Triple Screen on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The triple test, also called triple screen, the Kettering test or the Bart's test, is an investigation performed during
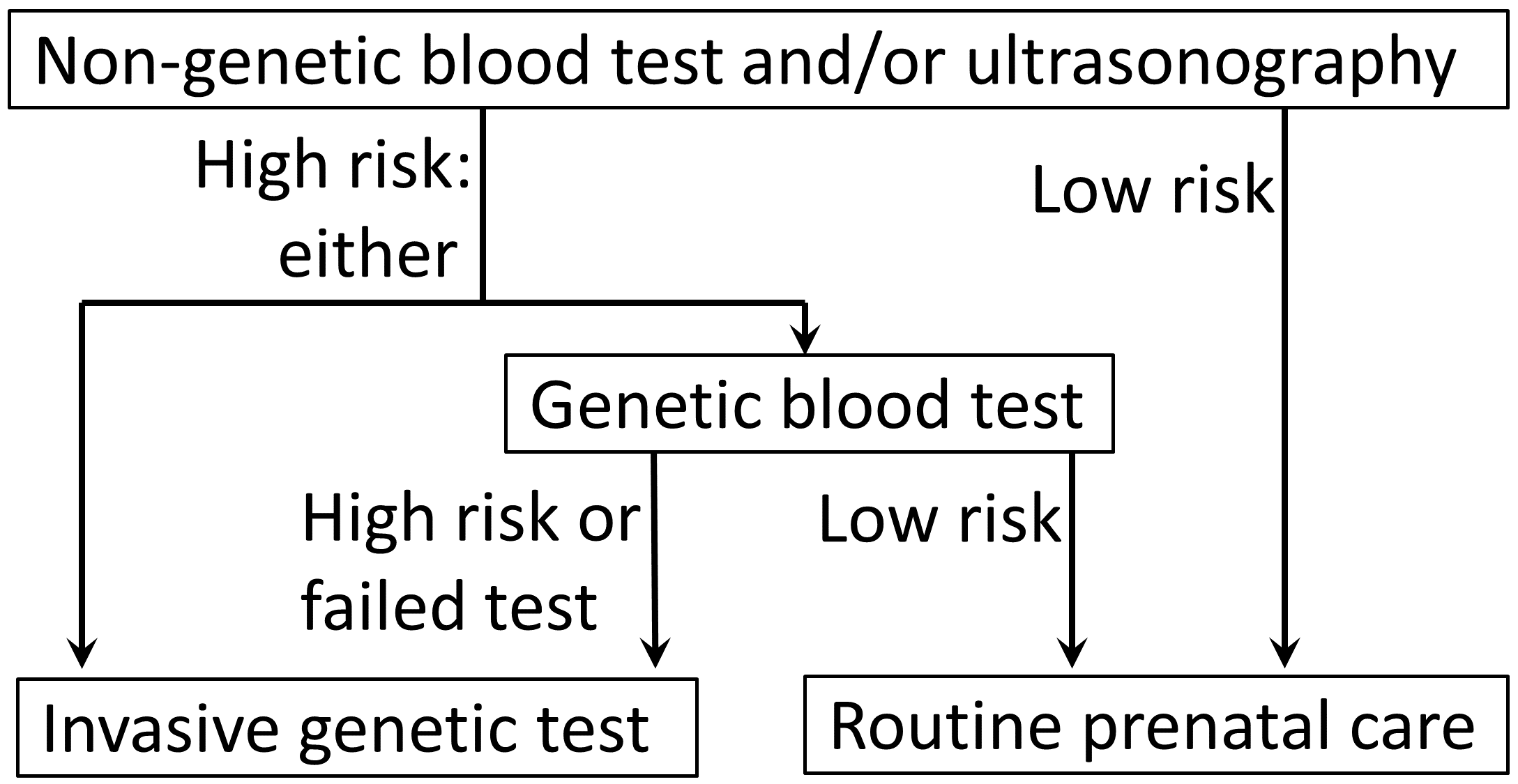 The test is for screening, not for
The test is for screening, not for
AmericanPregnancy.org
{{DEFAULTSORT:Triple Test Tests during pregnancy
pregnancy
Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring gestation, gestates inside a woman's uterus. A multiple birth, multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins.
Conception (biology), Conception usually occurs ...
in the second trimester to classify a patient as either high-risk or low-risk for chromosomal abnormalities (and neural tube defects).
The term "multiple-marker screening test" is sometimes used instead. This term can encompass the "double test" and "quadruple test" (described below).
The Triple screen measures serum levels of AFP, estriol
Estriol (E3), also spelled oestriol, is a steroid, a weak estrogen, and a minor female sex hormone. It is one of three major endogenous estrogens, the others being estradiol and estrone. Levels of estriol in women who are not pregnant are almost ...
, and beta-hCG, with a 70% sensitivity and 5% false-positive
A false positive is an error in binary classification in which a test result incorrectly indicates the presence of a condition (such as a disease when the disease is not present), while a false negative is the opposite error, where the test resu ...
rate. It is complemented in some regions of the United States, as the ''Quad screen'' (adding inhibin A to the panel, resulting in an 81% sensitivity and 5% false-positive rate for detecting Down syndrome when taken at 15–18 weeks of gestational age
In obstetrics, gestational age is a measure of the age of a pregnancy taken from the beginning of the woman's last menstrual period (LMP), or the corresponding age of the gestation as estimated by a more accurate method, if available. Such metho ...
) and other prenatal diagnosis
Prenatal testing is a tool that can be used to detect some birth defects at various stages prior to birth. Prenatal testing consists of prenatal screening and prenatal diagnosis, which are aspects of prenatal care that focus on detecting problem ...
techniques, although it remains widely used in Canada and other countries. A positive screen indicates an increased risk of chromosomal abnormalities (and neural tube defects), and such patients are then referred for more sensitive and specific procedures to receive a definitive diagnosis, often prenatal diagnosis via amniocentesis
Amniocentesis is a medical procedure used primarily in the prenatal diagnosis of genetic conditions. It has other uses such as in the assessment of infection and fetal lung maturity. Prenatal diagnostic testing, which includes amniocentesis, is ...
, although the stronger screening option of cell-free fetal DNA
Cell-free fetal DNA (cffDNA) is fetal DNA that circulates freely in the maternal blood. Maternal blood is sampled by venipuncture. Analysis of cffDNA is a method of non-invasive prenatal diagnosis frequently ordered for pregnant women of advance ...
screening (also popularly known as noninvasive prenatal screening) is frequently offered. The Triple test can be understood as an early predecessor to a long line of subsequent technological improvements. In some American states, such as Missouri, Medicaid reimburses only for the Triple test and not other potentially more accurate screening tests, whereas California offers Quad tests to all pregnant women.
While the triple test can be performed at any point between 15 and 21.9 weeks of gestation, the highest detection rate for open neural defects is given by a test performed between 16 and 18 weeks of gestation.
Conditions screened
The most common abnormality the test can screen istrisomy 21
A trisomy is a type of polysomy in which there are three instances of a particular chromosome, instead of the normal two. A trisomy is a type of aneuploidy (an abnormal number of chromosomes).
Description and causes
Most organisms that repro ...
( Down syndrome). In addition to Down syndrome, the triple and quadruple screens assess risk for fetal trisomy 18 also known as Edwards syndrome Edwards may refer to:
People
* Edwards (surname), an English surname
* Edwards family, a prominent family from Chile
* Edwards Barham (1937–2014), American politician
* Edwards Davis (1873–1936), American actor, producer, and playwright
* Edwa ...
, open neural tube defects
Neural tube defects (NTDs) are a group of birth defects in which an opening in the spine or cranium remains from early in human development. In the third week of pregnancy called gastrulation, specialized cells on the dorsal side of the embry ...
, and may also detect an increased risk of Turner syndrome
Turner syndrome (TS), commonly known as 45,X, or 45,X0,Also written as 45,XO. is a chromosomal disorder in which cells of females have only one X chromosome instead of two, or are partially missing an X chromosome (sex chromosome monosomy) lea ...
, triploidy, trisomy 16
Trisomy 16 is a chromosomal abnormality in which there are 3 copies of chromosome 16 (human), chromosome 16 rather than two. It is the most common autosomal trisomy leading to miscarriage, and the second most common chromosomal cause (closely foll ...
mosaicism, fetal death
Perinatal mortality (PNM) is the death of a fetus or neonate and is the basis to calculate the perinatal mortality rate. ''Perinatal'' means "relating to the period starting a few weeks before birth and including the birth and a few weeks after bi ...
, Smith–Lemli–Opitz syndrome
Smith–Lemli–Opitz syndrome is an inborn error of metabolism, inborn error of cholesterol synthesis. It is an autosome, autosomal recessive (genetics), recessive, multiple malformation syndrome caused by a mutation in the enzyme 7-Dehydrochole ...
, and steroid sulfatase deficiency.
Values measured
The triple test measures the following three levels in the maternal serum: #alpha-fetoprotein
Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP, α-fetoprotein; also sometimes called alpha-1-fetoprotein, alpha-fetoglobulin, or alpha fetal protein) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''AFP'' gene. The ''AFP'' gene is located on the ''q'' arm of chromosome ...
(AFP)
# human chorionic gonadotropin
Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) is a hormone for the maternal recognition of pregnancy produced by trophoblast cells that are surrounding a growing embryo (syncytiotrophoblast initially), which eventually forms the placenta after implantat ...
(hCG)
# unconjugated estriol
Estriol (E3), also spelled oestriol, is a steroid, a weak estrogen, and a minor female sex hormone. It is one of three major endogenous estrogens, the others being estradiol and estrone. Levels of estriol in women who are not pregnant are almost ...
(UE3)
Interpretation
The levels may indicate increased risk for certain conditions or may be benign: An estimated risk is calculated and adjusted for the expectant mother'sage
Age or AGE may refer to:
Time and its effects
* Age, the amount of time someone has been alive or something has existed
** East Asian age reckoning, an Asian system of marking age starting at 1
* Ageing or aging, the process of becoming older
...
; if she is diabetic; if she is having twins or other multiples, and the gestational age of the fetus. Weight and ethnicity may also be used in adjustments.Henry's Clinical Diagnosis and Management by Laboratory Methods, 22nd ed. Chapter 25 Many of these factors affect the levels of the substances being measured and the interpretation of the results:
* As maternal weight increases, MSAFP level decreases
* African-American women have MSAFP levels that are 10-15% higher than those of Caucasian women for unknown reasons
* Women with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus have MSAFP levels that are 20% lower than the rest of the population
* Having multiple gestations, such as twins, increases MSAFP because each fetus secretes its own AFP
* Incorrect estimation of gestational age is the most common cause of abnormal MSAFP levels
 The test is for screening, not for
The test is for screening, not for diagnosis
Diagnosis (: diagnoses) is the identification of the nature and cause of a certain phenomenon. Diagnosis is used in a lot of different academic discipline, disciplines, with variations in the use of logic, analytics, and experience, to determine " ...
, and does not have nearly the same predictive power as that of genetic blood testing (testing cell-free fetal DNA
Cell-free fetal DNA (cffDNA) is fetal DNA that circulates freely in the maternal blood. Maternal blood is sampled by venipuncture. Analysis of cffDNA is a method of non-invasive prenatal diagnosis frequently ordered for pregnant women of advance ...
, or invasive genetic testing
Genetic testing, also known as DNA testing, is used to identify changes in DNA sequence or chromosome structure. Genetic testing can also include measuring the results of genetic changes, such as RNA analysis as an output of gene expression, or ...
which are performed by amniocentesis
Amniocentesis is a medical procedure used primarily in the prenatal diagnosis of genetic conditions. It has other uses such as in the assessment of infection and fetal lung maturity. Prenatal diagnostic testing, which includes amniocentesis, is ...
or chorionic villus sampling
Chorionic villus sampling (CVS), sometimes called "chorionic ''villous'' sampling" (as "villous" is the adjectival form of the word "villus"), is a form of prenatal diagnosis done to determine chromosomal or genetic disorders in the fetus. It en ...
. The screening test carries a much lower risk to the fetus
A fetus or foetus (; : fetuses, foetuses, rarely feti or foeti) is the unborn offspring of a viviparous animal that develops from an embryo. Following the embryonic development, embryonic stage, the fetal stage of development takes place. Pren ...
than invasive testing, however, and in conjunction with the age-related risk of the patient it is useful to help determine the need for more invasive tests.
Variations
If only two of the hormones above are tested for, then the test is called a double test. A quad test tests an additional hormone,inhibin
Activin and inhibin are two closely related protein complexes that have almost directly opposite biological effects. Identified in 1986, activin enhances FSH biosynthesis and secretion, and participates in the regulation of the menstrual c ...
. Furthermore, the triple test may be combined with an ultrasound
Ultrasound is sound with frequency, frequencies greater than 20 Hertz, kilohertz. This frequency is the approximate upper audible hearing range, limit of human hearing in healthy young adults. The physical principles of acoustic waves apply ...
measurement of nuchal translucency.
Double test
Free beta hCG and PAPP-A are measured. However, the maternal age, weight, ethnicity etc. are still included. In the UK the double test is part of the combined test for prenatal diagnostics.Quadruple test
A test of levels of dimericinhibin
Activin and inhibin are two closely related protein complexes that have almost directly opposite biological effects. Identified in 1986, activin enhances FSH biosynthesis and secretion, and participates in the regulation of the menstrual c ...
A (DIA) is sometimes added to the other three tests, under the name "quadruple test." Other names used include "quad test", "quad screen", or "tetra screen." Inhibin A will be found high in cases of trisomy 21 and unchanged in cases of trisomy 18.
See also
*Triple bolus test __NOTOC__
A combined rapid anterior pituitary evaluation panel or triple bolus test or a dynamic pituitary function test is a medical diagnostic procedure used to assess a patient's pituitary function.
A triple bolus test is usually ordered and int ...
* Cell free fetal DNA test
References
External links
AmericanPregnancy.org
{{DEFAULTSORT:Triple Test Tests during pregnancy