
Various types of electrical
transformer
In electrical engineering, a transformer is a passive component that transfers electrical energy from one electrical circuit to another circuit, or multiple Electrical network, circuits. A varying current in any coil of the transformer produces ...
are made for different purposes. Despite their design differences, the various types employ the same basic principle as discovered in 1831 by
Michael Faraday
Michael Faraday (; 22 September 1791 – 25 August 1867) was an English chemist and physicist who contributed to the study of electrochemistry and electromagnetism. His main discoveries include the principles underlying electromagnetic inducti ...
, and share several key functional parts.
Power transformer
Laminated core
This is the most common type of transformer, widely used in
electric power transmission and appliances to convert
mains voltage to low voltage to power electronic devices. They are available in power ratings ranging from mW to MW. The insulated laminations minimize
eddy current losses in the iron core.
Small appliance and electronic transformers may use a split bobbin, giving a high level of insulation between the windings. The rectangular cores are made up of stampings, often in E-I shape pairs, but other shapes are sometimes used. Shields between primary and secondary may be fitted to reduce EMI (electromagnetic interference), or a screen winding is occasionally used.
Small appliance and electronics transformers may have a
thermal cut-out built into the winding, to shut-off power at high temperatures to prevent further overheating.
Toroidal

Donut-shaped
toroidal transformers save space compared to E-I cores, and may reduce external magnetic field. These use a ring shaped core, copper windings wrapped around this ring (and thus threaded through the ring during winding), and tape for insulation.
Toroidal transformers have a lower external magnetic field compared to rectangular transformers, and can be smaller for a given power rating. However, they cost more to make, as winding requires more complex and slower equipment.
They can be mounted by a bolt through the center, using washers and rubber pads or by potting in resin. Care must be taken that the bolt does not form part of a short-circuit turn.
Autotransformer
An
autotransformer consists of only one winding that is tapped at some point along the winding. Voltage is applied across a terminal of the winding, and a higher (or lower) voltage is produced across another portion of the same winding. The equivalent power rating of the autotransformer is lower than the actual load power rating. It is calculated by: load VA × (, Vin – Vout, )/Vin. For example, an auto transformer that adapts a 1000 VA load rated at 120 volts to a 240 volt supply has an equivalent rating of at least: 1,000 VA (240 V – 120 V) / 240 V = 500 VA. However, the actual rating (shown on the tally plate) must be at least 1000 VA.
For voltage ratios that don't exceed about 3:1, an autotransformer is cheaper, lighter, smaller, and more efficient than an isolating (two-winding) transformer of the same rating. Large three-phase autotransformers are used in electric power distribution systems, for example, to interconnect 220 kV and 33 kV sub-transmission networks or other high voltage levels.
Variable autotransformer

By exposing part of the winding coils of an autotransformer, and making the secondary connection through a sliding carbon
brush, an autotransformer with a near-continuously variable turns ratio can be obtained, allowing for wide voltage adjustment in very small increments.
Induction regulator
The induction regulator is similar in design to a wound-rotor
induction motor but it is essentially a transformer whose output voltage is varied by rotating its secondary relative to the primary—i.e., rotating the angular position of the rotor. It can be seen as a
power transformer
Power may refer to:
Common meanings
* Power (physics), meaning "rate of doing work"
** Engine power, the power put out by an engine
** Electric power, a type of energy
* Power (social and political), the ability to influence people or events
Ma ...
exploiting
rotating magnetic fields. The major advantage of the induction regulator is that unlike variacs, they are practical for transformers over 5 kVA. Hence, such regulators find widespread use in high-voltage laboratories.
Polyphase transformer
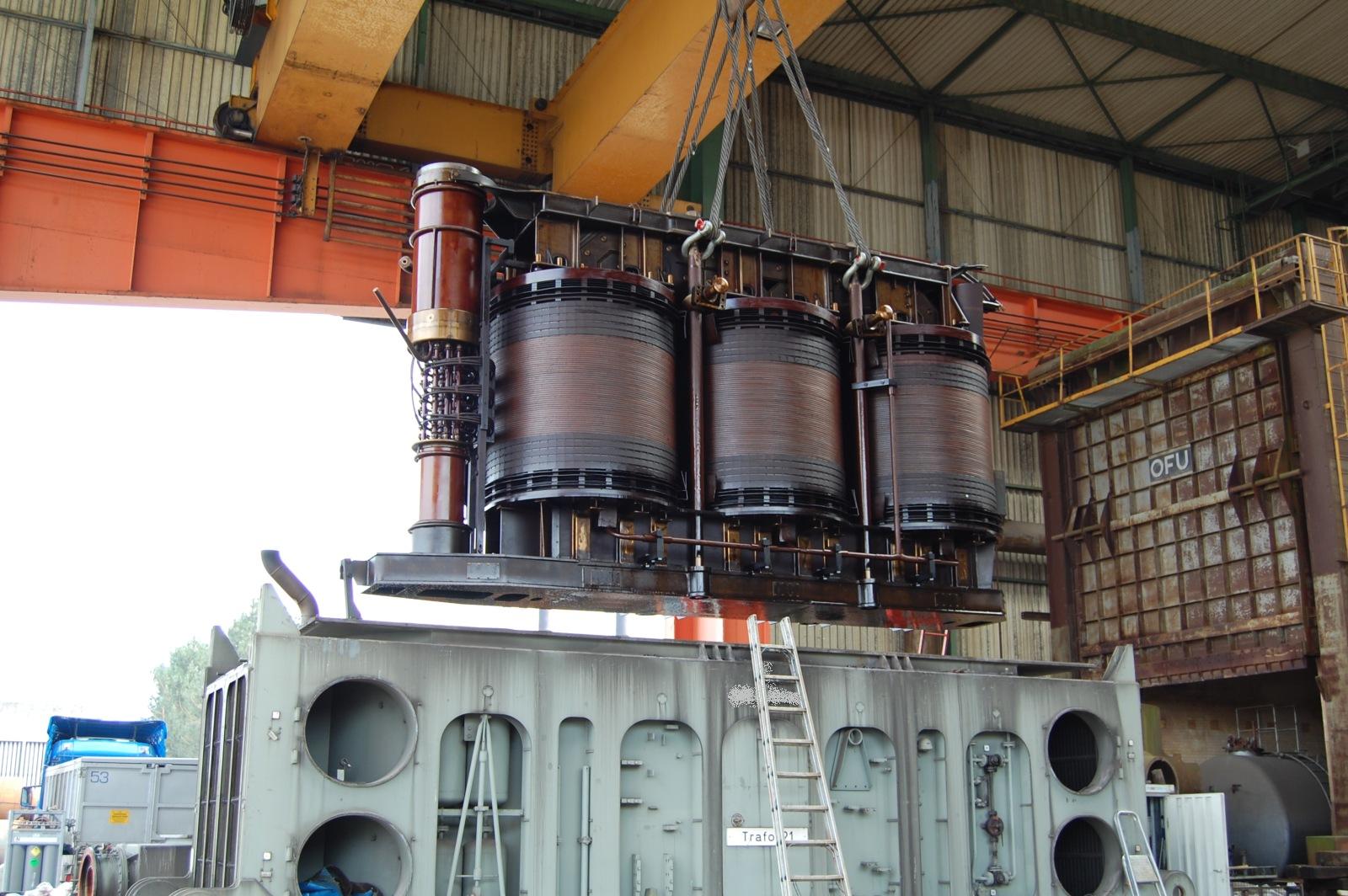


For
polyphase systems, multiple single-phase transformers can be used, or all phases can be connected to a single polyphase transformer. For a three phase transformer, the three primary windings are connected together and the three secondary windings are connected together. Examples of connections are wye-delta, delta-wye, delta-delta, and wye-wye. A
vector group indicates the configuration of the windings and the
phase angle difference between them. If a winding is connected to earth (
grounded), the earth connection point is usually the center point of a wye winding. If the secondary is a delta winding, the ground may be connected to a center tap on one winding (
high leg delta) or one phase may be grounded (corner grounded delta). A special purpose polyphase transformer is the
zigzag transformer. There are many possible configurations that may involve more or fewer than six windings and various tap connections.
Grounding transformer
''Grounding'' or ''earthing transformers'' let three wire (delta)
polyphase system supplies accommodate phase to neutral loads by providing a return path for current to a neutral. Grounding transformers most commonly incorporate a single winding transformer with a zigzag winding configuration but may also be created with a wye-delta isolated winding transformer connection.
Phase-shifting transformer
This is a specialized type of transformer which can be configured to adjust the phase relationship between input and output. This allows power flow in an
electric grid to be controlled, e.g. to steer power flows away from a shorter (but overloaded) link to a longer path with excess capacity.
Variable-frequency transformer
A ''variable-frequency transformer'' is a specialized three-phase power transformer which allows the phase relationship between the input and output windings to be continuously adjusted by rotating one half. They are used to interconnect
electrical grid
An electrical grid (or electricity network) is an interconnected network for electricity delivery from producers to consumers. Electrical grids consist of power stations, electrical substations to step voltage up or down, electric power tran ...
s with the same nominal frequency but without synchronous phase coordination.
Leakage or stray field transformer
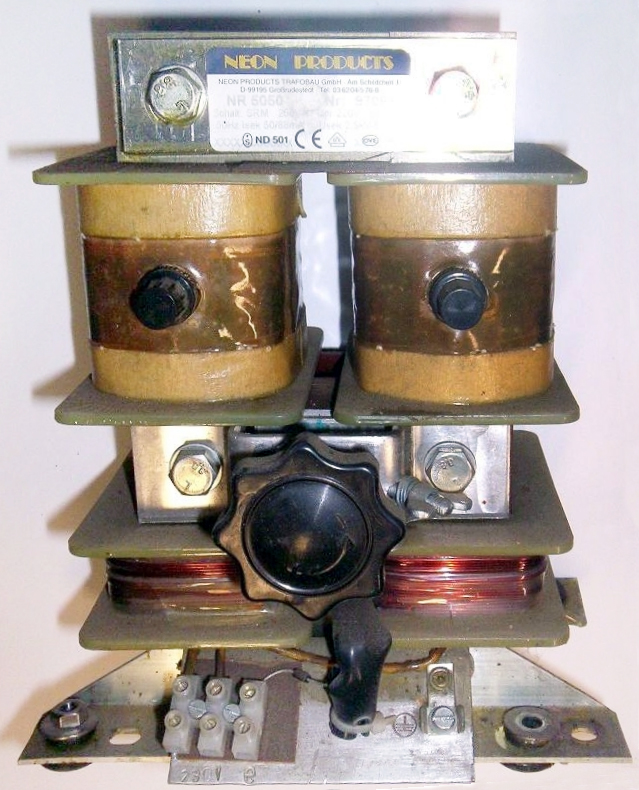

A leakage transformer, also called a stray-field transformer, has a significantly higher
leakage inductance than other transformers, sometimes increased by a magnetic bypass or shunt in its core between primary and secondary, which is sometimes adjustable with a set screw. This provides a transformer with an inherent current limitation due to the loose coupling between its primary and the secondary windings. The adjustable
short-circuit inductance acts as a current limiting parameter.
The output and input currents are kept low enough to preclude thermal overload under any load conditions — even if the secondary is shorted.
Uses
Leakage transformers are used for
arc welding
Arc welding is a welding process that is used to join metal to metal by using electricity to create enough heat to melt metal, and the melted metals, when cool, result in a joining of the metals. It is a type of welding that uses a welding power ...
and high voltage discharge lamps (
neon lights and
cold cathode fluorescent lamp
A fluorescent lamp, or fluorescent tube, is a low-pressure mercury-vapor gas-discharge lamp that uses fluorescence to produce visible light. An electric current in the gas excites mercury vapor, to produce ultraviolet and make a phosphor ...
s, which are series connected up to 7.5 kV AC). It acts both as a voltage transformer and as a
magnetic ballast.
Other applications are short-circuit-proof
extra-low voltage transformers for toys or
doorbell
A doorbell is a signaling device typically placed near a door to a building's entrance. When a visitor presses a button (control), button, the bell rings inside the building, alerting the occupant to the presence of the visitor. Although the ...
installations.
Resonant transformer
A
resonant transformer is a transformer in which one or both windings has a capacitor across it and functions as a
tuned circuit
An LC circuit, also called a resonant circuit, tank circuit, or tuned circuit, is an electric circuit consisting of an inductor, represented by the letter L, and a capacitor, represented by the letter C, connected together. The circuit can act ...
. Used at
radio frequencies, resonant transformers can function as high
Q factor
In physics and engineering, the quality factor or factor is a dimensionless parameter that describes how underdamped an oscillator or resonator is. It is defined as the ratio of the initial energy stored in the resonator to the energy lost ...
bandpass filter
A band-pass filter or bandpass filter (BPF) is a device that passes frequencies within a certain range and rejects ( attenuates) frequencies outside that range.
It is the inverse of a '' band-stop filter''.
Description
In electronics and s ...
s. The transformer windings have either air or ferrite cores and the
bandwidth can be adjusted by varying the coupling (
mutual inductance). One common form is the IF (
intermediate frequency
In communications and electronic engineering, an intermediate frequency (IF) is a frequency to which a carrier wave is shifted as an intermediate step in Transmission (telecommunications), transmission or reception. The intermediate frequency is ...
) transformer, used in
superheterodyne radio receivers. They are also used in radio transmitters.
Resonant transformers are also used in
electronic ballasts for
gas discharge lamps, and high voltage power supplies. They are also used in some types of
switching power supplies. Here the
short-circuit inductance value is an important parameter that determines the resonance frequency of the resonant transformer. Often only secondary winding has a resonant capacitor (or stray capacitance) and acts as a serial resonant tank circuit. When the short-circuit inductance of the secondary side of the transformer is L
sc and the resonant capacitor (or stray capacitance) of the secondary side is C
r, The resonance frequency ω
s of 1' is as follows
:
The transformer is driven by a pulse or square wave for efficiency, generated by an
electronic oscillator
An electronic oscillator is an electronic circuit that produces a periodic, oscillating or alternating current (AC) signal, usually a sine wave, square wave or a triangle wave, powered by a direct current (DC) source. Oscillators are found ...
circuit. Each pulse serves to drive resonant sinusoidal oscillations in the tuned winding, and due to resonance a high voltage can be developed across the secondary.
Applications:
*
Intermediate frequency
In communications and electronic engineering, an intermediate frequency (IF) is a frequency to which a carrier wave is shifted as an intermediate step in Transmission (telecommunications), transmission or reception. The intermediate frequency is ...
(IF) transformer in
superheterodyne radio receiver
* Tank transformers in
radio transmitters
*
Tesla coil
*
Power inverter
*
Oudin coil (or Oudin resonator; named after its inventor
Paul Oudin)
*
D'Arsonval apparatus
*
Ignition coil or
induction coil used in the
ignition system
Ignition systems are used by heat engines to initiate combustion by igniting the fuel-air mixture. In a spark ignition versions of the internal combustion engine (such as petrol engines), the ignition system creates a spark to ignite the fuel-ai ...
of a
petrol engine
A petrol engine (gasoline engine in American and Canadian English) is an internal combustion engine designed to run on petrol (gasoline). Petrol engines can often be adapted to also run on fuels such as liquefied petroleum gas and ethanol blends ...
*
Electrical breakdown and insulation testing of high voltage equipment and cables. In the latter case, the transformer's secondary is resonated with the cable's capacitance.
Constant voltage transformer
By arranging particular magnetic properties of a transformer core, and installing a
ferro-resonant tank circuit (a capacitor and an additional winding), a transformer can be arranged to automatically keep the secondary winding voltage relatively constant for varying primary supply without additional circuitry or manual adjustment. Ferro-resonant transformers run hotter than standard power transformers, because regulating action depends on core saturation, which reduces efficiency. The output waveform is heavily distorted unless careful measures are taken to prevent this. Saturating transformers provide a simple rugged method to stabilize an AC power supply.
Ferrite core
Ferrite core power transformers are widely used in
switched-mode power supplies (SMPSs). The powder core enables high-frequency operation, and hence much smaller size-to-power ratio than laminated-iron transformers.
Ferrite transformers are not used as power transformers at mains frequency since laminated iron cores cost less than an equivalent ferrite core.
Planar transformer

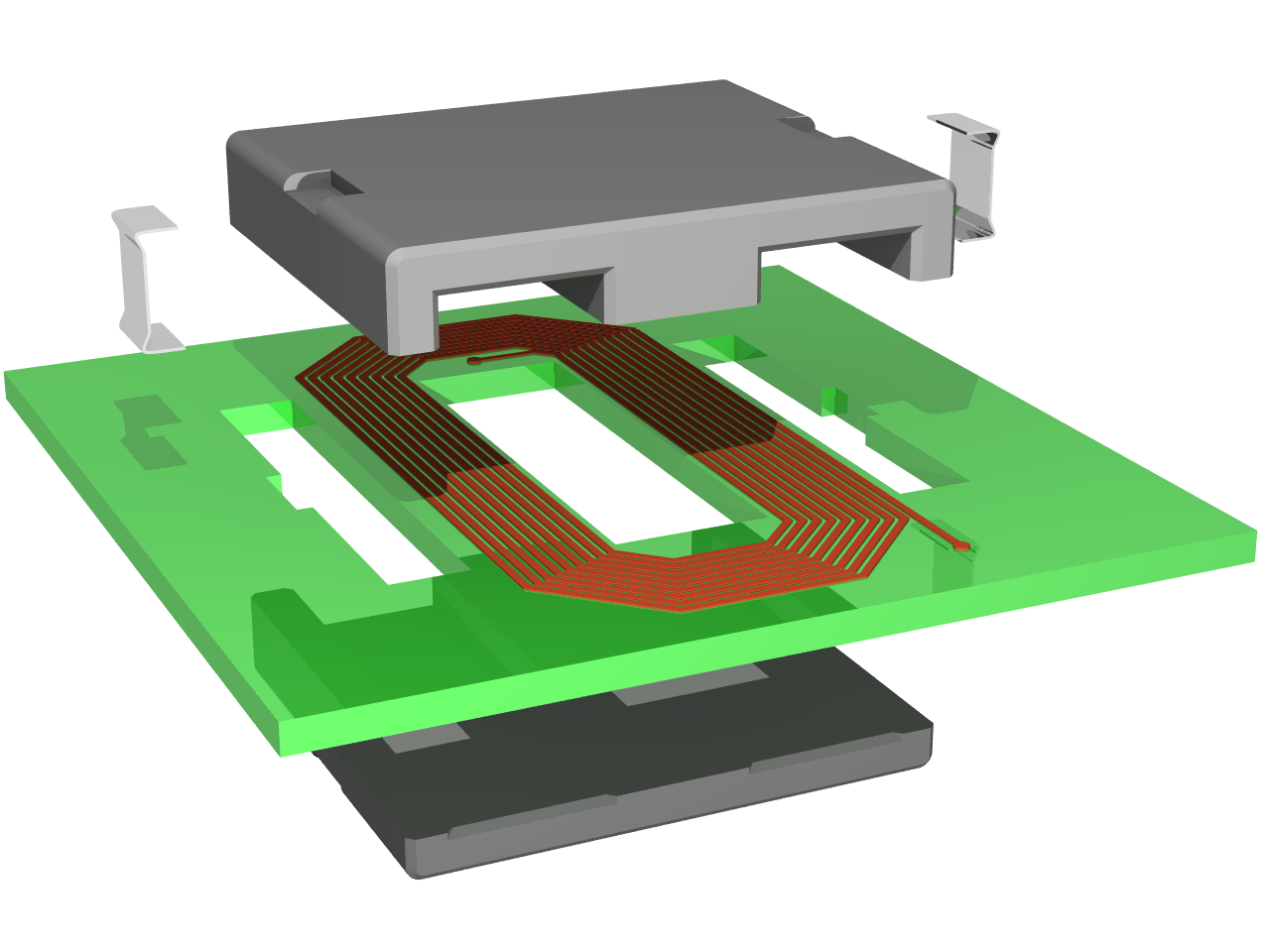
Manufacturers either use flat copper sheets or etch spiral patterns on a
printed circuit board
A printed circuit board (PCB), also called printed wiring board (PWB), is a Lamination, laminated sandwich structure of electrical conduction, conductive and Insulator (electricity), insulating layers, each with a pattern of traces, planes ...
to form the "windings" of a planar transformer, replacing the turns of wire used to make other types. Some planar transformers are commercially sold as discrete components, other planar transformers are etched directly into the main printed circuit board and only need a ferrite core to be attached over the PCB. A planar transformer can be thinner than other transformers, which is useful for low-profile applications or when several printed circuit boards are stacked. Almost all planar transformers use a ferrite
planar core.
Liquid-cooled transformer
Large transformers used in power distribution or electrical substations have their core and coils immersed in
oil, which cools and insulates. Oil circulates through ducts in the coil and around the coil and core assembly, moved by convection. The oil is cooled by the outside of the tank in small ratings, and by an air-cooled radiator in larger ratings. Where a higher rating is required, or where the transformer is in a building or underground, oil pumps circulate the oil, fans may force air over the radiators, or an oil-to-water heat exchanger may also be used.
Transformer oil is flammable, so oil-filled transformers inside a building are installed in vaults to prevent spread of fire and smoke from a burning transformer. Some transformers were built to use fire-resistant
PCBs, but because these compounds persist in the environment and have adverse effects on organisms, their use has been discontinued in most areas; for example, after 1979 in South Africa.
Substitute fire-resistant liquids such as
silicone
In Organosilicon chemistry, organosilicon and polymer chemistry, a silicone or polysiloxane is a polymer composed of repeating units of siloxane (, where R = Organyl group, organic group). They are typically colorless oils or elastomer, rubber ...
oils are now used instead.
Cast resin transformer
Cast-resin power transformers encase the windings in epoxy resin. These transformers simplify installation since they are dry, without cooling oil, and so require no fire-proof vault for indoor installations. The epoxy protects the windings from dust and corrosive atmospheres. However, because the molds for casting the coils are only available in fixed sizes, the design of the transformers is less flexible, which may make them more costly if customized features (voltage, turns ratio, taps) are required.
Isolating transformer
An
isolation transformer links two circuits magnetically, but provides no metallic conductive path between the circuits. An example application would be in the power supply for medical equipment, when it is necessary to prevent any leakage from the AC power system into devices connected to a patient. Special purpose isolation transformers may include shielding to prevent coupling of electromagnetic noise between circuits, or may have reinforced insulation to withstand thousands of volts of potential difference between primary and secondary circuits.
Solid-state transformer
A solid-state transformer is actually a power converter that performs the same function as a conventional transformer, sometimes with added functionality. Most contain a smaller high-frequency transformer. It can consist of an AC-to-AC converter, or a rectifier powering an inverter.
Instrument transformer
Instrument transformers are typically used to operate instruments from high voltage lines or high current circuits, safely isolating measurement and control circuitry from the high voltages or currents. The primary winding of the transformer is connected to the high voltage or high current circuit, and the meter or relay is connected to the secondary circuit. Instrument transformers may also be used as an
isolation transformer so that secondary quantities may be used without affecting the primary circuitry.
Terminal identifications (either alphanumeric such as H
1, X
1, Y
1, etc. or a colored spot or dot impressed in the case) indicate one end of each winding, indicating the same instantaneous polarity and phase between windings. This applies to both types of instrument transformers. Correct identification of terminals and wiring is essential for proper operation of metering and protective relay instrumentation.
Current transformer

A current transformer (CT) is a series connected measurement device designed to provide a current in its secondary coil proportional to the current flowing in its primary. Current transformers are commonly used in
metering and
protective relay
In electrical engineering, a protective relay is a relay device designed to trip a circuit breaker when a Electrical fault, fault is detected. The first protective relays were electromagnetic devices, relying on coils operating on moving parts ...
s in the
electrical power industry
Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and motion of matter possessing an electric charge. Electricity is related to magnetism, both being part of the phenomenon of electromagnetism, as described by Maxwel ...
.
Current transformers are often constructed by passing a single primary turn (either an
insulated cable or an uninsulated bus bar) through a well-insulated
toroidal core wrapped with many turns of wire. The CT is typically described by its current ratio from primary to secondary. For example, a 1000:1 CT provides an output current of 1 amperes when 1000 amperes flow through the primary winding. Standard secondary current ratings are 5 amperes or 1 ampere, compatible with standard measuring instruments. The secondary winding can be single ratio or have several
tap points to provide a range of ratios. Care must be taken to make sure the secondary winding is not disconnected from its low-impedance load while current flows in the primary, as this may produce a dangerously high voltage across the open secondary and may permanently affect the accuracy of the transformer.
Specially constructed
wideband
In communications, a system is wideband when the message bandwidth significantly exceeds the coherence bandwidth of the channel. Some communication links have such a high data rate that they are forced to use a wide bandwidth; other links ma ...
CTs are also used, usually with an
oscilloscope
An oscilloscope (formerly known as an oscillograph, informally scope or O-scope) is a type of electronic test instrument that graphically displays varying voltages of one or more signals as a function of time. Their main purpose is capturing i ...
, to measure
high frequency
High frequency (HF) is the ITU designation for the band of radio waves with frequency between 3 and 30 megahertz (MHz). It is also known as the decameter band or decameter wave as its wavelengths range from one to ten decameters (ten to one ...
waveform
In electronics, acoustics, and related fields, the waveform of a signal is the shape of its Graph of a function, graph as a function of time, independent of its time and Magnitude (mathematics), magnitude Scale (ratio), scales and of any dis ...
s or pulsed currents within
pulsed power Pulsed power is the science and technology of accumulating energy over a relatively long period of time and releasing it instantly, thus increasing the instantaneous power. They can be used in some applications such as food processing, water treatme ...
systems. One type provides a voltage output that is proportional to the measured current. Another, called a
Rogowski coil, requires an external
integrator
An integrator in measurement and control applications is an element whose output signal is the time integral of its input signal. It accumulates the input quantity over a defined time to produce a representative output.
Integration is an importan ...
in order to provide a proportional output.
A
current clamp uses a current transformer with a split core that can be easily wrapped around a conductor in a circuit. This is a common method used in portable current measuring instruments but permanent installations use more economical types of current transformer.
Voltage transformer or potential transformer
Voltage transformers (VT), also called potential transformers (PT), are a parallel connected type of instrument transformer, used for metering and protection in high-voltage circuits or phasor phase shift isolation. They are designed to present negligible load to the supply being measured and to have an accurate voltage ratio to enable accurate metering. A potential transformer may have several secondary windings on the same core as a primary winding, for use in different metering or protection circuits. The primary may be connected phase to ground or phase to phase. The secondary is usually grounded on one terminal.
There are three primary types of voltage transformers (VT): electromagnetic, capacitor, and optical. The electromagnetic voltage transformer is a wire-wound transformer. The capacitor voltage transformer uses a capacitance potential divider and is used at higher voltages due to a lower cost than an electromagnetic VT. An optical voltage transformer exploits the electrical properties of optical materials. Measurement of high voltages is possible by the potential transformers. An optical voltage transformer is not strictly a transformer, but a sensor similar to a
Hall effect sensor.
Combined instrument transformer
A combined instrument transformer encloses a current transformer and a voltage transformer in the same transformer. There are two main combined current and voltage transformer designs: oil-paper insulated and SF
6 insulated. One advantage of applying this solution is reduced
substation footprint, due to reduced number of transformers in a bay, supporting structures and connections as well as lower costs for civil works, transportation and installation.
Pulse transformer
A pulse transformer is a transformer that is optimised for transmitting rectangular electrical pulses (that is, pulses with fast rise and fall times and a relatively constant
amplitude
The amplitude of a periodic variable is a measure of its change in a single period (such as time or spatial period). The amplitude of a non-periodic signal is its magnitude compared with a reference value. There are various definitions of am ...
). Small versions called ''signal'' types are used in
digital logic and
telecommunications
Telecommunication, often used in its plural form or abbreviated as telecom, is the transmission of information over a distance using electronic means, typically through cables, radio waves, or other communication technologies. These means of ...
circuits such as in
Ethernet
Ethernet ( ) is a family of wired computer networking technologies commonly used in local area networks (LAN), metropolitan area networks (MAN) and wide area networks (WAN). It was commercially introduced in 1980 and first standardized in 198 ...
, often for matching logic drivers to
transmission line
In electrical engineering, a transmission line is a specialized cable or other structure designed to conduct electromagnetic waves in a contained manner. The term applies when the conductors are long enough that the wave nature of the transmis ...
s. These are also called Ethernet transformer modules.
Medium-sized ''power'' versions are used in power-control circuits such as
camera flash controllers. Larger ''power'' versions are used in the
electrical power distribution
Electric power distribution is the final stage in the delivery of electricity. Electricity is carried from the transmission system to individual consumers. Distribution substations connect to the transmission system and lower the transmission ...
industry to interface low-voltage control circuitry to the high-voltage gates of
power semiconductors. Special
high voltage
High voltage electricity refers to electrical potential large enough to cause injury or damage. In certain industries, ''high voltage'' refers to voltage above a certain threshold. Equipment and conductors that carry high voltage warrant sp ...
pulse transformers are also used to generate high power pulses for
radar
Radar is a system that uses radio waves to determine the distance ('' ranging''), direction ( azimuth and elevation angles), and radial velocity of objects relative to the site. It is a radiodetermination method used to detect and track ...
,
particle accelerator
A particle accelerator is a machine that uses electromagnetic fields to propel electric charge, charged particles to very high speeds and energies to contain them in well-defined particle beam, beams. Small accelerators are used for fundamental ...
s, or other high energy
pulsed power Pulsed power is the science and technology of accumulating energy over a relatively long period of time and releasing it instantly, thus increasing the instantaneous power. They can be used in some applications such as food processing, water treatme ...
applications.
To minimize distortion of the pulse shape, a pulse transformer needs to have low values of
leakage inductance and distributed
capacitance
Capacitance is the ability of an object to store electric charge. It is measured by the change in charge in response to a difference in electric potential, expressed as the ratio of those quantities. Commonly recognized are two closely related ...
, and a high open-circuit inductance. In power-type pulse transformers, a low coupling capacitance (between the primary and secondary) is important to protect the circuitry on the primary side from high-powered transients created by the load. For the same reason, high insulation resistance and high breakdown voltage are required. A good transient response is necessary to maintain the rectangular pulse shape at the secondary, because a pulse with slow edges would create in the power semiconductors.
The product of the peak pulse voltage and the duration of the pulse (or more accurately, the voltage-time integral) is often used to characterise pulse transformers. Generally speaking, the larger this product, the larger and more expensive the transformer.
Pulse transformers by definition have a
duty cycle of less than ; whatever energy stored in the coil during the pulse must be "dumped" out before the pulse is fired again.
RF transformer
There are several types of transformer used in
radio frequency
Radio frequency (RF) is the oscillation rate of an alternating electric current or voltage or of a magnetic, electric or electromagnetic field or mechanical system in the frequency range from around to around . This is roughly between the u ...
(RF) work, distinguished by how their windings are connected, and by the type of cores (if any) the coil turns are wound onto.
Laminated steel used for power transformer cores is very inefficient at RF, wasting a lot of RF power as heat, so transformers for use at radio frequencies tends to use magnetic ceramics for winding cores, such as
powdered iron (for
mediumwave
Medium wave (MW) is a part of the medium frequency (MF) radio band used mainly for AM broadcasting, AM radio broadcasting. The spectrum provides about 120 channels with more limited sound quality than FM stations on the FM broadcast band. Duri ...
and lower
shortwave frequencies) or
ferrite (for upper
shortwave).
The core material a coil is wrapped around can increase its inductance dramatically – hundreds to thousands of times more than “air” – thereby raising the transformer's
. The cores of such transformers tend to help performance the most at the lower end of the
frequency band
Spectral bands are regions of a given spectrum, having a specific range of wavelengths or frequencies. Most often, it refers to electromagnetic bands, regions of the electromagnetic spectrum.
More generally, spectral bands may also be means in ...
transformer was designed for.
Old RF transformers sometimes included an extra, third coil (called a tickler winding) to inject
feedback
Feedback occurs when outputs of a system are routed back as inputs as part of a chain of cause and effect that forms a circuit or loop. The system can then be said to ''feed back'' into itself. The notion of cause-and-effect has to be handle ...
into an earlier (
detector) stage in
antique regenerative radio receivers.
Air-core transformer
So-called “air-core” transformers actually have no core at all – they are wound onto non-magnetic forms or frames, or merely held in shape by the stiffness of the coiled wire. These are used for
very high frequency and upper
shortwave work.
The lack of a magnetically reactive core means very low
inductance
Inductance is the tendency of an electrical conductor to oppose a change in the electric current flowing through it. The electric current produces a magnetic field around the conductor. The magnetic field strength depends on the magnitude of the ...
per turn, requiring many turns of wire on the transformer coil. All forward current excites reverse current and induces secondary voltage which is proportional to the mutual inductance. At
VHF, such transformers may be nothing more than a few turns of wire soldered onto a
printed circuit board
A printed circuit board (PCB), also called printed wiring board (PWB), is a Lamination, laminated sandwich structure of electrical conduction, conductive and Insulator (electricity), insulating layers, each with a pattern of traces, planes ...
.
Ferrite-core transformer
Ferrite core transformers are widely used in RF transformers, especially for
current balancing (
see below) and
impedance matching for TV and radio antennas. Because of the enormous improvement in inductance that ferrite produces, many
ferrite cored transformers work well with only one or two turns.
Ferrite is an intensely magnetically reactive
ceramic
A ceramic is any of the various hard, brittle, heat-resistant, and corrosion-resistant materials made by shaping and then firing an inorganic, nonmetallic material, such as clay, at a high temperature. Common examples are earthenware, porcela ...
material made from
iron oxide
An iron oxide is a chemical compound composed of iron and oxygen. Several iron oxides are recognized. Often they are non-stoichiometric. Ferric oxyhydroxides are a related class of compounds, perhaps the best known of which is rust.
Iron ...
(rust) mixed with small fractions of other metals or their
oxide
An oxide () is a chemical compound containing at least one oxygen atom and one other element in its chemical formula. "Oxide" itself is the dianion (anion bearing a net charge of −2) of oxygen, an O2− ion with oxygen in the oxidation st ...
s, such as
magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It is a shiny gray metal having a low density, low melting point and high chemical reactivity. Like the other alkaline earth metals (group 2 ...
,
zinc
Zinc is a chemical element; it has symbol Zn and atomic number 30. It is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodic tabl ...
, and
nickel
Nickel is a chemical element; it has symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel is a hard and ductile transition metal. Pure nickel is chemically reactive, but large pieces are slo ...
. Different mixtures respond best at different frequencies.
Because they are ceramics, ferrites are (almost) non-conductive, so they respond only to the
magnetic field
A magnetic field (sometimes called B-field) is a physical field that describes the magnetic influence on moving electric charges, electric currents, and magnetic materials. A moving charge in a magnetic field experiences a force perpendicular ...
s created by nearby currents, and not to the
electric field
An electric field (sometimes called E-field) is a field (physics), physical field that surrounds electrically charged particles such as electrons. In classical electromagnetism, the electric field of a single charge (or group of charges) descri ...
s created by the accompanying voltages.
Choke transformer
For
radio frequency
Radio frequency (RF) is the oscillation rate of an alternating electric current or voltage or of a magnetic, electric or electromagnetic field or mechanical system in the frequency range from around to around . This is roughly between the u ...
use, "
choke" transformers are sometimes made from windings of transmission line wired in parallel. Sometimes the windings are
coaxial cable, sometimes
bifilar (paired parallel wire); either is wound around a
ferrite, powdered iron, or "air" core. This style of transformer gives an extremely wide
bandwidth but only a limited number of impedance ratios (such as 1:1, 1:4, or 1:9) can be achieved with this technique.
Choke transformers are sometimes called ''transmission-line transformers'' (although see below for a
different transformer type with the same name), or ''Guanella transformers'', or ''current baluns'', or ''line isolators''. Although called a "transmission line" transformer, it is distinct from the
transformers made from segments of transmission line.
* The name "transmission-line" is used because actual coaxial line is sometimes used, and when paired wires are used, the builder is expected to take special care with the wire spacing, to ensure that the
transmission line
In electrical engineering, a transmission line is a specialized cable or other structure designed to conduct electromagnetic waves in a contained manner. The term applies when the conductors are long enough that the wave nature of the transmis ...
impedance of the coax or paired wires lies near the
geometric mean
In mathematics, the geometric mean is a mean or average which indicates a central tendency of a finite collection of positive real numbers by using the product of their values (as opposed to the arithmetic mean which uses their sum). The geometri ...
of the input and output impedances.
* The name "
choke" is used because the equal and opposite (anti-parallel, balanced) currents in the coax or paired wires cancel each others' magnetic fields, allowing them to pass through unhindered, but magnetic field of the unbalanced flow inhibits the unbalanced current, "choking" it off. Similar reasoning applies to the name "line isolator".
* It is called a "current balun" or "current transformer" because the transformed flow produces balanced currents, rather than balanced voltages typical of other transformer types.
Line section transformer
At
radio frequencies and
microwave frequencies, a
quarter-wave impedance transformer can provide impedance matching between circuits over a limited range of frequencies, using only a section of transmission line no more than a
wave
In physics, mathematics, engineering, and related fields, a wave is a propagating dynamic disturbance (change from List of types of equilibrium, equilibrium) of one or more quantities. ''Periodic waves'' oscillate repeatedly about an equilibrium ...
long. The line may be coaxial cable, waveguide,
stripline, or
microstrip. For upper
VHF and
UHF frequencies, where coil
self resonance interferes with proper operation, it is usually the only feasible method for transforming line impedances.
Single frequency transformers are made using sections of transmission line, often called a "matching section" or a "matching stub". Like the choke transformer above, it is also called a "transmission line transformer" even though the two are very different in form and operation.
Unless it is terminated in its
characteristic impedance
The characteristic impedance or surge impedance (usually written Z0) of a uniform transmission line is the ratio of the amplitudes of voltage and current of a wave travelling in one direction along the line in the absence of reflections in th ...
, any
transmission line
In electrical engineering, a transmission line is a specialized cable or other structure designed to conduct electromagnetic waves in a contained manner. The term applies when the conductors are long enough that the wave nature of the transmis ...
will produce standing waves of
impedance along its length, repeating exactly every full
wavelength
In physics and mathematics, wavelength or spatial period of a wave or periodic function is the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.
In other words, it is the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same ''phase (waves ...
, and covering its full range of
absolute values over
only a quarter wave. One may exploit this behavior to transform currents and voltages by connecting sections of transmission line with mismatched impedances to deliberately create a standing wave on a line, and the cut and reconnect to the line at the position where a desired impedance is reached – never requiring more than a
wave
In physics, mathematics, engineering, and related fields, a wave is a propagating dynamic disturbance (change from List of types of equilibrium, equilibrium) of one or more quantities. ''Periodic waves'' oscillate repeatedly about an equilibrium ...
of mismatched line.
This type of transformer is very efficient (very little loss) but severely limited in the frequency span it will operate on: Whereas the
choke transformer, above, is very
broadbanded, a line section transformer is very narrowbanded.
Balun
"Balun" is a generic name for any transformer configured specifically to connect between
balanced (non-grounded) and
unbalanced (grounded) circuits. They can be made using any transformer type, but the actual balance achieved depends on the type; for example, "choke" baluns produce balanced current and autotransformer-type baluns produce balanced voltages. Baluns can also be made from configurations of transmission line, using
bifilar or
coaxial cable similar to transmission line transformers in construction and operation.
In addition to interfacing between balanced and unbalanced loads by producing balanced current or balanced voltage (or both), baluns can in addition separately transform (match) impedance between the loads.
IF transformer
Ferrite-core transformers are widely used in (intermediate frequency) (IF) stages in
superheterodyne radio receiver
In radio communications, a radio receiver, also known as a receiver, a wireless, or simply a radio, is an electronic device that receives radio waves and converts the information carried by them to a usable form. It is used with an antenna. ...
s. They are mostly tuned transformers, containing a threaded ferrite slug that is screwed in or out to adjust IF tuning. The transformers are usually canned (shielded) for stability and to reduce interference.
Audio transformer


Audio transformers are those specifically designed for use in audio circuits to carry
audio signal
An audio signal is a representation of sound, typically using either a changing level of electrical voltage for analog signals or a series of binary numbers for Digital signal (signal processing), digital signals. Audio signals have frequencies i ...
. They can be used to block radio frequency interference or the DC component of an audio signal, to split or combine audio signals, or to provide
impedance matching
In electrical engineering, impedance matching is the practice of designing or adjusting the input impedance or output impedance of an electrical device for a desired value. Often, the desired value is selected to maximize power transfer or ...
between
high impedance and low impedance circuits, such as between a high impedance
tube (valve) amplifier output and a low impedance
loudspeaker
A loudspeaker (commonly referred to as a speaker or, more fully, a speaker system) is a combination of one or more speaker drivers, an enclosure, and electrical connections (possibly including a crossover network). The speaker driver is an ...
, or between a high impedance instrument output and the low impedance input of a
mixing console
A mixing console or mixing desk is an electronic device for Audio mixing (recorded music), mixing audio signals, used in sound recording and reproduction and sound reinforcement systems. Inputs to the console include microphones, signals fro ...
. Audio transformers that operate with loudspeaker voltages and current are larger than those that operate at microphone or line level, which carry much less power.
Bridge transformers connect 2-wire and
4-wire communication circuits.
Being magnetic devices, audio transformers are susceptible to external magnetic fields such as those generated by AC current-carrying conductors. "
Hum" is a term commonly used to describe unwanted signals originating from the "
mains" power supply (typically 50 or 60 Hz). Audio transformers used for low-level signals, such as those from microphones, often include
magnetic shielding to protect against extraneous magnetically coupled signals.
Audio transformers were originally designed to connect different telephone systems to one another while keeping their respective power supplies isolated, and are still commonly used to interconnect
professional audio systems or system components, to eliminate buzz and hum. Such transformers typically have a 1:1 ratio between the primary and the secondary. These can also be used for splitting signals,
balancing unbalanced signals, or feeding a balanced signal to unbalanced equipment. Transformers are also used in
DI boxes to convert high-impedance instrument signals (e.g.,
bass guitar
The bass guitar (), also known as the electric bass guitar, electric bass, or simply the bass, is the lowest-pitched member of the guitar family. It is similar in appearance and construction to an Electric guitar, electric but with a longer nec ...
) to low impedance signals to enable them to connect to a microphone input on the
mixing console
A mixing console or mixing desk is an electronic device for Audio mixing (recorded music), mixing audio signals, used in sound recording and reproduction and sound reinforcement systems. Inputs to the console include microphones, signals fro ...
.
A particularly critical component is the output transformer of a
valve amplifier
A valve amplifier or tube amplifier is a type of electronic amplifier that uses vacuum tubes to increase the amplitude or power of a Signal (information theory), signal. Low to medium power valve amplifiers for frequencies below the microwaves ...
. Valve circuits for quality reproduction have long been produced with no other (inter-stage) audio transformers, but an output transformer is needed to
couple the relatively high impedance (up to a few hundred ohms depending upon configuration) of the output valve(s) to the low impedance of a
loudspeaker
A loudspeaker (commonly referred to as a speaker or, more fully, a speaker system) is a combination of one or more speaker drivers, an enclosure, and electrical connections (possibly including a crossover network). The speaker driver is an ...
. (The valves can deliver a low current at a high voltage; the speakers require high current at low voltage.) Most solid-state power amplifiers need no output transformer at all.
Audio transformers affect the sound quality because they are non-linear. They add
harmonic distortion to the original signal, especially odd-order harmonics, with an emphasis on third-order harmonics. When the incoming signal amplitude is very low there is not enough level to energize the magnetic core (see
coercivity
Coercivity, also called the magnetic coercivity, coercive field or coercive force, is a measure of the ability of a ferromagnetic material to withstand an external magnetic field without becoming Magnetization, demagnetized. Coercivity is usual ...
and
magnetic hysteresis). When the incoming signal amplitude is very high the transformer saturates and adds harmonics from soft clipping. Another non-linearity comes from limited frequency response. For good low-frequency response a relatively large
magnetic core
A magnetic core is a piece of magnetism, magnetic material with a high magnetic permeability used to confine and guide magnetic fields in electrical, electromechanical and magnetic devices such as electromagnets, transformers, electric motors, ele ...
is required; high power handling increases the required core size. Good high-frequency response requires carefully designed and implemented
windings without excessive
leakage inductance or
stray capacitance. All this makes for an expensive component.
Early
transistor
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to Electronic amplifier, amplify or electronic switch, switch electrical signals and electric power, power. It is one of the basic building blocks of modern electronics. It is composed of semicondu ...
audio power amplifiers often had output transformers, but they were eliminated as advances in semiconductors allowed the design of amplifiers with sufficiently low output impedance to drive a loudspeaker directly.
Loudspeaker transformer
In the same way that transformers create high voltage power transmission circuits that minimize transmission losses,
loudspeaker
A loudspeaker (commonly referred to as a speaker or, more fully, a speaker system) is a combination of one or more speaker drivers, an enclosure, and electrical connections (possibly including a crossover network). The speaker driver is an ...
transformers can power many individual loudspeakers from a single audio circuit operated at higher than normal loudspeaker voltages. This application is common in
public address
A public address system (or PA system) is an electronic system comprising microphones, amplifiers, loudspeakers, and related equipment. It increases the apparent volume (loudness) of a human voice, musical instrument, or other acoustic sound sou ...
applications. Such circuits are commonly referred to as
constant-voltage speaker systems. Such systems are also known by the nominal voltage of the loudspeaker line, such as ''25-'', ''70-'' and ''100-volt'' speaker systems (the voltage corresponding to the power rating of a speaker or amplifier). A transformer steps up the output of the system's amplifier to the distribution voltage. At the distant loudspeaker locations, a step-down transformer matches the speaker to the rated voltage of the line, so the speaker produces rated nominal output when the line is at nominal voltage. Loudspeaker transformers commonly have multiple primary taps to adjust the volume at each speaker in steps.
Output transformer
Valve (tube) amplifiers almost always use an output transformer to match the high load impedance requirement of the valves (several kilohms) to a low impedance speaker
Small-signal transformer
Moving coil phonograph cartridges produce a very small voltage. A transformer may be used to convert the voltage to the range of the more common moving-magnet cartridges.
Microphones may also be matched to their load with a small transformer that is shielded with
mu-metal to minimise noise pickup.
Interstage and coupling transformer
In a
push–pull amplifier
Push–pull may refer to:
In electronic technology
* Push–pull output, type of electronic circuit
* Push–pull converter, in electronics, is a type of DC to DC converter that uses a transformer
* Push–pull connector, an electronic cable conn ...
, an inverted signal is required and can be obtained from a transformer with a center-tapped winding, used to drive two active devices in opposite phase. These phase splitting transformers are not much used today.
Other types
Transactor
A transactor is a combination of a transformer and a
reactor. A transactor has an iron core with an air-gap, which limits the coupling between windings.
Hedgehog
Hedgehog transformers are occasionally encountered in homemade 1920s radios. They are homemade audio interstage coupling transformers.
Enameled copper wire is wound round the central half of the length of a bundle of insulated iron wire (e.g., florists' wire), to make the windings. The ends of the iron wires are then bent around the electrical winding to complete the magnetic circuit, and the whole is wrapped with tape or string to hold it together.
Variometer and variocoupler

A variometer is a type of continuously variable air-core RF
inductor
An inductor, also called a coil, choke, or reactor, is a Passivity (engineering), passive two-terminal electronic component, electrical component that stores energy in a magnetic field when an electric current flows through it. An inductor typic ...
with two windings.
One common form consisted of a coil wound on a short hollow cylindrical form, with a second smaller coil inside, mounted on a shaft so its magnetic axis can be rotated with respect to the outer coil. The two coils are connected in series. When the two coils are collinear, with their magnetic fields pointed in the same direction, the two magnetic fields add, and the inductance is maximum. If the inner coil is rotated so its axis is at an angle to the outer coil, the magnetic fields do not add and the inductance is less. If the inner coil is rotated so it is collinear with the outer coil but their magnetic fields point in opposite directions, the fields cancel each other out and the inductance is very small or zero. The advantage of the variometer is that inductance can be adjusted continuously, over a wide range. Variometers were widely used in 1920s radio receivers. One of their main uses today is as antenna matching coils to match
longwave
In radio, longwave (also spelled long wave or long-wave and commonly abbreviated LW) is the part of the radio spectrum with wavelengths longer than what was originally called the medium-wave (MW) broadcasting band. The term is historic, dati ...
radio transmitters to their antennas.
The ''vario-coupler'' was a device with similar construction, but the two coils were not connected but attached to separate circuits. So it functioned as an air-core RF
transformer
In electrical engineering, a transformer is a passive component that transfers electrical energy from one electrical circuit to another circuit, or multiple Electrical network, circuits. A varying current in any coil of the transformer produces ...
with variable coupling. The inner coil could be rotated from 0° to 90° angle with the outer, reducing the mutual inductance from maximum to near zero.
The pancake coil variometer was another common construction used in both 1920s receivers and transmitters. It consists of two flat spiral coils suspended vertically facing each other, hinged at one side so one could swing away from the other to an angle of 90° to reduce the coupling. The flat spiral design served to reduce
parasitic capacitance
Parasitic capacitance or stray capacitance is the unavoidable and usually unwanted capacitance that exists between the parts of an electronic component or circuit simply because of their proximity to each other. When two electrical conductors a ...
and losses at radio frequencies.
Pancake or "honeycomb" coil vario-couplers were used in the 1920s in the common
Armstrong or "tickler"
regenerative radio receivers. One coil was connected to the detector tube's
grid circuit. The other coil, the "tickler" coil was connected to the tube's
plate (output) circuit. It fed back some of the signal from the plate circuit into the input again, and this
positive feedback
Positive feedback (exacerbating feedback, self-reinforcing feedback) is a process that occurs in a feedback loop where the outcome of a process reinforces the inciting process to build momentum. As such, these forces can exacerbate the effects ...
increased the tube's
gain and selectivity.
Rotary transformer
A rotary (rotatory) transformer is a specialized transformer that couples electrical signals between two parts that rotate in relation to each other—as an alternative to
slip rings, which are prone to wear and contact noise. They are commonly used in
helical scan magnetic tape applications.
Variable differential transformer
A variable differential transformer is a rugged non-contact position sensor. It has two oppositely-phased primaries which nominally produce zero output in the secondary, but any movement of the core changes the coupling to produce a signal.
Resolver and synchro
The two-phase resolver and related three-phase synchro are rotary position sensors which work over a full 360°. The primary is rotated within two or three secondaries at different angles, and the amplitudes of the secondary signals can be decoded into an angle. Unlike variable differential transformers, the coils, and not just the core, move relative to each other, so slip rings are required to connect the primary.
Resolvers produce
in-phase and quadrature components which are useful for computation. Synchros produce three-phase signals which can be connected to other synchros to rotate them in a generator/motor configuration.
Piezoelectric transformer
Two
piezoelectric
Piezoelectricity (, ) is the electric charge that accumulates in certain solid materials—such as crystals, certain ceramics, and biological matter such as bone, DNA, and various proteins—in response to applied stress (mechanics), mechanical s ...
transducer
A transducer is a device that Energy transformation, converts energy from one form to another. Usually a transducer converts a signal in one form of energy to a signal in another.
Transducers are often employed at the boundaries of automation, M ...
s can be mechanically coupled or integrated in one piece of material, creating a
piezoelectric transformer.
Flyback
A
Flyback transformer
A flyback transformer (FBT), also called a line output transformer (LOPT), is a special type of electrical transformer. It was initially designed to generate high-voltage sawtooth signals at a relatively high frequency. In modern applications ...
is a high-voltage, high-frequency transformer used in plasma balls and with
cathode-ray tube
A cathode-ray tube (CRT) is a vacuum tube containing one or more electron guns, which emit electron beams that are manipulated to display images on a phosphorescent screen. The images may represent electrical waveforms on an oscilloscope, a ...
s (CRTs). It provides the high (often several kV) anode DC voltage required for operation of CRTs. Variations in anode voltage supplied by the flyback can result in distortions in the image displayed by the CRT. CRT flybacks may contain multiple secondary windings to provide several other, lower voltages. Its output is often pulsed because it is often used with a voltage multiplier, which may be integrated with the flyback.
See also
*
Buck–boost transformer
*
Center tap
*
Magnetic amplifier
*
Motor-generator
*
Saturable reactor
*
Tap changer
*
Three-phase electric power
Three-phase electric power (abbreviated 3ϕ) is a common type of alternating current (AC) used in electricity generation, transmission, and distribution. It is a type of polyphase system employing three wires (or four including an optional n ...
*
Three-phase
Three-phase electric power (abbreviated 3ϕ) is a common type of alternating current (AC) used in electricity generation, Electric power transmission, transmission, and Electric power distribution, distribution. It is a type of polyphase system ...
*
Transformer
In electrical engineering, a transformer is a passive component that transfers electrical energy from one electrical circuit to another circuit, or multiple Electrical network, circuits. A varying current in any coil of the transformer produces ...
References
{{Electric transformers
Electric transformers
Electronics lists
 Various types of electrical
Various types of electrical  Donut-shaped toroidal transformers save space compared to E-I cores, and may reduce external magnetic field. These use a ring shaped core, copper windings wrapped around this ring (and thus threaded through the ring during winding), and tape for insulation.
Toroidal transformers have a lower external magnetic field compared to rectangular transformers, and can be smaller for a given power rating. However, they cost more to make, as winding requires more complex and slower equipment.
They can be mounted by a bolt through the center, using washers and rubber pads or by potting in resin. Care must be taken that the bolt does not form part of a short-circuit turn.
Donut-shaped toroidal transformers save space compared to E-I cores, and may reduce external magnetic field. These use a ring shaped core, copper windings wrapped around this ring (and thus threaded through the ring during winding), and tape for insulation.
Toroidal transformers have a lower external magnetic field compared to rectangular transformers, and can be smaller for a given power rating. However, they cost more to make, as winding requires more complex and slower equipment.
They can be mounted by a bolt through the center, using washers and rubber pads or by potting in resin. Care must be taken that the bolt does not form part of a short-circuit turn.
 By exposing part of the winding coils of an autotransformer, and making the secondary connection through a sliding carbon brush, an autotransformer with a near-continuously variable turns ratio can be obtained, allowing for wide voltage adjustment in very small increments.
By exposing part of the winding coils of an autotransformer, and making the secondary connection through a sliding carbon brush, an autotransformer with a near-continuously variable turns ratio can be obtained, allowing for wide voltage adjustment in very small increments.

 For polyphase systems, multiple single-phase transformers can be used, or all phases can be connected to a single polyphase transformer. For a three phase transformer, the three primary windings are connected together and the three secondary windings are connected together. Examples of connections are wye-delta, delta-wye, delta-delta, and wye-wye. A vector group indicates the configuration of the windings and the phase angle difference between them. If a winding is connected to earth ( grounded), the earth connection point is usually the center point of a wye winding. If the secondary is a delta winding, the ground may be connected to a center tap on one winding ( high leg delta) or one phase may be grounded (corner grounded delta). A special purpose polyphase transformer is the zigzag transformer. There are many possible configurations that may involve more or fewer than six windings and various tap connections.
For polyphase systems, multiple single-phase transformers can be used, or all phases can be connected to a single polyphase transformer. For a three phase transformer, the three primary windings are connected together and the three secondary windings are connected together. Examples of connections are wye-delta, delta-wye, delta-delta, and wye-wye. A vector group indicates the configuration of the windings and the phase angle difference between them. If a winding is connected to earth ( grounded), the earth connection point is usually the center point of a wye winding. If the secondary is a delta winding, the ground may be connected to a center tap on one winding ( high leg delta) or one phase may be grounded (corner grounded delta). A special purpose polyphase transformer is the zigzag transformer. There are many possible configurations that may involve more or fewer than six windings and various tap connections.
 A leakage transformer, also called a stray-field transformer, has a significantly higher leakage inductance than other transformers, sometimes increased by a magnetic bypass or shunt in its core between primary and secondary, which is sometimes adjustable with a set screw. This provides a transformer with an inherent current limitation due to the loose coupling between its primary and the secondary windings. The adjustable short-circuit inductance acts as a current limiting parameter.
The output and input currents are kept low enough to preclude thermal overload under any load conditions — even if the secondary is shorted.
A leakage transformer, also called a stray-field transformer, has a significantly higher leakage inductance than other transformers, sometimes increased by a magnetic bypass or shunt in its core between primary and secondary, which is sometimes adjustable with a set screw. This provides a transformer with an inherent current limitation due to the loose coupling between its primary and the secondary windings. The adjustable short-circuit inductance acts as a current limiting parameter.
The output and input currents are kept low enough to preclude thermal overload under any load conditions — even if the secondary is shorted.

 Manufacturers either use flat copper sheets or etch spiral patterns on a
Manufacturers either use flat copper sheets or etch spiral patterns on a  A current transformer (CT) is a series connected measurement device designed to provide a current in its secondary coil proportional to the current flowing in its primary. Current transformers are commonly used in metering and
A current transformer (CT) is a series connected measurement device designed to provide a current in its secondary coil proportional to the current flowing in its primary. Current transformers are commonly used in metering and 
 Audio transformers are those specifically designed for use in audio circuits to carry
Audio transformers are those specifically designed for use in audio circuits to carry  A variometer is a type of continuously variable air-core RF
A variometer is a type of continuously variable air-core RF