Tawa (dinosaur) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''Tawa'' (named after the Hopi word for the
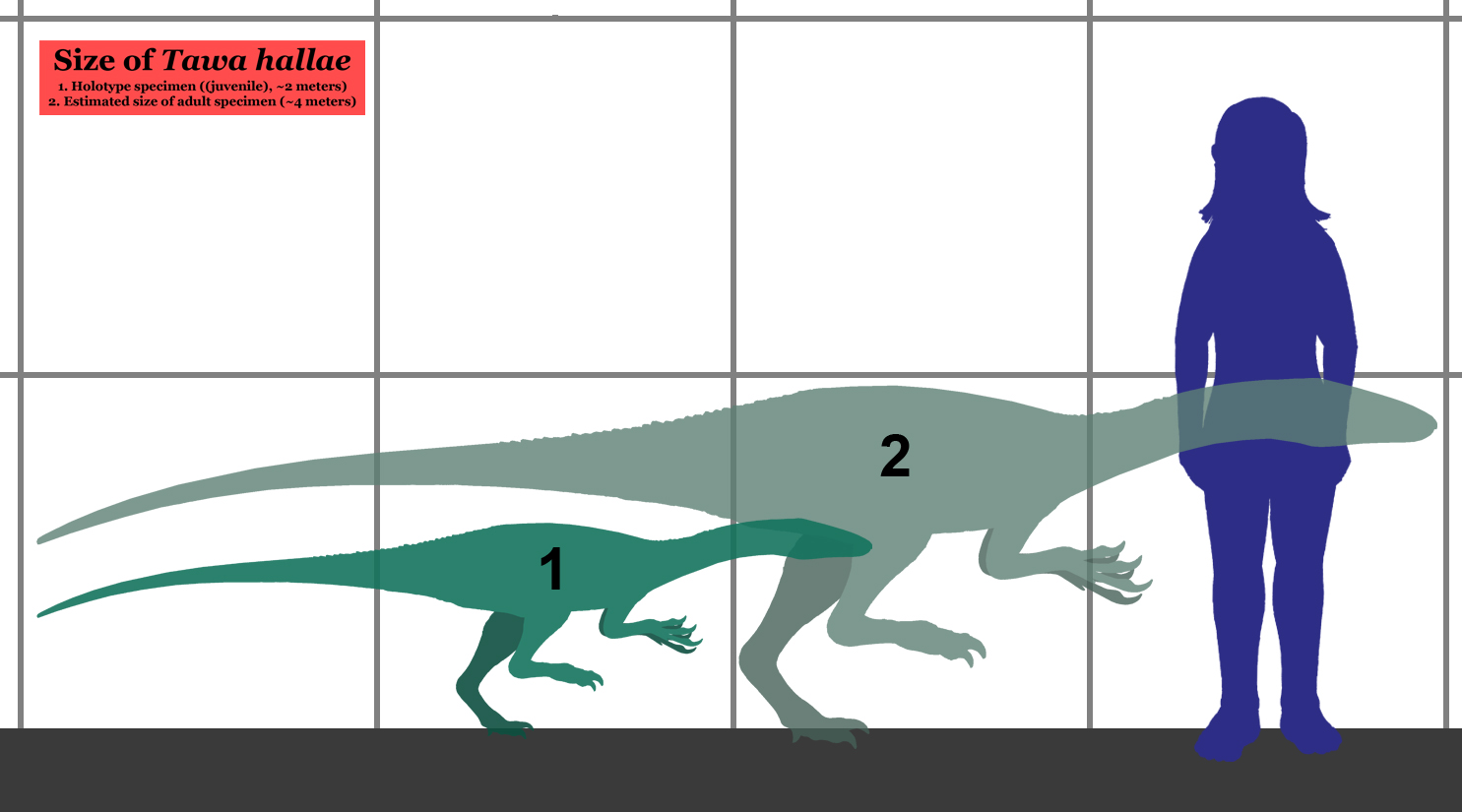
 ''Tawa'' was estimated to have been long as an adult, with a weight of . ''Tawa'' preserves characters that can be associated with different dinosaur taxa. Its skull morphology resembles that of
''Tawa'' was estimated to have been long as an adult, with a weight of . ''Tawa'' preserves characters that can be associated with different dinosaur taxa. Its skull morphology resembles that of
 Fossils now attributed to ''Tawa'' were first discovered in 2004. The
Fossils now attributed to ''Tawa'' were first discovered in 2004. The
 The Hayden Quarry at
The Hayden Quarry at
{{Taxonbar, from=Q132888 Late Triassic dinosaurs of North America Prehistoric theropods Fossil taxa described in 2009 Taxa named by Mark Norell Paleontology in New Mexico
Puebloan
The Puebloans or Pueblo peoples, are Native Americans in the Southwestern United States who share common agricultural, material, and religious practices. Currently 100 pueblos are actively inhabited, among which Taos, San Ildefonso, Acoma, Zu ...
sun god) is a genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family. In binomial nom ...
of possible basal theropod
Theropoda (; ), whose members are known as theropods, is a dinosaur clade that is characterized by hollow bones and three toes and claws on each limb. Theropods are generally classed as a group of saurischian dinosaurs. They were ancestrally c ...
dinosaur
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic period, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago (mya), although the exact origin and timing of the evolution of dinosaurs is t ...
s from the Late Triassic
The Triassic ( ) is a geologic period and system (stratigraphy), system which spans 50.6 million years from the end of the Permian Period 251.902 million years ago (Year#Abbreviations yr and ya, Mya), to the beginning of the Jurassic Period 201.36 ...
period. The fossil remains of ''Tawa hallae'', the type and only species were found in the Hayden Quarry of Ghost Ranch
Ghost Ranch is a retreat and education center located close to the village of Abiquiú in Rio Arriba County in north central New Mexico, United States. It was the home and studio of Georgia O'Keeffe, as well as the subject of many of her painti ...
, New Mexico
)
, population_demonym = New Mexican ( es, Neomexicano, Neomejicano, Nuevo Mexicano)
, seat = Santa Fe
, LargestCity = Albuquerque
, LargestMetro = Tiguex
, OfficialLang = None
, Languages = English, Spanish ( New Mexican), Navajo, Ke ...
, US. Its discovery alongside the relatives of ''Coelophysis
''Coelophysis'' ( traditionally; or , as heard more commonly in recent decades) is an extinct genus of coelophysid theropod dinosaur that lived approximately 228 to 201.3 million years ago during the latter part of the Triassic Period fro ...
''and '' Herrerasaurus'' supports the hypothesis that the earliest dinosaurs arose in Gondwana during the early Late Triassic
The Late Triassic is the third and final epoch of the Triassic Period in the geologic time scale, spanning the time between Ma and Ma (million years ago). It is preceded by the Middle Triassic Epoch and followed by the Early Jurassic Epoch. ...
period in what is now South America, and radiated from there around the globe. The specific name honours Ruth Hall, founder of the Ghost Ranch Museum of Paleontology.
Description
 ''Tawa'' was estimated to have been long as an adult, with a weight of . ''Tawa'' preserves characters that can be associated with different dinosaur taxa. Its skull morphology resembles that of
''Tawa'' was estimated to have been long as an adult, with a weight of . ''Tawa'' preserves characters that can be associated with different dinosaur taxa. Its skull morphology resembles that of coelophysoids
Coelophysoidea were common dinosaurs of the Late Triassic and Early Jurassic periods. They were widespread geographically, probably living on all continents. Coelophysoids were all slender, carnivorous forms with a superficial similarity to the ...
and the ilium approximates that of a herrerasaurid. Like the coelophysoids, ''Tawa'' has a kink in its upper jaws, between the maxilla
The maxilla (plural: ''maxillae'' ) in vertebrates is the upper fixed (not fixed in Neopterygii) bone of the jaw formed from the fusion of two maxillary bones. In humans, the upper jaw includes the hard palate in the front of the mouth. T ...
and the premaxilla
The premaxilla (or praemaxilla) is one of a pair of small cranial bones at the very tip of the upper jaw of many animals, usually, but not always, bearing teeth. In humans, they are fused with the maxilla. The "premaxilla" of therian mammal has ...
. With respect to limb proportion, the femur
The femur (; ), or thigh bone, is the proximal bone of the hindlimb in tetrapod vertebrates. The head of the femur articulates with the acetabulum in the pelvic bone forming the hip joint, while the distal part of the femur articulates wit ...
is very long compared to the tibia
The tibia (; ), also known as the shinbone or shankbone, is the larger, stronger, and anterior (frontal) of the two bones in the leg below the knee in vertebrates (the other being the fibula, behind and to the outside of the tibia); it connects ...
. A neck vertebra
The spinal column, a defining synapomorphy shared by nearly all vertebrates, Hagfish are believed to have secondarily lost their spinal column is a moderately flexible series of vertebrae (singular vertebra), each constituting a characteristi ...
l adaptation in ''Tawa'' supports the hypothesis that cervical air sacs antedate the origin of the Neotheropoda and may be ancestral for saurischia
Saurischia ( , meaning "reptile-hipped" from the Greek ' () meaning 'lizard' and ' () meaning 'hip joint') is one of the two basic divisions of dinosaurs (the other being Ornithischia), classified by their hip structure. Saurischia and Ornithis ...
ns, and also links the dinosaurs with the evolution of birds. Compared to earlier dinosaurs such as '' Herrerasaurus ''and ''Eoraptor
''Eoraptor'' () is a genus of small, lightly built, basal sauropodomorph. One of the earliest-known dinosaurs, it lived approximately 231 to 228 million years ago, during the Late Triassic in Western Gondwana, in the region that is now northwes ...
'', ''Tawa'' had a relatively slender build.
A diagnosis is a statement of the anatomical features of an organism (or group) that collectively distinguish it from all other organisms. Some, but not all, of the features in a diagnosis are also autapomorphies. An autapomorphy is a distinctive anatomical feature that is unique to a given organism or group. According to Nesbitt et al. (2009) ''Tawa'' can be distinguished based on the following features: the prootic bones meet on the ventral midline of the endocranial cavity, the anterior tympanic recess is greatly enlarged on the anterior surface of the basioccipital and extends onto the prootic and the parabasisphenoid, a deep recess is present on posterodorsal base of the paroccipital process, a sharp ridge extending dorsoventrally on the middle of the posterior face of the basal tuber, an incomplete ligamental sulcus is present on the posterior side of the femoral head, a semicircular muscle scar/excavation is present on the posterior face of femoral head, a small semicircular excavation on posterior margin of medial posterior condyle
A condyle (;Entry "condyle"
in
tibia The tibia (; ), also known as the shinbone or shankbone, is the larger, stronger, and anterior (frontal) of the two bones in the leg below the knee in vertebrates (the other being the fibula, behind and to the outside of the tibia); it connects ...
, a "step" is present on the ventral surface of the in
tibia The tibia (; ), also known as the shinbone or shankbone, is the larger, stronger, and anterior (frontal) of the two bones in the leg below the knee in vertebrates (the other being the fibula, behind and to the outside of the tibia); it connects ...
astragalus
''Astragalus'' is a large genus of over 3,000 species of herbs and small shrubs, belonging to the legume family Fabaceae and the subfamily Faboideae. It is the largest genus of plants in terms of described species. The genus is native to tempe ...
, metatarsal
The metatarsal bones, or metatarsus, are a group of five long bones in the foot, located between the tarsal bones of the hind- and mid-foot and the phalanges of the toes. Lacking individual names, the metatarsal bones are numbered from the me ...
I is similar in length to the other metatarsals.
Discovery
 Fossils now attributed to ''Tawa'' were first discovered in 2004. The
Fossils now attributed to ''Tawa'' were first discovered in 2004. The holotype
A holotype is a single physical example (or illustration) of an organism, known to have been used when the species (or lower-ranked taxon) was formally described. It is either the single such physical example (or illustration) or one of sever ...
, a juvenile individual, cataloged GR 241, consists of a mostly complete, but disarticulated skull, forelimbs, a partial vertebral
The vertebral column, also known as the backbone or spine, is part of the axial skeleton. The vertebral column is the defining characteristic of a vertebrate in which the notochord (a flexible rod of uniform composition) found in all chordates ...
column, hindlimbs, ribs, and gastralia
Gastralia (singular gastralium) are dermal bones found in the ventral body wall of modern crocodilians and tuatara, and many prehistoric tetrapods. They are found between the sternum and pelvis, and do not articulate with the vertebrae. In thes ...
. The determination was made that this specimen is a juvenile based on the presence of an open braincase and unfused neurocentral sutures. Fossils of at least seven other individuals were also discovered at the site. One of these specimens, cataloged GR 242, is also nearly complete. An isolated femur, GR 244, suggests that adults were at least 30% larger than the juvenile holotype. GR 242 was assigned as a paratype
In zoology and botany, a paratype is a specimen of an organism that helps define what the scientific name of a species and other taxon actually represents, but it is not the holotype (and in botany is also neither an isotype nor a syntype). O ...
for the genus along with specimens representing a femora, pelvis, and tail (GR 155); and cervical vertebrae
The spinal column, a defining synapomorphy shared by nearly all vertebrates, Hagfish are believed to have secondarily lost their spinal column is a moderately flexible series of vertebrae (singular vertebra), each constituting a characteristi ...
(GR 243).
All of these specimens are from the Hayden Quarry, a site in New Mexico
)
, population_demonym = New Mexican ( es, Neomexicano, Neomejicano, Nuevo Mexicano)
, seat = Santa Fe
, LargestCity = Albuquerque
, LargestMetro = Tiguex
, OfficialLang = None
, Languages = English, Spanish ( New Mexican), Navajo, Ke ...
, which preserves many fossils of early dinosaurs and their close relatives. They were discovered in gray/green siltstone dating to the Norian stage of the Triassic
The Triassic ( ) is a geologic period and system (stratigraphy), system which spans 50.6 million years from the end of the Permian Period 251.902 million years ago (Year#Abbreviations yr and ya, Mya), to the beginning of the Jurassic Period 201.36 ...
period, about 215-213 million years ago. ''Tawa'' was formally described in 2009 by a group of six American researchers led by Sterling J. Nesbitt
Sterling Nesbitt (born March 25, 1982, in Mesa, Arizona) is an American paleontologist best known for his work on the origin and early evolutionary patterns of archosaurs. He is currently an associate professor at Virginia Tech in the Department of ...
of the American Museum of Natural History. At the time of publication in the journal ''Science
Science is a systematic endeavor that Scientific method, builds and organizes knowledge in the form of Testability, testable explanations and predictions about the universe.
Science may be as old as the human species, and some of the earli ...
'', Nesbitt was a postdoctoral researcher at the University of Texas at Austin
The University of Texas at Austin (UT Austin, UT, or Texas) is a public research university in Austin, Texas. It was founded in 1883 and is the oldest institution in the University of Texas System. With 40,916 undergraduate students, 11,07 ...
's Jackson School of Geosciences
The Jackson School of Geosciences at The University of Texas at Austin unites the Department of Geological Sciences with two research units, the Institute for Geophysics and the Bureau of Economic Geology.
The Jackson School is both old and new. ...
.
Based on the study of the overlapping material of '' Dromomeron romeri'' and ''Tawa'', S. Christopher Bennett proposed that the two taxa were conspecific, forming a single growth series with ''D. romeri'' being the juvenile and ''Tawa'' being the adult. However, noting prominent differences between their femora which cannot be attributed to variation with age, Rodrigo Müller rejected this proposal in 2017. He further noted that while ''D. romeri'' is known from juveniles only, it shares many traits in common with ''D. gigas'', which is known from mature specimens.
Classification
Thetype species
In zoological nomenclature, a type species (''species typica'') is the species name with which the name of a genus or subgenus is considered to be permanently taxonomically associated, i.e., the species that contains the biological type specime ...
is ''Tawa hallae'', which was described in 2009 by Nesbitt ''et al.'', and considered more basal than ''Coelophysis
''Coelophysis'' ( traditionally; or , as heard more commonly in recent decades) is an extinct genus of coelophysid theropod dinosaur that lived approximately 228 to 201.3 million years ago during the latter part of the Triassic Period fro ...
'', an early theropod from the Late Triassic. In 2009, Mortimer cautioned that the analysis by Nesbitt ''et al.'' was limited because it failed to consider all the characters of the relevant dinosaurs treated by the old analysis (e.g. ''Guaibasaurus'','' Panphagia'', ''Sinosaurus
''Sinosaurus'' (meaning "Chinese lizard") is an extinct genus of theropod dinosaur which lived during the Early Jurassic Period. It was a bipedal carnivore approximately in length and in body mass. Fossils of the animal were found at the Lufen ...
'', ''Dracovenator'', ''Lophostropheus'', etc.)DML: http://dml.cmnh.org/2009Dec/msg00122.html ''Tawa'' was however found to be more advanced than the earliest theropod
Theropoda (; ), whose members are known as theropods, is a dinosaur clade that is characterized by hollow bones and three toes and claws on each limb. Theropods are generally classed as a group of saurischian dinosaurs. They were ancestrally c ...
dinosaurs, ''Eoraptor
''Eoraptor'' () is a genus of small, lightly built, basal sauropodomorph. One of the earliest-known dinosaurs, it lived approximately 231 to 228 million years ago, during the Late Triassic in Western Gondwana, in the region that is now northwes ...
'' and '' Herrerasaurus'', and '' Staurikosaurus''.
Sues ''et al.'' (2011) considered ''Tawa'' a derived early theropod
Theropoda (; ), whose members are known as theropods, is a dinosaur clade that is characterized by hollow bones and three toes and claws on each limb. Theropods are generally classed as a group of saurischian dinosaurs. They were ancestrally c ...
. A cladistic analysis
Cladistics (; ) is an approach to biological classification in which organisms are categorized in groups ("clades") based on hypotheses of most recent common ancestry. The evidence for hypothesized relationships is typically shared derived chara ...
of ''Tawa'' and other early theropods indicate that the Coelophysoidea
Coelophysoidea were common dinosaurs of the Late Triassic and Early Jurassic periods. They were widespread geographically, probably living on all continents. Coelophysoids were all slender, carnivorous forms with a superficial similarity to the ...
, a group of early dinosaurs, may be an artificial grouping because ''Tawa'' combines classic coelophysoid features with features which appear to be ancestral to the neotheropods. ''Tawa'' is believed to be the sister taxon
In phylogenetics, a sister group or sister taxon, also called an adelphotaxon, comprises the closest relative(s) of another given unit in an evolutionary tree.
Definition
The expression is most easily illustrated by a cladogram:
Taxon A and ...
of Neotheropoda
Neotheropoda (meaning "new theropods") is a clade that includes coelophysoids and more advanced theropod dinosaurs, and is the only group of theropods that survived the Triassic–Jurassic extinction event. All neotheropods became extinct by the ...
, a group of carnivorous dinosaurs which largely bore only three functional digits on their feet.
In 2011, Martinez and colleagues concluded that ''Tawa'' was the basalmost coelophysoid, while a second 2011 analysis by paleontologists Martin D. Ezcurra and Stephen L. Brusatte, as well as a follow-up analysis modified with additional data by You Hai-Lu and colleagues in 2014, found ''Tawa'' to be a primitive theropod. This position for ''Tawa'' was also recovered in the large analysis of early dinosaurs by Matthew Baron, David B. Norman and Paul Barrett in 2017.
Cau (2018) and Novas ''et al''. (2021) considered ''Tawa'' a non- herrerasaurid herrerasaur, although the first study placed Herrerasauria outside Dinosauria and the second placed it in Saurischia.
Paleoecology
 The Hayden Quarry at
The Hayden Quarry at Ghost Ranch
Ghost Ranch is a retreat and education center located close to the village of Abiquiú in Rio Arriba County in north central New Mexico, United States. It was the home and studio of Georgia O'Keeffe, as well as the subject of many of her painti ...
belongs to the lower portion of the Petrified Forest Member of the Chinle Formation in New Mexico
)
, population_demonym = New Mexican ( es, Neomexicano, Neomejicano, Nuevo Mexicano)
, seat = Santa Fe
, LargestCity = Albuquerque
, LargestMetro = Tiguex
, OfficialLang = None
, Languages = English, Spanish ( New Mexican), Navajo, Ke ...
. The discovery of ''Tawa'' alongside the relatives of ''Coelophysis
''Coelophysis'' ( traditionally; or , as heard more commonly in recent decades) is an extinct genus of coelophysid theropod dinosaur that lived approximately 228 to 201.3 million years ago during the latter part of the Triassic Period fro ...
'' and '' Herrerasaurus'' supports the hypothesis that the earliest dinosaurs arose in Gondwana during the Late Triassic period in what is now South America, and radiated around the globe from there.
Ghost Ranch was located close to the equator 200 million years ago, and had a warm, monsoon-like climate with heavy seasonal precipitation. Hayden Quarry, an excavation site at Ghost Ranch, has yielded a diverse collection of fossil material that included the first evidence of dinosaurs and less-advanced dinosauromorphs from the same time period. The discovery indicates that the two groups lived together during the early Triassic period 235 million years ago. ''Tawas paleoenvironment included various archosauriforms such as crocodylomorphs, "rauisuchia
"Rauisuchia" is a paraphyletic group of mostly large and carnivorous Triassic archosaurs. Rauisuchians are a category of archosaurs within a larger group called Pseudosuchia, which encompasses all archosaurs more closely related to crocodilians ...
ns", phytosaurs
Phytosaurs (Φυτόσαυροι in greek) are an extinct group of large, mostly semiaquatic Late Triassic archosauriform reptiles. Phytosaurs belong to the order Phytosauria. Phytosauria and Phytosauridae are often considered to be equivalen ...
, and dinosauriforms like '' Dromomeron'', ''Chindesaurus
''Chindesaurus'' ( ) is an extinct genus of basal saurischian dinosaur from the Late Triassic (213-210 million years ago) of the southwestern United States. It is known from a single species, ''C. bryansmalli'', based on a partial skeleton recovere ...
'', '' Eucoelophysis,'' and possibly ''Coelophysis
''Coelophysis'' ( traditionally; or , as heard more commonly in recent decades) is an extinct genus of coelophysid theropod dinosaur that lived approximately 228 to 201.3 million years ago during the latter part of the Triassic Period fro ...
''.Irmis et al. 2007
Based on their review of the early carnivorous dinosaur fauna from Ghost Ranch and the Ischigualasto Formation
The Ischigualasto Formation is a Late Triassic fossiliferous formation and Lagerstätte in the Ischigualasto-Villa Unión Basin of the southwestern La Rioja Province and northeastern San Juan Province in northwestern Argentina. The formation ...
Nesbit et al. (2009) observed that each was descended from a separate lineage, and inferred that the "South American" protocontinent Gondwana was the ancestral range for basal dinosaurs. Nesbit et al. (2009) went on to note that dinosaurs left their ancestral range in Gondwana and 200 million years ago they dispersed across the adjoined continents of Pangea.
Nesbit ''et al.'' (2009) noted that repeated flooding events collected vertebrate bones, carcasses, and plant material from the landscape surface, possibly in hyperconcentrated flows, and deposited them at what is now Hayden Quarry. It was observed that these flooding events were separated by intervals where there was standing water and weakly developed, poorly drained (hydromorphic) soil formation. The ''Tawa'' specimens were very well preserved which suggests that they were buried extremely soon after dying.
See also
*2009 in paleontology
Arthropods
Cephalopods
Three new species of extinct Octopoda discovered in 2009. The species – '' Keuppia hyperbolaris'', ''Keuppia levante'', and '' Styletoctopus annae'' – lived about 95 million years ago, and bear a strong resemblan ...
References
External links
*National Science Foundation
The National Science Foundation (NSF) is an independent agency of the United States government that supports fundamental research and education in all the non-medical fields of science and engineering. Its medical counterpart is the National ...
br>special report on ''Tawa hallae{{Taxonbar, from=Q132888 Late Triassic dinosaurs of North America Prehistoric theropods Fossil taxa described in 2009 Taxa named by Mark Norell Paleontology in New Mexico