Tectonic burial on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Tectonic Burial is the deformation of rocks caused by extreme pressure over millions of years. It often causes temperature evolutions and deep burials. Tectonic burial is usually the result of continental collisions or subduction in a region. An increase in burial depth leads to a weakened basin and basement but creates better preservation structure within the basement.
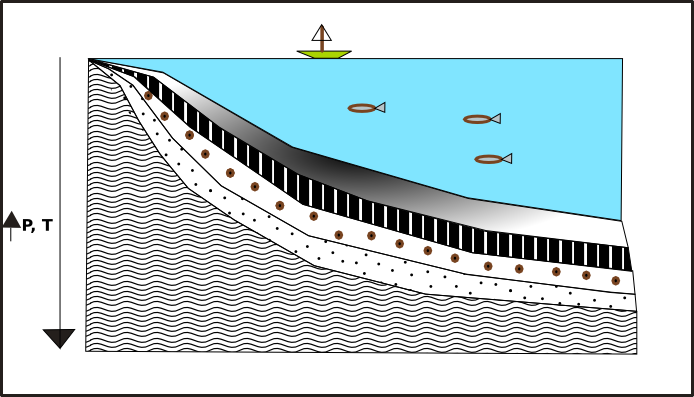 Sedimentary burial is more typical when thinking of burial processes. Sedimentary burial is the deposition of sediments on and area of interest such as a sedimentary basin, oceans, or other locations typically leading to
Sedimentary burial is more typical when thinking of burial processes. Sedimentary burial is the deposition of sediments on and area of interest such as a sedimentary basin, oceans, or other locations typically leading to
Geologic Processes
Sedimentary Burial
 Sedimentary burial is more typical when thinking of burial processes. Sedimentary burial is the deposition of sediments on and area of interest such as a sedimentary basin, oceans, or other locations typically leading to
Sedimentary burial is more typical when thinking of burial processes. Sedimentary burial is the deposition of sediments on and area of interest such as a sedimentary basin, oceans, or other locations typically leading to Diagenesis
Diagenesis () is the process that describes physical and chemical changes in sediments first caused by water-rock interactions, microbial activity, and compaction after their deposition. Increased pressure and temperature only start to play a ...
.
Tectonic Burial
Tectonic Burial specifically refers to burial of material on a area of interest as a result of tectonic processes such as aThrust fault
A thrust fault is a break in the Earth's crust, across which older rocks are pushed above younger rocks.
Thrust geometry and nomenclature
Reverse faults
A thrust fault is a type of reverse fault that has a dip of 45 degrees or less.
If ...
or other processes of crustal thickening. Tectonic burial is common in orogenic systems such as mountain belts or collisional zones. This is a critical part of the rock cycle and can lead to burial metamorphism and heating.
Evidence for tectonic burial
Radiometric Dating
One way of identifying a tectonic burial event is throughradiometric dating
Radiometric dating, radioactive dating or radioisotope dating is a technique which is used to date materials such as rocks or carbon, in which trace radioactive impurities were selectively incorporated when they were formed. The method compares ...
. Burial events may be radiometric dated by looking at the cooling of the event and its impact on the minerals within the formation.
Metamorphism
When rocks or sediments get buried they begin to increase in temperature and pressure as the mass above accumulates. Metamorphism occurs at temperatures greater than 200 °C and pressures greater than 300 MPa. Burial metamorphism overlaps with diagenesis with an increase in pressure and temperature. Sedimentary rocks buried at depths of a couple kilo meters will begin generating temperatures above 300 °C without differential stress.Thermochronology
Tectonic burial events can be distinguished by Thermochronology. During a tectonic burial event rocks increase in heat until they reach theirClosure temperature
In radiometric dating, closure temperature or blocking temperature refers to the temperature of a system, such as a mineral, at the time given by its radiometric date. In physical terms, the closure temperature is the temperature at which a syste ...
. These closure temperatures are an indication of burial depth history and are used by thermochronogists in dating a tectonic burial event.
Vitrinite Reflectance
Sediment deposition over a basin with organic material can create a primary component of coal,Vitrinite
Vitrinite is one of the primary components of coals and most sedimentary kerogens. Vitrinite is a type of maceral, where "macerals" are organic components of coal analogous to the "minerals" of rocks. Vitrinite has a shiny appearance resembling gla ...
. High temperatures and pressures associated with Tectonic burial could produce vitrinite from woody organic material thus the presence of vitrinite may be a good indicator for a tectonic burial event.
Effects
Coalification
It has been debated that burial depth may play a role into the advancement of coalification. Early in the 19th century it was thought to be caused purely by the pressure caused by burial, in some coal fields high ranking coal was found that made some geologists think that burial pressure increased the coalification rate.Oil
Oil can be another product of tectonic burial. Oil is created in this fashion over a series of steps starting with the deposition of carbonate sediments followed by cracking and multiple stages of filling of oil like inclusions.Pressure-Temperature-Time paths
One of the largest effects that tectonic burial has is a change in the pressure-temperature time paths, this can be identified by looking for metamorphism or by using thermochronology. Burial of greater depths have the ability to reset fission track dates.Examples
Tectonic burial in southern Apennines.
In the southern Apennines fold and thrust belts, indicators record timing of exhumation of sedimentary units.Tectonic burial in the Persian Gulf.
Evidence for the timing of diagenesis and oil migration.Tectonic burial and Coal production.
Tectonic burial and its relationship to the advancement of coalification.References
{{Reflist