Teething on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 Teething is the process by which an
Teething is the process by which an
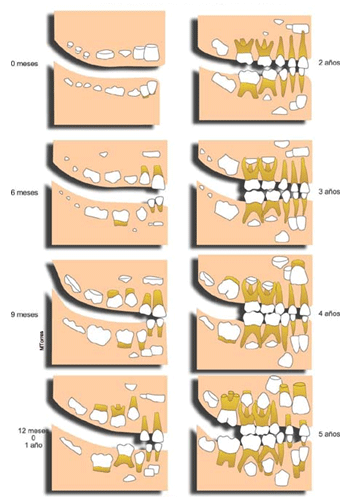 The infant teeth tend to emerge in pairs – first one lower incisor emerges, then the other lower incisor, after which the next set begin to emerge. The general pattern of emergence is:
# Lower central incisors (2) at approximately 6 months
# Upper central incisors (2) at approximately 8 months
# Upper lateral incisors (2) at approximately 10 months
# Lower lateral incisors (2) at approximately 10 months
# First molars (4) at approximately 14 months
# Canines (4) at approximately 18 months
# Second molars (4) at approximately 2–3 years
Milk teeth tend to emerge sooner in females than in males. The exact pattern and initial starting times of teething appear to be hereditary. When and how teeth appear in an infant has no bearing on the health of the child.
The infant teeth tend to emerge in pairs – first one lower incisor emerges, then the other lower incisor, after which the next set begin to emerge. The general pattern of emergence is:
# Lower central incisors (2) at approximately 6 months
# Upper central incisors (2) at approximately 8 months
# Upper lateral incisors (2) at approximately 10 months
# Lower lateral incisors (2) at approximately 10 months
# First molars (4) at approximately 14 months
# Canines (4) at approximately 18 months
# Second molars (4) at approximately 2–3 years
Milk teeth tend to emerge sooner in females than in males. The exact pattern and initial starting times of teething appear to be hereditary. When and how teeth appear in an infant has no bearing on the health of the child.
 Infants may chew on objects to aid in the teething process. Teething necklaces or bracelets are not recommended as they can cause choking, strangulation, or irritation of the mouth. Teething rings and other toys, called teethers, are often designed with textures. Some infants gain relief from chewing on cold objects. Some people freeze small chunks of fresh fruits or vegetables and put them in teething nets.
Infants may chew on objects to aid in the teething process. Teething necklaces or bracelets are not recommended as they can cause choking, strangulation, or irritation of the mouth. Teething rings and other toys, called teethers, are often designed with textures. Some infants gain relief from chewing on cold objects. Some people freeze small chunks of fresh fruits or vegetables and put them in teething nets.
 Teething used to be considered (wrongly) a cause of death, as many children died in the first years of life, at the same time as teething occurs. "The tendency in the past to attribute serious disease to teething was so prevalent that in 1842 teething was the registered cause of death in 4.8% of all infants who died in London under the age of 1 year and 7.3% of those between the ages of 1 to 3 years according to the Registrar General's report."
Ironically, while teething is a natural process which creates little more than discomfort, some methods for relieving teething pain have caused serious harm and even death. Old remedies for teething include "blistering, bleeding, placing leeches on the gums, and applying cautery to the back of the head". In the sixteenth century the French surgeon Ambroise Paré introduced the lancing of gums using a lancet, in the belief that teeth were failing to emerge from the gums due to lack of a pathway, and that this failure was a cause of death. This belief and practice persisted for centuries, with some exceptions, until towards the end of the nineteenth century lancing became increasingly controversial and was then abandoned, although as late as 1938 an Anglo-American dental textbook advised in favour of lancing, and described the procedure. In the first half of the twentieth century, teething powders in the English-speaking world often contained calomel, a form of mercury. It was removed from most powders in 1954 when it was shown to cause "pink disease" ( acrodynia), a form of mercury poisoning.
Teething toys have a long history. In England in the 17th–19th centuries, a ''coral'' meant a teething toy made of coral, ivory, or bone, often mounted in silver as the handle of a rattle. A museum curator has suggested that these substances were used as sympathetic magic, and that the animal bone could symbolize animal strength to help the child cope with pain.
Teething used to be considered (wrongly) a cause of death, as many children died in the first years of life, at the same time as teething occurs. "The tendency in the past to attribute serious disease to teething was so prevalent that in 1842 teething was the registered cause of death in 4.8% of all infants who died in London under the age of 1 year and 7.3% of those between the ages of 1 to 3 years according to the Registrar General's report."
Ironically, while teething is a natural process which creates little more than discomfort, some methods for relieving teething pain have caused serious harm and even death. Old remedies for teething include "blistering, bleeding, placing leeches on the gums, and applying cautery to the back of the head". In the sixteenth century the French surgeon Ambroise Paré introduced the lancing of gums using a lancet, in the belief that teeth were failing to emerge from the gums due to lack of a pathway, and that this failure was a cause of death. This belief and practice persisted for centuries, with some exceptions, until towards the end of the nineteenth century lancing became increasingly controversial and was then abandoned, although as late as 1938 an Anglo-American dental textbook advised in favour of lancing, and described the procedure. In the first half of the twentieth century, teething powders in the English-speaking world often contained calomel, a form of mercury. It was removed from most powders in 1954 when it was shown to cause "pink disease" ( acrodynia), a form of mercury poisoning.
Teething toys have a long history. In England in the 17th–19th centuries, a ''coral'' meant a teething toy made of coral, ivory, or bone, often mounted in silver as the handle of a rattle. A museum curator has suggested that these substances were used as sympathetic magic, and that the animal bone could symbolize animal strength to help the child cope with pain.
NHS Choices Birth to Five Planner
Teething
NHS Choices Health A–Z
Teething * {{Infants and their care Infancy Pediatrics Teeth Pedodontology

 Teething is the process by which an
Teething is the process by which an infant
In common terminology, a baby is the very young offspring of adult human beings, while infant (from the Latin word ''infans'', meaning 'baby' or 'child') is a formal or specialised synonym. The terms may also be used to refer to juveniles of ...
's first teeth (the deciduous teeth
Deciduous teeth or primary teeth, also informally known as baby teeth, milk teeth, or temporary teeth,Fehrenbach, MJ and Popowics, T. (2026). ''Illustrated Dental Embryology, Histology, and Anatomy'', 6th edition, Elsevier, page 287–296. are ...
, often called "baby teeth" or "milk teeth") appear by emerging through the gums, typically arriving in pairs. The mandibular central incisors are the first primary teeth to erupt, usually between 6 and 10 months of age and usually causes discomfort and pain to the infant. It can take several years for all 20 teeth to complete the tooth eruption. Though the process of teething is sometimes referred to as "cutting teeth", when teeth emerge through the gums they do not cut through the flesh. Instead, hormones
A hormone (from the Greek participle , "setting in motion") is a class of signaling molecules in multicellular organisms that are sent to distant organs or tissues by complex biological processes to regulate physiology and behavior. Hormones a ...
are released within the body that cause some cells in the gums to die and separate, allowing the teeth to come through.
Teething may cause a slightly elevated temperature, but not rising into the fever
Fever or pyrexia in humans is a symptom of an anti-infection defense mechanism that appears with Human body temperature, body temperature exceeding the normal range caused by an increase in the body's temperature Human body temperature#Fever, s ...
range of greater than . Higher temperatures during teething are due to some form of infection, such as a herpes virus, initial infection of which is extremely widespread among children of teething age.
Signs and symptoms
The level of pain that a baby can handle will be different for each child. Some may appear to suffer more than others while they are teething. The soreness and swelling of the gums before a tooth comes through is the cause of the pain and fussiness a baby experiences during this change. These symptoms usually begin about three to five days before the tooth shows, and they disappear as soon as the tooth breaks the skin. Some babies are not even bothered by teething. Common symptoms include drooling or dribbling, increased chewing, mood changes, irritability or crankiness, and swollen gums. Crying, sleeplessness, restless sleep at night, and mild fever are also associated with teething. Teething can begin as early as 3 months and continue until a child's third birthday. In rare cases, an area can be filled with fluid appearing over where a tooth is erupting and causing the gums to be even more sensitive. Pain is more often associated with the eruption of molars since they are larger, and do not penetrate through the gums as easily as the other teeth. Some noticeable symptoms that a baby has entered the teething stage include chewing on their fingers or toys to help relieve pressure on their gums. Babies might also refuse to eat or drink due to the pain. Symptoms will generally fade on their own, but a doctor should be notified if they worsen or are persistent. Teething may cause signs and symptoms in the mouth and gums, but does not cause problems elsewhere in the body. Pulling on the ears is another sign of pain: the pain in the mouth throbs throughout the baby's head, so they pull their ears believing that it will provide relief. Mild rash can develop around the mouth due to the skin irritation caused by excessive drooling or dribbling.Sequence of appearance
 The infant teeth tend to emerge in pairs – first one lower incisor emerges, then the other lower incisor, after which the next set begin to emerge. The general pattern of emergence is:
# Lower central incisors (2) at approximately 6 months
# Upper central incisors (2) at approximately 8 months
# Upper lateral incisors (2) at approximately 10 months
# Lower lateral incisors (2) at approximately 10 months
# First molars (4) at approximately 14 months
# Canines (4) at approximately 18 months
# Second molars (4) at approximately 2–3 years
Milk teeth tend to emerge sooner in females than in males. The exact pattern and initial starting times of teething appear to be hereditary. When and how teeth appear in an infant has no bearing on the health of the child.
The infant teeth tend to emerge in pairs – first one lower incisor emerges, then the other lower incisor, after which the next set begin to emerge. The general pattern of emergence is:
# Lower central incisors (2) at approximately 6 months
# Upper central incisors (2) at approximately 8 months
# Upper lateral incisors (2) at approximately 10 months
# Lower lateral incisors (2) at approximately 10 months
# First molars (4) at approximately 14 months
# Canines (4) at approximately 18 months
# Second molars (4) at approximately 2–3 years
Milk teeth tend to emerge sooner in females than in males. The exact pattern and initial starting times of teething appear to be hereditary. When and how teeth appear in an infant has no bearing on the health of the child.
Misdiagnosis as teething
Teething has not been shown to cause fever or diarrhea; however, the belief that teething causes fever is extremely common among parents. Whilst there is some evidence that teething can cause an elevated temperature, it does not causefever
Fever or pyrexia in humans is a symptom of an anti-infection defense mechanism that appears with Human body temperature, body temperature exceeding the normal range caused by an increase in the body's temperature Human body temperature#Fever, s ...
(medically defined as rectal temperature greater than ). One small 1992 study found a significant rise in temperature on the day of eruption of the first tooth. Another study in 2000 found "mild temperature elevation" but not fever over .
There is a risk that fever around the age of teething is dismissed as due to teething when it is actually due to illness, particularly infection by herpes viruses. "Coincidentally, primary tooth eruption begins at about the time that infants are losing maternal antibody protection against the herpes virus. Also, reports on teething difficulties have recorded symptoms which are remarkably consistent with primary oral herpetic infection, such as fever, irritability, sleeplessness, and difficulty with eating." "Younger infants with higher residual levels of antibodies would experience milder infections, and these would be more likely to go unrecognized or be dismissed as teething difficulty." Herpes virus infection may take the form of primary herpetic gingivostomatitis (HSV-1) or of infection by human herpesvirus 6 (HHV-6), which infects 90% of children by age 2. "The symptoms of elevated temperature and facial rash could be explainable by infection with the HHV-6 agent, which is ubiquitous among infants of teething age." Other viruses may also cause fevers which might be misattributed to teething, but the oral involvement that may occur with herpes viruses makes misdiagnosis a particular risk for such infections.
Treatment
 Infants may chew on objects to aid in the teething process. Teething necklaces or bracelets are not recommended as they can cause choking, strangulation, or irritation of the mouth. Teething rings and other toys, called teethers, are often designed with textures. Some infants gain relief from chewing on cold objects. Some people freeze small chunks of fresh fruits or vegetables and put them in teething nets.
Infants may chew on objects to aid in the teething process. Teething necklaces or bracelets are not recommended as they can cause choking, strangulation, or irritation of the mouth. Teething rings and other toys, called teethers, are often designed with textures. Some infants gain relief from chewing on cold objects. Some people freeze small chunks of fresh fruits or vegetables and put them in teething nets.
Medication
In cases where the infant is in obvious pain, some doctors recommend the use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or child-safe pain-relief treatments containingbenzocaine
Benzocaine, sold under the brand name Orajel amongst others, is a local anesthetic, belonging to the amino ester drug class, commonly used as a topical painkiller or in cough drops. It is the active ingredient in many over-the-counter ...
, lidocaine, or choline salicylate. Benzocaine must be used cautiously because it can cause methemoglobinemia; choline salicylate is related to aspirin and "may cause Reye's syndrome in susceptible children, especially those with or recovering from viral infections, or when used in combination with other NSAIDs". 5% lidocaine gel produces anaesthesia
Anesthesia (American English) or anaesthesia (British English) is a state of controlled, temporary loss of sensation or awareness that is induced for medical or veterinary purposes. It may include some or all of analgesia (relief from or prev ...
(numbing) within 2–5 minutes, lasting for 10–20 minutes. However, one author concludes that, "Overall, the risks and adverse effects from inappropriate or prolonged use of pharmacological agents outweigh their potential benefits." She points out that "the psychological trauma involved in administering medications or applying topical preparations to infants must be considered", and argues that "the placebo effect must not be overlooked. For example, applying a gel of 20% benzocaine in polyethylene glycol
Polyethylene glycol (PEG; ) is a polyether compound derived from petroleum with many applications, from industrial manufacturing to medicine. PEG is also known as polyethylene oxide (PEO) or polyoxyethylene (POE), depending on its molecular wei ...
may give only a modest benefit over applying the placebo, which gives an efficacy of 60% compared with 90% for the active preparation."
Medicines are often applied to the babies' gums to relieve swelling and pain. These gels are similar to the toothache gel that is used by adults for sore gums and toothaches, but is administered in much smaller doses. Teething gels work as a numbing agent to dull the nerves in the gums so that the pain is less noticeable. It is important to follow the directions on the package to ensure that the correct amount of medication is administered and that proper techniques are used to reduce the risk for infection. It is important not to let the medicine numb the throat as it may interfere with the normal gag reflex and may make it possible for food to enter the lungs. Similar medicines are also available in powder form, as "teething powder".
Some traditional medicines used to treat teething pain have been found to be harmful due to high lead content, with effects including toxic encephalopathy. Surma or kohl has traditionally been used in the Middle East and Indian subcontinent as a teething powder, as have the Middle Eastern saoott/cebagin. Santrinj – a 98% lead oxide product otherwise used as a paint primer – is also used in the Middle East as a home remedy for teething.
History
 Teething used to be considered (wrongly) a cause of death, as many children died in the first years of life, at the same time as teething occurs. "The tendency in the past to attribute serious disease to teething was so prevalent that in 1842 teething was the registered cause of death in 4.8% of all infants who died in London under the age of 1 year and 7.3% of those between the ages of 1 to 3 years according to the Registrar General's report."
Ironically, while teething is a natural process which creates little more than discomfort, some methods for relieving teething pain have caused serious harm and even death. Old remedies for teething include "blistering, bleeding, placing leeches on the gums, and applying cautery to the back of the head". In the sixteenth century the French surgeon Ambroise Paré introduced the lancing of gums using a lancet, in the belief that teeth were failing to emerge from the gums due to lack of a pathway, and that this failure was a cause of death. This belief and practice persisted for centuries, with some exceptions, until towards the end of the nineteenth century lancing became increasingly controversial and was then abandoned, although as late as 1938 an Anglo-American dental textbook advised in favour of lancing, and described the procedure. In the first half of the twentieth century, teething powders in the English-speaking world often contained calomel, a form of mercury. It was removed from most powders in 1954 when it was shown to cause "pink disease" ( acrodynia), a form of mercury poisoning.
Teething toys have a long history. In England in the 17th–19th centuries, a ''coral'' meant a teething toy made of coral, ivory, or bone, often mounted in silver as the handle of a rattle. A museum curator has suggested that these substances were used as sympathetic magic, and that the animal bone could symbolize animal strength to help the child cope with pain.
Teething used to be considered (wrongly) a cause of death, as many children died in the first years of life, at the same time as teething occurs. "The tendency in the past to attribute serious disease to teething was so prevalent that in 1842 teething was the registered cause of death in 4.8% of all infants who died in London under the age of 1 year and 7.3% of those between the ages of 1 to 3 years according to the Registrar General's report."
Ironically, while teething is a natural process which creates little more than discomfort, some methods for relieving teething pain have caused serious harm and even death. Old remedies for teething include "blistering, bleeding, placing leeches on the gums, and applying cautery to the back of the head". In the sixteenth century the French surgeon Ambroise Paré introduced the lancing of gums using a lancet, in the belief that teeth were failing to emerge from the gums due to lack of a pathway, and that this failure was a cause of death. This belief and practice persisted for centuries, with some exceptions, until towards the end of the nineteenth century lancing became increasingly controversial and was then abandoned, although as late as 1938 an Anglo-American dental textbook advised in favour of lancing, and described the procedure. In the first half of the twentieth century, teething powders in the English-speaking world often contained calomel, a form of mercury. It was removed from most powders in 1954 when it was shown to cause "pink disease" ( acrodynia), a form of mercury poisoning.
Teething toys have a long history. In England in the 17th–19th centuries, a ''coral'' meant a teething toy made of coral, ivory, or bone, often mounted in silver as the handle of a rattle. A museum curator has suggested that these substances were used as sympathetic magic, and that the animal bone could symbolize animal strength to help the child cope with pain.
See also
* Tooth eruption *Deciduous teeth
Deciduous teeth or primary teeth, also informally known as baby teeth, milk teeth, or temporary teeth,Fehrenbach, MJ and Popowics, T. (2026). ''Illustrated Dental Embryology, Histology, and Anatomy'', 6th edition, Elsevier, page 287–296. are ...
* Permanent teeth
* Dentition
Dentition pertains to the development of teeth and their arrangement in the mouth. In particular, it is the characteristic arrangement, kind, and number of teeth in a given species at a given age. That is, the number, type, and morpho-physiology ...
References
External links
NHS Choices Birth to Five Planner
Teething
NHS Choices Health A–Z
Teething * {{Infants and their care Infancy Pediatrics Teeth Pedodontology