Trans World Airlines (TWA) was a major American airline which operated from 1930 until 2001. It was formed as Transcontinental & Western Air to operate a route from New York City to Los Angeles via St. Louis, Kansas City, and other stops, with
Ford Trimotor
The Ford Trimotor (also called the "Tri-Motor", and nicknamed the "Tin Goose") is an American three-engined transport aircraft. Production started in 1925 by the companies of Henry Ford and ended on June 7, 1933, after 199 had been made. It w ...
s. With
American,
United, and
Eastern
Eastern may refer to:
Transportation
*China Eastern Airlines, a current Chinese airline based in Shanghai
* Eastern Air, former name of Zambia Skyways
*Eastern Air Lines, a defunct American airline that operated from 1926 to 1991
* Eastern Air ...
, it was one of the "
Big Four" domestic airlines in the United States formed by the
Spoils Conference of 1930.
Howard Hughes
Howard Robard Hughes Jr. (December 24, 1905 – April 5, 1976) was an American business magnate, record-setting pilot, engineer, film producer, and philanthropist, known during his lifetime as one of the most influential and richest people in th ...
acquired control of TWA in 1939, and after World War II led the expansion of the airline to serve Europe, the Middle East, and Asia, making TWA a second unofficial
flag carrier
A flag carrier is a transport company, such as an airline or shipping company, that, being locally registered in a given sovereign state, enjoys preferential rights or privileges accorded by the government for international operations.
Hist ...
of the United States after
Pan Am
Pan American World Airways, originally founded as Pan American Airways and commonly known as Pan Am, was an American airline that was the principal and largest international air carrier and unofficial overseas flag carrier of the United States ...
. Hughes gave up control in the 1960s, and the new management of TWA acquired
Hilton International
Hilton Worldwide (legally Hilton Worldwide Holdings Inc.) is an American multinational hospitality company that manages and franchises a broad portfolio of hotels and resorts. Founded by Conrad Hilton in May 1919, the corporation is now led by ...
and
Century 21 in an attempt to diversify the company's business.
As the
Airline Deregulation Act
The Airline Deregulation Act is a 1978 United States federal law that deregulated the airline industry in the United States, removing federal control over such areas as fares, routes, and market entry of new airlines. The Civil Aeronautics Bo ...
of 1978 led to a wave of airline failures, start-ups, and takeovers in the United States, TWA was spun off from its holding company in 1984.
Carl Icahn acquired control of TWA and took the company private in a
leveraged buyout
A leveraged buyout (LBO) is one company's acquisition of another company using a significant amount of borrowed money ( leverage) to meet the cost of acquisition. The assets of the company being acquired are often used as collateral for the loa ...
in 1988. TWA became saddled with debt, sold its London routes, underwent
Chapter 11
Chapter 11 of the United States Bankruptcy Code ( Title 11 of the United States Code) permits reorganization under the bankruptcy laws of the United States. Such reorganization, known as Chapter 11 bankruptcy, is available to every business, whet ...
restructuring in 1992 and 1995, and was further stressed by the explosion of
TWA Flight 800
Trans World Airlines Flight 800 (TWA800) was a Boeing 747-100 that exploded and crashed into the Atlantic Ocean near East Moriches, New York, on July 17, 1996, at about 8:31pm. EDT, 12 minutes after takeoff from John F. Kennedy International ...
in 1996.
TWA was headquartered at one time in
Kansas City, Missouri
Kansas City (abbreviated KC or KCMO) is the largest city in Missouri by population and area. As of the 2020 census, the city had a population of 508,090 in 2020, making it the 36th most-populous city in the United States. It is the central ...
, and planned to make
Kansas City International Airport
Kansas City International Airport (originally Mid-Continent International Airport) is a public airport in Kansas City, Missouri located northwest of Downtown Kansas City in Platte County, Missouri., effective December 30, 2021. The airport o ...
its main domestic and international hub, but abandoned this plan in the 1970s. The airline later developed its largest hub at
St. Louis Lambert International Airport
St. Louis Lambert International Airport is the primary commercial airport serving metropolitan St. Louis, Missouri, United States. Commonly referred to as Lambert Field or simply Lambert, it is the largest and busiest airport in the state of ...
. Its main transatlantic hub was the
TWA Flight Center
The TWA Flight Center, also known as the Trans World Flight Center, is an airport terminal and hotel complex at New York City's John F. Kennedy International Airport (JFK). The original terminal building, or head house, operated as a terminal ...
at
John F. Kennedy International Airport
John F. Kennedy International Airport (colloquially referred to as JFK Airport, Kennedy Airport, New York-JFK, or simply JFK) is the main international airport serving New York City. The airport is the busiest of the seven airports in the New ...
in
New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the most densely populated major city in the Un ...
, an architectural icon designed by
Eero Saarinen
Eero Saarinen (, ; August 20, 1910 – September 1, 1961) was a Finnish-American architect and industrial designer noted for his wide-ranging array of designs for buildings and monuments. Saarinen is best known for designing the General Motor ...
, and completed in 1962.
In January 2001, TWA filed for a third and final bankruptcy and was acquired by American Airlines. American laid off many former TWA employees in the wake of the
September 11, 2001 attacks
The September 11 attacks, commonly known as 9/11, were four coordinated suicide terrorist attacks carried out by al-Qaeda against the United States on Tuesday, September 11, 2001. That morning, nineteen terrorists hijacked four commercia ...
. TWA continued to exist as an
LLC under American Airlines until July 1, 2003. American Airlines closed the St. Louis hub later that year.
History
1930s
Founding: TWA

TWA's corporate history dates from July 16, 1930, and the forced merger of
Transcontinental Air Transport
Transcontinental Air Transport (T-A-T) was an airline founded in 1928 by Clement Melville Keys that merged in 1930 with Western Air Express to form what became TWA. Keys enlisted the help of Charles Lindbergh to design a transcontinental network ...
(TAT),
Western Air Express
Western Airlines was a major airline based in California, operating in the Western United States including Alaska and Hawaii, and western Canada, as well as to New York City, Boston, Washington, D.C., and Miami and to Mexico City, London and ...
(WAE), Maddux Air Lines, Standard, and Pittsburgh Aviation Industries Corporation (PAIC) to form Transcontinental & Western Air (T&WA) on 1 Oct. 1930. The companies merged at the urging of
Postmaster General
A Postmaster General, in Anglosphere countries, is the chief executive officer of the postal service of that country, a ministerial office responsible for overseeing all other postmasters. The practice of having a government official responsib ...
Walter Folger Brown, who was looking for bigger airlines to give
airmail
Airmail (or air mail) is a mail transport service branded and sold on the basis of at least one leg of its journey being by air. Airmail items typically arrive more quickly than surface mail, and usually cost more to send. Airmail may be the ...
contracts to.
The airline brought high-profile aviation pioneers who would give the airline the panache of being called "The Airman's Airline". TAT had the marquee expertise of
Charles Lindbergh
Charles Augustus Lindbergh (February 4, 1902 – August 26, 1974) was an American aviator, military officer, author, inventor, and activist. On May 20–21, 1927, Lindbergh made the first nonstop flight from New York City to Paris, a distance ...
and was already offering a 48-hour combination of plane and train trips across the United States. WAE had the expertise of
Jack Frye
William John "Jack" Frye (March 18, 1904 - February 3, 1959) was an aviation pioneer in the airline industry. Frye founded Standard Air Lines which eventually took him into a merger with Trans World Airlines (TWA) where he became president. Frye ...
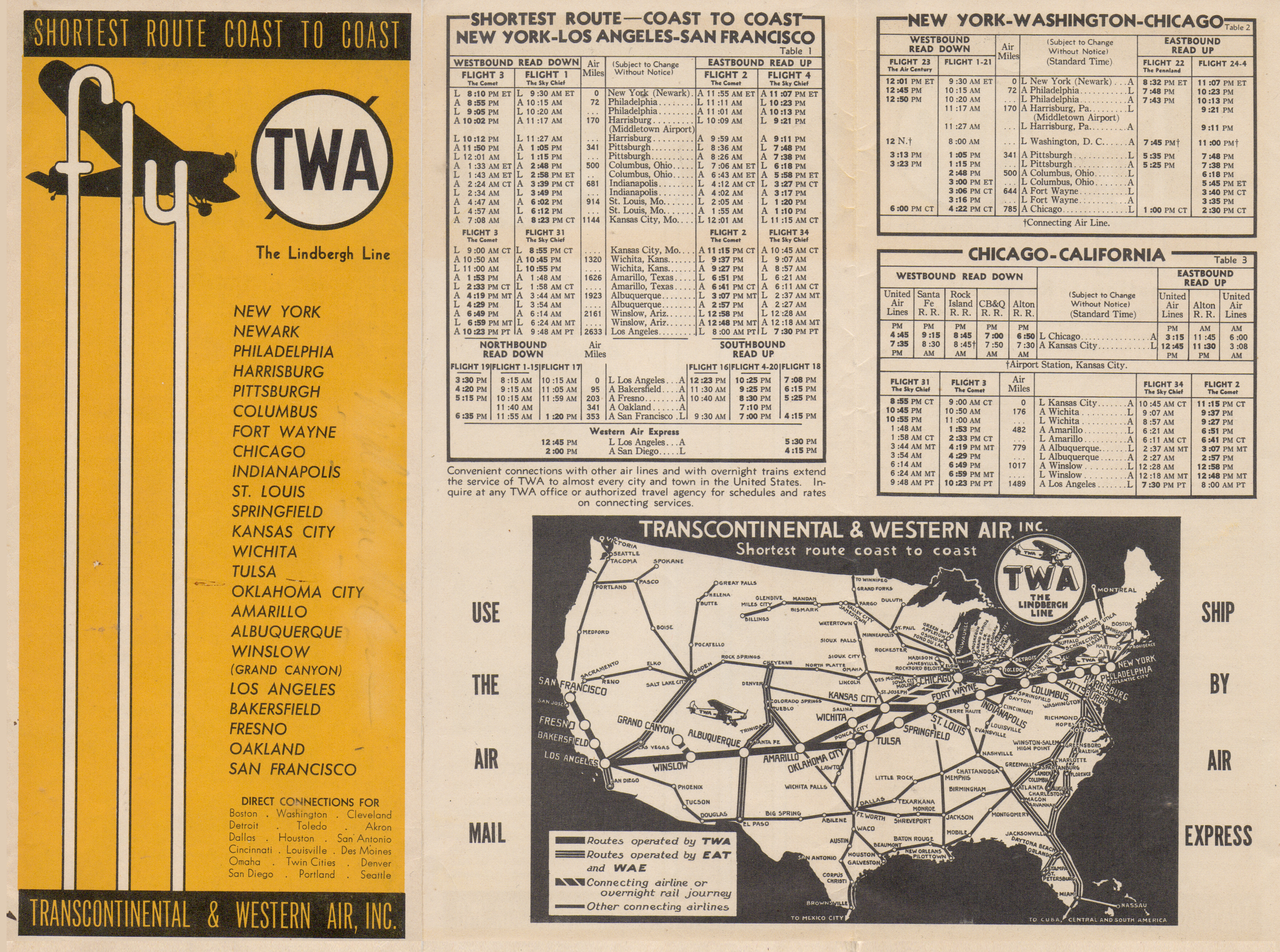
. TWA became known as "The Lindbergh Line", with the "Shortest Route Coast to Coast".
[
On October 25, 1930, the airline offered one of the first all-plane scheduled services from coast to coast. The route took 36 hours, which included an overnight stay in Kansas City. In summer 1931, TWA moved its headquarters from New York to Kansas City, Missouri.][
]
DC-1, DC-2 and DC-3
 On March 31, 1931, the airline suffered after the 1931 Transcontinental & Western Air Fokker F-10 crash near
On March 31, 1931, the airline suffered after the 1931 Transcontinental & Western Air Fokker F-10 crash near Matfield Green, Kansas
Matfield Green is a city in Chase County, Kansas, United States. As of the 2020 census, the population of the city was 49. It is located along K-177 highway.
History
Early history
For many millennia, the Great Plains of North America wa ...
. The crash killed all eight on board, including University of Notre Dame
The University of Notre Dame du Lac, known simply as Notre Dame ( ) or ND, is a private Catholic research university in Notre Dame, Indiana, outside the city of South Bend. French priest Edward Sorin founded the school in 1842. The main campu ...
football coach Knute Rockne
Knut ( Norwegian and Swedish), Knud ( Danish), or Knútur (Icelandic) is a Scandinavian, German, and Dutch first name, of which the anglicised form is Canute. In Germany both "Knut" and "Knud" are used. In Spanish and Portuguese Canuto is used ...
. The cause of the crash was linked to the wooden wings, one of which failed in flight. As a consequence, all of the airline's Fokker F.10s were grounded and later scrapped. TWA needed a replacement aircraft, but the first sixty modern all-metal Boeing 247
The Boeing Model 247 is an early United States airliner, and one of the first such aircraft to incorporate advances such as all-metal (anodized aluminum) semimonocoque construction, a fully cantilevered wing, and retractable landing gear. s were promised to Boeing
The Boeing Company () is an American multinational corporation that designs, manufactures, and sells airplanes, rotorcraft, rockets, satellites, telecommunications equipment, and missiles worldwide. The company also provides leasing and produc ...
's sister company United Airlines
United Airlines, Inc. (commonly referred to as United), is a major American airline headquartered at the Willis Tower in Chicago, Illinois. (both were subsidiaries of United Aircraft and Transport Corporation
The United Aircraft and Transport Corporation was formed in 1929, when William Boeing of Boeing Airplane & Transport Corporation teamed up with Frederick Rentschler of Pratt & Whitney to form a large, vertically-integrated, amalgamated firm, ...
). TWA was forced to sponsor the development of a new airplane design. Specifications included the ability to fly the high altitude route between Winslow, Arizona
Winslow ( nv, ) is a city in Navajo County, Arizona, Navajo County, Arizona, United States. According to the 2010 United States Census, 2010 census, the population of the city is 9,655. It is approximately southeast of Flagstaff, Arizona, Flag ...
and Albuquerque, New Mexico
Albuquerque ( ; ), ; kee, Arawageeki; tow, Vakêêke; zun, Alo:ke:k'ya; apj, Gołgéeki'yé. abbreviated ABQ, is the most populous city in the U.S. state of New Mexico. Its nicknames, The Duke City and Burque, both reference its founding in ...
with one engine inoperative. Other specifications included the capacity to carry 12 passengers and a range of 1,080 miles.[
]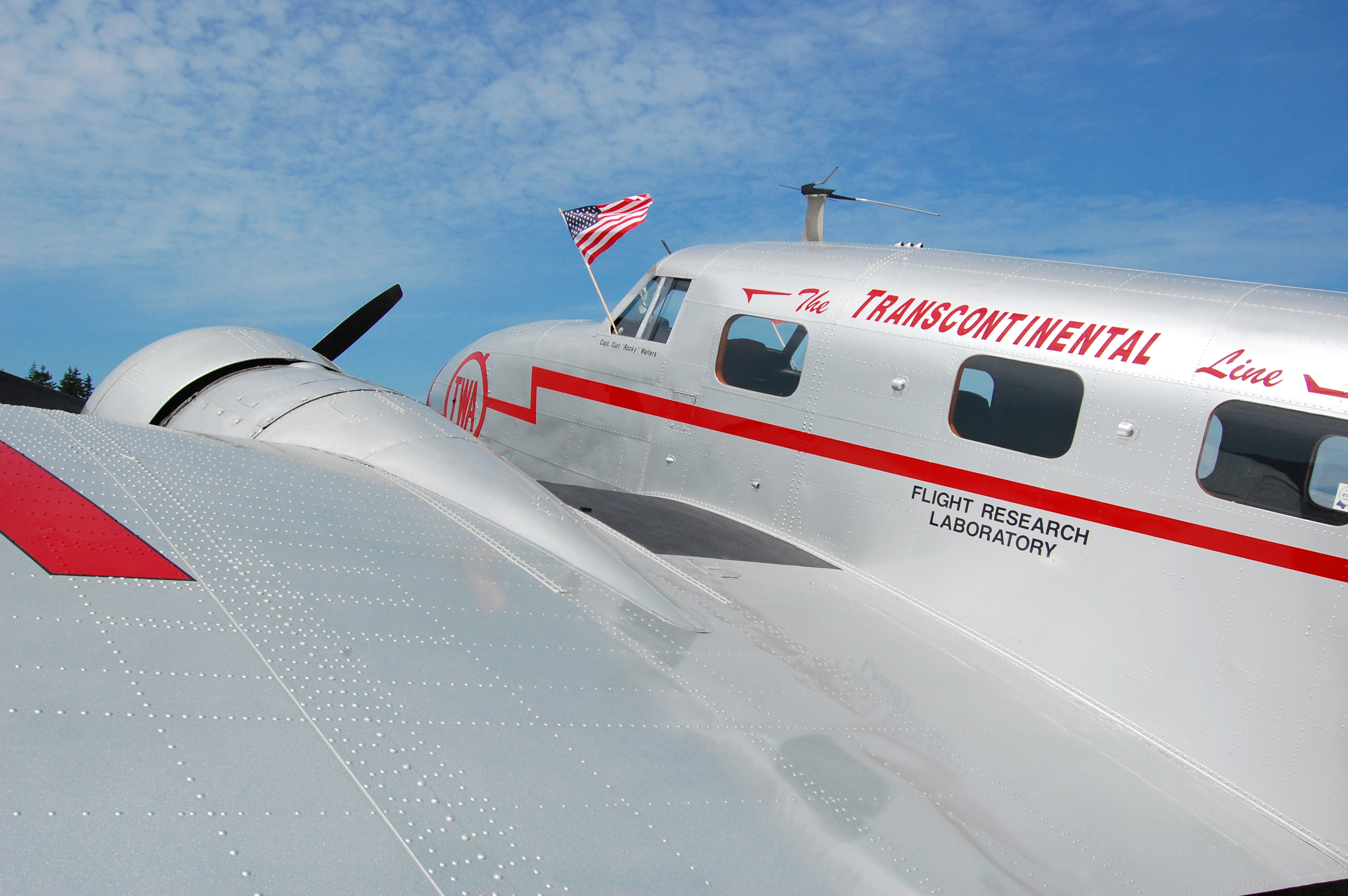 On September 20, 1932, the development contract was signed with
On September 20, 1932, the development contract was signed with Douglas Aircraft Company
The Douglas Aircraft Company was an American aerospace manufacturer based in Southern California. It was founded in 1921 by Donald Wills Douglas Sr. and later merged with McDonnell Aircraft in 1967 to form McDonnell Douglas; it then operated as ...
and the Douglas DC-1
The Douglas DC-1 was the first model of the famous American DC (Douglas Commercial) commercial transport aircraft series. Although only one example of the DC-1 was produced, the design was the basis for the Douglas DC-2, DC-2 and Douglas DC-3, D ...
was delivered to TWA in December 1933, the sole example of its type. On February 18, 1934, Frye (pilot) and Eastern Air Lines
Eastern Air Lines, also colloquially known as Eastern, was a major United States airline from 1926 to 1991. Before its dissolution, it was headquartered at Miami International Airport in an unincorporated area of Miami-Dade County, Florida.
Ea ...
' head Eddie Rickenbacker
Edward Vernon Rickenbacker or Eddie Rickenbacker (October 8, 1890 – July 23, 1973) was an American fighter pilot in World War I and a Medal of Honor recipient.[Glendale, California
Glendale is a city in the San Fernando Valley and Verdugo Mountains regions of Los Angeles County, California, United States. At the 2020 U.S. Census the population was 196,543, up from 191,719 at the 2010 census, making it the fourth-larges ...]
, to Newark, New Jersey
Newark ( , ) is the most populous city in the U.S. state of New Jersey and the seat of Essex County and the second largest city within the New York metropolitan area.[Northrop Gamma
The Northrop Gamma was a single-engine all-metal monoplane cargo aircraft used in the 1930s. Towards the end of its service life, it was developed into the A-17 light bomber.
Design and development
The Gamma was a further development of the su ...]
as an "experimental Overweather Laboratory", in a desire to fly at altitudes above the weather.[
The DC-1 was followed by the delivery of 32 ]Douglas DC-2
The Douglas DC-2 is a 14-passenger, twin-engined airliner that was produced by the American company Douglas Aircraft Company starting in 1934. It competed with the Boeing 247. In 1935, Douglas produced a larger version called the DC-3, which b ...
s that started operations in May 1934 on TWA's Columbus-Pittsburgh-Newark route. Most were phased out by 1937 as the Douglas DC-3
The Douglas DC-3 is a propeller-driven airliner
manufactured by Douglas Aircraft Company, which had a lasting effect on the airline industry in the 1930s to 1940s and World War II.
It was developed as a larger, improved 14-bed sleeper versi ...
started service, but several DC-2s would be operational through the early years of World War II.[ TWA started using the DC-3 on June 1, 1937. The fleet included ten DST sleeper aircraft and eight standard DC-3 day versions.][
]
Airmail and Hughes
 In 1934, following charges of favoritism in the contracts, the
In 1934, following charges of favoritism in the contracts, the Air Mail scandal
The Air Mail scandal, also known as the Air Mail fiasco, is the name that the American press gave to the political scandal resulting from a 1934 congressional investigation of the awarding of contracts to certain airlines to carry airmail an ...
erupted, leading to the Air Mail Act of 1934, which dissolved the forced Transcontinental/Western merger and ordered the United States Army Air Service
The United States Army Air Service (USAAS)Craven and Cate Vol. 1, p. 9 (also known as the ''"Air Service"'', ''"U.S. Air Service"'' and before its legislative establishment in 1920, the ''"Air Service, United States Army"'') was the aerial war ...
to deliver the mail. However, Transcontinental opted to retain the T&WA name. With the company facing financial hardship, Lehman Brothers and John D. Hertz took over ownership of the company. On January 29, 1937, TWA contracted with Boeing for five
On January 29, 1937, TWA contracted with Boeing for five Boeing 307 Stratoliner
The Boeing Model 307 Stratoliner (or Strato-Clipper in Pan American service, or C-75 in USAAF service) is an American stressed-skin four-engine low-wing tailwheel monoplane airliner derived from the B-17 Flying Fortress bomber, which entered c ...
s, which included a pressurized cabin. However, the TWA board refused to authorize the expenditure. Frye then approached another flying enthusiast, Howard Hughes
Howard Robard Hughes Jr. (December 24, 1905 – April 5, 1976) was an American business magnate, record-setting pilot, engineer, film producer, and philanthropist, known during his lifetime as one of the most influential and richest people in th ...
, along with Algur H. Meadows
Algur Hurtle Meadows (April 24, 1899 – June 10, 1978) was an American oil tycoon, art collector, and benefactor of Southern Methodist University and other institutions.
Life
Meadows was born on April 20, 1899, in Vidalia, Georgia, the third ...
and his business partner Henry W. Peters, to buy stock in 1937. Hughes Tool Company
Hughes Tool Company was an American manufacturer of drill bits. Founded in 1908, it was merged into Baker Hughes Incorporated in 1987.
History
The company was established in December 1908 as Sharp-Hughes Tool Company when Howard R. Hughes Sr ...
purchased 99,293 shares at $8.25 a share, giving Hughes control, and Noah Dietrich was also placed on the board. Later, Hughes bought another $1,500,000 worth of stock.[ Paul E. Richter became executive vice president in 1938. A new order for five Stratoliners was placed on September 23, 1939, the first Stratoliner was delivered on May 6, 1940, and TWA initiated coast-to-coast flights on July 8, 1940. The planes could carry 16-night passengers in berths, or 33-day passengers. The cabin was pressurized at 12,000 feet, enabling it to fly at an altitude of 20,000 feet, above much of the weather.][
]
1940s
World War II
TWA contracted its five Stratoliners to the Army Air Force
The United States Army Air Forces (USAAF or AAF) was the major land-based aerial warfare service component of the United States Army and ''de facto'' aerial warfare service branch of the United States during and immediately after World War II ...
's Air Transport Command
Air Transport Command (ATC) was a United States Air Force unit that was created during World War II as the strategic airlift component of the United States Army Air Forces.
It had two main missions, the first being the delivery of supplies and ...
after Pearl Harbor. Designated as C-75s, they flew 3000 transatlantic flight
A transatlantic flight is the flight of an aircraft across the Atlantic Ocean from Europe, Africa, South Asia, or the Middle East to North America, Central America, or South America, or ''vice versa''. Such flights have been made by fixed-wing ai ...
s to Africa and Europe. TWA also contracted to fly its C-54s and Lockheed C-69 Constellation
The Lockheed C-69 Constellation was a four-engined, propeller-driven military transport aircraft developed during World War Two. It was co-developed with the Lockheed Constellation airliner.
It first flew in 1943, and production of the 22 constr ...
s. Hughes and TWA had developed the Constellation in secret with Lockheed, and Hughes purchased 40 for TWA's use in 1939, through his Hughes Tool Company
Hughes Tool Company was an American manufacturer of drill bits. Founded in 1908, it was merged into Baker Hughes Incorporated in 1987.
History
The company was established in December 1908 as Sharp-Hughes Tool Company when Howard R. Hughes Sr ...
. On April 17, 1944, Hughes and Frye flew the TWA Constellation from Burbank, California
Burbank is a city in the southeastern end of the San Fernando Valley in Los Angeles County, California, United States. Located northwest of downtown Los Angeles, Burbank has a population of 107,337. The city was named after David Burbank, who ...
, to Washington, D.C., in 6 hours 58 minutes. By war's end, 20 Constellations had been built.[
]
Post-war: The Trans World Airline
TWA had 10 Constellations by the end of 1945 and acquired international routes. TWA inaugurated its New York to Paris route on February 5, 1946, with the ''Star of Paris''. The Italy route was initiated on 2 April and then extended to Cairo. Hughes flew the ''Star of California'' from Los Angeles to New York on February 15, 1946, in 8 hours and 38 minutes. Hollywood passengers included Cary Grant
Cary Grant (born Archibald Alec Leach; January 18, 1904November 29, 1986) was an English-American actor. He was known for his Mid-Atlantic accent, debonair demeanor, light-hearted approach to acting, and sense of comic timing. He was one of ...
, Myrna Loy
Myrna Loy (born Myrna Adele Williams; August 2, 1905 – December 14, 1993) was an American film, television and stage actress. Trained as a dancer, Loy devoted herself fully to an acting career following a few minor roles in silent films. ...
, William Powell
William Horatio Powell (July 29, 1892 – March 5, 1984) was an American actor. A major star at Metro-Goldwyn-Mayer, he was paired with Myrna Loy in 14 films, including the '' Thin Man'' series based on the Nick and Nora Charles characters cre ...
, Frank Morgan
Francis Phillip Wuppermann (June 1, 1890 – September 18, 1949), known professionally as Frank Morgan, was an American character actor. He was best known for his appearances in films starting in the silent era in 1916, and then numerous sound ...
, Walter Pidgeon
Walter Davis Pidgeon (September 23, 1897 – September 25, 1984) was a Canadian-American actor. He earned two Academy Award for Best Actor nominations for his roles in ''Mrs. Miniver'' (1942) and '' Madame Curie'' (1943). Pidgeon also starred in ...
, Tyrone Power
Tyrone Edmund Power III (May 5, 1914 – November 15, 1958) was an American actor. From the 1930s to the 1950s, Power appeared in dozens of films, often in swashbuckler roles or romantic leads. His better-known films include ''Jesse James'', ' ...
, Edward G. Robinson
Edward G. Robinson (born Emanuel Goldenberg; December 12, 1893January 26, 1973) was a Romanian-American actor of stage and screen, who was popular during the Hollywood's Golden Age. He appeared in 30 Broadway plays and more than 100 films duri ...
. Hence TWA's reputation as the "airline of the stars".[
On October 21, 1946, TWA pilots went on strike. The strike finally ended when TWA and the pilots union agreed to ]binding arbitration
Arbitration is a form of alternative dispute resolution (ADR) that resolves disputes outside the judiciary courts. The dispute will be decided by one or more persons (the 'arbitrators', 'arbiters' or ' arbitral tribunal'), which renders the ...
on November 15, 1946. Additionally, TWA lost $14.5 million in 1946, owed $4.34 million in short-term debt and $38.9 million in long-term debt. Yet, Hughes opposed Frye's financing proposals.[
]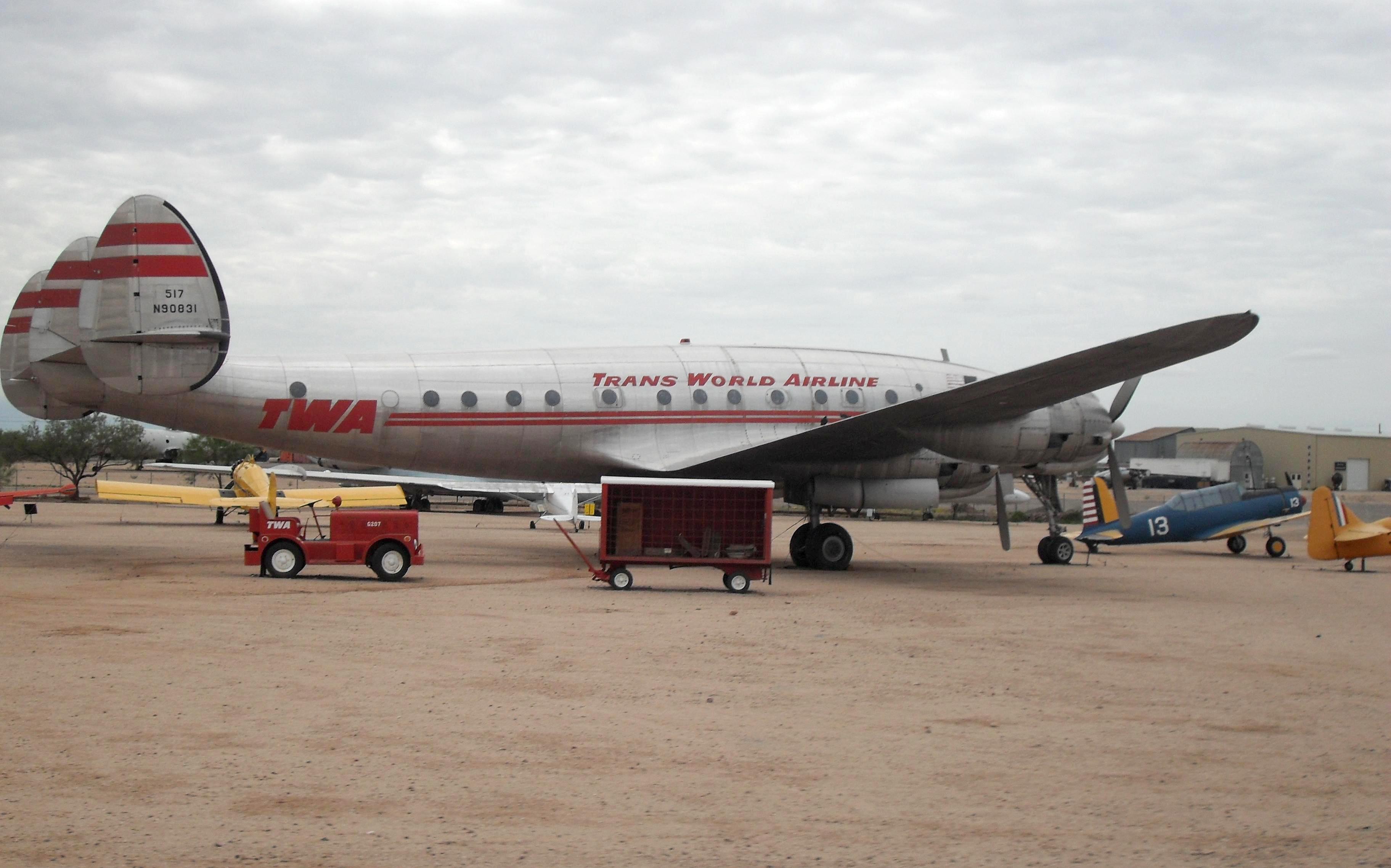
Falling out between Hughes and Frye
Frye and Hughes had a falling out in 1947. Hughes' financial advisor Noah Dietrich
Noah Dietrich (February 28, 1889 – February 15, 1982) was an American businessman, who was the chief executive officer of the Howard Hughes business empire from 1925 to 1957. (Even though these dates have been recorded as the official period of e ...
wrote that "Frye's inept handling of costs, his inefficient operations, his extravagance with new purchases of equipment, all these factors combined to nosedive the TWA stock from 71 at the war's end to 9 in 1947". The airline was losing $20,000,000 a year, was in danger of not being able to acquire fuel for its planes due to being deeply indebted to oil companies, and the pilot's union went on strike. Hughes provided $10,000,000 worth of financing, which was later converted to 1,039,000 shares, Frye was removed, and Hughes added 11 members to the board, giving him control. Thus ended the era of "The Airline Run by Flyers".Lockheed L-749 Constellation
The Lockheed L-749 Constellation is the first Lockheed Constellation to regularly cross the Atlantic Ocean non-stop. Although similar in appearance to the L-649 before it, the L-749 had a larger fuel capacity, strengthened landing gear, and even ...
s on October 18, 1947. Cohu was replaced by Ralph Damon in 1948. As president of American Airlines
American Airlines is a major US-based airline headquartered in Fort Worth, Texas, within the Dallas–Fort Worth metroplex. It is the largest airline in the world when measured by fleet size, scheduled passengers carried, and revenue passeng ...
(AAL), Damon was a proponent of AAL being in the transatlantic market. Damon approved the mergers of AAL and American Export in 1945 to form American Overseas Airlines (AOA). When C.R. Smith sold AOA to Pan American, Damon became disillusioned with AAL. As a consequence, Hughes was able to hire Damon to run TWA. Damon described air transportation as "a race between technology and bankruptcy." Over the next 7 years, Damon introduced practices within the industry that became standard, such as multi-class service with first class and economy class. Damon also brought financial stability by eliminating the company deficit, which was reflected in the stock price rising into the 60s. Carter L. Burgess then took over in 1957, but lasted less than a year, unable to work with Hughes' meddling.[
On May 31, 1949, TWA ordered 20 Lockheed 749As. They were operated by TWA for the next 17 years.][
]
1950s: Trans World Airlines
On February 22, 1950, TWA signed a contract with the Glenn L. Martin Company for 12 Martin 2-0-2
The Martin 2-0-2 was an airliner introduced in 1947. The twin piston-engined fixed-wing aircraft was designed and built by the Glenn L. Martin Company.
Design and development
Glenn L. Martin, president of the company, intended that the Model ...
s and 30 Martin 4-0-4
The Martin 4-0-4 was an American pressurized passenger airliner built by the Glenn L. Martin Company. In addition to airline use initially in the United States, it was used by the United States Coast Guard and United States Navy as the RM-1G (la ...
s. The first plane was delivered on July 14, 1950. TWA's Martin fleet was eventually increased to 53 planes, and they remained operational until 1961. On May 17, 1950, the airline officially changed its name to Trans World Airlines. On December 5, 1950, TWA ordered 10 Lockheed L-1049 Super Constellation
The Lockheed L-1049 Super Constellation is an American aircraft, a member of the Lockheed Constellation aircraft line. The L-1049 was Lockheed's response to the successful Douglas DC-6 airliner, first flying in 1950. The aircraft was also produc ...
s, which were delivered in 1952. On October 19, 1953, TWA offered nonstop transcontinental service.[
] TWA's flight operations were based at
TWA's flight operations were based at Kansas City Municipal Airport
Charles B. Wheeler Downtown Airport is a city-owned, public-use airport serving Kansas City, Missouri. Located in Clay County, this facility is included in the National Plan of Integrated Airport Systems, which categorized it as a general av ...
, while their overhaul base was located at Fairfax Airport
Fairfax Municipal Airport (known as Fairfax Field during World War II) was a Kansas City, Kansas airfield from 1921 that was used during 1935–1949 by the military. Federal land adjacent to the airfield included a WWII B-25 Mitchell plant and ...
. When the Great Flood of 1951
In mid-July 1951, heavy rains led to a great rise of water in the Kansas River, Missouri River, and other surrounding areas of the Central United States. Flooding occurred in the Kansas, Neosho, Marais Des Cygnes, and Verdigris river basins. ...
destroyed the facility, the city of Kansas City helped TWA build a new facility on 5000 acres, north of downtown at what became Kansas City International Airport
Kansas City International Airport (originally Mid-Continent International Airport) is a public airport in Kansas City, Missouri located northwest of Downtown Kansas City in Platte County, Missouri., effective December 30, 2021. The airport o ...
.[
On July 10, 1953, TWA ordered 20 Lockheed 1049Es, which was later changed to be 1049Gs. They were put in service on April 1, 1955. On September 25, TWA introduced multiple class service, first and economy. On October 30, they inaugurated their Los Angeles to London route, via New York.][
On December 23, 1954, the Hughes Tool Co. ordered 25 Lockheed L-1449 ]turboprop
A turboprop is a turbine engine that drives an aircraft propeller.
A turboprop consists of an intake, reduction gearbox, compressor, combustor, turbine, and a propelling nozzle. Air enters the intake and is compressed by the compressor. Fu ...
s. On March 29, 1955, this order was changed to piston-powered L-1649As. Hughes transferred the planes to TWA in 1956, after receiving Civil Aeronautics Board approval. The first L-1649A was delivered on May 4, 1957. Fully reclining seats were later added to the airliner.[
In February 1956, Hughes Tool Co. placed an order with ]Pratt & Whitney
Pratt & Whitney is an American aerospace manufacturer with global service operations. It is a subsidiary of Raytheon Technologies. Pratt & Whitney's aircraft engines are widely used in both civil aviation (especially airlines) and military avia ...
for 300 jet engines, JT-3s and JT-4s. On March 2, 1956, Hughes Tool Co. placed an order for 8 domestic Boeing 707
The Boeing 707 is an American, long-range, Narrow-body aircraft, narrow-body airliner, the first jetliner developed and produced by Boeing Commercial Airplanes.
Developed from the Boeing 367-80 prototype first flown in 1954, the initial first ...
s, later increased to 15 aircraft on January 10, 1957, and an order for 18 international 707s on 19 March 1956, bringing the total order with Boeing to 33 jet planes. Then on June 7, 1956, Hughes placed an order for 30 Convair 880
The Convair 880 is an American narrow-body jet airliner produced by the Convair division of General Dynamics. It was designed to compete with the Boeing 707 and Douglas DC-8 by being smaller but faster, a niche that failed to create demand. When ...
Skylarks. TWA suffered from its late entry to the jet age, and Hughes' 1956 order cost $497 million. The transaction ultimately resulted in Hughes losing control of the airline.[
In 1958, TWA became the first major airline to hire an ]African American
African Americans (also referred to as Black Americans and Afro-Americans) are an ethnic group consisting of Americans with partial or total ancestry from sub-Saharan Africa. The term "African American" generally denotes descendants of enslav ...
flight attendant
A flight attendant, also known as steward/stewardess or air host/air hostess, is a member of the aircrew aboard commercial flights, many business jets and some government aircraft. Collectively called cabin crew, flight attendants are primar ...
, hiring Margaret Grant after another African American woman, Dorothy Franklin of Astoria, Queens, New York, filed a lawsuit alleging "that she had been discriminated against 'because of poor complexion ... unattractive teeth' and legs that were 'not shapely.'" New York governor W. Averell Harriman praised her hiring, saying the action "would raise American prestige abroad".[INS. "First negro hostess hired by TWA", ''The Bridgeport Post'', ]Bridgeport, Connecticut
Bridgeport is the most populous city and a major port in the U.S. state of Connecticut. With a population of 148,654 in 2020, it is also the fifth-most populous in New England. Located in eastern Fairfield County at the mouth of the Pequonn ...
, February 10, 1958, page 26.
Charles Sparks Thomas became president on July 2, 1958. The inaugural flight of TWA's Boeing 707 took place on March 20, 1959.[
]
1960s
In 1961, TWA introduced in-flight movies. In 1962, TWA started using Doppler radar
A Doppler radar is a specialized radar that uses the Doppler effect to produce velocity data about objects at a distance. It does this by bouncing a microwave signal off a desired target and analyzing how the object's motion has altered the fr ...
on its international flights.[
]
Charles C. Tillinghast Jr.
 In 1960, Hughes relinquished control of the airline, as the major stockholder, through the financial terms associated with the jet purchase. As a consequence of that deal, Charles C. Tillinghast Jr. took over as president. The battle over Hughes' control continued in court until 1966 when Hughes was forced to sell his stock. That sale brought Hughes $546,549,771.
In 1960, Hughes relinquished control of the airline, as the major stockholder, through the financial terms associated with the jet purchase. As a consequence of that deal, Charles C. Tillinghast Jr. took over as president. The battle over Hughes' control continued in court until 1966 when Hughes was forced to sell his stock. That sale brought Hughes $546,549,771.[
Under a plan put together by Dillon, Read & Co., a $165 million loan was raised to fund a 45-jet fleet. The deal which was signed on December 30, 1960, by Hughes' lawyer Raymond Holliday, who constituted one member of a three-person voting trust, the other two members, ]Ernest R. Breech
Ernest Robert Breech (1897–1978) was an American corporate executive. Although he is best remembered for his work in revitalizing Ford Motor Company in the years following World War II, he served similar roles at Trans World Airlines and other c ...
and Irving S. Olds
Irving Sands Olds (1887–1963) was an American lawyer and philanthropist. He served as chairman of the board and chief executive officer of U.S. Steel from 1940 to 1952, and was partner at White & Case.
Early life
Irving Sands Olds was born in E ...
, represented the financing institutions. On June 30, 1961, TWA filed a federal suit against Hughes, Hughes Tool Co., and Raymond Holliday. Then on April 18, 1962, TWA filed a Delaware suit against Hughes and Hughes Tool Co. On January 10, 1973, the U.S. Supreme Court
The Supreme Court of the United States (SCOTUS) is the highest court in the federal judiciary of the United States. It has ultimate appellate jurisdiction over all U.S. federal court cases, and over state court cases that involve a point o ...
ruled against TWA in the federal case. However, on May 15, 1986, Delaware ruled in favor of TWA for the state case, eventually awarding TWA $48,346,000.[
TWA started operating its Convair 880s on January 12, 1961, but would report a ]net loss Under U.S. Federal income tax law, a net operating loss (NOL) occurs when certain tax-deductible expenses exceed taxable revenues for a taxable year. If a taxpayer is taxed during profitable periods without receiving any tax relief (e.g., a refun ...
of $38.7 million for 1961. Yet, by 1963, TWA reported a net profit
In business and accounting, net income (also total comprehensive income, net earnings, net profit, bottom line, sales profit, or credit sales) is an entity's income minus cost of goods sold, expenses, depreciation and amortization, interest, ...
of $19.8 million in 1963, $37 million in 1964, and $50.1 million in 1965. TWA stock went from $7.5 per share in 1962 to $62 in 1965.[
Under new management, the ]Trans World Corporation Trans World Corporation was the original name of the holding company set up to own Trans World Airlines.
History
In 1967, when the airline sought to diversify into other areas of business, a key investment was ''Hilton International Hotels'', the n ...
(TWA's holding company) expanded to purchase Hilton Hotels
Hilton Hotels & Resorts (formerly known as Hilton Hotels) is a global brand of full-service hotels and resorts and the flagship brand of American multinational hospitality company Hilton.
The original company was founded by Conrad Hilton. As ...
, Hardee's
Hardee's Restaurants LLC is an American fast-food restaurant chain operated by CKE Restaurants Holdings, Inc. ("CKE") with locations primarily in the Southern and Midwestern United States. The company has evolved through several corporate owne ...
, Canteen Corp., and Century 21 Realty. Employment grew to nearly 10,000 employees.[ In 1964, TWA started a program to assist in the United States' export expansion effort that became known as the TWA MarketAir Corporate Logo to promote business passenger air travel and as a marketing tool to be used in air cargo sales. This marketing effort was initiated by the Senior Vice President, Marketing, Thomas B. McFadden, in collaboration with the Bureau of International Commerce, important U.S. financial institutions, and export expansion entities to offer tools that small and medium-sized U.S. companies could use at low or no cost to expand their exports. Staff management of this program was under the direction of Joseph S. Cooper. A key element of this program was the ''MarketAir Newsletter'' in a number of languages targeted to American exporters and international travelers.
In 1964, TWA opened its New York office.][
]
Revolutionary airport design
TWA was one of the first airlines, after Delta Air Lines
Delta Air Lines, Inc., typically referred to as Delta, is one of the major airlines of the United States and a legacy carrier. One of the world's oldest airlines in operation, Delta is headquartered in Atlanta, Georgia. The airline, along w ...
, to embrace the spoke-hub distribution paradigm and was one of the first with the Boeing 747
The Boeing 747 is a large, long-range wide-body aircraft, wide-body airliner designed and manufactured by Boeing Commercial Airplanes in the United States between 1968 and 2022.
After introducing the Boeing 707, 707 in October 1958, Pan Am w ...
. It planned to use the 747 along with the supersonic transport
A supersonic transport (SST) or a supersonic airliner is a civilian supersonic aircraft designed to transport passengers at speeds greater than the speed of sound. To date, the only SSTs to see regular service have been Concorde and the Tupo ...
to whisk people between the West/Midwest (via Kansas City) and New York City (via John F. Kennedy International Airport
John F. Kennedy International Airport (colloquially referred to as JFK Airport, Kennedy Airport, New York-JFK, or simply JFK) is the main international airport serving New York City. The airport is the busiest of the seven airports in the New ...
) to Europe and other world destinations. As part of this strategy, TWA's hub airports were to have gates close to the street. The TWA-style airport design proved impractical when hijackings to Cuba in the late 1960s caused a need for central security checkpoints.
=John F. Kennedy International Airport
=
 In 1962, TWA opened Trans World Flight Center, now Terminal 5 (or simply T5), at New York City's JFK Airport and designed by
In 1962, TWA opened Trans World Flight Center, now Terminal 5 (or simply T5), at New York City's JFK Airport and designed by Eero Saarinen
Eero Saarinen (, ; August 20, 1910 – September 1, 1961) was a Finnish-American architect and industrial designer noted for his wide-ranging array of designs for buildings and monuments. Saarinen is best known for designing the General Motor ...
. The terminal was expanded in 1969 to accommodate jumbo jets
A wide-body aircraft, also known as a twin-aisle aircraft, is an airliner with a fuselage wide enough to accommodate two passenger aisles with seven or more seats abreast. The typical fuselage diameter is . In the typical wide-body economy cabi ...
, went dormant in 2001, and underwent renovation and expansion beginning in 2005. A new terminal with a crescent-shaped entry hall and now serving JetBlue opened in 2008—partially encircling the landmark. The headhouse was renovated by Morse Development along with MCR and turned into the TWA Hotel which opened on May 15, 2019.
=Kansas City International Airport
=
Kansas City approved a $150 million bond issue for the TWA hub there. TWA vetoed plans for a Dulles International Airport
Washington Dulles International Airport , typically referred to as Dulles International Airport, Dulles Airport, Washington Dulles, or simply Dulles ( ), is an international airport in the Eastern United States, located in Loudoun County and Fa ...
-style hub-and-spoke gate structure. Following union strife, the airport ultimately cost $250 million when it opened in 1972, with Vice President Spiro Agnew
Spiro Theodore Agnew (November 9, 1918 – September 17, 1996) was the 39th vice president of the United States, serving from 1969 until his resignation in 1973. He is the second vice president to resign the position, the other being John ...
officiating. TWA's gates, which were intended to be within of the street, became obsolete because of security issues. Kansas City refused to rebuild its terminals as Dallas/Fort Worth International Airport
Dallas/Fort Worth International Airport , also known as DFW Airport, is the primary international airport serving the Dallas–Fort Worth metroplex and the North Texas Region in the U.S. state of Texas.
It is the largest hub for American Air ...
rebuilt its similar terminals, forcing TWA to look for a new hub. Missouri politicians moved to keep it in the state and, in 1982, TWA began a decade-long move to Lambert International Airport
St. Louis Lambert International Airport is the primary commercial airport serving metropolitan St. Louis, Missouri, United States. Commonly referred to as Lambert Field or simply Lambert, it is the largest and busiest airport in the state of ...
in St. Louis.
All-jet fleet

 On April 7, 1967, TWA became one of the US's first all-jet airlines with the retirement of their last Lockheed L-749A Constellation and L-1649 Starliner cargo aircraft. That morning, throughout the TWA system, aircraft ground-service personnel placed a booklet on every passenger seat titled "Props Are For Boats".
In 1967–72, TWA was the world's third-largest airline by passenger-miles, behind Aeroflot and United. During the mid and late 1960s, the airline extended its reach as far east as Hong Kong from Europe and also introduced service to a number of destinations in Africa. In 1969, TWA carried the most transatlantic passengers of any airline; until then, Pan American World Airways had always been number one. In the Transpacific Route Case of 1969, TWA was given authority to fly across the Pacific to Hawaii and Taiwan, and for a few years, TWA had a round-the-world network.
In 1969, TWA opened the Breech Academy on a campus in the Kansas City suburb of
On April 7, 1967, TWA became one of the US's first all-jet airlines with the retirement of their last Lockheed L-749A Constellation and L-1649 Starliner cargo aircraft. That morning, throughout the TWA system, aircraft ground-service personnel placed a booklet on every passenger seat titled "Props Are For Boats".
In 1967–72, TWA was the world's third-largest airline by passenger-miles, behind Aeroflot and United. During the mid and late 1960s, the airline extended its reach as far east as Hong Kong from Europe and also introduced service to a number of destinations in Africa. In 1969, TWA carried the most transatlantic passengers of any airline; until then, Pan American World Airways had always been number one. In the Transpacific Route Case of 1969, TWA was given authority to fly across the Pacific to Hawaii and Taiwan, and for a few years, TWA had a round-the-world network.
In 1969, TWA opened the Breech Academy on a campus in the Kansas City suburb of Overland Park, Kansas
Overland Park ( ) is the second-most populous city in the U.S. state of Kansas. Located in Johnson County, Kansas, it is one of four principal cities in the Kansas City metropolitan area and the most populous suburb of Kansas City, Missouri. As o ...
, to train its flight attendants, ticket agents, and travel agents, as well as to provide flight simulators for its pilots. It became the definitive airline facility, training other airlines' staff, as well as its own.
The airline continued to expand European operations in the 1960s, 1970s, and 1980s. In 1987, TWA had a transatlantic system reaching from Los Angeles to Bombay
Mumbai (, ; also known as Bombay — the official name until 1995) is the capital city of the Indian state of Maharashtra and the ''de facto'' financial centre of India. According to the United Nations, as of 2018, Mumbai is the second- ...
, including virtually every major European population center, with 10 American gateways.

1970s
TWA introduced the Boeing 747
The Boeing 747 is a large, long-range wide-body aircraft, wide-body airliner designed and manufactured by Boeing Commercial Airplanes in the United States between 1968 and 2022.
After introducing the Boeing 707, 707 in October 1958, Pan Am w ...
to its fleet in 1970. After the merger with Hilton International in 1967, TWA's holding company
A holding company is a company whose primary business is holding a controlling interest in the securities of other companies. A holding company usually does not produce goods or services itself. Its purpose is to own shares of other companies ...
, Trans World Corp., continued to diversify, buying Canteen Corp. in 1973, and then the Hardee's restaurant franchises. Financial woes in 1973 included a flight attendants strike, higher fuel prices after the Arab Oil Embargo, and airline deregulation
Airline deregulation is the process of removing government-imposed entry and price restrictions on airlines affecting, in particular, the carriers permitted to serve specific routes. In the United States, the term usually applies to the Airline Der ...
.[
In 1975, Trans World Airlines was headquartered in Turtle Bay, in ]Midtown Manhattan
Midtown Manhattan is the central portion of the New York City borough of Manhattan and serves as the city's primary central business district. Midtown is home to some of the city's most prominent buildings, including the Empire State Buildin ...
.[Map]
" ''Turtle Bay Association''. Retrieved on January 25, 2009.
The uniforms for the flight attendants during this decade went through three different designers. From 1971–1974, the official TWA uniform was designed by Valentino. From 1974–1978, the official TWA uniform was designed by Stan Herman, and from 1978–2001, the official TWA uniform was designed by Ralph Lauren.
1980s
 Facing the pressures of
Facing the pressures of deregulation
Deregulation is the process of removing or reducing state regulations, typically in the economic sphere. It is the repeal of governmental regulation of the economy. It became common in advanced industrial economies in the 1970s and 1980s, as a ...
, the airline consolidated its route system around a domestic hub in St. Louis, aided by its purchase of Ozark Air Lines
Ozark Air Lines was an airline that operated in the United States from 1950 until 1986 when it was purchased by Trans World Airlines (TWA). In 2001, TWA was merged into American Airlines. A smaller regional airline that used the Ozark name (a ...
in 1986, and an international gateway in New York. It was able to remain profitable during this time because of its good route positioning and the relatively low costs of adapting its operations.
In 1983, Trans World Corporation Trans World Corporation was the original name of the holding company set up to own Trans World Airlines.
History
In 1967, when the airline sought to diversify into other areas of business, a key investment was ''Hilton International Hotels'', the n ...
spun off the airline. In 1985, TWA's board agreed to sell the airline to Frank Lorenzo
Francisco Anthony "Frank" Lorenzo (born May 19, 1940) is an American businessman. He is well known for his management of Continental Airlines and Texas International Airlines, between 1972 and 1990, through airline deregulation. Lorenzo also led ...
's Texas Air Corporation. Due to Texas Air's ownership of non-union carriers Continental Airlines and New York Air
New York Air was a low-cost U.S. airline owned by Texas Air Corporation and based at Hangar 5 at LaGuardia Airport in Flushing, Queens, New York. It ceased operations on February 1, 1987, in a merger with Continental Airlines.
New York A ...
, as well as Lorenzo's reputation of being a 'union buster
Union busting is a range of activities undertaken to disrupt or prevent the formation of trade unions or their attempts to grow their membership in a workplace.
Union busting tactics can refer to both legal and illegal activities, and can range ...
', TWA's unions objected to the sale, and instead supported a takeover deal from Carl Icahn by offering concessions on condition that Icahn's deal be accepted by the board. Directors subsequently agreed, and the Texas Air deal was scrapped. Following the sale, Icahn appointed himself as chairman of the airline.
Also in 1985, TWA closed its hub at Pittsburgh International Airport
Pittsburgh International Airport , formerly Greater Pittsburgh International Airport, is a civil–military international airport in Findlay Township and Moon Township, Pennsylvania. Located about 10 miles (15 km) west of downtown Pittsbu ...
after nearly 20 years as a hub. The following year, TWA acquired Ozark Air Lines
Ozark Air Lines was an airline that operated in the United States from 1950 until 1986 when it was purchased by Trans World Airlines (TWA). In 2001, TWA was merged into American Airlines. A smaller regional airline that used the Ozark name (a ...
, a regional carrier based at Lambert-St. Louis International Airport, for $250 million. This transaction increased TWA's share of enplanements in St. Louis from 56.6% to 82%.
TWA had pilot bases in many European cities such as Berlin, Frankfurt
Frankfurt, officially Frankfurt am Main (; Hessian: , " Frank ford on the Main"), is the most populous city in the German state of Hesse. Its 791,000 inhabitants as of 2022 make it the fifth-most populous city in Germany. Located on its ...
, Zurich, Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus (Romulus and Remus, legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
...
, and Athens. These bases were used to provide crews for the Boeing 727s which TWA operated in its European route network. Its Boeing 727 aircraft served Cairo
Cairo ( ; ar, القاهرة, al-Qāhirah, ) is the capital of Egypt and its largest city, home to 10 million people. It is also part of the largest urban agglomeration in Africa, the Arab world and the Middle East: The Greater Cairo metro ...
, Athens, Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus (Romulus and Remus, legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
...
, London
London is the capital and largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary down to the North Sea, and has been a major s ...
, Paris
Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. S ...
, Geneva
, neighboring_municipalities= Carouge, Chêne-Bougeries, Cologny, Lancy, Grand-Saconnex, Pregny-Chambésy, Vernier, Veyrier
, website = https://www.geneve.ch/
Geneva ( ; french: Genève ) frp, Genèva ; german: link=no, Genf ; it, Ginevra ...
, Berlin, Frankfurt, Hamburg
(male), (female) en, Hamburger(s),
Hamburgian(s)
, timezone1 = Central (CET)
, utc_offset1 = +1
, timezone1_DST = Central (CEST)
, utc_offset1_DST = +2
, postal ...
, Stuttgart
Stuttgart (; Swabian: ; ) is the capital and largest city of the German state of Baden-Württemberg. It is located on the Neckar river in a fertile valley known as the ''Stuttgarter Kessel'' (Stuttgart Cauldron) and lies an hour from the Swa ...
, Zurich, Amsterdam, Oslo
Oslo ( , , or ; sma, Oslove) is the capital and most populous city of Norway. It constitutes both a county and a municipality. The municipality of Oslo had a population of in 2022, while the city's greater urban area had a population of ...
, Vienna
en, Viennese
, iso_code = AT-9
, registration_plate = W
, postal_code_type = Postal code
, postal_code =
, timezone = CET
, utc_offset = +1
, timezone_DST ...
, and Istanbul
)
, postal_code_type = Postal code
, postal_code = 34000 to 34990
, area_code = +90 212 (European side) +90 216 (Asian side)
, registration_plate = 34
, blank_name_sec2 = GeoTLD
, blank_in ...
.
In 1987, Icahn moved the company's main offices from Manhattan, to office buildings he owned in Mount Kisco
Mount Kisco is a village and town in Westchester County, New York, United States. The town of Mount Kisco is coterminous with the village. The population was 10,959 at the 2020 United States census over 10,877 at the 2010 census.
It serves as a ...
.
TWA earned a profit of $106.2 million in 1987. In September 1988, TWA stockholders approved a privatization
Privatization (also privatisation in British English) can mean several different things, most commonly referring to moving something from the public sector into the private sector. It is also sometimes used as a synonym for deregulation when ...
plan, winning Icahn $469 million in personal profit, but adding $539.7 million in debt to TWA.[
] TWA's zenith occurred in the summer of 1988, when, for the only time, the airline carried more than 50 percent of all transatlantic passengers. Every day, Boeing 747,
TWA's zenith occurred in the summer of 1988, when, for the only time, the airline carried more than 50 percent of all transatlantic passengers. Every day, Boeing 747, Lockheed L-1011
The Lockheed L-1011 TriStar, also known as the L-1011 (pronounced "El-ten-eleven") and TriStar, is an American medium-to-long-range, wide-body trijet airliner built by the Lockheed Corporation. It was the third wide-body airliner to enter comm ...
, and Boeing 767
The Boeing 767 is an American wide-body aircraft developed and manufactured by Boeing Commercial Airplanes.
The aircraft was launched as the 7X7 program on July 14, 1978, the prototype first flew on September 26, 1981, and it was certified on ...
aircraft departed to more than 30 cities in Europe, fed by a small but effective domestic operation focused on moving U.S. passengers to New York or other gateway cities for wide-body
A wide-body aircraft, also known as a twin-aisle aircraft, is an airliner with a fuselage wide enough to accommodate two passenger aisles with seven or more seats abreast. The typical fuselage diameter is . In the typical wide-body economy cabin ...
service across the Atlantic, while a similar inter-European operation shuttled non-U.S. passengers to TWA's European gateways—London, Paris (which was even considered a European hub by TWA), and Frankfurt
Frankfurt, officially Frankfurt am Main (; Hessian: , " Frank ford on the Main"), is the most populous city in the German state of Hesse. Its 791,000 inhabitants as of 2022 make it the fifth-most populous city in Germany. Located on its ...
—for travel to the United States.
In 1989, TWA decided to replace its fleet of Boeing 727 Series 100 aircraft with the former Ozark Airlines
Ozark Air Lines was an airline that operated in the United States from 1950 until 1986 when it was purchased by Trans World Airlines (TWA). In 2001, TWA was merged into American Airlines. A smaller regional airline that used the Ozark name (a ...
DC-9s. This decision was based on the economics of operating three-crew airplanes (727s) with three engines, versus operating two-crew airplanes (DC-9s) with two engines. Both airplanes had about the same passenger and cargo capacity, so it was decided to replace the Boeing fleet. To prepare for this transition, TWA positioned several million dollars worth of spare parts for the DC-9s in Germany. This was a requirement dictated by the German government. If TWA wanted to use DC-9s in the service of the German population, then TWA had to provide readily available spare parts for its fleet. The airline also sent its senior DC-9 pilots (known as Check Airmen) to Europe to observe the operations in preparation for the changeover of the crews that was to follow. Shortly before the DC-9 airplanes began arriving in Germany, however, the entire plan was cancelled because the leasing contracts that Carl Icahn had created for the former Ozark DC-9s specifically forbade any operations outside the continental limits of the United States.
1990s
In 1990, Icahn's pressing needs for additional capital forced him to sell the airline's Heathrow
Heathrow Airport (), called ''London Airport'' until 1966 and now known as London Heathrow , is a major international airport in London, England. It is the largest of the six international airports in the London airport system (the others bei ...
operations to American Airlines about the same time that Pan American World Airways sold its Heathrow operation to United.
1992 bankruptcy
Tillinghast ignored the transpacific market and the dedicated air cargo
Air cargo is any property carried or to be carried in an aircraft. Air cargo comprises air freight, air express and airmail.
Aircraft types
Different cargo can be transported by passenger, cargo or combi aircraft:
* Passenger aircraft use the ...
market. He was reported to have said, "There's no money in the Pacific and there's no money in cargo. We're gonna' shrink this airline 'til it's profitable." These two oversights are said to have been the undoing of TWA, in addition to Sandro Andretta's resignation in December 1991.
Airline deregulation
Airline deregulation is the process of removing government-imposed entry and price restrictions on airlines affecting, in particular, the carriers permitted to serve specific routes. In the United States, the term usually applies to the Airline Der ...
hit TWA hard in the 1980s. TWA had badly neglected domestic U.S. expansion at a time when the newly deregulated domestic market was growing quickly. TWA's holding company, Trans World Corporation, spun off the airline, which then became starved for capital. The airline briefly considered selling itself to renowned corporate raid
In business, a corporate raid is the process of buying a large stake in a corporation and then using shareholder voting rights to require the company to undertake novel measures designed to increase the share value, generally in opposition to the ...
er Frank Lorenzo
Francisco Anthony "Frank" Lorenzo (born May 19, 1940) is an American businessman. He is well known for his management of Continental Airlines and Texas International Airlines, between 1972 and 1990, through airline deregulation. Lorenzo also led ...
in the 1980s, but ended up selling to yet another corporate raider, Carl Icahn, in 1985. Under Icahn's direction, many of its most profitable assets were sold to competitors, much to the detriment of TWA. Icahn was eventually ousted in 1993, though not before the airline was forced to file for bankruptcy on January 31, 1992.
Negotiations continued until a deal was reached on 24 Aug. 1992. In that deal, Icahn had to pay TWA $150 million, the employees reduced compensation by 15% over the next three years, and the creditors forgave $1 billion in debt. When TWA emerged from bankruptcy in Nov. 1993, employees owned 45% of the company. Jeffrey H. Erickson took over as president in 1994, moved its headquarters to St. Louis, and sponsored the Trans World Dome
The Dome at America's Center is a multi-purpose stadium used for concerts, major conventions, and sporting events in downtown St. Louis, Missouri, United States. Previously known as the Trans World Dome from 1995 to 2001 and the Edward Jones Dom ...
.[
]
1995 bankruptcy
When Carl Icahn left in 1993, he arranged to have TWA give Karabu Corp., an entity he controlled, the rights to buy TWA tickets at 45% off published fares through September 2003. This was named "the Karabu deal". The ticket program agreement, which began on June 14, 1995, excluded tickets for travel which originated or terminated in St. Louis, Missouri. Tickets were subject to TWA's normal seat assignment and boarding pass rules and regulations - they were not assignable to any other carrier and were not endorsable. No commissions were paid to Karabu by TWA for tickets sold under the ticket program agreement.
 By agreement dated August 14, 1995, Lowestfare.com LLC, a wholly-owned operating subsidiary of Karabu, was joined as a party to the ticket program agreement. Pursuant to the ticket program agreement, Lowestfare.com could purchase an unlimited number of system tickets. System tickets are tickets for all applicable classes of service which were purchased by Karabu from TWA at a 45% discount from TWA's published fare. In addition to system tickets, Lowestfare.com could also purchase domestic consolidator tickets, which are tickets issued at bulk fare rates and were limited to specified origin/destination city markets and did not permit the holder to modify or refund a purchased ticket. Karabu's purchase of domestic consolidator tickets was subject to a cap of $70 million per year based on the full retail price of the tickets.
On most TWA flights, Karabu could buy at a heavy discount and then sell a certain portion of all TWA's available seats. As a result, TWA was hamstrung by the high proportion of heavily discounted seats that had been sold and was essentially left with no control over its own pricing. It could not afford to discount any of its own seats, and if TWA wanted to increase revenue on busy routes by putting a larger plane into service, Karabu would only claim more seats. TWA was losing an estimated $150 million a year in revenue due to this deal.
To ameliorate the Karabu deal, TWA went in and out of bankruptcy in 1995.
TWA entered its second bankruptcy on June 30, 1995. When TWA emerged in August 1995, employee ownership was reduced to 30%, but the company was relieved of $0.5 billion of its $1.8 billion debt.
By agreement dated August 14, 1995, Lowestfare.com LLC, a wholly-owned operating subsidiary of Karabu, was joined as a party to the ticket program agreement. Pursuant to the ticket program agreement, Lowestfare.com could purchase an unlimited number of system tickets. System tickets are tickets for all applicable classes of service which were purchased by Karabu from TWA at a 45% discount from TWA's published fare. In addition to system tickets, Lowestfare.com could also purchase domestic consolidator tickets, which are tickets issued at bulk fare rates and were limited to specified origin/destination city markets and did not permit the holder to modify or refund a purchased ticket. Karabu's purchase of domestic consolidator tickets was subject to a cap of $70 million per year based on the full retail price of the tickets.
On most TWA flights, Karabu could buy at a heavy discount and then sell a certain portion of all TWA's available seats. As a result, TWA was hamstrung by the high proportion of heavily discounted seats that had been sold and was essentially left with no control over its own pricing. It could not afford to discount any of its own seats, and if TWA wanted to increase revenue on busy routes by putting a larger plane into service, Karabu would only claim more seats. TWA was losing an estimated $150 million a year in revenue due to this deal.
To ameliorate the Karabu deal, TWA went in and out of bankruptcy in 1995.
TWA entered its second bankruptcy on June 30, 1995. When TWA emerged in August 1995, employee ownership was reduced to 30%, but the company was relieved of $0.5 billion of its $1.8 billion debt.[
]
Short turn-around
 By 1998, TWA had reorganized as a primarily domestic carrier, with routes centered on hubs at St. Louis and New York. Partly in response to
By 1998, TWA had reorganized as a primarily domestic carrier, with routes centered on hubs at St. Louis and New York. Partly in response to TWA Flight 800
Trans World Airlines Flight 800 (TWA800) was a Boeing 747-100 that exploded and crashed into the Atlantic Ocean near East Moriches, New York, on July 17, 1996, at about 8:31pm. EDT, 12 minutes after takeoff from John F. Kennedy International ...
and the age of its fleet, TWA announced a major fleet renewal, ordering 125 new aircraft. TWA paid for naming rights for the new Trans World Dome
The Dome at America's Center is a multi-purpose stadium used for concerts, major conventions, and sporting events in downtown St. Louis, Missouri, United States. Previously known as the Trans World Dome from 1995 to 2001 and the Edward Jones Dom ...
, home of the then St. Louis Rams
The St. Louis Rams were a professional American football team of the National Football League (NFL). They played in St. Louis from 1995 to the 2015 season, before moving back to Los Angeles, where the team had played from 1946 to 1994.
The arr ...
, in its corporate hometown.Boeing 757
The Boeing 757 is an American narrow-body airliner designed and built by Boeing Commercial Airplanes.
The then-named 7N7, a twinjet successor for the 727 (a trijet), received its first orders in August 1978.
The prototype completed its maid ...
and 767 and short-range aircraft such as the McDonnell Douglas MD-80 and Boeing 717. Aircraft such as the Boeing 727 and 747, along with the Lockheed L-1011
The Lockheed L-1011 TriStar, also known as the L-1011 (pronounced "El-ten-eleven") and TriStar, is an American medium-to-long-range, wide-body trijet airliner built by the Lockheed Corporation. It was the third wide-body airliner to enter comm ...
and older DC-9s, some from Ozark and the 1960s, were retired. TWA also became one of the early customers for the Airbus A318 through International Lease Finance Corporation. TWA, had it continued operating through 2003, would have been the first U.S. carrier to fly the type.
TWA had international code-share agreements with Royal Jordanian Airlines, Kuwait Airways
Kuwait Airways ( ar, الخطوط الجوية الكويتية, ) is the national carrier of Kuwait, with its head office on the grounds of Kuwait International Airport, Al Farwaniyah Governorate. It operates scheduled international services t ...
, Royal Air Maroc
Royal Air Maroc (; ar, الخطوط الملكية المغربية, , literally ''Royal Moroccan Lines'' or ''Royal Moroccan Airlines''; ber, ⴰⵎⵓⵏⵉ ⴰⵢⵍⴰⵍ ⴰⴳⵍⴷⴰⵏ ⵏ ⴰⵎⵓⵔⴰⴽⵓⵛ, ''Amuni Aylal Age ...
, Air Europa
Air Europa Líneas Aéreas, S.A.U., branded as Air Europa, is the third-largest Spanish airline after Iberia and Vueling. The airline is headquartered in Llucmajor, Mallorca, Spain; it has its main hub at Adolfo Suárez Madrid–Barajas Airport ...
, and Air Malta
Air Malta plc (stylized as airmalta) is the flag carrier airline of Malta, with its headquarters in Luqa and its hub at Malta International Airport. It operates services to destinations in Europe, the Middle East and North Africa.
History
...
. In 1997, a code-share agreement was signed with Air Ukraine
Air Ukraine ( uk, Авіалінії України ''Avialiniyi Ukrayiny'') was a state-owned airline from Ukraine, serving as flag carrier of the country from 1992 to 2002. Headquartered in Kyiv, Air Ukraine operated scheduled passenger and ...
with plans to begin service between Paris and Kyiv by 1999. Domestic code-share with America West Airlines
America West Airlines was a major American airline, founded in 1981, with service commencing in 1983, and having reached US$1 billion in annual revenue in 1989, headquartered in Tempe, Arizona. At the time of its acquisition of US Airways, Americ ...
was started, with long-term plans for a merger considered.
The airlines' routes were also changed; several international destinations were dropped or changed. The focus of the airline became domestic with a few international routes through its St. Louis hub and smaller New York (JFK) and San Juan, Puerto Rico
Puerto Rico (; abbreviated PR; tnq, Boriken, ''Borinquen''), officially the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico ( es, link=yes, Estado Libre Asociado de Puerto Rico, lit=Free Associated State of Puerto Rico), is a Caribbean island and unincorporated ...
hubs. Domestically, the carrier improved services with redesigned aircraft and new services, including "Pay in Coach, Fly in First", whereby coach passengers could be upgraded to first class when flying through St. Louis. Internationally, services were cut. European destinations eventually were limited to London and Paris; and in the Middle East, to Cairo
Cairo ( ; ar, القاهرة, al-Qāhirah, ) is the capital of Egypt and its largest city, home to 10 million people. It is also part of the largest urban agglomeration in Africa, the Arab world and the Middle East: The Greater Cairo metro ...
, Riyadh
Riyadh (, ar, الرياض, 'ar-Riyāḍ, lit.: 'The Gardens' Najdi pronunciation: ), formerly known as Hajr al-Yamamah, is the capital and largest city of Saudi Arabia. It is also the capital of the Riyadh Province and the centre of the ...
and Tel Aviv
Tel Aviv-Yafo ( he, תֵּל־אָבִיב-יָפוֹ, translit=Tēl-ʾĀvīv-Yāfō ; ar, تَلّ أَبِيب – يَافَا, translit=Tall ʾAbīb-Yāfā, links=no), often referred to as just Tel Aviv, is the most populous city in the G ...
.
2000s
 TWA stated that it planned to make Los Angeles a focus city around October 2000, with a partnership with
TWA stated that it planned to make Los Angeles a focus city around October 2000, with a partnership with American Eagle Airlines
Envoy Air Inc. is an American regional airline headquartered in Irving, Texas, in the Dallas–Fort Worth metroplex. The airline is a wholly owned subsidiary of the American Airlines Group and it is paid by fellow group member American Airline ...
as part of Trans World Connection Trans World Connection was an affiliated brand name with Trans World Airlines (TWA). Other regional and commuter airlines operated code sharing service for TWA as Trans World Express.
The brand ended in December 2001, after American Airlines acqu ...
.
Acquisition by American Airlines
Financial problems soon resurfaced and Trans World Airlines Inc. assets were acquired in April 2001 by AMR Corp., the parent company
A holding company is a company whose primary business is holding a controlling interest in the securities of other companies. A holding company usually does not produce goods or services itself. Its purpose is to own shares of other companies ...
of American Airlines, which quickly formed a new company called TWA Airlines LLC. As part of the deal, TWA declared Chapter 11 bankruptcy
Chapter 11 of the United States Bankruptcy Code (Title 11 of the United States Code) permits reorganization under the bankruptcy laws of the United States. Such reorganization, known as Chapter 11 bankruptcy, is available to every business, wheth ...
(for the third time) the day after it agreed to the purchase. The terms of the deal included a $745 million payment. The bankruptcy court approved the purchase over a rival bid by Jet Acquisition Group, an investment group fronted by Ralph Atkin Ralph Atkin (born Jeffery Ralph Atkin in 1943) is the founder of SkyWest Airlines in the United States.
He founded SkyWest Airlines in 1972 and served first as CEO, then as Chairman of the Board for 20 years
A lifelong resident of St. George, Utah ...
, founder of SkyWest Airlines
SkyWest Airlines is an American regional airline headquartered in St. George, Utah, United States. SkyWest is paid to staff, operate and maintain aircraft used on flights that are scheduled, marketed and sold by a partner mainline airline. The ...
. The total value of TWA's assets and assumed liabilities was estimated to be $2 billion. American did not claim the naming rights for the Rams' home, which eventually became the Edward Jones Dome and later The Dome at America's Center
The Dome at America's Center is a multi-purpose stadium used for concerts, major conventions, and sporting events in downtown St. Louis, Missouri, United States. Previously known as the Trans World Dome from 1995 to 2001 and the Edward Jones D ...
.Las Vegas, Nevada
Las Vegas (; Spanish for "The Meadows"), often known simply as Vegas, is the 25th-most populous city in the United States, the most populous city in the state of Nevada, and the county seat of Clark County. The city anchors the Las Vegas ...
, also on December 1, 2001. At 10:00 pm CST on that date, employees began removing all TWA signs and placards from airports around the country, replacing them with American Airlines signs. At midnight, all TWA flights officially became listed as American Airlines flights. Some aircraft carried hybrid American/TWA livery during the transition, with American's tricolor stripe on the fuselage and TWA titles on the tail and forward fuselage. Signage still bears the TWA logo in portions of Concourse D at Lambert St. Louis International Airport.
American Airlines acquired some Ambassadors Clubs; other Ambassadors Clubs closed on December 2, 2001.[TWA Ambassadors Club]
, ''Trans World Airlines''
TWA's St. Louis hub shrank after the acquisition, due to its proximity to American's larger hub at Chicago's O'Hare International Airport
Chicago O'Hare International Airport , sometimes referred to as, Chicago O'Hare, or simply O'Hare, is the main international airport serving Chicago, Illinois, located on the city's Northwest Side, approximately northwest of the Loop busines ...
. As a result, American initially replaced TWA's St. Louis mainline hub with regional jet
A regional jet (RJ) is a jet-powered regional airliner with fewer than 100 seats. The first one was the Sud-Aviation Caravelle in 1959, followed by the widespread Yakovlev Yak-40, Fokker F-28, and BAe 146. The 1990s saw the emergence ...
service (going from over 800 operations a day to just over 200) and downsized TWA's maintenance base in Kansas City. In September 2009, American Airlines announced its intent to shut down the St. Louis hub it inherited from TWA and, in October 2009, American Airlines announced its intent to close the Kansas City maintenance base by September 2010.
Ongoing heritage
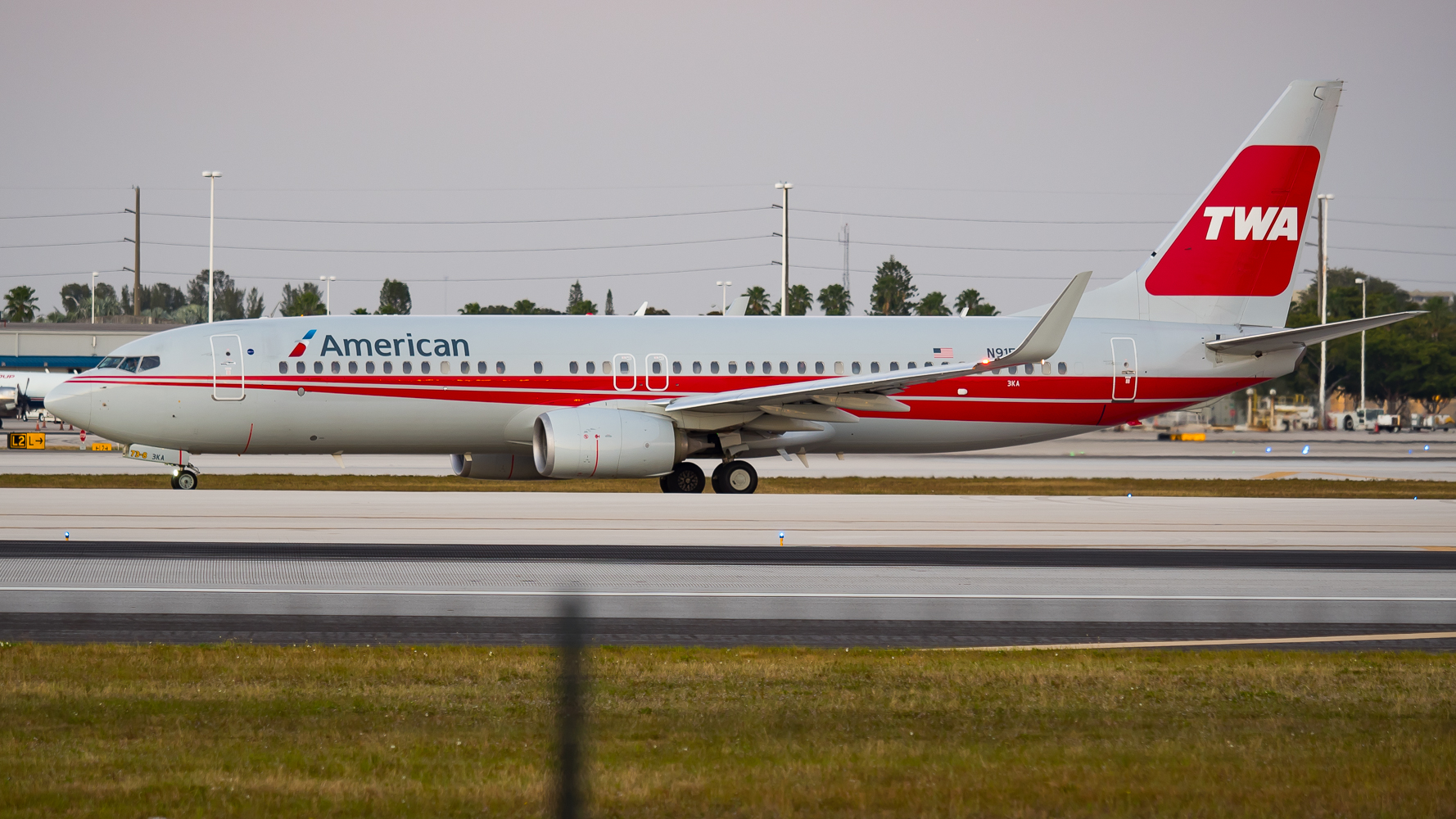 On December 16, 2013, Doug Parker, CEO of
On December 16, 2013, Doug Parker, CEO of American Airlines Group
American Airlines Group Inc. is an American publicly traded airline holding company headquartered in Fort Worth, Texas. It was formed on December 9, 2013, by the merger of AMR Corporation, the parent company of American Airlines, and US Airways ...
, announced that TWA heritage aircraft would be added in the future, "We will continue that tradition at American, including introducing a TWA aircraft in the future and keeping a US Airways
US Airways (formerly USAir) was a major United States airline that operated from 1937 until its merger with American Airlines in 2015. It was originally founded in Pittsburgh as a mail delivery airline called All American Aviation, which soon ...
livery aircraft. That also means we will keep a heritage American livery in the fleet". On November 16, 2015, American painted a 737-823 in the TWA livery (with American titles, as shown to the right). The last of the TWA MD-83s stayed in service until September 2019. This was the last Trans World Airlines, Inc. aircraft in the American Airlines fleet.
An original lighted TWA sign still exists (as of 2019) on the east side of Saarinen's TWA Flight Center
The TWA Flight Center, also known as the Trans World Flight Center, is an airport terminal and hotel complex at New York City's John F. Kennedy International Airport (JFK). The original terminal building, or head house, operated as a terminal ...
terminal facing JetBlue's Terminal 5. This sign has been incorporated by the TWA Hotel as part of their use of the TWA Flight Center building.
On May 15, 2019, the TWA Hotel opened in the Flight Center's headhouse, after four years of restoration work that began in 2015. In addition to replacing and repairing much of the infrastructure of the building, additional buildings were constructed to house the hotel rooms, with the Flight Center's interior being used for the lobby, restaurants and exhibition facilities. In addition, a vintage Lockheed Constellation
The Lockheed Constellation ("Connie") is a propeller-driven, four-engined airliner built by Lockheed Corporation starting in 1943. The Constellation series was the first pressurized-cabin civil airliner series to go into widespread use. Its press ...
L-1649 Starliner was acquired and fully restored for use as the hotel's cocktail bar, being placed on a section of apron in front of the hotel.
Destinations
For commuter destinations, see Trans World Express
Trans World Express (TWE) was the fully owned and certificated, regional carrier for Trans World Airlines (TWA) and an airline trademark name for TWA's corporation.
* Trans World Express - The formerly independent regional airline known as Ran ...
and Trans World Connection Trans World Connection was an affiliated brand name with Trans World Airlines (TWA). Other regional and commuter airlines operated code sharing service for TWA as Trans World Express.
The brand ended in December 2001, after American Airlines acqu ...
.
TWA had codeshare agreements with the following airlines:
* Air Europa
Air Europa Líneas Aéreas, S.A.U., branded as Air Europa, is the third-largest Spanish airline after Iberia and Vueling. The airline is headquartered in Llucmajor, Mallorca, Spain; it has its main hub at Adolfo Suárez Madrid–Barajas Airport ...
* Air Malta
Air Malta plc (stylized as airmalta) is the flag carrier airline of Malta, with its headquarters in Luqa and its hub at Malta International Airport. It operates services to destinations in Europe, the Middle East and North Africa.
History
...
* America West Airlines
America West Airlines was a major American airline, founded in 1981, with service commencing in 1983, and having reached US$1 billion in annual revenue in 1989, headquartered in Tempe, Arizona. At the time of its acquisition of US Airways, Americ ...
* American Airlines
American Airlines is a major US-based airline headquartered in Fort Worth, Texas, within the Dallas–Fort Worth metroplex. It is the largest airline in the world when measured by fleet size, scheduled passengers carried, and revenue passeng ...
* Kuwait Airways
Kuwait Airways ( ar, الخطوط الجوية الكويتية, ) is the national carrier of Kuwait, with its head office on the grounds of Kuwait International Airport, Al Farwaniyah Governorate. It operates scheduled international services t ...
* Royal Air Maroc
Royal Air Maroc (; ar, الخطوط الملكية المغربية, , literally ''Royal Moroccan Lines'' or ''Royal Moroccan Airlines''; ber, ⴰⵎⵓⵏⵉ ⴰⵢⵍⴰⵍ ⴰⴳⵍⴷⴰⵏ ⵏ ⴰⵎⵓⵔⴰⴽⵓⵛ, ''Amuni Aylal Age ...
* Royal Jordanian
Royal Jordanian Airlines ( ar, ; transliterated: ''Al-Malakiyyah al-'Urduniyyah''), formerly known as Alia Royal Jordanian Airlines, is the flag carrier airline of Jordan with its head office in the capital, Amman. The airline operates schedule ...
Fleet
Final fleet
When Trans World Airlines was acquired by American Airlines in 2001, their fleet contained these aircraft:
Retired fleet
Trans World Airlines had previously operated the following aircraft:
TWA, at one time, also held orders for the BAC-Aérospatiale Concorde, Sud Aviation Caravelle, Boeing 2707, and the Airbus A330-300
The Airbus A330 is a wide-body aircraft developed and produced by Airbus.
Airbus conceived several derivatives of the A300, its first airliner in the mid-1970s. Then the company began development on the A330 twinjet in parallel with the A3 ...
. The remaining A330 orders were eventually converted to A318 orders. TWA, along with Southwest Airlines
Southwest Airlines Co., typically referred to as Southwest, is one of the major airlines of the United States and the world's largest low-cost carrier. It is headquartered in Dallas, Texas, and has scheduled service to 121 destinations in the U ...
and USAir
US Airways (formerly USAir) was a major United States airline that operated from 1937 until its merger with American Airlines in 2015. It was originally founded in Pittsburgh as a mail delivery airline called All American Aviation, which soon b ...
, are the only major U.S.-based airlines to never have operated the McDonnell Douglas DC-10
The McDonnell Douglas DC-10 is an American trijet wide-body aircraft manufactured by McDonnell Douglas.
The DC-10 was intended to succeed the DC-8 for long- range flights. It first flew on August 29, 1970; it was introduced on August 5, 19 ...
.
Fleet in 1970
Accidents and incidents
Since 1942, TWA was involved in 84 incidents.
One of the first to gain wide press coverage was the crash of NC1946 (a DC-3
The Douglas DC-3 is a propeller-driven airliner
manufactured by Douglas Aircraft Company, which had a lasting effect on the airline industry in the 1930s to 1940s and World War II.
It was developed as a larger, improved 14-bed sleeper version ...
), operating as Flight 3, which killed Hollywood film star Carole Lombard, her mother, and 20 others.
On July 11, 1946, a TWA Lockheed Constellation, NC86513, operating as TWA Flight 513, a training flight, crashed in Reading, Pennsylvania. Of six crew members, only one survived. The crash was caused by a fire in the cargo hold and grounded all Constellations from July 12 until August 23, 1946.
Another disaster that gained widespread coverage was the collision of a TWA Lockheed L-1049 Super Constellation
The Lockheed L-1049 Super Constellation is an American aircraft, a member of the Lockheed Constellation aircraft line. The L-1049 was Lockheed's response to the successful Douglas DC-6 airliner, first flying in 1950. The aircraft was also produc ...
with a United Airlines' Douglas DC-7
The Douglas DC-7 is an American transport aircraft built by the Douglas Aircraft Company from 1953 to 1958. A derivative of the DC-6, it was the last major piston engine-powered transport made by Douglas, being developed shortly after the earl ...
over the Grand Canyon
The Grand Canyon (, yuf-x-yav, Wi:kaʼi:la, , Southern Paiute language: Paxa’uipi, ) is a steep-sided canyon carved by the Colorado River in Arizona, United States. The Grand Canyon is long, up to wide and attains a depth of over a mi ...
in 1956, which killed all 128 people on board both airliners. This accident led to groundbreaking changes in the regulation of flight operations in the United States.
A similar event occurred in 1960, this time in New York City, when another TWA L-1049 collided with a United Douglas DC-8. The disaster killed 134 people: 84 on board the UAL DC-8, 44 on board the TWA L-1049, and six people on the ground. No one survived from either airliner.
On June 26, 1959, a TWA Lockheed L-1649 Starliner
The Lockheed L-1649 Starliner was the last model of the Lockheed Constellation line of airliners. Powered by four Wright R-3350 TurboCompound engines, it was built at Lockheed's Burbank, California plant from 1956 to 1958.
Design and developm ...
, N7313C, operating as TWA Flight 891, crashed in a violent thunderstorm after it departed from Malpensa Airport, some 30 miles north of Milan, at 16.20. The aircraft was struck by lightning while flying at 11,000 feet above the ground, disintegrated with a tremendous explosion, burst into flames and crashed in several charred parts scattered over an area of five miles
Terrorist target
 From 1969 to 1986, six TWA airliners were
From 1969 to 1986, six TWA airliners were terrorist
Terrorism, in its broadest sense, is the use of criminal violence to provoke a state of terror or fear, mostly with the intention to achieve political or religious aims. The term is used in this regard primarily to refer to intentional violen ...
targets for Palestinian ''fedayeen'', four of which were hijackings and two were bombings, mainly because the airline had a strong European presence, was a flag carrier for the United States, and flew to Israel.
* In 1969, TWA Flight 840 from Rome to Athens was hijacked and forcibly diverted to Damascus
)), is an adjective which means "spacious".
, motto =
, image_flag = Flag of Damascus.svg
, image_seal = Emblem of Damascus.svg
, seal_type = Seal
, map_caption =
, ...
. Nobody was injured, but the aircraft's nose was blown up (although replaced and the plane returned to service).
* In 1970, TWA Flight 741 was hijacked after taking off from Frankfurt am Main en route to New York City. It was taken to Dawson's Field in Jordan
Jordan ( ar, الأردن; tr. ' ), officially the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan,; tr. ' is a country in Western Asia. It is situated at the crossroads of Asia, Africa, and Europe, within the Levant region, on the East Bank of the Jordan Rive ...
, along with two other hijacked aircraft. All three aircraft were empty of passengers and crew when they were destroyed. A fourth aircraft landed in Cairo and had a similar fate.
* In 1971, three members of the group " Republic of New Afrika" who had murdered a New Mexico State Police officer on November 8 hijacked TWA Flight 106, a Boeing 727, from Albuquerque
Albuquerque ( ; ), ; kee, Arawageeki; tow, Vakêêke; zun, Alo:ke:k'ya; apj, Gołgéeki'yé. abbreviated ABQ, is the most populous city in the U.S. state of New Mexico. Its nicknames, The Duke City and Burque, both reference its founding in ...
to Havana. Passengers were released in Tampa, Florida
Tampa () is a city on the Gulf Coast of the U.S. state of Florida. The city's borders include the north shore of Tampa Bay and the east shore of Old Tampa Bay. Tampa is the largest city in the Tampa Bay area and the seat of Hillsborough County ...
.
* In 1974, TWA Flight 841 from Tel Aviv
Tel Aviv-Yafo ( he, תֵּל־אָבִיב-יָפוֹ, translit=Tēl-ʾĀvīv-Yāfō ; ar, تَلّ أَبِيب – يَافَا, translit=Tall ʾAbīb-Yāfā, links=no), often referred to as just Tel Aviv, is the most populous city in the G ...
to New York City crashed into the Ionian Sea
The Ionian Sea ( el, Ιόνιο Πέλαγος, ''Iónio Pélagos'' ; it, Mar Ionio ; al, Deti Jon ) is an elongated bay of the Mediterranean Sea. It is connected to the Adriatic Sea to the north, and is bounded by Southern Italy, including ...
shortly after takeoff from Athens en route to Rome after a bomb believed to have been in the cargo hold exploded, killing all 88 on board.
* In 1976, TWA Flight 355 was hijacked by five Croatian separatists as it flew from New York–LaGuardia to O'Hare International. They ordered the pilot to fly to Montreal
Montreal ( ; officially Montréal, ) is the second-most populous city in Canada and most populous city in the Canadian province of Quebec. Founded in 1642 as '' Ville-Marie'', or "City of Mary", it is named after Mount Royal, the triple-pe ...
, where the plane was refueled, and then made additional refueling stops in Gander and Keflavik; at some of these stops, the hijackers unloaded propaganda pamphlets that they demanded to be dropped over Montreal, Chicago, New York, London, and Paris. At the plane's final stop, Paris-Charles de Gaulle
Paris Charles de Gaulle Airport (french: Aéroport de Paris-Charles-de-Gaulle, ), also known as Roissy Airport or simply Paris CDG, is the principal airport serving the French capital, Paris ( and its metropolitan area), and the largest intern ...
, the hijackers surrendered after direct talks with U.S. Ambassador Kenneth Rush
David Kenneth Rush (January 17, 1910 – December 11, 1994) was a United States Ambassador who helped negotiate the groundbreaking Four-Power Agreement in 1971 that ended the post-war crisis over Berlin.
Early life
Kenneth Rush was born Davi ...
, and their explosives were revealed to be fakes.
* In 1985, TWA Flight 847 from Athens to Rome was hijacked first to Beirut
Beirut, french: Beyrouth is the capital and largest city of Lebanon. , Greater Beirut has a population of 2.5 million, which makes it the third-largest city in the Levant region. The city is situated on a peninsula at the midpoint of ...
, then to Algiers, back to Beirut, back to Algiers, and finally back to Beirut—with some of its fuel being paid for by the Shell
Shell may refer to:
Architecture and design
* Shell (structure), a thin structure
** Concrete shell, a thin shell of concrete, usually with no interior columns or exterior buttresses
** Thin-shell structure
Science Biology
* Seashell, a hard o ...
credit card of flight attendant Uli Derickson
Uli Derickson (née Patzelt, August 8, 1944 – February 18, 2005), was a German American flight attendant best known for her role in helping protect 152 passengers and crew members during the June 14, 1985, hijacking of TWA Flight 847 by militan ...
. United States Navy Petty Officer 2nd Class Robert Stethem was singled out by Hezbollah as a member of the American military. The hijackers beat and tortured Stethem; Mohammed Ali Hammadi murdered the dying sailor and dumped his body on the tarmac. Robert Stethem was awarded the Purple Heart
The Purple Heart (PH) is a United States military decoration awarded in the name of the President to those wounded or killed while serving, on or after 5 April 1917, with the U.S. military. With its forerunner, the Badge of Military Merit, w ...
and Bronze Star
The Bronze Star Medal (BSM) is a United States Armed Forces decoration awarded to members of the United States Armed Forces for either heroic achievement, heroic service, meritorious achievement, or meritorious service in a combat zone.
Wh ...
with burial in Arlington National Cemetery. The memory of Robert Dean Stethem is honored by his nation with a namesake U.S. Navy destroyer, the USS'' Stethem'' (DDG-63).
* In 1986, TWA Flight 840, on approach to Athens, Greece
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Greece, largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh List ...
, was attacked with an on-board bomb, causing four Americans (including a nine-month-old infant) to be ejected from the aircraft to their deaths. Five others on the aircraft were injured as the cabin experienced a rapid decompression. The remaining 110 passengers survived the incident, and pilot Richard "Pete" Petersen made an emergency landing in Athens.
TWA Flight 800
TWA's worst accident occurred on July 17, 1996, when Flight 800, a Boeing 747
The Boeing 747 is a large, long-range wide-body aircraft, wide-body airliner designed and manufactured by Boeing Commercial Airplanes in the United States between 1968 and 2022.
After introducing the Boeing 707, 707 in October 1958, Pan Am w ...
en route to Paris, exploded over the Atlantic Ocean near Long Island
Long Island is a densely populated island in the southeastern region of the U.S. state of New York, part of the New York metropolitan area. With over 8 million people, Long Island is the most populous island in the United States and the 18th ...
, killing all 230 people on board. The National Transportation Safety Board
The National Transportation Safety Board (NTSB) is an independent U.S. government investigative agency responsible for civil transportation accident investigation. In this role, the NTSB investigates and reports on aviation accidents and inc ...
concluded that the most likely cause of the disaster was a center-fuel-tank explosion sparked by exposed wiring. In their subsequent coverage, the media focused heavily on the fact that TWA's airline fleet was among the oldest in service (the 747 used for Flight 800 was manufactured in 1971, making it 25 years old at the time of the incident). The flight was under the command of Captain Steven Snyder, a veteran TWA pilot.
Crew bases
TWA had crew bases in Boston, New York, Washington, D.C., St. Louis, Kansas City, Chicago, San Francisco, Los Angeles, and Frankfurt. International flight attendants' crew bases were located in Paris, Rome, Hong Kong, and, at one time, Cairo. Starting in 1996, TWA had a "West Coast Regional Domicile", in which pilots and flight attendants covered originating flights out of major West Coast U.S. airports from San Diego, California, north to San Francisco.
Ambassadors Club
TWA operated Ambassadors Club locations in various airports. American Airlines acquired some clubs, and other clubs closed on December 2, 2001.
Clubs in North America open on December 1, 2001
, ''Trans World Airlines''
*
** California
*** Los Angeles (Los Angeles International Airport
Los Angeles International Airport , commonly referred to as LAX (with each letter pronounced individually), is the primary international airport serving Los Angeles, California and its surrounding metropolitan area. LAX is located in the W ...
) (Converted into Alaska Airlines
Alaska Airlines is a major American airline headquartered in SeaTac, Washington, within the Seattle metropolitan area. It is the sixth largest airline in North America when measured by fleet size, scheduled passengers carried, and the num ...
Board Room)San Francisco International Airport
San Francisco International Airport is an international airport in an unincorporated area of San Mateo County, south of Downtown San Francisco. It has flights to points throughout North America and is a major gateway to Europe, the Middl ...
) (Converted into Alaska Airlines
Alaska Airlines is a major American airline headquartered in SeaTac, Washington, within the Seattle metropolitan area. It is the sixth largest airline in North America when measured by fleet size, scheduled passengers carried, and the num ...
Board Room)Boston
Boston (), officially the City of Boston, is the state capital and most populous city of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, as well as the cultural and financial center of the New England region of the United States. It is the 24th- most p ...
(Logan International Airport
General Edward Lawrence Logan International Airport , also known as Boston Logan International Airport and commonly as Boston Logan, Logan Airport or simply Logan, is an international airport that is located mostly in East Boston and partiall ...
)
** Missouri
Missouri is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. Ranking List of U.S. states and territories by area, 21st in land area, it is bordered by eight states (tied for the most with Tennessee ...
*** Kansas City
The Kansas City metropolitan area is a bi-state metropolitan area anchored by Kansas City, Missouri. Its 14 counties straddle the border between the U.S. states of Missouri (9 counties) and Kansas (5 counties). With and a population of more ...
(Kansas City International Airport
Kansas City International Airport (originally Mid-Continent International Airport) is a public airport in Kansas City, Missouri located northwest of Downtown Kansas City in Platte County, Missouri., effective December 30, 2021. The airport o ...
) (Converted into Admirals ClubSt. Louis
St. Louis () is the second-largest city in Missouri, United States. It sits near the confluence of the Mississippi and the Missouri Rivers. In 2020, the city proper had a population of 301,578, while the bi-state metropolitan area, which ...
( Lambert-St. Louis International Airport) (Converted into Admirals ClubNew York
New York most commonly refers to:
* New York City, the most populous city in the United States, located in the state of New York
* New York (state), a state in the northeastern United States
New York may also refer to:
Film and television
* ...
*** New York City (LaGuardia Airport
LaGuardia Airport is a civil airport in East Elmhurst, Queens, New York City. Covering , the facility was established in 1929 and began operating as a public airport in 1939. It is named after former New York City mayor Fiorello La Guardia. ...
)
** Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States, between the Atlantic Coast and the Appalachian Mountains. The geography and climate of the Commonwealth are ...
*** Washington, D.C., area (Washington Dulles International Airport
Washington Dulles International Airport , typically referred to as Dulles International Airport, Dulles Airport, Washington Dulles, or simply Dulles ( ), is an international airport in the Eastern United States, located in Loudoun County and F ...
)
Clubs in North America and the Caribbean closed prior to dissolution
[TWA North America Destinations]
, ''Trans World Airlines''
*
** Arizona
*** Phoenix
Phoenix most often refers to:
* Phoenix (mythology), a legendary bird from ancient Greek folklore
* Phoenix, Arizona, a city in the United States
Phoenix may also refer to:
Mythology
Greek mythological figures
* Phoenix (son of Amyntor), a ...
(Sky Harbor International Airport
Phoenix Sky Harbor International Airport is a civil–military public airport east of downtown Phoenix, in Maricopa County, Arizona, United States. It is Arizona's largest and busiest airport, and among the largest commercial airports in th ...
)
** California
*** (San Diego International Airport
San Diego International Airport , formerly known as Lindbergh Field, is an international airport northwest of Downtown San Diego, California, United States. It is owned and operated by the San Diego County Regional Airport Authority.. US Fede ...
)
** New Mexico
)
, population_demonym = New Mexican ( es, Neomexicano, Neomejicano, Nuevo Mexicano)
, seat = Santa Fe, New Mexico, Santa Fe
, LargestCity = Albuquerque, New Mexico, Albuquerque
, LargestMetro = Albuquerque metropolitan area, Tiguex
, Offi ...
*** Albuquerque
Albuquerque ( ; ), ; kee, Arawageeki; tow, Vakêêke; zun, Alo:ke:k'ya; apj, Gołgéeki'yé. abbreviated ABQ, is the most populous city in the U.S. state of New Mexico. Its nicknames, The Duke City and Burque, both reference its founding in ...
(Albuquerque International Sunport
Albuquerque International Sunport is the primary international airport serving the U.S. state of New Mexico, the Albuquerque metropolitan area, and the larger Albuquerque– Santa Fe–Las Vegas combined statistical area. It handles around 5 ...
)
** New Jersey
New Jersey is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Northeastern regions of the United States. It is bordered on the north and east by the state of New York; on the east, southeast, and south by the Atlantic Ocean; on the west by the Delaware ...
*** Newark (Newark Liberty International Airport
Newark Liberty International Airport , originally Newark Metropolitan Airport and later Newark International Airport, is an international airport straddling the boundary between the cities of Newark in Essex County and Elizabeth in Union Cou ...
)
** New York
New York most commonly refers to:
* New York City, the most populous city in the United States, located in the state of New York
* New York (state), a state in the northeastern United States
New York may also refer to:
Film and television
* ...
*** New York City (John F. Kennedy International Airport
John F. Kennedy International Airport (colloquially referred to as JFK Airport, Kennedy Airport, New York-JFK, or simply JFK) is the main international airport serving New York City. The airport is the busiest of the seven airports in the New ...
)
** Ohio
Ohio () is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States. Of the fifty U.S. states, it is the 34th-largest by area, and with a population of nearly 11.8 million, is the seventh-most populous and tenth-most densely populated. The sta ...
*** Columbus (Port Columbus International Airport
John Glenn Columbus International Airport is an international airport located east of downtown Columbus, Ohio. Formerly known as Port Columbus International Airport, it is managed by the Columbus Regional Airport Authority, which also over ...
)
*** Dayton
Dayton () is the List of cities in Ohio, sixth-largest city in the U.S. state of Ohio and the county seat of Montgomery County, Ohio, Montgomery County. A small part of the city extends into Greene County, Ohio, Greene County. The 2020 United S ...
(Dayton International Airport
Dayton International Airport (officially James M. Cox Dayton International Airport), formerly Dayton Municipal Airport and James M. Cox-Dayton Municipal Airport, is 10 miles north of downtown Dayton, in Montgomery County, Ohio, United States. ...
)
** Texas
Texas (, ; Spanish: ''Texas'', ''Tejas'') is a state in the South Central region of the United States. At 268,596 square miles (695,662 km2), and with more than 29.1 million residents in 2020, it is the second-largest U.S. state by b ...
*** Dallas/Fort Worth (Dallas/Fort Worth International Airport
Dallas/Fort Worth International Airport , also known as DFW Airport, is the primary international airport serving the Dallas–Fort Worth metroplex and the North Texas Region in the U.S. state of Texas.
It is the largest hub for American Air ...
)
*** Houston
Houston (; ) is the most populous city in Texas, the most populous city in the Southern United States, the fourth-most populous city in the United States, and the sixth-most populous city in North America, with a population of 2,304,580 i ...
(George Bush Intercontinental Airport
George Bush Intercontinental Airport is an international airport in Houston, Texas, United States, serving the Greater Houston metropolitan area. Located about north of Downtown Houston between Interstate 45 and Interstate 69/ U.S. Highway 5 ...
)
** Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States, between the Atlantic Coast and the Appalachian Mountains. The geography and climate of the Commonwealth are ...
*** Washington, D.C., area ( Washington Reagan National Airport)
** Washington
*** Seattle-Tacoma International Airport)
*
** San Juan (Luis Muñoz Marín International Airport
Luis Muñoz Marín International Airport ( es, link=no, Aeropuerto Internacional Luis Muñoz Marín) is a joint civil-military international airport located in suburban Carolina, Puerto Rico, southeast of San Juan. It is named for Luis Muño ...
)
Clubs in Europe closed prior to dissolution
[TWA Transatlantic Destinations Europe and the Middle East]
, ''Trans World Airlines''
*
** London (London Gatwick Airport
Gatwick Airport (), also known as London Gatwick , is a major international airport near Crawley, West Sussex, England, south of Central London. In 2021, Gatwick was the third-busiest airport by total passenger traffic in the UK, after He ...
)
*
** Paris (Charles de Gaulle Airport
Paris Charles de Gaulle Airport (french: Aéroport de Paris-Charles-de-Gaulle, ), also known as Roissy Airport or simply Paris CDG, is the principal airport serving the French capital, Paris ( and its metropolitan area), and the largest intern ...
)
*
** Milan
Milan ( , , Lombard: ; it, Milano ) is a city in northern Italy, capital of Lombardy, and the second-most populous city proper in Italy after Rome. The city proper has a population of about 1.4 million, while its metropolitan city has ...
(Malpensa Airport
Milan Malpensa Airport is the largest international airport in northern Italy, serving Lombardy, Piedmont and Liguria, as well as the Swiss Canton of Ticino. The airport is northwest of Milan, next to the Ticino river dividing Lombardy and Pie ...
)
** Rome (Leonardo Da Vinci Airport
Leonardo is a masculine given name, the Italian, Spanish, and Portuguese equivalent of the English, German, and Dutch name, Leonard.
People
Notable people with the name include:
* Leonardo da Vinci (1452–1519), Italian Renaissance scient ...
)
*
** Frankfurt (Frankfurt Airport
Frankfurt Airport (; german: link=no, Flughafen Frankfurt Main , also known as ''Rhein-Main-Flughafen'') is a major international airport located in Frankfurt, the fifth-largest city of Germany and one of the world's leading financial centres. ...
) (became an American Airlines Admirals Club in 1997)
See also
* Ransome Airlines
Ransome Airlines was a regional airline from the United States, headquartered at Northeast Philadelphia Airport in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. Founded in 1967, it operated feeder flights on behalf of different mainline carriers via specific airl ...
the Trans World Express
Trans World Express (TWE) was the fully owned and certificated, regional carrier for Trans World Airlines (TWA) and an airline trademark name for TWA's corporation.
* Trans World Express - The formerly independent regional airline known as Ran ...
* TWE – TW Express
* Trans World Connection Trans World Connection was an affiliated brand name with Trans World Airlines (TWA). Other regional and commuter airlines operated code sharing service for TWA as Trans World Express.
The brand ended in December 2001, after American Airlines acqu ...
* List of defunct airlines of the United States
A ''list'' is any set of items in a row. List or lists may also refer to:
People
* List (surname)
Organizations
* List College, an undergraduate division of the Jewish Theological Seminary of America
* SC Germania List, German rugby unio ...
References
External links
TWA Museum at Charles B. Wheeler Downtown Airport in Kansas City
*
US Airways and American Airlines merger site
American Airlines site
*
has many TWA timetables from 1931 until 1968, showing where they flew, how long it took and how much it cost.
Wayback Machine
has three TWA timetables including the final TWA timetable.
The karabu deal contract
Historical TWA aircraft images
Trans World Airlines records
at the University of Wyoming
The University of Wyoming (UW) is a public land-grant research university in Laramie, Wyoming. It was founded in March 1886, four years before the territory was admitted as the 44th state, and opened in September 1887. The University of Wyoming ...
– American Heritage Center
The American Heritage Center is the University of Wyoming's repository of manuscripts, rare books, and the university archives. Its collections focus on Wyoming and the Rocky Mountain West (including politics, settlement, and western trails) and ...
Digital collection of ''TWA Skyliner''
(in-house magazine of TWA) via the State Historical Society of Missouri
TWA Retired Pilots Association
{{Authority control
Airlines disestablished in 2001
Airlines established in 1930
American Airlines
Companies based in Kansas City, Missouri
Companies based in St. Louis
Companies that filed for Chapter 11 bankruptcy in 1992
Companies that filed for Chapter 11 bankruptcy in 1995
Companies that filed for Chapter 11 bankruptcy in 2001
Defunct airlines of the United States
Defunct companies based in Missouri
Howard Hughes
Defunct companies based in New York City
 TWA's corporate history dates from July 16, 1930, and the forced merger of
TWA's corporate history dates from July 16, 1930, and the forced merger of  On March 31, 1931, the airline suffered after the 1931 Transcontinental & Western Air Fokker F-10 crash near
On March 31, 1931, the airline suffered after the 1931 Transcontinental & Western Air Fokker F-10 crash near  On September 20, 1932, the development contract was signed with
On September 20, 1932, the development contract was signed with  In 1934, following charges of favoritism in the contracts, the
In 1934, following charges of favoritism in the contracts, the  On January 29, 1937, TWA contracted with Boeing for five
On January 29, 1937, TWA contracted with Boeing for five 
 TWA's flight operations were based at
TWA's flight operations were based at  In 1960, Hughes relinquished control of the airline, as the major stockholder, through the financial terms associated with the jet purchase. As a consequence of that deal, Charles C. Tillinghast Jr. took over as president. The battle over Hughes' control continued in court until 1966 when Hughes was forced to sell his stock. That sale brought Hughes $546,549,771.
Under a plan put together by Dillon, Read & Co., a $165 million loan was raised to fund a 45-jet fleet. The deal which was signed on December 30, 1960, by Hughes' lawyer Raymond Holliday, who constituted one member of a three-person voting trust, the other two members,
In 1960, Hughes relinquished control of the airline, as the major stockholder, through the financial terms associated with the jet purchase. As a consequence of that deal, Charles C. Tillinghast Jr. took over as president. The battle over Hughes' control continued in court until 1966 when Hughes was forced to sell his stock. That sale brought Hughes $546,549,771.
Under a plan put together by Dillon, Read & Co., a $165 million loan was raised to fund a 45-jet fleet. The deal which was signed on December 30, 1960, by Hughes' lawyer Raymond Holliday, who constituted one member of a three-person voting trust, the other two members,  In 1962, TWA opened Trans World Flight Center, now Terminal 5 (or simply T5), at New York City's JFK Airport and designed by
In 1962, TWA opened Trans World Flight Center, now Terminal 5 (or simply T5), at New York City's JFK Airport and designed by 
 On April 7, 1967, TWA became one of the US's first all-jet airlines with the retirement of their last Lockheed L-749A Constellation and L-1649 Starliner cargo aircraft. That morning, throughout the TWA system, aircraft ground-service personnel placed a booklet on every passenger seat titled "Props Are For Boats".
In 1967–72, TWA was the world's third-largest airline by passenger-miles, behind Aeroflot and United. During the mid and late 1960s, the airline extended its reach as far east as Hong Kong from Europe and also introduced service to a number of destinations in Africa. In 1969, TWA carried the most transatlantic passengers of any airline; until then, Pan American World Airways had always been number one. In the Transpacific Route Case of 1969, TWA was given authority to fly across the Pacific to Hawaii and Taiwan, and for a few years, TWA had a round-the-world network.
In 1969, TWA opened the Breech Academy on a campus in the Kansas City suburb of
On April 7, 1967, TWA became one of the US's first all-jet airlines with the retirement of their last Lockheed L-749A Constellation and L-1649 Starliner cargo aircraft. That morning, throughout the TWA system, aircraft ground-service personnel placed a booklet on every passenger seat titled "Props Are For Boats".
In 1967–72, TWA was the world's third-largest airline by passenger-miles, behind Aeroflot and United. During the mid and late 1960s, the airline extended its reach as far east as Hong Kong from Europe and also introduced service to a number of destinations in Africa. In 1969, TWA carried the most transatlantic passengers of any airline; until then, Pan American World Airways had always been number one. In the Transpacific Route Case of 1969, TWA was given authority to fly across the Pacific to Hawaii and Taiwan, and for a few years, TWA had a round-the-world network.
In 1969, TWA opened the Breech Academy on a campus in the Kansas City suburb of 
 Facing the pressures of
Facing the pressures of  TWA's zenith occurred in the summer of 1988, when, for the only time, the airline carried more than 50 percent of all transatlantic passengers. Every day, Boeing 747,
TWA's zenith occurred in the summer of 1988, when, for the only time, the airline carried more than 50 percent of all transatlantic passengers. Every day, Boeing 747,  By agreement dated August 14, 1995, Lowestfare.com LLC, a wholly-owned operating subsidiary of Karabu, was joined as a party to the ticket program agreement. Pursuant to the ticket program agreement, Lowestfare.com could purchase an unlimited number of system tickets. System tickets are tickets for all applicable classes of service which were purchased by Karabu from TWA at a 45% discount from TWA's published fare. In addition to system tickets, Lowestfare.com could also purchase domestic consolidator tickets, which are tickets issued at bulk fare rates and were limited to specified origin/destination city markets and did not permit the holder to modify or refund a purchased ticket. Karabu's purchase of domestic consolidator tickets was subject to a cap of $70 million per year based on the full retail price of the tickets.
On most TWA flights, Karabu could buy at a heavy discount and then sell a certain portion of all TWA's available seats. As a result, TWA was hamstrung by the high proportion of heavily discounted seats that had been sold and was essentially left with no control over its own pricing. It could not afford to discount any of its own seats, and if TWA wanted to increase revenue on busy routes by putting a larger plane into service, Karabu would only claim more seats. TWA was losing an estimated $150 million a year in revenue due to this deal.
To ameliorate the Karabu deal, TWA went in and out of bankruptcy in 1995.
TWA entered its second bankruptcy on June 30, 1995. When TWA emerged in August 1995, employee ownership was reduced to 30%, but the company was relieved of $0.5 billion of its $1.8 billion debt.
By agreement dated August 14, 1995, Lowestfare.com LLC, a wholly-owned operating subsidiary of Karabu, was joined as a party to the ticket program agreement. Pursuant to the ticket program agreement, Lowestfare.com could purchase an unlimited number of system tickets. System tickets are tickets for all applicable classes of service which were purchased by Karabu from TWA at a 45% discount from TWA's published fare. In addition to system tickets, Lowestfare.com could also purchase domestic consolidator tickets, which are tickets issued at bulk fare rates and were limited to specified origin/destination city markets and did not permit the holder to modify or refund a purchased ticket. Karabu's purchase of domestic consolidator tickets was subject to a cap of $70 million per year based on the full retail price of the tickets.
On most TWA flights, Karabu could buy at a heavy discount and then sell a certain portion of all TWA's available seats. As a result, TWA was hamstrung by the high proportion of heavily discounted seats that had been sold and was essentially left with no control over its own pricing. It could not afford to discount any of its own seats, and if TWA wanted to increase revenue on busy routes by putting a larger plane into service, Karabu would only claim more seats. TWA was losing an estimated $150 million a year in revenue due to this deal.
To ameliorate the Karabu deal, TWA went in and out of bankruptcy in 1995.
TWA entered its second bankruptcy on June 30, 1995. When TWA emerged in August 1995, employee ownership was reduced to 30%, but the company was relieved of $0.5 billion of its $1.8 billion debt.
 By 1998, TWA had reorganized as a primarily domestic carrier, with routes centered on hubs at St. Louis and New York. Partly in response to
By 1998, TWA had reorganized as a primarily domestic carrier, with routes centered on hubs at St. Louis and New York. Partly in response to  TWA stated that it planned to make Los Angeles a focus city around October 2000, with a partnership with
TWA stated that it planned to make Los Angeles a focus city around October 2000, with a partnership with  On December 16, 2013, Doug Parker, CEO of
On December 16, 2013, Doug Parker, CEO of  From 1969 to 1986, six TWA airliners were
From 1969 to 1986, six TWA airliners were