Token coins on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In
In
 Coin-like objects from the
Coin-like objects from the  Most such tokens show the issuer's full name or initials. Where initials were shown, it was common practice to show three initials: the first names of husband and wife and their surname. Tokens would also normally indicate the merchant establishment, either by name or by picture. Most were round, but they are also found in square, heart or octagonal shapes.
Thousands of towns and merchants issued these tokens from 1648 until 1672, when official production of farthings resumed, and private production was suppressed.
There were again coin shortages in the late 18th century, when the British
Most such tokens show the issuer's full name or initials. Where initials were shown, it was common practice to show three initials: the first names of husband and wife and their surname. Tokens would also normally indicate the merchant establishment, either by name or by picture. Most were round, but they are also found in square, heart or octagonal shapes.
Thousands of towns and merchants issued these tokens from 1648 until 1672, when official production of farthings resumed, and private production was suppressed.
There were again coin shortages in the late 18th century, when the British  These were issued by merchants in payment for goods with the agreement that they would be redeemed in goods to an equivalent value at the merchants' own outlets. The transaction is therefore one of barter, with the tokens playing a role of convenience, allowing the seller to receive his goods at a rate and time convenient to himself, and the merchant to tie the holder of the token coin to his shop. Trade tokens often gradually changed into barter tokens, as evidenced by the continued circulation of former trade tokens when the need for their use had passed.
These were issued by merchants in payment for goods with the agreement that they would be redeemed in goods to an equivalent value at the merchants' own outlets. The transaction is therefore one of barter, with the tokens playing a role of convenience, allowing the seller to receive his goods at a rate and time convenient to himself, and the merchant to tie the holder of the token coin to his shop. Trade tokens often gradually changed into barter tokens, as evidenced by the continued circulation of former trade tokens when the need for their use had passed.
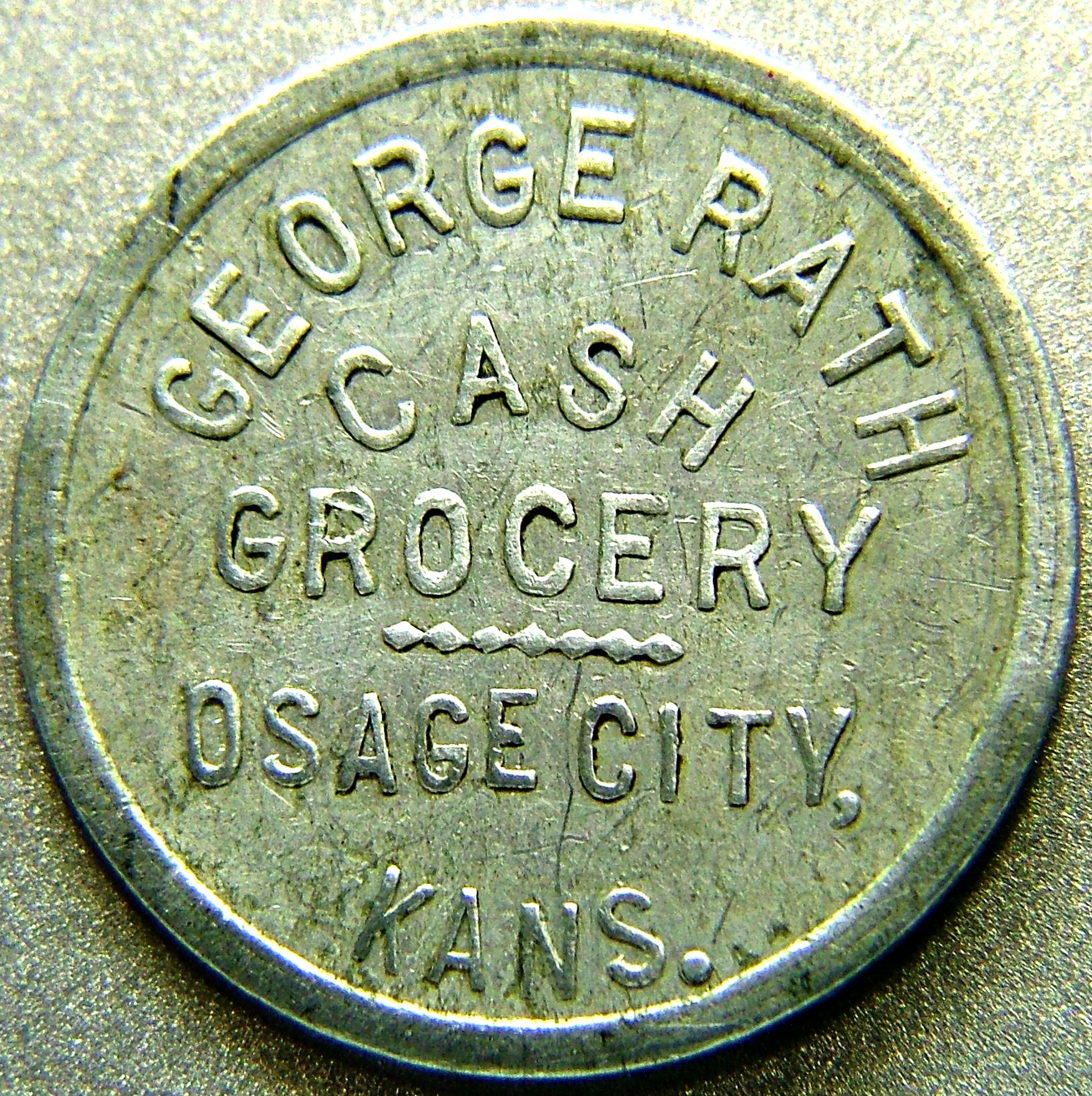 In the United States of America, Hard times tokens issued from 1832 to 1844 and
In the United States of America, Hard times tokens issued from 1832 to 1844 and
 Metal token coins are used in lieu of cash in some coin-operated
Metal token coins are used in lieu of cash in some coin-operated

 *
*
New York City Subway Tokens
Museum of English Rural Life Trade Tokens
{{DEFAULTSORT:Token Coin Fare collection systems Exonumia
 In
In numismatics
Numismatics is the study or collection of currency, including coins, tokens, paper money, medals and related objects.
Specialists, known as numismatists, are often characterized as students or collectors of coins, but the discipline also includ ...
, token coins or trade tokens are coin-like objects used instead of coin
A coin is a small, flat (usually depending on the country or value), round piece of metal or plastic used primarily as a medium of exchange or legal tender. They are standardized in weight, and produced in large quantities at a mint in order to ...
s. The field of token coins is part of exonumia
Exonumia are numismatic items (such as tokens, medals, or scrip) other than coins and paper money. This includes "Good For" tokens, badges, counterstamped coins, elongated coins, encased coins, souvenir medallions, tags, wooden nickels and o ...
and token coins are token money
Token money, or token, is a form of money that has a lesser intrinsic value compared to its face value. Token money is anything that is accepted as money, not due to its intrinsic value but instead because of custom or legal enactment. Token mo ...
. Their denomination is shown or implied by size, color or shape. They are often made of cheaper metals like copper, pewter
Pewter () is a malleable metal alloy consisting of tin (85–99%), antimony (approximately 5–10%), copper (2%), bismuth, and sometimes silver. Copper and antimony (and in antiquity lead) act as hardeners, but lead may be used in lower grades ...
, aluminium
Aluminium (aluminum in American and Canadian English) is a chemical element with the symbol Al and atomic number 13. Aluminium has a density lower than those of other common metals, at approximately one third that of steel. It has ...
, brass
Brass is an alloy of copper (Cu) and zinc (Zn), in proportions which can be varied to achieve different mechanical, electrical, and chemical properties. It is a substitutional alloy: atoms of the two constituents may replace each other wit ...
and tin
Tin is a chemical element with the symbol Sn (from la, stannum) and atomic number 50. Tin is a silvery-coloured metal.
Tin is soft enough to be cut with little force and a bar of tin can be bent by hand with little effort. When bent, t ...
, or non-metals like bakelite
Polyoxybenzylmethylenglycolanhydride, better known as Bakelite ( ), is a thermosetting polymer, thermosetting phenol formaldehyde resin, formed from a condensation reaction of phenol with formaldehyde. The first plastic made from synthetic compo ...
, leather
Leather is a strong, flexible and durable material obtained from the tanning, or chemical treatment, of animal skins and hides to prevent decay. The most common leathers come from cattle, sheep, goats, equine animals, buffalo, pigs and hogs ...
and porcelain
Porcelain () is a ceramic material made by heating substances, generally including materials such as kaolinite, in a kiln to temperatures between . The strength and translucence of porcelain, relative to other types of pottery, arises mainl ...
.
A legal tender
Legal tender is a form of money that courts of law are required to recognize as satisfactory payment for any monetary debt. Each jurisdiction determines what is legal tender, but essentially it is anything which when offered ("tendered") in pa ...
coin is issued by a governmental authority and is freely exchangeable for goods. A token coin is less useful and issued by a private entity.
Trade or barter
 Coin-like objects from the
Coin-like objects from the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post-Roman Republic, Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings aro ...
called have been interpreted as an early form of token. Their functions are not documented, but they appear to have been brothel tokens or possibly gaming tokens.
Medieval English monasteries issued tokens to pay for services from outsiders. These tokens circulated in nearby villages, where they were called "Abbot's money". Also, counters called jeton
Jetons or jettons are tokens or coin-like medals produced across Europe from the 13th through the 18th centuries. They were produced as counters for use in calculation on a counting board, a lined board similar to an abacus. They also found use ...
s were used as small change without official blessing.
From the 17th to the early 19th century in the British Isles
The British Isles are a group of islands in the North Atlantic Ocean off the north-western coast of continental Europe, consisting of the islands of Great Britain, Ireland, the Isle of Man, the Inner and Outer Hebrides, the Northern Isles, ...
(and also elsewhere in the British Empire
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading posts esta ...
) and North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the C ...
, tokens were commonly issued by merchants in times of acute shortage of coins of the state. These tokens were in effect a pledge redeemable in goods, but not necessarily for currency. These tokens never received official sanction from government but were accepted and circulated quite widely.
In England, the production of copper farthing
Farthing or farthings may refer to:
Coinage
*Farthing (British coin), an old British coin valued one quarter of a penny
** Half farthing (British coin)
** Third farthing (British coin)
** Quarter farthing (British coin)
*Farthing (English c ...
s was permitted by royal licence in the first few decades of the 17th century, but production ceased during the English Civil War
The English Civil War (1642–1651) was a series of civil wars and political machinations between Parliamentarians ("Roundheads") and Royalists led by Charles I ("Cavaliers"), mainly over the manner of Kingdom of England, England's governanc ...
and a great shortage of small change resulted. This shortage was felt more keenly because of the rapid growth of trade in the towns and cities, and this in turn prompted both local authorities and merchants to issue tokens.
These tokens were most commonly made of copper or brass
Brass is an alloy of copper (Cu) and zinc (Zn), in proportions which can be varied to achieve different mechanical, electrical, and chemical properties. It is a substitutional alloy: atoms of the two constituents may replace each other wit ...
, but pewter
Pewter () is a malleable metal alloy consisting of tin (85–99%), antimony (approximately 5–10%), copper (2%), bismuth, and sometimes silver. Copper and antimony (and in antiquity lead) act as hardeners, but lead may be used in lower grades ...
, lead
Lead is a chemical element with the symbol Pb (from the Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a heavy metal that is denser than most common materials. Lead is soft and malleable, and also has a relatively low melting point. When freshly cut, l ...
and occasionally leather
Leather is a strong, flexible and durable material obtained from the tanning, or chemical treatment, of animal skins and hides to prevent decay. The most common leathers come from cattle, sheep, goats, equine animals, buffalo, pigs and hogs ...
tokens are also found. Most were not given a specific denomination and were intended to substitute for farthing
Farthing or farthings may refer to:
Coinage
*Farthing (British coin), an old British coin valued one quarter of a penny
** Half farthing (British coin)
** Third farthing (British coin)
** Quarter farthing (British coin)
*Farthing (English c ...
s, but there are also a large number of halfpenny and sometimes penny
A penny is a coin ( pennies) or a unit of currency (pl. pence) in various countries. Borrowed from the Carolingian denarius (hence its former abbreviation d.), it is usually the smallest denomination within a currency system. Presently, it is ...
tokens. Halfpenny and penny tokens usually, but not always, bear the denomination on their face.
Royal Mint
The Royal Mint is the United Kingdom's oldest company and the official maker of British coins.
Operating under the legal name The Royal Mint Limited, it is a limited company that is wholly owned by His Majesty's Treasury and is under an exclu ...
almost ceased production. Merchants once again produced tokens, but they were now machine made and typically larger than their 17th century predecessors, with values of a halfpenny or more. While many were used in trade, they were also produced for advertising and political purposes, and some series were produced for the primary purpose of sale to collectors. These tokens are usually known as Conder token
Conder tokens, also known as 18th-century provincial tokens, were a form of privately minted token coinage struck and used during the latter part of the 18th century and the early part of the 19th century in England, Anglesey and Wales, Scotland ...
s, after the writer of the first reference book on them.
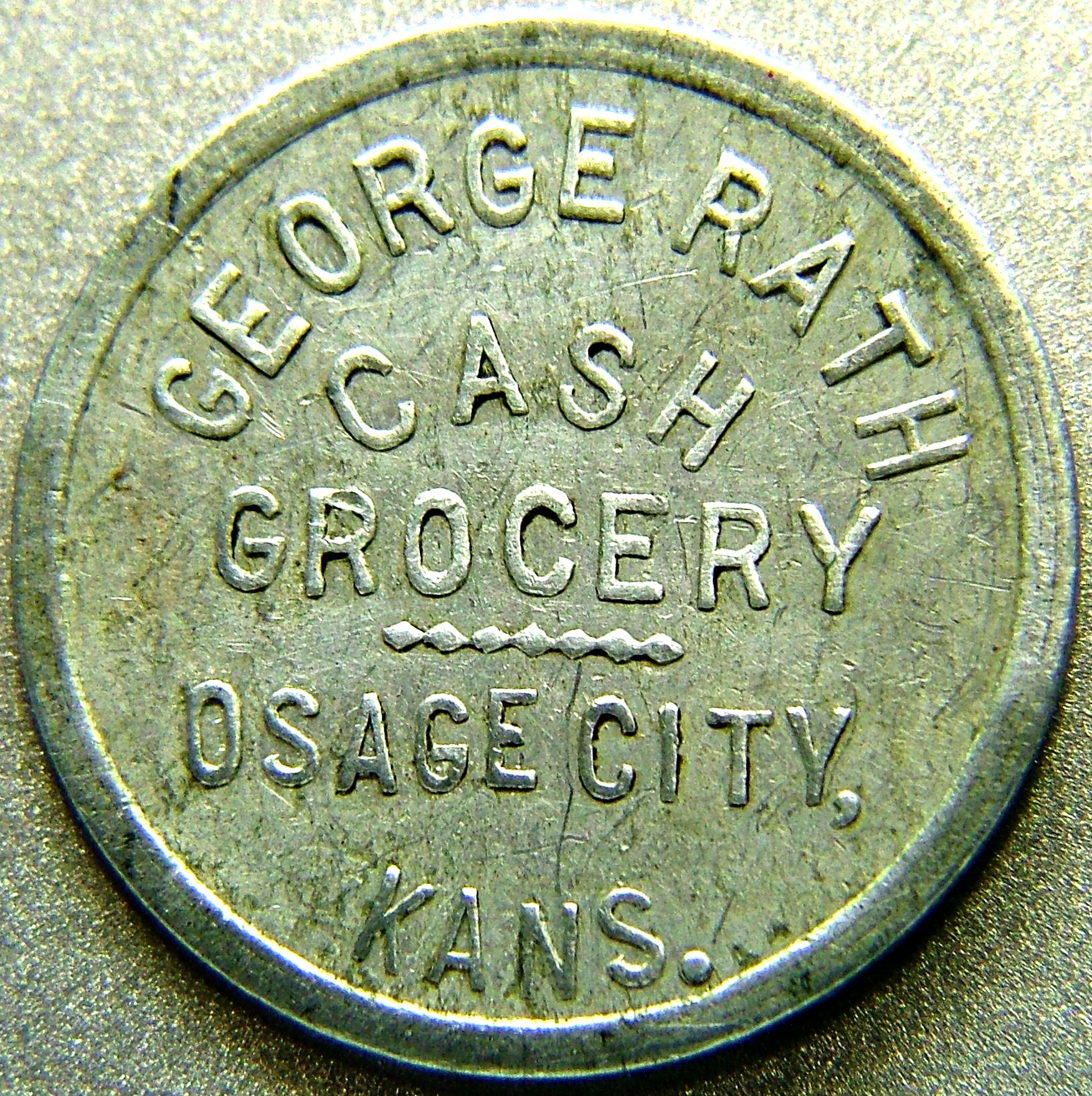 In the United States of America, Hard times tokens issued from 1832 to 1844 and
In the United States of America, Hard times tokens issued from 1832 to 1844 and Civil War token
Civil War tokens are token coins that were privately minted and distributed in the United States between 1861 and 1864. They were used mainly in the Northeast and Midwest. The widespread use of the tokens was a result of the scarcity of government ...
s issued in the 1860s made up for shortages of official money.A Guide Book of United States Coins, R. S. Yeoman and Kenneth Bresset, pages 372 and 376 of the 61st edition
Because of weight, the U.S. Treasury Department
The Department of the Treasury (USDT) is the national treasury and finance department of the federal government of the United States, where it serves as an executive department. The department oversees the Bureau of Engraving and Printing and ...
does not ship coins to the Armed Forces serving overseas, so Army and Air Force Exchange Service officials chose to make pogs in denominations of 5, 10, and 25 cents. The pogs are about 38 mm (1.5816″ to be exact) in diameter, and feature various military-themed graphics.
The collecting of trade tokens is part of the field of exonumia
Exonumia are numismatic items (such as tokens, medals, or scrip) other than coins and paper money. This includes "Good For" tokens, badges, counterstamped coins, elongated coins, encased coins, souvenir medallions, tags, wooden nickels and o ...
, and includes other types of tokens, including transit tokens, encased cents, and many others. In a narrow sense, trade tokens are "good for" tokens, issued by merchants. Generally, they have a merchant's name or initials, sometimes a town and state, and a value legend (such as "good for 5¢" or other denomination) somewhere on the token. Merchants that issued tokens included general stores, grocers, department stores, dairies, meat markets, drug stores, saloons, bars, taverns, barbers, coal mines, lumber mills and many other businesses. The era of 1870 through 1920 marked the highest use of "trade tokens" in the United States, spurred by the proliferation of small stores in rural areas. There were thousands of small general and merchandise stores all over the United States, and many of them used trade tokens to promote trade and extend credit to customers. Aluminum
Aluminium (aluminum in American and Canadian English) is a chemical element with the symbol Al and atomic number 13. Aluminium has a density lower than those of other common metals, at approximately one third that of steel. It h ...
tokens almost always date after 1890, when low-cost production began.
Slot machines
 Metal token coins are used in lieu of cash in some coin-operated
Metal token coins are used in lieu of cash in some coin-operated arcade game
An arcade game or coin-op game is a coin-operated entertainment machine typically installed in public businesses such as restaurants, bars and amusement arcades. Most arcade games are presented as primarily games of skill and include arcade ...
s and casino
A casino is a facility for certain types of gambling. Casinos are often built near or combined with hotels, resorts, restaurants, retail shopping, cruise ships, and other tourist attractions. Some casinos are also known for hosting live entertai ...
slot machine
A slot machine (American English), fruit machine (British English) or poker machine (Australian English and New Zealand English) is a gambling machine that creates a game of chance for its customers. Slot machines are also known pejoratively a ...
s. Money is exchanged for the token coins or chips
''CHiPs'' is an American crime drama television series created by Rick Rosner and originally aired on NBC from September 15, 1977, to May 1, 1983. It follows the lives of two motorcycle officers of the California Highway Patrol (CHP). The se ...
in a casino at the casino cage, gaming tables, slot machines or cashier stations for slot token coins. The tokens are interchangeable with money at the casino and generally have no value outside of the casino.
In many jurisdictions, casinos are not permitted to use currency in slot machines, necessitating tokens for smaller denominations. After the increase in the value of silver stopped the circulation of silver coins in the United States around 1964, casinos rushed to find a substitute, as most slot machine
A slot machine (American English), fruit machine (British English) or poker machine (Australian English and New Zealand English) is a gambling machine that creates a game of chance for its customers. Slot machines are also known pejoratively a ...
s at that time used that particular coin. The Nevada State Gaming Control Board consulted with the U.S. Treasury, and casinos were soon allowed to start using their own tokens to operate their slot machines. The Franklin Mint
The Franklin Mint is a private mint founded by Joseph Segel in 1964 in Wawa, Pennsylvania. The building is in Middletown Township.
The brand name was previously owned by Sequential Brands Group headquartered in New York City, New York. It is ...
was the main minter of casino tokens at that time.
In 1971, many casinos adopted the Eisenhower Dollar
The Eisenhower dollar was a one-dollar coin issued by the United States Mint from 1971 to 1978; it was the first coin of that denomination issued by the Mint since the Peace dollar series ended in 1935. The coin depicts President Dwight D. E ...
for use in machines and on tables. When the dollar was replaced with the Susan B. Anthony dollar
The Susan B. Anthony dollar is a United States dollar coin minted from 1979 to 1981 when production was suspended due to poor public acceptance, and then again in 1999. Intended as a replacement for the larger Eisenhower dollar, the new smalle ...
in 1979, most casinos reinstituted tokens, fearing confusion with quarters and not wishing to extensively retool their slot machines. Those casinos which still use tokens in slot machines still use Eisenhower-sized ones.
Tokens are being phased out by many casinos in favor of coinless machines which accept banknotes and print receipts for payout. These receipts, abbreviated "TITOs" for ticket-in, ticket-out, can also be inserted into the machines. In video arcades, they are also being phased out in favor of magnetic cards, which can also count how many tickets one has, allowing arcades to also do away with paper tickets.
Other services

Railway
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the vehicles run on a prep ...
s and public transport
Public transport (also known as public transportation, public transit, mass transit, or simply transit) is a system of transport for passengers by group travel systems available for use by the general public unlike private transport, typical ...
agencies used fare tokens for years, to sell rides in advance at a discount, or to allow patrons to use turnstile
A turnstile (also called a turnpike, gateline, baffle gate, automated gate, turn gate in some regions) is a form of gate which allows one person to pass at a time. A turnstile can be configured to enforce one-way human traffic. In addition, a t ...
s geared only to take tokens (as opposed to coins, currency, or fare cards
A fare is the fee paid by a passenger for use of a public transport system: rail, bus, taxi, etc. In the case of air transport, the term airfare is often used. Fare structure is the system set up to determine how much is to be paid by various pas ...
). Many transport organizations still offer their own tokens for bus
A bus (contracted from omnibus, with variants multibus, motorbus, autobus, etc.) is a road vehicle that carries significantly more passengers than an average car or van. It is most commonly used in public transport, but is also in use for cha ...
and subway services, toll bridges, tunnels, and highways, although the use of computer-readable tickets has replaced these in most areas.
 *
* Car wash
A car wash, carwash, or auto wash is a facility used to clean the exterior, and in some cases the interior of motor vehicles. Car washes can be self-service, full-service (with attendants who wash the vehicle), or fully automated (possi ...
es – Though their use has decreased in favor of coins and credit card
A credit card is a payment card issued to users (cardholders) to enable the cardholder to pay a merchant for goods and services based on the cardholder's accrued debt (i.e., promise to the card issuer to pay them for the amounts plus the o ...
s.
* Video arcade
An amusement arcade (often referred to as a video arcade, amusements or simply arcade) is a venue where people play arcade games, including arcade video games, pinball machines, electro-mechanical games, redemption games, merchandisers (such as ...
s
* Parking garage
A multistorey car park (British and Singapore English) or parking garage (American English), also called a multistory, parking building, parking structure, parkade (mainly Canadian), parking ramp, parking deck or indoor parking, is a build ...
s
* Pay toilet
A pay toilet is a public toilet that requires the user to pay. It may be street furniture or be inside a building, e.g. a shopping mall, department store, or railway station. The reason for charging money is usually for the maintenance of the equ ...
s
* Subways
* Shopping cart rental
* Public telephone booths in countries with unstable currency were usually configured to accept tokens sold by the telephone company for variable prices. This system was in effect in Brazil until 1997 when magnetic cards were introduced. The practice was also recently discontinued in Israel, leading to a trend of wearing the devalued tokens as necklaces.
* Fast food
Fast food is a type of mass-produced food designed for commercial resale, with a strong priority placed on speed of service. It is a commercial term, limited to food sold in a restaurant or store with frozen, preheated or precooked ingredien ...
restaurant
A restaurant is a business that prepares and serves food and drinks to customers. Meals are generally served and eaten on the premises, but many restaurants also offer take-out and food delivery services. Restaurants vary greatly in appearance ...
s – Often given to children to collect and redeem for prizes.
* Commemorative coin
Commemorative coins are coins issued to commemorate some particular event or issue with a distinct design with reference to the occasion on which they were issued. Many coins of this category serve as collectors items only, although some countries ...
s have been produced with no monetary value to distribute by a company, country or organization.
In North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the C ...
tokens were originally issued by merchants from the 18th century in regions where national or local colonial governments did not issue enough small denomination coins for circulation. They were later used to create a monopoly
A monopoly (from Greek el, μόνος, mónos, single, alone, label=none and el, πωλεῖν, pōleîn, to sell, label=none), as described by Irving Fisher, is a market with the "absence of competition", creating a situation where a speci ...
; to pay labor; for discounts (pay in advance, get something free or discounted); or for a multitude of other reasons. In the United States, a well-known type is the wooden nickel, a five-cent piece distributed by cities to raise money for their anniversaries in the 1940s to 1960s.
Churches used to give tokens to members passing a religious test prior to the day of communion, then required the token for entry. While mostly Scottish Protestant, some U.S. churches used communion tokens. Generally, these were pewter
Pewter () is a malleable metal alloy consisting of tin (85–99%), antimony (approximately 5–10%), copper (2%), bismuth, and sometimes silver. Copper and antimony (and in antiquity lead) act as hardeners, but lead may be used in lower grades ...
, often cast by the minister in church-owned molds. Replicas of these tokens have been made available for sale at some churches recently.
See also
References
Further reading
*Angus, Ian. ''Coins & Money Tokens''. London:Ward Lock
Ward, Lock & Co. was a publishing house in the United Kingdom that started as a partnership and developed until it was eventually absorbed into the publishing combine of Orion Publishing Group.
History
Ebenezer Ward and George Lock started a pu ...
, 1973.
*"Church Tokens", ''New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''the Times'', ''NYT'', or the Gray Lady) is a daily newspaper based in New York City with a worldwide readership reported in 2020 to comprise a declining 840,000 paid print subscribers, and a growing 6 million paid ...
'', 11 April 1993
External links
New York City Subway Tokens
Museum of English Rural Life Trade Tokens
{{DEFAULTSORT:Token Coin Fare collection systems Exonumia