Tuberculous Lymphadenitis on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
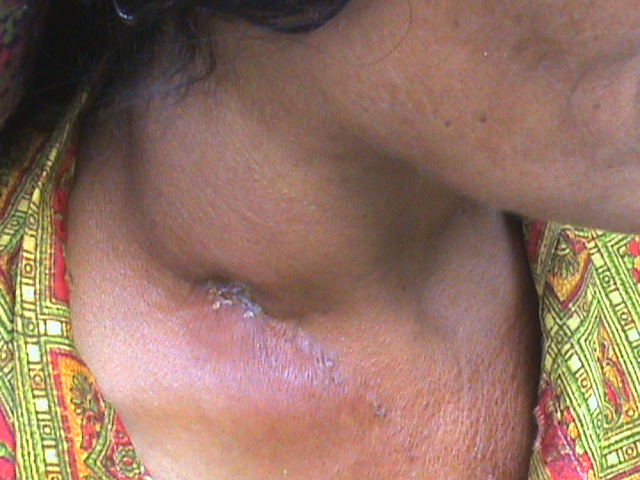 Peripheral tuberculous lymphadenitis (or tuberculous adenitis) is a form of
Peripheral tuberculous lymphadenitis (or tuberculous adenitis) is a form of
 ''
''
 The gold standard for diagnosis of tuberculous lymphadenitis is to obtain a
The gold standard for diagnosis of tuberculous lymphadenitis is to obtain a
tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB), also known colloquially as the "white death", or historically as consumption, is a contagious disease usually caused by ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can al ...
infection occurring outside of the lungs
The lungs are the primary organs of the respiratory system in many animals, including humans. In mammals and most other tetrapods, two lungs are located near the backbone on either side of the heart. Their function in the respiratory syste ...
. In general, it describes tuberculosis infection of the lymph nodes
A lymph node, or lymph gland, is a kidney-shaped Organ (anatomy), organ of the lymphatic system and the adaptive immune system. A large number of lymph nodes are linked throughout the body by the lymphatic vessels. They are major sites of lymphoc ...
, leading to lymphadenopathy
Lymphadenopathy or adenopathy is a disease of the lymph nodes, in which they are abnormal in size or consistency. Lymphadenopathy of an inflammatory type (the most common type) is lymphadenitis, producing swollen or enlarged lymph nodes. In c ...
. When cervical lymph nodes
Cervical lymph nodes are lymph nodes found in the neck. Of the 800 lymph nodes in the human body, 300 are in the neck. Cervical lymph nodes are subject to a number of different pathological conditions including tumours, infection and inflamma ...
are affected, it is commonly referred to as " Scrofula." A majority of tuberculosis infections affect the lungs, and extra-pulmonary tuberculosis infections account for the remainder; these most commonly involve the lymphatic system
The lymphatic system, or lymphoid system, is an organ system in vertebrates that is part of the immune system and complementary to the circulatory system. It consists of a large network of lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, lymphoid organs, lympha ...
. Although the cervical region is most commonly affected, tuberculous lymphadenitis can occur all around the body, including the axillary
Axillary means "related to the axilla (armpit)" or "related to the leaf axils".
"Axillary" may refer to: Biology
* Axillary artery
* Axillary border
* Axillary fascia
* Axillary feathers
* Axillary hairs
* Axillary lines
* Axillary lymph nodes ...
and inguinal regions.
The characteristic morphological element is the tuberculous granuloma
A granuloma is an aggregation of macrophages (along with other cells) that forms in response to chronic inflammation. This occurs when the immune system attempts to isolate foreign substances that it is otherwise unable to eliminate. Such sub ...
(caseating tubercule). This consists of giant multinucleated cells and ( Langhans cells), surrounded by epithelioid cell
Epithelioid cells (also called epithelioid histiocytes)
are derivatives of activated macrophages resembling Epithelium, epithelial cells.
Structure and function
Structurally, epithelioid cells (when examined by light microscopy after stained ...
s aggregates, T cell lymphocytes
A lymphocyte is a type of white blood cell (leukocyte) in the immune system of most vertebrates. Lymphocytes include T cells (for cell-mediated and cytotoxic adaptive immunity), B cells (for humoral, antibody-driven adaptive immunity), and ...
and fibroblasts
A fibroblast is a type of biological cell typically with a spindle shape that synthesizes the extracellular matrix and collagen, produces the structural framework ( stroma) for animal tissues, and plays a critical role in wound healing. Fibrobla ...
. Granulomatous tubercules eventually develop central caseous necrosis and tend to become confluent, replacing the lymphoid tissue.
Epidemiology
The exact prevalence of tuberculous lymphadenitis varies between countries and regions, with higher rates seen in developing countries. Studies have shown that women may have higher rates of tuberculous lymphadenitis compared to men. Conversely, men appear to have higher rates ofpulmonary tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB), also known colloquially as the "white death", or historically as consumption, is a contagious disease usually caused by ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can al ...
. In regions where tuberculosis is not endemic, many of those affected with tuberculous lymphadenitis are foreign-born. In general, tuberculous lymphadenitis is more frequently seen in immunocompromised patients, such as those with uncontrolled HIV.
Causes
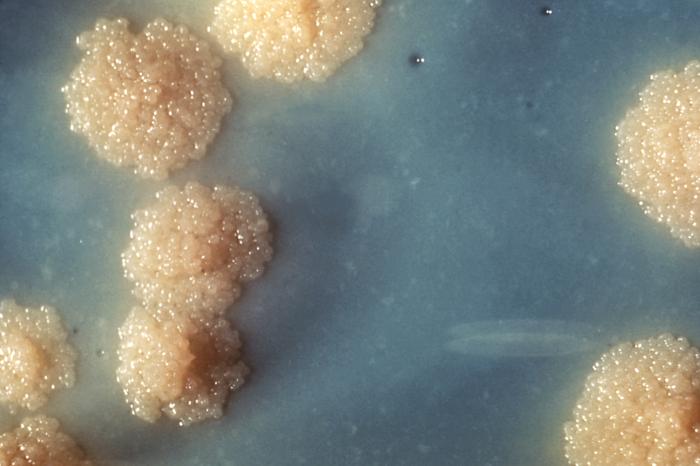
 ''
''Mycobacterium tuberculosis
''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (M. tb), also known as Koch's bacillus, is a species of pathogenic bacteria in the family Mycobacteriaceae and the causative agent of tuberculosis.
First discovered in 1882 by Robert Koch, ''M. tuberculosis'' ha ...
'' is the most common cause of both pulmonary tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB), also known colloquially as the "white death", or historically as consumption, is a contagious disease usually caused by ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can al ...
and tuberculous lymphadenitis. Historically, transmission of ''Mycobacterium bovis
''Mycobacterium bovis'' is a slow-growing (16- to 20-hour generation time) Aerobic organism, aerobic bacterium and the causative agent of tuberculosis in cattle (known as bovine TB). It is related to ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'', the bacterium ...
'' from dairy consumption was another frequent cause of tuberculous lymphadenitis, but incidence has drastically decreased in developed countries since the advent of pasteurization and other efforts to prevent bovine tuberculosis. Tuberculous lymphadenitis has sometimes been caused by other related bacteria, including ''M. kansasii
''Mycobacterium kansasii'' is a bacterium in the ''Mycobacterium'' genus. It is an environmental bacteria that causes opportunistic infections in humans, and is one of the leading mycobacterial causes of human disease after tuberculosis and lepr ...
'', ''M. fortuitum
''Mycobacterium fortuitum'' is a nontuberculous species of the phylum Actinomycetota (Gram-positive bacteria with high guanine and cytosine content, one of the dominant phyla of all bacteria), belonging to the genus ''Mycobacterium''.
Backgroun ...
'', ''M. marinum
''Mycobacterium marinum'' is a slow growing fresh and saltwater mycobacterium (SGM) belonging to the genus ''Mycobacterium'' and the phylum Actinobacteria. It was formerly known as ''Mycobacterium balnei''. The strain marinum was first identified ...
'', and ''Mycobacterium ulcerans
''Mycobacterium ulcerans'' is a species of bacteria found in various aquatic environments. The bacteria can infect humans and some other animals, causing persistent open wounds called Buruli ulcer. ''M. ulcerans'' is closely related to ''Mycoba ...
''.
Signs and symptoms
Tuberculous lymphadenitis typically involves a gradual and usually painless swelling of the affected lymph nodes (termedlymphadenitis
Lymphadenopathy or adenopathy is a disease of the lymph nodes, in which they are abnormal in size or consistency. Lymphadenopathy of an inflammatory type (the most common type) is lymphadenitis, producing swollen or enlarged lymph nodes. In cl ...
). Duration of symptoms can vary, and ranges between weeks to months following initial onset. Unilateral lymph node involvement accounts for the majority of cases, and involvement of the cervical lymph nodes
Cervical lymph nodes are lymph nodes found in the neck. Of the 800 lymph nodes in the human body, 300 are in the neck. Cervical lymph nodes are subject to a number of different pathological conditions including tumours, infection and inflamma ...
is the most common.
In addition to swollen lymph nodes, the person may experience mild fevers, decreased appetite, or weight loss. Pulmonary tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB), also known colloquially as the "white death", or historically as consumption, is a contagious disease usually caused by ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can al ...
infection may co-occur with tuberculous lymphadenitis and account for additional symptoms such as cough.
Stages
Stages of tubercular lymphadenitis: # Lymphadenitis # Periadenitis # Cold abscess # 'Collar stud' abscess # Sinus Tuberculous lymphadenitis is popularly known as collar stud abscess, due to its proximity to thecollar bone
The clavicle, collarbone, or keybone is a slender, S-shaped long bone approximately long that serves as a strut between the shoulder blade and the sternum (breastbone). There are two clavicles, one on each side of the body. The clavicle is the ...
and its superficial resemblance to a collar stud
A detachable collar or a false collar is a shirt collar separate from the shirt, fastened to it by studs. The collar is usually made of a different fabric from the shirt, in which case it is almost always white, and, being unattached to the shir ...
, although this is just one of the five stages of the disease. One or more affected lymph nodes can also be in a different body part, although it is most typical to have at least one near the collar bone. The characteristic morphological element is the tuberculous granuloma (caseating tubercule): giant multinucleated cells (Langhans cells), surrounded by epithelioid cells aggregates, T cell lymphocytes and few fibroblasts. Granulomatous tubercules evolve to central caseous necrosis and tend to become confluent, replacing the lymphoid tissue.
Diagnosis
culture
Culture ( ) is a concept that encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and Social norm, norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, Social norm, customs, capabilities, Attitude (psychology), attitudes ...
, though results may take weeks. A positive acid-fast bacteria (AFB) stain can support the diagnosis. Other possible methods include nucleic acid amplification tests, fine needle aspiration
Fine-needle aspiration (FNA) is a diagnostic procedure used to investigate lumps or masses. In this technique, a thin (23–25 gauge (0.52 to 0.64 mm outer diameter)), hollow needle is inserted into the mass for sampling of cells that, ...
(FNA), or excisional biopsy
A biopsy is a medical test commonly performed by a surgeon, an interventional radiologist, or an interventional cardiologist. The process involves the extraction of sample cells or tissues for examination to determine the presence or extent of ...
, the most invasive method.
Supplementary studies to aid in diagnosis include tuberculin skin tests, interferon-gamma release assays, or chest X-rays
A chest radiograph, chest X-ray (CXR), or chest film is a Projectional radiography, projection radiograph of the chest used to diagnose conditions affecting the chest, its contents, and nearby structures. Chest radiographs are the most common fi ...
.
Treatment
Treatment of tuberculous lymphadenitis involves an anti-tuberculosis medication regimen for at least 6 months. This includesisoniazid
Isoniazid, also known as isonicotinic acid hydrazide (INH), is an antibiotic used for the treatment of tuberculosis. For active tuberculosis, it is often used together with rifampicin, pyrazinamide, and either streptomycin or ethambutol. F ...
, rifampin
Rifampicin, also known as rifampin, is an ansamycin antibiotic used to treat several types of bacterial infections, including tuberculosis (TB), ''Mycobacterium avium'' complex, leprosy, and Legionnaires' disease. It is almost always used tog ...
, pyrazinamide
Pyrazinamide is a medication used to treat tuberculosis. For active tuberculosis, it is often used with rifampicin, isoniazid, and either streptomycin or ethambutol. It is not generally recommended for the treatment of latent tuberculosis. It i ...
, and ethambutol
Ethambutol (EMB, E) is a medication primarily used to treat tuberculosis. It is usually given in combination with other tuberculosis medications, such as isoniazid, rifampicin and pyrazinamide. It may also be used to treat ''Mycobacterium avi ...
depending on susceptibility to the drug.
While surgical removal of affected lymph nodes alongside antibiotic therapy has shown some efficacy, there are no formal recommendations for surgery to treat tuberculous lymphadenitis.
References
External links
{{Gram-positive actinobacteria diseases Anatomical pathology Tuberculosis