transcranial direct-current stimulation on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) is a form of
 In
In
neuromodulation
Neuromodulation is the physiological process by which a given neuron uses one or more chemicals to regulate diverse populations of neurons. Neuromodulators typically bind to metabotropic, G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs) to initiate a sec ...
that uses constant, low direct current
Direct current (DC) is one-directional electric current, flow of electric charge. An electrochemical cell is a prime example of DC power. Direct current may flow through a conductor (material), conductor such as a wire, but can also flow throug ...
delivered via electrodes on the head. This type of neurotherapy
Neurotherapy is medical treatment that implements systemic targeted delivery of an energy stimulus or chemical agents to a specific neurological zone in the body to alter neuronal activity and stimulate neuroplasticity in a way that develops (or b ...
was originally developed to help patients with brain injuries or neuropsychiatric conditions such as major depressive disorder
Major depressive disorder (MDD), also known as clinical depression, is a mental disorder characterized by at least two weeks of pervasive depression (mood), low mood, low self-esteem, and anhedonia, loss of interest or pleasure in normally ...
. It can be contrasted with cranial electrotherapy stimulation
Cranial electrotherapy stimulation (CES) is a form of neurostimulation that delivers a small, pulsed, alternating current via electrodes on the head. CES is used with the intention of treating a variety of conditions such as anxiety, clinical depr ...
, which generally uses alternating current
Alternating current (AC) is an electric current that periodically reverses direction and changes its magnitude continuously with time, in contrast to direct current (DC), which flows only in one direction. Alternating current is the form in w ...
the same way, as well as transcranial magnetic stimulation
Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) is a noninvasive neurostimulation technique in which a changing magnetic field is used to induce an electric current in a targeted area of the brain through electromagnetic induction. A device called a st ...
.
Research shows increasing evidence for tDCS as a treatment for depression. There is mixed evidence about whether tDCS is useful for cognitive enhancement in healthy people. There is no strong evidence that tDCS is useful for memory deficits in Parkinson's disease
Parkinson's disease (PD), or simply Parkinson's, is a neurodegenerative disease primarily of the central nervous system, affecting both motor system, motor and non-motor systems. Symptoms typically develop gradually and non-motor issues become ...
and Alzheimer's disease
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disease and the cause of 60–70% of cases of dementia. The most common early symptom is difficulty in remembering recent events. As the disease advances, symptoms can include problems wit ...
, non-neuropathic pain, nor for improving arm or leg functioning and muscle strength in people recovering from a stroke. There is emerging supportive evidence for tDCS in the management of schizophreniaespecially for negative symptoms.
Efficacy
Depression
There is some evidence tDCS might be of moderate benefit as treatment for mild and moderate depression,major depressive disorder
Major depressive disorder (MDD), also known as clinical depression, is a mental disorder characterized by at least two weeks of pervasive depression (mood), low mood, low self-esteem, and anhedonia, loss of interest or pleasure in normally ...
and treatment-resistant depression
Treatment-resistant depression (TRD) is often defined as major depressive disorder in which an affected person does not respond adequately to at least two different antidepressant medications at an adequate dose and for an adequate duration. Inad ...
.
Other medical use
Recent research on tDCS has shown promising results in treating other mental health conditions such as anxiety and PTSD. More research is required on the topic. There is also evidence that tDCS is useful in treatingneuropathic pain
Neuropathic pain is pain caused by a lesion or disease of the somatosensory nervous system. Neuropathic pain may be associated with abnormal sensations called dysesthesia or pain from normally non-painful stimuli (allodynia). It may have continuo ...
after spinal cord injury. There is evidence of very low to moderate quality that tDCS can improve activities of daily living
Activities of daily living (ADLs) is a term used in healthcare to refer to an individual's daily self-care activities. Health professionals often use a person's ability or inability to perform ADLs as a measure of their Performance status, functi ...
assessment in the short-term after stroke.
Transcranial direct-current stimulaiton is also used to augment speech therapy
Speech is the use of the human voice as a medium for language. Spoken language combines vowel and consonant sounds to form units of meaning like words, which belong to a language's lexicon. There are many different intentional speech acts, suc ...
in patients with acquired language disorders like aphasia
Aphasia, also known as dysphasia, is an impairment in a person's ability to comprehend or formulate language because of dysfunction in specific brain regions. The major causes are stroke and head trauma; prevalence is hard to determine, but aph ...
, or to help maintain language abilities in the case of primary progressive aphasia
In neurology, primary progressive aphasia (PPA) is a type of neurological syndrome in which language capabilities slowly and progressively become impaired. As with other types of aphasia, the symptoms that accompany PPA depend on what parts of ...
, a neurodegenerative condition.
Safety
According to the BritishNational Institute for Health and Care Excellence
The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) is an executive non-departmental public body of the Department of Health and Social Care (United Kingdom), Department of Health and Social Care.
As the national health technolog ...
(NICE), the evidence on tDCS for depression raises no major safety concerns.
As of 2017, at stimulation up to 60 min and up to 4 mA over two weeks, adverse effects include skin irritation, a phosphene at the start of stimulation, nausea
Nausea is a diffuse sensation of unease and discomfort, sometimes perceived as an urge to vomit. It can be a debilitating symptom if prolonged and has been described as placing discomfort on the chest, abdomen, or back of the throat.
Over 30 d ...
, headache
A headache, also known as cephalalgia, is the symptom of pain in the face, head, or neck. It can occur as a migraine, tension-type headache, or cluster headache. There is an increased risk of Depression (mood), depression in those with severe ...
, dizziness, and itching under the electrode. Typical treatment sessions lasting for about 20–30 min repeated daily for several weeks in the treatment of depression. Adverse effects of long term treatment were not known as of 2017. Nausea most commonly occurs when the electrodes are placed above the mastoid
The mastoid part of the temporal bone is the posterior (back) part of the temporal bone, one of the bones of the skull. Its rough surface gives attachment to various muscles (via tendons) and it has openings for blood vessels. From its borders, t ...
for stimulation of the vestibular system
The vestibular system, in vertebrates, is a sensory system that creates the sense of balance and spatial orientation for the purpose of coordinating motor coordination, movement with balance. Together with the cochlea, a part of the auditory sys ...
. A phosphene is a brief flash of light that can occur if an electrode is placed near the eye.
People susceptible to seizure
A seizure is a sudden, brief disruption of brain activity caused by abnormal, excessive, or synchronous neuronal firing. Depending on the regions of the brain involved, seizures can lead to changes in movement, sensation, behavior, awareness, o ...
s, such as people with epilepsy
Epilepsy is a group of Non-communicable disease, non-communicable Neurological disorder, neurological disorders characterized by a tendency for recurrent, unprovoked Seizure, seizures. A seizure is a sudden burst of abnormal electrical activit ...
should not receive tDCS. Studies have been completed to determine the current density at which overt brain damage
Brain injury (BI) is the destruction or degeneration of brain cells. Brain injuries occur due to a wide range of internal and external factors. In general, brain damage refers to significant, undiscriminating trauma-induced damage.
A common ...
occurs in rats. It was found that in cathodal stimulation, a current density
In electromagnetism, current density is the amount of charge per unit time that flows through a unit area of a chosen cross section. The current density vector is defined as a vector whose magnitude is the electric current per cross-sectional ...
of 142.9 A/m2 delivering a charge density
In electromagnetism, charge density is the amount of electric charge per unit length, surface area, or volume. Volume charge density (symbolized by the Greek letter ρ) is the quantity of charge per unit volume, measured in the SI system in co ...
of 52400 C/m2 or higher caused a brain lesion
A lesion is any damage or abnormal change in the tissue of an organism, usually caused by injury or diseases. The term ''Lesion'' is derived from the Latin meaning "injury". Lesions may occur in both plants and animals.
Types
There is no de ...
in the rat. This is over two orders of magnitude
In a ratio scale based on powers of ten, the order of magnitude is a measure of the nearness of two figures. Two numbers are "within an order of magnitude" of each other if their ratio is between 1/10 and 10. In other words, the two numbers are wi ...
higher than protocols that were in use as of 2009.
Mechanism of action
tDCS stimulates and activates brain cells by delivering electrical signals. The lasting modulation of cortical excitability produced by tDCS makes it an effective solution to facilitate rehabilitation and treat a range of neuropsychiatric disorders. The way that the stimulation changes brain function is either by causing the neuron’sresting membrane potential
The relatively static membrane potential of quiescent cells is called the resting membrane potential (or resting voltage), as opposed to the specific dynamic electrochemical phenomena called action potential and graded membrane potential. The re ...
to depolarize or hyperpolarize. When positive stimulation (anodal tDCS) is delivered, the current causes a depolarization of the resting membrane potential, which increases neuronal excitability and allows for more spontaneous cell firing. When negative stimulation (cathodal tDCS) is delivered, the current causes a hyperpolarization of the resting membrane potential. This decreases neuron excitability due to the decreased spontaneous cell firing.
In case of treating depression, tDCS currents specifically target the left side of the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (DLPFC) located in the frontal lobe. Left DLPFC has been shown to be associated with lower activity in the depressed population.
tDCS is able to achieve cortical changes even after the stimulation is ended. The duration of this change depends on the length of stimulation as well as the intensity of stimulation. The effects of stimulation increase as the duration of stimulation increases or the strength of the current increases. tDCS has been proposed to promote both long term potentiation and long term depression, and further research is needed for validation.
Operation
Transcranial direct current stimulation works by sending constant, lowdirect current
Direct current (DC) is one-directional electric current, flow of electric charge. An electrochemical cell is a prime example of DC power. Direct current may flow through a conductor (material), conductor such as a wire, but can also flow throug ...
through the electrode
An electrode is an electrical conductor used to make contact with a nonmetallic part of a circuit (e.g. a semiconductor, an electrolyte, a vacuum or a gas). In electrochemical cells, electrodes are essential parts that can consist of a varie ...
s. When these electrodes are placed in the region of interest, the current induces intracerebral current flow. This current flow then either increases or decreases the neuronal excitability in the specific area being stimulated based on which type of stimulation is being used. This change of neuronal excitability leads to alteration of brain function, which can be used in various therapies as well as to provide more information about the functioning of the human brain.
Parts
Transcranial direct current stimulation is a relatively simple technique requiring only a few parts. These include two electrodes and a battery-powered device that delivers constant current. Control software can also be used in experiments that require multiple sessions with differing stimulation types so that neither the person receiving the stimulation nor the experimenter knows which type is being administered. Each device has an anodal, positively charged electrode and a cathodal, negative electrode. Current is "conventionally" described as flowing from the positive anode, through the intervening conducting tissue, to the cathode, creating a circuit. Note that in traditional electric circuits constructed from metal wires, charge drift is created by the motion of negatively charged electrons, which actually flow from cathode to anode. However, in biological systems, such as the head, current is usually created by the flow ofion
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge. The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by convent ...
s, which may be positively or negatively chargedpositive ions will flow towards the cathode; negative ions will flow toward the anode. The device may control the current as well as the duration of stimulation.
Setup
To set up the tDCS device, the electrodes and the skin need to be prepared. This ensures a low resistance connection between the skin and theelectrode
An electrode is an electrical conductor used to make contact with a nonmetallic part of a circuit (e.g. a semiconductor, an electrolyte, a vacuum or a gas). In electrochemical cells, electrodes are essential parts that can consist of a varie ...
. The careful placement of the electrodes is crucial to successful tDCS technique. The electrode pads come in various sizes with benefits to each size. A smaller sized electrode achieves a more focused stimulation of a site while a larger electrode ensures that the entirety of the region of interest is being stimulated. If the electrode is placed incorrectly, a different site or more sites than intended may be stimulated resulting in faulty results. One of the electrodes is placed over the region of interest and the other electrode, the reference electrode, is placed in another location in order to complete the circuit. This reference electrode is usually placed on the neck or shoulder of the opposite side of the body than the region of interest. Since the region of interest may be small, it is often useful to locate this region before placing the electrode by using a brain imaging
Neuroimaging is the use of quantitative (computational) techniques to study the structure and function of the central nervous system, developed as an objective way of scientifically studying the healthy human brain in a non-invasive manner. Incre ...
technique such as fMRI
Functional magnetic resonance imaging or functional MRI (fMRI) measures brain activity by detecting changes associated with blood flow. This technique relies on the fact that cerebral blood flow and neuronal activation are coupled. When an area o ...
or PET
A pet, or companion animal, is an animal kept primarily for a person's company or entertainment rather than as a working animal, livestock, or a laboratory animal. Popular pets are often considered to have attractive/ cute appearances, inte ...
. Once the electrodes are placed correctly, the stimulation can be started. Many devices have a built-in capability that allows the current to be "ramped up" or increased gradually until the necessary current is reached. This decreases the amount of stimulation effects felt by the person receiving the tDCS. After the stimulation has been started, the current will continue for the amount of time set on the device and then will automatically be shut off. Recently a new approach has been introduced where instead of using two large pads, multiple (more than two) smaller sized gel electrodes are used to target specific cortical structures. This new approach is called High Definition tDCS (HD-tDCS). In a pilot study, HD-tDCS was found to have greater and longer lasting motor cortex excitability changes than sponge tDCS.
Types of stimulation
There are three different types of stimulation: anodal, cathodal, and sham. The anodal stimulation is positive (V+) stimulation that increases the neuronal excitability of the area being stimulated. Cathodal (V−) stimulation decreases the neuronal excitability of the area being stimulated. Cathodal stimulation can treat psychiatric disorders that are caused by the hyper-activity of an area of the brain. Sham stimulation is used as a control in experiments. Sham stimulation emits a brief current but then remains off for the remainder of the stimulation time. With sham stimulation, the person receiving the tDCS does not know that they are not receiving prolonged stimulation. By comparing the results in subjects exposed to sham stimulation with the results of subjects exposed to anodal or cathodal stimulation, researchers can see how much of an effect is caused by the current stimulation, rather than by theplacebo effect
A placebo ( ) can be roughly defined as a sham medical treatment. Common placebos include inert tablets (like sugar pills), inert injections (like saline), sham surgery, and other procedures.
Placebos are used in randomized clinical trials ...
.
At-home administration
Recently, tDCS devices are being researched and created intended for at-home useranging from treating medical conditions such as depression to enhancing general cognitive well-being. Clinical trials are needed to establish the efficacy, feasibility and acceptability of home-based tDCS treatment.History
The basic design of tDCS, usingdirect current
Direct current (DC) is one-directional electric current, flow of electric charge. An electrochemical cell is a prime example of DC power. Direct current may flow through a conductor (material), conductor such as a wire, but can also flow throug ...
(DC) to stimulate the area of interest, has existed for over 100 years. There were a number of rudimentary experiments completed before the 19th century using this technique that tested animal and human electricity. Luigi Galvani
Luigi Galvani ( , , ; ; 9 September 1737 – 4 December 1798) was an Italian physician, physicist, biologist and philosopher who studied animal electricity. In 1780, using a frog, he discovered that the muscles of dead frogs' legs twitched when ...
and Alessandro Volta
Alessandro Giuseppe Antonio Anastasio Volta (, ; ; 18 February 1745 – 5 March 1827) was an Italian chemist and physicist who was a pioneer of electricity and Power (physics), power, and is credited as the inventor of the electric battery a ...
were two such researchers that utilized the technology of tDCS in their explorations of the source of animal cell electricity itation needed It was due to these initial studies that tDCS was first brought into the clinical scene. In 1801, Giovanni Aldini (Galvani's nephew) started a study in which he successfully used the technique of direct current stimulation to improve the mood of melancholy patients. (''Lanzarini'' pdf 5 of 9)
*
There was a brief rise of interest in transcranial direct current stimulation in the 1960s when studies by researcher D. J. Albert proved that the stimulation could affect brain function by changing the cortical excitability. He also discovered that positive and negative stimulation had different effects on the cortical excitability.
Research continued, further fueled by knowledge gained from other techniques like TMS and fMRI
Functional magnetic resonance imaging or functional MRI (fMRI) measures brain activity by detecting changes associated with blood flow. This technique relies on the fact that cerebral blood flow and neuronal activation are coupled. When an area o ...
.
Comparison to other devices
 In
In transcranial magnetic stimulation
Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) is a noninvasive neurostimulation technique in which a changing magnetic field is used to induce an electric current in a targeted area of the brain through electromagnetic induction. A device called a st ...
(TMS), an electric coil is held above the region of interest on the scalp that uses rapidly changing magnetic fields to induce small electrical current
Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and motion of matter possessing an electric charge. Electricity is related to magnetism, both being part of the phenomenon of electromagnetism, as described by Maxwel ...
s in the brain. There are two types of TMS: repetitive TMS and single pulse TMS. Both are used in research therapy but effects lasting longer than the stimulation period are only observed in repetitive TMS. Similar to tDCS, an increase or decrease in neuronal activity can be achieved using this technique, but the method of how this is induced is very different. Transcranial direct current stimulation has the two different directions of current that cause the different effects. Increased neuronal activity is induced in repetitive TMS by using a higher frequency and decreased neuronal activity is induced by using a lower frequency.
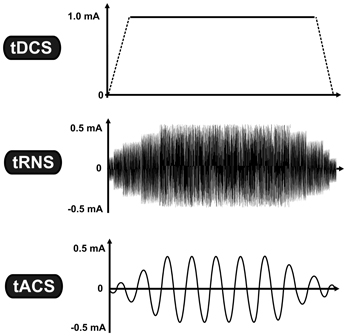
Variants related to tDCS include tACS
Total Access Communication System (TACS) and ETACS are variants of Advanced Mobile Phone System (AMPS) which were announced as the choice for the first two UK national cellular systems in February 1983, less than a year after the UK government an ...
, tPCS and transcranial random noise stimulation ( tRNS), a group of technologies commonly referred to as transcranial electrical stimulation, or TES.
Research
Depression
Determining the safety and effectiveness of tDCS treatment for people with depression is being investigated: * A systematic review of placebo-controlled trials investigating tDCS treatment formajor depressive disorder
Major depressive disorder (MDD), also known as clinical depression, is a mental disorder characterized by at least two weeks of pervasive depression (mood), low mood, low self-esteem, and anhedonia, loss of interest or pleasure in normally ...
was published 2020. The meta-analysis collated results across nine eligible studies (572 participants) up until December 2018 to estimate odds ratio (OR) and number needed to treat (NNT) of response and remission, and depression improvement. The results showed statistically superior efficacy of active tDCS compared to sham for nine eligible studies (572 participants), presenting moderate/high certainty of evidence, were included. Active tDCS was significantly superior to sham for response (30.9% vs. 18.9% respectively; OR = 1.96, 95%CI .30–2.95 NNT = 9), remission (19.9% vs. 11.7%, OR = 1.94 .19–3.16 NNT = 13) and depression improvement (effect size of β = 0.31, .15–0.47.
* A 2016 meta-analysis showed that 34% of people treated with tDCS showed at least 50% symptom reduction (compared to 19% placebo).
* A 2017 study conducted by Brunoni showed 6-weeks of tDCS treatment resulted in reduction of at least half of depression symptoms in 41% of depressed people (vs. 22% placebo and 47% antidepressants).
* In 2015, the British National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) found tDCS to be safe and to appear effective for depression treatment. Up until 2014, there have been several small randomized clinical trials (RCT) in major depressive disorder
Major depressive disorder (MDD), also known as clinical depression, is a mental disorder characterized by at least two weeks of pervasive depression (mood), low mood, low self-esteem, and anhedonia, loss of interest or pleasure in normally ...
(MDD); most found alleviation of depressive symptoms. There have been only two RCTs in treatment-resistant MDD; both were small, and one found an effect and the other did not. One meta-analysis of the data focused on reduction in symptoms and found an effect compared to sham treatment, but another that was focused on relapse found no effect compared to sham.
Other disorders
Cognition
There is mixed evidence about whether tDCS is useful for cognitive enhancement in healthy people. Several reviews have found evidence of small yet significant cognitive improvements. Other reviews found no evidence at all, although one of them has been criticized for overlooking within-subject effects and evidence from multiple-session tDCS trials. However, the original authors addressed these raised concerns in a further analysis and continued to find no evidence of impact A 2015 review of results from hundreds of tDCS experiments found that there was no statistically conclusive evidence to support any net cognitive effect, positive or negative, of single session tDCS in healthy populationsthere is no evidence that tDCS is useful for cognitive enhancement. A second study by the same authors found there was little-to-no statistically reliable impact of tDCS on any neurophysiologic outcome.Parkinson's, Alzheimer's disease, and schizophrenia
There is no strong evidence that tDCS is useful for memory deficits inAlzheimer's disease
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disease and the cause of 60–70% of cases of dementia. The most common early symptom is difficulty in remembering recent events. As the disease advances, symptoms can include problems wit ...
, schizophrenia
Schizophrenia () is a mental disorder characterized variously by hallucinations (typically, Auditory hallucination#Schizophrenia, hearing voices), delusions, thought disorder, disorganized thinking and behavior, and Reduced affect display, f ...
, non-neuropathic pain. A few clinical trials have been conducted on the use of tDCS to ameliorate memory deficits in Parkinson's disease
Parkinson's disease (PD), or simply Parkinson's, is a neurodegenerative disease primarily of the central nervous system, affecting both motor system, motor and non-motor systems. Symptoms typically develop gradually and non-motor issues become ...
and Alzheimer's disease
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disease and the cause of 60–70% of cases of dementia. The most common early symptom is difficulty in remembering recent events. As the disease advances, symptoms can include problems wit ...
and healthy subjects, with mixed results. Research conducted as of 2013 in schizophrenia
Schizophrenia () is a mental disorder characterized variously by hallucinations (typically, Auditory hallucination#Schizophrenia, hearing voices), delusions, thought disorder, disorganized thinking and behavior, and Reduced affect display, f ...
, has found that while large effect sizes were initially found for symptom improvement, later and larger studies have found smaller effect sizes (see also section on use of tDCS in psychiatric disorders below). Studies have mostly concentrated on positive symptoms like auditory hallucinations; research on negative symptoms is lacking.
Stroke
There is no strong evidence that tDCS can help improve upper limb function after stroke. In stroke, research conducted as of 2014, has found that tDCS is not effective for improving upper limb function after stroke. While some reviews have suggested an effect of tDCS for improving post-strokeaphasia
Aphasia, also known as dysphasia, is an impairment in a person's ability to comprehend or formulate language because of dysfunction in specific brain regions. The major causes are stroke and head trauma; prevalence is hard to determine, but aph ...
, a 2015 Cochrane review could find no improvement from combining tDCS with conventional treatment. Research conducted as of 2013 suggests that tDCS may be effective for improve vision deficits following stroke.
Motor Learning and Memory Function
There is evidence that certain tDCS montages can increase learning rates for particular tasks in healthy individuals, namely motor tasks and memory function. However, reproducibility remains to be fully tested across studies and standardization for these kinds of studies has not been implemented fully, though an attempt at formalizing standards was released in 2017.
Other
Research conducted as of 2012 on the use of tDCS to treat pain, found that the research has been of low quality and cannot be used as a basis to recommend use of tDCS to treat pain. In chronic pain following spinal cord injury, research is of high quality and has found tDCS to be ineffective. tDCS has also been studied in addiction. There is some moderate (level B) evidence to indicate that, in addition to treating major depressive disorder, tDCS may also be appropriate to treatfibromyalgia
Fibromyalgia (FM) is a functional somatic syndrome with symptoms of widespread chronic pain, accompanied by fatigue, sleep disturbance including awakening unrefreshed, and Cognitive deficit, cognitive symptoms. Other symptoms can include he ...
, and craving disorders.
tDCS has been used in neuroscience research, particularly to try to link specific brain regions to specific cognitive tasks or psychological phenomena. The cerebellum has been a focus of research, due to its high concentration of neurons, its location immediately below the skull, and its multiple reciprocal anatomical connections to motor and associative parts of the brain. Most such studies focus on the impact of cerebellar tDCS on motor, cognitive, and affective functions in healthy and patient populations, but some also employ tDCS over the cerebellum to study the functional connectivity of the cerebellum to other areas of the brain.
Limitations
While growing literature shows the efficacy of transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) for treating nervous diseases such as acute depressive episodes, the lack of knowledge about the nature of this treatment at the cell level raises concerns regarding possible adverse effects that would appear long after the treatment has ended. First, tDCS therapy involves exposure of the brain to an intense electric field, which is several times and even orders of magnitude higher than natural ones in the brain.Grimaldi G, Argyropoulos GP, Boehringer A, Celnik P, Edwards MJ, Ferrucci R, et al. (2014). "Non-invasive cerebellar stimulation--a consensus paper" (PDF). ''Cerebellum.'' 13 (1): 121–138. doi:10.1007/s12311-013-0514-7 While the therapeutic effect is observed in a short period of months, the impact of the electric fields on the brain, specifically on the treated neuronal structures, is a question of further long-term research. Second, tDCS brain tissue stimulation targets a large area of poorly characterized tissue.Sparing R, Mottaghy FM (2008). "Noninvasive brain stimulation with transcranial magnetic or direct current stimulation (TMS/tDCS)-From insights into human memory to therapy of its dysfunction". ''Methods.'' 44 (4): 329–337. doi:10.1016/j.ymeth.2007.02.001 Therefore, it is unclear whether electrical fields reach only the neural structures of the brain that need treatment. The radiation can destroy healthy cells which don't need treatment during tDCS therapy.Regulatory approvals
tDCS is a CE approved treatment formajor depressive disorder
Major depressive disorder (MDD), also known as clinical depression, is a mental disorder characterized by at least two weeks of pervasive depression (mood), low mood, low self-esteem, and anhedonia, loss of interest or pleasure in normally ...
(MDD) in the UK, EU, Australia, and Mexico. As of 2015, tDCS has not been approved for any use by the US FDA. An FDA briefing document prepared in 2012 stated that "there is no regulation for therapeutic tDCS".
See also
*Cranial electrotherapy stimulation
Cranial electrotherapy stimulation (CES) is a form of neurostimulation that delivers a small, pulsed, alternating current via electrodes on the head. CES is used with the intention of treating a variety of conditions such as anxiety, clinical depr ...
* Neurotechnology
* Transcranial alternating current stimulation
* Transcranial random noise stimulation
* Transcranial magnetic stimulation
Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) is a noninvasive neurostimulation technique in which a changing magnetic field is used to induce an electric current in a targeted area of the brain through electromagnetic induction. A device called a st ...
* Brainwave entrainment
* Non-invasive cerebellar stimulation
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation Neurophysiology Medical treatments Electrotherapy Neurotechnology Neurostimulation Medical devices