and The Manassa Mauler, was an American professional boxer who competed from 1914 to 1927, and reigned as the world heavyweight champion from 1919 to 1926 ...
won the world heavyweight boxing championship from Jess Willard on July 4, 1919.
* Golf – Inverness Club
Inverness Club is a private golf club in Toledo, Ohio.
Opened in 1903, the club has hosted four U.S. Opens, two PGA Championships, two NCAA Men's Championships, and the Solheim Cup. Inverness is the only club to have hosted the U.S. Open, U.S. ...
is a golf club in Toledo. It is known for hosting six major
Major ( commandant in certain jurisdictions) is a military rank of commissioned officer status, with corresponding ranks existing in many military forces throughout the world. When used unhyphenated and in conjunction with no other indicato ...
USGA events, most recently the 1993 PGA Championship. In 2020, Inverness Club
Inverness Club is a private golf club in Toledo, Ohio.
Opened in 1903, the club has hosted four U.S. Opens, two PGA Championships, two NCAA Men's Championships, and the Solheim Cup. Inverness is the only club to have hosted the U.S. Open, U.S. ...
hosted the LPGA Drive-On Championship, and in 2021, it hosted the Solheim Cup
The Solheim Cup is a biennial golf tournament for professional women golfers contested by teams representing Europe and the United States. It is named after the Norwegian-American golf club manufacturer Karsten Solheim, who was a driving force ...
. The U.S. Senior Open took place at Inverness in 2003 and 2011. Highland Meadows Golf Club has been home to the LPGA
The Ladies Professional Golf Association (LPGA) is an American organization for female golfers. The organization is headquartered at the LPGA International in Daytona Beach, Florida, and is best known for running the LPGA Tour, a series of wee ...
's Marathon Classic
The Dana Open Presented By Marathon, is a women's professional golf tournament on the LPGA Tour. It was founded in 1984 and has been played yearly, except in 1986 and 2011, in Sylvania, Ohio, a suburb northwest of Toledo. The tournament is tel ...
in the nearby suburb of Sylvania since 1984 (yearly except for 1986 and 2011).
* Hockey – The Toledo Walleye
The Toledo Walleye are a professional ice hockey team based in Toledo, Ohio. The Walleye are members of the Central Division of the Western Conference of the ECHL. The Walleye were founded in 1991 as the Toledo Storm and play their home games at ...
are an ECHL
The ECHL (formerly the East Coast Hockey League) is a mid-level professional ice hockey league based in Shrewsbury, New Jersey, with teams scattered across the United States and Canada. It is a tier below the American Hockey League (AHL).
The ...
hockey team that began play at the Huntington Center in 2009. The Walleye are an affiliate of the Grand Rapids Griffins
The Grand Rapids Griffins are a professional hockey team in the American Hockey League (AHL) based in Grand Rapids, Michigan, and play home games at Van Andel Arena. They are the AHL affiliate to the Detroit Red Wings of the National Hockey Leag ...
of the American Hockey League
The American Hockey League (AHL) is a professional ice hockey league based in the United States and Canada that serves as the primary developmental league for the National Hockey League (NHL). Since the 2010–11 season, every team in the lea ...
, and the Detroit Red Wings
The Detroit Red Wings (colloquially referred to as the Wings) are a professional ice hockey team based in Detroit. The Red Wings compete in the National Hockey League (NHL) as a member of the Atlantic Division in the Eastern Conference, and are ...
of the NHL. Toledo has a rich history of pro hockey, which includes 11 championships between four teams in the International Hockey League and ECHL.
* Football – The Toledo Reign are a women's full-contact tackle football team in the Women's Football Alliance
The Women's Football Alliance (WFA) is a professional full-contact Women's American football tackle minor league that began play in 2009. It is the largest 11-on-11 football league for women in the world, and the longest running active women's ...
. Established in 2003, the Reign plays regular season games from April through June. The Toledo Crush
The Toledo Crush were a women's indoor football team in the Legends Football League, formerly known as the Lingerie Football League before 2013. The Crush began play for the 2011–12 season as the Cleveland Crush with home games at Quicken Loans ...
of the Legends Football League
The Extreme Football League (X League) is an American women's semi-professional tackle football league.
The league was originally founded in 2009 as the Lingerie Football League (LFL), and later rebranded as the Legends Football League in 2013.
...
played at the Huntington Center in 2014 after relocating from Cleveland, where it played from 2011 to 2013. The Toledo Maroons
The Toledo Maroons were a professional American football team based in Toledo, Ohio in the National Football League in 1922 and 1923. Prior to joining the NFL, the Maroons played in the unofficial " Ohio League" from 1902 until 1921.
History
O ...
played in the Ohio League
The Ohio League was an informal and loose association of American football clubs active between 1902 and 1919 that competed for the Ohio Independent Championship (OIC). As the name implied, its teams were mostly based in Ohio. It is the direct pr ...
from 1902 until 1921 and the NFL from 1922 until 1923 before moving to Kenosha, Wisconsin
Kenosha () is a city in the U.S. state of Wisconsin and the seat of Kenosha County. Per the 2020 census, the population was 99,986 which made it the fourth-largest city in Wisconsin. Situated on the southwestern shore of Lake Michigan, Kenos ...
.
* Roller Derby – The Glass City Rollers is a full member of the Women's Flat Track Derby Association. The league was formed in 2007 and became a full member of the WFTDA in 2012. Their bouts are held at the International Boxing Club in the suburb of Oregon
Oregon () is a U.S. state, state in the Pacific Northwest region of the Western United States. The Columbia River delineates much of Oregon's northern boundary with Washington (state), Washington, while the Snake River delineates much of it ...
.
*Soccer - Founded in 2017, Toledo Villa FC is a semi-professional soccer team located in Toledo, OH. The team plays out of the United Soccer League (USL) League Two. The club is committed to its vision to place the best product on the pitch, develop players that are committed to upholding the traditions of the game, inspire young athletes for the future of the game and provide a model business that positively impacts the community.
* Wrestling – Toledo could be proudly called a "Wrestling Capital of the World," as the city hosted the International Federation of Associated Wrestling Styles
International is an adjective (also used as a noun) meaning "between nations".
International may also refer to:
Music Albums
* ''International'' (Kevin Michael album), 2011
* ''International'' (New Order album), 2002
* ''International'' (The T ...
(FILA) Congress in 1966, two editions of World Championships
A world championship is generally an international competition open to elite competitors from around the world, representing their nations, and winning such an event will be considered the highest or near highest achievement in the sport, game, ...
(both freestyle and Greco-Roman), seventeen editions of Freestyle Wrestling World Cup, and numerous high-profile international duals were held at the Toledo Field House and Centennial Hall.
Parks and recreation
Toledo Zoo
The Toledo Zoo & Aquarium, located in Toledo, Ohio, is a member of the World Association of Zoos and Aquariums (WAZA), and is accredited by the Association of Zoos and Aquariums (AZA), through the year 2022. The Toledo Zoo & Aquarium houses over ...
was the first zoo
A zoo (short for zoological garden; also called an animal park or menagerie) is a facility in which animals are kept within enclosures for public exhibition and often bred for conservation purposes.
The term ''zoological garden'' refers to z ...
to feature a '' hippoquarium''-style exhibit. In 2014 it was ranked as the #1 zoo in the country by ''USA Today
''USA Today'' (stylized in all uppercase) is an American daily middle-market newspaper and news broadcasting company. Founded by Al Neuharth on September 15, 1982, the newspaper operates from Gannett's corporate headquarters in Tysons, Virgini ...
.''
* The National Museum of the Great Lakes (NMGL) is located in the Marina District, downstream from downtown Toledo.
* Adjacent to the NMGL, the '' Col. James M. Schoonmaker'' is a former Cleveland-Cliffs lake freighter open to the public as a museum. Moored in the Maumee River, the ship was recently repainted in the original Shenango Furnace fleet colors and, on 1 July 2011, rechristened with her original name.
* The R. A. Stranahan Arboretum is a arboretum
An arboretum (plural: arboreta) in a general sense is a botanical collection composed exclusively of trees of a variety of species. Originally mostly created as a section in a larger garden or park for specimens of mostly non-local species, man ...
maintained by the University of Toledo
The University of Toledo (UToledo or UT) is a public research university in Toledo, Ohio. It is the northernmost campus of the University System of Ohio. The university also operates a Health Science campus, which includes the University of ...
.
* Tony Packo's Cafe
Tony Packo's Cafe is a restaurant that started in the Hungarian neighborhood of Birmingham, on the east side of Toledo, Ohio, at 1902 Front Street. Starting in 1932, the restaurant became famous when it was mentioned in several ''M*A*S*H'' episode ...
is located in the Hungarian neighborhood on the east side of Toledo known as Birmingham; it features hundreds of hot dog bun
A hot dog bun is a type of soft bun shaped specifically to contain a hot dog or another type of sausage.
The side-loading bun is common in most of the United States, while the top-loading New England-style hot dog bun is popular in that regio ...
s signed by celebrities.
* The Toledo Metroparks system includes over of land, and features the University/Parks Bicycle Trail and the Toledo Botanical Garden.
* On January 15, 1936, the first building to be completely covered in glass was constructed in Toledo. It was a building for the Owens-Illinois Glass Company
O-I Glass, Inc. is an American company that specializes in container glass products. It is one of the world's leading manufacturers of packaging products, holding the position of largest manufacturer of glass containers in North America, South A ...
and marked a milestone in architectural design
Building design refers to the broadly based architectural, engineering and technical applications to the design of buildings. All building projects require the services of a building designer, typically a licensed architect. Smaller, less complica ...
representative of the International style of architecture, which was at that time becoming increasingly popular in the US.
* The Imagination Station
Imagination Station (formerly the Center of Science and Industry (COSI)) is a non-profit, hands-on science museum located on the Maumee riverfront in downtown Toledo, Ohio. The facility has over 300 exhibits for "children of all ages."
The museum ...
hands-on science museum (formerly COSI Toledo), is located downtown.
* The Toledo Lucas County Public Library was 4-star rated for 2009 by the ''Library Journal
''Library Journal'' is an American trade publication for librarians. It was founded in 1876 by Melvil Dewey. It reports news about the library world, emphasizing public libraries, and offers feature articles about aspects of professional pract ...
,'' and it is sixth among the biggest-spending libraries in the United States.
* Hollywood Casino Toledo
Hollywood Casino Toledo is a casino in Toledo, Ohio, that opened on May 29, 2012. The casino is owned by Gaming and Leisure Properties and operated by Penn Entertainment, and has of gaming space, with 2,002 slot machines, 60 table games, and 20 ...
opened on May 29, 2012.
Education
Colleges and universities
These higher education institutions operate campuses in Toledo: *TheUniversity of Toledo
The University of Toledo (UToledo or UT) is a public research university in Toledo, Ohio. It is the northernmost campus of the University System of Ohio. The university also operates a Health Science campus, which includes the University of ...
* University of Toledo College of Medicine and Life Sciences
* Davis College
* Mercy College of Ohio
* Owens Community College ( Perrysburg Township)
* Toledo Academy of Beauty
* Toledo Professional Skills Institute
*Tiffin University
Tiffin University is a private university in Tiffin, Ohio. It was founded in 1888 and is accredited by the Higher Learning Commission. The university offers undergraduate and graduate degree programs at the main campus in Tiffin, Ohio; the Unive ...
(Toledo Campus)
*Toledo Career Institute
Primary and secondary schools
Toledo Public Schools
Toledo Public Schools, also known as Toledo City School District, is a public school district headquartered in Toledo, Ohio, in the United States. The district encompasses 70 square miles, serving students of the city of Toledo. Toledo Public S ...
operates public schools within much of the city limits, along with the Washington Local School District in northern Toledo. Toledo is also home to several public charter schools including two Imagine Schools, several Leona Group Schools, and top ranking Toledo Preparatory and Fitness Academy. Additionally, several private and parochial primary and secondary schools are present within the Toledo area. The Roman Catholic Diocese of Toledo operates Roman Catholic primary and secondary schools in 19 counties in Northwest Ohio, including Lucas County and the Toledo area. Notable private high schools in Toledo include:
* Maumee Valley Country Day School
* Central Catholic High School
* St. Francis de Sales High School
* St. John's Jesuit High School and Academy
* Notre Dame Academy
* St. Ursula Academy (Ottawa Hills)
* Cardinal Stritch Catholic High School (Oregon)
* Toledo Christian Schools
Toledo Christian Schools is a non-denominational, co-educational Christian school in Toledo, Ohio
Toledo ( ) is a city in and the county seat of Lucas County, Ohio, United States. A major Midwestern United States port city, Toledo is the f ...
* Emmanuel Christian School
Media
The eleven-county Northwest Ohio/Toledo/Fremont media market includes over 1 million residents. '' The Blade'', a daily newspaper founded in 1835, is the primary newspaper in Toledo. The front page claims that it is "One of America's Great Newspapers." The city's arts and entertainment weekly is the '' Toledo City Paper''. From March 2005 to 2015, the weekly newspaper ''Toledo Free Press
The ''Toledo Free Press'' was a weekly newspaper which was published from 2005 to 2015 in Toledo, Ohio.
History
It was founded in March 2005 by Thomas Pounds, a veteran administrator of daily newspapers in Toledo and Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. O ...
'' was published, and it had a focus on news and sports. Other weeklies include the ''West Toledo Herald'', ''El Tiempo'', ''La Prensa'', ''Sojourner's Truth'', and ''Toledo Journal''. ''Toledo Tales'' provides satire and parody of life in the Glass City. The ''Toledo Journal'' is an African-American owned newspaper. It is published weekly, and normally focuses on African-American issues.
Eight television stations are in Toledo. They are: WTOL 11 ( CBS), WTVG 13 (ABC), WTVG-DT2 (CW), WNWO
WNWO-TV (channel 24) is a television station in Toledo, Ohio, United States, affiliated with NBC. Owned by Sinclair Broadcast Group, the station maintains a transmitter on Cousino Road in Jerusalem Township. Its studios are located on South Byrn ...
24 (NBC
The National Broadcasting Company (NBC) is an American English-language commercial broadcast television and radio network. The flagship property of the NBC Entertainment division of NBCUniversal, a division of Comcast, its headquarters are l ...
), WGTE 30 (PBS)
The Public Broadcasting Service (PBS) is an American public broadcaster and non-commercial, free-to-air television network based in Arlington, Virginia. PBS is a publicly funded nonprofit organization and the most prominent provider of edu ...
, WUPW 36 (Fox), WLMB
WLMB (channel 40) is a religious independent television station in Toledo, Ohio, United States, owned by Dominion Broadcasting. The station's studios are located on Capital Commons Drive in Toledo, and its transmitter is located in Jasper, Michi ...
40 (Independent), and WMNT 48 (MyNetworkTV
MyNetworkTV (unofficially abbreviated MyTV, MyNet, MNT or MNTV, and sometimes referred to as My Network) is an American commercial broadcast television syndication service and former television network owned by Fox Corporation, operated by its ...
). WBGU 27 (PBS)
The Public Broadcasting Service (PBS) is an American public broadcaster and non-commercial, free-to-air television network based in Arlington, Virginia. PBS is a publicly funded nonprofit organization and the most prominent provider of edu ...
in Bowling Green is also viewable. Toledoans can also watch the adjacent Detroit market stations, both over-the air and on cable. There are also fourteen radio stations licensed in Toledo.
Infrastructure
Transportation
Major highways

interstate highway
The Dwight D. Eisenhower National System of Interstate and Defense Highways, commonly known as the Interstate Highway System, is a network of controlled-access highways that forms part of the National Highway System in the United States. T ...
s run through Toledo. Interstate 75
Interstate 75 (I-75) is a major north–south Interstate Highway in the Great Lakes and Southeastern regions of the United States. As with most Interstates that end in 5, it is a major cross-country, north–south route, traveling from St ...
(I-75) travels north–south and provides a direct route to Detroit and Cincinnati. The Ohio Turnpike
The Ohio Turnpike, officially the James W. Shocknessy Ohio Turnpike, is a limited-access toll highway in the U.S. state of Ohio, serving as a primary corridor between Chicago and Pittsburgh. The road runs east–west in the northern section of ...
carries east–west traffic on I- 80/ 90. The Turnpike serves Toledo via exits 52, 59, 64, 71, and 81. The Turnpike connects Toledo to Chicago
(''City in a Garden''); I Will
, image_map =
, map_caption = Interactive Map of Chicago
, coordinates =
, coordinates_footnotes =
, subdivision_type = List of sovereign states, Count ...
in the west and Cleveland
Cleveland ( ), officially the City of Cleveland, is a city in the United States, U.S. U.S. state, state of Ohio and the county seat of Cuyahoga County, Ohio, Cuyahoga County. Located in the northeastern part of the state, it is situated along ...
in the east.
In addition, there are two auxiliary interstate highways in the area. Interstate 475 is a 20-mile bypass that begins in Perrysburg and ends in west Toledo, meeting I-75 at both ends. It is cosigned with US 25 for its first 13 miles. Interstate 280 is a spur that connects the Ohio Turnpike to I-75 through east and central Toledo. The Veterans' Glass City Skyway
The Veterans' Glass City Skyway, commonly called the Toledo Skyway Bridge, is a cable-stayed bridge on Interstate 280 in Toledo, Ohio. After many delays, it opened in 2007. The bridge has taken traffic and reduced delays on the Robert Craig ...
is part of this route, which was the most expensive ODOT project ever at its completion. This tall bridge includes a glass covered pylon, which lights up at night, adding a distinctive feature to Toledo's skyline
A skyline is the outline or shape viewed near the horizon. It can be created by a city’s overall structure, or by human intervention in a rural setting, or in nature that is formed where the sky meets buildings or the land.
City skylin ...
. The Anthony Wayne Bridge
The Anthony Wayne Bridge, commonly called the High Level Bridge, was designed by Waddell & Hardesty and constructed by the McClintic-Marshall Company in 1931, and is a downtown Toledo, Ohio landmark named after General Anthony Wayne. It is a suspen ...
, a suspension bridge
A suspension bridge is a type of bridge in which the deck is hung below suspension cables on vertical suspenders. The first modern examples of this type of bridge were built in the early 1800s. Simple suspension bridges, which lack vertical ...
crossing the Maumee River
The Maumee River (pronounced ) ( sjw, Hotaawathiipi; mia, Taawaawa siipiiwi) is a river running in the United States Midwest from northeastern Indiana into northwestern Ohio and Lake Erie. It is formed at the confluence of the St. Joseph and ...
, has been a staple of Toledo's skyline for more than 80 years. It is locally known as the "High-Level Bridge."
Mass transit
Local bus service is provided by the Toledo Area Regional Transit Authority; commonly shortened to TARTA. Toledo area Paratransit Services; TARPS are used for the disabled. Intercity bus service is provided byGreyhound Lines
Greyhound Lines, Inc. (commonly known as simply Greyhound) operates the largest intercity bus service in North America, including Greyhound Mexico. It also operates charter bus services, Amtrak Thruway services, commuter bus services, and ...
and Barons Bus Lines
Barons Bus Lines is an intercity bus company operating in the United States. It serves passengers in the U.S. states of Illinois, Indiana, Michigan, New York, Ohio, Pennsylvania, and West Virginia. Barons Bus operates GoBus, a federally funded b ...
. The station is located at Martin Luther King, Jr. Plaza which it shares with Amtrak. Barons Bus Lines
Barons Bus Lines is an intercity bus company operating in the United States. It serves passengers in the U.S. states of Illinois, Indiana, Michigan, New York, Ohio, Pennsylvania, and West Virginia. Barons Bus operates GoBus, a federally funded b ...
also provides daily trips to Ann Arbor
Anne, alternatively spelled Ann, is a form of the Latin female given name Anna. This in turn is a representation of the Hebrew Hannah, which means 'favour' or 'grace'. Related names include Annie.
Anne is sometimes used as a male name in the ...
, Chicago
(''City in a Garden''); I Will
, image_map =
, map_caption = Interactive Map of Chicago
, coordinates =
, coordinates_footnotes =
, subdivision_type = List of sovereign states, Count ...
, Cleveland
Cleveland ( ), officially the City of Cleveland, is a city in the United States, U.S. U.S. state, state of Ohio and the county seat of Cuyahoga County, Ohio, Cuyahoga County. Located in the northeastern part of the state, it is situated along ...
, Detroit
Detroit ( , ; , ) is the largest city in the U.S. state of Michigan. It is also the largest U.S. city on the United States–Canada border, and the seat of government of Wayne County. The City of Detroit had a population of 639,111 at t ...
, Columbus
Columbus is a Latinized version of the Italian surname "''Colombo''". It most commonly refers to:
* Christopher Columbus (1451-1506), the Italian explorer
* Columbus, Ohio, capital of the U.S. state of Ohio
Columbus may also refer to:
Places ...
, and Cincinnati
Cincinnati ( ) is a city in the U.S. state of Ohio and the county seat of Hamilton County. Settled in 1788, the city is located at the northern side of the confluence of the Licking and Ohio rivers, the latter of which marks the state line w ...
. Toledo has various cab companies within its city limits and other ones that surround the metro.
Airports
Toledo Express Airport
Toledo Express Airport, officially Eugene F. Kranz Toledo Express Airport , is a civil-military airport in Swanton and Monclova townships west of Toledo in western Lucas County, Ohio, United States. It opened in 1954-55 as a replacement to t ...
, located in the suburbs of Monclova and Swanton Townships, is the primary airport that serves the city. Additionally, Detroit Metropolitan Wayne County Airport is 45 miles north. Toledo Executive Airport
Toledo Executive Airport is seven miles southeast of Toledo, in Wood County, Ohio. It is an FAA designated reliever to Toledo Express Airport (TOL), Toledo's primary airport. Toledo Executive Airport was renamed from Metcalf Field in 2010.
(formerly Metcalf Field) is a general aviation
General aviation (GA) is defined by the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) as all civil aviation aircraft operations with the exception of commercial air transport or aerial work, which is defined as specialized aviation services ...
airport southeast of Toledo near the I-280 and Ohio SR 795 interchange. Toledo Suburban Airport is another general aviation airport located in Lambertville, MI just north of the state border.
Railroads at present
Amtrak
The National Railroad Passenger Corporation, doing business as Amtrak () , is the national passenger railroad company of the United States. It operates inter-city rail service in 46 of the 48 contiguous U.S. States and nine cities in Canada. ...
, the national passenger rail system, provides service to Toledo and other major cities under the '' Capitol Limited'' and the '' Lake Shore Limited''. Both lines stop at Martin Luther King, Jr. Plaza, which was built as Central Union Terminal by the New York Central Railroad
The New York Central Railroad was a railroad primarily operating in the Great Lakes and Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States. The railroad primarily connected greater New York and Boston in the east with Chicago and St. Louis in the Mi ...
—along its Water Level Route
The New York Central Railroad was a railroad primarily operating in the Great Lakes and Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States. The railroad primarily connected greater New York and Boston in the east with Chicago and St. Louis in the Mid ...
—in 1950. Of the seven Ohio stations served by Amtrak, Toledo was the busiest in fiscal year 2011, boarding or detraining 66,413 passengers. Freight rail service presently in Toledo is operated by the Norfolk Southern Railway
The Norfolk Southern Railway is a Class I freight railroad in the United States formed in 1982 with the merger of Norfolk and Western Railway and Southern Railway. With headquarters in Atlanta, the company operates 19,420 route miles (31 ...
, CSX Transportation
CSX Transportation , known colloquially as simply CSX, is a Class I freight railroad operating in the Eastern United States and the Canadian provinces of Ontario and Quebec. The railroad operates approximately 21,000 route miles () of track. ...
, Canadian National Railway
The Canadian National Railway Company (french: Compagnie des chemins de fer nationaux du Canada) is a Canadian Class I freight railway headquartered in Montreal, Quebec, which serves Canada and the Midwestern and Southern United States.
CN i ...
, Ann Arbor Railroad, and Wheeling and Lake Erie Railway. All except the Wheeling have local terminals; the Wheeling operates into Toledo from the east through trackage rights
Railway companies can interact with and control others in many ways. These relationships can be complicated by bankruptcies.
Operating
Often, when a railroad first opens, it is only a short spur of a main line. The owner of the spur line may ...
on Norfolk Southern to connect with the Ann Arbor and CN railroads.
Railroads in the past
Historically, Toledo was a major rail hub where theNew York Central
The New York Central Railroad was a railroad primarily operating in the Great Lakes and Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States. The railroad primarily connected greater New York and Boston in the east with Chicago and St. Louis in the Mid ...
(later, the Penn Central
The Penn Central Transportation Company, commonly abbreviated to Penn Central, was an American class I railroad that operated from 1968 to 1976. Penn Central combined three traditional corporate rivals (the Pennsylvania, New York Central and th ...
), Baltimore and Ohio
The Baltimore and Ohio Railroad was the first common carrier railroad and the oldest railroad in the United States, with its first section opening in 1830. Merchants from Baltimore, which had benefited to some extent from the construction of ...
, Wabash Railroad
The Wabash Railroad was a Class I railroad that operated in the mid-central United States. It served a large area, including track in the states of Ohio, Indiana, Illinois, Iowa, Michigan, and Missouri and the province of Ontario. Its primary co ...
, Nickel Plate Road
The New York, Chicago and St. Louis Railroad , abbreviated NYC&St.L, was a railroad that operated in the mid-central United States. Commonly referred to as the "Nickel Plate Road", the railroad served parts of the states of New York, Pennsylv ...
, Ann Arbor Railroad, Detroit, Toledo and Ironton Railroad, Toledo, Peoria and Western Railway
The Toledo, Peoria and Western Railway is a short line railroad that operates of track from Mapleton, Illinois, through Peoria across Illinois to Logansport, Indiana. TP&W has trackage rights between Galesburg, Illinois, and Peoria, between Lo ...
, Pennsylvania Railroad
The Pennsylvania Railroad (reporting mark PRR), legal name The Pennsylvania Railroad Company also known as the "Pennsy", was an American Class I railroad that was established in 1846 and headquartered in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. It was named ...
, Chesapeake and Ohio Railway
The Chesapeake and Ohio Railway was a Class I railroad formed in 1869 in Virginia from several smaller Virginia railroads begun in the 19th century. Led by industrialist Collis P. Huntington, it reached from Virginia's capital city of Richmond t ...
/Pere Marquette Railway
The Pere Marquette Railway operated in the Great Lakes region of the United States and southern parts of Ontario in Canada. It had trackage in the states of Michigan, Ohio, Indiana and the Canadian province of Ontario. Its primary connections in ...
, Wheeling and Lake Erie railroads moved a large amount of freight to and from Toledo's many industries such as Libbey-Owens-Ford Glass, and Willys-Overland (Jeep) Motors. Most of these companies used Central Union Terminal on Emerald Avenue. The Ann Arbor Railroad used its station on Cherry Street. The Pennsylvania Railroad used its station on Summit Street.
Interurbans
Toledo had astreetcar
A tram (called a streetcar or trolley in North America) is a rail vehicle that travels on tramway tracks on public urban streets; some include segments on segregated right-of-way. The tramlines or networks operated as public transport a ...
system and interurban
The Interurban (or radial railway in Europe and Canada) is a type of electric railway, with streetcar-like electric self-propelled rail cars which run within and between cities or towns. They were very prevalent in North America between 1900 ...
railways linking it to other nearby towns but these are no longer in existence. Seven interurban companies radiated from Toledo. In the early 1930s, three of the seven, the Cincinnati and Lake Erie from Cincinnati, Columbus, Dayton, and Springfield, the Lake Shore Electric from Cleveland, and the Eastern Michigan Ry from Detroit, moved a large amount of freight and number of passengers between those heavily industrialized cities. The Great Depression and growing inter city competition from trucks on newly improved roads by the Ohio caused abandonment of all by 1938, and some interurban lines much earlier. The interurban station where all lines met and exchanged passengers was on N. Summit Street. Freight was exchanged in a rail yard with a warehouse off Lucas Street.
Healthcare
Originating in Toledo,ProMedica
ProMedica is a non-profit health care system with locations in northwest Ohio and southeast Michigan. The system includes a health education and research center, the health maintenance organization Paramount Health Care, nursing homes, a loc ...
is an integrated healthcare organization founded in 2009. It has grown rapidly to become the country's 15th largest non-profit
A nonprofit organization (NPO) or non-profit organisation, also known as a non-business entity, not-for-profit organization, or nonprofit institution, is a legal entity organized and operated for a collective, public or social benefit, in co ...
health care system
Health, according to the World Health Organization, is "a state of complete physical, Mental health, mental and social well-being and not merely the absence of disease and infirmity".World Health Organization. (2006)''Constitution of the World H ...
in the United States, with 2018 revenues of $7 billion. It is headquartered on Madison Avenue in Downtown Toledo and maintains 13 hospitals in Northwest Ohio and Southeast Michigan, including ProMedica Toledo Hospital
ProMedica Toledo Hospital is a 794-bed non-profit hospital in Toledo, Ohio operated by ProMedica. The hospital is a Level I trauma center and the largest acute care hospital in the Toledo metropolitan area with at least 4,800 health care professi ...
, the largest acute care hospital in the area.
Mercy Health - St. Vincent Medical Center, Toledo's first hospital and part of
Mercy Health Partners
Mercy Health, formerly Catholic Health Partners, is a Catholic health care system with locations in Ohio and Kentucky. Cincinnati-based Mercy Health operates more than 250 healthcare organizations in Ohio and Kentucky. Mercy Health is the largest h ...
, holds the highest designation for treating high-risk mothers and babies, is a Level I Trauma Center for children and adults, and is an accredited Chest Pain Center. It is located in the Vistula Historic District
Vistula Historic District is a designated historic district in the city of Toledo, Ohio, USA, listed on the National Register of Historic Places. The district comprises Toledo's oldest extant neighborhood and encompasses an area roughly bounded ...
on the city's north side.
There are also 18 community health centers
A healthcare center, health center, or community health center is one of a network of clinics staffed by a group of general practitioners and nurses providing healthcare services to people in a certain area. Typical services covered are family pr ...
in Toledo. Some examples include the Cordelia Martin Community Health Center, the East Toledo Community Health Center, and the Monroe Street Neighborhood Center.
Utilities
Water
The Division of Water Treatment filters an average of 80 million gallons of water per day for 500,000 people in the greater Toledo Metropolitan area. The Division of Water Distribution serves 136,000 metered accounts and 10,000 fire hydrants and maintains more than of water mains. The Toledo Metropolitan Area receives its water from Lake Erie, with the process being managed by the City of Toledo Public Utilities Water Treatment Division, under the authority of the Mayor and City Council with direction provided by the Toledo Regional Water Commission. Water is collected through a water intake pipe that is situated a few miles off the shore of Lake Erie. In August 2014, two samples from a water treatment plant toxin test showed signs ofmicrocystis
''Microcystis'' is a genus of freshwater cyanobacteria that includes the harmful algal bloom-forming ''Microcystis aeruginosa''. Many members of a ''Microcystis'' community can produce neurotoxins and hepatotoxins, such as microcystin and cyan ...
. Roughly 400,000, including residents of Toledo and several surrounding communities in Ohio and Michigan were affected by the water contamination. Residents were told not to use, drink, cook with, or boil any tap water on the evening of August 1, 2014. The Ohio National Guard
The Ohio National Guard comprises the Ohio Army National Guard and the Ohio Air National Guard. The commander-in-chief of the Ohio Army National Guard is the governor of the U.S. state of Ohio. If the Ohio Army National Guard is called to f ...
delivered water and food to residents living in contaminated areas. , no one had reported being sick and the governor had declared a state of emergency in three counties. The ban was lifted on August 4.
Notable people
Sister cities
Toledo was twinned withToledo, Spain
Toledo ( , ) is a city and municipality of Spain, capital of the province of Toledo and the ''de jure'' seat of the government and parliament of the autonomous community of Castilla–La Mancha. Toledo was declared a World Heritage Site by UN ...
, in 1931, creating the first sister city
A sister city or a twin town relationship is a form of legal or social agreement between two geographically and politically distinct localities for the purpose of promoting cultural and commercial ties.
While there are early examples of inter ...
relationship in the United States.
Toledo's sister cities are:
* Beqaa Valley
The Beqaa Valley ( ar, links=no, وادي البقاع, ', Lebanese ), also transliterated as Bekaa, Biqâ, and Becaa and known in classical antiquity as Coele-Syria, is a fertile valley in eastern Lebanon. It is Lebanon's most important ...
, Lebanon
* Coburg
Coburg () is a town located on the Itz river in the Upper Franconia region of Bavaria, Germany. Long part of one of the Thuringian states of the Wettin line, it joined Bavaria by popular vote only in 1920. Until the revolution of 1918, it ...
, Germany
* Coimbatore
Coimbatore, also spelt as Koyamputhur (), sometimes shortened as Kovai (), is one of the major metropolitan cities in the Indian state of Tamil Nadu. It is located on the banks of the Noyyal River and surrounded by the Western Ghats. Coimbat ...
, India
* Delmenhorst
Delmenhorst (; Northern Low Saxon: ''Demost'') is an urban district ('' Kreisfreie Stadt'') in Lower Saxony, Germany. It has a population of 74,500 and is located west of downtown Bremen with which it forms a contiguous urban area, whereas the ...
, Germany
* Hyderabad
Hyderabad ( ; , ) is the capital and largest city of the Indian state of Telangana and the ''de jure'' capital of Andhra Pradesh. It occupies on the Deccan Plateau along the banks of the Musi River, in the northern part of Southern Indi ...
, Pakistan
* Londrina, Brazil
* Nanchong
Nanchong (; Sichuanese: lan2cong1) is a prefecture-level city in the northeast of Sichuan province, China, with an area of . At the 2020 census it was home to 5,607,565 people, of whom 1,936,534 lived in the built-up (or 'metro') area made of th ...
, China
* Poznań
Poznań () is a city on the River Warta in west-central Poland, within the Greater Poland region. The city is an important cultural and business centre, and one of Poland's most populous regions with many regional customs such as Saint Joh ...
, Poland
* Qinhuangdao
Qinhuangdao (; ) is a port city on the coast of China in northern Hebei. It is administratively a prefecture-level city, about east of Beijing, on the Bohai Sea, the innermost gulf of the Yellow Sea. Its population during the 2020 national ...
, China
* Szeged
Szeged ( , ; see also other alternative names) is the third largest city of Hungary, the largest city and regional centre of the Southern Great Plain and the county seat of Csongrád-Csanád county. The University of Szeged is one of the m ...
, Hungary
* Tanga, Tanzania
* Toledo, Spain
* Toyohashi
is a city in Aichi Prefecture, Japan. , the city had an estimated population of 377,453 in 160,516 households and a population density of 1,400 persons per km2. The total area of the city was . By area, Toyohashi was Aichi Prefecture's second-lar ...
, Japan
See also
* Auto-Lite strike * Baseball parks of Toledo, Ohio * Glassmen Drum and Bugle Corps, Drum Corps International World Class Drum and Bugle Corps * Greater Toledo * Outbreak of green-blue algae in Lake Erie * Roman Catholic Diocese of Toledo * Toledo Area Regional Transit Authority, local bus transportation * Toledo City League, high school sports leagueNotes
References
Further reading
* * DeMatteo, Arthur Edward. "Urban reform, politics, and the working class: Detroit, Toledo, and Cleveland, 1890-1922" (PhD dissertation, University of Akron; ProQuest Dissertations Publishing, 1999. 9940602).External links
Official website
Greater Toledo Convention and Visitors Bureau
Toledo, Ohio, 1876
from the
World Digital Library
The World Digital Library (WDL) is an international digital library operated by UNESCO and the United States Library of Congress.
The WDL has stated that its mission is to promote international and intercultural understanding, expand the volume ...
* AbouToledo, Ohio
(via Britannica) {{Authority control Cities in Ohio Cities in Lucas County, Ohio County seats in Ohio Ohio populated places on Lake Erie Populated places established in 1833 1833 establishments in Ohio Inland port cities and towns in Ohio